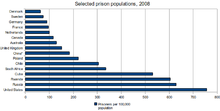
Mentally ill people are over represented in United States jail and prison populations relative to the general population. There are three times more seriously mentally ill persons in jails and prisons than in hospitals
in the United States. The exact cause of this over representation is
disputed by scholars; proposed causes include the deinstitutionalization
of mentally ill individuals in the mid-twentieth century; inadequate
community mental health treatment resources; and the criminalization of
mental illness itself. The majority of prisons in the United States
employ a psychiatrist and a psychologist. While much research claims mentally ill offenders have comparable rates of recidivism
to non-mentally ill offenders, other research claims that mentally ill
offenders have higher rates of recidivism. Mentally ill people
experience solitary confinement
at disproportionate rates and are more vulnerable to its adverse
psychological effects. Twenty-five states have laws addressing the
emergency detention of the mentally ill within jails, and the United States Supreme Court has upheld the right of inmates to mental health treatment.
Prevalence
There
is broad scholarly consensus that mentally ill individuals are
over represented within the United States jail and prison populations.
In the 2010 study titled "More mentally ill persons are in jails and
prisons than hospitals: a survey of the states", researchers concluded
that, based on statistics from sources including the Bureau of Justice
Statistics and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, there
are currently three times more seriously mentally ill persons in jails
and prisons than in hospitals in the United States, with the ratio being
nearly ten to one in Arizona and Nevada. "Serious mental illness" is defined here as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder or major depression. Further, they found that sixteen percent of the jail and prison
population in the U. S. has a serious mental illness (compared to 6.4
percent in 1983), although this statistic does not reflect differences among individual states.
For example, in North Dakota they found that a person with a serious
mental illness is equally likely to be in prison or a jail versus
hospital, whereas in states such as Arizona, Nevada and Texas, the
imbalance is much more severe.
Finally, they noted that a 1991 survey through the National Alliance
for the Mentally Ill concluded that jail and/or prison is part of the
life experience of forty percent of mentally ill individuals.
A separate research study "The Prevalence of Mental Illness among
Inmates in a Rural State" noted that national statistics like those
previously mentioned primarily pull data from urban jails and prisons.
In order to investigate possible differences in rural areas,
researchers interviewed a random sample of inmates in both jails and
prisons in a rural northeastern state.
They found that in this rural setting, there was little evidence of
high rates of mental illness within jails, "suggesting the
criminalization of mental illness may not be as evident in rural
settings as urban areas." However, high rates of serious mental illness
were found among the rural prison inmates.
A 2017 report issued by the Bureau of Justice Statistics used
self-report survey data from inmates to assess the prevalence of mental
health problems among prisoners and jail inmates. They found that 14% of
prisoners and 25% of jail inmates had past 30-day serious psychological
distress, compared to 5% of the general population. In addition, 37% of
prisoners and 44% of jail inmates had a history of a mental health
problem.
In 2015 lawyer and activist Bryan Stevenson claimed in his book Just Mercy
that over fifty percent of inmates in jails and prisons in the United
States had been diagnosed with a mental illness and that one in five
jail inmates had a serious mental illness.
As for the gender, age, and racial demographics of mentally ill
offenders, the 2017 Bureau of Justice Statistics report found that
female inmates when compared to male inmates had statistically
significant higher rates of serious psychological distress (20.5% of
female prisoners and 32.3% of female jail inmates had serious
psychological distress, versus 14% of male prisoners and 25.5% of male
jail inmates) and a history of a mental health problem (65.8% of female
prisoners and 67.9% of female jail inmates compared to 34.8% of male
prisoners and 40.8% of male jail inmates). Significant differences
between race and ethnicity were also observed. White prisoners and jail
inmates were more likely than black or Hispanic inmates to have serious
psychological distress or a history of a mental health problems. For
example, in local jails, 31% of white inmates compared to 22.3% of black
inmates and 23.2% of Hispanic inmates had serious psychological
distress. Finally, with regards to age, there were virtually no
statistical differences between age groups and the percentage who has
serious psychological distress or a history of a mental health problem .
Causes
Deinstitutionalization
Researchers commonly cite deinstitutionalization,
or the emptying of state mental hospitals in the mid-twentieth century,
as a direct cause of the rise of mentally ill people in prisons.
In the 2010 study "More mentally ill persons are in jails and prisons
than hospitals: a survey of the states," researchers noted, at least in
part due to deinstitutionalization, it is increasingly difficult to find
beds for mentally ill people who need hospitalization. Using data
collected by the Department of Health and Human Services, they
determined there was one psychiatric bed for every 3,000 Americans,
compared to one for every 300 Americans in 1955. They also noted increased percentages of mentally ill people in prisons throughout the 1970s and 1980s
and found a strong correlation between the amount of mentally ill
persons in a state's jails and prisons and how much money that state
spends on mental health services. In the book Criminalizing the Seriously Mentally Ill: The Abuse of Jails As Mental Hospitals,
researchers note that while deinstitutionalization was carried out with
good intentions, it was not accompanied with alternate avenues for
mental health treatment for those with serious mental illnesses.
According to the authors, Community Mental Health Centers focused their
limited resources on individuals with less serious mental illnesses,
federal training funds for mental health professionals resulted in lots
more psychiatrists in wealthy areas but not in low-income areas, and a
policy that made individuals eligible for federal programs and benefits
only after they'd been discharged from state mental hospitals
unintentionally incentivized discharging patients without follow-up.
In the article "Assessing the Contribution of the
Deinstitutionalization of the Mentally Ill to Growth in the U.S.
Incarceration Rate" researchers Steven Raphael
and Michael A. Stoll discuss transinstitutionalization, or how many
patients released from mental hospitals in the mid-twentieth century
ended up in jail or prison. Using U.S. census data collected between
1950-2000, they concluded that "those most likely to be incarcerated as
of the 2000 census experienced pronounced increases in overall
institutionalization between 1950 and 2000 (with particularly large
increases for black males). Thus, the impression created by aggregate
trends is somewhat misleading, as the 1950 demographic composition of
the mental hospital population differs considerably from the 2000
demographic composition of prison and jail inmates." However, when
estimating (using a panel data set) how many individuals incarcerated
between 1980 and 2000 would have been institutionalized in years past,
they found significant transinstitutionalization rates for all men and
women, with the largest rate for white men.
Criminalization
A related cause of the disproportionate amount of mentally ill people in prisons is criminalization
of mental illness itself. In the 1984 study "Criminalizing mental
disorder: The comparative arrest rate of the mentally ill", researcher
L. A. Teplin notes that in addition to a decline in federal support for
mental illness resulting in more people being denied treatment, mentally
ill people are often stereotyped as dangerous, making fear a factor in
action taken against them. Bureaucratic and legal impediments to
initiating mental health referrals means arrest can be easier, and in
Teplin's words, "Due to the lack of exclusionary criteria, the criminal
justice system may have become the institution that cannot say no."
Mentally ill people do indeed experience higher arrest rates than those
without mental illness, but in order to investigate whether or not this
was due to criminalization of mental illness, researchers observed
police officers over a period of time. As a result, they concluded
"within similar types of situations, persons exhibiting signs of mental
disorder have a higher probability of being arrested than those who do
not show such signs."
The authors of the book Criminalizing the Seriously Mentally Ill: The Abuse of Jails As Mental Hospitals
claim that nationwide, 29% of jails will hold mentally ill individuals
with no charges brought against them, sometimes as a means of 'holding'
them when psychiatric hospitals are very far away. This practice occurs
even in states where it is explicitly forbidden.
Beyond that, according to the authors, the vast majority of people with
mental illnesses in jails in prisons are held on minor charges like
theft, disorderly conduct, alcohol/drug related charges, and
trespassing. These are sometimes "mercy bookings" intended to get the homeless
mentally ill off the street, a warm meal, etc. Family members have
reported being encouraged by mental health professionals or police to
get their loved ones arrested as a means of getting them treatment. Finally, some mentally ill people are in jails and prisons on serious charges, such as murder. The authors of Criminalizing the Seriously Mentally Ill claim many such crimes wouldn't have been committed if the individuals had been receiving proper care.
Mental health care in prisons and jails
Psychologists
report that one in every eight prisoners were receiving some mental
health therapy or counseling services by the middle of the year in 2000.
Inmates are generally screened at admission and depending on the
severity of the mental illness they are placed in either general
confinement or specialized facilities. Inmates can self report mental
illness if they feel it is necessary. In the middle of the year in 2000,
inmates self reported that State prisons held 191,000 mentally ill
inmates.
A 2011 survey of 230 correctional mental health service providers from
165 state correctional facilities found that 83% of facilities employed
at least one psychologist and 81% employed at least one psychiatrist.
The study also found that 52% of mentally ill offenders voluntarily
received mental health services, 24% were referred by staff, and 11%
were mandated by a court to receive services.
Although 64% of providers of mental health services reported feeling
supported by prison administration and 71% were involved in continuity
of care after release from prison, 65% reported being dissatisfied with
funding. Only 16% of participants reported offering vocational training, and the researchers noted that although risk/need/responsivity
theory has been shown to reduce the risk for recidivism (or committing
another crime after being released), it is unknown whether it is
incorporated into mental health services in prisons and jails.
A 2005 article by researcher Terry A. Kupers noted that male prisoners
tend to under report emotional problems and don't request help until a
crisis, and that prison fosters an environment of toxic masculinity, which increases resistance to psychotherapy.
A 2017 report from the Bureau of Justice Statistics noted that 54.3% of
prisoners and 35% of jail inmates who had past 30-day serious
psychological distress has received mental health treatment since
admission to the current facility; and 63% of prisoners and 44.5% of
jail inmates with a history of a mental health problem said they had
received mental health treatment since admission.
Finally, the book Criminalizing the Seriously Mentally Ill: The Abuse of Jails As Mental Hospitals
points out that 20% of jails have no mental health resources. In
addition, small jails are less likely to have access to mental health
resources and are more likely to hold individuals with mental illnesses
without charges brought against them. Jails in richer areas are more
likely to have access to mental health resources, and jails with more
access to mental health resources also dealt less with medication
refusal.
Recidivism
Research shows that rates of recidivism,
or re-entry into prison, are not significantly higher for mentally ill
offenders. A 2004 study found that although 77% of mentally ill
offenders studied were arrested or charged with a new crime within the
27-55 month follow-up period, when compared with the general population,
"our mentally ill inmates were neither more likely nor more serious
recidivists than general population inmates."
In contrast, a 2009 study that examined the incarceration history of
those in Texas Department of Criminal Justice facilities found that
"Texas prison inmates with major psychiatric disorders were far more
likely to have had previous incarcerations compared with inmates without
a serious mental illness." In the discussion, the researchers noted
that their study's results differed from most research on this subject,
and hypothesized that this novelty could be due to specific conditions
within the state of Texas.
A 1991 study by L. Feder noted that although mentally ill
offenders were significantly less like to receive support from family
and friends upon release from prison,
mentally ill offenders were actually less likely to be revoked on
parole. However, for nuisance arrests, mentally ill offenders were less
likely to have the charges dropped, although they were more likely to
have charges dropped for drug arrests. In both cases, mentally ill
offenders were more likely to be tracked into mental health. Finally,
there were no significant differences in charges for violent arrests.
Solitary confinement
A broad range of scholarly research maintains that mentally ill offenders are disproportionately represented in solitary confinement and are more vulnerable to the adverse psychological effects of solitary confinement.
Due to differing schemes of classification, empirical data on the
makeup of inmates in segregated housing units can be difficult to
obtain, and estimates of the percentage of inmates in solitary confinement who are mentally ill range from nearly a third, to 11% (with a "major mental disorder"), to 30% (from a study conducted in Washington), to "over half" (from a study conducted in Indiana),
depending on how mental illness is determined, where the study is
conducted, and other differences in methodology. Researchers J. Metzner
and J. Fellner note that mentally ill offenders in solitary confinement
"all too frequently" require crisis care or psychiatric hospitalization,
and that "many simply won't get better as long as they are isolated." Researchers T. L. Hafemeister and J. George note that mentally ill offenders in isolation are at higher risk for psychiatric injury, self-harm and suicide. A 2014 study that analyzed data from medical records in the New York City jail system
found that while self-harm was significantly correlated with having a
serious mental illness regardless of whether or not an inmate was in
solitary confinement, inmates with serious mental illness in solitary
confinement under 18 years of age accounted for the majority of acts of
self-harm studied. When brought before federal courts, judges have prohibited or curtailed this practice, and many organizations that deal with human rights, including the United Nations, have condemned it.
In addition, scholars argue the conditions of solitary
confinement make it much more difficult to deliver proper psychiatric
care. According to researchers J. Metzner and J. Fellner, "Mental health services in segregation units are typically limited to psychotropic medication,
a health care clinician stopping at the cell front to ask how the
prisoner is doing (i.e., mental health rounds), and occasional meetings
in private with a clinician." One study in the American Journal of Public Health
claimed that health care professionals must "frequently" conduct
consultation through a slit in a cell door or an open tier that provides
no privacy.
However, some researchers disagree with the scope of claims
surrounding the psychological effects of solitary confinement. For
example, in 2006 researchers G. D. Glancy and E. L. Murray conducted a
literature review in which they claimed that many frequently-cited
studies have methodological concerns, including researcher bias, the use
of "volunteer non-prisoners, naturalistic experiments, or case reports,
case series, and anecdotes" and concluded "there is little evidence to
suggest the majority...kept in SC...experience negative mental health
effects."
However, they did support claims that inmates with preexisting mental
illnesses are more vulnerable and do suffer adverse effects. In their
conclusion they claim "we should therefore be concerned about those with
pre-existing mental illness who are housed in segregation because there
is nowhere else to put them within the correctional system."
Legal aspects
Emergency detention
One
major area of legal concern is the emergency detention of the
non-criminal mentally ill in jails while waiting for formal procedures
for involuntary hospitalization. Twenty-five states and the District of Columbia
have laws that specifically address this practice; eight of these
states as well as D. C. explicitly forbid it. Seventeen states, on the
other hand, explicitly allow it. Within this set, the criteria and
circumstances necessary differ by state, and most states limit the
detention periods in jails to one to three days. One distinguishing factor of this practice is that it is often initiated by a non-medical professional such as a police officer.
In many states, especially those in which a non-public official such as
a medical health professional or concerned citizen can initiate the
detention, a judge or magistrate is required to approve it before or
soon after the initiation.
When emergency detention in jails has been brought to court,
judges have generally agreed that the practice itself is not
unconstitutional. One notable exception was Lynch v. Baxley; however, later cases, particularly Boston v. Lafeyette County, Mississippi,
have connected the ruling of unconstitutionality in that case with the
conditions of the jails themselves rather than the fact that they were
jails. That being said, the Supreme Court of Illinois has stated that this practice is unconstitutional if the person being detained doesn't pose an imminent threat to himself or others.
Supreme court cases
Several landmark Supreme Court cases, notably Estelle v. Gamble, have established the constitutional right of prison inmates to mental health treatment. Estelle v. Gamble determined that "deliberate indifference to serious medical needs" of prisoners was a violation of the Eighth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution.
This case was the first time the phrase "deliberate indifference" was
used; it is now a legal term. In order to determine "serious medical
need" later cases would use tests such as the treatment being mandated
by a physician or an obvious need to a layman. On the other hand, other
cases, notably McGukin v. Smith, used much stricter terms, and in
1993 researchers Henry J. Steadman and Joseph J. Cocozza commented that
"serious medical need" had little definitional clarity. Langley v. Coughlin
involved a prisoner "regularly isolated without proper screening or
care" and clarified that a single, distinctive act is not necessary to
constitute deliberate indifference but rather "if seriously ill inmates
are consistently made to wait for care while their condition
deteriorates, or if diagnoses are haphazard and records minimally
adequate then, over time, the mental state of deliberate indifference
may be attributed to those in charge."
The landmark case Washington v. Harper
determined that although inmates do have an interest in and the right
to refusal of treatment, this can be overridden without judicial process
even if the inmate is competent provided there this act is "reasonably
related to legitimate penological interest". Washington's internal process for determining this need was seen as affording due process. In contrast, in Breads v. Moehrle,
the forcible injection of drugs in a jail was not upheld because
sufficient procedures were not taken to ensure "substantive
determination of need".
Court cases
George
Daniel, mentally ill man on Alabama's death row was arrested and
charged with capital murder. In jail, George became acutely psychotic
and couldn't speak in complete sentences. Daniel, had been on death row
until several years later, Lawyer Bryan Stevenson uncovered the truth of
the doctor who lied about the examination of Daniels mental illness.
Daniel's trial was then overturned and has been in a mental institution.
Another mentally ill man, Avery Jenkins, was convicted of murder and
sentenced to death. Throughout Jenkins's childhood, he had been in and
out of foster homes and developed a serious mental illness. Jenkins
erratic behavior didn't change, so his foster mother decided to get rid
of him by tying him to a tree and left him there. Around the age of
sixteen he was left homeless and started to experience psychotic
episodes. At the age of twenty, Jenkins had wandered into a strange
house, and stabbed a man to death as he perceived it to being a demon.
He then was sentenced to death and spent several years in prison as if
he had been sane and responsible for his actions. Jenkins the got off
death row and was put into a mental institution.