From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Induced hydraulic fracturing | |
|---|---|
Schematic depiction of hydraulic fracturing for shale gas.
|
|
| Process type | Mechanical |
| Industrial sector(s) | Mining |
| Main technologies or sub-processes | Fluid pressure |
| Product(s) | Natural gas, petroleum |
| Inventor | Floyd Farris, (Stanolind Oil and Gas Corporation) |
| Year of invention | 1947 |
Hydraulic fracturing (also hydrofracturing, hydrofracking, fracking or fraccing), is a well-stimulation technique in which rock is fractured by a hydraulically pressurized liquid made of water, sand, and chemicals. Some hydraulic fractures form naturally—certain veins or dikes are examples.[1] A high-pressure fluid (usually chemicals and sand suspended in water) is injected into a wellbore to create cracks in the deep-rock formations through which natural gas, petroleum, and brine will flow more freely. When the hydraulic pressure is removed from the well, small grains of hydraulic fracturing proppants (either sand or aluminium oxide) hold the fractures open.
Hydraulic fracturing began as an experiment in 1947, and the first commercially successful application followed in 1950. As of 2012, 2.5 million "frac jobs" had been performed worldwide on oil and gas wells; over one million of those within the U.S.[2][3] Such treatment is generally necessary to achieve adequate flow rates in shale gas, tight gas, tight oil, and coal seam gas wells.[4]
Hydraulic fracturing is highly controversial; whereas its proponents advocate the economic benefits of more extensively accessible hydrocarbons,[5][6] its environmental impacts include the risk of contaminating ground water, depletion of fresh water, degradation of the air quality, the potential triggering of earthquakes, noise pollution, surface pollution, and the consequential risks to health and the environment.[7]
Increases in seismic activity following hydraulic fracturing along dormant or previously unknown faults are sometimes caused by the deep-injection disposal of hydraulic fracturing flowback (a byproduct of hydraulically fractured wells),[8] and produced formation brine (a byproduct of both fractured and nonfractured oil and gas wells).[9] For these reasons, hydraulic fracturing is under international scrutiny, restricted in some countries, and banned altogether in others.[10][11][12] Some of those countries, notably the U.K., contemplated repeal of bans on hydraulic fracturing in favor of regulation. The European Union is drafting regulations that would permit controlled application of hydraulic fracturing.[13]
Geology
Main article: Fracture (geology)
Mechanics
Fracturing in rocks at depth tends to be suppressed by the pressure due to the weight of the overlying rock strata, and the cementation of the formation. This is particularly significant in "tensile" (Mode 1) fractures which require the walls of the fracture to move against this pressure. Fracturing occurs when effective stress is overcome by the pressure of fluids within the rock. The minimum principal stress becomes tensile and exceeds the tensile strength of the material.[14][15] Fractures formed in this way are generally oriented in a plane perpendicular to the minimum principal stress, and for this reason, hydraulic fractures in well bores can be used to determine the orientation of stresses.[16] In natural examples, such as dikes or vein-filled fractures, the orientations can be used to infer past states of stress.[17]Veins
Most mineral vein systems are a result of repeated natural fracturing during periods of relatively high pore fluid pressure. This is particularly evident in "crack-seal" veins, where the vein material is part of a series of discrete fracturing events, and extra vein material is deposited on each occasion.[18] One example of long-term repeated natural fracturing is in the effects of seismic activity. Stress levels rise and fall episodically, and earthquakes can cause large volumes of connate water to be expelled from fluid-filled fractures. This process is referred to as "seismic pumping".[19]Dikes
Minor intrusions in the upper part of the crust, such as dikes, propagate in the form of fluid-filled cracks. In such cases, the fluid is magma. In sedimentary rocks with a significant water content, fluid at fracture tip will be steam.[20]History
Precursors
Fracturing as a method to stimulate shallow, hard rock oil wells dates back to the 1860s. Dynamite or nitroglycerin detonations were used to increase oil and natural gas production from petroleum bearing formations. On April 25, 1865, Civil War veteran Col. Edward A. L. Roberts received a patent for an "exploding torpedo".[21] It was employed in Pennsylvania, New York, Kentucky, and West Virginia using liquid and also, later, solidified nitroglycerin. Later still the same method was applied to water and gas wells. Stimulation of wells with acid, instead of explosive fluids, was introduced in the 1930s. Due to acid etching, fractures would not close completely resulting in further productivity increase.[22]Oil and gas wells
The relationship between well performance and treatment pressures was studied by Floyd Farris of Stanolind Oil and Gas Corporation. This study was the basis of the first hydraulic fracturing experiment, conducted in 1947 at the Hugoton gas field in Grant County of southwestern Kansas by Stanolind.[4][23] For the well treatment, 1,000 US gallons (3,800 l; 830 imp gal) of gelled gasoline (essentially napalm) and sand from the Arkansas River was injected into the gas-producing limestone formation at 2,400 feet (730 m). The experiment was not very successful as deliverability of the well did not change appreciably. The process was further described by J.B. Clark of Stanolind in his paper published in 1948. A patent on this process was issued in 1949 and exclusive license was granted to the Halliburton Oil Well Cementing Company. On March 17, 1949, Halliburton performed the first two commercial hydraulic fracturing treatments in Stephens County, Oklahoma, and Archer County, Texas.[23] Since then, hydraulic fracturing has been used to stimulate approximately one million oil and gas wells[24] in various geologic regimes with good success.In contrast with large-scale hydraulic fracturing used in low-permeability formations, small hydraulic fracturing treatments are commonly used in high-permeability formations to remedy "skin damage", a low-permeability zone that sometimes forms at the rock-borehole interface. In such cases the fracturing may extend only a few feet from the borehole.[25]
In the Soviet Union, the first hydraulic proppant fracturing was carried out in 1952. Other countries in Europe and Northern Africa subsequently employed hydraulic fracturing techniques including Norway, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, Hungary, Austria, France, Italy, Bulgaria, Romania, Turkey, Tunisia, and Algeria.[26]
Massive fracturing
Massive hydraulic fracturing (also known as high-volume hydraulic fracturing) is a technique first applied by Pan American Petroleum in Stephens County, Oklahoma, USA in 1968. The definition of massive hydraulic fracturing varies somewhat, but is generally reference to treatments injecting greater than about 150 short tons, or approximately 300,000 pounds (136 metric tonnes), of proppant.[27]
American geologists became increasingly aware that there were huge volumes of gas-saturated sandstones with permeability too low (generally less than 0.1 millidarcy) to recover the gas economically.[27] Starting in 1973, massive hydraulic fracturing was used in thousands of gas wells in the San Juan Basin, Denver Basin,[28] the Piceance Basin,[29] and the Green River Basin, and in other hard rock formations of the western US. Other tight sandstone wells in the US made economically viable by massive hydraulic fracturing were in the Clinton-Medina Sandstone, and Cotton Valley Sandstone.[27]
Massive hydraulic fracturing quickly spread in the late 1970s to western Canada, Rotliegend and Carboniferous gas-bearing sandstones in Germany, Netherlands (onshore and offshore gas fields), and the United Kingdom in the North Sea.[26]
Horizontal oil or gas wells were unusual until the late 1980s. Then, operators in Texas began completing thousands of oil wells by drilling horizontally in the Austin Chalk, and giving massive slickwater hydraulic fracturing treatments to the wellbores. Horizontal wells proved much more effective than vertical wells in producing oil from tight chalk;[30] sedimentary beds are usually nearly horizontal, so horizontal wells have much larger contact areas with the target formation.[31]
Shales
Due to shale's high porosity and low permeability, technological research, development and demonstration were necessary before hydraulic fracturing was accepted for commercial application to shale gas deposits. In 1976, the United States government started the Eastern Gas Shales Project, a set of dozens of public-private hydraulic fracturing demonstration projects.[32] During the same period, the Gas Research Institute, a gas industry research consortium, received approval for research and funding from the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission.[33]In 1997, taking the slickwater fracturing technique used in East Texas by Union Pacific Resources (now part of Anadarko Petroleum Corporation), Mitchell Energy (now part of Devon Energy), applied the technique in the Barnett Shale of north Texas.[31] This made gas extraction widely economical in the Barnett Shale, and was later applied to other shales.[34][35][36] George P. Mitchell has been called the "father of fracking" because of his role in applying it in shales.[37] The first horizontal well in the Barnett Shale was drilled in 1991, but was not widely done in the Barnett until it was demonstrated that gas could be economically extracted from vertical wells in the Barnett.[31]
As of 2013, massive hydraulic fracturing is being applied on a commercial scale to shales in the United States, Canada, and China. Several additional countries are planning to use hydraulic fracturing.[38][39][40]
Process
According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) hydraulic fracturing is a process to stimulate a natural gas, oil, or geothermal energy well to maximize extraction. EPA defines the broader process as including the acquisition of source water, well construction, well stimulation, and waste disposal.[41]Method
A hydraulic fracture is formed by pumping fracturing fluid into a wellbore at a rate sufficient to increase pressure at the target depth (determined by the location of the well casing perforations), to exceed that of the fracture gradient (pressure gradient) of the rock.[42] The fracture gradient is defined as pressure increase per unit of depth relative to density, and is usually measured in pounds per square inch, per foot, or bars per metre. The rock cracks, and the fracture fluid permeates the rock extending the crack further, and further, and so on. Fractures are localized as pressure drops off with the rate of frictional loss, which is relevant to the distance from the well. Operators typically try to maintain "fracture width", or slow its decline following treatment, by introducing a proppant into the injected fluid – a material such as grains of sand, ceramic, or other particulate, thus preventing the fractures from closing when injection is stopped and pressure removed. Consideration of proppant strength and prevention of proppant failure becomes more important at greater depths where pressure and stresses on fractures are higher. The propped fracture is permeable enough to allow the flow of gas, oil, salt water and hydraulic fracturing fluids to the well.[42]During the process, fracturing fluid leakoff (loss of fracturing fluid from the fracture channel into the surrounding permeable rock) occurs. If not controlled, it can exceed 70% of the injected volume. This may result in formation matrix damage, adverse formation fluid interaction, and altered fracture geometry, thereby decreasing efficiency.[43]
The location of one or more fractures along the length of the borehole is strictly controlled by various methods that create or seal holes in the side of the wellbore. Hydraulic fracturing is performed in cased wellbores, and the zones to be fractured are accessed by perforating the casing at those locations.[44]
Hydraulic-fracturing equipment used in oil and natural gas fields usually consists of a slurry blender, one or more high-pressure, high-volume fracturing pumps (typically powerful triplex or quintuplex pumps) and a monitoring unit. Associated equipment includes fracturing tanks, one or more units for storage and handling of proppant, high-pressure treating iron[clarification needed], a chemical additive unit (used to accurately monitor chemical addition), low-pressure flexible hoses, and many gauges and meters for flow rate, fluid density, and treating pressure.[45] Chemical additives are typically 0.5% percent of the total fluid volume. Fracturing equipment operates over a range of pressures and injection rates, and can reach up to 100 megapascals (15,000 psi) and 265 litres per second (9.4 cu ft/s) (100 barrels per minute).[46]
Well types
A distinction can be made between conventional, low-volume hydraulic fracturing, used to stimulate high-permeability reservoirs for a single well, and unconventional, high-volume hydraulic fracturing, used in the completion of tight gas and shale gas wells. Unconventional wells are deeper and require higher pressures than conventional vertical wells.[47]Horizontal drilling involves wellbores with a terminal drillhole completed as a "lateral" that extends parallel with the rock layer containing the substance to be extracted. For example, laterals extend 1,500 to 5,000 feet (460 to 1,520 m) in the Barnett Shale basin in Texas, and up to 10,000 feet (3,000 m) in the Bakken formation in North Dakota. In contrast, a vertical well only accesses the thickness of the rock layer, typically 50–300 feet (15–91 m). Horizontal drilling reduces surface disruptions as fewer wells are required to access the same volume of rock. Drilling usually induces damage to the pore space at the wellbore wall, reducing permeability at and near the wellbore. This reduces flow into the borehole from the surrounding rock formation, and partially seals off the borehole from the surrounding rock. Hydraulic fracturing can be used to restore permeability,[48] but is not typically administered in this way.
Fracturing fluids
The main purposes of fracturing fluid are to extend fractures, add lubrication, change gel strength, and to carry proppant into the formation. There are two methods of transporting proppant in the fluid – high-rate and high-viscosity. High-viscosity fracturing tends to cause large dominant fractures, while high-rate (slickwater) fracturing causes small spread-out micro-fractures.[citation needed]Water-soluble gelling agents (such as guar gum) increase viscosity and efficiently deliver proppant into the formation.[49]
Fluid is typically a slurry of water, proppant, and chemical additives.[50] Additionally, gels, foams, and compressed gases, including nitrogen, carbon dioxide and air can be injected. Typically, 90% of the fluid is water and 9.5% is sand with chemical additives accounting to about 0.5%.[42][51][52] However, fracturing fluids have been developed using liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) and propane in which water is unnecessary.[53]
The proppant is a granular material that prevents the created fractures from closing after the fracturing treatment. Types of proppant include silica sand, resin-coated sand, bauxite, and man-made ceramics. The choice of proppant depends on the type of permeability or grain strength needed. In some formations, where the pressure is great enough to crush grains of natural silica sand, higher-strength proppants such as bauxite or ceramics may be used. The most commonly used proppant is silica sand, though proppants of uniform size and shape, such as a ceramic proppant, are believed to be more effective.[54]
The fracturing fluid varies depending on fracturing type desired, and the conditions of specific wells being fractured, and water characteristics. The fluid can be gel, foam, or slickwater-based. Fluid choices are tradeoffs: more viscous fluids, such as gels, are better at keeping proppant in suspension; while less-viscous and lower-friction fluids, such as slickwater, allow fluid to be pumped at higher rates, to create fractures farther out from the wellbore. Important material properties of the fluid include viscosity, pH, various rheological factors, and others.
A typical fracture treatment uses between 3 and 12 additive chemicals.[42] Although there may be unconventional fracturing fluids, typical chemical additives can include one or more of the following:
- Acids—hydrochloric acid or acetic acid is used in the pre-fracturing stage for cleaning the perforations and initiating fissure in the near-wellbore rock.[52]
- Sodium chloride (salt)—delays breakdown of gel polymer chains.[52]
- Polyacrylamide and other friction reducers decrease turbulence in fluid flow and pipe friction, thus allowing the pumps to pump at a higher rate without having greater pressure on the surface.[52]
- Ethylene glycol—prevents formation of scale deposits in the pipe.[52]
- Borate salts—used for maintaining fluid viscosity during the temperature increase.[52]
- Sodium and potassium carbonates—used for maintaining effectiveness of crosslinkers.[52]
- Glutaraldehyde—used as disinfectant of the water (bacteria elimination).[52]
- Guar gum and other water-soluble gelling agents—increases viscosity of the fracturing fluid to deliver proppant into the formation more efficiently.[49][52]
- Citric acid—used for corrosion prevention.
- Isopropanol—used to winterize the chemicals to ensure it doesn't freeze.[52]
Typical fluid types are:
- Conventional linear gels. These gels are cellulose derivative (carboxymethyl cellulose, hydroxyethyl cellulose, carboxymethyl hydroxyethyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hydroxyethyl methyl cellulose), guar or its derivatives (hydroxypropyl guar, carboxymethyl hydroxypropyl guar), mixed with other chemicals.
- Borate-crosslinked fluids. These are guar-based fluids cross-linked with boron ions (from aqueous borax/boric acid solution). These gels have higher viscosity at pH 9 onwards and are used to carry proppant. After the fracturing job, the pH is reduced to 3–4 so that the cross-links are broken, and the gel is less viscous and can be pumped out.
- Organometallic-crosslinked fluids zirconium, chromium, antimony, titanium salts are known to crosslink the guar-based gels. The crosslinking mechanism is not reversible, so once the proppant is pumped down along with cross-linked gel, the fracturing part is done. The gels are broken down with appropriate breakers[clarification needed].[49]
- Aluminium phosphate-ester oil gels. Aluminium phosphate and ester oils are slurried to form cross-linked gel. These are one of the first known gelling systems.
Fracture monitoring
Measurements of the pressure and rate during the growth of a hydraulic fracture, with knowledge of fluid properties and proppant being injected into the well, provides the most common and simplest method of monitoring a hydraulic fracture treatment. This data along with knowledge of the underground geology can be used to model information such as length, width and conductivity of a propped fracture.[42]Injection of radioactive tracers along with the fracturing fluid is sometimes used to determine the injection profile and location of created fractures.[57] Radiotracers are selected to have the readily detectable radiation, appropriate chemical properties, and a half life and toxicity level that will minimize initial and residual contamination.[58] Radioactive isotopes chemically bonded to glass (sand) and/or resin beads may also be injected to track fractures.[59] For example, plastic pellets coated with 10 GBq of Ag-110mm may be added to the proppant, or sand may be labelled with Ir-192, so that the proppant's progress can be monitored.[58] Radiotracers such as Tc-99m and I-131 are also used to measure flow rates.[58] The Nuclear Regulatory Commission publishes guidelines which list a wide range of radioactive materials in solid, liquid and gaseous forms that may be used as tracers and limit the amount that may be used per injection and per well of each radionuclide.[59]
Microseismic monitoring
For more advanced applications, microseismic monitoring is sometimes used to estimate the size and orientation of induced fractures. Microseismic activity is measured by placing an array of geophones in a nearby wellbore. By mapping the location of any small seismic events associated with the growing fracture, the approximate geometry of the fracture is inferred. Tiltmeter arrays deployed on the surface or down a well provide another technology for monitoring strain[60]Microseismic mapping is very similar geophysically to seismology. In earthquake seismology, seismometers scattered on or near the surface of the earth record S-waves and P-waves that are released during an earthquake event. This allows for motion[clarification needed] along the fault plane to be estimated and its location in the earth’s subsurface mapped. Hydraulic fracturing, an increase in formation stress proportional to the net fracturing pressure, as well as an increase in pore pressure due to leakoff.[61] Tensile stresses are generated ahead of the fractures tip generating large amounts of shear stress. The increase in pore water pressure and formation stress combine and affect weaknesses (natural fractures, joints, and bedding planes) near the hydraulic fracture.[62]
Different methods have different location errors[clarification needed] and advantages. Accuracy of microseismic event mapping is dependent on the signal-to-noise ratio and the distribution of sensors. Accuracy of events located by seismic inversion is improved by sensors placed in multiple azimuths from the monitored borehole. In a downhole array location, accuracy of events is improved by being close to the monitored borehole (high signal-to-noise ratio).
Monitoring of microseismic events induced by reservoir[clarification needed] stimulation has become a key aspect in evaluation of hydraulic fractures, and their optimization. The main goal of hydraulic fracture monitoring is to completely characterize the induced fracture structure, and distribution of conductivity within a formation. Geomechanical analysis, such as understanding a formations material properties, in-situ conditions, and geometries, helps monitoring by providing a better definition of the environment in which the fracture network propagates.[63] The next task is to know the location of proppant within the fracture and the distribution of fracture conductivity. This can be monitored using multiple types of techniques to finally develop a reservoir model than accurately predicts well performance.
Horizontal completions
Since the early 2000s, advances in drilling and completion technology have made horizontal wellbores much[clarification needed] more economical. Horizontal wellbores allow far greater exposure to a formation than conventional vertical wellbores. This is particularly useful in shale formations which do not have sufficient permeability to produce economically with a vertical well. Such wells, when drilled onshore, are now usually hydraulically fractured in a number of stages, especially in North America. The type of wellbore completion is used to determine how many times a formation is fractured, and at what locations along the horizontal section.[64]In North America, shale reservoirs such as the Bakken, Barnett, Montney, Haynesville, Marcellus, and most recently the Eagle Ford, Niobrara and Utica shales are drilled horizontally through the producing interval(s), completed and fractured.[citation needed] The method by which the fractures are placed along the wellbore is most commonly achieved by one of two methods, known as "plug and perf" and "sliding sleeve".[65]
The wellbore for a plug-and-perf job is generally composed of standard steel casing, cemented or uncemented, set in the drilled hole. Once the drilling rig has been removed, a wireline truck is used to perforate near the bottom of the well, and then fracturing fluid is pumped. Then the wireline truck sets a plug in the well to temporarily seal off that section so the next section of the wellbore can be treated. Another stage is pumped, and the process is repeated along the horizontal length of the wellbore.[66]
The wellbore for the sliding sleeve[clarification needed] technique is different in that the sliding sleeves are included at set spacings in the steel casing at the time it is set in place. The sliding sleeves are usually all closed at this time. When the well is due to be fractured, the bottom sliding sleeve is opened using one of several activation techniques and the first stage gets pumped. Once finished, the next sleeve is opened, concurrently isolating the previous stage, and the process repeats. For the sliding sleeve method, wireline is usually not required.[citation needed]
These completion techniques may allow for more than 30 stages to be pumped into the horizontal section of a single well if required, which is far more than would typically be pumped into a vertical well that had far fewer feet of producing zone exposed.[67]
Uses
Hydraulic fracturing is used to increase the rate at which fluids, such as petroleum, water, or natural gas can be recovered from subterranean natural reservoirs. Reservoirs are typically porous sandstones, limestones or dolomite rocks, but also include "unconventional reservoirs" such as shale rock or coal beds. Hydraulic fracturing enables the extraction of natural gas and oil from rock formations deep below the earth's surface (generally 2,000–6,000 m (5,000–20,000 ft)), which is greatly below typical groundwater reservoir levels. At such depth, there may be insufficient permeability or reservoir pressure to allow natural gas and oil to flow from the rock into the wellbore at high economic return. Thus, creating conductive fractures in the rock is instrumental in extraction from naturally impermeable shale reservoirs. Permeability is measured in the microdarcy to nanodarcy range.[68] Fractures are a conductive path connecting a larger volume of reservoir to the well. So-called "super fracking," creates cracks deeper in the rock formation to release more oil and gas, and increases efficiency.[69] The yield for typical shale bores generally falls off after the first year or two, but the peak producing life of a well can be extended to several decades.[70]While the main industrial use of hydraulic fracturing is in stimulating production from oil and gas wells,[71][72][73] hydraulic fracturing is also applied:
- To stimulate groundwater wells[74]
- To precondition or induce rock cave-ins mining[75]
- As a means of enhancing waste remediation, usually hydrocarbon waste or spills[76]
- To dispose waste by injection deep into rock[77]
- To measure stress in the Earth[78]
- For electricity generation in enhanced geothermal systems[79]
- To increase injection rates for geologic sequestration of CO
2[80]
Economic effects
Hydraulic fracturing has been seen as one of the key methods of extracting unconventional oil and gas resources. According to the International Energy Agency, the remaining technically recoverable resources of shale gas are estimated to amount to 208 trillion cubic metres (208,000 km3), tight gas to 76 trillion cubic metres (76,000 km3), and coalbed methane to 47 trillion cubic metres (47,000 km3). As a rule, formations of these resources have lower permeability than conventional gas formations. Therefore depending on the geological characteristics of the formation, specific technologies (such as hydraulic fracturing) are required. Although there are also other methods to extract these resources, such as conventional drilling or horizontal drilling, hydraulic fracturing is one of the key methods making their extraction economically viable. The multi-stage fracturing technique has facilitated the development of shale gas and light tight oil production in the United States and is believed to do so in the other countries with unconventional hydrocarbon resources.[5]The National Petroleum Council estimates that hydraulic fracturing will eventually account for nearly 70% of natural gas development in North America.[84] Hydraulic fracturing and horizontal drilling apply the latest technologies and make it commercially viable to recover shale gas and oil. In the United States, 45% of domestic natural gas production and 17% of oil production would be lost within 5 years without usage of hydraulic fracturing.[85]
U.S.-based refineries have gained a competitive edge with their access to relatively inexpensive shale oil and Canadian crude. The U.S. is exporting more refined petroleum products, and also more liquified petroleum gas (LP gas). LP gas is produced from hydrocarbons called natural gas liquids, released by the hydraulic fracturing of petroliferous shale, in a variety of shale gas that's relatively easy to export. Propane, for example, costs around $620 a ton in the U.S. compared with more than $1,000 a ton in China, as of early 2014. Japan, for instance, is importing extra LP gas to fuel power plants, replacing idled nuclear plants. Trafigura Beheer BV, the third-largest independent trader of crude oil and refined products, said at the start of 2014 that "growth in U.S. shale production has turned the distillates market on its head."[86]
Some studies call into question the claim that what has been called the "shale gas revolution" has a significant macro-economic impact. A study released in the beginning of 2014 by the IDDRI concluded the contrary. It states that, on the long-term as well as on the short-run, the "shale gas revolution" due to hydraulic fracturing in the United States has had very little impact on economic growth and competitiveness.[87] The same report concludes that in Europe, using hydraulic fracturing would have very little advantage in terms of competitiveness and energy security. Indeed, for the period 2030-2035, shale gas is estimated to cover 3 to 10% of EU projected energy demand, which is not enough to have a significant impact on energetic independence and competitiveness.[87]
Hydrofracked shale oil and gas has the potential to alter the geography of energy production in the US.[88][better source needed][89] In the short run, in counties with hydrofracturing employment in the oil and gas sector more than doubled in the last 10 years, with spill-overs in local transport-, construction but also manufacturing sectors.[88][better source needed] The manufacturing sector benefits from lower energy prices, giving the US manufacturing sector a competitive edge. On average, natural gas prices have decreased by more than 30% in counties above shale deposits compared to the rest of the US. Some research has highlighted the negative effects on house prices for properties in the direct vicinity of fracturing wells.[90] Local house prices in Pennsylvania decrease if the property is close to a hydrofracking gas well and is not connected to city water, suggesting that the concerns of ground water pollution are priced by markets.
Public debate
Politics and public policy
An anti-fracking movement has emerged both internationally with involvement of international environmental organizations and nation states such as France and locally in affected areas such as Balcombe in Sussex where the Balcombe drilling protest was in progress during summer 2013.[91]The considerable opposition against hydraulic fracturing activities in local townships in the United States has led companies to adopt a variety of public relations measures to reassure the public, including the employment of former military personnel with training in psychological warfare operations. According to Matt Pitzarella, the communications director at Range Resources, employees trained in the Middle East have been valuable to Range Resources in Pennsylvania, when dealing with emotionally charged township meetings and advising townships on zoning and local ordinances dealing with hydraulic fracturing.[92][93]
Protests have occasionally been marred by acts of violence. In March 2013, ten people were arrested[94] during an "anti-fracking protest" near New Matamoras, Ohio, after they illegally entered a development zone and latched themselves to drilling equipment. In northwest Pennsylvania, there was a drive-by shooting at a well site, in which an individual shot two rounds of a small-caliber rifle in the direction of a drilling rig, just before shouting profanities at the site and fleeing the scene.[95] In Washington County, Pennsylvania, a contractor working on a gas pipeline found a pipe bomb that had been placed where a pipeline was to be constructed, which local authorities said would have caused a "catastrophe" had they not discovered and detonated it.[96]
In 2014 a number of officials in Europe and NATO provided circumstantial evidence that protests against fracking may be sponsored by Gazprom. Russian officials have on numerous occasions warned Europe that fracking "poses a huge environmental problem". At the same time Gazprom is also searching for shale gas in Romania (via its subsidiary "Nis") and it has always reacted aggressively to any criticism by environmental organisations.[97]
Documentary films
Josh Fox's 2010 Academy Award nominated film Gasland [98] became a center of opposition to hydraulic fracturing of shale. The movie presented problems with ground water contamination near well sites in Pennsylvania, Wyoming, and Colorado.[99] Energy in Depth, an oil and gas industry lobbying group, called the film's facts into question.[100] In response, a rebuttal of Energy in Depth's claims of inaccuracy was posted on Gasland's website.[101]The Director of the Colorado Oil and Gas Conservation Commission (COGCC) offered to be interviewed as part of the film if he could review what was included from the interview in the final film but Fox declined the offer.[102] Exxon Mobil, Chevron Corporation and ConocoPhillips aired advertisements during 2011 and 2012 that claimed to describe the economic and environmental benefits of natural gas and argue that hydraulic fracturing was safe.[103]
The film Promised Land, starring Matt Damon, takes on hydraulic fracturing.[104] The gas industry is making plans to try to counter the film's criticisms of hydraulic fracturing with informational flyers, and Twitter and Facebook posts.[103]
On January 22, 2013 Northern Irish journalist and filmmaker Phelim McAleer released a crowdfunded[105] documentary called FrackNation as a response to the statements made by Fox in Gasland. FrackNation premiered on Mark Cuban's AXS TV. The premiere corresponded with the release of Promised Land.[106]
On April 21, 2013, Josh Fox released Gasland 2, a documentary that states that the gas industry's portrayal of natural gas as a clean and safe alternative to oil is a myth, and that hydraulically fractured wells inevitably leak over time, contaminating water and air, hurting families, and endangering the earth's climate with the potent greenhouse gas methane.
Research issues
Typically the funding source of the research studies is a focal point of controversy. Concerns have been raised about research funded by foundations and corporations, or by environmental groups, which can at times lead to at least the appearance of unreliable studies.[107][108] Several organizations, researchers, and media outlets have reported difficulty in conducting and reporting the results of studies on hydraulic fracturing due to industry[109] and governmental pressure,[10] and expressed concern over possible censoring of environmental reports.[109][110][111] There is a need for more research into the environmental and health effects of the technique.[112][113][114][115]Health risks
There is concern over the possible adverse public health implications of hydraulic fracturing activity.[112] A 2013 review on shale gas production in the United States stated, "with increasing numbers of drilling sites, more people are at risk from accidents and exposure to harmful substances used at fractured wells."[116] A 2011 hazard assessment recommended full disclosure of chemicals used for hydraulic fracturing and drilling as many have immediate health effects, and many may have long-term health effects.[117]In June 2014 Public Health England published a review of the potential public health impacts of exposures to chemical and radioactive pollutants as a result of shale gas extraction in the UK, based on the examination of literature and data from countries where hydraulic fracturing already occurs.[113] The executive summary of the report stated: "An assessment of the currently available evidence indicates that the potential risks to public health from exposure to the emissions associated with shale gas extraction will be low if the operations are properly run and regulated. Most evidence suggests that contamination of groundwater, if it occurs, is most likely to be caused by leakage through the vertical borehole. Contamination of groundwater from the underground hydraulic fracturing process itself (ie the fracturing of the shale) is unlikely. However, surface spills of hydraulic fracturing fluids or wastewater may affect groundwater, and emissions to air also have the potential to impact on health. Where potential risks have been identified in the literature, the reported problems are typically a result of operational failure and a poor regulatory environment."[118]:iii
A 2012 report prepared for the European Union Directorate-General for the Environment identified potential risks to humans from air pollution and ground water contamination posed by hydraulic fracturing.[119] This lead to a series of recommendations in 2014 to mitigate these concerns.[120][121] A 2012 guidance for pediatric nurses in the US, said that hydraulic fracturing had a potential negative impact on public health, and that pediatric nurses should be prepared to gather information on such topics so as to advocate for improved community health.[122]
Environmental impacts
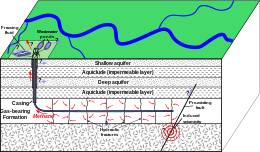
The environmental impacts of hydraulic fracturing are air emissions and climate change, high water consumption, water contamination, land use, risk of earthquakes, noise pollution, and health effects on humans. Air emissions are primarily methane that escapes from wells, along with industrial emissions from equipment used in the extraction process.[119] Modern UK and EU regulation requires zero emissions of methane, a potent greenhouse gas.[123] Escape of methane is a bigger problem in older wells than in ones built under more recent EU legislation.[119]Hydraulic fracturing uses between 1.2 and 3.5 million US gallons (4,500 and 13,200 m3) of water per well, with large projects using up to 5 million US gallons (19,000 m3). Additional water is used when wells are refractured.[49][124] An average well requires 3 to 8 million US gallons (11,000 to 30,000 m3) of water over its lifetime.[42] According to the Oxford Institute for Energy Studies, greater volumes of fracturing fluids are required in Europe, where the shale depths average 1.5 times greater than in the U.S.[125] Surface water may be contaminated through spillage and improperly built and maintained waste pits,[126] and ground water can be contaminated if the fluid is able to escape the formation being fractured (through, for example, abandoned wells) or by produced water (the returning fluids, which also contain dissolved constituents such as minerals and brine waters).[113] Produced water is managed by underground injection, municipal and commercial wastewater treatment and discharge, self‐contained systems at well sites or fields, and recycling to fracture future wells.[127] Typically less than half of the produced water used to fracture the formation is recovered.[128]
About 3.6 hectares (8.9 acres) of land is needed per each drill pad for surface installations. These sites need to be remediated after wells are exhausted.[119] Each well pad (in average 10 wells per pad) needs during preparatory and hydraulic fracturing process about 800 to 2,500 days of noisy activity, which affect both residents and local wildlife. In addition, noise is created by continuous truck traffic (sand, etc.) needed in hydraulic fracturing.[119] Research is underway to determine if human health has been affected by air and water pollution, and rigorous following of safety procedures and regulation is required to avoid harm and to manage the risk of accidents that could cause harm.[113]
In July 2013, the US Federal Railroad Administration listed oil contamination by hydraulic fracturing chemicals as "a possible cause" of corrosion in oil tank cars.[129]
Hydraulic fracturing sometimes causes induced seismicity or earthquakes. The magnitude of these events is usually too small to be detected at the surface, although tremors attributed to fluid injection into disposal wells have been large enough to have often been felt by people, and to have caused property damage and possibly injuries.[8][130][131][132][133]
Microseismic events are often used to map the horizontal and vertical extent of the fracturing.[60] A better understanding of the geology of the area being fracked and used for injection wells can be helpful in mitigating the potential for significant seismic events.[134]
Regulations
Countries using or considering to use hydraulic fracturing have implemented different regulations, including developing federal and regional legislation, and local zoning limitations.[135][136] In 2011, after public pressure France became the first nation to ban hydraulic fracturing, based on the precautionary principle as well as the principal of preventive and corrective action of environmental hazards.[11][12][137][138] The ban was upheld by an October 2013 ruling of the Constitutional Council.[139] Some other countries have placed a temporary moratorium on the practice.[140]
Countries like the United Kingdom and South Africa have lifted their bans, choosing to focus on regulation instead of outright prohibition.[141][142] Germany has announced draft regulations that would allow using hydraulic fracturing for the exploitation of shale gas deposits with the exception of wetland areas.[143]
The European Union has adopted a recommendation for minimum principles for using high-volume hydraulic fracturing.[13] Its regulatory regime requires full disclosure of all additives.[144] In the United States, the Ground Water Protection Council launched FracFocus.org, an online voluntary disclosure database for hydraulic fracturing fluids funded by oil and gas trade groups and the U.S. Department of Energy.[145][146] Hydraulic fracturing is excluded from the Safe Drinking Water Act's underground injection control's regulation, except when diesel fuel is used. The EPA assures surveillance of the issuance of drilling permits when diesel fuel is employed.[147]
In 2012, Vermont became the first state in the United States to ban hydraulic fracturing. On December 17, 2014, New York became the second state to issue a full and complete ban on any hydraulic fracturing due to potential risks to human health and the environment.[148][149][150]
The European Union has adopted a recommendation for minimum principles for using high-volume hydraulic fracturing.[13] Its regulatory regime requires full disclosure of all additives.[144] In the United States, the Ground Water Protection Council launched FracFocus.org, an online voluntary disclosure database for hydraulic fracturing fluids funded by oil and gas trade groups and the U.S. Department of Energy.[145][146] Hydraulic fracturing is excluded from the Safe Drinking Water Act's underground injection control's regulation, except when diesel fuel is used. The EPA assures surveillance of the issuance of drilling permits when diesel fuel is employed.[147]
In 2012, Vermont became the first state in the United States to ban hydraulic fracturing. On December 17, 2014, New York became the second state to issue a full and complete ban on any hydraulic fracturing due to potential risks to human health and the environment.[148][149][150]










