From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Cell | |
|---|---|
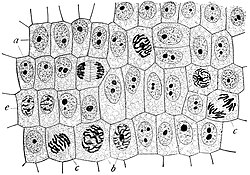
Onion (Allium) cells in different phases of the cell cycle
|
|

The cells of eukaryotes (left) and prokaryotes (right)
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| TH | H1.00.01.0.00001 |
| FMA | 68646 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The cell (from Latin cella, meaning "small room"[1]) is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of cells is called cell biology.
Cells consist of a protoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids.[2] Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including most bacteria) or multicellular (including plants and animals). While the number of cells in plants and animals varies from species to species, humans contain about 100 trillion (1014) cells.[3] Most plant and animal cells are visible only under the microscope, with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres.[4]
The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, who named the biological unit for its resemblance to cells inhabited by Christian monks in a monastery.[5][6] The cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that all cells come from preexisting cells, that vital functions of an organism occur within cells, and that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells.[7] Cells emerged on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago.[8][9][10]
Anatomy
There are two types of cells, eukaryotes, which contain a nucleus, and prokaryotes, which do not. Prokaryotic cells are usually single-celled organisms, while eukaryotic cells can be either single-celled or part of multicellular organisms.| Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes | |
|---|---|---|
| Typical organisms | bacteria, archaea | protists, fungi, plants, animals |
| Typical size | ~ 1–5 µm[11] | ~ 10–100 µm[11] |
| Type of nucleus | nucleoid region; no true nucleus | true nucleus with double membrane |
| DNA | circular (usually) | linear molecules (chromosomes) with histone proteins |
| RNA/protein synthesis | coupled in the cytoplasm | RNA synthesis in the nucleus protein synthesis in the cytoplasm |
| Ribosomes | 50S and 30S | 60S and 40S |
| Cytoplasmic structure | very few structures | highly structured by endomembranes and a cytoskeleton |
| Cell movement | flagella made of flagellin | flagella and cilia containing microtubules; lamellipodia and filopodia containing actin |
| Mitochondria | none | one to several thousand (though some lack mitochondria) |
| Chloroplasts | none | in algae and plants |
| Organization | usually single cells | single cells, colonies, higher multicellular organisms with specialized cells |
| Cell division | Binary fission (simple division) | Mitosis (fission or budding) Meiosis |
| chromosomes | single chromosome | more than one chromosome |
| membranes | none | has membrane bound organelles |
Prokaryotic cells

Diagram of a typical prokaryotic cell
Prokaryotic cells were the first form of life on Earth, as they have signaling and self-sustaining processes. They are simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells, and lack membrane-bound organelles such as the nucleus. Prokaryotes include two of the domains of life, bacteria and archaea. The DNA of a prokaryotic cell consists of a single chromosome that is in direct contact with the cytoplasm. The nuclear region in the cytoplasm is called the nucleoid. Most of the prokaryotes are smallest of all organisms. Most prokaryotes range from 0.5 to 2.0 µm in diameter.[12]
A prokaryotic cell has three architectural regions:
- On the outside, flagella and pili project from the cell's surface. These are structures (not present in all prokaryotes) made of proteins that facilitate movement and communication between cells.
- Enclosing the cell is the cell envelope – generally consisting of a cell wall covering a plasma membrane though some bacteria also have a further covering layer called a capsule. The envelope gives rigidity to the cell and separates the interior of the cell from its environment, serving as a protective filter. Though most prokaryotes have a cell wall, there are exceptions such as Mycoplasma (bacteria) and Thermoplasma (archaea). The cell wall consists of peptidoglycan in bacteria, and acts as an additional barrier against exterior forces. It also prevents the cell from expanding and bursting (cytolysis) from osmotic pressure due to a hypotonic environment. Some eukaryotic cells (plant cells and fungal cells) also have a cell wall.
- Inside the cell is the cytoplasmic region that contains the genome (DNA), ribosomes and various sorts of inclusions. The prokaryotic chromosome is usually a circular molecule (an exception is that of the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, which causes Lyme disease).[13] Though not forming a nucleus, the DNA is condensed in a nucleoid. Prokaryotes can carry extrachromosomal DNA elements called plasmids, which are usually circular. Plasmids encode additional genes, such as antibiotic resistance genes.
Eukaryotic cells

Plants, animals, fungi, slime moulds, protozoa, and algae are all eukaryotic. These cells are about fifteen times wider than a typical prokaryote and can be as much as a thousand times greater in volume. The main distinguishing feature of eukaryotes as compared to prokaryotes is compartmentalization: the presence of membrane-bound compartments in which specific metabolic activities take place. Most important among these is a cell nucleus, a membrane-delineated compartment that houses the eukaryotic cell's DNA. This nucleus gives the eukaryote its name, which means "true nucleus". Other differences include:
- The plasma membrane resembles that of prokaryotes in function, with minor differences in the setup. Cell walls may or may not be present.
- The eukaryotic DNA is organized in one or more linear molecules, called chromosomes, which are associated with histone proteins. All chromosomal DNA is stored in the cell nucleus, separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane. Some eukaryotic organelles such as mitochondria also contain some DNA.
- Many eukaryotic cells are ciliated with primary cilia. Primary cilia play important roles in chemosensation, mechanosensation, and thermosensation. Cilia may thus be "viewed as a sensory cellular antennae that coordinates a large number of cellular signaling pathways, sometimes coupling the signaling to ciliary motility or alternatively to cell division and differentiation."[14]
- Eukaryotes can move using motile cilia or flagella. Eukaryotic flagella are less complex than those of prokaryotes.
Subcellular components
All cells, whether prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have a membrane that envelops the cell, regulates what moves in and out (selectively permeable), and maintains the electric potential of the cell. Inside the membrane, a salty cytoplasm takes up most of the cell volume. All cells (except red blood cells which lack a cell nucleus and most organelles to accommodate maximum space for hemoglobin) possess DNA, the hereditary material of genes, and RNA, containing the information necessary to build various proteins such as enzymes, the cell's primary machinery. There are also other kinds of biomolecules in cells. This article lists these primary components of the cell, then briefly describes their function.
Membrane
The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell. In animals, the plasma membrane is the outer boundary of the cell, while in plants and prokaryotes it is usually covered by a cell wall. This membrane serves to separate and protect a cell from its surrounding environment and is made mostly from a double layer of phospholipids, which are amphiphilic (partly hydrophobic and partly hydrophilic). Hence, the layer is called a phospholipid bilayer, or sometimes a fluid mosaic membrane. Embedded within this membrane is a variety of protein molecules that act as channels and pumps that move different molecules into and out of the cell. The membrane is said to be 'semi-permeable', in that it can either let a substance (molecule or ion) pass through freely, pass through to a limited extent or not pass through at all. Cell surface membranes also contain receptor proteins that allow cells to detect external signaling molecules such as hormones.Cytoskeleton
A fluorescent image of an endothelial cell. Nuclei are stained blue, mitochondria are stained red, and microfilaments are stained green.
The cytoskeleton acts to organize and maintain the cell's shape; anchors organelles in place; helps during endocytosis, the uptake of external materials by a cell, and cytokinesis, the separation of daughter cells after cell division; and moves parts of the cell in processes of growth and mobility. The eukaryotic cytoskeleton is composed of microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules. There are a great number of proteins associated with them, each controlling a cell's structure by directing, bundling, and aligning filaments. The prokaryotic cytoskeleton is less well-studied but is involved in the maintenance of cell shape, polarity and cytokinesis.[15]The subunit protein of microfilaments is a small, monomeric protein called actin. The subunit of microtubules is a dimeric molecule called tubulin. Intermediate filaments are heteropolymers whose subunits varies among the cell types in different tissues. But some of the subunit protein of intermediate filaments include vimentin, desmin, lamin (lamins A, B and C), keratin (multiple acidic and basic keratins), neurofilament proteins (NF - L, NF - M).
Genetic material
Two different kinds of genetic material exist: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Cells use DNA for their long-term information storage. The biological information contained in an organism is encoded in its DNA sequence. RNA is used for information transport (e.g., mRNA) and enzymatic functions (e.g., ribosomal RNA). Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules are used to add amino acids during protein translation.Prokaryotic genetic material is organized in a simple circular DNA molecule (the bacterial chromosome) in the nucleoid region of the cytoplasm. Eukaryotic genetic material is divided into different, linear molecules called chromosomes inside a discrete nucleus, usually with additional genetic material in some organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts (see endosymbiotic theory).
A human cell has genetic material contained in the cell nucleus (the nuclear genome) and in the mitochondria (the mitochondrial genome). In humans the nuclear genome is divided into 46 linear DNA molecules called chromosomes, including 22 homologous chromosome pairs and a pair of sex chromosomes. The mitochondrial genome is a circular DNA molecule distinct from the nuclear DNA. Although the mitochondrial DNA is very small compared to nuclear chromosomes, it codes for 13 proteins involved in mitochondrial energy production and specific tRNAs.
Foreign genetic material (most commonly DNA) can also be artificially introduced into the cell by a process called transfection. This can be transient, if the DNA is not inserted into the cell's genome, or stable, if it is. Certain viruses also insert their genetic material into the genome.
Organelles
Organelles are parts of the cell which are adapted and/or specialized for carrying out one or more vital functions, analogous to the organs of the human body (such as the heart, lung, and kidney, with each organ performing a different function). Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells have organelles, but prokaryotic organelles are generally simpler and are not membrane-bound.There are several types of organelles in a cell. Some (such as the nucleus and golgi apparatus) are typically solitary, while others (such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, peroxisomes and lysosomes) can be numerous (hundreds to thousands). The cytosol is the gelatinous fluid that fills the cell and surrounds the organelles.
Eukaryotic

Human cancer cells with nuclei (specifically the DNA) stained blue. The central and rightmost cell are in interphase, so the entire nuclei are labeled. The cell on the left is going through mitosis and its DNA has condensed.
- Cell nucleus: A cell's information center, the cell nucleus is the most conspicuous organelle found in a eukaryotic cell. It houses the cell's chromosomes, and is the place where almost all DNA replication and RNA synthesis (transcription) occur. The nucleus is spherical and separated from the cytoplasm by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. The nuclear envelope isolates and protects a cell's DNA from various molecules that could accidentally damage its structure or interfere with its processing. During processing, DNA is transcribed, or copied into a special RNA, called messenger RNA (mRNA). This mRNA is then transported out of the nucleus, where it is translated into a specific protein molecule. The nucleolus is a specialized region within the nucleus where ribosome subunits are assembled. In prokaryotes, DNA processing takes place in the cytoplasm.
- Mitochondria and Chloroplasts: the power generators: Mitochondria are self-replicating organelles that occur in various numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells. Mitochondria play a critical role in generating energy in the eukaryotic cell. Respiration occurs in the cell mitochondria, which generate the cell's energy by oxidative phosphorylation, using oxygen to release energy stored in cellular nutrients (typically pertaining to glucose) to generate ATP. Mitochondria multiply by binary fission, like prokaryotes. Chloroplasts can only be found in plants and algae, and they capture the sun's energy to make ATP through photosynthesis.
- Endoplasmic reticulum: The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a transport network for molecules targeted for certain modifications and specific destinations, as compared to molecules that float freely in the cytoplasm. The ER has two forms: the rough ER, which has ribosomes on its surface that secrete proteins into the ER, and the smooth ER, which lacks ribosomes. The smooth ER plays a role in calcium sequestration and release.
- Golgi apparatus: The primary function of the Golgi apparatus is to process and package the macromolecules such as proteins and lipids that are synthesized by the cell.
- Lysosomes and Peroxisomes: Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes (acid hydrolases). They digest excess or worn-out organelles, food particles, and engulfed viruses or bacteria. Peroxisomes have enzymes that rid the cell of toxic peroxides. The cell could not house these destructive enzymes if they were not contained in a membrane-bound system.
- Centrosome – the cytoskeleton organiser: The centrosome produces the microtubules of a cell – a key component of the cytoskeleton. It directs the transport through the ER and the Golgi apparatus. Centrosomes are composed of two centrioles, which separate during cell division and help in the formation of the mitotic spindle. A single centrosome is present in the animal cells. They are also found in some fungi and algae cells.
- Vacuoles: Vacuoles store food and waste. Some vacuoles store extra water. They are often described as liquid filled space and are surrounded by a membrane. Some cells, most notably Amoeba, have contractile vacuoles, which can pump water out of the cell if there is too much water. The vacuoles of eukaryotic cells are usually larger in those of plants than animals.
Eukaryotic and prokaryotic
- Ribosomes: The ribosome is a large complex of RNA and protein molecules. They each consist of two subunits, and act as an assembly line where RNA from the nucleus is used to synthesise proteins from amino acids. Ribosomes can be found either floating freely or bound to a membrane (the rough endoplasmatic reticulum in eukaryotes, or the cell membrane in prokaryotes).[16]
Structures outside the cell membrane
Many cells also have structures which exist wholly or partially outside the cell membrane. These structures are notable because they are not protected from the external environment by the impermeable cell membrane. In order to assemble these structures, their components must be carried across the cell membrane by export processes.Cell wall
Many types of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have a cell wall. The cell wall acts to protect the cell mechanically and chemically from its environment, and is an additional layer of protection to the cell membrane. Different types of cell have cell walls made up of different materials; plant cell walls are primarily made up of pectin, fungi cell walls are made up of chitin and bacteria cell walls are made up of peptidoglycan.Prokaryotic
Capsule
A gelatinous capsule is present in some bacteria outside the cell membrane and cell wall. The capsule may be polysaccharide as in pneumococci, meningococci or polypeptide as Bacillus anthracis or hyaluronic acid as in streptococci. (See Bacterial capsule.) Capsules are not marked by normal staining protocols and can be detected by India ink or methyl blue; which allows for higher contrast between the cells for observation.[17]:87Flagella
Flagella are organelles for cellular mobility. The bacterial flagellum stretches from cytoplasm through the cell membrane(s) and extrudes through the cell wall. They are long and thick thread-like appendages, protein in nature. Are most commonly found in bacteria cells but are found in animal cells as well.Fimbriae (pili)
They are short and thin hair-like filaments, formed of protein called pilin (antigenic). Fimbriae are responsible for attachment of bacteria to specific receptors of human cell (adherence). There are special types of pili called (sex pili) involved in conjunction. (See Pilus.)Cellular processes
Growth and metabolism
Between successive cell divisions, cells grow through the functioning of cellular metabolism. Cell metabolism is the process by which individual cells process nutrient molecules. Metabolism has two distinct divisions: catabolism, in which the cell breaks down complex molecules to produce energy and reducing power, and anabolism, in which the cell uses energy and reducing power to construct complex molecules and perform other biological functions. Complex sugars consumed by the organism can be broken down into a less chemically complex sugar molecule called glucose. Once inside the cell, glucose is broken down to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a form of energy, through two different pathways.The first pathway, glycolysis, requires no oxygen and is referred to as anaerobic metabolism. Each reaction produces ATP and NADH, which are used in cellular functions, as well as two pyruvate molecules that derived from the original glucose molecule. In prokaryotes, all energy is produced by glycolysis.
The second pathway, called the Krebs cycle or citric acid cycle, is performed only by eukaryotes and involves further breakdown of the pyruvate produced in glycolysis. It occurs inside the mitochondria and generates much more energy than glycolysis, mostly through oxidative phosphorylation.
Replication
Haploid cells serve as gametes in multicellular organisms, fusing to form new diploid cells.
DNA replication, or the process of duplicating a cell's genome, always happens when a cell divides through mitosis or binary fission. This occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle.
In meiosis, the DNA is replicated only once, while the cell divides twice. DNA replication only occurs before meiosis I. DNA replication does not occur when the cells divide the second time, in meiosis II.[18] Replication, like all cellular activities, requires specialized proteins for carrying out the job.
Protein synthesis

An overview of protein synthesis.
Within the nucleus of the cell (light blue), genes (DNA, dark blue) are transcribed into RNA. This RNA is then subject to post-transcriptional modification and control, resulting in a mature mRNA (red) that is then transported out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm (peach), where it undergoes translation into a protein. mRNA is translated by ribosomes (purple) that match the three-base codons of the mRNA to the three-base anti-codons of the appropriate tRNA. Newly synthesized proteins (black) are often further modified, such as by binding to an effector molecule (orange), to become fully active.
Within the nucleus of the cell (light blue), genes (DNA, dark blue) are transcribed into RNA. This RNA is then subject to post-transcriptional modification and control, resulting in a mature mRNA (red) that is then transported out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm (peach), where it undergoes translation into a protein. mRNA is translated by ribosomes (purple) that match the three-base codons of the mRNA to the three-base anti-codons of the appropriate tRNA. Newly synthesized proteins (black) are often further modified, such as by binding to an effector molecule (orange), to become fully active.
Transcription is the process where genetic information in DNA is used to produce a complementary RNA strand. This RNA strand is then processed to give messenger RNA (mRNA), which is free to migrate through the cell. mRNA molecules bind to protein-RNA complexes called ribosomes located in the cytosol, where they are translated into polypeptide sequences. The ribosome mediates the formation of a polypeptide sequence based on the mRNA sequence. The mRNA sequence directly relates to the polypeptide sequence by binding to transfer RNA (tRNA) adapter molecules in binding pockets within the ribosome. The new polypeptide then folds into a functional three-dimensional protein molecule.
Movement or motility
Unicellular organisms can move in order to find food or escape predators. Common mechanisms of motion include flagella and cilia.In multicellular organisms, cells can move during processes such as wound healing, the immune response and cancer metastasis. For example, in wound healing in animals, white blood cells move to the wound site to kill the microorganisms that cause infection. Cell motility involves many receptors, crosslinking, bundling, binding, adhesion, motor and other proteins.[19] The process is divided into three steps – protrusion of the leading edge of the cell, adhesion of the leading edge and de-adhesion at the cell body and rear, and cytoskeletal contraction to pull the cell forward. Each step is driven by physical forces generated by unique segments of the cytoskeleton.[20][21]
Multicellularity
Cell specialization
Multicellular organisms are organisms that consist of more than one cell, in contrast to single-celled organisms.[22]
In complex multicellular organisms, cells specialize into different cell types that are adapted to particular functions. In mammals, major cell types include skin cells, muscle cells, neurons, blood cells, fibroblasts, stem cells, and others. Cell types differ both in appearance and function, yet are genetically identical. Cells are able to be of the same genotype but different cell type due to the differential regulation of the genes they contain.
Most distinct cell types arise from a single totipotent cell, called a zygote, that differentiates into hundreds of different cell types during the course of development. Differentiation of cells is driven by different environmental cues (such as cell–cell interaction) and intrinsic differences (such as those caused by the uneven distribution of molecules during division).
Origin of multicellularity
Multicellularity has evolved independently at least 25 times,[23] including in some prokaryotes, like cyanobacteria, myxobacteria, actinomycetes, Magnetoglobus multicellularis or Methanosarcina.However, complex multicellular organisms evolved only in six eukaryotic groups: animals, fungi, brown algae, red algae, green algae, and plants.[24] It evolved repeatedly for plants (Chloroplastida), once or twice for animals, once for brown algae, and perhaps several times for fungi, slime molds, and red algae.[25] Multicellularity may have evolved from colonies of interdependent organisms, from cellularization, or from organisms in symbiotic relationships.
The first evidence of multicellularity is from cyanobacteria-like organisms that lived between 3 and 3.5 billion years ago.[23] Other early fossils of multicellular organisms include the contested Grypania spiralis and the fossils of the black shales of the Palaeoproterozoic Francevillian Group Fossil B Formation in Gabon.[26]
The evolution of multicellularity from unicellular ancestors has been replicated in the laboratory, in evolution experiments using predation as the selective pressure.[23]
Origins
The origin of cells has to do with the origin of life, which began the history of life on Earth.Origin of the first cell

Stromatolites are left behind by cyanobacteria, also called blue-green algae. They are the oldest known fossils of life on Earth. This one-billion-year-old fossil is from Glacier National Park in the United States.
Cells emerged at least 3.5 billion years ago.[8][9][10] The current belief is that these cells were heterotrophs. The early cell membranes were probably more simple and permeable than modern ones, with only a single fatty acid chain per lipid. Lipids are known to spontaneously form bilayered vesicles in water, and could have preceded RNA, but the first cell membranes could also have been produced by catalytic RNA, or even have required structural proteins before they could form.[28]
Origin of eukaryotic cells
The eukaryotic cell seems to have evolved from a symbiotic community of prokaryotic cells. DNA-bearing organelles like the mitochondria and the chloroplasts are descended from ancient symbiotic oxygen-breathing proteobacteria and cyanobacteria, respectively, which were endosymbiosed by an ancestral archaean prokaryote.There is still considerable debate about whether organelles like the hydrogenosome predated the origin of mitochondria, or vice versa: see the hydrogen hypothesis for the origin of eukaryotic cells.
History of research
- 1632–1723: Antonie van Leeuwenhoek teaches himself to make lenses, constructs basic optical microscopes and draws protozoa, such as Vorticella from rain water, and bacteria from his own mouth.
- 1665: Robert Hooke discovers cells in cork, then in living plant tissue using an early compound microscope. He coins the term cell (from Latin cella, meaning "small room"[29]) in his book Micrographia (1665).[30]
- 1839: Theodor Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden elucidate the principle that plants and animals are made of cells, concluding that cells are a common unit of structure and development, and thus founding the cell theory.
- 1855: Rudolf Virchow states that new cells come from pre-existing cells by cell division (omnis cellula ex cellula).
- 1859: The belief that life forms can occur spontaneously (generatio spontanea) is contradicted by Louis Pasteur (1822–1895) (although Francesco Redi had performed an experiment in 1668 that suggested the same conclusion).
- 1931: Ernst Ruska builds the first transmission electron microscope (TEM) at the University of Berlin. By 1935, he has built an EM with twice the resolution of a light microscope, revealing previously unresolvable organelles.
- 1953: Watson and Crick made their first announcement on the double helix structure of DNA on February 28.
- 1981: Lynn Margulis published Symbiosis in Cell Evolution detailing the endosymbiotic theory.