Fish fulfill several criteria proposed as indicating that non-human animals may experience pain. These fulfilled criteria include a suitable nervous system and sensory receptors, opioid receptors and reduced responses to noxious stimuli when given analgesics and local anaesthetics, physiological changes to noxious stimuli, displaying protective motor reactions, exhibiting avoidance learning and making trade-offs between noxious stimulus avoidance and other motivational requirements.
If fish feel pain, there are ethical and animal welfare implications including the consequences of exposure to pollutants, and practices involving commercial and recreational fishing, aquaculture, in ornamental fish and genetically modified fish and for fish used in scientific research.
Background
The possibility that fish and other non-human animals may experience pain has a long history. Initially, this was based around theoretical and philosophical argument, but more recently has turned to scientific investigation.
Philosophy
The idea that non-human animals might not feel pain goes back to the 17th-century French philosopher, René Descartes, who argued that animals do not experience pain and suffering because they lack consciousness. In 1789, the British philosopher and social reformist, Jeremy Bentham, addressed in his book An Introduction to the Principles of Morals and Legislation the issue of our treatment of animals with the following often quoted words: "The question is not, Can they reason? nor, Can they talk? but, Can they suffer?"
Peter Singer, a bioethicist and author of Animal Liberation published in 1975, suggested that consciousness is not necessarily the key issue: just because animals have smaller brains, or are 'less conscious' than humans, does not mean that they are not capable of feeling pain. He goes on further to argue that we do not assume newborn infants, people suffering from neurodegenerative brain diseases or people with learning disabilities experience less pain than we would.
Bernard Rollin, the principal author of two U.S. federal laws regulating pain relief for animals, writes that researchers remained unsure into the 1980s as to whether animals experience pain, and veterinarians trained in the U.S. before 1989 were taught to simply ignore animal pain. In his interactions with scientists and other veterinarians, Rollin was regularly asked to "prove" that animals are conscious, and to provide "scientifically acceptable" grounds for claiming that they feel pain.
Continuing into the 1990s, discussions were further developed on the roles that philosophy and science had in understanding animal cognition and mentality. In subsequent years, it was argued there was strong support for the suggestion that some animals (most likely amniotes) have at least simple conscious thoughts and feelings and that the view animals feel pain differently to humans is now a minority view.
Scientific investigation
In the 20th and 21st centuries, there were many scientific investigations of pain in non-human animals.
Mammals
In 2001 studies were published showing that arthritic rats self-select analgesic opiates. In 2014, the veterinary Journal of Small Animal Practice published an article on the recognition of pain which started – "The ability to experience pain is universally shared by all mammals..." and in 2015, it was reported in the science journal Pain, that several mammalian species (rat, mouse, rabbit, cat and horse) adopt a facial expression in response to a noxious stimulus that is consistent with the expression of pain in humans.
Birds
At the same time as the investigations using arthritic rats, studies were published showing that birds with gait abnormalities self-select for a diet that contains carprofen, a human analgesic. In 2005, it was written "Avian pain is likely analogous to pain experienced by most mammals" and in 2014, "...it is accepted that birds perceive and respond to noxious stimuli and that birds feel pain"
Reptiles and amphibians
Veterinary articles have been published stating both reptiles and amphibians experience pain in a way analogous to humans, and that analgesics are effective in these two classes of vertebrates.
Argument by analogy
In 2012 the American philosopher Gary Varner reviewed the research literature on pain in animals. His findings are summarised in the following table.
| Argument by analogy | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Property | |||||||||
| Fish | Amphibians | Reptiles | Birds | Mammals | |||||
| Has nociceptors | |||||||||
| Has brain | |||||||||
| Nociceptors and brain linked | |
? | ? | ||||||
| Has endogenous opioids | |||||||||
| Analgesics affect responses | ? | ? | |||||||
| Response to damaging stimuli similar to humans | |||||||||
Arguing by analogy, Varner claims that any animal which exhibits the properties listed in the table could be said to experience pain. On that basis, he concludes that all vertebrates, including fish, probably experience pain, but invertebrates apart from cephalopods probably do not experience pain.
Crustaceans
Some studies however find crustaceans do show responses consistent with signs of pain and distress.
Experiencing pain
Although there are numerous definitions of pain, almost all involve two key components.
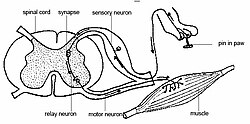
First, nociception is required. This is the ability to detect noxious stimuli which evoke a reflex response that rapidly moves the entire animal, or the affected part of its body, away from the source of the stimulus. The concept of nociception does not imply any adverse, subjective "feeling" – it is a reflex action. An example in humans would be the rapid withdrawal of a finger that has touched something hot – the withdrawal occurs before any sensation of pain is actually experienced.
The second component is the experience of "pain" itself, or suffering – the internal, emotional interpretation of the nociceptive experience. Again in humans, this is when the withdrawn finger begins to hurt, moments after the withdrawal. Pain is therefore a private, emotional experience. Pain cannot be directly measured in other animals, including other humans; responses to putatively painful stimuli can be measured, but not the experience itself. To address this problem when assessing the capacity of other species to experience pain, argument-by-analogy is used. This is based on the principle that if an animal responds to a stimulus in a similar way to ourselves, it is likely to have had an analogous experience.
Nociception
Nociception usually involves the transmission of a signal along a chain of nerve fibers from the site of a noxious stimulus at the periphery to the spinal cord and brain. This process evokes a reflex arc response generated at the spinal cord and not involving the brain, such as flinching or withdrawal of a limb. Nociception is found, in one form or another, across all major animal taxa. Nociception can be observed using modern imaging techniques; and a physiological and behavioral response to nociception can often be detected. However, nociceptive responses can be so subtle in prey animals that trained (human) observers cannot perceive them, whereas natural predators can and subsequently target injured individuals.
Emotional pain
Sometimes a distinction is made between "physical pain" and "emotional" or "psychological pain". Emotional pain is the pain experienced in the absence of physical trauma, for example, the pain experienced by humans after the loss of a loved one, or the break-up of a relationship. It has been argued that only primates and humans can feel "emotional pain", because they are the only animals that have a neocortex – a part of the brain's cortex considered to be the "thinking area". However, research has provided evidence that monkeys, dogs, cats and birds can show signs of emotional pain and display behaviours associated with depression during or after a painful experience, specifically, a lack of motivation, lethargy, anorexia, and unresponsiveness to other animals.
Physical pain
The nerve impulses of the nociception response may be conducted to the brain thereby registering the location, intensity, quality and unpleasantness of the stimulus. This subjective component of pain involves conscious awareness of both the sensation and the unpleasantness (the aversive, negative affect). The brain processes underlying conscious awareness of the unpleasantness (suffering), are not well understood.
There have been several published lists of criteria for establishing whether non-human animals experience pain, e.g. Some criteria that may indicate the potential of another species, including fishes, to feel pain include:
- Has a suitable nervous system and sensory receptors
- Has opioid receptors and shows reduced responses to noxious stimuli when given analgesics and local anaesthetics
- Physiological changes to noxious stimuli
- Displays protective motor reactions that might include reduced use of an affected area such as limping, rubbing, holding or autotomy
- Shows avoidance learning
- Shows trade-offs between noxious stimulus avoidance and other motivational requirements
- High cognitive ability and sentience
Adaptive value
The adaptive value of nociception is obvious; an organism detecting a noxious stimulus immediately withdraws the limb, appendage or entire body from the noxious stimulus and thereby avoids further (potential) injury. However, a characteristic of pain (in mammals at least) is that pain can result in hyperalgesia (a heightened sensitivity to noxious stimuli) and allodynia (a heightened sensitivity to non-noxious stimuli). When this heightened sensitisation occurs, the adaptive value is less clear. First, the pain arising from the heightened sensitisation can be disproportionate to the actual tissue damage caused. Second, the heightened sensitisation may also become chronic, persisting well beyond the tissues healing. This can mean that rather than the actual tissue damage causing pain, it is the pain due to the heightened sensitisation that becomes the concern. This means the sensitisation process is sometimes termed maladaptive. It is often suggested hyperalgesia and allodynia assist organisms to protect themselves during healing, but experimental evidence to support this has been lacking.
In 2014, the adaptive value of sensitisation due to injury was tested using the predatory interactions between longfin inshore squid (Doryteuthis pealeii) and black sea bass (Centropristis striata) which are natural predators of this squid. If injured squid are targeted by a bass, they began their defensive behaviours sooner (indicated by greater alert distances and longer flight initiation distances) than uninjured squid. If anaesthetic (1% ethanol and MgCl2) is administered prior to the injury, this prevents the sensitisation and blocks the behavioural effect. The authors claim this study is the first experimental evidence to support the argument that nociceptive sensitisation is actually an adaptive response to injuries.
The question has been asked, "If fish cannot feel pain, why do stingrays have purely defensive tail spines that deliver venom? Stingrays' ancestral predators are fish. And why do many fishes possess defensive fin spines, some also with venom that produces pain in humans?"
Research findings
Peripheral nervous system
Receptors
Primitive fish such as lampreys (Petromyzon marinus) have free nerve endings in the skin that respond to heat and mechanical pressure. However, behavioural reactions associated with nociception have not been recorded, and it is also difficult to determine whether the mechanoreceptors in lamprey are truly nociceptive-specific or simply pressure-specific.
Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) have polymodal nociceptors on the face and snout that respond to mechanical pressure, temperatures in the noxious range (> 40 °C), and 1% acetic acid (a chemical irritant). Further studies found nociceptors to be more widely distributed over the bodies of rainbow trout, as well as those of cod and carp. The most sensitive areas of the body are around the eyes, nostrils, fleshy parts of the tail, and pectoral and dorsal fins.
Rainbow trout also have corneal nociceptors. Out of 27 receptors investigated in one study, seven were polymodal nociceptors and six were mechanothermal nociceptors. Mechanical and thermal thresholds were lower than those of cutaneous receptors, indicating greater sensitivity in the cornea.
Bony fish possess nociceptors that are similar in function to those in mammals.
Nerve fibres
There are two types of nerve fibre relevant to pain in fish. Group C nerve fibres are a type of sensory nerve fibre which lack a myelin sheath and have a small diameter, meaning they have a low nerve conduction velocity. The suffering that humans associate with burns, toothaches, or crushing injury are caused by C fibre activity. A typical human cutaneous nerve contains 83% Group C nerve fibres. A-delta fibres are another type of sensory nerve fibre, however, these are myelinated and therefore transmit impulses faster than non-myelinated C fibres. A-delta fibres carry cold, pressure and some pain signals, and are associated with acute pain that results in "pulling away" from noxious stimuli.
Bony fish possess both Group C and A-delta fibres representing 38.7% (combined) of the fibres in the tail nerves of common carp and 36% of the trigeminal nerve of rainbow trout. However, only 5% and 4% of these are C fibres in the carp and rainbow trout, respectively.
Some species of cartilagenous fish possess A-delta fibres, however, C fibres are either absent or found in very low numbers. The Agnatha (hagfishes and lamprey) primarily have Group C fibres.
Central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) of fish contains a spinal cord, medulla oblongata, and the brain, divided into telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon and cerebellum.
In fish, similar to other vertebrates, nociception travels from the peripheral nerves along the spinal nerves and is relayed through the spinal cord to the thalamus. The thalamus is connected to the telencephalon by multiple connections through the grey matter pallium, which has been demonstrated to receive nerve relays for noxious and mechanical stimuli.
The major tracts that convey pain information from the periphery to the brain are the spinothalamic tract (body) and the trigeminal tract (head). Both have been studied in agnathans, teleost, and elasmobranch fish (trigeminal in the common carp, spinothalamic tract in the sea robin, Prionotus carolinus).
Brain
If sensory responses in fish are limited to the spinal cord and hindbrain, they might be considered as simply reflexive. However, recordings from the spinal cord, cerebellum, tectum and telencephalon in both trout and goldfish (Carassius auratus) show these all respond to noxious stimuli. This indicates a nociceptive pathway from the periphery to the higher CNS of fish.
Microarray analysis of gene expression shows the brain is active at the molecular level in the forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain of common carp and rainbow trout. Several genes involved in mammalian nociception, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and the cannabinoid CB1 receptor are regulated in the fish brain after a nociceptive event.
Somatosensory evoked potentials (SEPs) are weak electric responses in the CNS following stimulation of peripheral sensory nerves. These further indicate there is a pathway from the peripheral nociceptors to higher brain regions. In goldfish, rainbow trout, Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua), it has been demonstrated that putatively non-noxious and noxious stimulation elicit SEPs in different brain regions, including the telencephalon which may mediate the co-ordination of pain information. Moreover, multiple functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies with several species of fishes have shown that when suffering from putative pain, there is profound activity in the forebrain which is highly reminiscent of that observed in humans and would be taken as evidence of the experience of pain in mammals.
Therefore, "higher" brain areas are activated at the molecular, physiological, and functional levels in fish experiencing a potentially painful event. Sneddon stated "This gives much weight to the proposal that fish experience some form of pain rather than a nociceptive event".
Opioid system and effects of analgesics
Teleost fish have a functional opioid system which includes the presence of opioid receptors similar to those of mammals. All four of the main opioid receptor types (delta, kappa, mu, and NOP) are conserved in vertebrates, even in primitive jawless fishes (agnathastoma).
The same analgesics and anaesthetics used in humans and other mammals, are often used for fish in veterinary medicine. These chemicals act on the nociceptive pathways, blocking signals to the brain where emotional responses to the signals are further processed by certain parts of the brain found in amniotes ("higher vertebrates").
Effects of morphine
Pre-treatment with morphine (an analgesic in humans and other mammals) has a dose-dependent anti-nociceptive effect and mitigates the behavioural and ventilation rate responses of rainbow trout to noxious stimuli.
When acetic acid is injected into the lips of rainbow trout, they exhibit anomalous behaviours such as side-to-side rocking and rubbing their lips along the sides and floors of the tanks, and their ventilation rate increases. Injections of morphine reduce both the anomalous, noxious-stimulus related behaviours and the increase in ventilation rate. When the same noxious stimulus is applied to zebrafish (Danio rerio), they respond by decreasing their activity. As with the rainbow trout, morphine injected prior to the acid injection attenuates the decrease in activity in a dose-dependent manner.
Injection of acetic acid into the lips of rainbow trout causes a reduction in their natural neophobia (fear of novelty); this is reversed by the administration of morphine.
In goldfish injected with morphine or saline and then exposed to unpleasant temperatures, fish injected with saline acted with defensive behaviours indicating anxiety, wariness and fear, whereas those given morphine did not.
Effects of other analgesics
The neurotransmitter, Substance P and the analgesic opioid enkephalins and β-endorphin, which act as endogenous analgesics in mammals, are present in fish.
Different analgesics have different effects on fish. In a study on the efficacy of three types of analgesic, buprenorphine (an opioid), carprofen (a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug) and lidocaine (a local anaesthetic), ventilation rate and time to resume feeding were used as pain indicators. Buprenorphine had limited impact on the fish's response, carprofen ameliorated the effects of noxious stimulation on time to resume feeding, however, lidocaine reduced all the behavioural indicators.
Tramadol also increases the nociceptive threshold in fish, providing further evidence of an anti-nociceptive opioid system in fish.
Effects of naloxone
Naloxone is an μ-opioid receptor antagonist which, in mammals, negates the analgesic effects of opioids. Both adult and five-day-old zebrafish larvae show behavioural responses indicative of pain in response to injected or diluted acetic acid. The anti-nociceptive properties of morphine or buprenorphine are reversed if adults, or larvae, are co-treated with naloxone. Both naloxone and prolyl-leucyl-glycinamide (another opiate antagonist in mammals) reduced the analgesic effects of morphine to electric shocks received by goldfish, indicating they can act as an opiate antagonist in fish.
Physiological changes
The physiological changes of fish in response to noxious stimuli include elevations of ventilation rate and cortisol levels.
Protective responses
Studies show that fish exhibit protective behavioural responses to putatively painful stimuli.
When acetic acid or bee venom is injected into the lips of rainbow trout, they exhibit an anomalous side-to-side rocking behaviour on their pectoral fins, rub their lips along the sides and floors of the tanks and increase their ventilation rate. When acetic acid is injected into the lips of zebrafish, they respond by decreasing their activity. The magnitude of this behavioural response depends on the concentration of the acetic acid.
The behavioural responses to a noxious stimulus differ between species of fish. Noxiously stimulated common carp (Cyprinus carpio) show anomalous rocking behaviour and rub their lips against the tank walls, but do not change other behaviours or their ventilation rate. In contrast, zebrafish (Danio rerio) reduce their frequency of swimming and increase their ventilation rate but do not display anomalous behaviour. Rainbow trout, like the zebrafish, reduce their frequency of swimming and increase their ventilation rate. Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), in response to a tail fin clip, increase their swimming activity and spend more time in the light area of their tank.
Since this initial work, Sneddon and her co-workers have shown that rainbow trout, common carp and zebrafish experiencing a noxious stimulation exhibit rapid changes in physiology and behavior that persist for up to 6 hours and thus are not simple reflexes.
Five-day old zebrafish larvae show a concentration dependent increase in locomotor activity in response to different concentrations of diluted acetic acid. This increase in locomotor activity is accompanied by an increase in cox-2 mRNA, demonstrating that nociceptive pathways are also activated.
Fish show different responses to different noxious stimuli, even when these are apparently similar. This indicates the response is flexible and not simply a nociceptive reflex. Atlantic cod injected in the lip with acetic acid, capsaicin, or piercing the lip with a commercial fishing hook, showed different responses to these three types of noxious stimulation. Those cod treated with acetic acid and capsaicin displayed increased hovering close to the bottom of the tank and reduced use of shelter. However, hooked cod only showed brief episodes of head shaking.
Avoidance learning
Early experiments provided evidence that fish learn to respond to putatively noxious stimuli. For instance, toadfish (Batrachoididae) grunt when they are electrically shocked, but after repeated shocks, they grunt simply at the sight of the electrode. More recent studies show that both goldfish and trout learn to avoid locations in which they receive electric shocks. Furthermore, this avoidance learning is flexible and is related to the intensity of the stimulus.
Trade-offs in motivation
A painful experience may change the motivation for normal behavioural responses.
In a 2007 study, goldfish were trained to feed at a location of the aquarium where subsequently they would receive an electric shock. The number of feeding attempts and time spent in the feeding/shock zone decreased with increased shock intensity and with increased food deprivation the number and the duration of feeding attempts increased as did escape responses as this zone was entered. The researchers suggested that goldfish make a trade-off in their motivation to feed with their motivation to avoid an acute noxious stimulus.
Rainbow trout naturally avoid novelty (i.e. they are neophobic). Victoria Braithwaite describes a study in which a brightly coloured Lego brick is placed in the tank of rainbow trout. Trout injected in the lip with a small amount of saline strongly avoided the Lego brick, however, trout injected with acetic acid spent considerably more time near the Lego block. When the study was repeated but with the fish also being given morphine, the avoidance response returned in those fish injected with acetic acid and could not be distinguished from the responses of saline injected fish.
To explore the possibility of a trade-off between responding to a noxious stimulus and predation, researchers presented rainbow trout with a competing stimulus, a predator cue. Noxiously stimulated fish cease showing anti-predator responses, indicating that pain becomes their primary motivation. The same study investigated the potential trade-off between responding to a noxious stimulus and social status. The responses of the noxiously treated trout varied depending on the familiarity of the fish they were placed with. The researchers suggested the findings of the motivational changes and trade-offs provide evidence for central processing of pain rather than merely showing a nociceptive reflex.
Paying a cost for analgesia
Zebrafish given access to a barren, brightly lit chamber or an enriched chamber prefer the enriched area. When these fish are injected with acetic acid or saline as a control they still choose the same enriched chamber. However, if an analgesic is dissolved in the barren, less-preferred chamber, zebrafish injected with noxious acid lose their preference and spend over half their time in the previously less-favourable, barren chamber. This suggests a trade-off in motivation and furthermore, they are willing to pay a cost to enter a less preferred environment to access pain relief.
Cognitive ability and sentience
The learning abilities of fish demonstrated in a range of studies indicate sophisticated cognitive processes that are more complex than simple associative learning. Examples include the ability to recognise social companions, avoidance (for some months or years) of places where they encountered a predator or were caught on a hook and forming mental maps.
It has been argued that although a high cognitive capacity may indicate a greater likelihood of experiencing pain, it also gives these animals a greater ability to deal with this, leaving animals with a lower cognitive ability a greater problem in coping with pain.
Criteria for pain perception
Scientists have also proposed that in conjunction with argument-by-analogy, criteria of physiology or behavioural responses can be used to assess the possibility of non-human animals perceiving pain. The following is a table of criteria suggested by Sneddon et al.
| Criteria | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jawless fish | Cartilaginous fish | Bony fish | Lobe-finned fish | |
| Has nociceptors | ? | ? | ? | |
| Pathways to central nervous system | ? | ? | ? | |
| Central processing in brain | ? | ? | ? | |
| Receptors for analgesic drugs | ? | ? | ? | |
| Physiological responses | ? | ? | ? | |
| Movement away from noxious stimuli | ? | ? | ? | |
| Behavioural changes from norm | ? | ? | ? | |
| Protective behaviour | ? | ? | ? | |
| Responses reduced by analgesic drugs | ? | ? | ? | |
| Self-administration of analgesia | ? | ? | ? | |
| Responses with high priority over other stimuli | ? | ? | ? | |
| Pay cost to access analgesia | ? | ? | ? | |
| Altered behavioural choices/preferences | ? | ? | ? | |
| Relief learning | ? | ? | ? | |
| Rubbing, limping or guarding | ? | ? | ? | |
| Paying a cost to avoid stimulus | ? | ? | ? | |
| Tradeoffs with other requirements | ? | ? | ? |
In the table, ![]() indicates positive evidence and ? denotes it has not been tested or there is insufficient evidence.
indicates positive evidence and ? denotes it has not been tested or there is insufficient evidence.
Societal implications
Given that some have interpreted the existing scientific information to suggest that fish may feel pain, it has been suggested that precautionary principles should be applied to commercial fishing, which would likely have multiple consequences.
Both scientists and animal protection advocates have raised concerns about the possible suffering (pain and fear) of fish caused by angling.
Other societal implications of fish experiencing pain include acute and chronic exposure to pollutants, commercial and sporting fisheries (e.g. injury during trawling, tagging/fin clipping during stock assessment, tissue damage, physical exhaustion and severe oxygen deficit during capture, pain and stress during slaughter, use of live bait), aquaculture (e.g. tagging/fin clipping, high stocking densities resulting in increased aggression, food deprivation for disease treatment or before harvest, removal from water for routine husbandry, pain during slaughter), ornamental fish (e.g. capture by sub-lethal poisoning, permanent adverse physical states due to selective breeding), scientific research (e.g. genetic-modification) may have detrimental effects on welfare, deliberately-imposed adverse physical, physiological and behavioural states, electrofishing, tagging, fin clipping or otherwise marking fish, handling procedures which may cause injury.
Browman et al. suggest that if the regulatory environment continues on its current trajectory (adding more aquatic animal taxa to those already regulated), activity in some sectors could be severely restricted, even banned. They further argue that extending legal protection to aquatic animals is a societal choice, but they emphasize that choice should not be ascribed to strong support from a body of research that does not yet exist, and may never exist, and the consequences of making that decision must be carefully weighed.
Legislation
In the UK, the legislation protecting animals during scientific research, the "Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986", protects fish from the moment they become capable of independent feeding. The legislation protecting animals in most other circumstances in the UK is "The Animal Welfare Act, 2006" which states that in the Act, " "animal" means a vertebrate other than man", clearly including fish.
In the US, the legislation protecting animals during scientific research is "The Animal Welfare Act". This excludes protection of "cold-blooded" animals, including fish.
The 1974 Norwegian Animal Rights Law states it relates to mammals, birds, frogs, salamander, reptiles, fish, and crustaceans.
A 2018 article by Howard Browman and colleagues provides an overview of what different perspectives regarding fish pain and welfare mean to in the context of aquaculture, commercial fisheries, recreational fisheries, and research.
Controversy
Nervous system
Receptors and nerve fibres
It has been argued that fish can not feel pain because they do not have a sufficient density of appropriate nerve fibres. A typical human cutaneous nerve contains 83% Group C nerve fibres, however, the same nerves in humans with congenital insensitivity to pain have only 24–28% C-type fibres. Based on this, James Rose, from the University of Wyoming, has argued that the absence of C-type fibres in cartilagenous sharks and rays indicates that signalling leading to pain perception is likely to be impossible, and the low numbers for bony fish (e.g. 5% for carp and trout) indicate this is also highly unlikely for these fish. Rose concludes there is little evidence that sharks and rays possess the nociceptors required to initiate pain detection in the brain, and that, while bony fish are able to unconsciously learn to avoid injurious stimuli, they are little more likely to experience conscious pain than sharks.
A-delta-type fibres, believed to trigger avoidance reactions, are common in bony fish, although they have not been found in sharks or rays.
Rose concludes that fish have survived well in an evolutionary sense without the full range of nociception typical of humans or other mammals.
Brain
In 2002, Rose published reviews arguing that fish cannot feel pain because they lack a neocortex in the brain. This argument would also rule out pain perception in most mammals, and all birds and reptiles. However, in 2003, a research team led by Lynne Sneddon concluded that the brains of rainbow trout fire neurons in the same way human brains do when experiencing pain. Rose criticized the study, claiming it was flawed, mainly because it did not provide proof that fish possess "conscious awareness, particularly a kind of awareness that is meaningfully like ours".
Rose, and more recently Brian Key from The University of Queensland, argue that because the fish brain is very different to humans, fish are probably not conscious in the manner humans are, and while fish may react in a way similar to the way humans react to pain, the reactions in the case of fish have other causes. Studies indicating that fish can feel pain were confusing nociception with feeling pain, says Rose. "Pain is predicated on awareness. The key issue is the distinction between nociception and pain. A person who is anaesthetised in an operating theatre will still respond physically to an external stimulus, but he or she will not feel pain." According to Rose and Key, the literature relating to the question of consciousness in fish is prone to anthropomorphisms and care is needed to avoid erroneously attributing human-like capabilities to fish. Sneddon suggests it is entirely possible that a species with a different evolutionary path could evolve different neural systems to perform the same functions (i.e. convergent evolution), as studies on the brains of birds have shown. Key agrees that phenomenal consciousness is likely to occur in mammals and birds, but not in fish. Animal behaviouralist Temple Grandin argues that fish could still have consciousness without a neocortex because "different species can use different brain structures and systems to handle the same functions." Sneddon proposes that to suggest a function suddenly arises without a primitive form defies the laws of evolution.
Other researchers also believe that animal consciousness does not require a neocortex, but can arise from homologous subcortical brain networks. It has been suggested that brainstem circuits can generate pain. This includes research with anencephalic children who, despite missing large portions of their cortex, express emotions. There is also evidence from activation studies showing brainstem mediated feelings in normal humans and foetal withdrawal responses to noxious stimulation but prior to development of the cortex.
In papers published in 2017 and 2018, Michael Woodruff summarized a significant number of research articles that, in contradiction to the conclusions of Rose and Key, strongly support the hypothesis that the neuroanatomical organization of the fish pallium and its connections with subpallial structures, especially those with the preglomerular nucleus and the tectum, are complex enough to be analogous to the circuitry of the cortex and thalamus assumed to underlie sentience in mammals. He added neurophysiological and behavioral data to these anatomical observations that also support the hypothesis that the pallium is an important part of the hierarchical network proposed by Feinberg and Mallatt to underlie consciousness in fishes.
Protective responses
Initial work by Sneddon and her co-workers characterised behavioural responses in rainbow trout, common carp and zebrafish. However, when these experiments were repeated by Newby and Stevens without anaesthetic, rocking and rubbing behaviour was not observed, suggesting that some of the alleged pain responses observed by Sneddon and co-workers were likely to be due to recovery of the fish from anaesthesia.
Several researchers argue about the definition of pain used in behavioural studies, as the observations recorded were contradictory, non-validated and non-repeatable by other researchers. In 2012, Rose argued that fishes resume "normal feeding and activity immediately or soon after surgery".
Nordgreen said that the behavioural differences they found in response to uncomfortable temperatures showed that fish feel both reflexive and cognitive pain. "The experiment shows that fish do not only respond to painful stimuli with reflexes, but change their behavior also after the event," Nordgreen said. "Together with what we know from experiments carried out by other groups, this indicates that the fish consciously perceive the test situation as painful and switch to behaviors indicative of having been through an aversive experience." In 2012, Rose and others reviewed this and further studies which concluded that pain had been found in fish. They concluded that the results from such research are due to poor design and misinterpretation, and that the researchers were unable to distinguish unconscious detection of injurious stimuli (nociception) from conscious pain.