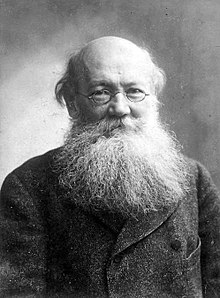Some forms of anarchist communism, such as insurrectionary anarchism, are strongly influenced by egoism and radical individualism, believing anarcho-communism is the best social system for the realization of individual freedom. Most anarcho-communists view anarcho-communism as a way of reconciling the opposition between the individual and society.
Anarcho-communism developed out of radical socialist currents after the French Revolution, but was first formulated as such in the Italian section of the First International. The theoretical work of Peter Kropotkin took importance later as it expanded and developed pro-organizationalist and insurrectionary anti-organizationalist sections. To date, the best-known examples of an anarchist communist society (i.e. established around the ideas as they exist today and achieving worldwide attention and knowledge in the historical canon) are the anarchist territories during the Spanish Revolution and the Free Territory during the Russian Revolution. Through the efforts and influence of the Spanish anarchists during the Spanish Revolution within the Spanish Civil War, starting in 1936 anarchist communism existed in most of Aragon, parts of the Levante and Andalusia as well as in the stronghold of anarchist Catalonia before being crushed by the combined forces of the regime that won the war, Adolf Hitler, Benito Mussolini, Spanish Communist Party repression (backed by the Soviet Union) as well as economic and armaments blockades from the capitalist countries and the Spanish Republic itself. During the Russian Revolution, anarchists such as Nestor Makhno worked to create and defend—through the Revolutionary Insurrectionary Army of Ukraine—anarchist communism in the Free Territory of the Ukraine from 1919 before being conquered by the Bolsheviks in 1921.
Anarcho-communism developed out of radical socialist currents after the French Revolution, but was first formulated as such in the Italian section of the First International. The theoretical work of Peter Kropotkin took importance later as it expanded and developed pro-organizationalist and insurrectionary anti-organizationalist sections. To date, the best-known examples of an anarchist communist society (i.e. established around the ideas as they exist today and achieving worldwide attention and knowledge in the historical canon) are the anarchist territories during the Spanish Revolution and the Free Territory during the Russian Revolution. Through the efforts and influence of the Spanish anarchists during the Spanish Revolution within the Spanish Civil War, starting in 1936 anarchist communism existed in most of Aragon, parts of the Levante and Andalusia as well as in the stronghold of anarchist Catalonia before being crushed by the combined forces of the regime that won the war, Adolf Hitler, Benito Mussolini, Spanish Communist Party repression (backed by the Soviet Union) as well as economic and armaments blockades from the capitalist countries and the Spanish Republic itself. During the Russian Revolution, anarchists such as Nestor Makhno worked to create and defend—through the Revolutionary Insurrectionary Army of Ukraine—anarchist communism in the Free Territory of the Ukraine from 1919 before being conquered by the Bolsheviks in 1921.
History
Early precursors
The Diggers are often seen as the first practicing anarchists, having held common ownership over land and resources around the time of the English Civil War
Lahontan's
1703 novel documented the author's experiences with various indigenous
American tribes and cultures. The novel explores various agrarian socialist
societies and how they were able to provide property for all their
inhabitants through collective ownership. The recurring theme of these
many cultures were their non-hierarchial structure, early egalitarian
styles of living, and how mutual aid played a significant role in maintaining health
Sylvain Maréchal, 18th-century atheist philosopher and whose egalitarian beliefs pre-staged ideological developments of anarchism and utopian socialism
Anarchist communist currents appeared during the English Civil War and the French Revolution of the 17th and 18th centuries, respectively. Gerrard Winstanley, who was part of the radical Diggers movement in England, wrote in his 1649 pamphlet, The New Law of Righteousness,
that there "shall be no buying or selling, no fairs nor markets, but
the whole earth shall be a common treasury for every man," and "there
shall be none Lord over others, but every one shall be a Lord of
himself".
The Diggers themselves resisted tyranny of the ruling class and
of kings, instead operating in a cooperative fashion in order to get
work done, manage supplies, and increase economic productivity. Due to
the communes established by the Diggers being free from private
property, along with economic exchange (as all items, goods and services
were held collectively), their communes could be called early,
functioning communist societies, spread out across the rural lands of England.
Prior to the Industrial Revolution,
common ownership of land and property was much more prevalent across
the European continent, but the Diggers were set apart by their struggle
against monarchical rule. They sprung up by means of workers' self-management after the fall of Charles I.
In 1703, Louis Armand, Baron de Lahontan wrote the novel New Voyages to North America where he outlined how indigenous communities of the North American continent cooperated and organised. The author found the agrarian societies and communities of pre-colonial North America to be nothing like the monarchical, unequal states of Europe,
both in their economic structure and lack of any state. He wrote that
the life natives lived was "anarchy", this being the first usage of the
term to mean something other than chaos.
He wrote that there were no priests, courts, laws, police, ministers of
state, and no distinction of property, no way to differentiate rich
from poor, as they were all equal and thriving cooperatively.
During the French Revolution, Sylvain Maréchal, in his Manifesto of the Equals
(1796), demanded "the communal enjoyment of the fruits of the earth"
and looked forward to the disappearance of "the revolting distinction of
rich and poor, of great and small, of masters and valets, of governors
and governed".
Maréchal was critical not only of the unequal distribution of property,
but how religion would often be used to justify evangelical immorality.
He viewed the link between religion and what later came to be known as
capitalism (though not in his time) as two sides of the same corrupted
coin. He had once said, "Do not be afraid of your God - be afraid of
yourself. You are the creator of your own troubles and joys. Heaven and
hell are in your own soul".
Sylvain Maréchal was personally involved with the Conspiracy of the Equals,
a failed attempt at overthrowing the monarchy of France and
establishing a stateless, agrarian socialist utopia. He worked with Gracchus Babeuf
in not only writing about what an anarchist country might look like,
but how it will be achieved. The two of them were friends, though didn't
always see eye to eye, particularly with Maréchal's statement on
equality being more important than the arts.
Joseph Déjacque and the Revolutions of 1848
An early anarchist communist was Joseph Déjacque, the first person to describe himself as "libertarian". Unlike Proudhon,
he argued that, "it is not the product of his or her labor that the
worker has a right to, but to the satisfaction of his or her needs,
whatever may be their nature". According to the anarchist historian Max Nettlau, the first use of the term libertarian communism was in November 1880, when a French anarchist congress employed it to more clearly identify its doctrines. The French anarchist journalist Sébastien Faure, later founder and editor of the four-volume Anarchist Encyclopedia, started the weekly paper Le Libertaire (The Libertarian) in 1895.
Déjacque "rejected Blanquism,
which was based on a division between the 'disciples of the great
people's Architect' and 'the people, or vulgar herd,' and was equally
opposed to all the variants of social republicanism, to the dictatorship
of one man and to 'the dictatorship of the little prodigies of the
proletariat.' With regard to the last of these, he wrote that: 'a
dictatorial committee composed of workers is certainly the most
conceited and incompetent, and hence the most anti-revolutionary, thing
that can be found [...] (It is better to have doubtful enemies in power
than dubious friends)'. He saw 'anarchic initiative,' 'reasoned will'
and 'the autonomy of each' as the conditions for the social revolution
of the proletariat, the first expression of which had been the
barricades of June 1848.
In Déjacque's view, a government resulting from an insurrection remains
a reactionary fetter on the free initiative of the proletariat. Or
rather, such free initiative can only arise and develop by the masses
ridding themselves of the 'authoritarian prejudices' by means of which
the state reproduces itself in its primary function of representation
and delegation. Déjacque wrote that: 'By government I understand all
delegation, all power outside the people,' for which must be
substituted, in a process whereby politics is transcended, the 'people
in direct possession of their sovereignty,' or the 'organised commune.'
For Déjacque, the communist anarchist utopia would fulfil the function
of inciting each proletarian to explore his or her own human
potentialities, in addition to correcting the ignorance of the
proletarians concerning 'social science.'"
The International Workingmen's Association
The collectivist anarchists advocated remuneration for the type and amount of labor adhering to the principle "to each according to deeds"; but held out the possibility of a post-revolutionary transition to a communist system of distribution according to need. As Mikhail Bakunin's associate, James Guillaume, put it in his essay, Ideas on Social Organization
(1876): "When [...] production comes to outstrip consumption ...
everyone will draw what he needs from the abundant social reserve of
commodities, without fear of depletion; and the moral sentiment which
will be more highly developed among free and equal workers will prevent,
or greatly reduce, abuse and waste."
Anarchist communism as a coherent, modern economic-political philosophy was first formulated in the Italian section of the First International by Carlo Cafiero, Emilio Covelli, Errico Malatesta, Andrea Costa and other ex Mazzinian Republicans.
The collectivist anarchists sought to collectivize ownership of the
means of production while retaining payment proportional to the amount
and kind of labor of each individual, but the anarcho-communists sought
to extend the concept of collective ownership to the products of labor
as well. While both groups argued against capitalism, the anarchist
communists departed from Proudhon and Bakunin, who maintained that
individuals have a right to the product of their individual labor and to
be remunerated for their particular contribution to production. But,
Errico Malatesta stated that "instead of running the risk of making a
confusion in trying to distinguish what you and I each do, let us all
work and put everything in common. In this way each will give to society
all that his strength permits until enough is produced for every one;
and each will take all that he needs, limiting his needs only in those
things of which there is not yet plenty for every one".
Cafiero explains in Anarchy and Communism (1880) that private property
in the product of labor will lead to unequal accumulation of capital
and therefore the reappearance of social classes and their antagonisms;
and thus the resurrection of the state: "If we preserve the individual
appropriation of the products of labour, we would be forced to preserve
money, leaving more or less accumulation of wealth according to more or
less merit rather than need of individuals". At the Florence Conference of the Italian Federation of the International in 1876, held in a forest outside Florence due to police activity, they declared the principles of anarcho-communism, beginning with:
The Italian Federation considers the collective property of the products of labour as the necessary complement to the collectivist programme, the aid of all for the satisfaction of the needs of each being the only rule of production and consumption which corresponds to the principle of solidarity. The federal congress at Florence has eloquently demonstrated the opinion of the Italian International on this point...
The above report was made in an article by Malatesta and Cafiero in the Swiss Jura Federation's bulletin later that year.
Peter Kropotkin
Peter Kropotkin (1842–1921), often seen as the most important theorist of anarchist communism, outlined his economic ideas in The Conquest of Bread and Fields, Factories and Workshops. Kropotkin felt that cooperation is more beneficial than competition, arguing in his major scientific work Mutual Aid: A Factor of Evolution that this was well-illustrated in nature. He advocated the abolition of private property (while retaining respect for personal property) through the "expropriation of the whole of social wealth" by the people themselves, and for the economy to be co-ordinated through a horizontal network of voluntary associations where goods are distributed according to the physical needs of the individual, rather than according to labor.
He further argued that these "needs," as society progressed, would not
merely be physical needs but "[a]s soon as his material wants are
satisfied, other needs, of an artistic character, will thrust themselves
forward the more ardently. Aims of life vary with each and every
individual; and the more society is civilized, the more will
individuality be developed, and the more will desires be varied." He maintained that in anarcho-communism "houses, fields, and factories will no longer be private property, and that they will belong to the commune or the nation and money, wages, and trade would be abolished".
Individuals and groups would use and control whatever resources they
needed, as the aim of anarchist communism was to place "the product
reaped or manufactured at the disposal of all, leaving to each the
liberty to consume them as he pleases in his own home". He supported the expropriation of private property into the commons or public goods (while retaining respect for personal property) to ensure that everyone would have access to what they needed without being forced to sell their labour to get it:
We do not want to rob any one of his coat, but we wish to give to the workers all those things the lack of which makes them fall an easy prey to the exploiter, and we will do our utmost that none shall lack aught, that not a single man shall be forced to sell the strength of his right arm to obtain a bare subsistence for himself and his babes. This is what we mean when we talk of Expropriation...
— Peter Kropotkin, The Conquest of Bread
He said that a "peasant who is in possession of just the amount of
land he can cultivate" and "a family inhabiting a house which affords
them just enough space [...] considered necessary for that number of
people" and the artisan "working with their own tools or handloom" would not be interfered with,
arguing that "[t]he landlord owes his riches to the poverty of the
peasants, and the wealth of the capitalist comes from the same source".
In summation, Kropotkin described an anarchist communist economy as functioning like this:
Imagine a society, comprising a few million inhabitants, engaged in agriculture and a great variety of industries—Paris, for example, with the Department of Seine-et-Oise. Suppose that in this society all children learn to work with their hands as well as with their brains. Admit that all adults... bind themselves to work 5 hours a day from the age of twenty or twenty-two to forty-five or fifty, and that they follow occupations they have chosen in any one branch of human work considered necessary. Such a society could in return guarantee well-being to all its members; that is to say, a more substantial well-being than that enjoyed to-day by the middle classes. And, moreover, each worker belonging to this society would have at his disposal at least 5 hours a day which he could devote to science, art, and individual needs which do not come under the category of necessities, but will probably do so later on, when man's productivity will have augmented, and those objects will no longer appear luxurious or inaccessible.
— Peter Kropotkin, The Conquest of Bread
Organizationalism vs. insurrectionarism and expansion
In 1876, at the Berne conference of the International Workingmen's Association, the Italian anarchist Errico Malatesta argued that the revolution "consists more of deeds than words", and that action was the most effective form of propaganda. In the bulletin of the Jura Federation
he declared "the Italian federation believes that the insurrectional
fact, destined to affirm socialist principles by deed, is the most
efficacious means of propaganda".
As anarcho-communism emerged in the mid-19th century it had an intense debate with Bakuninist collectivism and as such within the anarchist movement over participation in syndicalism and the workers movement as well as on other issues. So "In the theory of the revolution" of anarcho-communism as elaborated by Peter Kropotkin
and others "it is the risen people who are the real agent and not the
working class organised in the enterprise (the cells of the capitalist mode of production)
and seeking to assert itself as labour power, as a more 'rational'
industrial body or social brain (manager) than the employers".
Luigi Galleani influential anarchist advocate of insurrectionary anarchism
So "between 1880 and 1890" with the "perspective of an immanent revolution", who was "opposed to the official workers' movement, which was then in the process of formation (general Social Democratisation).
They were opposed not only to political (statist) struggles but also to
strikes which put forward wage or other claims, or which were organised
by trade unions." But "While they were not opposed to strikes as such, they were opposed to trade unions and the struggle for the eight-hour day.
This anti-reformist tendency was accompanied by an anti-organisational
tendency, and its partisans declared themselves in favour of agitation
amongst the unemployed for the expropriation of foodstuffs and other
articles, for the expropriatory strike and, in some cases, for 'individual recuperation' or acts of terrorism."
Even after Peter Kropotkin and others overcame their initial reservations and decided to enter labor unions,[26] there remained "the anti-syndicalist anarchist-communists, who in France were grouped around Sebastien Faure's Le Libertaire.
From 1905 onwards, the Russian counterparts of these anti-syndicalist
anarchist-communists become partisans of economic terrorism and illegal 'expropriations'." Illegalism as a practice emerged and within it "[t]he acts of the anarchist bombers and assassins ("propaganda by the deed") and the anarchist burglars ("individual reappropriation")
expressed their desperation and their personal, violent rejection of an
intolerable society. Moreover, they were clearly meant to be exemplary,
invitations to revolt."
Proponents and activists of these tactics among others included Johann Most, Luigi Galleani, Victor Serge, Giuseppe Ciancabilla, and Severino Di Giovanni. The Italian Giuseppe Ciancabilla
(1872–1904) wrote in "Against organization" that "we don't want
tactical programs, and consequently we don't want organization. Having
established the aim, the goal to which we hold, we leave every anarchist
free to choose from the means that his sense, his education, his
temperament, his fighting spirit suggest to him as best. We don't form
fixed programs and we don't form small or great parties. But we come
together spontaneously, and not with permanent criteria, according to
momentary affinities for a specific purpose, and we constantly change
these groups as soon as the purpose for which we had associated ceases
to be, and other aims and needs arise and develop in us and push us to
seek new collaborators, people who think as we do in the specific
circumstance."
By the 1880s, anarcho-communism was already present in the United States as can be seen in the publication of the journal Freedom: A Revolutionary Anarchist-Communist Monthly by Lucy Parsons and Lizzy Holmes. Lucy Parsons debated in her time in the US with fellow anarcho-communist Emma Goldman over issues of free love and feminism. Another anarcho-communist journal later appeared in the US called The Firebrand. Most anarchist publications in the US were in Yiddish, German, or Russian, but Free Society
was published in English, permitting the dissemination of anarchist
communist thought to English-speaking populations in the US. Around that time these American anarcho-communist sectors entered in debate with the individualist anarchist group around Benjamin Tucker. In February 1888 Berkman left for the United States from his native Russia. Soon after his arrival in New York City, Berkman became an anarchist through his involvement with groups that had formed to campaign to free the men convicted of the 1886 Haymarket bombing. He as well as Emma Goldman soon came under the influence of Johann Most, the best-known anarchist in the United States; and an advocate of propaganda of the deed—attentat, or violence carried out to encourage the masses to revolt. Berkman became a typesetter for Most's newspaper Freiheit.
According to anarchist historian Max Nettlau,
the first use of the term "libertarian communism" was in November 1880,
when a French anarchist congress employed it to more clearly identify
its doctrines. The French anarchist journalist Sébastien Faure started the weekly paper Le Libertaire (The Libertarian) in 1895.
Methods of Organising: Platformism vs Synthesism
In Ukraine the anarcho-communist guerrilla leader Nestor Makhno led an independent anarchist army in Ukraine during the Russian Civil War. A commander of the peasant Revolutionary Insurrectionary Army of Ukraine, also known as the Anarchist Black Army, Makhno led a guerrilla
campaign opposing both the Bolshevik "Reds" and monarchist "Whites".
The revolutionary autonomous movement of which he was a part made
various tactical military pacts while fighting various forces of
reaction and organizing the Free Territory of Ukraine, an anarchist society, committed to resisting state authority, whether capitalist or Bolshevik.
After successfully repelling Austro-Hungarian, White, and Ukrainian
Nationalist forces, the Makhnovists militia forces and anarchist
communist territories in the Ukraine were eventually crushed by
Bolshevik military forces.
In the Mexican Revolution the Mexican Liberal Party
was established and during the early 1910s it led a series of military
offensives leading to the conquest and occupation of certain towns and
districts in Baja California with the leadership of anarcho-communist Ricardo Flores Magón. Kropotkin's The Conquest of Bread, which Flores Magón considered a kind of anarchist bible, served as basis for the short-lived revolutionary communes in Baja California during the "Magónista" Revolt of 1911 During the Mexican Revolution Emiliano Zapata and his army and allies, including Pancho Villa, fought for agrarian reform in Mexico. Specifically, they wanted to establish communal land rights for Mexico's indigenous
population, which had mostly lost its land to the wealthy elite of
European descent. Zapata was partly influenced by Ricardo Flores Magón.
The influence of Flores Magón on Zapata can be seen in the Zapatistas' Plan de Ayala, but even more noticeably in their slogan (this slogan was never used by Zapata) "Tierra y libertad"
or "land and liberty", the title and maxim of Flores Magón's most
famous work. Zapata's introduction to anarchism came via a local
schoolteacher, Otilio Montaño Sánchez – later a general in Zapata's
army, executed on May 17, 1917 – who exposed Zapata to the works of Peter Kropotkin
and Flores Magón at the same time as Zapata was observing and beginning
to participate in the struggles of the peasants for the land.
A group of exiled Russian anarchists attempted to address and explain the anarchist movement's failures during the Russian Revolution. They wrote the Organizational Platform of the General Union of Anarchists which was written in 1926 by Dielo Truda
("Workers' Cause"). The pamphlet is an analysis of the basic anarchist
beliefs, a vision of an anarchist society, and recommendations as to how
an anarchist organization should be structured. The four main
principles by which an anarchist organization should operate, according
to the Platform, are ideological unity, tactical unity, collective action, and federalism.
The platform argues that "We have vital need of an organization which,
having attracted most of the participants in the anarchist movement,
would establish a common tactical and political line for anarchism and
thereby serve as a guide for the whole movement".
The Platform attracted strong criticism from many sectors on the
anarchist movement of the time including some of the most influential
anarchists such as Voline, Errico Malatesta, Luigi Fabbri, Camillo Berneri, Max Nettlau, Alexander Berkman, Emma Goldman and Gregori Maximoff.
Malatesta, after initially opposing the Platform, later came to
agreement with the Platform confirming that the original difference of
opinion was due to linguistic confusion: "I find myself more or less in
agreement with their way of conceiving the anarchist organisation (being
very far from the authoritarian spirit which the "Platform" seemed to
reveal) and I confirm my belief that behind the linguistic differences
really lie identical positions."
Sébastien Faure, French anarcho-communist proponent of synthesis anarchism
Two texts were made by the anarchist communists Sébastien Faure and Volin
as responses to the Platform, each proposing different models, are the
basis for what became known as the organisation of synthesis, or simply "synthesism". Voline published in 1924 a paper calling for "the anarchist synthesis" and was also the author of the article in Sébastien Faure's Encyclopedie Anarchiste on the same topic.
The main purpose behind the synthesis was that the anarchist movement
in most countries was divided into three main tendencies: communist anarchism, anarcho-syndicalism, and individualist anarchism
and so such an organization could contain anarchists of this 3
tendencies very well. Faure in his text "Anarchist synthesis" has the
view that "these currents were not contradictory but complementary, each
having a role within anarchism: anarcho-syndicalism as the strength of the mass organisations and the best way for the practice of anarchism; libertarian communism as a proposed future society based on the distribution of the fruits of labour according to the needs of each one; anarcho-individualism
as a negation of oppression and affirming the individual right to
development of the individual, seeking to please them in every way. The Dielo Truda platform in Spain also met with strong criticism. Miguel Jimenez, a founding member of the Iberian Anarchist Federation (FAI), summarized this as follows: too much influence in it of marxism,
it erroneously divided and reduced anarchists between individualist
anarchists and anarcho-communist sections, and it wanted to unify the
anarchist movement along the lines of the anarcho-communists. He saw
anarchism as more complex than that, that anarchist tendencies are not
mutually exclusive as the platformists saw it and that both
individualist and communist views could accommodate anarchosyndicalism.
Sébastian Faure had strong contacts in Spain and so his proposal had
more impact in Spanish anarchists than the Dielo Truda platform even
though individualist anarchist influence in Spain was less strong than
it was in France. The main goal there was conciling anarcho-communism
with anarcho-syndicalism.
Gruppo Comunista Anarchico di Firenze held that the during early twentieth century, the terms libertarian communism and anarchist communism became synonymous within the international anarchist movement as a result of the close connection they had in Spain.
The Spanish Revolution
Flag originally designed and used by the CNT-FAI - a confederation of labour unions - during the war in Spain, representing the anarchist faction of the conflict. Today, the flag is commonly used by anarcho-syndicalists, libertarian socialists, and anarcho-communists alike
The most extensive application of anarcho-communist ideas (i.e.,
established around the ideas as they exist today and achieving worldwide
attention and knowledge in the historical canon), happened in the
anarchist territories during the Spanish Revolution. In Spain, the national anarcho-syndicalist trade union Confederación Nacional del Trabajo
initially refused to join a popular front electoral alliance, and
abstention by CNT supporters led to a right wing election victory. In
1936, the CNT changed its policy and anarchist votes helped bring the
popular front back to power. Months later, the former ruling class
responded with an attempted coup causing the Spanish Civil War (1936–1939). In response to the army rebellion, an anarchist-inspired movement of peasants and workers, supported by armed militias, took control of Barcelona and of large areas of rural Spain where they collectivised the land. But even before the fascist victory in 1939, the anarchists were losing ground in a bitter struggle with the Stalinists, who controlled the distribution of military aid to the Republican cause from the Soviet Union. The events known as the Spanish Revolution was a workers' social revolution that began during the outbreak of the Spanish Civil War in 1936 and resulted in the widespread implementation of anarchist and more broadly libertarian socialist organizational principles throughout various portions of the country for two to three years, primarily Catalonia, Aragon, Andalusia, and parts of the Levante. Much of Spain's economy was put under worker control; in anarchist strongholds like Catalonia, the figure was as high as 75%, but lower in areas with heavy Communist Party of Spain influence, as the Soviet-allied party actively resisted attempts at collectivization enactment. Factories were run through worker committees, agrarian areas became collectivised and run as libertarian communes. Anarchist historian Sam Dolgoff estimated that about eight million people participated directly or at least indirectly in the Spanish Revolution,
which he claimed "came closer to realizing the ideal of the free
stateless society on a vast scale than any other revolution in history". Stalinist-led troops suppressed the collectives and persecuted both dissident Marxists and anarchists.
Post-war years
Anarcho-communism
entered into internal debates once again over the issue of organization
in the post-World War II era. Founded in October 1935 the
Anarcho-Communist Federation of Argentina (FACA, Federación
Anarco-Comunista Argentina) in 1955 renamed itself as the Argentine Libertarian Federation. The Fédération Anarchiste
(FA) was founded in Paris on December 2, 1945, and elected the
platformist anarcho-communist George Fontenis as its first secretary the
next year. It was composed of a majority of activists from the former
FA (which supported Voline's Synthesis)
and some members of the former Union Anarchiste, which supported the
CNT-FAI support to the Republican government during the Spanish Civil
War, as well as some young Resistants. On 1950 a clandestin group formed
within the FA called Organisation Pensée Bataille (OPB) led by George
Fontenis. The Manifesto of Libertarian Communism was written in 1953 by Georges Fontenis for the Federation Communiste Libertaire of France. It is one of the key texts of the anarchist-communist current known as platformism.
The OPB pushed for a move which saw the FA change its name into the
Fédération Communiste Libertaire (FCL) after the 1953 Congress in Paris,
while an article in Le Libertaire indicated the end of the cooperation with the French Surrealist Group led by André Breton. The new decision making process was founded on unanimity: each person has a right of veto on the orientations of the federation. The FCL published the same year the Manifeste du communisme libertaire.
Several groups quit the FCL in December 1955, disagreeing with the
decision to present "revolutionary candidates" to the legislative
elections. On August 15–20, 1954, the Ve intercontinental plenum of the
CNT took place. A group called Entente anarchiste appeared which was
formed of militants who didn't like the new ideological orientation that
the OPB was giving the FCL seeing it was authoritarian and almost
marxist.
The FCL lasted until 1956 just after it participated in state
legislative elections with 10 candidates. This move alienated some
members of the FCL and thus produced the end of the organization.
A group of militants who didn't agree with the FA turning into FCL
reorganized a new Federation Anarchiste which was established on
December, 1953. This included those who formed L'Entente anarchiste
who joined the new FA and then dissolved L'Entente. The new base
principles of the FA were written by the individualist anarchist Charles-Auguste Bontemps and the non-platformist anarcho-communist Maurice Joyeux which established an organization with a plurality of tendencies and autonomy of groups organized around synthesist principles. According to historian Cédric Guérin, "the unconditional rejection of Marxism
became from that moment onwards an identity element of the new
Federation Anarchiste" and this was motivated in a big part after the
previous conflict with George Fontenis and his OPB.
In Italy the Italian Anarchist Federation was founded in 1945 in Carrara. It adopted an "Associative Pact" and the "Anarchist Program" of Errico Malatesta. It decided to publish the weekly Umanità Nova retaking the name of the journal published by Errico Malatesta.
Inside the FAI, the Anarchist Groups of Proletarian Action (GAAP) was
founded, led by Pier Carlo Masini, which "proposed a Libertarian Party
with an anarchist theory and practice adapted to the new economic,
political and social reality of post-war Italy, with an internationalist
outlook and effective presence in the workplaces [...] The GAAP allied
themselves with the similar development within the French Anarchist movement" as led by George Fontenis.
Another tendency which didn't identify either with the more classical
FAI or with the GAAP started to emerge as local groups. These groups
emphasized direct action, informal affinity groups and expropriation for financing anarchist activity. From within these groups the influential insurrectionary anarchist Alfredo Maria Bonanno will emerge influenced by the practice of the Spanish exiled anarchist José Lluis Facerías. In the early seventies a platformist tendency emerged within the Italian Anarchist Federation which argued for more strategic coherence and social insertion in the workers movement while rejecting the syntesist "Associative Pact" of Malatesta which the FAI adhered to. These groups started organizing themselves outside the FAI in organizations such as O.R.A. from Liguria which organized a Congress attended by 250 delegates of grupos from 60 locations. This movement was influential in the autonomia movements of the seventies. They published Fronte Libertario della lotta di classe in Bologna and Comunismo libertario from Modena. The Federation of Anarchist Communists (Federazione dei Comunisti Anarchici), or FdCA, was established in 1985 in Italy from the fusion of the Organizzazione Rivoluzionaria Anarchica (Revolutionary Anarchist Organisation) and the Unione dei Comunisti Anarchici della Toscana (Tuscan Union of Anarchist Communists).
The International of Anarchist Federations (IAF/IFA) was founded during an international anarchist conference in Carrara in 1968 by the three existing European anarchist federations of France (Fédération Anarchiste), Italy (Federazione Anarchica Italiana) and Spain (Federación Anarquista Ibérica) as well as the Bulgarian federation in French exile. These organizations were also inspired on synthesist principles.
Contemporary times
Libertarian Communism was a socialist journal founded in 1974 and produced in part by members of the Socialist Party of Great Britain. The synthesist Italian Anarchist Federation and the platformist Federation of Anarchist Communists continue existing today in Italy but insurrectionary anarchism continues to be relevant as the recent establishment of the Informal Anarchist Federation shows.
In the seventies in France the Fédération Anarchiste evolved into a joining of the principles of both synthesis anarchism and platformism but later the platformist organizations Libertarian Communist Organization (France) in 1976 and Alternative libertaire in 1991 appeared with this last one existing until today alongside the synthesist Fédération Anarchiste. In recent times platformist organisations founded the now-defunct International Libertarian Solidarity
network and its successor, the Anarkismo network; which is run
collaboratively by roughly 30 platformist organisations around the
world.
On the other hand, contemporary insurrectionary anarchism
inherits the views and tactics of anti-organizational anarcho-communism and "illegalism". The Informal Anarchist Federation (not to be confused with the synthesist Italian Anarchist Federation also FAI) is an Italian insurrectionary anarchist organization.
It has been described by Italian intelligence sources as a "horizontal"
structure of various anarchist terrorist groups, united in their
beliefs in revolutionary armed action. In 2003, the group claimed
responsibility for a bomb campaign targeting several European Union
institutions.
Currently alongside the previously mentioned federations, the International of Anarchist Federations includes the Argentine Libertarian Federation,
the Anarchist Federation of Belarus, the Federation of Anarchists in
Bulgaria, the Czech-Slovak Anarchist Federation, the Federation of
German speaking Anarchists in Germany and Switzerland, and the Anarchist Federation in the United Kingdom and Ireland.
Economic theory
The abolition of money, prices, and wage labor
is central to anarchist communism. With distribution of wealth being
based on self-determined needs, people would be free to engage in
whatever activities they found most fulfilling and would no longer have
to engage in work for which they have neither the temperament nor the
aptitude.
Anarchist communists argue that there is no valid way of
measuring the value of any one person's economic contributions because
all wealth is a common product of current and preceding generations.
For instance, one could not measure the value of a factory worker's
daily production without taking into account how transportation, food,
water, shelter, relaxation, machine efficiency, emotional mood etc.
contributed to their production. To truly give numerical economic value
to anything, an overwhelming amount of externalities and contributing
factors would need to be taken into account – especially current or past
labor contributing to the ability to utilize future labor. As Kropotkin
put it: "No distinction can be drawn between the work of each man.
Measuring the work by its results leads us to absurdity; dividing and
measuring them by hours spent on the work also leads us to absurdity.
One thing remains: put the needs above the works, and first of all
recognize the right to live, and later on, to the comforts of life, for
all those who take their share in production.."
The Conquest of Bread by Peter Kropotkin, influential work which presents the economic vision of anarcho-communism
Communist anarchism shares many traits with collectivist anarchism,
but the two are distinct. Collectivist anarchism believes in collective
ownership while communist anarchism negates the entire concept of
ownership in favor of the concept of usage.
Crucially, the abstract relationship of "landlord" and "tenant" would
no longer exist, as such titles are held to occur under conditional
legal coercion and are not absolutely necessary to occupy buildings or
spaces (intellectual property rights would also cease, since they are a form of private property).
In addition to believing rent and other fees are exploitative,
anarcho-communists feel these are arbitrary pressures inducing people to
carry out unrelated functions. For example, they question why one
should have to work for 'X hours' a day to merely live somewhere. So
instead of working conditionally for the sake of the wage earned, they
believe in working directly for the objective at hand.
Philosophical debates
Motivation
Anarchist
communists reject the claim that wage labor is necessary because people
are lazy and selfish by "human nature". They often point out that even
the so-called "idle rich" sometimes find useful things to do despite
having all their needs satisfied by the labour of others.
Anarcho-communists generally do not agree with the belief in a pre-set
"human nature", arguing that human culture and behavior is very largely
determined by socialization and the mode of production.
Many anarchist communists, like Peter Kropotkin, also believe that
human evolutionary tendency is for humans to cooperate with each other
for mutual benefit and survival instead of existing as lone competitors.
While anarchist communists such as Peter Kropotkin and Murray Bookchin
believed that the members of such a society would voluntarily perform
all necessary labour because they would recognize the benefits of
communal enterprise and mutual aid,
other anarchist communists such as Nestor Makhno and Ricardo Flores
Magón argue that all those able to work in an anarchist communist
society should be obligated to do so, excepting groups like children,
the elderly, the sick, or the infirm. Kropotkin did not think laziness or sabotage
would be a major problem in an authentically anarchist-communist
society, but he did agree that a freely associated anarchist commune
could, and probably should, deliberately disassociate from those not
fulfilling their communal agreement to do their share of work. Peter Gelderloos, based off the Kibbutz,
argues that motivation in a moneyless society would be found in the
satisfaction of work, concern for community, competition for prestige
and praise from other community members.
Freedom, work and leisure
Anarchist
communists support communism as a means for ensuring the greatest
freedom and well-being for everyone, rather than only the wealthy and
powerful. In this sense, anarchist communism is a profoundly egalitarian philosophy.
Anarchist communism as an anarchist philosophy is against hierarchy in all its forms.
Anarchist communists do not think that anyone has the right to be
anyone else's master, or 'boss' as this is a concept of capitalism and
the state and implies authority over the individual. Some contemporary
anarchist communists and advocates of post-left anarchy, such as Bob Black, reject the concept of work altogether in favor of turning necessary subsistence tasks into voluntary free play.
Peter Kropotkin said that the main authoritarian mistakes in communist experiments of the past were their being based on "religious enthusiasm" and the desire to live "as a family" where the individual had to "submit to the dictates of a punctilious morality".
For him anarcho-communism should be based on the right of free
association and disassociation for individuals and groups and on
significantly lowering the number of hours each individual dedicates to
necessary labor.
He says that "to recognise a variety of occupations as the basis of all
progress and to organise in such a way that man may be absolutely free
during his leisure time, whilst he may also vary his work, a change for
which his early education and instruction will have prepared him—this
can easily be put in practice in a Communist society—this, again, means
the emancipation of the individual, who will find doors open in every
direction for his complete development".
Individualism and collectivism
Some anarcho-communists (and collectivist anarchists as well) reject "individualism" and "collectivism" as illusory concepts.
They argue that individuals sacrificing themselves for the "greater",
or being ruled by the "community" or "society", is not possible because
society is composed of individuals rather than being a cohesive unit
separate from the individual, and argue that collective control over the
individual is tyrannical and thus antithetical to anarchism.
Others, such as Lucien van der Walt and Michael Schmidt, argue that:
"The anarchists did not [...] identify freedom with the right of
everybody to do exactly what one pleased but with a social order in
which collective effort and responsibilities—that is to say,
obligations—would provide the material basis and social nexus in which
individual freedom could exist." They argued that "genuine freedom and
individuality could only exist in a free society" and that in contrast
to "misanthropic bourgeois individualism" anarchism was based in "a deep
love of freedom, understood as a social product, a deep respect for
human rights, a profound celebration of humankind and its potential and a
commitment to a form of society where a 'true individuality' was
irrevocably linked to 'the highest communist socieability'".
Egoist philosophical positions are important in anarcho-communist insurrectionary anarchism. In the early 20th century the Italian individualist anarchist Renzo Novatore
advocated both revolution and anarcho-communism when he said
"revolution is the fire of our will and a need of our solitary minds; it
is an obligation of the libertarian aristocracy. To create new ethical
values. To create new aesthetic values. To communalize material wealth.
To individualize spiritual wealth." From Stirnerist
positions he also disrespected private property when he said that
"[o]nly ethical and spiritual wealth" was "invulnerable. This is the
true property of individuals. The rest no! The rest is vulnerable! And
all that is vulnerable will be violated!" This can also be seen in the contemporary writings of insurrectionary anarchism, as can be seen in the work of Wolfi Landstreicher, Alfredo Bonanno, and others. Post-left anarcho-communist Bob Black, after analysing insurrectionary anarcho-communist Luigi Galleani's view on anarcho-communism, went as far as saying that "communism is the final fulfillment of individualism
[...] The apparent contradiction between individualism and communism
rests on a misunderstanding of both [...] Subjectivity is also
objective: the individual really is subjective. It is nonsense to speak
of 'emphatically prioritizing the social over the individual,' [...] You
may as well speak of prioritizing the chicken over the egg. Anarchy is a
'method of individualization.' It aims to combine the greatest
individual development with the greatest communal unity."
On the article by Max Baginski called "Stirner: The Ego and His Own", published in the American anarchist magazine Mother Earth,
there is the following affirmation: "Modern Communists are more
individualistic than Stirner. To them, not merely religion, morality,
family and State are spooks, but property also is no more than a spook,
in whose name the individual is enslaved—and how enslaved! The
individuality is nowadays held in far stronger bondage by property, than
by the combined power of State, religion and morality [...] The prime
condition is that the individual should not be forced to humiliate and
lower himself for the sake of property and subsistence. Communism thus
creates a basis for the liberty and Eigenheit of the individual. I am a
Communist because I am an Individualist. Fully as heartily the
Communists concur with Stirner when he puts the word take in place of
demand—that leads to the dissolution of private property, to expropriation. Individualism and Communism go hand in hand."
Property
Alexander Berkman advocated for profit to be replaced with communities of common property, where all members of a group shared possessions
Anarchist communists counter the capitalist conception that communal
property can only be maintained by force and that such a position is
neither fixed in nature nor unchangeable in practice, citing numerous examples of communal behavior occurring naturally even within capitalist systems. Anarchist communists call for the abolition of private property while maintaining respect for personal property. As such the prominent anarcho-communist Alexander Berkman
maintained that "The revolution abolishes private ownership of the
means of production and distribution, and with it goes capitalistic
business. Personal possession remains only in the things you use. Thus,
your watch is your own, but the watch factory belongs to the people.
Land, machinery, and all other public utilities will be collective
property, neither to be bought nor sold. Actual use will be considered
the only title-not to ownership but to possession. The organization of
the coal miners, for example, will be in charge of the coal mines, not
as owners but as the operating agency. Similarly will the railroad
brotherhoods run the railroads, and so on. Collective possession,
cooperatively managed in the interests of the community, will take the
place of personal ownership privately conducted for profit."
An important difference between anarchist communism and Marxist communism is who the product of the worker's labor belongs to. Both ideologies believe that the product of labor does not belong to the capitalist
due to it being produced by the worker and not the employer, however,
there are slight differences between the opinions taken by anarchist
communist Peter Kropotkin and Karl Marx.
Marx stated that the product of the worker's labor belongs to the
worker due to it being produced by the worker. In contrast, Kropotkin
believed that the product of the worker's labor belongs to the community
as a whole. Kropotkin argued that this was the case because the worker
relied on the previous work of untold millions in to even begin his
particular form of labor, and therefore, his work should belong to the
community, since he benefited from the community.
The commune as an economic democracy
Anarcho-communism
has been critical of a simple call for worker's ownership of workplaces
and their administration as cooperatives. While not at odds with
syndicalism as a tactic, it opposes the vision of anarcho-syndicalism as a theory, which sees a post-capitalist economy being made up of federations of industrial syndicates.
Instead, anarcho-communism proposes that the future society be
organised territorially through free communes (localities), instead of
industrially through workers' unions (syndicates). Each commune is
perceived as an integrated political-economic unit, removing the
distinction between work and community, as well as existing as part of a
wider communal-confederation made up of other such autonomous communes,
linked together via voluntary contractual agreements. This is seen as
overcoming the economic-centrism of more "workerist" forms of socialism
which focus on the workplace alone as a site of struggle.
Murray Bookchin has put it this way:
But what of the syndicalist ideal of "collectivized" self-managed enterprises that are coordinated by like occupations on a national level and coordinated geographically by "collectives" on a local level? [...] Here, the traditional socialist criticism of this syndicalist form of economic management is not without its point: the corporate or private capitalist, "worker-controlled" or not—ironically, a technique in the repertoire of industrial management that is coming very much into vogue today as "workplace democracy" and "employee ownership" and constitutes no threat whatever to private property and capitalism [...] In any case, "economic democracy" has not simply meant "workplace democracy" and "employee ownership."
Many workers, in fact, would like to get away from their factories if they could and find more creative artisanal types of work, not simply "participate" in "planning" their own misery. What "economic democracy" meant in its profoundest sense was free, "democratic" access to the means of life, the counterpart of political democracy, that is, the guarantee of freedom from material want. It is a dirty bourgeois trick, in which many radicals unknowingly participate, that "economic democracy" has been re-interpreted as "employee ownership" and "workplace democracy" and has come to mean workers' "participation" in profit sharing and industrial management rather than freedom from the tyranny of the factory, rationalized labor, and "planned production," which is usually exploitative production with the complicity of the workers.
As such:
Whereas the syndicalist alternative re-privatizes the economy into "self-managed" collectives and opens the way to their degeneration into traditional forms of private property—whether "collectively" owned or not—libertarian municipalism politicizes the economy and dissolves it into the civic domain. Neither factory or land appear as separate interests within the communal collective. Nor can workers, farmers, technicians, engineers, professionals, and the like perpetuate their vocational identities as separate interests that exist apart from the citizen body in face-to-face assemblies. "Property" is integrated into the commune as a material constituent of its libertarian institutional framework, indeed as a part of a larger whole that is controlled by the citizen body in assembly as citizens—not as vocationally oriented interest groups.
The word "communism" in anarcho-communism should thus be taken to refer to a polity of communes as well as an economy of the commons.
The revolution and the transition
For platformist anarcho-communist Wayne Price:
Today's proposals for Parecon, in which workers are rewarded for the intensity and duration of their labor in a cooperative economy, would fit into Bakunin's or Marx's concept of a transitory, beginning, phase, of a free society [...] Kropotkin rejected the two-phase approach of the Marxists and the anarchist-collectivists. Instead he proposed that a revolutionary society should "transform itself immediately into a communist society, that is, should go immediately into what Marx had regarded as the "more advanced", completed, phase of communism. Kropotkin and those who agreed with him called themselves "anarchist-communists" (or "communist anarchists"), although they continued to regard themselves as a part of the broader socialist movement.
Leninists believe that without a transitional period of state control (their interpretation of the dictatorship of the proletariat),
it would be impossible for any revolution to maintain the momentum or
cohesion to defend the new society against external and internal
threats. Friedrich Engels
noted: "Without a previous social revolution the abolition of the state
is nonsense; the abolition of capital is in itself the social
revolution and involves a change in the whole method of production."
Alternatively, such quotations have been interpreted by
Anarcho-communists supportive of Marx and Engels to suggest the
abolition of capitalism and the state simultaneously, not the creation
of a new state. Anarchists reject the Marxist–Leninist model of the
"dictatorship of the proletariat," arguing that any revolutionary
minority taking over state power would be just as authoritarian as the
ruling class in capitalism to defend the new state, and would eventually
constitute itself as a new ruling class. As an extension of this,
Anarcho-communists counter-argue that decentralized, stateless
collective federations are sufficient to give both power to workers and
preserve personal freedom and point to the fact that no socialist state
has ever showed signs of "withering away". Again, the Spanish Revolution
is cited as an example of successful anarchist military mobilization,
albeit one crushed by superior forces.
Free association of communes as opposed to the nation-state
Anarcho-communism calls for a confederal form in relationships of mutual aid and free association between communes as an alternative to the centralism of the nation-state. Peter Kropotkin thus suggested:
Representative government has accomplished its historical mission; it has given a mortal blow to court-rule; and by its debates it has awakened public interest in public questions. But to see in it the government of the future socialist society is to commit a gross error. Each economic phase of life implies its own political phase; and it is impossible to touch the very basis of the present economic life—private property—without a corresponding change in the very basis of the political organization. Life already shows in which direction the change will be made. Not in increasing the powers of the State, but in resorting to free organization and free federation in all those branches which are now considered as attributes of the State.
As such:
[N]o community can hope to achieve economic autarchy, nor should it try to do so unless it wishes to become self-enclosed and parochial, not only "self-sufficient". Hence the confederation of communes "the Commune of communes" is reworked economically as well as politically into a shared universe of publicly managed resources. The management of the economy, precisely because it is a public activity, does not degenerate into privatized interactions between enterprises; rather it develops into confederalized interactions between municipalities. That is to say, the very elements of societal interaction are expanded from real or potential privatized components to institutionally real public components. Confederation becomes a public project by definition, not only because of shared needs and resources. If there is any way to avoid the emergence of the city-state, not to speak of self-serving bourgeois "cooperatives," it is through a municipalization of political life that is so complete that politics embraces not only what we call the public sphere but material means of life as well.
Example societies through history
Early examples
There
have been several attempts, both successful and unsuccessful, at
creating other anarchist-communist societies throughout much of the
world. Anarchist-communists and some green anarchists (especially anarcho-primitivists) argue that hunter-gatherer tribes, like families, were early forms of anarchist-communism due to their egalitarian nature.
The Andaman Islands in the Bay of Bengal
were said to be inhabited by wolf-headed people, who were depicted in a
"book of wonders" produced in Paris in the early 15th century. Such
manuscripts, commissioned by wealthy patrons, presented tales of distant
lands for the entertainment of their readers
Both an ancient and modern day example of anarcho-communism being
utilised by an isolated population would be by the hunter-gatherers of North Sentinel Island. North Sentinel Island is one of the Andaman Islands in the Bay of Bengal, occupied by the Sentinelese tribe who've inhabited the island for a least 60,000 years. They practice a kind of primitive communism,
where all property is held collectively by the community, and there
exists no hierarchy between different members of the group. The workers,
both male and female, control the means of production, as all materials
found and collected go toward building small-scale structures for
housing and storing of items. Though geographically close to the Indian Subcontinent, the Indian government
doesn't disturb them, as they remain ungoverned. If North Sentinel
Island could be called a country, it would be the last remaining
anarchist country on the planet.
The Andaman Islands were often said to be inhabited by various tribes
and factions, including humanoid wolves in clothing. These claims
originate from French fiction, written to create curiosity for places people of Europe had never travelled.
Early Christian communities have also been described as having anarcho-communist characteristics. Frank Seaver Billings described "Jesusism" as a combination of anarchism and communism. Examples of later Christian egalitarian communities include the Diggers.
Gift economies and commons-based organising
In anthropology and the social sciences, a gift economy (or gift culture) is a mode of exchange where valuable goods and services are regularly given without any explicit agreement for immediate or future rewards (i.e. no formal quid pro quo exists).
Ideally, voluntary and recurring gift exchange circulates and
redistributes wealth throughout a community, and serves to build
societal ties and obligations. In contrast to a barter economy or a market economy, social norms and custom governs gift exchange, rather than an explicit exchange of goods or services for money or some other commodity.
Watercolor by James G. Swan depicting the Klallam people of chief Chetzemoka at Port Townsend, with one of Chetzemoka's wives distributing potlatch
Traditional societies dominated by gift exchange
were small in scale and geographically remote from each other. As
states formed to regulate trade and commerce within their boundaries,
market exchange came to dominate. Nonetheless, the practice of gift exchange continues to play an important role in modern society. One prominent example is scientific research, which can be described as a gift economy. Contrary to popular conception, there is no evidence that societies relied primarily on barter before using money for trade. Instead, non-monetary societies operated largely along the principles of gift economics, and in more complex economies, on debt. When barter did in fact occur, it was usually between either complete strangers or would-be enemies.
The expansion of the Internet has witnessed a resurgence of the gift
economy, especially in the technology sector. Engineers, scientists and
software developers create open-source software projects. The Linux kernel and the GNU
operating system are prototypical examples for the gift economy's
prominence in the technology sector and its active role in instating the
use of permissive free software and copyleft licenses, which allow free reuse of software and knowledge. Other examples include: file-sharing, the commons, open access. Anarchist scholar Uri Gordon has said that:
"the collaborative development of free software like the Linux operating system and applications such as OpenOffice clearly approximate an informational anarchist communism. Moreover, for anarchists it is precisely the logic of expropriation and electronic piracy that enables a radical political extension of the cultural ideals of the free manipulation, circulation and use of information associated with the "hacker ethic" (Himanen 2001). The space of illegality created by P2P (peer-to-peer) file-sharing opens up the possibility, not only of the open circulation of freely-given information and software as it is on the Internet today, but also of conscious copyright violation. The Internet, then, enables not only communist relations around information, but also the militant contamination and erosion of non-communist regimes of knowledge—a technological "weapon" to equalise access to information, eating away at intellectual property rights by rendering them unenforceable.
The interest in such economic forms goes back to Peter Kropotkin, who saw in the hunter-gatherer tribes he had visited the paradigm of "mutual aid". anarchist anthropologist David Graeber in his 2011 book Debt: The First 5000 Years argues that with the advent of the great Axial Age
civilizations, the nexus between coinage and the calculability of
economic values was concomitant with the disrupt of what Graeber calls
"human economies," as found among the Iroquois, Celts, Inuit, Tiv, Nuer, and the Malagasy people of Madagascar
among other groups which, according to Graeber, held a radically
different conception of debt and social relations, based on the radical
incalculability of human life and the constant creation and recreation
of social bonds through gifts, marriages and general sociability. The
author postulates the growth of a "military-coinage-slave complex"
around this time, through which mercenary armies looted cities and human
beings were cut from their social context to work as slaves in Greece,
Rome and elsewhere in the Eurasian continent. The extreme violence of
the period marked by the rise of great empires in China, India and the
Mediterranean was, in this way, connected with the advent of large-scale
slavery and the use of coins to pay soldiers, together with the
obligation enforced by the State for its subjects to pay its taxes in
currency. This was also the same time that the great religions spread
out and the general questions of philosophical enquiry emerged on world
history—many of those directly related, as in Plato's Republic, with the
nature of debt and its relation to ethics.
Korean Anarchist Movement
Korean People's Association in Manchuria, a Korean anarchist society that existed without markets, instead structured on mutual aid and gift economics
The Korean Anarchist Movement in Korea led by Kim Chwa-chin briefly brought anarcho-communism to Korea. The success was short-lived and much less widespread than the anarchism in Spain. The Korean People's Association in Manchuria had established a stateless, classless
society where all means of production were run and operated by the
workers, and where all possessions were held in common by the community.
Inside Utrecht Giveaway shop
the banner reads: "The earth has enough for everyone's need, but not
for everyone's greed. Take no more than you could use yourself"
Urban communities
Trumbullplex, as an example of an anarchist community, operates to serve the common good through sheltering residents within a neighbourhood of Detroit, Michigan.
This allows individuals who've previously gone into debt by means of
rent to escape their economic burdens and join a democratic commune. The
commune has served as a hangout for young members of the locality,
alongside a place intended for teamwork and cooperative decision making. This is often accompanied by music of the punk rock
genre and frequent parties and celebrations thrown by Trumbullplex
members. The commune has existed since 1993. Its current ideology, the
same as its founding ideology, was to establish a settlement based on
principles of mutual aid and the absence of hierarchy.
Give-away shops
Give-away shops, free shops, or free stores, are stores where all goods are free. They are similar to charity shops, with mostly second-hand items—only everything is available at no cost. Whether it is a book, a piece of furniture, a garment or a household
item, it is all freely given away, although some operate a one-in,
one-out–type policy (swap shops). The free store is a form of
constructive direct action that provides a shopping alternative to a monetary framework, allowing people to exchange goods and services outside of a money-based economy. The anarchist 1960s countercultural group The Diggers opened free stores
which simply gave away their stock, provided free food, distributed
free drugs, gave away money, organized free music concerts, and
performed works of political art. The Diggers took their name from the original English Diggers led by Gerrard Winstanley and sought to create a mini-society free of money and capitalism. Although free stores have not been uncommon in the United States since the 1960s, the freegan movement has inspired the establishment of more free stores. Today the idea is kept alive by the new generations of social centres, anarchists and environmentalists who view the idea as an intriguing way to raise awareness about consumer culture and to promote the reuse of commodities.