Comets – nucleus, coma and tail:
- Top: 9P/Tempel (impactor collision: Deep Impact), and 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko (Rosetta)
- Middle: 17P/Holmes and its blue ionized tail, and 81P/Wild (Wild 2) visited by Stardust
- Bottom: Hale–Bopp seen from Earth in 1997, and C/2011 W3 (Lovejoy) imaged from Earth orbit
Comets usually have highly eccentric elliptical orbits, and they have a wide range of orbital periods, ranging from several years to potentially several millions of years. Short-period comets originate in the Kuiper belt or its associated scattered disc, which lie beyond the orbit of Neptune. Long-period comets are thought to originate in the Oort cloud, a spherical cloud of icy bodies extending from outside the Kuiper belt to halfway to the nearest star. Long-period comets are set in motion towards the Sun from the Oort cloud by gravitational perturbations caused by passing stars and the galactic tide. Hyperbolic comets may pass once through the inner Solar System before being flung to interstellar space. The appearance of a comet is called an apparition.
Comets are distinguished from asteroids by the presence of an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere surrounding their central nucleus. This atmosphere has parts termed the coma (the central part immediately surrounding the nucleus) and the tail (a typically linear section consisting of dust or gas blown out from the coma by the Sun's light pressure or outstreaming solar wind plasma). However, extinct comets that have passed close to the Sun many times have lost nearly all of their volatile ices and dust and may come to resemble small asteroids. Asteroids are thought to have a different origin from comets, having formed inside the orbit of Jupiter rather than in the outer Solar System. The discovery of main-belt comets and active centaur minor planets has blurred the distinction between asteroids and comets. Recent years, the discovery of some minor bodies that has a long-period comet orbit but has the characteristics of a inner solar system asteroid sometimes is called Manx Object (It will still be classified as Comet, such as C/2014 S3 (PANSTARRS)). 27 Manxes were found from 2013-2017.
As of July 2018 there are 6,339 known comets, a number that is steadily increasing as they are discovered. However, this represents only a tiny fraction of the total potential comet population, as the reservoir of comet-like bodies in the outer Solar System (in the Oort cloud) is estimated to be one trillion. Roughly one comet per year is visible to the naked eye, though many of those are faint and unspectacular. Particularly bright examples are called "great comets". Comets have been visited by unmanned probes such as the European Space Agency's Rosetta, which became the first ever to land a robotic spacecraft on a comet, and NASA's Deep Impact, which blasted a crater on Comet Tempel 1 to study its interior.
Etymology
A comet was mentioned in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle that allegedly made an appearance in 729 AD.
The word comet derives from the Old English cometa from the Latin comēta or comētēs. That, in turn, is a latinisation of the Greek κομήτης ("wearing long hair"), and the Oxford English Dictionary
notes that the term (ἀστὴρ) κομήτης already meant "long-haired star,
comet" in Greek. Κομήτης was derived from κομᾶν ("to wear the hair
long"), which was itself derived from κόμη ("the hair of the head") and
was used to mean "the tail of a comet".
The astronomical symbol for comets is ☄ (in Unicode U+2604), consisting of a small disc with three hairlike extensions.
Physical characteristics
Nucleus
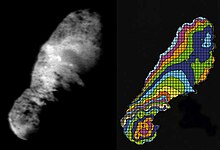
Nucleus of 103P/Hartley as imaged during a spacecraft flyby. The nucleus is about 2 km in length.
Comet 81P/Wild exhibits jets on light side and dark side, stark relief, and is dry.
The solid, core structure of a comet is known as the nucleus. Cometary nuclei are composed of an amalgamation of rock, dust, water ice, and frozen carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, methane, and ammonia. As such, they are popularly described as "dirty snowballs" after Fred Whipple's model. However, some comets may have a higher dust content, leading them to be called "icy dirtballs". Research conducted in 2014 suggests that comets are like "deep fried ice cream", in that their surfaces are formed of dense crystalline ice mixed with organic compounds, while the interior ice is colder and less dense.
Comet Borrelly exhibits jets, but has no surface ice.
The surface of the nucleus is generally dry, dusty or rocky,
suggesting that the ices are hidden beneath a surface crust several
metres thick. In addition to the gases already mentioned, the nuclei
contain a variety of organic compounds, which may include methanol, hydrogen cyanide, formaldehyde, ethanol, and ethane and perhaps more complex molecules such as long-chain hydrocarbons and amino acids. In 2009, it was confirmed that the amino acid glycine had been found in the comet dust recovered by NASA's Stardust mission. In August 2011, a report, based on NASA studies of meteorites found on Earth, was published suggesting DNA and RNA components (adenine, guanine, and related organic molecules) may have been formed on asteroids and comets.
The outer surfaces of cometary nuclei have a very low albedo, making them among the least reflective objects found in the Solar System. The Giotto space probe found that the nucleus of Halley's Comet reflects about four percent of the light that falls on it, and Deep Space 1 discovered that Comet Borrelly's surface reflects less than 3.0%; by comparison, asphalt reflects seven percent. The dark surface material of the nucleus may consist of complex organic compounds. Solar heating drives off lighter volatile compounds, leaving behind larger organic compounds that tend to be very dark, like tar or crude oil. The low reflectivity of cometary surfaces causes them to absorb the heat that drives their outgassing processes.
Comet nuclei with radii of up to 30 kilometres (19 mi) have been observed, but ascertaining their exact size is difficult. The nucleus of 322P/SOHO is probably only 100–200 metres (330–660 ft) in diameter.
A lack of smaller comets being detected despite the increased
sensitivity of instruments has led some to suggest that there is a real
lack of comets smaller than 100 metres (330 ft) across. Known comets have been estimated to have an average density of 0.6 g/cm3 (0.35 oz/cu in). Because of their low mass, comet nuclei do not become spherical under their own gravity and therefore have irregular shapes.
Roughly six percent of the near-Earth asteroids are thought to be extinct nuclei of comets that no longer experience outgassing, including 14827 Hypnos and 3552 Don Quixote.
Results from the Rosetta and Philae spacecraft show that the nucleus of 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko has no magnetic field, which suggests that magnetism may not have played a role in the early formation of planetesimals. Further, the ALICE spectrograph on Rosetta determined that electrons (within 1 km (0.62 mi) above the comet nucleus) produced from photoionization of water molecules by solar radiation, and not photons from the Sun as thought earlier, are responsible for the degradation of water and carbon dioxide molecules released from the comet nucleus into its coma. Instruments on the Philae lander found at least sixteen organic compounds at the comet's surface, four of which (acetamide, acetone, methyl isocyanate and propionaldehyde) have been detected for the first time on a comet.
| Name | Dimensions (km) |
Density (g/cm3) |
Mass (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Halley's Comet | 15 × 8 × 8 | 0.6 | 3×1014 |
| Tempel 1 | 7.6 × 4.9 | 0.62 | 7.9×1013 |
| 19P/Borrelly | 8 × 4 × 4 | 0.3 | 2.0×1013 |
| 81P/Wild | 5.5 × 4.0 × 3.3 | 0.6 | 2.3×1013 |
| 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko | 4.1 × 3.3 × 1.8 | 0.47 | 1.0×1013 |
Coma
Hubble image of Comet ISON shortly before perihelion.
The streams of dust
and gas thus released form a huge and extremely thin atmosphere around
the comet called the "coma". The force exerted on the coma by the Sun's radiation pressure and solar wind cause an enormous "tail" to form pointing away from the Sun.
The coma is generally made of H2O and dust, with water making up to 90% of the volatiles
that outflow from the nucleus when the comet is within 3 to 4
astronomical units (450,000,000 to 600,000,000 km; 280,000,000 to
370,000,000 mi) of the Sun. The H2O parent molecule is destroyed primarily through photodissociation and to a much smaller extent photoionization, with the solar wind playing a minor role in the destruction of water compared to photochemistry.
Larger dust particles are left along the comet's orbital path whereas
smaller particles are pushed away from the Sun into the comet's tail by light pressure.
C/2006 W3 (Chistensen) emitting carbon gas (IR image)
Although the solid nucleus of comets is generally less than 60
kilometres (37 mi) across, the coma may be thousands or millions of
kilometres across, sometimes becoming larger than the Sun. For example, about a month after an outburst in October 2007, comet 17P/Holmes briefly had a tenuous dust atmosphere larger than the Sun. The Great Comet of 1811 also had a coma roughly the diameter of the Sun. Even though the coma can become quite large, its size can decrease about the time it crosses the orbit of Mars around 1.5 astronomical units (220,000,000 km; 140,000,000 mi) from the Sun.
At this distance the solar wind becomes strong enough to blow the gas
and dust away from the coma, and in doing so enlarging the tail. Ion tails have been observed to extend one astronomical unit (150 million km) or more.
Both the coma and tail are illuminated by the Sun and may become
visible when a comet passes through the inner Solar System, the dust
reflects sunlight directly while the gases glow from ionisation. Most comets are too faint to be visible without the aid of a telescope, but a few each decade become bright enough to be visible to the naked eye.
Occasionally a comet may experience a huge and sudden outburst of gas
and dust, during which the size of the coma greatly increases for a
period of time. This happened in 2007 to Comet Holmes.
In 1996, comets were found to emit X-rays. This greatly surprised astronomers because X-ray emission is usually associated with very high-temperature bodies.
The X-rays are generated by the interaction between comets and the
solar wind: when highly charged solar wind ions fly through a cometary
atmosphere, they collide with cometary atoms and molecules, "stealing"
one or more electrons from the atom in a process called "charge
exchange". This exchange or transfer of an electron to the solar wind
ion is followed by its de-excitation into the ground state of the ion by
the emission of X-rays and far ultraviolet photons.
Bow shock
Bow shocks form at as a result of the interaction between the solar wind
and the cometary ionosphere, which is created by ionization of gases in
the coma. As the comet approaches the Sun, increasing outgassing rates
cause the coma to expand, and the sunlight ionizes gases in the coma.
When the solar wind passes through this ion coma, the bow shock appears.
The first observations were made in the 1980s and 90s as several spacecraft flew by comets 21P/Giacobini–Zinner, 1P/Halley, and 26P/Grigg–Skjellerup.
It was then found that the bow shocks at comets are wider and more
gradual than the sharp planetary bow shocks seen at, for example, Earth.
These observations were all made near perihelion when the bow shocks already were fully developed.
The Rosetta spacecraft observed the bow shock at comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko
at an early stage of bow shock development when the outgassing
increased during the comet's journey toward the Sun. This young bow
shock was called the "infant bow shock". The infant bow shock is
asymmetric and, relative to the distance to the nucleus, wider than
fully developed bow shocks.
Tails
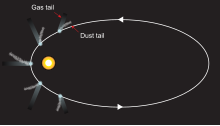
Diagram of a comet showing the dust trail (or antitail), the dust tail, and the ion gas tail, which is formed by the solar wind flow.
In the outer Solar System,
comets remain frozen and inactive and are extremely difficult or
impossible to detect from Earth due to their small size. Statistical
detections of inactive comet nuclei in the Kuiper belt have been reported from observations by the Hubble Space Telescope but these detections have been questioned. As a comet approaches the inner Solar System, solar radiation causes the volatile materials within the comet to vaporize and stream out of the nucleus, carrying dust away with them.
Typical direction of tails over a comet's orbit near the Sun
The streams of dust and gas each form their own distinct tail,
pointing in slightly different directions. The tail of dust is left
behind in the comet's orbit in such a manner that it often forms a
curved tail called the type II or dust tail.
At the same time, the ion or type I tail, made of gases, always points
directly away from the Sun because this gas is more strongly affected by
the solar wind than is dust, following magnetic field lines rather than
an orbital trajectory.
On occasions - such as when the Earth passes through a comet's orbital
plane, a tail pointing in the opposite direction to the ion and dust
tails called the antitail may be seen.
The observation of antitails contributed significantly to the discovery of solar wind.
The ion tail is formed as a result of the ionisation by solar
ultra-violet radiation of particles in the coma. Once the particles have
been ionized, they attain a net positive electrical charge, which in
turn gives rise to an "induced magnetosphere"
around the comet. The comet and its induced magnetic field form an
obstacle to outward flowing solar wind particles. Because the relative
orbital speed of the comet and the solar wind is supersonic, a bow shock
is formed upstream of the comet in the flow direction of the solar
wind. In this bow shock, large concentrations of cometary ions (called
"pick-up ions") congregate and act to "load" the solar magnetic field
with plasma, such that the field lines "drape" around the comet forming
the ion tail.
If the ion tail loading is sufficient, the magnetic field lines
are squeezed together to the point where, at some distance along the ion
tail, magnetic reconnection occurs. This leads to a "tail disconnection event". This has been observed on a number of occasions, one notable event being recorded on 20 April 2007, when the ion tail of Encke's Comet was completely severed while the comet passed through a coronal mass ejection. This event was observed by the STEREO space probe.
In 2013, ESA scientists reported that the ionosphere of the planet Venus streams outwards in a manner similar to the ion tail seen streaming from a comet under similar conditions."
Jets
Gas and snow jets of 103P/Hartley
Uneven heating can cause newly generated gases to break out of a weak spot on the surface of comet's nucleus, like a geyser. These streams of gas and dust can cause the nucleus to spin, and even split apart. In 2010 it was revealed dry ice (frozen carbon dioxide) can power jets of material flowing out of a comet nucleus. Infrared imaging of Hartley 2 shows such jets exiting and carrying with it dust grains into the coma.
Orbital characteristics
Most comets are small Solar System bodies with elongated elliptical orbits
that take them close to the Sun for a part of their orbit and then out
into the further reaches of the Solar System for the remainder. Comets are often classified according to the length of their orbital periods: The longer the period the more elongated the ellipse.
Short period
Periodic comets or short-period comets are generally defined as those having orbital periods of less than 200 years. They usually orbit more-or-less in the ecliptic plane in the same direction as the planets. Their orbits typically take them out to the region of the outer planets (Jupiter and beyond) at aphelion; for example, the aphelion of Halley's Comet is a little beyond the orbit of Neptune. Comets whose aphelia are near a major planet's orbit are called its "family". Such families are thought to arise from the planet capturing formerly long-period comets into shorter orbits.
At the shorter orbital period extreme, Encke's Comet has an orbit that does not reach the orbit of Jupiter, and is known as an Encke-type comet.
Short-period comets with orbital periods less than 20 years and low
inclinations (up to 30 degrees) to the ecliptic are called traditional Jupiter-family comets (JFCs).
Those like Halley, with orbital periods of between 20 and 200 years and
inclinations extending from zero to more than 90 degrees, are called Halley-type comets (HTCs). As of 2018, only 83 HTCs have been observed, compared with 660 identified JFCs.
Recently discovered main-belt comets form a distinct class, orbiting in more circular orbits within the asteroid belt.
Because their elliptical orbits frequently take them close to the giant planets, comets are subject to further gravitational perturbations. Short-period comets have a tendency for their aphelia to coincide with a giant planet's semi-major axis, with the JFCs being the largest group.
It is clear that comets coming in from the Oort cloud often have their
orbits strongly influenced by the gravity of giant planets as a result
of a close encounter. Jupiter is the source of the greatest
perturbations, being more than twice as massive as all the other planets
combined. These perturbations can deflect long-period comets into
shorter orbital periods.
Based on their orbital characteristics, short-period comets are thought to originate from the centaurs and the Kuiper belt/scattered disc
—a disk of objects in the trans-Neptunian region—whereas the source of
long-period comets is thought to be the far more distant spherical Oort cloud (after the Dutch astronomer Jan Hendrik Oort who hypothesised its existence).
Vast swarms of comet-like bodies are thought to orbit the Sun in these
distant regions in roughly circular orbits. Occasionally the
gravitational influence of the outer planets (in the case of Kuiper belt
objects) or nearby stars (in the case of Oort cloud objects) may throw
one of these bodies into an elliptical orbit that takes it inwards
toward the Sun
to form a visible comet. Unlike the return of periodic comets, whose
orbits have been established by previous observations, the appearance of
new comets by this mechanism is unpredictable.
Long period
Orbits of Comet Kohoutek (red) and the Earth (blue), illustrating the high eccentricity of its orbit and its rapid motion when close to the Sun.
Long-period comets have highly eccentric orbits and periods ranging from 200 years to thousands of years. An eccentricity greater than 1 when near perihelion does not necessarily mean that a comet will leave the Solar System. For example, Comet McNaught had a heliocentric osculating eccentricity of 1.000019 near its perihelion passage epoch in January 2007 but is bound to the Sun with roughly a 92,600-year orbit because the eccentricity drops below 1 as it moves farther from the Sun. The future orbit of a long-period comet is properly obtained when the osculating orbit is computed at an epoch after leaving the planetary region and is calculated with respect to the center of mass of the Solar System.
By definition long-period comets remain gravitationally bound to the
Sun; those comets that are ejected from the Solar System due to close
passes by major planets are no longer properly considered as having
"periods". The orbits of long-period comets take them far beyond the
outer planets at aphelia, and the plane of their orbits need not lie
near the ecliptic. Long-period comets such as Comet West and C/1999 F1 can have aphelion distances of nearly 70,000 AU with orbital periods estimated around 6 million years.
Single-apparition or non-periodic comets are similar to long-period comets because they also have parabolic or slightly hyperbolic trajectories
when near perihelion in the inner Solar System. However, gravitational
perturbations from giant planets cause their orbits to change.
Single-apparition comets have a hyperbolic or parabolic osculating orbit which allows them to permanently exit the Solar System after a single pass of the Sun. The Sun's Hill sphere has an unstable maximum boundary of 230,000 AU (1.1 parsecs (3.6 light-years)). Only a few hundred comets have been seen to reach a hyperbolic orbit (e > 1) when near perihelion that using a heliocentric unperturbed two-body best-fit suggests they may escape the Solar System.
As of 2018, 1I/ʻOumuamua is the only object with an eccentricity
significantly greater than one that has been detected, indicating an
origin outside the Solar System. While ʻOumuamua showed no optical signs
of cometary activity during its passage through the inner Solar System
in October 2017, changes to its trajectory—which suggests outgassing—indicate that it is indeed a comet. Comet C/1980 E1
had an orbital period of roughly 7.1 million years before the 1982
perihelion passage, but a 1980 encounter with Jupiter accelerated the
comet giving it the largest eccentricity (1.057) of any known hyperbolic
comet. Comets not expected to return to the inner Solar System include C/1980 E1, C/2000 U5, C/2001 Q4 (NEAT), C/2009 R1, C/1956 R1, and C/2007 F1 (LONEOS).
Some authorities use the term "periodic comet" to refer to any
comet with a periodic orbit (that is, all short-period comets plus all
long-period comets), whereas others use it to mean exclusively short-period comets.
Similarly, although the literal meaning of "non-periodic comet" is the
same as "single-apparition comet", some use it to mean all comets that
are not "periodic" in the second sense (that is, to also include all
comets with a period greater than 200 years).
Early observations have revealed a few genuinely hyperbolic (i.e.
non-periodic) trajectories, but no more than could be accounted for by
perturbations from Jupiter. If comets pervaded interstellar space,
they would be moving with velocities of the same order as the relative
velocities of stars near the Sun (a few tens of km per second). If such
objects entered the Solar System, they would have positive specific orbital energy
and would be observed to have genuinely hyperbolic trajectories. A
rough calculation shows that there might be four hyperbolic comets per
century within Jupiter's orbit, give or take one and perhaps two orders
of magnitude.
| Year | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 12 | 7 | 8 | 4 | 13 | 10 | 16 | 9 | 16 | 5 | 18 | 3 |
Oort cloud and Hills cloud
The Oort cloud thought to surround the Solar System
The Oort cloud is thought to occupy a vast space starting from between 2,000 and 5,000 AU (0.03 and 0.08 ly) to as far as 50,000 AU (0.79 ly) from the Sun. Some estimates place the outer edge at between 100,000 and 200,000 AU (1.58 and 3.16 ly).
The region can be subdivided into a spherical outer Oort cloud of
20,000–50,000 AU (0.32–0.79 ly), and a doughnut-shaped inner cloud, the
Hills cloud, of 2,000–20,000 AU (0.03–0.32 ly).
The outer cloud is only weakly bound to the Sun and supplies the
long-period (and possibly Halley-type) comets that fall to inside the
orbit of Neptune. The inner Oort cloud is also known as the Hills cloud, named after J. G. Hills, who proposed its existence in 1981. Models predict that the inner cloud should have tens or hundreds of times as many cometary nuclei as the outer halo;
it is seen as a possible source of new comets that resupply the
relatively tenuous outer cloud as the latter's numbers are gradually
depleted. The Hills cloud explains the continued existence of the Oort
cloud after billions of years.
Exocomets
Exocomets beyond the Solar System have also been detected and may be common in the Milky Way. The first exocomet system detected was around Beta Pictoris, a very young A-type main-sequence star, in 1987. A total of 10 such exocomet systems have been identified as of 2013, using the absorption spectrum caused by the large clouds of gas emitted by comets when passing close to their star.
Effects of comets
Connection to meteor showers
Diagram of Perseids meteors
As a result of outgassing, comets leave in their wake a trail of solid debris too large to be swept away by radiation pressure and the solar wind. If the Earth's orbit sends it through that debris, there are likely to be meteor showers as Earth passes through. The Perseid meteor shower, for example, occurs every year between 9 and 13 August, when Earth passes through the orbit of Comet Swift–Tuttle. Halley's Comet is the source of the Orionid shower in October.
Comets and impact on life
Many
comets and asteroids collided with Earth in its early stages. Many
scientists think that comets bombarding the young Earth about 4 billion
years ago brought the vast quantities of water that now fill the Earth's oceans, or at least a significant portion of it. Others have cast doubt on this idea. The detection of organic molecules, including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, in significant quantities in comets has led to speculation that comets or meteorites may have brought the precursors of life—or even life itself—to Earth. In 2013 it was suggested that impacts between rocky and icy surfaces, such as comets, had the potential to create the amino acids that make up proteins through shock synthesis.
In 2015, scientists found significant amounts of molecular oxygen in
the outgassings of comet 67P, suggesting that the molecule may occur
more often than had been thought, and thus less an indicator of life as
has been supposed.
It is suspected that comet impacts have, over long timescales, also delivered significant quantities of water to the Earth's Moon, some of which may have survived as lunar ice. Comet and meteoroid impacts are also thought to be responsible for the existence of tektites and australites.
Fear of comets
Fear of comets as acts of God and signs of impending doom was highest in Europe from AD 1200 to 1650. The year after the Great Comet of 1618, for example, Gotthard Arthusius published a pamphlet stating that it was a sign that the Day of Judgment was near.
He listed ten pages of comet-related disasters, including "earthquakes,
floods, changes in river courses, hail storms, hot and dry weather,
poor harvests, epidemics, war and treason and high prices". By 1700 most
scholars concluded that such events occurred whether a comet was seen
or not. Using Edmund Halley's records of comet sightings, however, William Whiston in 1711 wrote that the Great Comet of 1680 had a periodicity of 574 years and was responsible for the worldwide flood in the Book of Genesis,
by pouring water on the Earth. His announcement revived for another
century fear of comets, now as direct threats to the world instead of
signs of disasters. Spectroscopic analysis in 1910 found the toxic gas cyanogen in the tail of Halley's Comet, causing panicked buying of gas masks and quack "anti-comet pills" and "anti-comet umbrellas" by the public.
Fate of comets
Departure (ejection) from Solar System
If
a comet is traveling fast enough, it may leave the Solar System. Such
comets follow the open path of a hyperbola, and as such they are called
hyperbolic comets. To date, comets are only known to be ejected by interacting with another object in the Solar System, such as Jupiter. An example of this is thought to be Comet C/1980 E1, which was shifted from a predicted orbit of 7.1 million years around the Sun, to a hyperbolic trajectory, after a 1980 close pass by the planet Jupiter.
Volatiles exhausted
Jupiter-family comets and long-period comets appear to follow very
different fading laws. The JFCs are active over a lifetime of about
10,000 years or ~1,000 orbits whereas long-period comets fade much
faster. Only 10% of the long-period comets survive more than 50 passages
to small perihelion and only 1% of them survive more than 2,000
passages.
Eventually most of the volatile material contained in a comet nucleus
evaporates, and the comet becomes a small, dark, inert lump of rock or
rubble that can resemble an asteroid. Some asteroids in elliptical orbits are now identified as extinct comets. Roughly six percent of the near-Earth asteroids are thought to be extinct comet nuclei.
Breakup and collisions
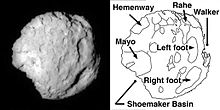
The nucleus of some comets may be fragile, a conclusion supported by the observation of comets splitting apart. A significant cometary disruption was that of Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9,
which was discovered in 1993. A close encounter in July 1992 had broken
it into pieces, and over a period of six days in July 1994, these
pieces fell into Jupiter's atmosphere—the first time astronomers had
observed a collision between two objects in the Solar System. Other splitting comets include 3D/Biela in 1846 and 73P/Schwassmann–Wachmann from 1995 to 2006. Greek historian Ephorus reported that a comet split apart as far back as the winter of 372–373 BC. Comets are suspected of splitting due to thermal stress, internal gas pressure, or impact.
Comets 42P/Neujmin and 53P/Van Biesbroeck
appear to be fragments of a parent comet. Numerical integrations have
shown that both comets had a rather close approach to Jupiter in January
1850, and that, before 1850, the two orbits were nearly identical.
Some comets have been observed to break up during their perihelion passage, including great comets West and Ikeya–Seki. Biela's
Comet was one significant example, when it broke into two pieces during
its passage through the perihelion in 1846. These two comets were seen
separately in 1852, but never again afterward. Instead, spectacular meteor showers were seen in 1872 and 1885 when the comet should have been visible. A minor meteor shower, the Andromedids, occurs annually in November, and it is caused when the Earth crosses the orbit of Biela's Comet.
Some comets meet a more spectacular end – either falling into the Sun
or smashing into a planet or other body. Collisions between comets and
planets or moons were common in the early Solar System: some of the many
craters on the Moon, for example, may have been caused by comets. A recent collision of a comet with a planet occurred in July 1994 when Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 broke up into pieces and collided with Jupiter.
Disintegration of P/2013 R3 (2014)
Nomenclature
Halley's Comet in 1910
The names given to comets have followed several different conventions
over the past two centuries. Prior to the early 20th century, most
comets were simply referred to by the year when they appeared, sometimes
with additional adjectives for particularly bright comets; thus, the "Great Comet of 1680", the "Great Comet of 1882", and the "Great January Comet of 1910".
After Edmund Halley
demonstrated that the comets of 1531, 1607, and 1682 were the same body
and successfully predicted its return in 1759 by calculating its orbit,
that comet became known as Halley's Comet. Similarly, the second and third known periodic comets, Encke's Comet and Biela's Comet,
were named after the astronomers who calculated their orbits rather
than their original discoverers. Later, periodic comets were usually
named after their discoverers, but comets that had appeared only once
continued to be referred to by the year of their appearance.
In the early 20th century, the convention of naming comets after
their discoverers became common, and this remains so today. A comet can
be named after its discoverers, or an instrument or program that helped
to find it.
History of study
Early observations and thought
Halley's Comet appeared in 1066, prior to the Battle of Hastings (Bayeux Tapestry).
From ancient sources, such as Chinese oracle bones, it is known that comets have been noticed by humans for millennia. Until the sixteenth century, comets were usually considered bad omens
of deaths of kings or noble men, or coming catastrophes, or even
interpreted as attacks by heavenly beings against terrestrial
inhabitants.
Aristotle believed that comets were atmospheric phenomena, due to the fact that they could appear outside of the Zodiac and vary in brightness over the course of a few days. Pliny the Elder believed that comets were connected with political unrest and death.
In India,
by the 6th century astronomers believed that comets were celestial
bodies that re-appeared periodically. This was the view expressed in the
6th century by the astronomers Varāhamihira and Bhadrabahu, and the 10th-century astronomer Bhaṭṭotpala
listed the names and estimated periods of certain comets, but it is not
known how these figures were calculated or how accurate they were.
In the 16th century Tycho Brahe demonstrated that comets must exist outside the Earth's atmosphere by measuring the parallax of the Great Comet of 1577
from observations collected by geographically separated observers.
Within the precision of the measurements, this implied the comet must be
at least four times more distant than from the Earth to the Moon.
Orbital studies
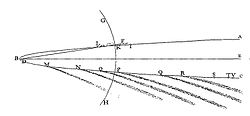
The orbit of the comet of 1680, fitted to a parabola, as shown in Isaac Newton's Principia
Isaac Newton, in his Principia Mathematica of 1687, proved that an object moving under the influence of gravity must trace out an orbit shaped like one of the conic sections, and he demonstrated how to fit a comet's path through the sky to a parabolic orbit, using the comet of 1680 as an example.
In 1705, Edmond Halley
(1656–1742) applied Newton's method to twenty-three cometary
apparitions that had occurred between 1337 and 1698. He noted that three
of these, the comets of 1531, 1607, and 1682, had very similar orbital elements,
and he was further able to account for the slight differences in their
orbits in terms of gravitational perturbation caused by Jupiter and Saturn.
Confident that these three apparitions had been three appearances of
the same comet, he predicted that it would appear again in 1758–9. Halley's predicted return date was later refined by a team of three French mathematicians: Alexis Clairaut, Joseph Lalande, and Nicole-Reine Lepaute, who predicted the date of the comet's 1759 perihelion to within one month's accuracy.
When the comet returned as predicted, it became known as Halley's Comet
(with the latter-day designation of 1P/Halley). It will next appear in
2061.
Studies of physical characteristics
From his huge vapouring train perhaps to shake
Reviving moisture on the numerous orbs,
Thro' which his long ellipsis winds; perhaps
To lend new fuel to declining suns,
To light up worlds, and feed th' ethereal fire.
James Thomson The Seasons (1730; 1748)
Reviving moisture on the numerous orbs,
Thro' which his long ellipsis winds; perhaps
To lend new fuel to declining suns,
To light up worlds, and feed th' ethereal fire.
Isaac Newton described comets as compact and durable solid bodies
moving in oblique orbit and their tails as thin streams of vapor emitted
by their nuclei, ignited or heated by the Sun. Newton suspected that
comets were the origin of the life-supporting component of air.
As early as the 18th century, some scientists had made correct hypotheses as to comets' physical composition. In 1755, Immanuel Kant
hypothesized that comets are composed of some volatile substance, whose
vaporization gives rise to their brilliant displays near perihelion. In 1836, the German mathematician Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel, after observing streams of vapor during the appearance of Halley's Comet in 1835, proposed that the jet forces
of evaporating material could be great enough to significantly alter a
comet's orbit, and he argued that the non-gravitational movements of
Encke's Comet resulted from this phenomenon.
In 1950, Fred Lawrence Whipple proposed that rather than being rocky objects containing some ice, comets were icy objects containing some dust and rock. This "dirty snowball" model soon became accepted and appeared to be supported by the observations of an armada of spacecraft (including the European Space Agency's Giotto probe and the Soviet Union's Vega 1 and Vega 2) that flew through the coma of Halley's Comet in 1986, photographed the nucleus, and observed jets of evaporating material.
On 22 January 2014, ESA scientists reported the detection, for the first definitive time, of water vapor on the dwarf planet Ceres, the largest object in the asteroid belt. The detection was made by using the far-infrared abilities of the Herschel Space Observatory. The finding is unexpected because comets, not asteroids,
are typically considered to "sprout jets and plumes". According to one
of the scientists, "The lines are becoming more and more blurred between
comets and asteroids." On 11 August 2014, astronomers released studies, using the Atacama Large Millimeter/Submillimeter Array (ALMA) for the first time, that detailed the distribution of HCN, HNC, H
2CO, and dust inside the comae of comets C/2012 F6 (Lemmon) and C/2012 S1 (ISON).
2CO, and dust inside the comae of comets C/2012 F6 (Lemmon) and C/2012 S1 (ISON).
Spacecraft missions
- The Halley Armada describes the collection of spacecraft missions that visited and/or made observations of Halley's Comet 1980s perihelion.
- Deep Impact. Debate continues about how much ice is in a comet. In 2001, the Deep Space 1 spacecraft obtained high-resolution images of the surface of Comet Borrelly. It was found that the surface of comet Borrelly is hot and dry, with a temperature of between 26 to 71 °C (79 to 160 °F), and extremely dark, suggesting that the ice has been removed by solar heating and maturation, or is hidden by the soot-like material that covers Borrelly. In July 2005, the Deep Impact probe blasted a crater on Comet Tempel 1 to study its interior. The mission yielded results suggesting that the majority of a comet's water ice is below the surface and that these reservoirs feed the jets of vaporised water that form the coma of Tempel 1. Renamed EPOXI, it made a flyby of Comet Hartley 2 on 4 November 2010.
- Stardust. Data from the Stardust mission show that materials retrieved from the tail of Wild 2 were crystalline and could only have been "born in fire," at extremely high temperatures of over 1,000 °C (1,830 °F). Although comets formed in the outer Solar System, radial mixing of material during the early formation of the Solar System is thought to have redistributed material throughout the proto-planetary disk. As a result, comets also contain crystalline grains that formed in the early, hot inner Solar System. This is seen in comet spectra as well as in sample return missions. More recent still, the materials retrieved demonstrate that the "comet dust resembles asteroid materials". These new results have forced scientists to rethink the nature of comets and their distinction from asteroids.
- Rosetta. The Rosetta probe orbited Comet Churyumov–Gerasimenko. On 12 November 2014, its lander Philae successfully landed on the comet's surface, the first time a spacecraft has ever landed on such an object in history.
Great comets
Woodcut of the Great Comet of 1577
Approximately once a decade, a comet becomes bright enough to be
noticed by a casual observer, leading such comets to be designated as great comets.
Predicting whether a comet will become a great comet is notoriously
difficult, as many factors may cause a comet's brightness to depart
drastically from predictions.
Broadly speaking, if a comet has a large and active nucleus, will pass
close to the Sun, and is not obscured by the Sun as seen from the Earth
when at its brightest, it has a chance of becoming a great comet.
However, Comet Kohoutek in 1973 fulfilled all the criteria and was expected to become spectacular but failed to do so. Comet West, which appeared three years later, had much lower expectations but became an extremely impressive comet.
The late 20th century saw a lengthy gap without the appearance of
any great comets, followed by the arrival of two in quick succession—Comet Hyakutake in 1996, followed by Hale–Bopp,
which reached maximum brightness in 1997 having been discovered two
years earlier. The first great comet of the 21st century was C/2006 P1 (McNaught), which became visible to naked eye observers in January 2007. It was the brightest in over 40 years.
Sungrazing comets
A sungrazing comet is a comet that passes extremely close to the Sun at perihelion, generally within a few million kilometres. Although small sungrazers can be completely evaporated during such a close approach to the Sun, larger sungrazers can survive many perihelion passages. However, the strong tidal forces they experience often lead to their fragmentation.
About 90% of the sungrazers observed with SOHO are members of the Kreutz group,
which all originate from one giant comet that broke up into many
smaller comets during its first passage through the inner Solar System.
The remainder contains some sporadic sungrazers, but four other related
groups of comets have been identified among them: the Kracht, Kracht
2a, Marsden, and Meyer groups. The Marsden and Kracht groups both appear
to be related to Comet 96P/Machholz, which is also the parent of two meteor streams, the Quadrantids and the Arietids.
Unusual comets
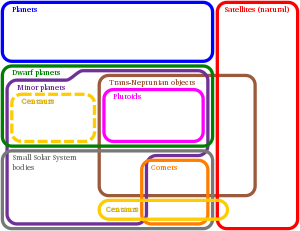
Euler diagram showing the types of bodies in the Solar System.
Of the thousands of known comets, some exhibit unusual properties. Comet Encke (2P/Encke) orbits from outside the asteroid belt to just inside the orbit of the planet Mercury whereas the Comet 29P/Schwassmann–Wachmann currently travels in a nearly circular orbit entirely between the orbits of Jupiter and Saturn. 2060 Chiron, whose unstable orbit is between Saturn and Uranus, was originally classified as an asteroid until a faint coma was noticed. Similarly, Comet Shoemaker–Levy 2 was originally designated asteroid 1990 UL3.
Centaurs
Centaurs typically behave with characteristics of both asteroids and comets. Centaurs can be classified as comets such as 60558 Echeclus, and 166P/NEAT. 166P/NEAT was discovered while it exhibited a coma, and so is classified as a comet despite its orbit, and 60558 Echeclus was discovered without a coma but later became active, and was then classified as both a comet and an asteroid (174P/Echeclus). One plan for Cassini involved sending it to a centaur, but NASA decided to destroy it instead.
Observation
A comet may be discovered photographically using a wide-field telescope or visually with binoculars. However, even without access to optical equipment, it is still possible for the amateur astronomer to discover a sungrazing comet online by downloading images accumulated by some satellite observatories such as SOHO. SOHO's 2000th comet was discovered by Polish amateur astronomer Michał Kusiak on 26 December 2010 and both discoverers of Hale-Bopp used amateur equipment (although Hale was not an amateur).
Lost
A number of periodic comets discovered in earlier decades or previous centuries are now lost comets.
Their orbits were never known well enough to predict future appearances
or the comets have disintegrated. However, occasionally a "new" comet
is discovered, and calculation of its orbit shows it to be an old "lost"
comet. An example is Comet 11P/Tempel–Swift–LINEAR,
discovered in 1869 but unobservable after 1908 because of perturbations
by Jupiter. It was not found again until accidentally rediscovered by LINEAR in 2001. There are at least 18 comets that fit this category.
In popular culture
The depiction of comets in popular culture is firmly rooted in the long Western tradition of seeing comets as harbingers of doom and as omens of world-altering change.
Halley's Comet alone has caused a slew of sensationalist publications
of all sorts at each of its reappearances. It was especially noted that
the birth and death of some notable persons coincided with separate
appearances of the comet, such as with writers Mark Twain (who correctly speculated that he'd "go out with the comet" in 1910) and Eudora Welty, to whose life Mary Chapin Carpenter dedicated the song "Halley Came to Jackson".
In times past, bright comets often inspired panic and hysteria in
the general population, being thought of as bad omens. More recently,
during the passage of Halley's Comet in 1910, the Earth passed through
the comet's tail, and erroneous newspaper reports inspired a fear that cyanogen in the tail might poison millions, whereas the appearance of Comet Hale–Bopp in 1997 triggered the mass suicide of the Heaven's Gate cult.
In science fiction, the impact of comets has been depicted as a threat overcome by technology and heroism (as in the 1998 films Deep Impact and Armageddon), or as a trigger of global apocalypse (Lucifer's Hammer, 1979) or zombies (Night of the Comet, 1984). In Jules Verne's Off on a Comet a group of people are stranded on a comet orbiting the Sun, while a large manned space expedition visits Halley's Comet in Sir Arthur C. Clarke's novel 2061: Odyssey Three.