From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Malaria | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| A Plasmodium from the saliva of a female mosquito moving across a mosquito cell | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Fever, vomiting, headache[1] |
| Usual onset | 10–15 days post exposure[2] |
| Causes | Plasmodium spread by mosquitos[1] |
| Diagnostic method | Examination of the blood, antigen detection tests[1] |
| Prevention | Mosquito nets, insect repellent, mosquito control, medications[1] |
| Medication | Antimalarial medication[2] |
| Frequency | 296 million (2015)[3] |
| Deaths | 730,500 (2015)[4] |
The disease is most commonly transmitted by an infected female Anopheles mosquito. The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into a person's blood.[2] The parasites travel to the liver where they mature and reproduce. Five species of Plasmodium can infect and be spread by humans.[1] Most deaths are caused by P. falciparum because P. vivax, P. ovale, and P. malariae generally cause a milder form of malaria.[2][1] The species P. knowlesi rarely causes disease in humans.[2] Malaria is typically diagnosed by the microscopic examination of blood using blood films, or with antigen-based rapid diagnostic tests.[1] Methods that use the polymerase chain reaction to detect the parasite's DNA have been developed, but are not widely used in areas where malaria is common due to their cost and complexity.[5]
The risk of disease can be reduced by preventing mosquito bites through the use of mosquito nets and insect repellents, or with mosquito control measures such as spraying insecticides and draining standing water.[1] Several medications are available to prevent malaria in travellers to areas where the disease is common. Occasional doses of the combination medication sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine are recommended in infants and after the first trimester of pregnancy in areas with high rates of malaria. Despite a need, no effective vaccine exists, although efforts to develop one are ongoing.[2] The recommended treatment for malaria is a combination of antimalarial medications that includes an artemisinin.[2][1] The second medication may be either mefloquine, lumefantrine, or sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine.[6] Quinine along with doxycycline may be used if an artemisinin is not available.[6] It is recommended that in areas where the disease is common, malaria is confirmed if possible before treatment is started due to concerns of increasing drug resistance. Resistance among the parasites has developed to several antimalarial medications; for example, chloroquine-resistant P. falciparum has spread to most malarial areas, and resistance to artemisinin has become a problem in some parts of Southeast Asia.[2]
The disease is widespread in the tropical and subtropical regions that exist in a broad band around the equator.[1] This includes much of Sub-Saharan Africa, Asia, and Latin America.[2] In 2015, there were 296 million cases of malaria worldwide resulting in an estimated 731,000 deaths.[3][4] Approximately 90% of both cases and deaths occurred in Africa.[7] Rates of disease have decreased from 2000 to 2015 by 37%,[7] but increased from 2014 during which there were 198 million cases.[8] Malaria is commonly associated with poverty and has a major negative effect on economic development.[9][10] In Africa, it is estimated to result in losses of US$12 billion a year due to increased healthcare costs, lost ability to work, and negative effects on tourism.[11]
Signs and symptoms
Main symptoms of malaria[12]
The signs and symptoms of malaria typically begin 8–25 days following infection;[12] however, symptoms may occur later in those who have taken antimalarial medications as prevention.[5] Initial manifestations of the disease—common to all malaria species—are similar to flu-like symptoms,[13] and can resemble other conditions such as sepsis, gastroenteritis, and viral diseases.[5] The presentation may include headache, fever, shivering, joint pain, vomiting, hemolytic anemia, jaundice, hemoglobin in the urine, retinal damage, and convulsions.[14]
The classic symptom of malaria is paroxysm—a cyclical occurrence of sudden coldness followed by shivering and then fever and sweating, occurring every two days (tertian fever) in P. vivax and P. ovale infections, and every three days (quartan fever) for P. malariae. P. falciparum infection can cause recurrent fever every 36–48 hours, or a less pronounced and almost continuous fever.[15]
Severe malaria is usually caused by P. falciparum (often referred to as falciparum malaria). Symptoms of falciparum malaria arise 9–30 days after infection.[13] Individuals with cerebral malaria frequently exhibit neurological symptoms, including abnormal posturing, nystagmus, conjugate gaze palsy (failure of the eyes to turn together in the same direction), opisthotonus, seizures, or coma.[13]
Complications
Malaria has several serious complications. Among these is the development of respiratory distress, which occurs in up to 25% of adults and 40% of children with severe P. falciparum malaria. Possible causes include respiratory compensation of metabolic acidosis, noncardiogenic pulmonary oedema, concomitant pneumonia, and severe anaemia. Although rare in young children with severe malaria, acute respiratory distress syndrome occurs in 5–25% of adults and up to 29% of pregnant women.[16]Coinfection of HIV with malaria increases mortality.[17] Renal failure is a feature of blackwater fever, where hemoglobin from lysed red blood cells leaks into the urine.[13]
Infection with P. falciparum may result in cerebral malaria, a form of severe malaria that involves encephalopathy. It is associated with retinal whitening, which may be a useful clinical sign in distinguishing malaria from other causes of fever.[18] Enlarged spleen, enlarged liver or both of these, severe headache, low blood sugar, and hemoglobin in the urine with renal failure may occur.[13] Complications may include spontaneous bleeding, coagulopathy, and shock.[19]
Malaria in pregnant women is an important cause of stillbirths, infant mortality, abortion and low birth weight,[20] particularly in P. falciparum infection, but also with P. vivax.[21]
Cause
Malaria parasites belong to the genus Plasmodium (phylum Apicomplexa). In humans, malaria is caused by P. falciparum, P. malariae, P. ovale, P. vivax and P. knowlesi.[22][23] Among those infected, P. falciparum is the most common species identified (~75%) followed by P. vivax (~20%).[5] Although P. falciparum traditionally accounts for the majority of deaths,[24] recent evidence suggests that P. vivax malaria is associated with potentially life-threatening conditions about as often as with a diagnosis of P. falciparum infection.[25] P. vivax proportionally is more common outside Africa.[26] There have been documented human infections with several species of Plasmodium from higher apes; however, except for P. knowlesi—a zoonotic species that causes malaria in macaques[23]—these are mostly of limited public health importance.[27]Global warming is likely to affect malaria transmission, but the severity and geographic distribution of such effects is uncertain.[28][29]
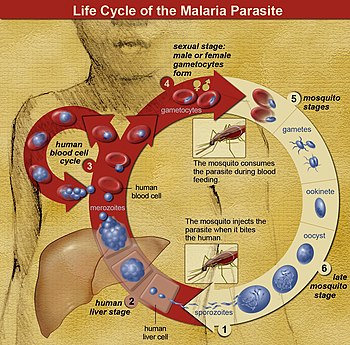
Life cycle
The life cycle of malaria parasites. A mosquito causes an infection by a
bite. First, sporozoites enter the bloodstream, and migrate to the
liver. They infect liver cells,
where they multiply into merozoites, rupture the liver cells, and
return to the bloodstream. The merozoites infect red blood cells, where
they develop into ring forms, trophozoites and schizonts that in turn
produce further merozoites. Sexual forms are also produced, which, if taken up by a mosquito, will infect the insect and continue the life cycle.
In the life cycle of Plasmodium, a female Anopheles mosquito (the definitive host) transmits a motile infective form (called the sporozoite) to a vertebrate host such as a human (the secondary host), thus acting as a transmission vector. A sporozoite travels through the blood vessels to liver cells (hepatocytes), where it reproduces asexually (tissue schizogony), producing thousands of merozoites. These infect new red blood cells and initiate a series of asexual multiplication cycles (blood schizogony) that produce 8 to 24 new infective merozoites, at which point the cells burst and the infective cycle begins anew.[30]
Other merozoites develop into immature gametocytes, which are the precursors of male and female gametes. When a fertilized mosquito bites an infected person, gametocytes are taken up with the blood and mature in the mosquito gut. The male and female gametocytes fuse and form an ookinete—a fertilized, motile zygote. Ookinetes develop into new sporozoites that migrate to the insect's salivary glands, ready to infect a new vertebrate host. The sporozoites are injected into the skin, in the saliva, when the mosquito takes a subsequent blood meal.[31]
Only female mosquitoes feed on blood; male mosquitoes feed on plant nectar and do not transmit the disease. The females of the Anopheles genus of mosquito prefer to feed at night. They usually start searching for a meal at dusk and will continue throughout the night until taking a meal.[32] Malaria parasites can also be transmitted by blood transfusions, although this is rare.[33]
Recurrent malaria
Symptoms of malaria can recur after varying symptom-free periods. Depending upon the cause, recurrence can be classified as either recrudescence, relapse, or reinfection. Recrudescence is when symptoms return after a symptom-free period. It is caused by parasites surviving in the blood as a result of inadequate or ineffective treatment.[34] Relapse is when symptoms reappear after the parasites have been eliminated from blood but persist as dormant hypnozoites in liver cells. Relapse commonly occurs between 8–24 weeks and is commonly seen with P. vivax and P. ovale infections.[5]P. vivax malaria cases in temperate areas often involve overwintering by hypnozoites, with relapses beginning the year after the mosquito bite.[35] Reinfection means the parasite that caused the past infection was eliminated from the body but a new parasite was introduced. Reinfection cannot readily be distinguished from recrudescence, although recurrence of infection within two weeks of treatment for the initial infection is typically attributed to treatment failure.[36] People may develop some immunity when exposed to frequent infections.[37]
Pathophysiology
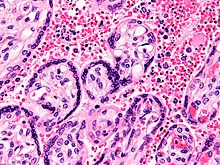
Micrograph of a placenta from a stillbirth due to maternal malaria. H&E stain.
Red blood cells are anuclear; blue/black staining in bright red
structures (red blood cells) indicate foreign nuclei from the parasites.
Electron micrograph of a Plasmodium falciparum-infected red blood cell (center), illustrating adhesion protein "knobs"
Malaria infection develops via two phases: one that involves the liver (exoerythrocytic phase), and one that involves red blood cells, or erythrocytes (erythrocytic phase). When an infected mosquito pierces a person's skin to take a blood meal, sporozoites in the mosquito's saliva enter the bloodstream and migrate to the liver where they infect hepatocytes, multiplying asexually and asymptomatically for a period of 8–30 days.[38]
After a potential dormant period in the liver, these organisms differentiate to yield thousands of merozoites, which, following rupture of their host cells, escape into the blood and infect red blood cells to begin the erythrocytic stage of the life cycle.[38] The parasite escapes from the liver undetected by wrapping itself in the cell membrane of the infected host liver cell.[39]
Within the red blood cells, the parasites multiply further, again asexually, periodically breaking out of their host cells to invade fresh red blood cells. Several such amplification cycles occur. Thus, classical descriptions of waves of fever arise from simultaneous waves of merozoites escaping and infecting red blood cells.[38]
Some P. vivax sporozoites do not immediately develop into exoerythrocytic-phase merozoites, but instead, produce hypnozoites that remain dormant for periods ranging from several months (7–10 months is typical) to several years. After a period of dormancy, they reactivate and produce merozoites. Hypnozoites are responsible for long incubation and late relapses in P. vivax infections,[35] although their existence in P. ovale is uncertain.[40]
The parasite is relatively protected from attack by the body's immune system because for most of its human life cycle it resides within the liver and blood cells and is relatively invisible to immune surveillance. However, circulating infected blood cells are destroyed in the spleen. To avoid this fate, the P. falciparum parasite displays adhesive proteins on the surface of the infected blood cells, causing the blood cells to stick to the walls of small blood vessels, thereby sequestering the parasite from passage through the general circulation and the spleen.[41] The blockage of the microvasculature causes symptoms such as in placental malaria.[42] Sequestered red blood cells can breach the blood–brain barrier and cause cerebral malaria.[43]
Genetic resistance
According to a 2005 review, due to the high levels of mortality and morbidity caused by malaria—especially the P. falciparum species—it has placed the greatest selective pressure on the human genome in recent history. Several genetic factors provide some resistance to it including sickle cell trait, thalassaemia traits, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, and the absence of Duffy antigens on red blood cells.[44][45]The impact of sickle cell trait on malaria immunity illustrates some evolutionary trade-offs that have occurred because of endemic malaria. Sickle cell trait causes a change in the hemoglobin molecule in the blood. Normally, red blood cells have a very flexible, biconcave shape that allows them to move through narrow capillaries; however, when the modified hemoglobin S molecules are exposed to low amounts of oxygen, or crowd together due to dehydration, they can stick together forming strands that cause the cell to sickle or distort into a curved shape. In these strands the molecule is not as effective in taking or releasing oxygen, and the cell is not flexible enough to circulate freely. In the early stages of malaria, the parasite can cause infected red cells to sickle, and so they are removed from circulation sooner. This reduces the frequency with which malaria parasites complete their life cycle in the cell. Individuals who are homozygous (with two copies of the abnormal hemoglobin beta allele) have sickle-cell anaemia, while those who are heterozygous (with one abnormal allele and one normal allele) experience resistance to malaria without severe anemia. Although the shorter life expectancy for those with the homozygous condition would tend to disfavor the trait's survival, the trait is preserved in malaria-prone regions because of the benefits provided by the heterozygous form.[45][46]
Liver dysfunction
Liver dysfunction as a result of malaria is uncommon and usually only occurs in those with another liver condition such as viral hepatitis or chronic liver disease. The syndrome is sometimes called malarial hepatitis.[47] While it has been considered a rare occurrence, malarial hepatopathy has seen an increase, particularly in Southeast Asia and India. Liver compromise in people with malaria correlates with a greater likelihood of complications and death.[47]Diagnosis
The blood film is the gold standard for malaria diagnosis.
Ring-forms and gametocytes of Plasmodium falciparum in human blood
Owing to the non-specific nature of the presentation of symptoms, diagnosis of malaria in non-endemic areas requires a high degree of suspicion, which might be elicited by any of the following: recent travel history, enlarged spleen, fever, low number of platelets in the blood, and higher-than-normal levels of bilirubin in the blood combined with a normal level of white blood cells.[5]
Malaria is usually confirmed by the microscopic examination of blood films or by antigen-based rapid diagnostic tests (RDT).[48][49] In some areas, RDTs need to be able to distinguish whether the malaria symptoms are caused by Plasmodium falciparum or by other species of parasites since treatment strategies could differ for non-P. falciparum infections.[50] Microscopy is the most commonly used method to detect the malarial parasite—about 165 million blood films were examined for malaria in 2010.[51] Despite its widespread usage, diagnosis by microscopy suffers from two main drawbacks: many settings (especially rural) are not equipped to perform the test, and the accuracy of the results depends on both the skill of the person examining the blood film and the levels of the parasite in the blood. The sensitivity of blood films ranges from 75–90% in optimum conditions, to as low as 50%. Commercially available RDTs are often more accurate than blood films at predicting the presence of malaria parasites, but they are widely variable in diagnostic sensitivity and specificity depending on manufacturer, and are unable to tell how many parasites are present.[51]
In regions where laboratory tests are readily available, malaria should be suspected, and tested for, in any unwell person who has been in an area where malaria is endemic. In areas that cannot afford laboratory diagnostic tests, it has become common to use only a history of fever as the indication to treat for malaria—thus the common teaching "fever equals malaria unless proven otherwise". A drawback of this practice is overdiagnosis of malaria and mismanagement of non-malarial fever, which wastes limited resources, erodes confidence in the health care system, and contributes to drug resistance.[52] Although polymerase chain reaction-based tests have been developed, they are not widely used in areas where malaria is common as of 2012, due to their complexity.[5]
Classification
Malaria is classified into either "severe" or "uncomplicated" by the World Health Organization (WHO).[5] It is deemed severe when any of the following criteria are present, otherwise it is considered uncomplicated.[53]- Decreased consciousness
- Significant weakness such that the person is unable to walk
- Inability to feed
- Two or more convulsions
- Low blood pressure (less than 70 mmHg in adults and 50 mmHg in children)
- Breathing problems
- Circulatory shock
- Kidney failure or hemoglobin in the urine
- Bleeding problems, or hemoglobin less than 50 g/L (5 g/dL)
- Pulmonary oedema
- Blood glucose less than 2.2 mmol/L (40 mg/dL)
- Acidosis or lactate levels of greater than 5 mmol/L
- A parasite level in the blood of greater than 100,000 per microlitre (µL) in low-intensity transmission areas, or 250,000 per µL in high-intensity transmission areas
Various types of malaria have been called by the names below:[55]
| Name | Pathogen | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| algid malaria | Plasmodium falciparum | severe malaria affecting the cardiovascular system and causing chills and circulatory shock |
| bilious malaria | Plasmodium falciparum | severe malaria affecting the liver and causing vomiting and jaundice |
| cerebral malaria | Plasmodium falciparum | severe malaria affecting the cerebrum |
| congenital malaria | various plasmodia | plasmodium introduced from the mother via the fetal circulation |
| falciparum malaria, Plasmodium falciparum malaria, pernicious malaria | Plasmodium falciparum | |
| ovale malaria, Plasmodium ovale malaria | Plasmodium ovale | |
| quartan malaria, malariae malaria, Plasmodium malariae malaria | Plasmodium malariae | paroxysms every fourth day (quartan), counting the day of occurrence as the first day |
| quotidian malaria | Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax | paroxysms daily (quotidian) |
| tertian malaria | Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium ovale, Plasmodium vivax | paroxysms every third day (tertian), counting the day of occurrence as the first |
| transfusion malaria | various plasmodia | plasmodium introduced by blood transfusion, needle sharing, or needlestick injury |
| vivax malaria, Plasmodium vivax malaria | Plasmodium vivax |
Prevention
An Anopheles stephensi
mosquito shortly after obtaining blood from a human (the droplet of
blood is expelled as a surplus). This mosquito is a vector of malaria,
and mosquito control is an effective way of reducing its incidence.
Methods used to prevent malaria include medications, mosquito elimination and the prevention of bites. There is no vaccine for malaria. The presence of malaria in an area requires a combination of high human population density, high anopheles mosquito population density and high rates of transmission from humans to mosquitoes and from mosquitoes to humans. If any of these is lowered sufficiently, the parasite will eventually disappear from that area, as happened in North America, Europe and parts of the Middle East. However, unless the parasite is eliminated from the whole world, it could become re-established if conditions revert to a combination that favors the parasite's reproduction. Furthermore, the cost per person of eliminating anopheles mosquitoes rises with decreasing population density, making it economically unfeasible in some areas.[56]
Prevention of malaria may be more cost-effective than treatment of the disease in the long run, but the initial costs required are out of reach of many of the world's poorest people. There is a wide difference in the costs of control (i.e. maintenance of low endemicity) and elimination programs between countries. For example, in China—whose government in 2010 announced a strategy to pursue malaria elimination in the Chinese provinces—the required investment is a small proportion of public expenditure on health. In contrast, a similar program in Tanzania would cost an estimated one-fifth of the public health budget.[57]
In areas where malaria is common, children under five years old often have anemia which is sometimes due to malaria. Giving children with anemia in these areas preventive antimalarial medication improves red blood cell levels slightly but did not affect the risk of death or need for hospitalization.[58]
Mosquito control

Man spraying kerosene oil in standing water, Panama Canal Zone 1912
Vector control refers to methods used to decrease malaria by reducing the levels of transmission by mosquitoes. For individual protection, the most effective insect repellents are based on DEET or picaridin.[59] Insecticide-treated mosquito nets (ITNs) and indoor residual spraying (IRS) have been shown to be highly effective in preventing malaria among children in areas where malaria is common.[60][61] Prompt treatment of confirmed cases with artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) may also reduce transmission.[62]
Walls where indoor residual spraying of DDT has been applied. The
mosquitoes remain on the wall until they fall down dead on the floor.
A mosquito net in use.
Mosquito nets help keep mosquitoes away from people and reduce infection rates and transmission of malaria. Nets are not a perfect barrier and are often treated with an insecticide designed to kill the mosquito before it has time to find a way past the net. Insecticide-treated nets are estimated to be twice as effective as untreated nets and offer greater than 70% protection compared with no net.[63] Between 2000 and 2008, the use of ITNs saved the lives of an estimated 250,000 infants in Sub-Saharan Africa.[64] About 13% of households in Sub-Saharan countries owned ITNs in 2007[65] and 31% of African households were estimated to own at least one ITN in 2008. In 2000, 1.7 million (1.8%) African children living in areas of the world where malaria is common were protected by an ITN. That number increased to 20.3 million (18.5%) African children using ITNs in 2007, leaving 89.6 million children unprotected[66] and to 68% African children using mosquito nets in 2015.[67] Most nets are impregnated with pyrethroids, a class of insecticides with low toxicity. They are most effective when used from dusk to dawn.[68] It is recommended to hang a large "bed net" above the center of a bed and either tuck the edges under the mattress or make sure it is large enough such that it touches the ground.[69]
Indoor residual spraying is the spraying of insecticides on the walls inside a home. After feeding, many mosquitoes rest on a nearby surface while digesting the bloodmeal, so if the walls of houses have been coated with insecticides, the resting mosquitoes can be killed before they can bite another person and transfer the malaria parasite.[70] As of 2006, the World Health Organization recommends 12 insecticides in IRS operations, including DDT and the pyrethroids cyfluthrin and deltamethrin.[71] This public health use of small amounts of DDT is permitted under the Stockholm Convention, which prohibits its agricultural use.[72] One problem with all forms of IRS is insecticide resistance. Mosquitoes affected by IRS tend to rest and live indoors, and due to the irritation caused by spraying, their descendants tend to rest and live outdoors, meaning that they are less affected by the IRS.[73]
There are a number of other methods to reduce mosquito bites and slow the spread of malaria. Efforts to decrease mosquito larva by decreasing the availability of open water in which they develop or by adding substances to decrease their development is effective in some locations.[74] Electronic mosquito repellent devices which make very high-frequency sounds that are supposed to keep female mosquitoes away, do not have supporting evidence.[75]
Other methods
Community participation and health education strategies promoting awareness of malaria and the importance of control measures have been successfully used to reduce the incidence of malaria in some areas of the developing world.[76] Recognizing the disease in the early stages can prevent the disease from becoming fatal. Education can also inform people to cover over areas of stagnant, still water, such as water tanks that are ideal breeding grounds for the parasite and mosquito, thus cutting down the risk of the transmission between people. This is generally used in urban areas where there are large centers of population in a confined space and transmission would be most likely in these areas.[77] Intermittent preventive therapy is another intervention that has been used successfully to control malaria in pregnant women and infants,[78] and in preschool children where transmission is seasonal.[79]Medications
There are a number of drugs that can help prevent or interrupt malaria in travelers to places where infection is common. Many of these drugs are also used in treatment. Chloroquine may be used where chloroquine-resistant parasites are not common.[80] In places where Plasmodium is resistant to one or more medications, three medications—mefloquine (Lariam), doxycycline (available generically), or the combination of atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride (Malarone)—are frequently used when prophylaxis is needed.[80] Doxycycline and the atovaquone plus proguanil combination are the best tolerated; mefloquine is associated with death, suicide, and neurological and psychiatric symptoms.[80]The protective effect does not begin immediately, and people visiting areas where malaria exists usually start taking the drugs one to two weeks before arriving and continue taking them for four weeks after leaving (except for atovaquone/proguanil, which only needs to be started two days before and continued for seven days afterward).[81] The use of preventative drugs is often not practical for those who live in areas where malaria exists, and their use is usually only in pregnant women and short-term visitors. This is due to the cost of the drugs, side effects from long-term use, and the difficulty in obtaining anti-malarial drugs outside of wealthy nations.[82] During pregnancy, medication to prevent malaria has been found to improve the weight of the baby at birth and decrease the risk of anemia in the mother.[83] The use of preventative drugs where malaria-bearing mosquitoes are present may encourage the development of partial resistance.[84]
Treatment
An advertisement for quinine as a malaria treatment from 1927.
Malaria is treated with antimalarial medications; the ones used depends on the type and severity of the disease. While medications against fever are commonly used, their effects on outcomes are not clear.[85]
Simple or uncomplicated malaria may be treated with oral medications. The most effective treatment for P. falciparum infection is the use of artemisinins in combination with other antimalarials (known as artemisinin-combination therapy, or ACT), which decreases resistance to any single drug component.[86] These additional antimalarials include: amodiaquine, lumefantrine, mefloquine or sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine.[87] Another recommended combination is dihydroartemisinin and piperaquine.[88][89] ACT is about 90% effective when used to treat uncomplicated malaria.[64] To treat malaria during pregnancy, the WHO recommends the use of quinine plus clindamycin early in the pregnancy (1st trimester), and ACT in later stages (2nd and 3rd trimesters).[90] In the 2000s (decade), malaria with partial resistance to artemisins emerged in Southeast Asia.[91][92] Infection with P. vivax, P. ovale or P. malariae usually do not require hospitalization. Treatment of P. vivax requires both treatment of blood stages (with chloroquine or ACT) and clearance of liver forms with primaquine.[93] Treatment with tafenoquine prevents relapses after confirmed P. vivax malaria.[94]
Severe and complicated malaria are almost always caused by infection with P. falciparum. The other species usually cause only febrile disease.[95] Severe and complicated malaria are medical emergencies since mortality rates are high (10% to 50%).[96] Cerebral malaria is the form of severe and complicated malaria with the worst neurological symptoms.[97] Recommended treatment for severe malaria is the intravenous use of antimalarial drugs. For severe malaria, parenteral artesunate was superior to quinine in both children and adults.[98] In another systematic review, artemisinin derivatives (artemether and arteether) were as efficacious as quinine in the treatment of cerebral malaria in children.[99] Treatment of severe malaria involves supportive measures that are best done in a critical care unit. This includes the management of high fevers and the seizures that may result from it. It also includes monitoring for poor breathing effort, low blood sugar, and low blood potassium.[24]
Resistance
Drug resistance poses a growing problem in 21st-century malaria treatment.[100] Resistance is now common against all classes of antimalarial drugs apart from artemisinins. Treatment of resistant strains became increasingly dependent on this class of drugs. The cost of artemisinins limits their use in the developing world.[101] Malaria strains found on the Cambodia–Thailand border are resistant to combination therapies that include artemisinins, and may, therefore, be untreatable.[102] Exposure of the parasite population to artemisinin monotherapies in subtherapeutic doses for over 30 years and the availability of substandard artemisinins likely drove the selection of the resistant phenotype.[103] Resistance to artemisinin has been detected in Cambodia, Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam,[104] and there has been emerging resistance in Laos.[105][106]Prognosis
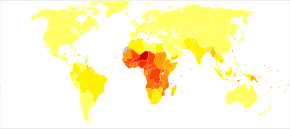
Disability-adjusted life year for malaria per 100,000 inhabitants in 2004
no data
<10 div="">
0–100
100–500
500–1000
1000–1500
1500–2000
2000–2500
2500–2750
2750–3000
3000–3250
3250–3500
≥3500
When properly treated, people with malaria can usually expect a complete recovery.[107] However, severe malaria can progress extremely rapidly and cause death within hours or days.[108] In the most severe cases of the disease, fatality rates can reach 20%, even with intensive care and treatment.[5] Over the longer term, developmental impairments have been documented in children who have suffered episodes of severe malaria.[109] Chronic infection without severe disease can occur in an immune-deficiency syndrome associated with a decreased responsiveness to Salmonella bacteria and the Epstein–Barr virus.[110]
During childhood, malaria causes anemia during a period of rapid brain development, and also direct brain damage resulting from cerebral malaria.[109] Some survivors of cerebral malaria have an increased risk of neurological and cognitive deficits, behavioural disorders, and epilepsy.[111] Malaria prophylaxis was shown to improve cognitive function and school performance in clinical trials when compared to placebo groups.[109]
Epidemiology
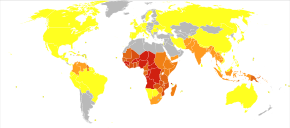
Distribution of malaria in the world:[112] ♦ Elevated occurrence of chloroquine- or multi-resistant malaria
♦ Occurrence of chloroquine-resistant malaria
♦ No Plasmodium falciparum or chloroquine-resistance
♦ No malaria
♦ Occurrence of chloroquine-resistant malaria
♦ No Plasmodium falciparum or chloroquine-resistance
♦ No malaria
Deaths due to malaria per million persons in 2012
0–0
1–2
3–54
55–325
326–679
680–949
950–1,358
The WHO estimates that in 2015 there were 214 million new cases of malaria resulting in 438,000 deaths.[113] Others have estimated the number of cases at between 350 and 550 million for falciparum malaria[114] The majority of cases (65%) occur in children under 15 years old.[115] About 125 million pregnant women are at risk of infection each year; in Sub-Saharan Africa, maternal malaria is associated with up to 200,000 estimated infant deaths yearly.[20] There are about 10,000 malaria cases per year in Western Europe, and 1300–1500 in the United States.[16] About 900 people died from the disease in Europe between 1993 and 2003.[59] Both the global incidence of disease and resulting mortality have declined in recent years. According to the WHO and UNICEF, deaths attributable to malaria in 2015 were reduced by 60%[67] from a 2000 estimate of 985,000, largely due to the widespread use of insecticide-treated nets and artemisinin-based combination therapies.[64] In 2012, there were 207 million cases of malaria. That year, the disease is estimated to have killed between 473,000 and 789,000 people, many of whom were children in Africa.[2] Efforts at decreasing the disease in Africa since the turn of millennium have been partially effective, with rates of the disease dropping by an estimated forty percent on the continent.[116]
Malaria is presently endemic in a broad band around the equator, in areas of the Americas, many parts of Asia, and much of Africa; in Sub-Saharan Africa, 85–90% of malaria fatalities occur.[117] An estimate for 2009 reported that countries with the highest death rate per 100,000 of population were Ivory Coast (86.15), Angola (56.93) and Burkina Faso (50.66).[118] A 2010 estimate indicated the deadliest countries per population were Burkina Faso, Mozambique and Mali.[115] The Malaria Atlas Project aims to map global endemic levels of malaria, providing a means with which to determine the global spatial limits of the disease and to assess disease burden.[119][120] This effort led to the publication of a map of P. falciparum endemicity in 2010.[121] As of 2010, about 100 countries have endemic malaria.[122][123] Every year, 125 million international travellers visit these countries, and more than 30,000 contract the disease.[59]
The geographic distribution of malaria within large regions is complex, and malaria-afflicted and malaria-free areas are often found close to each other.[124] Malaria is prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions because of rainfall, consistent high temperatures and high humidity, along with stagnant waters in which mosquito larvae readily mature, providing them with the environment they need for continuous breeding.[125] In drier areas, outbreaks of malaria have been predicted with reasonable accuracy by mapping rainfall.[126] Malaria is more common in rural areas than in cities. For example, several cities in the Greater Mekong Subregion of Southeast Asia are essentially malaria-free, but the disease is prevalent in many rural regions, including along international borders and forest fringes.[127] In contrast, malaria in Africa is present in both rural and urban areas, though the risk is lower in the larger cities.[128]
History

Ancient malaria oocysts preserved in Dominican amber
Although the parasite responsible for P. falciparum malaria has been in existence for 50,000–100,000 years, the population size of the parasite did not increase until about 10,000 years ago, concurrently with advances in agriculture[129] and the development of human settlements. Close relatives of the human malaria parasites remain common in chimpanzees. Some evidence suggests that the P. falciparum malaria may have originated in gorillas.[130]
References to the unique periodic fevers of malaria are found throughout recorded history.[131] Hippocrates described periodic fevers, labelling them tertian, quartan, subtertian and quotidian.[132] The Roman Columella associated the disease with insects from swamps.[132] Malaria may have contributed to the decline of the Roman Empire,[133] and was so pervasive in Rome that it was known as the "Roman fever".[134] Several regions in ancient Rome were considered at-risk for the disease because of the favourable conditions present for malaria vectors. This included areas such as southern Italy, the island of Sardinia, the Pontine Marshes, the lower regions of coastal Etruria and the city of Rome along the Tiber River. The presence of stagnant water in these places was preferred by mosquitoes for breeding grounds. Irrigated gardens, swamp-like grounds, runoff from agriculture, and drainage problems from road construction led to the increase of standing water.[135]
British doctor Ronald Ross received the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1902 for his work on malaria.
The term malaria originates from Medieval Italian: mala aria—"bad air"; the disease was formerly called ague or marsh fever due to its association with swamps and marshland.[136] The term first appeared in the English literature about 1829.[132] Malaria was once common in most of Europe and North America,[137] where it is no longer endemic,[138] though imported cases do occur.[139]
Scientific studies on malaria made their first significant advance in 1880, when Charles Louis Alphonse Laveran—a French army doctor working in the military hospital of Constantine in Algeria—observed parasites inside the red blood cells of infected people for the first time. He, therefore, proposed that malaria is caused by this organism, the first time a protist was identified as causing disease.[140] For this and later discoveries, he was awarded the 1907 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine. A year later, Carlos Finlay, a Cuban doctor treating people with yellow fever in Havana, provided strong evidence that mosquitoes were transmitting disease to and from humans.[141] This work followed earlier suggestions by Josiah C. Nott,[142] and work by Sir Patrick Manson, the "father of tropical medicine", on the transmission of filariasis.[143]
Chinese traditional Chinese medicine researcher Tu Youyou received the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 2015 for her work on antimalarial drug artemisin.
In April 1894, a Scottish physician Sir Ronald Ross visited Sir Patrick Manson at his house on Queen Anne Street, London. This visit was the start of four years of collaboration and fervent research that culminated in 1898 when Ross, who was working in the Presidency General Hospital in Calcutta, proved the complete life-cycle of the malaria parasite in mosquitoes. He thus proved that the mosquito was the vector for malaria in humans by showing that certain mosquito species transmit malaria to birds. He isolated malaria parasites from the salivary glands of mosquitoes that had fed on infected birds.[144] For this work, Ross received the 1902 Nobel Prize in Medicine. After resigning from the Indian Medical Service, Ross worked at the newly established Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine and directed malaria-control efforts in Egypt, Panama, Greece and Mauritius.[145] The findings of Finlay and Ross were later confirmed by a medical board headed by Walter Reed in 1900. Its recommendations were implemented by William C. Gorgas in the health measures undertaken during construction of the Panama Canal. This public-health work saved the lives of thousands of workers and helped develop the methods used in future public-health campaigns against the disease.[146]
Artemisia annua, source of the antimalarial drug artemisin
The first effective treatment for malaria came from the bark of cinchona tree, which contains quinine. This tree grows on the slopes of the Andes, mainly in Peru. The indigenous peoples of Peru made a tincture of cinchona to control fever. Its effectiveness against malaria was found and the Jesuits introduced the treatment to Europe around 1640; by 1677, it was included in the London Pharmacopoeia as an antimalarial treatment.[147] It was not until 1820 that the active ingredient, quinine, was extracted from the bark, isolated and named by the French chemists Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou.[148][149]
Quinine became the predominant malarial medication until the 1920s when other medications began to be developed. In the 1940s, chloroquine replaced quinine as the treatment of both uncomplicated and severe malaria until resistance supervened, first in Southeast Asia and South America in the 1950s and then globally in the 1980s.[150]
The medicinal value of Artemisia annua has been used by Chinese herbalists in traditional Chinese medicines for 2,000 years. In 1596, Li Shizhen recommended tea made from qinghao specifically to treat malaria symptoms in his "Compendium of Materia Medica". Artemisinins, discovered by Chinese scientist Tu Youyou and colleagues in the 1970s from the plant Artemisia annua, became the recommended treatment for P. falciparum malaria, administered in combination with other antimalarials as well as in severe disease.[151] Tu says she was influenced by a traditional Chinese herbal medicine source, The Handbook of Prescriptions for Emergency Treatments, written in 340 by Ge Hong.[152] For her work on malaria, Tu Youyou received the 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.[153]
Plasmodium vivax was used between 1917 and the 1940s for malariotherapy—deliberate injection of malaria parasites to induce a fever to combat certain diseases such as tertiary syphilis. In 1927, the inventor of this technique, Julius Wagner-Jauregg, received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discoveries. The technique was dangerous, killing about 15% of patients, so it is no longer in use.[154]
U.S. Marines with malaria in a rough field hospital on Guadalcanal, October 1942
The first pesticide used for indoor residual spraying was DDT.[155] Although it was initially used exclusively to combat malaria, its use quickly spread to agriculture. In time, pest control, rather than disease control, came to dominate DDT use, and this large-scale agricultural use led to the evolution of resistant mosquitoes in many regions. The DDT resistance shown by Anopheles mosquitoes can be compared to antibiotic resistance shown by bacteria. During the 1960s, awareness of the negative consequences of its indiscriminate use increased, ultimately leading to bans on agricultural applications of DDT in many countries in the 1970s.[72] Before DDT, malaria was successfully eliminated or controlled in tropical areas like Brazil and Egypt by removing or poisoning the breeding grounds of the mosquitoes or the aquatic habitats of the larva stages, for example by applying the highly toxic arsenic compound Paris Green to places with standing water.[156]
Malaria vaccines have been an elusive goal of research. The first promising studies demonstrating the potential for a malaria vaccine were performed in 1967 by immunizing mice with live, radiation-attenuated sporozoites, which provided significant protection to the mice upon subsequent injection with normal, viable sporozoites. Since the 1970s, there has been a considerable effort to develop similar vaccination strategies for humans.[157] The first vaccine, called RTS,S, was approved by European regulators in 2015.[158]
Society and culture
Economic impact
Malaria clinic in Tanzania
Malaria is not just a disease commonly associated with poverty: some evidence suggests that it is also a cause of poverty and a major hindrance to economic development.[9][10] Although tropical regions are most affected, malaria's furthest influence reaches into some temperate zones that have extreme seasonal changes. The disease has been associated with major negative economic effects on regions where it is widespread. During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, it was a major factor in the slow economic development of the American southern states.[159]
A comparison of average per capita GDP in 1995, adjusted for parity of purchasing power, between countries with malaria and countries without malaria gives a fivefold difference ($1,526 USD versus $8,268 USD). In the period 1965 to 1990, countries where malaria was common had an average per capita GDP that increased only 0.4% per year, compared to 2.4% per year in other countries.[160]
Poverty can increase the risk of malaria since those in poverty do not have the financial capacities to prevent or treat the disease. In its entirety, the economic impact of malaria has been estimated to cost Africa US$12 billion every year. The economic impact includes costs of health care, working days lost due to sickness, days lost in education, decreased productivity due to brain damage from cerebral malaria, and loss of investment and tourism.[11] The disease has a heavy burden in some countries, where it may be responsible for 30–50% of hospital admissions, up to 50% of outpatient visits, and up to 40% of public health spending.[161]
Child with malaria in Ethiopia
Cerebral malaria is one of the leading causes of neurological disabilities in African children.[111] Studies comparing cognitive functions before and after treatment for severe malarial illness continued to show significantly impaired school performance and cognitive abilities even after recovery.[109] Consequently, severe and cerebral malaria have far-reaching socioeconomic consequences that extend beyond the immediate effects of the disease.[162]
Counterfeit and substandard drugs
Sophisticated counterfeits have been found in several Asian countries such as Cambodia,[163] China,[164] Indonesia, Laos, Thailand, and Vietnam, and are an important cause of avoidable death in those countries.[165] The WHO said that studies indicate that up to 40% of artesunate-based malaria medications are counterfeit, especially in the Greater Mekong region and have established a rapid alert system to enable information about counterfeit drugs to be rapidly reported to the relevant authorities in participating countries.[166] There is no reliable way for doctors or lay people to detect counterfeit drugs without help from a laboratory. Companies are attempting to combat the persistence of counterfeit drugs by using new technology to provide security from source to distribution.[167]Another clinical and public health concern is the proliferation of substandard antimalarial medicines resulting from inappropriate concentration of ingredients, contamination with other drugs or toxic impurities, poor quality ingredients, poor stability and inadequate packaging.[168] A 2012 study demonstrated that roughly one-third of antimalarial medications in Southeast Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa failed chemical analysis, packaging analysis, or were falsified.[169]
War
World War II poster
Throughout history, the contraction of malaria has played a prominent role in the fates of government rulers, nation-states, military personnel, and military actions.[170] In 1910, Nobel Prize in Medicine-winner Ronald Ross (himself a malaria survivor), published a book titled The Prevention of Malaria that included a chapter titled "The Prevention of Malaria in War." The chapter's author, Colonel C. H. Melville, Professor of Hygiene at Royal Army Medical College in London, addressed the prominent role that malaria has historically played during wars: "The history of malaria in war might almost be taken to be the history of war itself, certainly the history of war in the Christian era. ... It is probably the case that many of the so-called camp fevers, and probably also a considerable proportion of the camp dysentery, of the wars of the sixteenth, seventeenth and eighteenth centuries were malarial in origin."[171]
Malaria was the most significant health hazard encountered by U.S. troops in the South Pacific during World War II, where about 500,000 men were infected.[172] According to Joseph Patrick Byrne, "Sixty thousand American soldiers died of malaria during the African and South Pacific campaigns."[173]
Significant financial investments have been made to procure existing and create new anti-malarial agents. During World War I and World War II, inconsistent supplies of the natural anti-malaria drugs cinchona bark and quinine prompted substantial funding into research and development of other drugs and vaccines. American military organizations conducting such research initiatives include the Navy Medical Research Center, Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, and the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases of the US Armed Forces.[174]
Additionally, initiatives have been founded such as Malaria Control in War Areas (MCWA), established in 1942, and its successor, the Communicable Disease Center (now known as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or CDC) established in 1946. According to the CDC, MCWA "was established to control malaria around military training bases in the southern United States and its territories, where malaria was still problematic".[175]
Eradication efforts
Members of the Malaria Commission of the League of Nations collecting larvae on the Danube delta, 1929
Several notable attempts are being made to eliminate the parasite from sections of the world, or to eradicate it worldwide. In 2006, the organization Malaria No More set a public goal of eliminating malaria from Africa by 2015, and the organization plans to dissolve if that goal is accomplished.[176] Several malaria vaccines are in clinical trials, which are intended to provide protection for children in endemic areas and reduce the speed of transmission of the disease. As of 2012, The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria has distributed 230 million insecticide-treated nets intended to stop mosquito-borne transmission of malaria.[177] The U.S.-based Clinton Foundation has worked to manage demand and stabilize prices in the artemisinin market.[178] Other efforts, such as the Malaria Atlas Project, focus on analysing climate and weather information required to accurately predict the spread of malaria based on the availability of habitat of malaria-carrying parasites.[119] The Malaria Policy Advisory Committee (MPAC) of the World Health Organization (WHO) was formed in 2012, "to provide strategic advice and technical input to WHO on all aspects of malaria control and elimination".[179] In November 2013, WHO and the malaria vaccine funders group set a goal to develop vaccines designed to interrupt malaria transmission with the long-term goal of malaria eradication.[180]
Malaria has been successfully eliminated or greatly reduced in certain areas. Malaria was once common in the United States and southern Europe, but vector control programs, in conjunction with the monitoring and treatment of infected humans, eliminated it from those regions. Several factors contributed, such as the draining of wetland breeding grounds for agriculture and other changes in water management practices, and advances in sanitation, including greater use of glass windows and screens in dwellings.[181] Malaria was eliminated from most parts of the USA in the early 20th century by such methods, and the use of the pesticide DDT and other means eliminated it from the remaining pockets in the South in the 1950s as part of the National Malaria Eradication Program.[182] Bill Gates has said that he thinks global eradication is possible by 2040.[183]
Research
The Malaria Eradication Research Agenda (malERA) initiative was a consultative process to identify which areas of research and development (R&D) needed to be addressed for the worldwide eradication of malaria.[184][185]Vaccine
A vaccine against malaria called RTS,S, was approved by European regulators in 2015.[158] It is undergoing pilot trials in select countries in 2016.Immunity (or, more accurately, tolerance) to P. falciparum malaria does occur naturally, but only in response to years of repeated infection.[37] An individual can be protected from a P. falciparum infection if they receive about a thousand bites from mosquitoes that carry a version of the parasite rendered non-infective by a dose of X-ray irradiation.[186] The highly polymorphic nature of many P. falciparum proteins results in significant challenges to vaccine design. Vaccine candidates that target antigens on gametes, zygotes, or ookinetes in the mosquito midgut aim to block the transmission of malaria. These transmission-blocking vaccines induce antibodies in the human blood; when a mosquito takes a blood meal from a protected individual, these antibodies prevent the parasite from completing its development in the mosquito.[187] Other vaccine candidates, targeting the blood-stage of the parasite's life cycle, have been inadequate on their own.[188] For example, SPf66 was tested extensively in areas where the disease is common in the 1990s, but trials showed it to be insufficiently effective.[189]
Medications
Malaria parasites contain apicoplasts, organelles usually found in plants, complete with their own genomes. These apicoplasts are thought to have originated through the endosymbiosis of algae and play a crucial role in various aspects of parasite metabolism, such as fatty acid biosynthesis. Over 400 proteins have been found to be produced by apicoplasts and these are now being investigated as possible targets for novel anti-malarial drugs.[190]With the onset of drug-resistant Plasmodium parasites, new strategies are being developed to combat the widespread disease. One such approach lies in the introduction of synthetic pyridoxal-amino acid adducts, which are taken up by the parasite and ultimately interfere with its ability to create several essential B vitamins.[191][192] Antimalarial drugs using synthetic metal-based complexes are attracting research interest.[193][194]
- (+)-SJ733: Part of a wider class of experimental drugs called spiroindolone. It inhibits the ATP4 protein of infected red blood cells that cause the cells to shrink and become rigid like the aging cells. This triggers the immune system to eliminate the infected cells from the system as demonstrated in a mouse model. As of 2014, a Phase 1 clinical trial to assess the safety profile in human is planned by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.[195]
- NITD246 and NITD609: Also belonged to the class of spiroindolone and target the ATP4 protein.[195]
Other
A non-chemical vector control strategy involves genetic manipulation of malaria mosquitoes. Advances in genetic engineering technologies make it possible to introduce foreign DNA into the mosquito genome and either decrease the lifespan of the mosquito, or make it more resistant to the malaria parasite. Sterile insect technique is a genetic control method whereby large numbers of sterile male mosquitoes are reared and released. Mating with wild females reduces the wild population in the subsequent generation; repeated releases eventually eliminate the target population.[63]Genomics is central to malaria research. With the sequencing of P. falciparum, one of its vectors Anopheles gambiae, and the human genome, the genetics of all three organisms in the malaria lifecycle can be studied.[196] Another new application of genetic technology is the ability to produce genetically modified mosquitoes that do not transmit malaria, potentially allowing biological control of malaria transmission.[197]
In one study, a genetically-modified strain of Anopheles stephensi was created that no longer supported malaria transmission, and this resistance was passed down to mosquito offspring.[198]
Gene drive is a technique for changing wild populations, for instance to combat insects so they cannot transmit diseases (in particular mosquitoes in the cases of malaria and zika).[199]