Created in 1982 and first published in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom,
the theory's original motivation was to explain that the velocities of
stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on
Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be
resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's second law),
or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with
radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's law of gravity).
In MOND, violation of Newton's laws occurs at extremely small
accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything
typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.
MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.
The accurate measurement of the speed of gravitational waves compared to the speed of light in 2017 ruled out many theories which used modified gravity to explain dark matter. However, both Milgrom’s bi-metric formulation of MOND and nonlocal MOND are not ruled out according to the same study.
MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.
The accurate measurement of the speed of gravitational waves compared to the speed of light in 2017 ruled out many theories which used modified gravity to explain dark matter. However, both Milgrom’s bi-metric formulation of MOND and nonlocal MOND are not ruled out according to the same study.
Overview
Comparison of the observed and expected rotation curves of the typical spiral galaxy M33
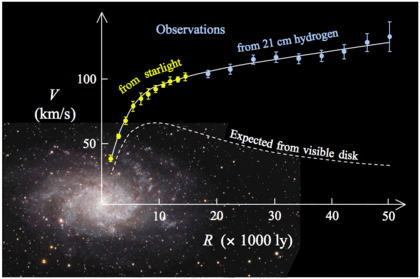
Several independent observations point to the fact that the visible
mass in galaxies and galaxy clusters is insufficient to account for
their dynamics, when analyzed using Newton's laws. This discrepancy –
known as the "missing mass problem" – was first identified for clusters
by Swiss astronomer Fritz Zwicky in 1933 (who studied the Coma cluster), and subsequently extended to include spiral galaxies by the 1939 work of Horace Babcock on Andromeda.
These early studies were augmented and brought to the attention of the
astronomical community in the 1960s and 1970s by the work of Vera Rubin at the Carnegie Institute
in Washington, who mapped in detail the rotation velocities of stars in
a large sample of spirals. While Newton's Laws predict that stellar
rotation velocities should decrease with distance from the galactic
centre, Rubin and collaborators found instead that they remain almost
constant – the rotation curves
are said to be "flat". This observation necessitates at least one of
the following: 1) There exists in galaxies large quantities of unseen
matter which boosts the stars' velocities beyond what would be expected
on the basis of the visible mass alone, or 2) Newton's Laws do not apply
to galaxies. The former leads to the dark matter hypothesis; the latter
leads to MOND.
MOND was proposed by Mordehai Milgrom in 1983
The basic premise of MOND is that while Newton's laws have been
extensively tested in high-acceleration environments (in the Solar
System and on Earth), they have not been verified for objects with
extremely low acceleration, such as stars in the outer parts of
galaxies. This led Milgrom to postulate a new effective gravitational
force law (sometimes referred to as "Milgrom's law") that relates the
true acceleration of an object to the acceleration that would be
predicted for it on the basis of Newtonian mechanics.
This law, the keystone of MOND, is chosen to reduce to the Newtonian
result at high acceleration but lead to different ("deep-MOND")
behavior at low acceleration:
Here FN is the Newtonian force, m is the object's (gravitational) mass, a is its acceleration, μ(x) is an as-yet unspecified function (known as the "interpolating function"), and a0
is a new fundamental constant which marks the transition between the
Newtonian and deep-MOND regimes. Agreement with Newtonian mechanics
requires
and consistency with astronomical observations requires
Beyond these limits, the interpolating function is not specified by
the theory, although it is possible to weakly constrain it empirically. Two common choices are the "simple interpolating function":
and the "standard interpolating function":
Thus, in the deep-MOND regime (a ≪ a0):
Applying this to an object of mass m in circular orbit around a point mass M (a crude approximation for a star in the outer regions of a galaxy), we find:
that is, the star's rotation velocity is independent of r, its
distance from the centre of the galaxy – the rotation curve is flat, as
required. By fitting his law to rotation curve data, Milgrom found to be optimal. This simple law is sufficient to make predictions for a broad range of galactic phenomena.
Milgrom's law can be interpreted in two different ways. One possibility is to treat it as a modification to the classical law of inertia (Newton's second law), so that the force on an object is not proportional to the particle's acceleration a but rather to μ(a/a0)a. In this case, the modified dynamics would apply not only to gravitational phenomena, but also those generated by other forces, for example electromagnetism.
Alternatively, Milgrom's law can be viewed as leaving Newton's Second
Law intact and instead modifying the inverse-square law of gravity, so
that the true gravitational force on an object of mass m due to another of mass M is roughly of the form
In this interpretation, Milgrom's modification would apply exclusively to gravitational phenomena.
By itself, Milgrom's law is not a complete and self-contained physical theory,
but rather an ad-hoc empirically motivated variant of one of the
several equations that constitute classical mechanics. Its status within
a coherent non-relativistic theory of MOND is akin to Kepler's Third Law
within Newtonian mechanics; it provides a succinct description of
observational facts, but must itself be explained by more fundamental
concepts situated within the underlying theory. Several complete
classical theories have been proposed (typically along "modified
gravity" as opposed to "modified inertia" lines), which generally yield
Milgrom's law exactly in situations of high symmetry
and otherwise deviate from it slightly. A subset of these
non-relativistic theories have been further embedded within relativistic
theories, which are capable of making contact with non-classical
phenomena (e.g., gravitational lensing) and cosmology. Distinguishing both theoretically and observationally between these alternatives is a subject of current research.
The majority of astronomers, astrophysicists and cosmologists accept ΛCDM
(based on general relativity, and hence Newtonian mechanics), and are
committed to a dark matter solution of the missing-mass problem. MOND,
by contrast, is actively studied by only a handful of researchers. The
primary difference between supporters of ΛCDM and MOND is in the
observations for which they demand a robust, quantitative explanation
and those for which they are satisfied with a qualitative account, or
are prepared to leave for future work. Proponents of MOND emphasize
predictions made on galaxy scales (where MOND enjoys its most notable
successes) and believe that a cosmological model consistent with galaxy
dynamics has yet to be discovered; proponents of ΛCDM require high
levels of cosmological accuracy (which concordance cosmology provides)
and argue that a resolution of galaxy-scale issues will follow from a
better understanding of the complicated baryonic astrophysics underlying
galaxy formation.
Observational evidence for MOND
Since
MOND was specifically designed to produce flat rotation curves, these
do not constitute evidence for the theory, but every matching
observation adds to support of the empirical law. Nevertheless, a broad
range of astrophysical phenomena are neatly accounted for within the
MOND framework.
Many of these came to light after the publication of Milgrom's original
papers and are difficult to explain using the alternative dark matter
hypothesis. The most prominent are the following:
- In addition to demonstrating that rotation curves in MOND are flat, equation 2 provides a concrete relation between a galaxy's total baryonic mass (the sum of its mass in stars and gas) and its asymptotic rotation velocity. Observationally, this is known as the baryonic Tully–Fisher relation (BTFR), and is found to conform quite closely to the MOND prediction.
- Milgrom's law fully specifies the rotation curve of a galaxy given only the distribution of its baryonic mass. In particular, MOND predicts a far stronger correlation between features in the baryonic mass distribution and features in the rotation curve than does the dark matter hypothesis (since dark matter dominates the galaxy's mass budget and is conventionally assumed not to closely track the distribution of baryons). Such a tight correlation is claimed to be observed in several spiral galaxies, a fact which has been referred to as "Renzo's rule".
- Since MOND modifies Newtonian dynamics in an acceleration-dependent way, it predicts a specific relationship between the acceleration of a star at any radius from the center of a galaxy and the amount of unseen (dark matter) mass within that radius that would be inferred in a Newtonian analysis. This is known as the "mass discrepancy-acceleration relation", and has been measured observationally. One aspect of the MOND prediction is that the mass of the inferred dark matter go to zero when the stellar centripetal acceleration becomes greater than a0, where MOND reverts to Newtonian mechanics. In dark matter theory, it is a challenge to understand why this mass should correlate so closely with acceleration, and why there appears to be a critical acceleration above which dark matter is not required.
- Both MOND and dark matter halos stabilize disk galaxies, helping them retain their rotation-supported structure and preventing their transformation into elliptical galaxies. In MOND, this added stability is only available for regions of galaxies within the deep-MOND regime (i.e., with a < a0), suggesting that spirals with a > a0 in their central regions should be prone to instabilities and hence less likely to survive to the present day. This may explain the "Freeman limit" to the observed central surface mass density of spiral galaxies, which is roughly a0/G. This scale must be put in by hand in dark matter-based galaxy formation models.
- Particularly massive galaxies are within the Newtonian regime (a > a0) out to radii enclosing the vast majority of their baryonic mass. At these radii, MOND predicts that the rotation curve should fall as 1/r, in accordance with Kepler's Laws. In contrast, from a dark matter perspective one would expect the halo to significantly boost the rotation velocity and cause it to asymptote to a constant value, as in less massive galaxies. Observations of high-mass ellipticals bear out the MOND prediction.
- In MOND, all gravitationally bound objects with a < a0 – regardless of their origin – should exhibit a mass discrepancy when analysed using Newtonian mechanics, and should lie on the BTFR. Under the dark matter hypothesis, objects formed from baryonic material ejected during the merger or tidal interaction of two galaxies ("tidal dwarf galaxies") are expected to be devoid of dark matter and hence show no mass discrepancy. Three objects unambiguously identified as Tidal Dwarf Galaxies appear to have mass discrepancies in close agreement with the MOND prediction.
- Recent work has shown that many of the dwarf galaxies around the Milky Way and Andromeda are located preferentially in a single plane and have correlated motions. This suggests that they may have formed during a close encounter with another galaxy and hence be Tidal Dwarf Galaxies. If so, the presence of mass discrepancies in these systems constitutes further evidence for MOND. In addition, it has been claimed that a gravitational force stronger than Newton's (such as Milgrom's) is required for these galaxies to retain their orbits over time.
Complete MOND theories
Milgrom's law requires incorporation into a complete theory if it is to satisfy conservation laws
and provide a unique solution for the time evolution of any physical
system. Each of the theories described here reduce to Milgrom's law in
situations of high symmetry (and thus enjoy the successes described
above), but produce different behavior in detail.
Nonrelativistic
The first complete theory of MOND (dubbed AQUAL) was constructed in 1984 by Milgrom and Jacob Bekenstein. AQUAL generates MONDian behaviour by modifying the gravitational term in the classical Lagrangian
from being quadratic in the gradient of the Newtonian potential to a
more general function. (AQUAL is an acronym for AQUAdratic Lagrangian.)
In formulae:
where is the standard Newtonian gravitational potential and F is a new dimensionless function. Applying the Euler–Lagrange equations in the standard way then leads to a non-linear generalization of the Newton–Poisson equation:
This can be solved given suitable boundary conditions and choice of F to yield Milgrom's law (up to a curl field correction which vanishes in situations of high symmetry).
An alternative way to modify the gravitational term in the
lagrangian is to introduce a distinction between the true (MONDian)
acceleration field a and the Newtonian acceleration field aN. The Lagrangian may be constructed so that aN satisfies the usual Newton-Poisson equation, and is then used to find a
via an additional algebraic but non-linear step, which is chosen to
satisfy Milgrom's law. This is called the "quasi-linear formulation of
MOND", or QUMOND,
and is particularly useful for calculating the distribution of
"phantom" dark matter that would be inferred from a Newtonian analysis
of a given physical situation.
Both AQUAL and QUMOND propose changes to the gravitational part
of the classical matter action, and hence interpret Milgrom's law as a
modification of Newtonian gravity as opposed to Newton's second law. The
alternative is to turn the kinetic term of the action into a functional
depending on the trajectory of the particle. Such "modified inertia"
theories, however, are difficult to use because they are time-nonlocal,
require energy and momentum to be non-trivially redefined to be conserved, and have predictions that depend on the entirety of a particle's orbit.
Relativistic
In 2004, Jacob Bekenstein formulated TeVeS, the first complete relativistic theory with MONDian behaviour. TeVeS is constructed from a local Lagrangian (and hence respects conservation laws), and employs a unit vector field, a dynamical and non-dynamical scalar field, a free function and a non-Einsteinian metric
in order to yield AQUAL in the non-relativistic limit (low speeds and
weak gravity). TeVeS has enjoyed some success in making contact with
gravitational lensing and structure formation observations, but faces problems when confronted with data on the anisotropy of the cosmic microwave background, the lifetime of compact objects, and the relationship between the lensing and matter overdensity potentials.
Several alternative relativistic generalizations of MOND exist, including BIMOND and generalized Einstein-Aether theories.
There is also a relativistic generalization of MOND that assumes a
Lorentz-type invariance as the physical basis of MOND phenomenology.
The external field effect
In
Newtonian mechanics, an object's acceleration can be found as the
vector sum of the acceleration due to each of the individual forces
acting on it. This means that a subsystem
can be decoupled from the larger system in which it is embedded simply
by referring the motion of its constituent particles to their center of
mass; in other words, the influence of the larger system is irrelevant
for the internal dynamics of the subsystem. Since Milgrom's law is non-linear
in acceleration, MONDian subsystems cannot be decoupled from their
environment in this way, and in certain situations this leads to
behaviour with no Newtonian parallel. This is known as the "external
field effect" (EFE).
The external field effect is best described by classifying physical systems according to their relative values of ain (the characteristic acceleration of one object within a subsystem due to the influence of another), aex (the acceleration of the entire subsystem due to forces exerted by objects outside of it), and a0:
- : Newtonian regime
- : Deep-MOND regime
- : The external field is dominant and the behavior of the system is Newtonian.
- : The external field is larger than the internal acceleration of the system, but both are smaller than the critical value. In this case, dynamics is Newtonian but the effective value of G is enhanced by a factor of a0/aex.
The external field effect implies a fundamental break with the strong equivalence principle (but not necessarily the weak equivalence principle). The effect was postulated by Milgrom in the first of his 1983 papers to explain why some open clusters were observed to have no mass discrepancy even though their internal accelerations were below a0. It has since come to be recognised as a crucial element of the MOND paradigm.
The dependence in MOND of the internal dynamics of a system on its external environment (in principle, the rest of the universe) is strongly reminiscent of Mach's principle, and may hint towards a more fundamental structure underlying Milgrom's law. In this regard, Milgrom has commented:
It has been long suspected that local dynamics is strongly influenced by the universe at large, a-la Mach's principle, but MOND seems to be the first to supply concrete evidence for such a connection. This may turn out to be the most fundamental implication of MOND, beyond its implied modification of Newtonian dynamics and general relativity, and beyond the elimination of dark matter.
Indeed, the potential link between MONDian dynamics and the universe
as a whole (that is, cosmology) is augmented by the observation that the
value of a0 (determined by fits to internal properties of galaxies) is within an order of magnitude of cH0, where c is the speed of light and H0 is the Hubble constant (a measure of the present-day expansion rate of the universe). It is also close to the acceleration rate of the universe, and hence the cosmological constant. However, as yet no full theory has been constructed which manifests these connections in a natural way.
Responses and criticism
Attempts to explain MOND phenomenology using dark matter
While
acknowledging that Milgrom's law provides a succinct and accurate
description of a range of galactic phenomena, many physicists reject the
idea that classical dynamics itself needs to be modified and attempt
instead to explain the law's success by reference to the behavior of
dark matter. Some effort has gone towards establishing the presence of a
characteristic acceleration scale as a natural consequence of the
behavior of cold dark matter halos, although Milgrom has argued that such arguments explain only a small subset of MOND phenomena. An alternative proposal is to modify the properties of dark matter (e.g., to make it interact strongly
with itself or baryons) in order to induce the tight coupling between
the baryonic and dark matter mass that the observations point to.
Finally, some researchers suggest that explaining the empirical success
of Milgrom's law requires a more radical break with conventional
assumptions about the nature of dark matter. One idea (dubbed "dipolar
dark matter") is to make dark matter gravitationally polarizable by ordinary matter and have this polarisation enhance the gravitational attraction between baryons.
Outstanding problems for MOND
The
most serious problem facing Milgrom's law is that it cannot completely
eliminate the need for dark matter in all astrophysical systems: galaxy
clusters show a residual mass discrepancy even when analyzed using MOND.
The fact that some form of unseen mass must exist in these systems
detracts from the elegance of MOND as a solution to the missing mass
problem, although the amount of extra mass required is 5 times less than
in a Newtonian analysis, and there is no requirement that the missing
mass be non-baryonic. It has been speculated that 2 eV neutrinos could
account for the cluster observations in MOND while preserving the
theory's successes at the galaxy scale.
Indeed, analysis of sharp lensing data for the galaxy cluster Abell
1689 shows that MOND only becomes distinctive at Mpc distance from the
center, so that Zwicky's conundrum remains, and 1.8 eV neutrinos are needed in clusters.
The 2006 observation of a pair of colliding galaxy clusters known as the "Bullet Cluster",
poses a significant challenge for all theories proposing a modified
gravity solution to the missing mass problem, including MOND.
Astronomers measured the distribution of stellar and gas mass in the
clusters using visible and X-ray
light, respectively, and in addition mapped the inferred dark matter
density using gravitational lensing. In MOND, one would expect the
missing mass (which is only apparent since it results from using
Newtonian as opposed to MONDian dynamics) to be centred on the visible
mass. In ΛCDM, on the other hand, one would expect the dark matter to be
significantly offset from the visible mass because the halos of the two
colliding clusters would pass through each other (assuming, as is
conventional, that dark matter is collisionless), whilst the cluster gas
would interact and end up at the centre. An offset is clearly seen in
the observations. It has been suggested, however, that MOND-based models
may be able to generate such an offset in strongly
non-spherically-symmetric systems, such as the Bullet Cluster.
Several other studies have noted observational difficulties with
MOND. For example, it has been claimed that MOND offers a poor fit to
the velocity dispersion profile of globular clusters and the temperature profile of galaxy clusters, that different values of a0 are required for agreement with different galaxies' rotation curves, and that MOND is naturally unsuited to forming the basis of a theory of cosmology.
Furthermore, many versions of MOND predict that the speed of light be
different from the speed of gravity, but in 2017 the speed of
gravitational waves was measured to be equal to the speed of light.
Besides these observational issues, MOND and its generalisations are plagued by theoretical difficulties.
Several ad-hoc and inelegant additions to general relativity are
required to create a theory with a non-Newtonian non-relativistic limit,
the plethora of different versions of the theory offer diverging
predictions in simple physical situations and thus make it difficult to
test the framework conclusively, and some formulations (most prominently
those based on modified inertia) have long suffered from poor
compatibility with cherished physical principles such as conservation
laws.
Proposals for testing MOND
Several observational and experimental tests have been proposed to help distinguish between MOND and dark matter-based models:
- The detection of particles suitable for constituting cosmological dark matter would strongly suggest that ΛCDM is correct and no modification to Newton's laws is required.
- MOND predicts the existence of anomalous accelerations on the Earth at particular places and times of the year. These could be detected in a precision experiment.
- It has been suggested that MOND could be tested in the Solar System using the LISA Pathfinder mission (launched in 2015). In particular, it may be possible to detect the anomalous tidal stresses predicted by MOND to exist at the Earth-Sun saddlepoint of the Newtonian gravitational potential. It may also be possible to measure MOND corrections to the perihelion precession of the planets in the Solar System, or a purpose-built spacecraft.
- One potential astrophysical test of MOND is to investigate whether isolated galaxies behave differently from otherwise-identical galaxies that are under the influence of a strong external field. Another is to search for non-Newtonian behaviour in the motion of binary star systems where the stars are sufficiently separated for their accelerations to be below a0.
- Testing modified gravity with black hole shadows - John Moffat calculates that the black hole shadow should appear larger by a factor of about ten in MOG as compared to general relativity.
- Testing MOND using the redshift-dependence of radial acceleration - Sabine Hossenfelder and Tobias Mistele propose a parameter-free MOND model they call Covariant Emergent Gravity and suggest that as measurements of radial acceleration improve, various MOND models and particle dark matter might be distinguishable because MOND predicts a much smaller redshift dependence.










![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\mathcal {L}}_{\text{Newton}}&=-{\frac {1}{8\pi G}}\cdot \|\nabla \phi \|^{2}\\[6pt]{\mathcal {L}}_{\text{AQUAL}}&=-{\frac {1}{8\pi G}}\cdot a_{0}^{2}F\left({\tfrac {\|\nabla \phi \|^{2}}{a_{0}^{2}}}\right)\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/909e7a8a7ad584b0897db979f3b9d55a560fbb0b)

![\nabla \cdot \left[\mu \left({\frac {\left\|\nabla \phi \right\|}{a_{0}}}\right)\nabla \phi \right]=4\pi G\rho](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/26c2ab74faa248ec947bca84541a19ba24d4bc45)




























