From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The cosmic microwave background (CMB) is the thermal radiation left over from the "Big Bang" of cosmology. In older literature, the CMB is also variously known as cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR) or "relic radiation." The CMB is a cosmic background radiation that is fundamental to observational cosmology because it is the oldest light in the Universe, dating to the epoch of recombination. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background glow, almost exactly the same in all directions, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of CMB in 1964 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson[1][2] was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and earned the discoverers the 1978 Nobel Prize.
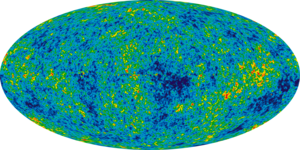
- The CMB is a snapshot of the oldest light in our Universe, imprinted on the sky when the Universe was just 380,000 years old. It shows tiny temperature fluctuations that correspond to regions of slightly different densities, representing the seeds of all future structure: the stars and galaxies of today.[3]
Precise measurements of the CMB are critical to cosmology, since any proposed model of the Universe must explain this radiation. The CMB has a thermal black body spectrum at a temperature of 2.72548±0.00057 K.[5] The spectral radiance dEν/dν peaks at 160.2 GHz, in the microwave range of frequencies. (Alternatively if spectral radiance is defined as dEλ/dλ then the peak wavelength is 1.063 mm.) The glow is very nearly uniform in all directions, but the tiny residual variations show a very specific pattern, the same as that expected of a fairly uniformly distributed hot gas that has expanded to the current size of the Universe. In particular, the spectral radiance at different angles of observation in the sky contains small anisotropies, or irregularities, which vary with the size of the region examined. They have been measured in detail, and match what would be expected if small thermal variations, generated by quantum fluctuations of matter in a very tiny space, had expanded to the size of the observable universe we see today. This is a very active field of study, with scientists seeking both better data (for example, the Planck spacecraft) and better interpretations of the initial conditions of expansion. Although many different processes might produce the general form of a black body spectrum, no model other than the Big Bang has yet explained the fluctuations. As a result, most cosmologists consider the Big Bang model of the Universe to be the best explanation for the CMB.
The high degree of uniformity throughout the observable universe and its faint but measured anisotropy lend strong support for the Big Bang model in general and the ΛCDM ("Lambda Cold Dark Matter") model in particular. Moreover, the WMAP[6] and BICEP[7] experiments have observed coherence of these fluctuations on angular scales that are larger than the apparent cosmological horizon at recombination. Either such coherence is acausally fine-tuned, or cosmic inflation occurred.[8][9]
Features

Graph of cosmic microwave background spectrum measured by the FIRAS instrument on the COBE, the most precisely measured black body spectrum in nature.[10] The error bars are too small to be seen even in an enlarged image, and it is impossible to distinguish the observed data from the theoretical curve.
The cosmic microwave background radiation is an emission of uniform, black body thermal energy coming from all parts of the sky. The radiation is isotropic to roughly one part in 100,000: the root mean square variations are only 18 µK,[11] after subtracting out a dipole anisotropy from the Doppler shift of the background radiation. The latter is caused by the peculiar velocity of the Earth relative to the comoving cosmic rest frame as the planet moves at some 371 km/s towards the constellation Leo. The CMB dipole as well as aberration at higher multipoles have been measured, consistent with galactic motion.[12]
In the Big Bang model for the formation of the universe, Inflationary Cosmology predicts that after about 10−37 seconds[13] the nascent universe underwent exponential growth that smoothed out nearly all inhomogeneities. The remaining inhomogeneities were caused by quantum fluctuations in the inflaton field that caused the inflation event.[14] After 10−6 seconds, the early universe was made up of a hot, interacting plasma of photons, electrons, and baryons. As the Universe expanded, adiabatic cooling caused the energy density of the plasma to decrease until it became favorable for electrons to combine with protons, forming hydrogen atoms. This recombination event happened when the temperature was around 3000 K or when the Universe was approximately 379,000 years old.[15] At this point, the photons no longer interacted with the now electrically neutral atoms and began to travel freely through space, resulting in the decoupling of matter and radiation.[16]
The color temperature of the ensemble of decoupled photons has continued to diminish ever since; now down to 2.7260±0.0013 K,[5] it will continue to drop as the Universe expands. The intensity of the radiation also corresponds to black-body radiation at 2.726 K because red-shifted black-body radiation is just like black-body radiation at a lower temperature. According to the Big Bang model, the radiation from the sky we measure today comes from a spherical surface called the surface of last scattering. This represents the set of locations in space at which the decoupling event is estimated to have occurred[17] and at a point in time such that the photons from that distance have just reached observers. Most of the radiation energy in the Universe is in the cosmic microwave background,[18] making up a fraction of roughly 6×10−5 of the total density of the Universe.[19]
Two of the greatest successes of the Big Bang theory are its prediction of the almost perfect black body spectrum and its detailed prediction of the anisotropies in the cosmic microwave background. The CMB spectrum has become the most precisely measured black body spectrum in nature.[10]
Density of energy for CMB is 0.25 eV/cm3[20] (4.005×10−14 J/m3) or (400–500 photons/cm3[21]).
History
The cosmic microwave background was first predicted in 1948 by Ralph Alpher, and Robert Herman.[22][23][24] Alpher and Herman were able to estimate the temperature of the cosmic microwave background to be 5 K, though two years later they re-estimated it at 28 K. This high estimate was due to a mis-estimate of the Hubble constant by Alfred Behr, which could not be replicated and was later abandoned for the earlier estimate. Although there were several previous estimates of the temperature of space, these suffered from two flaws. First, they were measurements of the effective temperature of space and did not suggest that space was filled with a thermal Planck spectrum. Next, they depend on our being at a special spot at the edge of the Milky Way galaxy and they did not suggest the radiation is isotropic. The estimates would yield very different predictions if Earth happened to be located elsewhere in the Universe.[25]The 1948 results of Alpher and Herman were discussed in many physics settings through about 1955, when both left the Applied Physics Laboratory at Johns Hopkins University. The mainstream astronomical community, however, was not intrigued at the time by cosmology. Alpher and Herman's prediction was rediscovered by Yakov Zel'dovich in the early 1960s, and independently predicted by Robert Dicke at the same time. The first published recognition of the CMB radiation as a detectable phenomenon appeared in a brief paper by Soviet astrophysicists A. G. Doroshkevich and Igor Novikov, in the spring of 1964.[26] In 1964, David Todd Wilkinson and Peter Roll, Dicke's colleagues at Princeton University, began constructing a Dicke radiometer to measure the cosmic microwave background.[27] In 1964, Arno Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson at the Crawford Hill location of Bell Telephone Laboratories in nearby Holmdel Township, New Jersey had built a Dicke radiometer that they intended to use for radio astronomy and satellite communication experiments. On 20 May 1964 they made their first measurement clearly showing the presence of the microwave background,[28] with their instrument having an excess 4.2K antenna temperature which they could not account for. After receiving a telephone call from Crawford Hill, Dicke famously quipped: "Boys, we've been scooped."[1][29][30] A meeting between the Princeton and Crawford Hill groups determined that the antenna temperature was indeed due to the microwave background. Penzias and Wilson received the 1978 Nobel Prize in Physics for their discovery.[31]
The interpretation of the cosmic microwave background was a controversial issue in the 1960s with some proponents of the steady state theory arguing that the microwave background was the result of scattered starlight from distant galaxies.[32] Using this model, and based on the study of narrow absorption line features in the spectra of stars, the astronomer Andrew McKellar wrote in 1941: "It can be calculated that the 'rotational temperature' of interstellar space is 2 K."[33] However, during the 1970s the consensus was established that the cosmic microwave background is a remnant of the big bang. This was largely because new measurements at a range of frequencies showed that the spectrum was a thermal, black body spectrum, a result that the steady state model was unable to reproduce.[34]
Harrison, Peebles, Yu and Zel'dovich realized that the early universe would have to have inhomogeneities at the level of 10−4 or 10−5.[35][36][37] Rashid Sunyaev later calculated the observable imprint that these inhomogeneities would have on the cosmic microwave background.[38] Increasingly stringent limits on the anisotropy of the cosmic microwave background were set by ground based experiments during the 1980s. RELIKT-1, a Soviet cosmic microwave background anisotropy experiment on board the Prognoz 9 satellite (launched 1 July 1983) gave upper limits on the large-scale anisotropy. The NASA COBE mission clearly confirmed the primary anisotropy with the Differential Microwave Radiometer instrument, publishing their findings in 1992.[39][40] The team received the Nobel Prize in physics for 2006 for this discovery.
Inspired by the COBE results, a series of ground and balloon-based experiments measured cosmic microwave background anisotropies on smaller angular scales over the next decade. The primary goal of these experiments was to measure the scale of the first acoustic peak, which COBE did not have sufficient resolution to resolve. This peak corresponds to large scale density variations in the early universe that are created by gravitational instabilities, resulting in acoustical oscillations in the plasma.[41] The first peak in the anisotropy was tentatively detected by the Toco experiment and the result was confirmed by the BOOMERanG and MAXIMA experiments.[42][43][44] These measurements demonstrated that the geometry of the Universe is approximately flat, rather than curved.[45] They ruled out cosmic strings as a major component of cosmic structure formation and suggested cosmic inflation was the right theory of structure formation.[46]
The second peak was tentatively detected by several experiments before being definitively detected by WMAP, which has also tentatively detected the third peak.[47] As of 2010, several experiments to improve measurements of the polarization and the microwave background on small angular scales are ongoing. These include DASI, WMAP, BOOMERanG, QUaD, Planck spacecraft, Atacama Cosmology Telescope, South Pole Telescope and the QUIET telescope.
Timeline
Thermal (non-microwave background) temperature predictions
- 1896 – Charles Édouard Guillaume estimates the "radiation of the stars" to be 5.6K.[48]
- 1926 – Sir Arthur Eddington estimates the non-thermal radiation of starlight in the galaxy "... by the formula E = σT4 the effective temperature corresponding to this density is 3.18° absolute ... black body"[49]
- 1930s – Cosmologist Erich Regener calculates that the non-thermal spectrum of cosmic rays in the galaxy has an effective temperature of 2.8 K
- 1931 – Term microwave first used in print: "When trials with wavelengths as low as 18 cm. were made known, there was undisguised surprise+that the problem of the micro-wave had been solved so soon." Telegraph & Telephone Journal XVII. 179/1
- 1934 – Richard Tolman shows that black-body radiation in an expanding universe cools but remains thermal
- 1938 – Nobel Prize winner (1920) Walther Nernst reestimates the cosmic ray temperature as 0.75K
- 1941 – Andrew McKellar was attempting to measure the average temperature of the interstellar medium, and used the excitation of CN doublet lines to measure that the "effective temperature of space" (the average bolometric temperature) is about 2.3 K[33][50]
- 1946 – Robert Dicke predicts "... radiation from cosmic matter" at <20 K, but did not refer to background radiation [51]
- 1946 – George Gamow calculates a temperature of 50 K (assuming a 3-billion year old Universe),[52] commenting it "... is in reasonable agreement with the actual temperature of interstellar space", but does not mention background radiation.[53]
- 1953 – Erwin Finlay-Freundlich in support of his tired light theory, derives a blackbody temperature for intergalactic space of 2.3K [54] with comment from Max Born suggesting radio astronomy as the arbitrator between expanding and infinite cosmologies.
Microwave background radiation predictions
- 1946 – George Gamow calculates a temperature of 50 K (assuming a 3-billion year old Universe),[52] commenting it "... is in reasonable agreement with the actual temperature of interstellar space", but does not mention background radiation.
- 1948 – Ralph Alpher and Robert Herman estimate "the temperature in the Universe" at 5 K. Although they do not specifically mention microwave background radiation, it may be inferred.[55]
- 1949 – Ralph Alpher and Robert Herman re-re-estimate the temperature at 28 K.
- 1953 – George Gamow estimates 7 K.[51]
- 1956 – George Gamow estimates 6 K.[51]
- 1955 – Émile Le Roux of the Nançay Radio Observatory, in a sky survey at λ = 33 cm, reported a near-isotropic background radiation of 3 kelvins, plus or minus 2.[51]
- 1957 – Tigran Shmaonov reports that "the absolute effective temperature of the radioemission background ... is 4±3 K".[56] It is noted that the "measurements showed that radiation intensity was independent of either time or direction of observation ... it is now clear that Shmaonov did observe the cosmic microwave background at a wavelength of 3.2 cm"[57][58]
- 1960s – Robert Dicke re-estimates a microwave background radiation temperature of 40 K[51][59]
- 1964 – A. G. Doroshkevich and Igor Dmitrievich Novikov publish a brief paper suggesting microwave searches for the black-body radiation predicted by Gamow, Alpher, and Herman, where they name the CMB radiation phenomenon as detectable.[60]
- 1964–65 – Arno Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson measure the temperature to be approximately 3 K. Robert Dicke, James Peebles, P. G. Roll, and D. T. Wilkinson interpret this radiation as a signature of the big bang.
- 1966 – Rainer K. Sachs and Arthur M. Wolfe theoretically predict microwave background fluctuation amplitudes created by gravitational potential variations between observers and the last scattering surface (see Sachs-Wolfe effect)
- 1968 – Martin Rees and Dennis Sciama theoretically predict microwave background fluctuation amplitudes created by photons traversing time-dependent potential wells
- 1969 – R. A. Sunyaev and Yakov Zel'dovich study the inverse Compton scattering of microwave background photons by hot electrons (see Sunyaev-Zel'dovich effect)
- 1983 – Researchers from the Cambridge Radio Astronomy Group and the Owens Valley Radio Observatory first detect the Sunyaev-Zel'dovich effect from clusters of galaxies
- 1983 – RELIKT-1 Soviet CMB anisotropy experiment was launched.
- 1990 – FIRAS on the Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE) satellite measures the black body form of the CMB spectrum with exquisite precision, and shows that the microwave background has a nearly perfect black-body spectrum and thereby strongly constrains the density of the intergalactic medium.
- January 1992 – Scientists that analysed data from the RELIKT-1 report the discovery of anisotropy in the cosmic microwave background at the Moscow astrophysical seminar.[61]
- 1992 – Scientists that analysed data from COBE DMR report the discovery of anisotropy in the cosmic microwave background.[62]
- 1995 – The Cosmic Anisotropy Telescope performs the first high resolution observations of the cosmic microwave background.
- 1999 – First measurements of acoustic oscillations in the CMB anisotropy angular power spectrum from the TOCO, BOOMERANG, and Maxima Experiments. The BOOMERanG experiment makes higher quality maps at intermediate resolution, and confirms that the Universe is "flat".
- 2002 – Polarization discovered by DASI.[63]
- 2003 – E-mode polarization spectrum obtained by the CBI.[64] The CBI and the Very Small Array produces yet higher quality maps at high resolution (covering small areas of the sky).
- 2003 – The WMAP spacecraft produces an even higher quality map at low and intermediate resolution of the whole sky (WMAP provides no high-resolution data, but improves on the intermediate resolution maps from BOOMERanG).
- 2004 – E-mode polarization spectrum obtained by the CBI.[65]
- 2004 – The Arcminute Cosmology Bolometer Array Receiver produces a higher quality map of the high resolution structure not mapped by WMAP.
- 2005 – The Arcminute Microkelvin Imager and the Sunyaev-Zel'dovich Array begin the first surveys for very high redshift clusters of galaxies using the Sunyaev-Zel'dovich effect.
- 2005 – Ralph A. Alpher is awarded the National Medal of Science for his groundbreaking work in nucleosynthesis and prediction that the Universe expansion leaves behind background radiation, thus providing a model for the Big Bang theory.
- 2006 – The long-awaited three-year WMAP results are released, confirming previous analysis, correcting several points, and including polarization data.
- 2006 – Two of COBE's principal investigators, George Smoot and John Mather, received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2006 for their work on precision measurement of the CMBR.
- 2006-2011 – Improved measurements from WMAP, new supernova surveys ESSENCE and SNLS, and baryon acoustic oscillations from SDSS and WiggleZ, continue to be consistent with the standard Lambda-CDM model.
- 2014 – On March 17, 2014, astrophysicists of the BICEP2 collaboration announced the detection of inflationary gravitational waves in the B-mode power spectrum, which if confirmed, would provide clear experimental evidence for the theory of inflation.[66][67][68][69][70][71] However, on 19 June 2014, lowered confidence in confirming the cosmic inflation findings was reported.[70][72][73]
Relationship to the Big Bang
The cosmic microwave background radiation and the cosmological redshift-distance relation are together regarded as the best available evidence for the Big Bang theory. Measurements of the CMB have made the inflationary Big Bang theory the Standard Model of Cosmology.[74] The discovery of the CMB in the mid-1960s curtailed interest in alternatives such as the steady state theory.[75]The CMB essentially confirms the Big Bang theory. In the late 1940s Alpher and Herman reasoned that if there was a big bang, the expansion of the Universe would have stretched and cooled the high-energy radiation of the very early Universe into the microwave region and down to a temperature of about 5 K. They were slightly off with their estimate, but they had exactly the right idea. They predicted the CMB. It took another 15 years for Penzias and Wilson to stumble into discovering that the microwave background was actually there.[76]
The CMB gives a snapshot of the universe when, according to standard cosmology, the temperature dropped enough to allow electrons and protons to form hydrogen atoms, thus making the Universe transparent to radiation. When it originated some 380,000 years after the Big Bang—this time is generally known as the "time of last scattering" or the period of recombination or decoupling—the temperature of the Universe was about 3000 K. This corresponds to an energy of about 0.25 eV, which is much less than the 13.6 eV ionization energy of hydrogen.[77]
Since decoupling, the temperature of the background radiation has dropped by a factor of roughly 1,100[78] due to the expansion of the Universe. As the Universe expands, the CMB photons are redshifted, making the radiation's temperature inversely proportional to a parameter called the Universe's scale length. The temperature Tr of the CMB as a function of redshift, z, can be shown to be proportional to the temperature of the CMB as observed in the present day (2.725 K or 0.235 meV):[79]
- Tr = 2.725(1 + z)
Primary anisotropy

The power spectrum of the cosmic microwave background radiation temperature anisotropy in terms of the angular scale (or multipole moment). The data shown comes from the WMAP (2006), Acbar (2004) Boomerang (2005), CBI (2004), and VSA (2004) instruments. Also shown is a theoretical model (solid line).
The anisotropy of the cosmic microwave background is divided into two types: primary anisotropy, due to effects which occur at the last scattering surface and before; and secondary anisotropy, due to effects such as interactions of the background radiation with hot gas or gravitational potentials, which occur between the last scattering surface and the observer.
The structure of the cosmic microwave background anisotropies is principally determined by two effects: acoustic oscillations and diffusion damping (also called collisionless damping or Silk damping). The acoustic oscillations arise because of a conflict in the photon–baryon plasma in the early universe. The pressure of the photons tends to erase anisotropies, whereas the gravitational attraction of the baryons—moving at speeds much slower than light—makes them tend to collapse to form dense haloes. These two effects compete to create acoustic oscillations which give the microwave background its characteristic peak structure. The peaks correspond, roughly, to resonances in which the photons decouple when a particular mode is at its peak amplitude.
The peaks contain interesting physical signatures. The angular scale of the first peak determines the curvature of the universe (but not the topology of the Universe). The next peak—ratio of the odd peaks to the even peaks—determines the reduced baryon density.[80] The third peak can be used to get information about the dark matter density.[81]
The locations of the peaks also give important information about the nature of the primordial density perturbations. There are two fundamental types of density perturbations—called adiabatic and isocurvature. A general density perturbation is a mixture of both, and different theories that purport to explain the primordial density perturbation spectrum predict different mixtures.
- Adiabatic density perturbations
- the fractional additional density of each type of particle (baryons, photons ...) is the same. That is, if at one place there is 1% more energy in baryons than average, then at that place there is also 1% more energy in photons (and 1% more energy in neutrinos) than average. Cosmic inflation predicts that the primordial perturbations are adiabatic.
- Isocurvature density perturbations
- in each place the sum (over different types of particle) of the fractional additional densities is zero. That is, a perturbation where at some spot there is 1% more energy in baryons than average, 1% more energy in photons than average, and 2% less energy in neutrinos than average, would be a pure isocurvature perturbation. Cosmic strings would produce mostly isocurvature primordial perturbations.
Collisionless damping is caused by two effects, when the treatment of the primordial plasma as fluid begins to break down:
- the increasing mean free path of the photons as the primordial plasma becomes increasingly rarefied in an expanding universe
- the finite depth of the last scattering surface (LSS), which causes the mean free path to increase rapidly during decoupling, even while some Compton scattering is still occurring.
The depth of the LSS refers to the fact that the decoupling of the photons and baryons does not happen instantaneously, but instead requires an appreciable fraction of the age of the Universe up to that era. One method of quantifying how long this process took uses the photon visibility function (PVF). This function is defined so that, denoting the PVF by P(t), the probability that a CMB photon last scattered between time t and t+dt is given by P(t)dt.
The maximum of the PVF (the time when it is most likely that a given CMB photon last scattered) is known quite precisely. The first-year WMAP results put the time at which P(t) is maximum as 372,000 years.[83] This is often taken as the "time" at which the CMB formed. However, to figure out how long it took the photons and baryons to decouple, we need a measure of the width of the PVF. The WMAP team finds that the PVF is greater than half of its maximum value (the "full width at half maximum", or FWHM) over an interval of 115,000 years. By this measure, decoupling took place over roughly 115,000 years, and when it was complete, the Universe was roughly 487,000 years old.
Late time anisotropy
Since the CMB came into existence, it has apparently been modified by several subsequent physical processes, which are collectively referred to as late-time anisotropy, or secondary anisotropy. When the CMB photons became free to travel unimpeded, ordinary matter in the Universe was mostly in the form of neutral hydrogen and helium atoms. However, observations of galaxies today seem to indicate that most of the volume of the intergalactic medium (IGM) consists of ionized material (since there are few absorption lines due to hydrogen atoms). This implies a period of reionization during which some of the material of the Universe was broken into hydrogen ions.The CMB photons are scattered by free charges such as electrons that are not bound in atoms. In an ionized universe, such charged particles have been liberated from neutral atoms by ionizing (ultraviolet) radiation. Today these free charges are at sufficiently low density in most of the volume of the Universe that they do not measurably affect the CMB. However, if the IGM was ionized at very early times when the Universe was still denser, then there are two main effects on the CMB:
- Small scale anisotropies are erased. (Just as when looking at an object through fog, details of the object appear fuzzy.)
- The physics of how photons are scattered by free electrons (Thomson scattering) induces polarization anisotropies on large angular scales. This broad angle polarization is correlated with the broad angle temperature perturbation.
The time following the emission of the cosmic microwave background—and before the observation of the first stars—is semi-humorously referred to by cosmologists as the dark age, and is a period which is under intense study by astronomers (See 21 centimeter radiation).
Two other effects which occurred between reionization and our observations of the cosmic microwave background, and which appear to cause anisotropies, are the Sunyaev–Zel'dovich effect, where a cloud of high-energy electrons scatters the radiation, transferring some of its energy to the CMB photons, and the Sachs–Wolfe effect, which causes photons from the Cosmic Microwave Background to be gravitationally redshifted or blueshifted due to changing gravitational fields.
Polarization
The cosmic microwave background is polarized at the level of a few microkelvin. There are two types of polarization, called E-modes and B-modes. This is in analogy to electrostatics, in which the electric field (E-field) has a vanishing curl and the magnetic field (B-field) has a vanishing divergence. The E-modes arise naturally from Thomson scattering in a heterogeneous plasma. The B-modes are not sourced by standard scalar type perturbations. Instead they can be sourced by two mechanisms: first one is by gravitational lensing of E-modes, which has been measured by South Pole Telescope in 2013.[84] Second one is from gravitational waves arising from cosmic inflation. Detecting the B-modes is extremely difficult, particularly as the degree of foreground contamination is unknown, and the weak gravitational lensing signal mixes the relatively strong E-mode signal with the B-mode signal.[85]E-modes
E-modes were first seen in 2002 by the Degree Angular Scale Interferometer (DASI).B-modes
Cosmologists predict two types of B-modes, the first generated during cosmic inflation shortly after the big bang,[86][87][88] and the second generated by gravitational lensing at later times.[89]Primordial gravitational waves
Primordial gravitational waves are gravitational waves that could be observed in the polarisation of the cosmic microwave background and having their origin in the early universe. Models of cosmic inflation predict that such gravitational waves should appear; thus, their detection supports the theory of inflation, and their strength can confirm and exclude different models of inflation. It is the result of three things: inflationary expansion of space itself, reheating after inflation, and turbulent fluid mixing of matter and radiation. [90]On 17 March 2014 it was announced that the BICEP2 instrument had detected the first type of B-modes, consistent with inflation and gravitational waves in the early universe at the level of r = 0.20+0.07
−0.05, which is the amount of power present in gravitational waves compared to the amount of power present in other scalar density perturbations in the very early universe. If confirmed this would provide strong evidence of cosmic inflation and the Big Bang.[91][92][93][66][67][68][69]
However, on 19 June 2014, lowered confidence in confirming the findings was reported[70][72][73][70][72][73] and on 19 September 2014 new results of the Planck experiment reported that the results of BICEP2 can be fully attributed to cosmic dust.[94][95]
In October 2014, a measurement of the B-mode polarization at 150 GHz was published by the POLARBEAR experiment.[96] Compared to BICEP2, POLARBEAR focuses on a smaller patch of the sky and is less susceptible to dust effects. The team reported that POLARBEAR's measured B-mode polarization was of cosmological origin (and not just due to dust) at a 97.2% confidence level.[97]
Paul Steinhardt is skeptical, suggesting that light scattering from cosmic dust and synchrotron radiation from electrons, both in the Milky Way Galaxy, could have caused the readings.[98]
Gravitational lensing
The second type of B-modes was discovered earlier using the South Pole Telescope with help from the Herschel Space Observatory.[99] This discovery may help test theories on the origin of the universe. Scientists are using data from the Planck mission by the European Space Agency, to gain a better understanding of these waves.[100][101][102]
Microwave background observations
Subsequent to the discovery of the CMB, hundreds of cosmic microwave background experiments have been conducted to measure and characterize the signatures of the radiation. The most famous experiment is probably the NASA Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE) satellite that orbited in 1989–1996 and which detected and quantified the large scale anisotropies at the limit of its detection capabilities. Inspired by the initial COBE results of an extremely isotropic and homogeneous background, a series of ground- and balloon-based experiments quantified CMB anisotropies on smaller angular scales over the next decade. The primary goal of these experiments was to measure the angular scale of the first acoustic peak, for which COBE did not have sufficient resolution. These measurements were able to rule out cosmic strings as the leading theory of cosmic structure formation, and suggested cosmic inflation was the right theory. During the 1990s, the first peak was measured with increasing sensitivity and by 2000 the BOOMERanG experiment reported that the highest power fluctuations occur at scales of approximately one degree. Together with other cosmological data, these results implied that the geometry of the Universe is flat. A number of ground-based interferometers provided measurements of the fluctuations with higher accuracy over the next three years, including the Very Small Array, Degree Angular Scale Interferometer (DASI), and the Cosmic Background Imager (CBI). DASI made the first detection of the polarization of the CMB and the CBI provided the first E-mode polarization spectrum with compelling evidence that it is out of phase with the T-mode spectrum.In June 2001, NASA launched a second CMB space mission, WMAP, to make much more precise measurements of the large scale anisotropies over the full sky. WMAP used symmetric, rapid-multi-modulated scanning, rapid switching radiometers to minimize non-sky signal noise.[78] The first results from this mission, disclosed in 2003, were detailed measurements of the angular power spectrum at a scale of less than one degree, tightly constraining various cosmological parameters. The results are broadly consistent with those expected from cosmic inflation as well as various other competing theories, and are available in detail at NASA's data bank for Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) (see links below). Although WMAP provided very accurate measurements of the large scale angular fluctuations in the CMB (structures about as broad in the sky as the moon), it did not have the angular resolution to measure the smaller scale fluctuations which had been observed by former ground-based interferometers.
A third space mission, the ESA (European Space Agency) Planck Surveyor, was launched in May 2009 and is currently performing an even more detailed investigation. Planck employs both HEMT radiometers and bolometer technology and will measure the CMB at a smaller scale than WMAP. Its detectors were trialled in the Antarctic Viper telescope as ACBAR (Arcminute Cosmology Bolometer Array Receiver) experiment—which has produced the most precise measurements at small angular scales to date—and in the Archeops balloon telescope.
On 21 March 2013, the European-led research team behind the Planck cosmology probe released the mission's all-sky map (565x318 jpeg, 3600x1800 jpeg) of the cosmic microwave background.[103][104] The map suggests the Universe is slightly older than researchers thought. According to the map, subtle fluctuations in temperature were imprinted on the deep sky when the cosmos was about 370,000 years old. The imprint reflects ripples that arose as early, in the existence of the Universe, as the first nonillionth of a second. Apparently, these ripples gave rise to the present vast cosmic web of galaxy clusters and dark matter. According to the team, the Universe is 13.798 ± 0.037 billion years old,[105] and contains 4.9% ordinary matter, 26.8% dark matter and 68.3% dark energy. Also, the Hubble constant was measured to be 67.80 ± 0.77 (km/s)/Mpc.[103][106][107][108]
Additional ground-based instruments such as the South Pole Telescope in Antarctica and the proposed Clover Project, Atacama Cosmology Telescope and the QUIET telescope in Chile will provide additional data not available from satellite observations, possibly including the B-mode polarization.
Data reduction and analysis
Raw CMBR data from the space vehicle (i.e. WMAP) contain foreground effects that completely obscure the fine-scale structure of the cosmic microwave background. The fine-scale structure is superimposed on the raw CMBR data but is too small to be seen at the scale of the raw data. The most prominent of the foreground effects is the dipole anisotropy caused by the Sun's motion relative to the CMBR background. The dipole anisotropy and others due to Earth's annual motion relative to the Sun and numerous microwave sources in the galactic plane and elsewhere must be subtracted out to reveal the extremely tiny variations characterizing the fine-scale structure of the CMBR background.The detailed analysis of CMBR data to produce maps, an angular power spectrum, and ultimately cosmological parameters is a complicated, computationally difficult problem. Although computing a power spectrum from a map is in principle a simple Fourier transform, decomposing the map of the sky into spherical harmonics, in practice it is hard to take the effects of noise and foreground sources into account. In particular, these foregrounds are dominated by galactic emissions such as Bremsstrahlung, synchrotron, and dust that emit in the microwave band; in practice, the galaxy has to be removed, resulting in a CMB map that is not a full-sky map. In addition, point sources like galaxies and clusters represent another source of foreground which must be removed so as not to distort the short scale structure of the CMB power spectrum.
Constraints on many cosmological parameters can be obtained from their effects on the power spectrum, and results are often calculated using Markov Chain Monte Carlo sampling techniques.
CMBR dipole anisotropy
From the CMB data it is seen that our local group of galaxies (the galactic cluster that includes the Solar System's Milky Way Galaxy) appears to be moving at 627±22 km/s relative to the reference frame of the CMB (also called the CMB rest frame, or the frame of reference in which there is no motion through the CMB) in the direction of galactic longitude l = 263.99°±0.14°, b = 48.26°±0.03°.[109][110] This motion results in an anisotropy of the data (CMB appearing slightly warmer in the direction of movement than in the opposite direction).[111] From a theoretical point of view, the existence of a CMB rest frame breaks Lorentz invariance even in empty space far away from any galaxy.[112] The standard interpretation of this temperature variation is a simple velocity red shift and blue shift due to motion relative to the CMB, but alternative cosmological models can explain some fraction of the observed dipole temperature distribution in the CMB.[113]Low multipoles and other anomalies
With the increasingly precise data provided by WMAP, there have been a number of claims that the CMB exhibits anomalies, such as very large scale anisotropies, anomalous alignments, and non-Gaussian distributions.[114][115][116][117] The most longstanding of these is the low-l multipole controversy. Even in the COBE map, it was observed that the quadrupole (l = 2, spherical harmonic) has a low amplitude compared to the predictions of the Big Bang. In particular, the quadrupole and octupole (l = 3) modes appear to have an unexplained alignment with each other and with both the ecliptic plane and equinoxes,[118][119][120] an alignment sometimes referred to as the axis of evil.[115] A number of groups have suggested that this could be the signature of new physics at the greatest observable scales; other groups suspect systematic errors in the data.[121][122][123] Ultimately, due to the foregrounds and the cosmic variance problem, the greatest modes will never be as well measured as the small angular scale modes. The analyses were performed on two maps that have had the foregrounds removed as far as possible: the "internal linear combination" map of the WMAP collaboration and a similar map prepared by Max Tegmark and others.[47][78][124]Later analyses have pointed out that these are the modes most susceptible to foreground contamination from synchrotron, dust, and Bremsstrahlung emission, and from experimental uncertainty in the monopole and dipole. A full Bayesian analysis of the WMAP power spectrum demonstrates that the quadrupole prediction of Lambda-CDM cosmology is consistent with the data at the 10% level and that the observed octupole is not remarkable.[125] Carefully accounting for the procedure used to remove the foregrounds from the full sky map further reduces the significance of the alignment by ~5%.[126][127][128][129]
Recent observations with the Planck telescope, which is very much more sensitive than WMAP and has a larger angular resolution, confirm the observation of the axis of evil. Since two different instruments recorded the same anomaly, instrumental error (but not foreground contamination) appears to be ruled out.[130] Coincidence is a possible explanation, chief scientist from WMAP, Charles L. Bennett suggested coincidence and human psychology were involved, "I do think there is a bit of a psychological effect; people want to find unusual things." [131]
Future evolution
Assuming the Universe keeps expanding and it does not suffer a Big Crunch, a Big Rip, or another similar fate, the cosmic microwave background will continue redshifting until it will no longer be detectable,[132] and will be overtaken first by the one produced by starlight, and later by the background radiations fields of process that are assumed will take place in the far future of the Universe.[133], §VD.In popular culture
- In the Stargate Universe TV series, an Ancient spaceship, Destiny, was built to study patterns in the CMBR which indicate that the Universe as we know it might have been created by some form of sentient intelligence.[134]
- In Wheelers, a novel by Ian Stewart & Jack Cohen, CMBR is explained as the encrypted transmissions of an ancient civilization. This allows the Jovian "blimps" to have a society older than the currently-observed age of the Universe.
- In The Three-Body Problem, a novel by Liu Cixin, CMBR becomes observable to the naked eye due to interference from an alien civilization.



![S_2=\frac{1}{4\pi\alpha'}\int d^2z\sqrt{\gamma}\left[\gamma^{ab}G_{\mu\nu}(X)\partial_aX^\mu\partial_bX^\nu+\alpha'\ ^{(2)}R\Phi(X)\right],](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/f/7/9/f793416dbff80ca9c204b3a128050741.png)
 is the
is the  the
the 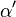 the string constant. The indices
the string constant. The indices  range over 1,2, and
range over 1,2, and  over
over 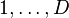 , where D the dimension of the target space. A further antisymmetric field could be added. This is generally considered when one wants this action generating a potential for inflation.
, where D the dimension of the target space. A further antisymmetric field could be added. This is generally considered when one wants this action generating a potential for inflation.


 is just the anomaly of the
is just the anomaly of the  , and from this cosmological models of a pre-big bang scenario can be constructed. Indeed, this low energy equations can be obtained from the following action:
, and from this cosmological models of a pre-big bang scenario can be constructed. Indeed, this low energy equations can be obtained from the following action:![S=\frac{1}{2\kappa_0^2}\int d^Dx\sqrt{-G}e^{-2\Phi}\left[-\frac{2(D-26)}{3\alpha'}+R+4\partial_\mu\Phi\partial^\mu\Phi+O(\alpha')\right],](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/5/6/c/56c3fa1a05ead707048c2be1327e879f.png)
 is a constant that can always be changed by redefining the dilaton field. One can also rewrite this action in a more familiar form by redefining the fields (Einstein frame) as
is a constant that can always be changed by redefining the dilaton field. One can also rewrite this action in a more familiar form by redefining the fields (Einstein frame) as

 one can write
one can write![S=\frac{1}{2\kappa^2}\int d^Dx\sqrt{-g}\left[-\frac{2(D-26)}{3\alpha'}e^{\frac{4\tilde\Phi}{D-2}}+\tilde R-\frac{4}{D-2}\partial_\mu\tilde\Phi\partial^\mu\tilde\Phi+O(\alpha')\right],](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/f/9/a/f9a4e2c5f50d53936f76183c181b5dd0.png)
![\tilde R=e^{-2\omega}[R-(D-1)\nabla^2\omega-(D-2)(D-1)\partial_\mu\omega\partial^\mu\omega].](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/7/d/c/7dc7271fcdf1fe4622f5fb8c77052b58.png)

 is the Newton constant in D dimensions and
is the Newton constant in D dimensions and  the corresponding Planck mass. When setting
the corresponding Planck mass. When setting  in this action, the conditions for inflation are not fulfilled unless a potential or antisymmetric term is added to the string action,
in this action, the conditions for inflation are not fulfilled unless a potential or antisymmetric term is added to the string action,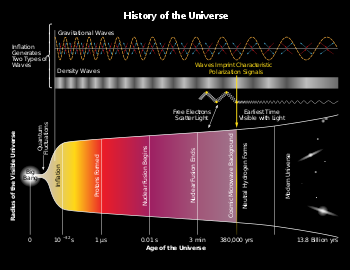
 with
with 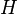 being the
being the 
