From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
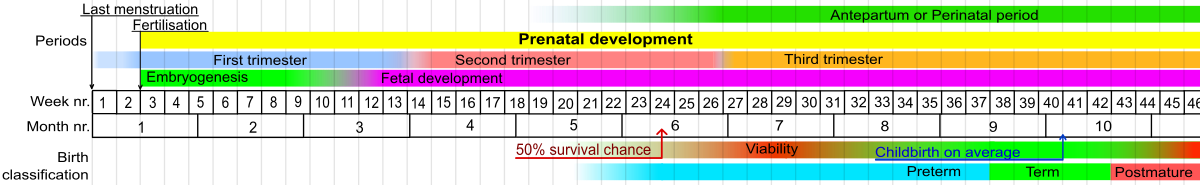
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal development begins from the ninth week after fertilization (or eleventh week gestational age) and continues until birth.
Prenatal development is a continuum, with no clear defining feature
distinguishing an embryo from a fetus. However, a fetus is characterized
by the presence of all the major body organs, though they will not yet
be fully developed and functional and some not yet situated in their
final anatomical location.
Etymology
The word fetus (plural fetuses or feti) is related to the Latin fētus ("offspring", "bringing forth", "hatching of young") and the Greek "φυτώ" to plant. The word "fetus" was used by Ovid in Metamorphoses, book 1, line 104.
The predominant British, Irish, and Commonwealth spelling is foetus, which has been in use since at least 1594. The spelling with -oe- arose in Late Latin, in which the distinction between the vowel sounds -oe- and -e- had been lost. This spelling is the most common in most Commonwealth nations, except in the medical literature, where fetus is used. The more classical spelling fetus is used in Canada and the United States. In addition, fetus is now the standard English spelling throughout the world in medical journals. The spelling faetus was also used historically.
Development in humans
Weeks 9 to 16 (2 to 3.6 months)
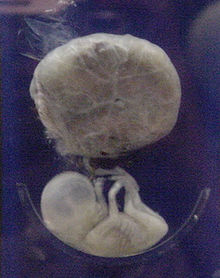
A human fetus, attached to
placenta, at three months gestational age.
In humans, the fetal stage starts nine weeks after fertilization. At the start of the fetal stage, the fetus is typically about 30 millimetres (1+1⁄4 in) in length from crown-rump, and weighs about 8 grams. The head makes up nearly half of the size of the fetus. Breathing-like movements of the fetus are necessary for the stimulation of lung development, rather than for obtaining oxygen.
The heart, hands, feet, brain and other organs are present, but are
only at the beginning of development and have minimal operation.
At this point in development, uncontrolled movements and twitches occur as muscles, the brain, and pathways begin to develop.
Weeks 17 to 25 (3.6 to 6.6 months)
A woman pregnant for the first time (nulliparous) typically feels fetal movements at about 21 weeks, whereas a woman who has given birth before will typically feel movements by 20 weeks. By the end of the fifth month, the fetus is about 20 cm (8 in) long.
Weeks 26 to 38 (6.6 to 8.6 months)
The amount of body fat rapidly increases. Lungs are not fully mature. Neural connections between the sensory cortex and thalamus
develop as early as 24 weeks' gestational age, but the first evidence
of their function does not occur until around 30 weeks, when minimal consciousness, dreaming, and the ability to feel pain emerges. Bones are fully developed, but are still soft and pliable. Iron, calcium, and phosphorus become more abundant. Fingernails reach the end of the fingertips. The lanugo,
or fine hair, begins to disappear, until it is gone except on the upper
arms and shoulders. Small breast buds are present on both sexes. Head
hair becomes coarse and thicker. Birth is imminent and occurs around the
38th week after fertilization. The fetus is considered full-term
between weeks 36 and 40, when it is sufficiently developed for life
outside the uterus.
It may be 48 to 53 cm (19 to 21 in) in length, when born. Control of
movement is limited at birth, and purposeful voluntary movements develop
all the way until puberty.
Variation in growth
There is much variation in the growth of the human fetus. When fetal size is less than expected, the condition is known as intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) also called fetal growth restriction (FGR); factors affecting fetal growth can be maternal, placental, or fetal.
Maternal factors include maternal weight, body mass index, nutritional state, emotional stress, toxin exposure (including tobacco, alcohol, heroin, and other drugs which can also harm the fetus in other ways), and uterine blood flow.
Placental factors include size, microstructure (densities and architecture), umbilical blood flow, transporters and binding proteins, nutrient utilization and nutrient production.
Fetal factors include the fetus genome, nutrient production, and hormone output. Also, female fetuses tend to weigh less than males, at full term.
Fetal growth is often classified as follows: small for
gestational age (SGA), appropriate for gestational age (AGA), and large
for gestational age (LGA). SGA can result in low birth weight, although premature birth can also result in low birth weight. Low birth weight increases risk for perinatal mortality (death shortly after birth), asphyxia, hypothermia, polycythemia, hypocalcemia, immune dysfunction, neurologic
abnormalities, and other long-term health problems. SGA may be
associated with growth delay, or it may instead be associated with
absolute stunting of growth.
Viability
Fetal viability
refers to a point in fetal development at which the fetus may survive
outside the womb. The lower limit of viability is approximately 5+3⁄4 months gestational age and is usually later.
There is no sharp limit of development, age, or weight at which a fetus automatically becomes viable. According to data from 2003 to 2005, survival rates are 20–35% for babies born at 23 weeks of gestation (5+3⁄4 months); 50–70% at 24–25 weeks (6 – 6+1⁄4 months); and >90% at 26–27 weeks (6+1⁄2 – 6+3⁄4 months) and over. It is rare for a baby weighing less than 500 g (1 lb 2 oz) to survive.
When such premature babies are born, the main causes of mortality
are that the respiratory system and the central nervous system are not
completely differentiated. If given expert postnatal care, some preterm
babies weighing less than 500 g (1 lb 2 oz) may survive, and are
referred to as extremely low birth weight or immature infants.
Preterm birth is the most common cause of infant mortality, causing almost 30 percent of neonatal deaths. At an occurrence rate of 5% to 18% of all deliveries, it is also more common than postmature birth, which occurs in 3% to 12% of pregnancies.
Circulatory system
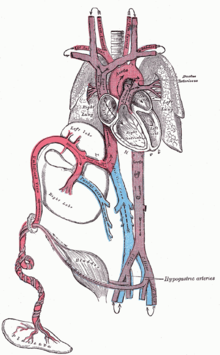
Before birth
The heart and blood vessels of the circulatory system, form relatively early during embryonic development,
but continue to grow and develop in complexity in the growing fetus. A
functional circulatory system is a biological necessity, since mammalian
tissues can not grow more than a few cell layers thick without an
active blood supply. The prenatal circulation of blood is different from
postnatal circulation, mainly because the lungs are not in use. The
fetus obtains oxygen and nutrients from the mother through the placenta and the umbilical cord.
Blood from the placenta is carried to the fetus by the umbilical vein. About half of this enters the fetal ductus venosus and is carried to the inferior vena cava, while the other half enters the liver
proper from the inferior border of the liver. The branch of the
umbilical vein that supplies the right lobe of the liver first joins
with the portal vein. The blood then moves to the right atrium of the heart. In the fetus, there is an opening between the right and left atrium (the foramen ovale), and most of the blood flows from the right into the left atrium, thus bypassing pulmonary circulation. The majority of blood flow is into the left ventricle from where it is pumped through the aorta
into the body. Some of the blood moves from the aorta through the
internal iliac arteries to the umbilical arteries, and re-enters the
placenta, where carbon dioxide and other waste products from the fetus are taken up and enter the mother's circulation.
Some of the blood from the right atrium does not enter the left atrium, but enters the right ventricle and is pumped into the pulmonary artery. In the fetus, there is a special connection between the pulmonary artery and the aorta, called the ductus arteriosus,
which directs most of this blood away from the lungs (which are not
being used for respiration at this point as the fetus is suspended in amniotic fluid).
Postnatal development
With the first breath after birth, the system changes suddenly. Pulmonary resistance is reduced dramatically, prompting more blood to move into the pulmonary arteries from the right atrium and ventricle of the heart and less to flow through the foramen ovale into the left atrium. The blood from the lungs travels through the pulmonary veins to the left atrium, producing an increase in pressure that pushes the septum primum against the septum secundum, closing the foramen ovale and completing the separation of the newborn's circulatory system into the standard left and right sides. Thereafter, the foramen ovale is known as the fossa ovalis.
The ductus arteriosus normally closes within one or two days of birth, leaving the ligamentum arteriosum, while the umbilical vein and ductus venosus usually closes within two to five days after birth, leaving, respectively, the liver's ligamentum teres and ligamentum venosus.
Immune system
The placenta functions as a maternal-fetal barrier against the transmission of microbes. When this is insufficient, mother-to-child transmission of infectious diseases can occur.
Maternal IgG antibodies cross the placenta, giving the fetus passive immunity
against those diseases for which the mother has antibodies. This
transfer of antibodies in humans begins as early as the fifth month
(gestational age) and certainly by the sixth month.
Developmental problems
A developing fetus is highly susceptible to anomalies in its growth and metabolism, increasing the risk of birth defects. One area of concern is the lifestyle choices made during pregnancy. Diet is especially important in the early stages of development. Studies show that supplementation of the person's diet with folic acid reduces the risk of spina bifida and other neural tube
defects. Another dietary concern is whether breakfast is eaten.
Skipping breakfast could lead to extended periods of lower than normal
nutrients in the maternal blood, leading to a higher risk of prematurity, or birth defects.
Alcohol consumption may increase the risk of the development of fetal alcohol syndrome, a condition leading to intellectual disability in some infants. Smoking during pregnancy may also lead to miscarriages and low birth weight
(2,500 grams (5 pounds 8 ounces). Low birth weight is a concern for
medical providers due to the tendency of these infants, described as "premature by weight", to have a higher risk of secondary medical problems.
X-rays
are known to have possible adverse effects on the development of the
fetus, and the risks need to be weighed against the benefits.
Congenital disorders are acquired before birth. Infants with certain congenital heart defects
can survive only as long as the ductus remains open: in such cases the
closure of the ductus can be delayed by the administration of prostaglandins to permit sufficient time for the surgical correction of the anomalies. Conversely, in cases of patent ductus arteriosus,
where the ductus does not properly close, drugs that inhibit
prostaglandin synthesis can be used to encourage its closure, so that
surgery can be avoided.
Other heart birth defects include ventricular septal defect, pulmonary atresia, and tetralogy of Fallot.
An abdominal pregnancy can result in the death of the fetus and where this is rarely not resolved it can lead to its formation into a lithopedion.
Fetal pain
Fetal pain,
its existence and its implications are debated politically and
academically. According to the conclusions of a review published in
2005, "Evidence regarding the capacity for fetal pain is limited but
indicates that fetal perception of pain is unlikely before the third
trimester." However, developmental neurobiologists argue that the establishment of thalamocortical connections (at about 6+1⁄2 months) is an essential event with regard to fetal perception of pain.
Nevertheless, the perception of pain involves sensory, emotional and
cognitive factors and it is "impossible to know" when pain is
experienced, even if it is known when thalamocortical connections are
established. Some authors argue that fetal pain is possible from the second half of pregnancy:
“The available scientific evidence makes it possible, even probable,
that fetal pain perception occurs well before late gestation” wrote KJS
Anand in the journal of the IASP.
Whether a fetus has the ability to feel pain and suffering is part of the abortion debate. In the United States, for example, anti-abortion advocates
have proposed legislation that would require providers of abortions to
inform pregnant women that their fetuses may feel pain during the
procedure and that would require each person to accept or decline anesthesia for the fetus.
Legal and social issues
Abortion of a human pregnancy is legal and/or tolerated in most countries, although with gestational time limits that normally prohibit late-term abortions.
Other animals
Fourteen phases of elephant development before birth
A fetus is a stage in the prenatal development of viviparous organisms. This stage lies between embryogenesis and birth.
Many vertebrates have fetal stages, ranging from most mammals to many
fish. In addition, some invertebrates bear live young, including some
species of onychophora and many arthropods.
The fetuses of most mammals are situated similarly to the human fetus within their mothers. However, the anatomy of the area surrounding a fetus is different in litter-bearing animals compared to humans: each fetus of a litter-bearing animal is surrounded by placental tissue and is lodged along one of two long uteri instead of the single uterus found in a human female.
Development at birth varies considerably among animals, and even among mammals. Altricial species are relatively helpless at birth and require considerable parental care and protection. In contrast, precocial
animals are born with open eyes, have hair or down, have large brains,
and are immediately mobile and somewhat able to flee from, or defend
themselves against, predators. Primates are precocial at birth, with the exception of humans.
The duration of gestation in placental mammals varies from 18 days in jumping mice to 23 months in elephants. Generally speaking, fetuses of larger land mammals require longer gestation periods.
The benefits of a fetal stage means that young are more developed
when they are born. Therefore, they may need less parental care and may
be better able to fend for themselves. However, carrying fetuses exerts
costs on the mother, who must take on extra food to fuel the growth of
her offspring, and whose mobility and comfort may be affected
(especially toward the end of the fetal stage).
In some instances, the presence of a fetal stage may allow organisms to time the birth of their offspring to a favorable season.