| Occupation | |
|---|---|
| Names | Physician |
Activity sectors | Medicine |
| Description | |
Education required | |
Related jobs | |
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of mental disorders. These include various maladaptations related to mood, behaviour, cognition, and perceptions.
Initial psychiatric assessment of a person typically begins with a case history and mental status examination. Physical examinations and psychological tests may be conducted. On occasion, neuroimaging or other neurophysiological techniques are used. Mental disorders are often diagnosed in accordance with clinical concepts listed in diagnostic manuals such as the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), edited and used by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the widely used Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). The fifth edition of the DSM (DSM-5) was published in 2013 which re-organized the larger categories of various diseases and expanded upon the previous edition to include information/insights that are consistent with current research.
Combined treatment with psychiatric medication and psychotherapy has become the most common mode of psychiatric treatment in current practice, but contemporary practice also includes a wide variety of other modalities, e.g., assertive community treatment, community reinforcement, and supported employment. Treatment may be delivered on an inpatient or outpatient basis, depending on the severity of functional impairment or on other aspects of the disorder in question. An inpatient may be treated in a psychiatric hospital. Research within psychiatry as a whole is conducted on an interdisciplinary basis with other professionals, such as epidemiologists, nurses, social workers, occupational therapists, or clinical psychologists.
Etymology
The term psychiatry was first coined by the German physician Johann Christian Reil in 1808 and literally means the 'medical treatment of the soul' (psych- 'soul' from Ancient Greek psykhē 'soul'; -iatry 'medical treatment' from Gk. iātrikos 'medical' from iāsthai 'to heal'). A medical doctor specializing in psychiatry is a psychiatrist.
Theory and focus
"Psychiatry, more than any other branch of medicine, forces its practitioners to wrestle with the nature of evidence, the validity of introspection, problems in communication, and other long-standing philosophical issues" (Guze, 1992, p.4).
Psychiatry refers to a field of medicine focused specifically on the mind, aiming to study, prevent, and treat mental disorders in humans. It has been described as an intermediary between the world from a social context and the world from the perspective of those who are mentally ill.
People who specialize in psychiatry often differ from most other mental health professionals and physicians in that they must be familiar with both the social and biological sciences. The discipline studies the operations of different organs and body systems as classified by the patient's subjective experiences and the objective physiology of the patient. Psychiatry treats mental disorders, which are conventionally divided into three very general categories: mental illnesses, severe learning disabilities, and personality disorders. While the focus of psychiatry has changed little over time, the diagnostic and treatment processes have evolved dramatically and continue to do so. Since the late 20th century, the field of psychiatry has continued to become more biological and less conceptually isolated from other medical fields.
Scope of practice
Though the medical specialty of psychiatry uses research in the field of neuroscience, psychology, medicine, biology, biochemistry, and pharmacology, it has generally been considered a middle ground between neurology and psychology. Because psychiatry and neurology are deeply intertwined medical specialties, all certification for both specialties and for their subspecialties is offered by a single board, the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology, one of the member boards of the American Board of Medical Specialties. Unlike other physicians and neurologists, psychiatrists specialize in the doctor–patient relationship and are trained to varying extents in the use of psychotherapy and other therapeutic communication techniques. Psychiatrists also differ from psychologists in that they are physicians and have post-graduate training called residency (usually 4 to 5 years) in psychiatry; the quality and thoroughness of their graduate medical training is identical to that of all other physicians. Psychiatrists can therefore counsel patients, prescribe medication, order laboratory tests, order neuroimaging, and conduct physical examinations.
Ethics
The World Psychiatric Association issues an ethical code to govern the conduct of psychiatrists (like other purveyors of professional ethics). The psychiatric code of ethics, first set forth through the Declaration of Hawaii in 1977 has been expanded through a 1983 Vienna update and in the broader Madrid Declaration in 1996. The code was further revised during the organization's general assemblies in 1999, 2002, 2005, and 2011.
The World Psychiatric Association code covers such matters as confidentiality, the death penalty, ethnic or cultural discrimination, euthanasia, genetics, the human dignity of incapacitated patients, media relations, organ transplantation, patient assessment, research ethics, sex selection, torture, and up-to-date knowledge.
In establishing such ethical codes, the profession has responded to a number of controversies about the practice of psychiatry, for example, surrounding the use of lobotomy and electroconvulsive therapy.
Discredited psychiatrists who operated outside the norms of medical ethics include Harry Bailey, Donald Ewen Cameron, Samuel A. Cartwright, Henry Cotton, and Andrei Snezhnevsky.
Approaches
Psychiatric illnesses can be conceptualised in a number of different ways. The biomedical approach examines signs and symptoms and compares them with diagnostic criteria. Mental illness can be assessed, conversely, through a narrative which tries to incorporate symptoms into a meaningful life history and to frame them as responses to external conditions. Both approaches are important in the field of psychiatry but have not sufficiently reconciled to settle controversy over either the selection of a psychiatric paradigm or the specification of psychopathology. The notion of a "biopsychosocial model" is often used to underline the multifactorial nature of clinical impairment. In this notion the word model is not used in a strictly scientific way though. Alternatively, a Niall McLaren acknowledges the physiological basis for the mind's existence but identifies cognition as an irreducible and independent realm in which disorder may occur. The biocognitive approach includes a mentalist etiology and provides a natural dualist (i.e., non-spiritual) revision of the biopsychosocial view, reflecting the efforts of Australian psychiatrist Niall McLaren to bring the discipline into scientific maturity in accordance with the paradigmatic standards of philosopher Thomas Kuhn.
Once a medical professional diagnoses a patient there are numerous ways that they could choose to treat the patient. Often psychiatrists will develop a treatment strategy that incorporates different facets of different approaches into one. Drug prescriptions are very commonly written to be regimented to patients along with any therapy they receive. There are three major pillars of psychotherapy that treatment strategies are most regularly drawn from. Humanistic psychology attempts to put the "whole" of the patient in perspective; it also focuses on self exploration. Behaviorism is a therapeutic school of thought that elects to focus solely on real and observable events, rather than mining the unconscious or subconscious. Psychoanalysis, on the other hand, concentrates its dealings on early childhood, irrational drives, the unconscious, and conflict between conscious and unconscious streams.
Practitioners
All physicians can diagnose mental disorders and prescribe treatments utilizing principles of psychiatry. Psychiatrists are trained physicians who specialize in psychiatry and are certified to treat mental illness. They may treat outpatients, inpatients, or both; they may practice as solo practitioners or as members of groups; they may be self-employed, be members of partnerships, or be employees of governmental, academic, nonprofit, or for-profit entities; employees of hospitals; they may treat military personnel as civilians or as members of the military; and in any of these settings they may function as clinicians, researchers, teachers, or some combination of these. Although psychiatrists may also go through significant training to conduct psychotherapy, psychoanalysis or cognitive behavioral therapy, it is their training as physicians that differentiates them from other mental health professionals.
As a career choice
Psychiatry was not a popular career choice among medical students, even though medical school placements are rated favorably. This has resulted in a significant shortage of psychiatrists in the United States and elsewhere. Strategies to address this shortfall have included the use of short 'taster' placements early in the medical school curriculum and attempts to extend psychiatry services further using telemedicine technologies and other methods. Recently, however, there has been an increase in the number of medical students entering into a psychiatry residency. There are several reasons for this surge including the interesting nature of the field, growing interest in genetic biomarkers involved in psychiatric diagnoses, and newer pharmaceuticals on the drug market to treat psychiatric illnesses.
Subspecialties
The field of psychiatry has many subspecialties that require additional training and certification by the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology (ABPN). Such subspecialties include:
- Addiction psychiatry, addiction medicine
- Brain Injury Medicine
- Child and adolescent psychiatry
- Clinical neurophysiology
- Consultation-liaison psychiatry
- Forensic psychiatry
- Geriatric psychiatry
- Hospice and palliative medicine
- Sleep medicine
Additional psychiatry subspecialties, for which the ABPN does not provide formal certification, include:
- Biological psychiatry
- Cognitive diseases, as in various forms of dementia
- Community psychiatry
- Cross-cultural psychiatry
- Emergency psychiatry
- Evolutionary Psychiatry
- Global mental health
- Learning disabilities
- Military psychiatry
- Neurodevelopmental disorders
- Neuropsychiatry
- Social psychiatry
Addiction psychiatry focuses on evaluation and treatment of individuals with alcohol, drug, or other substance-related disorders, and of individuals with dual diagnosis of substance-related and other psychiatric disorders. Biological psychiatry is an approach to psychiatry that aims to understand mental disorders in terms of the biological function of the nervous system. Child and adolescent psychiatry is the branch of psychiatry that specializes in work with children, teenagers, and their families. Community psychiatry is an approach that reflects an inclusive public health perspective and is practiced in community mental health services. Cross-cultural psychiatry is a branch of psychiatry concerned with the cultural and ethnic context of mental disorder and psychiatric services. Emergency psychiatry is the clinical application of psychiatry in emergency settings. Forensic psychiatry utilizes medical science generally, and psychiatric knowledge and assessment methods in particular, to help answer legal questions. Geriatric psychiatry is a branch of psychiatry dealing with the study, prevention, and treatment of mental disorders in the elderly. Global Mental Health is an area of study, research and practice that places a priority on improving mental health and achieving equity in mental health for all people worldwide, although some scholars consider it to be a neo-colonial, culturally insensitive project. Liaison psychiatry is the branch of psychiatry that specializes in the interface between other medical specialties and psychiatry. Military psychiatry covers special aspects of psychiatry and mental disorders within the military context. Neuropsychiatry is a branch of medicine dealing with mental disorders attributable to diseases of the nervous system. Social psychiatry is a branch of psychiatry that focuses on the interpersonal and cultural context of mental disorder and mental well-being.
In larger healthcare organizations, psychiatrists often serve in senior management roles, where they are responsible for the efficient and effective delivery of mental health services for the organization's constituents. For example, the Chief of Mental Health Services at most VA medical centers is usually a psychiatrist, although psychologists occasionally are selected for the position as well.
In the United States, psychiatry is one of the few specialties which qualify for further education and board-certification in pain medicine, palliative medicine, and sleep medicine.
Research
Psychiatric research is, by its very nature, interdisciplinary; combining social, biological and psychological perspectives in attempt to understand the nature and treatment of mental disorders. Clinical and research psychiatrists study basic and clinical psychiatric topics at research institutions and publish articles in journals. Under the supervision of institutional review boards, psychiatric clinical researchers look at topics such as neuroimaging, genetics, and psychopharmacology in order to enhance diagnostic validity and reliability, to discover new treatment methods, and to classify new mental disorders.
Clinical application
Diagnostic systems
Psychiatric diagnoses take place in a wide variety of settings and are performed by many different health professionals. Therefore, the diagnostic procedure may vary greatly based upon these factors. Typically, though, a psychiatric diagnosis utilizes a differential diagnosis procedure where a mental status examination and physical examination is conducted, with pathological, psychopathological or psychosocial histories obtained, and sometimes neuroimages or other neurophysiological measurements are taken, or personality tests or cognitive tests administered. In some cases, a brain scan might be used to rule out other medical illnesses, but at this time relying on brain scans alone cannot accurately diagnose a mental illness or tell the risk of getting a mental illness in the future. Some clinicians are beginning to utilize genetics and speech during the diagnostic process but on the whole these remain research topics.
Diagnostic manuals
Three main diagnostic manuals used to classify mental health conditions are in use today. The ICD-10 is produced and published by the World Health Organization, includes a section on psychiatric conditions, and is used worldwide. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, produced and published by the American Psychiatric Association, is primarily focused on mental health conditions and is the main classification tool in the United States. It is currently in its fifth revised edition and is also used worldwide. The Chinese Society of Psychiatry has also produced a diagnostic manual, the Chinese Classification of Mental Disorders.
The stated intention of diagnostic manuals is typically to develop replicable and clinically useful categories and criteria, to facilitate consensus and agreed upon standards, whilst being atheoretical as regards etiology. However, the categories are nevertheless based on particular psychiatric theories and data; they are broad and often specified by numerous possible combinations of symptoms, and many of the categories overlap in symptomology or typically occur together. While originally intended only as a guide for experienced clinicians trained in its use, the nomenclature is now widely used by clinicians, administrators and insurance companies in many countries.
The DSM has attracted praise for standardizing psychiatric diagnostic categories and criteria. It has also attracted controversy and criticism. Some critics argue that the DSM represents an unscientific system that enshrines the opinions of a few powerful psychiatrists. There are ongoing issues concerning the validity and reliability of the diagnostic categories; the reliance on superficial symptoms; the use of artificial dividing lines between categories and from 'normality'; possible cultural bias; medicalization of human distress and financial conflicts of interest, including with the practice of psychiatrists and with the pharmaceutical industry; political controversies about the inclusion or exclusion of diagnoses from the manual, in general or in regard to specific issues; and the experience of those who are most directly affected by the manual by being diagnosed, including the consumer/survivor movement. The publication of the DSM, with tightly guarded copyrights, now makes APA over $5 million a year, historically adding up to over $100 million.
Treatment
General considerations
Individuals with mental health conditions are commonly referred to as patients but may also be called clients, consumers, or service recipients. They may come under the care of a psychiatric physician or other psychiatric practitioners by various paths, the two most common being self-referral or referral by a primary care physician. Alternatively, a person may be referred by hospital medical staff, by court order, involuntary commitment, or, in the UK and Australia, by sectioning under a mental health law.
Persons who undergo a psychiatric assessment are evaluated by a psychiatrist for their mental and physical condition. This usually involves interviewing the person and often obtaining information from other sources such as other health and social care professionals, relatives, associates, law enforcement personnel, emergency medical personnel, and psychiatric rating scales. A mental status examination is carried out, and a physical examination is usually performed to establish or exclude other illnesses that may be contributing to the alleged psychiatric problems. A physical examination may also serve to identify any signs of self-harm; this examination is often performed by someone other than the psychiatrist, especially if blood tests and medical imaging are performed.
Like most medications, psychiatric medications can cause adverse effects in patients, and some require ongoing therapeutic drug monitoring, for instance full blood counts serum drug levels, renal function, liver function or thyroid function. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is sometimes administered for serious and disabling conditions, such as those unresponsive to medication. The efficacy and adverse effects of psychiatric drugs may vary from patient to patient.
For many years, controversy has surrounded the use of involuntary treatment and use of the term "lack of insight" in describing patients. Mental health laws vary significantly among jurisdictions, but in many cases, involuntary psychiatric treatment is permitted when there is deemed to be a risk to the patient or others due to the patient's illness. Involuntary treatment refers to treatment that occurs based on the treating physician's recommendations without requiring consent from the patient.
Mental health issues such as mood disorders and schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders were the most common principle diagnoses for Medicaid non-elderly super-utilizers in the United States in 2012.
Inpatient treatment
Psychiatric treatments have changed over the past several decades. In the past, psychiatric patients were often hospitalized for six months or more, with some cases involving hospitalization for many years.
Average inpatient psychiatric treatment stay has decreased significantly since the 1960s, a trend known as deinstitutionalization. Today in most countries, people receiving psychiatric treatment are more likely to be seen as outpatients. If hospitalization is required, the average hospital stay is around one to two weeks, with only a small number receiving long-term hospitalization. However, in Japan psychiatric hospitals continue to keep patients for long periods, sometimes even keeping them in physical restraints, strapped to their beds for periods of weeks or months.
Psychiatric inpatients are people admitted to a hospital or clinic to receive psychiatric care. Some are admitted involuntarily, perhaps committed to a secure hospital, or in some jurisdictions to a facility within the prison system. In many countries including the United States and Canada, the criteria for involuntary admission vary with local jurisdiction. They may be as broad as having a mental health condition, or as narrow as being an immediate danger to themselves or others. Bed availability is often the real determinant of admission decisions to hard pressed public facilities. European Human Rights legislation restricts detention to medically certified cases of mental disorder, and adds a right to timely judicial review of detention.
People may be admitted voluntarily if the treating doctor considers that safety isn't compromised by this less restrictive option. Inpatient psychiatric wards may be secure (for those thought to have a particular risk of violence or self-harm) or unlocked/open. Some wards are mixed-sex whilst same-sex wards are increasingly favored to protect women inpatients. Once in the care of a hospital, people are assessed, monitored, and often given medication and care from a multidisciplinary team, which may include physicians, pharmacists, psychiatric nurse practitioners, psychiatric nurses, clinical psychologists, psychotherapists, psychiatric social workers, occupational therapists and social workers. If a person receiving treatment in a psychiatric hospital is assessed as at particular risk of harming themselves or others, they may be put on constant or intermittent one-to-one supervision and may be put in physical restraints or medicated. People on inpatient wards may be allowed leave for periods of time, either accompanied or on their own.
In many developed countries there has been a massive reduction in psychiatric beds since the mid 20th century, with the growth of community care. Standards of inpatient care remain a challenge in some public and private facilities, due to levels of funding, and facilities in developing countries are typically grossly inadequate for the same reason. Even in developed countries, programs in public hospitals vary widely. Some may offer structured activities and therapies offered from many perspectives while others may only have the funding for medicating and monitoring patients. This may be problematic in that the maximum amount of therapeutic work might not actually take place in the hospital setting. This is why hospitals are increasingly used in limited situations and moments of crisis where patients are a direct threat to themselves or others. Alternatives to psychiatric hospitals that may actively offer more therapeutic approaches include rehabilitation centers or "rehab" as popularly termed.
Outpatient treatment
Outpatient treatment involves periodic visits to a psychiatrist for consultation in his or her office, or at a community-based outpatient clinic. Initial appointments, at which the psychiatrist conducts a psychiatric assessment or evaluation of the patient, are typically 45 to 75 minutes in length. Follow-up appointments are generally shorter in duration, i.e., 15 to 30 minutes, with a focus on making medication adjustments, reviewing potential medication interactions, considering the impact of other medical disorders on the patient's mental and emotional functioning, and counseling patients regarding changes they might make to facilitate healing and remission of symptoms (e.g., exercise, cognitive therapy techniques, sleep hygiene—to name just a few). The frequency with which a psychiatrist sees people in treatment varies widely, from once a week to twice a year, depending on the type, severity and stability of each person's condition, and depending on what the clinician and patient decide would be best.
Increasingly, psychiatrists are limiting their practices to psychopharmacology (prescribing medications), as opposed to previous practice in which a psychiatrist would provide traditional 50-minute psychotherapy sessions, of which psychopharmacology would be a part, but most of the consultation sessions consisted of "talk therapy." This shift began in the early 1980s and accelerated in the 1990s and 2000s. A major reason for this change was the advent of managed care insurance plans, which began to limit reimbursement for psychotherapy sessions provided by psychiatrists. The underlying assumption was that psychopharmacology was at least as effective as psychotherapy, and it could be delivered more efficiently because less time is required for the appointment. For example, most psychiatrists schedule three or four follow-up appointments per hour, as opposed to seeing one patient per hour in the traditional psychotherapy model. Because of this shift in practice patterns, psychiatrists often refer patients whom they think would benefit from psychotherapy to other mental health professionals, e.g., clinical social workers and psychologists.
History
The earliest known texts on mental disorders are from ancient India and include the Ayurvedic text, Charaka Samhita. The first hospitals for curing mental illness were established in India during the 3rd century BCE.
The Greeks also created early manuscripts about mental disorders. In the 4th century BCE, Hippocrates theorized that physiological abnormalities may be the root of mental disorders. In 4th to 5th Century B.C. Greece, Hippocrates wrote that he visited Democritus and found him in his garden cutting open animals. Democritus explained that he was attempting to discover the cause of madness and melancholy. Hippocrates praised his work. Democritus had with him a book on madness and melancholy. During the 5th century BCE, mental disorders, especially those with psychotic traits, were considered supernatural in origin, a view which existed throughout ancient Greece and Rome, as well as Egyptian regions. Religious leaders often turned to versions of exorcism to treat mental disorders often utilizing methods that many consider to be cruel or barbaric methods. Trepanning was one of these methods used throughout history.
The Islamic Golden Age fostered early studies in Islamic psychology and psychiatry, with many scholars writing about mental disorders. The Persian physician Muhammad ibn Zakariya al-Razi, also known as "Rhazes", wrote texts about psychiatric conditions in the 9th century. As chief physician of a hospital in Baghdad, he was also the director of one of the first psychiatric wards in the world. Two of his works in particular, El-Mansuri and Al-Hawi, provide descriptions and treatments for mental illnesses.
Abu Zayd al-Balkhi, was a Persian polymath during the 9th and 10th centuries and one of the first to classify neurotic disorders. He pioneered cognitive therapy in order to treat each of these classified neurotic disorders. He classified neurosis into four emotional disorders: fear and anxiety, anger and aggression, sadness and depression, and obsession. Al-Balkhi further classified three types of depression: normal depression or sadness (huzn), endogenous depression originating from within the body, and reactive clinical depression originating from outside the body.
The first bimaristan was founded in Baghdad in the 9th century, and several others of increasing complexity were created throughout the Arab world in the following centuries. Some of the bimaristans contained wards dedicated to the care of mentally ill patients, most of whom suffered from debilitating illnesses or exhibited violence. Specialist hospitals such as Bethlem Royal Hospital in London were built in medieval Europe from the 13th century to treat mental disorders, but were used only as custodial institutions and did not provide any type of treatment.
The beginning of psychiatry as a medical specialty is dated to the middle of the nineteenth century, although its germination can be traced to the late eighteenth century. In the late 17th century, privately run asylums for the insane began to proliferate and expand in size. In 1713 the Bethel Hospital Norwich was opened, the first purpose-built asylum in England. In 1656, Louis XIV of France created a public system of hospitals for those suffering from mental disorders, but as in England, no real treatment was applied.
During the Enlightenment attitudes towards the mentally ill began to change. It came to be viewed as a disorder that required compassionate treatment. In 1758 English physician William Battie wrote his Treatise on Madness on the management of mental disorder. It was a critique aimed particularly at the Bethlem Hospital, where a conservative regime continued to use barbaric custodial treatment. Battie argued for a tailored management of patients entailing cleanliness, good food, fresh air, and distraction from friends and family. He argued that mental disorder originated from dysfunction of the material brain and body rather than the internal workings of the mind.
The introduction of moral treatment was initiated independently by the French doctor Philippe Pinel and the English Quaker William Tuke. In 1792 Pinel became the chief physician at the Bicêtre Hospital. Patients were allowed to move freely about the hospital grounds, and eventually dark dungeons were replaced with sunny, well-ventilated rooms. Pinel's student and successor, Jean Esquirol (1772–1840), went on to help establish 10 new mental hospitals that operated on the same principles.
Although Tuke, Pinel and others had tried to do away with physical restraint, it remained widespread into the 19th century. At the Lincoln Asylum in England, Robert Gardiner Hill, with the support of Edward Parker Charlesworth, pioneered a mode of treatment that suited "all types" of patients, so that mechanical restraints and coercion could be dispensed with — a situation he finally achieved in 1838. In 1839 Sergeant John Adams and Dr. John Conolly were impressed by the work of Hill, and introduced the method into their Hanwell Asylum, by then the largest in the country.
The modern era of institutionalized provision for the care of the mentally ill, began in the early 19th century with a large state-led effort. In England, the Lunacy Act 1845 was an important landmark in the treatment of the mentally ill, as it explicitly changed the status of mentally ill people to patients who required treatment. All asylums were required to have written regulations and to have a resident qualified physician. In 1838, France enacted a law to regulate both the admissions into asylums and asylum services across the country. In the United States, the erection of state asylums began with the first law for the creation of one in New York, passed in 1842. The Utica State Hospital was opened around 1850. Many state hospitals in the United States were built in the 1850s and 1860s on the Kirkbride Plan, an architectural style meant to have curative effect.
At the turn of the century, England and France combined had only a few hundred individuals in asylums. By the late 1890s and early 1900s, this number had risen to the hundreds of thousands. However, the idea that mental illness could be ameliorated through institutionalization ran into difficulties. Psychiatrists were pressured by an ever-increasing patient population, and asylums again became almost indistinguishable from custodial institutions.
In the early 1800s, psychiatry made advances in the diagnosis of mental illness by broadening the category of mental disease to include mood disorders, in addition to disease level delusion or irrationality. The 20th century introduced a new psychiatry into the world, with different perspectives of looking at mental disorders. For Emil Kraepelin, the initial ideas behind biological psychiatry, stating that the different mental disorders are all biological in nature, evolved into a new concept of "nerves", and psychiatry became a rough approximation of neurology and neuropsychiatry. Following Sigmund Freud's pioneering work, ideas stemming from psychoanalytic theory also began to take root in psychiatry. The psychoanalytic theory became popular among psychiatrists because it allowed the patients to be treated in private practices instead of warehoused in asylums.
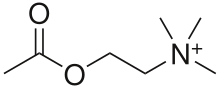
By the 1970s, however, the psychoanalytic school of thought became marginalized within the field. Biological psychiatry reemerged during this time. Psychopharmacology and neurochemistry became the integral parts of psychiatry starting with Otto Loewi's discovery of the neuromodulatory properties of acetylcholine; thus identifying it as the first-known neurotransmitter. Subsequently it has been shown that different neurotransmitters have different and multiple functions in regulation of behaviour. In a wide range of studies in neurochemistry using human and animal samples, individual differences in neurotransmitters' production, reuptake, receptors' density and locations were linked to differences in dispositions for specific psychiatric disorders. For example, the discovery of chlorpromazine's effectiveness in treating schizophrenia in 1952 revolutionized treatment of the disorder, as did lithium carbonate's ability to stabilize mood highs and lows in bipolar disorder in 1948. Psychotherapy was still utilized, but as a treatment for psychosocial issues. This proved the idea of neurochemical nature of many psychiatric disorders.
Another approach to look for biomarkers of psychiatric disorders is Neuroimaging that was first utilized as a tool for psychiatry in the 1980s.
In 1963, US president John F. Kennedy introduced legislation delegating the National Institute of Mental Health to administer Community Mental Health Centers for those being discharged from state psychiatric hospitals. Later, though, the Community Mental Health Centers focus shifted to providing psychotherapy for those suffering from acute but less serious mental disorders. Ultimately there were no arrangements made for actively following and treating severely mentally ill patients who were being discharged from hospitals, resulting in a large population of chronically homeless people suffering from mental illness.
Controversy and criticism
Controversy has surrounded psychiatry, with scholars producing critiques. It has been argued that psychiatry: is too influenced by ideas from medicine, causing it to misunderstand the nature of mental distress; that its use of drugs is in part due to lobbying by drug companies resulting in distortion of research; that the concept of "mental illness" is often used to label and control those with beliefs and behaviours that the majority of people disagree with; and that it confuses disorders of the mind with disorders of the brain that can be treated with drugs. Critique of psychiatry from within the field comes from the critical psychiatry group in the UK.
The term "anti-psychiatry" was coined by psychiatrist David Cooper in 1967 and was later made popular by Thomas Szasz. The word "Antipsychiatrie" was already used in Germany in 1904. The basic premise of the anti-psychiatry movement is that psychiatrists attempt to classify "normal" people as "deviant;" psychiatric treatments are ultimately more damaging than helpful to patients; and psychiatry's history involves (what may now be seen as) dangerous treatments, such as the frontal lobectomy (commonly called a lobotomy). Several former patient groups have been formed often referring to themselves as "survivors." In 1973, the Rosenhan experiment was conducted to determine the validity of psychiatric diagnosis. Volunteers feigned hallucinations to enter psychiatric hospitals, and acted normally afterwards. They were diagnosed with psychiatric disorders and were given antipsychotic drugs. The study was conducted by psychologist David Rosenhan, a Stanford University professor, and published by the journal Science under the title "On being sane in insane places". However, the neutrality of the project is nowadays often questioned and the project itself is seen by many experts as manipulated.
The Church of Scientology is critical of psychiatry, whereas others have questioned the veracity of information the Church of Scientology provides to the public.