Two traders in 16th century Germany
Trade involves the transfer of goods or services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct exchange of goods and services for other goods and services. Barter involves trading things without the use of money. When either bartering party started to involve precious metals, these gained symbolic as well as practical importance. Modern traders generally negotiate through a medium of exchange, such as money. As a result, buying can be separated from selling, or earning. The invention of money (and later of credit, paper money and non-physical money) greatly simplified and promoted trade. Trade between two traders is called bilateral trade, while trade involving more than two traders is called multilateral trade.
In one modern view, trade exists due to specialization and the division of labor, a predominant form of economic activity
in which individuals and groups concentrate on a small aspect of
production, but use their output in trades for other products and needs. Trade exists between regions because different regions may have a comparative advantage (perceived or real) in the production of some trade-able commodity—including production of natural resources scarce or limited elsewhere. For example: different regions' sizes may encourage mass production. In such circumstances, trade at market prices between locations can benefit both locations.
Retail trade consists of the sale of goods or merchandise from a very fixed location (such as a department store, boutique or kiosk), online or by mail, in small or individual lots for direct consumption or use by the purchaser. Wholesale trade is defined as traffic in goods that are sold as merchandise to retailers, or to industrial, commercial, institutional, or other professional business users, or to other wholesalers and related subordinated services.
Historically, openness to free trade substantially increased in some areas from 1815 to the outbreak of World War I in 1914. Trade openness increased again during the 1920s, but collapsed (in particular in Europe and North America) during the Great Depression of the 1930s. Trade openness increased substantially again from the 1950s onwards (albeit with a slowdown during the oil crisis of the 1970s). Economists and economic historians contend that current levels of trade openness are the highest they have ever been.
Etymology
Trade is from Middle English trade ("path, course of conduct"), introduced into English by Hanseatic merchants, from Middle Low German trade ("track, course"), from Old Saxon trada ("spoor, track"), from Proto-Germanic *tradō ("track, way"), and cognate with Old English tredan ("to tread").
Commerce is derived from the Latin commercium, from cum "together" and merx, "merchandise."
History
Prehistory
Trade originated with human communication in prehistoric times. Trading was the main facility of prehistoric people, who bartered goods and services from each other before the innovation of modern-day currency. Peter Watson dates the history of long-distance commerce from circa 150,000 years ago.
In the Mediterranean region the earliest contact between cultures involved members of the species Homo sapiens, principally using the Danube river, at a time beginning 35,000–30,000 BP.
Some trace the origins of commerce to the very start of transactions in prehistoric times. Apart from traditional self-sufficiency, trading became a principal facility of prehistoric people, who bartered what they had for goods and services from each other.
Ancient history
Ancient Etruscan "aryballoi" terracota vessels unearthed in the 1860s at Bolshaya Bliznitsa tumulus near Phanagoria, South Russia (formerly part of the Bosporan Kingdom of Cimmerian Bosporus, present-day Taman Peninsula); on exhibit at the Hermitage Museum in Saint Petersburg.
Trade is believed to have taken place throughout much of recorded human history. There is evidence of the exchange of obsidian and flint during the Stone Age. Trade in obsidian is believed to have taken place in New Guinea from 17,000 BCE.
The earliest use of obsidian in the Near East dates to the Lower and Middle paleolithic.
Robert Carr Bosanquet investigated trade in the Stone Age by excavations in 1901. Trade is believed to have first begun in south west Asia.
Archaeological evidence of obsidian use provides data on how this material was increasingly the preferred choice rather than chert from the late Mesolithic to Neolithic, requiring exchange as deposits of obsidian are rare in the Mediterranean region.
Obsidian is thought
to have provided the material to make cutting utensils or tools,
although since other more easily obtainable materials were available,
use was found exclusive to the higher status of the tribe using "the rich man's flint".
Obsidian was traded at distances of 900 kilometres within the Mediterranean region.
Trade in the Mediterranean during the Neolithic of Europe was greatest in this material. Networks were in existence at around 12,000 BCE Anatolia was the source primarily for trade with the Levant, Iran and Egypt according to Zarins study of 1990. Melos and Lipari sources produced among the most widespread trading in the Mediterranean region as known to archaeology.
The Sari-i-Sang mine in the mountains of Afghanistan was the largest source for trade of lapis lazuli. The material was most largely traded during the Kassite period of Babylonia beginning 1595 BCE.
Later trade
Mediterranean and Near East
Ebla was a prominent trading centre during the third millennia, with a network reaching into Anatolia and north Mesopotamia.
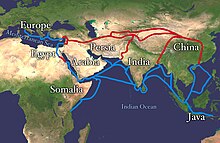
A map of the Silk Road trade route between Europe and Asia.
Materials used for creating jewelry were traded with Egypt since 3000 BCE. Long-range trade routes first appeared in the 3rd millennium BCE, when Sumerians in Mesopotamia traded with the Harappan civilization of the Indus Valley. The Phoenicians were noted sea traders, traveling across the Mediterranean Sea, and as far north as Britain for sources of tin to manufacture bronze. For this purpose they established trade colonies the Greeks called emporia.
From the beginning of Greek civilization until the fall of the Roman Empire in the 5th century, a financially lucrative trade brought valuable spice to Europe from the far east, including India and China. Roman commerce allowed its empire to flourish and endure. The latter Roman Republic and the Pax Romana
of the Roman empire produced a stable and secure transportation network
that enabled the shipment of trade goods without fear of significant piracy, as Rome had become the sole effective sea power in the Mediterranean with the conquest of Egypt and the near east.
In ancient Greece Hermes was the god of trade (commerce) and weights and measures, for Romans Mercurius also the god of merchants, whose festival was celebrated by traders on the 25th day of the fifth month.
The concept of free trade was an antithesis to the will and economic
direction of the sovereigns of the ancient Greek states. Free trade
between states was stifled by the need for strict internal controls (via
taxation) to maintain security within the treasury of the sovereign,
which nevertheless enabled the maintenance of a modicum of civility within the structures of functional community life.
The fall of the Roman empire and the succeeding Dark Ages brought instability to Western Europe
and a near-collapse of the trade network in the western world. Trade,
however, continued to flourish among the kingdoms of Africa, the Middle
East, India, China, and Southeast Asia. Some trade did occur in the
west. For instance, Radhanites were a medieval guild or group (the precise meaning of the word is lost to history) of Jewish merchants who traded between the Christians in Europe and the Muslims of the Near East.
Indo-Pacific
The first true maritime trade network in the Indian Ocean was by the Austronesian peoples of Island Southeast Asia, who built the first ocean-going ships. They established trade routes with Southern India and Sri Lanka as early as 1500 BC, ushering an exchange of material culture (like catamarans, outrigger boats, sewn-plank boats, and paan) and cultigens (like coconuts, sandalwood, bananas, and sugarcane); as well as connecting the material cultures of India and China. Indonesians, in particular were trading in spices (mainly cinnamon and cassia) with East Africa using catamaran and outrigger boats and sailing with the help of the Westerlies in the Indian Ocean. This trade network expanded to reach as far as Africa and the Arabian Peninsula, resulting in the Austronesian colonization of Madagascar by the first half of the first millennium AD. It continued up to historic times, later becoming the Maritime Silk Road.
Mesoamerica
Tajadero or axe money used as currency in Mesoamerica. It had a fixed worth of 8,000 cacao seeds, which were also used as currency.
The emergence of exchange networks in the Pre-Columbian societies of
and near to Mexico are known to have occurred within recent years before
and after 1500 BCE.
Trade networks reached north to Oasisamerica. There is evidence of established maritime trade with the cultures of northwestern South America and the Caribbean.
Middle Ages
During the Middle Ages, commerce developed in Europe by trading luxury goods at trade fairs. Wealth became converted into movable wealth or capital.
Banking systems developed where money on account was transferred across
national boundaries. Hand to hand markets became a feature of town
life, and were regulated by town authorities.
Western Europe established a complex and expansive trade network with
cargo ships being the main workhorse for the movement of goods, Cogs and Hulks are two examples of such cargo ships. Many ports would develop their own extensive trade networks. The English port city of Bristol traded with peoples from what is modern day Iceland, all along the western coast of France, and down to what is now Spain.
A map showing the main trade routes for goods within late medieval Europe.
During the Middle Ages, Central Asia was the economic center of the world. The Sogdians dominated the East-West trade route known as the Silk Road after the 4th century CE up to the 8th century CE, with Suyab and Talas ranking among their main centers in the north. They were the main caravan merchants of Central Asia.
From the 8th to the 11th century, the Vikings and Varangians traded as they sailed from and to Scandinavia. Vikings sailed to Western Europe, while Varangians to Russia. The Hanseatic League was an alliance of trading cities that maintained a trade monopoly over most of Northern Europe and the Baltic, between the 13th and 17th centuries.
The Age of Sail and the Industrial Revolution
Vasco da Gama pioneered the European Spice trade in 1498 when he reached Calicut after sailing around the Cape of Good Hope
at the southern tip of the African continent. Prior to this, the flow
of spice into Europe from India was controlled by Islamic powers,
especially Egypt. The spice trade was of major economic importance and
helped spur the Age of Discovery
in Europe. Spices brought to Europe from the Eastern world were some of
the most valuable commodities for their weight, sometimes rivaling gold.
From 1070 onward, kingdoms in West Africa became significant members of global trade. This came initially through the movement of gold and other resources sent out by Muslim traders on the Trans-Saharan trading network. Later, West Africa exported gold, spices, cloth, and slaves to European traders such as the Portuguese, Dutch, and English. This was often in exchange for cloth, iron, or cowrie shells which were used locally as currency.
Founded in 1352, the Bengal Sultanate was a major trading nation in the world and often referred to by the Europeans as the richest country to trade with.
In the 16th and 17th centuries, the Portuguese gained an economic advantage in the Kingdom of Kongo due to different philosophies of trade.
Whereas Portuguese traders concentrated on the accumulation of capital,
in Kongo spiritual meaning was attached to many objects of trade.
According to economic historian Toby Green, in Kongo "giving more than receiving was a symbol of spiritual and political power and privilege."
In the 16th century, the Seventeen Provinces were the center of free trade, imposing no exchange controls, and advocating the free movement of goods. Trade in the East Indies was dominated by Portugal in the 16th century, the Dutch Republic in the 17th century, and the British in the 18th century. The Spanish Empire developed regular trade links across both the Atlantic and the Pacific Oceans.
Danzig in the 17th century, a port of the Hanseatic League
In 1776, Adam Smith published the paper An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations. It criticized Mercantilism, and argued that economic specialization could benefit nations just as much as firms. Since the division of labour
was restricted by the size of the market, he said that countries having
access to larger markets would be able to divide labour more
efficiently and thereby become more productive. Smith said that he considered all rationalizations of import and export controls "dupery", which hurt the trading nation as a whole for the benefit of specific industries.
In 1799, the Dutch East India Company, formerly the world's largest company, became bankrupt, partly due to the rise of competitive free trade.
19th century
In 1817, David Ricardo, James Mill and Robert Torrens showed that free trade would benefit the industrially weak as well as the strong, in the famous theory of comparative advantage. In Principles of Political Economy and Taxation Ricardo advanced the doctrine still considered the most counterintuitive in economics:
- When an inefficient producer sends the merchandise it produces best to a country able to produce it more efficiently, both countries benefit.
The ascendancy of free trade was primarily based on national
advantage in the mid 19th century. That is, the calculation made was
whether it was in any particular country's self-interest to open its
borders to imports.
John Stuart Mill proved that a country with monopoly pricing power on the international market could manipulate the terms of trade through maintaining tariffs, and that the response to this might be reciprocity
in trade policy. Ricardo and others had suggested this earlier. This
was taken as evidence against the universal doctrine of free trade, as
it was believed that more of the economic surplus of trade would accrue to a country following reciprocal, rather than completely free, trade policies. This was followed within a few years by the infant industry scenario developed by Mill promoting the theory that the government had the duty to protect
young industries, although only for a time necessary for them to
develop full capacity. This became the policy in many countries
attempting to industrialize and out-compete English exporters. Milton Friedman
later continued this vein of thought, showing that in a few
circumstances tariffs might be beneficial to the host country; but never
for the world at large.
20th century
The Great Depression
was a major economic recession that ran from 1929 to the late 1930s.
During this period, there was a great drop in trade and other economic
indicators.
The lack of free trade was considered by many as a principal cause of the depression causing stagnation and inflation. Only during the World War II the recession ended in the United States. Also during the war, in 1944, 44 countries signed the Bretton Woods Agreement, intended to prevent national trade barriers, to avoid depressions. It set up rules and institutions to regulate the international political economy:
the International Monetary Fund and the International Bank for
Reconstruction and Development (later divided into the World Bank and
Bank for International Settlements). These organizations became
operational in 1946 after enough countries ratified the agreement. In
1947, 23 countries agreed to the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade to promote free trade.
The European Union became the world's largest exporter of manufactured goods and services, the biggest export market for around 80 countries.
21st century
Today, trade is merely a subset within a complex system of companies which try to maximize their profits by offering products and services to the market (which consists both of individuals and other companies) at the lowest production cost. A system of international trade has helped to develop the world economy but, in combination with bilateral or multilateral agreements to lower tariffs or to achieve free trade, has sometimes harmed third-world markets for local products.
Free trade
Free trade advanced further in the late 20th century and early 2000s:
- 1992 European Union lifted barriers to internal trade in goods and labour.
- January 1, 1994 the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) took effect.
- 1994 The GATT Marrakech Agreement specified formation of the WTO.
- January 1, 1995 World Trade Organization was created to facilitate free trade, by mandating mutual most favored nation trading status between all signatories.
- EC was transformed into the European Union, which accomplished the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) in 2002, through introducing the Euro, and creating this way a real single market between 13 member states as of January 1, 2007.
- 2005, the Central American Free Trade Agreement was signed; It includes the United States and the Dominican Republic.Intérêts des nations de l'Europe, dévélopés relativement au commerce (1766)
Perspectives
Protectionism
Protectionism is the policy of restraining and discouraging trade
between states and contrasts with the policy of free trade. This policy
often takes the form of tariffs and restrictive quotas. Protectionist policies were particularly prevalent in the 1930s, between the Great Depression and the onset of World War II.
Religion
Judeao-Christian teachings prohibit fraud and dishonest measures, and historically also forbade the charging of interest on loans.
Development of money
The first instances of money were objects with intrinsic value. This is called commodity money
and includes any commonly available commodity that has intrinsic value;
historical examples include pigs, rare seashells, whale's teeth, and
(often) cattle. In medieval Iraq, bread was used as an early form of
money. In Mexico under Montezuma, cocoa beans were money.
Currency
was introduced as standardised money to facilitate a wider exchange of
goods and services. This first stage of currency, where metals were
used to represent stored value, and symbols to represent commodities,
formed the basis of trade in the Fertile Crescent for over 1500 years.
Numismatists have examples of coins from the earliest large-scale societies, although these were initially unmarked lumps of precious metal.
Trends
Doha rounds
The Doha round of World Trade Organization negotiations aimed to lower barriers to trade around the world, with a focus on making trade fairer for developing countries. Talks have been hung over a divide between the rich developed countries, represented by the G20, and the major developing countries. Agricultural subsidies
are the most significant issue upon which agreement has been the
hardest to negotiate. By contrast, there was much agreement on trade facilitation and capacity building. The Doha round began in Doha, Qatar, and negotiations were continued in: Cancún, Mexico; Geneva, Switzerland; and Paris, France and Hong Kong.
China
Beginning around 1978, the government of the People's Republic of China (PRC) began an experiment in economic reform. In contrast to the previous Soviet-style centrally planned economy,
the new measures progressively relaxed restrictions on farming,
agricultural distribution and, several years later, urban enterprises
and labor. The more market-oriented approach reduced inefficiencies and
stimulated private investment, particularly by farmers, which led to
increased productivity and output. One feature was the establishment of
four (later five) Special Economic Zones located along the South-east coast.
The reforms proved spectacularly successful in terms of increased output, variety, quality, price and demand.
In real terms, the economy doubled in size between 1978 and 1986,
doubled again by 1994, and again by 2003. On a real per capita basis,
doubling from the 1978 base took place in 1987, 1996 and 2006. By 2008,
the economy was 16.7 times the size it was in 1978, and 12.1 times its
previous per capita levels. International trade progressed even more
rapidly, doubling on average every 4.5 years. Total two-way trade in
January 1998 exceeded that for all of 1978; in the first quarter of
2009, trade exceeded the full-year 1998 level. In 2008, China's two-way
trade totaled US$2.56 trillion.
In 1991 China joined the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation group, a trade-promotion forum. In 2001, it also joined the World Trade Organization.
International trade
International trade is the exchange of goods and services across
national borders. In most countries, it represents a significant part
of GDP. While international trade has been present throughout much of history, its economic, social, and political importance have increased in recent centuries, mainly because of Industrialization, advanced transportation, globalization, multinational corporations, and outsourcing.
Empirical evidence for the success of trade can be seen in the contrast between countries such as South Korea, which adopted a policy of export-oriented industrialization,
and India, which historically had a more closed policy. South Korea
has done much better by economic criteria than India over the past fifty
years, though its success also has to do with effective state
institutions.
Trade sanctions
Trade sanctions against a specific country are sometimes imposed, in order to punish that country for some action. An embargo,
a severe form of externally imposed isolation, is a blockade of all
trade by one country on another. For example, the United States has had
an embargo against Cuba for over 40 years.
Fair trade
The "fair trade" movement, also known as the "trade justice" movement, promotes the use of labour, environmental and social standards for the production of commodities, particularly those exported from the Third and Second Worlds to the First World. Such ideas have also sparked a debate on whether trade itself should be codified as a human right.
Importing firms voluntarily adhere to fair trade standards or governments may enforce them through a combination of employment and commercial law. Proposed and practiced fair trade policies vary widely, ranging from the common prohibition of goods made using slave labour to minimum price support schemes such as those for coffee in the 1980s. Non-governmental organizations also play a role in promoting fair trade standards by serving as independent monitors of compliance with labeling requirements. As such, it is a form of Protectionism.