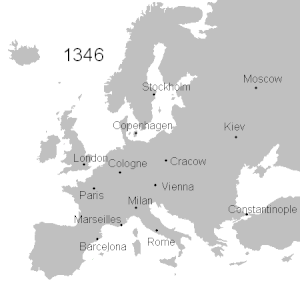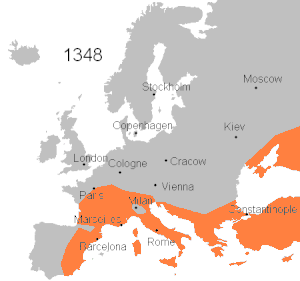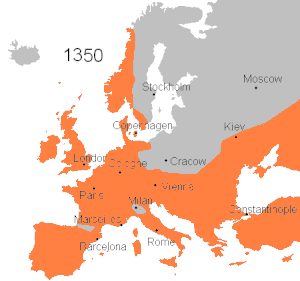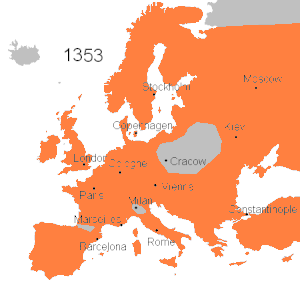
Spread of the Black Death in Europe (1346–53)
The
Black Death was one of the most devastating
pandemics in
human history, resulting in the deaths of an estimated
75 to 200 million people and peaking in Europe in the years 1346–53.
[1][2][3] Although there were several competing theories as to the
etiology of the Black Death, analysis of DNA from victims in northern and southern Europe published in 2010 and 2011 indicates that the
pathogen responsible was the
Yersinia pestis bacterium, probably causing several forms of
plague.
[4][5]
The Black Death is thought to have originated in the arid plains of
Central Asia, where it then travelled along the
Silk Road, reaching the
Crimea by 1343.
[6] From there, it was most likely carried by
Oriental rat fleas living on the
black rats that were regular passengers on
merchant ships. Spreading throughout the
Mediterranean and Europe, the Black Death is estimated to have killed 30–60% of Europe's total population.
[7] In total, the plague reduced the
world population from an estimated 450 million down to 350–375 million in the 14th century.
The aftermath of the plague created a series of religious, social, and economic upheavals, which had profound effects on the course of
European history. It took
150 years for Europe's population to recover.
[citation needed] The plague recurred occasionally in Europe until the 19th century.
Chronology
Origins of the disease
The plague disease, caused by
Yersinia pestis, is
enzootic (commonly present) in populations of fleas carried by ground
rodents, including
marmots, in various areas including Central Asia, Kurdistan, Western Asia, Northern India and Uganda.
Nestorian graves dating to 1338–9 near
Lake Issyk Kul in
Kyrgizstan have inscriptions referring to plague and are thought by many epidemiologists to mark the outbreak of the epidemic, from which it could easily have spread to China and India.
[9] In October 2010, medical geneticists suggested that all three of the great waves of the plague originated in China.
[10] In China, the 13th century
Mongol conquest caused a decline in farming and trading. However, economic recovery had been observed at the beginning of the 14th century. In the 1330s a large number of natural disasters and plagues led to widespread famine, starting in 1331, with a deadly plague arriving soon after.
[11] Epidemics which may have included plague killed an estimated 25 million Chinese and other Asians during the 15 years before it reached Constantinople in 1347.
[12] However, according to George Sussman, the first obvious medical description of plague in China dates to 1644.
[13]
The disease may have travelled along the Silk Road with
Mongol armies and traders or it could have come via ship.
[14] By the end of 1346, reports of plague had reached the seaports of Europe: "India was depopulated, Tartary, Mesopotamia, Syria, Armenia were covered with dead bodies".
[15]
Plague was reportedly first introduced to Europe at the trading city of
Caffa in the
Crimea in 1347. After a protracted siege, during which the Mongol army under
Jani Beg was suffering from the disease, the army catapulted the infected corpses over the
city walls to infect the inhabitants. The
Genoese traders fled, taking the plague by ship into
Sicily and the south of Europe, whence it spread north.
[16] Whether or not this hypothesis is accurate, it is clear that several existing conditions such as war, famine, and weather contributed to the severity of the Black Death.
European outbreak
The seventh year after it began, it came to England and first began in the towns and ports joining on the seacoasts, in Dorsetshire, where, as in other counties, it made the country quite void of inhabitants so that there were almost none left alive.
... But at length it came to Gloucester, yea even to Oxford and to London, and finally it spread over all England and so wasted the people that scarce the tenth person of any sort was left alive.
There appear to have been several introductions into Europe. The plague reached Sicily in October 1347, carried by twelve Genoese galleys,
[17] and rapidly spread all over the island. Galleys from
Caffa reached Genoa and Venice in January 1348, but it was the outbreak in Pisa a few weeks later that was the entry point to northern Italy. Towards the end of January, one of the galleys expelled from Italy arrived in
Marseille.
[18]
From Italy, the disease spread northwest across Europe, striking France, Spain, Portugal and England by June 1348, then turned and spread east through Germany and Scandinavia from 1348–50. It was introduced in Norway in 1349 when a ship landed at
Askøy, then spread to Bjørgvin (modern
Bergen) and
Iceland.
[19] Finally it spread to northwestern Russia in 1351. The plague was somewhat less common in parts of Europe that had smaller trade relations with their neighbours, including the
Kingdom of Poland, the majority of the
Basque Country, isolated parts of Belgium and the Netherlands, and isolated alpine villages throughout the continent.
[20][21]
Modern researchers do not think that the plague ever became endemic in Europe or its rat population. The disease repeatedly wiped out the rodent carriers so that the fleas died out until a new outbreak from Central Asia repeated the process. The outbreaks have been shown to occur roughly 15 years after a warmer and wetter period in areas where plague is endemic in other species such as gerbils.
[22][23]
Middle Eastern outbreak
The plague struck various countries in the Middle East during the
pandemic, leading to serious depopulation and permanent change in both economic and social structures. As it spread to western Europe, the disease entered the region from southern Russia also. By autumn 1347, the plague reached
Alexandria in Egypt, probably through the port's trade with
Constantinople, and ports on the
Black Sea. During 1347, the disease travelled eastward to
Gaza, and north along the eastern coast to cities in
Lebanon,
Syria and
Palestine, including
Ashkelon,
Acre,
Jerusalem,
Sidon,
Damascus,
Homs, and
Aleppo. In 1348–49, the disease reached
Antioch. The city's residents fled to the north, most of them dying during the journey, but the infection had been spread to the people of Asia Minor.
[citation needed]
Mecca became infected in 1349. During the same year, records show the city of
Mawsil (Mosul) suffered a massive epidemic, and the city of Baghdad experienced a second round of the disease. In 1351
Yemen experienced an outbreak of the plague, coinciding with the return of
King Mujahid of Yemen from imprisonment in
Cairo. His party may have brought the disease with them from Egypt.
[citation needed]
Symptoms

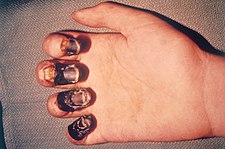
An inguinal bubo on the upper thigh of a person infected with bubonic plague. Swollen lymph glands (
buboes) often occur in the neck, armpit and groin (
inguinal) regions of plague victims
Contemporary accounts of the plague are often varied or imprecise. The most commonly noted symptom was the appearance of
buboes (or gavocciolos) in the groin, the neck and armpits, which oozed pus and bled when opened.
[24] Boccaccio's description is graphic:
In men and women alike it first betrayed itself by the emergence of certain tumours in the groin or armpits, some of which grew as large as a common apple, others as an egg...From the two said parts of the body this deadly gavocciolo soon began to propagate and spread itself in all directions indifferently; after which the form of the malady began to change, black spots or livid making their appearance in many cases on the arm or the thigh or elsewhere, now few and large, now minute and numerous. As the gavocciolo had been and still was an infallible token of approaching death, such also were these spots on whomsoever they showed themselves.[25]
Ziegler comments that the only medical detail that is questionable is the infallibility of approaching death, as if the bubo discharges, recovery is possible.
This was followed by acute fever and vomiting of blood. Most victims died two to seven days after initial infection. David Herlihy identifies freckle-like spots and rashes
[27] which could be caused by flea-bites as another potential sign of the plague.
Some accounts, like that of Louis Heyligen, a musician in
Avignon who died of the plague in 1348, noted a distinct form of the disease which infected the lungs and led to respiratory problems
[24] and which is identified with
pneumonic plague.
It is said that the plague takes three forms. In the first people suffer an infection of the lungs, which leads to breathing difficulties. Whoever has this corruption or contamination to any extent cannot escape but will die within two days. Another form...in which boils erupt under the armpits,...a third form in which people of both sexes are attacked in the groin.[28]
Naming
Medieval people called the catastrophe of the 14th century either the "Great Pestilence"' or the "Great Plague".
[29][30] Writers contemporary to the plague referred to the event as the "Great Mortality". Swedish and Danish chronicles of the 17th century described the events as "black" for the first time, not to describe the late-stage sign of the disease, in which the sufferer's skin would blacken due to
subepidermal hemorrhages and the extremities would darken with a form of
gangrene,
acral necrosis, but more likely to refer to black in the sense of glum or dreadful and to denote the terror and gloom of the events. Gasquet (1908) claimed that the Latin name "
atra mors" (Black Death) for an epidemic first appeared in modern times in 1631 in a book on Danish history by
J.I. Pontanus, where Pontanus wrote about a disease that occurred in 1348: "
Vulgo & ab effectu atram mortem
vocatibant." Commonly and from its effects, they called it the black death.
[31][32][33] This may have been a mistranslation, as
atra can mean
black,
brooding or
terrible. Nevertheless, the name spread through Scandinavia and then Germany.
[35] In England, it was not until 1823 that the medieval epidemic was first called the Black Death.
[36]
Causes
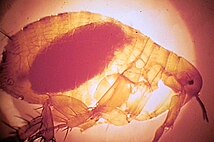
Oriental rat flea (
Xenopsylla cheopis) infected with the
Yersinia pestis bacterium which appears as a dark mass in the gut. The foregut (
proventriculus) of this flea is blocked by a
Y. pestis biofilm; when the flea attempts to feed on an uninfected
host Y. pestis is regurgitated into the wound, causing infection.
Medical knowledge had stagnated during the
Middle Ages. The most authoritative account at the time came from the medical faculty in Paris in a report to the
king of France that blamed the heavens, in the form of a
conjunction of three planets in 1345 that caused a "great pestilence in the air". This report became the first and most widely circulated of a series of plague tracts that sought to give advice to sufferers. That the plague was caused by bad air became the most widely accepted theory. The word 'plague' had no special significance at this time, and only the recurrence of outbreaks during the Middle Ages gave it the name that has become the medical term.
The importance of hygiene was recognised only in the nineteenth century; until then it was common that the streets were filthy, with live animals of all sorts around and human parasites abounding. A transmissible disease will spread easily in such conditions. One development as a result of the Black Death was the establishment of the idea of
quarantine in
Dubrovnik in 1377 after continuing outbreaks.
[39]
The dominant explanation for the Black Death is the
plague theory, which attributes the outbreak to
Yersinia pestis, also responsible for an epidemic that began in southern China in 1865, eventually spreading to India. The investigation of the pathogen that caused the 19th-century plague was begun by teams of scientists who visited Hong Kong in 1894, among whom was the French-Swiss bacteriologist
Alexandre Yersin, after whom the pathogen was named
Yersinia pestis.
[40] The mechanism by which
Y. pestis was usually transmitted was established in 1898 by
Paul-Louis Simond and was found to involve the bites of fleas whose
midguts had become obstructed by replicating
Y. pestis several days after feeding on an infected host. This blockage results in starvation and aggressive feeding behaviour by the fleas, which repeatedly attempt to clear their blockage by
regurgitation, resulting in thousands of plague bacteria being flushed into the feeding site, infecting the host. The bubonic plague mechanism was also dependent on two populations of rodents: one resistant to the disease, which act as hosts, keeping the disease
endemic, and a second that lack resistance. When the second population dies, the fleas move on to other hosts, including people, thus creating a human
epidemic.
[40]
The historian
Francis Aidan Gasquet, who had written about the 'Great Pestilence' in 1893 and suggested that "it would appear to be some form of the ordinary Eastern or bubonic plague" was able to adopt the epidemiology of the bubonic plague for the Black Death for the second edition in 1908, implicating rats and fleas in the process, and his interpretation was widely accepted for other ancient and medieval epidemics, such as the
Justinian plague that was prevalent in the
Eastern Roman Empire from 541 to 700 CE.
[40]
Other forms of plague have been implicated by modern scientists. The modern
bubonic plague has a
mortality rate of 30–75% and symptoms including fever of 38–41 °C (100–106 °F), headaches, painful aching joints,
nausea and vomiting, and a general feeling of
malaise. Left untreated, of those that contract the bubonic plague, 80 percent die within eight days.
[42] Pneumonic plague has a mortality rate of 90 to 95 percent. Symptoms include fever, cough, and blood-tinged
sputum. As the disease progresses, sputum becomes free flowing and bright red.
Septicemic plague is the least common of the three forms, with a mortality rate near 100%. Symptoms are high fevers and purple skin patches (
purpura due to
disseminated intravascular coagulation). In cases of pneumonic and particularly septicemic plague the progress of the disease is so rapid that there would often be no time for the development of the enlarged lymph nodes that were noted as buboes.
"Many modern scholars accept that the lethality of the Black Death stemmed from the combination of bubonic and pneumonic plague with other diseases and warn that every historical mention of 'pest' was not necessarily bubonic plague... In her study of 15th-century outbreaks, Ann Carmichael states that worms, the pox, fevers and dysentery clearly accompanied bubonic plague."
DNA evidence

Skeletons in a mass grave from 1720–1721 in
Martigues, France, yielded molecular evidence of the
orientalis strain of
Yersinia pestis, the organism responsible for bubonic plague. The second pandemic of bubonic plague was active in Europe from AD 1347, the beginning of the Black Death, until 1750.
In October 2010, the open-access scientific journal
PLoS Pathogens published a paper by a multinational team who undertook a new investigation into the role of
Yersinia pestis in the Black Death following the disputed identification by Drancourt and Raoult in 1998.
[45] Their surveys tested for DNA and protein signatures specific for
Y. pestis in human skeletons from widely distributed mass graves in northern, central and southern Europe that were associated archaeologically with the Black Death and subsequent resurgences. The authors concluded that this new research, together with prior analyses from the south of France and Germany
...ends the debate about the etiology of the Black Death, and unambiguously demonstrates that Y. pestis was the causative agent of the epidemic plague that devastated Europe during the Middle Ages.[46]
The study also found that there were two previously unknown but related
clades (genetic branches) of the
Y. pestis genome associated with medieval mass graves. These clades (which are thought to be extinct) were found to be ancestral to modern isolates of the modern
Y. pestis strains
Y. p. orientalis and
Y. p. medievalis, suggesting the plague may have entered Europe in two waves. Surveys of
plague pit remains in France and England indicate the first variant entered Europe through the port of
Marseille around November 1347 and spread through France over the next two years, eventually reaching England in the spring of 1349, where it spread through the country in three epidemics. Surveys of plague pit remains from the Dutch town of
Bergen op Zoom showed the
Y. pestis genotype responsible for the pandemic that spread through the Low Countries from 1350 differed from that found in Britain and France, implying Bergen op Zoom (and possibly other parts of the southern Netherlands) was not directly infected from England or France in 1349 and suggesting a second wave of plague, different from those in Britain and France, may have been carried to the Low Countries from Norway, the
Hanseatic cities or another site.
[46]
The results of the Haensch study have since been confirmed and amended. Based on genetic evidence derived from Black Death victims in the
East Smithfield burial site in England, Schuenemann et al. concluded in 2011 "that the Black Death in medieval Europe was caused by a variant of
Y. pestis that may no longer exist."
[47] A study published in
Nature in October 2011 sequenced the genome of
Y. pestis from plague victims and indicated that the strain that caused the Black Death is ancestral to most modern strains of the disease.
[5]
DNA taken from 25 skeletons in London that died in the 14th century have shown the plague is a strain of
Y. pestis that is almost identical to that which hit Madagascar in 2013.
[48][49]
Alternative explanations
This interpretation was first significantly challenged by the work of British bacteriologist J. F. D. Shrewsbury in 1970, who noted that the reported rates of mortality in rural areas during the 14th-century pandemic were inconsistent with the modern bubonic plague, leading him to conclude that contemporary accounts were exaggerations.
[40] In 1984 zoologist Graham Twigg produced the first major work to challenge the bubonic plague theory directly, and his doubts about the identity of the Black Death have been taken up by a number of authors, including Samuel K. Cohn, Jr. (2002),
David Herlihy (1997), and Susan Scott and Christopher Duncan (2001).
[40]
It is recognised that an
epidemiological account of the plague is as important as an identification of symptoms, but researchers are hampered by the lack of reliable statistics from this period. Most work has been done on the spread of the plague in England, and even estimates of overall population at the start vary by over 100% as no census was undertaken between the time of publication of the
Domesday Book and the year 1377. Estimates of plague victims are usually extrapolated from figures from the clergy.
In addition to arguing that the rat population was insufficient to account for a bubonic plague pandemic, sceptics of the bubonic plague theory point out that the symptoms of the Black Death are not unique (and arguably in some accounts may differ from bubonic plague); that transference via fleas in goods was likely to be of marginal significance and that the DNA results may be flawed and might not have been repeated elsewhere, despite extensive samples from other mass graves.
[40] Other arguments include the lack of accounts of the death of rats before outbreaks of plague between the 14th and 17th centuries; temperatures that are too cold in northern Europe for the survival of fleas; that, despite primitive transport systems, the spread of the Black Death was much faster than that of modern bubonic plague; that mortality rates of the Black Death appear to be very high; that, while modern bubonic plague is largely endemic as a rural disease, the Black Death indiscriminately struck urban and rural areas; and that the pattern of the Black Death, with major outbreaks in the same areas separated by 5 to 15 years, differs from modern bubonic plague—which often becomes endemic for decades with annual flare-ups.
[40]
Walløe complains that all of these authors "take it for granted that Simond's infection model, black rat → rat flea → human, which was developed to explain the spread of plague in India, is the only way an epidemic of
Yersinia pestis infection could spread", whilst pointing to several other possibilities.
[51]
A variety of alternatives to the
Y. pestis have been put forward. Twigg suggested that the cause was a form of
anthrax and
N. F. Cantor (2001) thought it may have been a combination of anthrax and other pandemics. Scott and Duncan have argued that the pandemic was a form of infectious disease that characterise as
hemorrhagic plague similar to
Ebola. Archaeologist Barney Sloane has argued that there is insufficient evidence of the extinction of large number of rats in the archaeological record of the medieval waterfront in London and that the plague spread too quickly to support the thesis that the
Y. pestis was spread from fleas on rats and argues that transmission must have been person to person.
[52][53] However, no single alternative solution has achieved widespread acceptance.
[40] Many scholars arguing for the
Y. pestis as the major agent of the pandemic suggest that its extent and symptoms can be explained by a combination of bubonic plague with other diseases, including
typhus,
smallpox and respiratory infections. In addition to the bubonic infection, others point to additional septicemic (a type of "blood poisoning") and pneumonic (an airborne plague that attacks the lungs before the rest of the body) forms of the plague, which lengthen the duration of outbreaks throughout the seasons and help account for its high mortality rate and additional recorded symptoms.
[24] In 2014, scientists with
Public Health England announced the results of an examination of 25 bodies exhumed from the Clerkenwell area of London, as well as of wills registered in London during the period, which supported the pneumonic hypothesis.
[48]
Consequences
Death toll

Citizens of
Tournai bury plague victims.
There are no exact figures for the
death toll; the rate varied widely by locality. It killed some
75 to 200 million people in
Eurasia.
[1][2][3] According to medieval historian
Philip Daileader in 2007:
The trend of recent research is pointing to a figure more like 45–50% of the European population dying during a four-year period. There is a fair amount of geographic variation. In Mediterranean Europe, areas such as Italy, the south of France and Spain, where plague ran for about four years consecutively, it was probably closer to 75–80% of the population. In Germany and England ... it was probably closer to 20%.[54]
The most widely accepted estimate for the Middle East, including Iraq, Iran and Syria, during this time, is for a death rate of about a third.
[55] The Black Death killed about 40% of Egypt's population.
[56] Half of Paris's population of 100,000 people died. In Italy,
Florence's population was reduced from 110–120 thousand inhabitants in 1338 down to 50 thousand in 1351. At least 60% of
Hamburg's and
Bremen's population perished,
[57] and a similar percentage of
Londoners may have died from the disease as well.
[48] Before 1350, there were about 170,000 settlements in Germany, and this was reduced by nearly 40,000 by 1450.
[58] In 1348, the plague spread so rapidly that before any physicians or government authorities had time to reflect upon its origins, about a third of the European population had already perished. In crowded cities, it was not uncommon for as much as 50% of the population to die. The disease bypassed some areas, and the most isolated areas were less vulnerable to contagion. Monks and priests were especially hard hit since they cared for the Black Death's victims.
[59]
Persecutions

Inspired by the Black Death,
The Dance of Death or
Danse Macabre, an allegory on the universality of death, is a common painting motif in the late medieval period.
Renewed religious fervor and fanaticism bloomed in the wake of the Black Death. Some Europeans targeted "various groups such as Jews, friars, foreigners, beggars, pilgrims",
[60] lepers
[60][61] and
Romani, thinking that they were to blame for the crisis.
Lepers, and other individuals with skin diseases such as
acne or
psoriasis, were singled out and exterminated throughout Europe.
Because 14th-century healers were at a loss to explain the cause, Europeans turned to astrological forces, earthquakes, and the poisoning of wells by Jews as possible reasons for the plague's emergence.
[29] The governments of Europe had no apparent response to the crisis because no one knew its cause or how it spread. The mechanism of infection and transmission of diseases was little understood in the 14th century; many people believed only God's anger could produce such horrific displays.
There were many attacks against
Jewish communities.
[62] In August 1349, the Jewish communities of
Mainz and
Cologne were exterminated. In February of that same year, the citizens of
Strasbourg murdered 2,000 Jews.
[62] By 1351, 60 major and 150 smaller Jewish communities were destroyed.
[63]
Recurrence

The Great Plague of London, in 1665, killed up to 100,000 people
The plague repeatedly returned to haunt Europe and the Mediterranean throughout the 14th to 17th centuries.
[64] According to Biraben, the plague was present somewhere in Europe in every year between 1346 and 1671.
[65] The
Second Pandemic was particularly widespread in the following years: 1360–63; 1374; 1400; 1438–39; 1456–57; 1464–66; 1481–85; 1500–03; 1518–31; 1544–48; 1563–66; 1573–88; 1596–99; 1602–11; 1623–40; 1644–54; and 1664–67. Subsequent outbreaks, though severe, marked the retreat from most of Europe (18th century) and northern Africa (19th century).
[66] According to Geoffrey Parker, "
France alone lost almost a million people to the plague in the epidemic of 1628–31."
[67]
In England, in the absence of census figures, historians propose a range of preincident population figures from as high as 7 million to as low as 4 million in 1300,
[68] and a postincident population figure as low as 2 million.
[69] By the end of 1350, the Black Death subsided, but it never really died out in England. Over the next few hundred years, further outbreaks occurred in 1361–62, 1369, 1379–83, 1389–93, and throughout the first half of the 15th century.
[70] An outbreak in 1471 took as much as 10–15% of the population, while the death rate of the plague of 1479–80 could have been as high as 20%.
[71] The most general outbreaks in
Tudor and
Stuart England seem to have begun in 1498, 1535, 1543, 1563, 1589, 1603, 1625, and 1636, and ended with the
Great Plague of London in 1665.
[72]

Plague Riot in Moscow in 1771: During the course of the
city's plague, between 50 and 100 thousand people died, comprising
1⁄6 to
1⁄3 of its population.
In 1466, perhaps 40,000 people died of the plague in Paris.
[73] During the 16th and 17th centuries, the plague was present in Paris around 30 per cent of the time.
[74] The Black Death ravaged Europe for three years before it continued on into Russia, where the disease was present somewhere in the country 25 times between 1350 to 1490. Plague epidemics ravaged London in 1563, 1593, 1603, 1625, 1636, and 1665,
[76] reducing its population by 10 to 30% during those years.
[77] Over 10% of
Amsterdam's population died in 1623–25, and again in 1635–36, 1655, and 1664.
[78] Plague occurred in
Venice 22 times between 1361 and 1528.
[79] The plague of 1576–77 killed 50,000 in Venice, almost a third of the population.
[80] Late outbreaks in central Europe included the
Italian Plague of 1629–1631, which is associated with troop movements during the
Thirty Years' War, and the
Great Plague of Vienna in 1679. Over 60% of Norway's population died in 1348–50.
[81] The last plague outbreak ravaged
Oslo in 1654.
[82]
In the first half of the 17th century, a plague claimed some 1.7 million victims in Italy, or about 14% of the population.
[83] In 1656, the plague killed about half of
Naples' 300,000 inhabitants.
[84] More than 1.25 million deaths resulted from the extreme incidence of plague in 17th-century
Spain.
[85] The
plague of 1649 probably reduced the population of
Seville by half.
[86] In 1709–13, a
plague epidemic that followed the Great Northern War (1700–21,
Sweden v. Russia and allies)
[87] killed about 100,000 in Sweden,
[88] and 300,000 in Prussia.
[86] The plague killed two-thirds of the inhabitants of
Helsinki,
[89] and claimed a third of
Stockholm's population.
[90] Europe's last major epidemic occurred in 1720 in
Marseille.
[81]

Worldwide distribution of plague-infected animals 1998
The Black Death ravaged much of the
Islamic world.
[91] Plague was present in at least one location in the Islamic world virtually every year between 1500 and 1850.
[92] Plague repeatedly struck the cities of North Africa.
Algiers lost 30 to 50 thousand inhabitants to it in 1620–21, and again in 1654–57, 1665, 1691, and 1740–42.
[93] Plague remained a major event in
Ottoman society until the second quarter of the 19th century. Between 1701 and 1750, thirty-seven larger and smaller epidemics were recorded in
Constantinople, and an additional thirty-one between 1751 and 1800.
[94] Baghdad has suffered severely from visitations of the plague, and sometimes two-thirds of its population has been wiped out.
[95]
Third plague pandemic
The Third plague pandemic (1855–1859) started in China in the middle of the 19th century, spreading to all inhabited continents and killing 10 million people in India alone.
[96] Twelve plague outbreaks in Australia in 1900–25 resulted in well over
1,000 deaths, chiefly in Sydney. This led to the establishment of a Public Health Department there which undertook some leading-edge research on plague transmission from rat fleas to humans via the bacillus
Yersinia pestis.
[97]
The first North American plague epidemic was the
San Francisco plague of 1900–04, followed by another outbreak in 1907–08.
[98] From 1944 through 1993, 362 cases of human plague were reported in the United States; approximately 90% occurred in four western states: Arizona, California, Colorado, and New Mexico.
[99] Plague was confirmed in the United States from 9 western states during 1995.
[100] Currently, 5 to 15 people in the United States are estimated to catch the disease each year—typically in western states.
[101][102]
Treatment
Modern treatment methods include
insecticides, the use of
antibiotics, and a
plague vaccine. The
plague bacterium could develop
drug-resistance and again become a major health threat. One case of a drug-resistant form of the bacterium was found in
Madagascar in 1995.
[103]A further outbreak in Madagascar was reported in November 2014.
[104]