First Nations (French: Premières Nations) is a term used to identify those Indigenous Canadian peoples who are neither Inuit nor Métis. Traditionally, First Nations in Canada were peoples who lived south of the tree line, and mainly south of the Arctic Circle. There are 634 recognized First Nations governments or bands across Canada. Roughly half are located in the provinces of Ontario and British Columbia.
Under Charter jurisprudence, First Nations are a "designated group," along with women, visible minorities, and people with physical or mental disabilities. First Nations are not defined as a visible minority by the criteria of Statistics Canada.
North American indigenous peoples have cultures spanning thousands of years. Some of their oral traditions accurately describe historical events, such as the Cascadia earthquake of 1700 and the 18th-century Tseax Cone eruption. Written records began with the arrival of European explorers and colonists during the Age of Discovery in the late 15th century. European accounts by trappers, traders, explorers, and missionaries give important evidence of early contact culture. In addition, archeological and anthropological research, as well as linguistics, have helped scholars piece together an understanding of ancient cultures and historic peoples.
Although not without conflict, early colonists' interactions with First Nations, Métis, and Inuit populations were less combative than the often violent battles between colonists and native peoples in the United States, and far less than those of other British colonies in modern-day Australia and South Africa.
Terminology
Collectively, First Nations, Inuit, and Métis (FNIM) peoples constitute Indigenous peoples in Canada, Indigenous peoples of the Americas, or "first peoples". "First Nation" as a term became officially used by the government beginning in 1980s to replace the term "Indian band" in referring to groups of Indians with common government and language. The First Nations people had begun to identify by this term during 1970s activism, in order to avoid using the word "Indian", which some considered offensive. No legal definition of the term exists.
Some indigenous peoples in Canada have also adopted the term First Nation to replace the word "band" in the formal name of their community. A band is a "body of Indians (a) for whose use and benefit in common lands ... have been set apart, (b) ... moneys are held ... or (c) declared ... to be a band for the purposes of", according to the Indian Act by the Canadian Crown.
The term 'Indian' is a misnomer, given to indigenous peoples of North America by European explorers who erroneously thought they had landed in the East Indies. The use of the term Native Americans, which the government and others have adopted in the United States, is not common in Canada. It refers more specifically to the Indigenous peoples residing within the boundaries of the US. The parallel term "Native Canadian" is not commonly used, but "Native" (in English) and "Autochtone" (in Canadian French; from the Greek auto, own, and chthon, land) are. Under the Royal Proclamation of 1763, also known as the "Indian Magna Carta," the Crown referred to indigenous peoples in British territory as tribes or nations. The term First Nations is capitalized. Bands and nations may have slightly different meanings.
Within Canada, the term First Nations has come into general use for indigenous peoples other than Inuit and Métis. Individuals using the term outside Canada include Indigenous Australians, U.S. tribes within the Pacific Northwest, as well as supporters of the Cascadian independence movement. The singular, commonly used on culturally politicized reserves, is the term "First Nations person" (when gender-specific, "First Nations man" or "First Nations woman"). Since the late 20th century, members of various nations more frequently identify by their tribal or national identity only, e.g., "I'm Haida", or "We're Kwantlens", in recognition of the distinct First Nations.
History
Nationhood
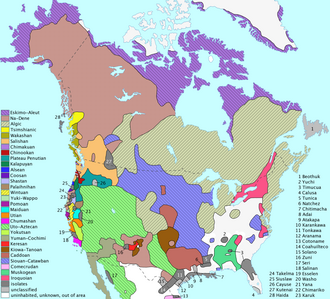
- First Nations by linguistic-cultural area: List of First Nations peoples
First Nations peoples had settled and established trade routes across what is now Canada by 1,000 BC to 500 BC. Communities developed, each with its own culture, customs, and character. In the northwest were the Athapaskan-speaking peoples, Slavey, Tłı̨chǫ, Tutchone-speaking peoples, and Tlingit. Along the Pacific coast were the Haida, Tsimshian, Salish, Kwakiutl, Nuu-chah-nulth, Nisga'a and Gitxsan. In the plains were the Blackfoot, Kainai, Sarcee and Northern Peigan. In the northern woodlands were the Cree and Chipewyan. Around the Great Lakes were the Anishinaabe, Algonquin, Iroquois and Wyandot. Along the Atlantic coast were the Beothuk, Maliseet, Innu, Abenaki and Mi'kmaq.
The Blackfoot Confederacy resides in the Great Plains of Montana and Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbia and Saskatchewan. The name Blackfoot came from the dye or paint on the bottoms the their leather moccasins. One account claimed that the Blackfoot Confederacies walked through the ashes of prairie fires, which in turn blackened the bottoms of their moccasins. They had migrated onto the Great Plains from the Plateau area. The Blackfoot may have lived in their homeland since the end of the Pleistocene 12,000 years ago. For thousands of years, they managed the prairie to support bison herds and cultivated berries and edible roots. Historically, they allowed only legitimate traders into their territory, making treaties only when the bison herds were exterminated in the 1870s.
Pre-contact Squamish history is passed on through oral tradition of the Squamish indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast. Prior to colonization and the introduction of writing had only oral tradition as a way to transmit stories, law, and knowledge across generations. The writing system established in the 1970s uses the Latin alphabet as a base. Knowledgeable elders have the responsibility to pass historical knowledge to the next generation. People lived and prospered for thousands of years until the Great Flood. In another story, after the Flood, they repopulated from the villages of Schenks and Chekwelp, located at Gibsons. When the water lines receded, the first Squamish came to be. The first man, named Tseḵánchten, built his longhouse in the village, and later on another man named Xelálten, appeared on his longhouse roof and sent by the Creator, or in the Squamish language keke7nex siyam. He called this man his brother. It was from these two men that the population began to rise and the Squamish spread back through their territory.
The Iroquois influence extended from northern New York into what are now southern Ontario and the Montreal area of modern Quebec. The Iroquois Confederacy is, from oral tradition, formed circa 1142. Adept at cultivating the Three Sisters (maize/beans/squash), the Iroquois became powerful because of their confederacy. Gradually the Algonquians adopted agricultural practises enabling larger populations to be sustained.
The Assiniboine were close allies and trading partners of the Cree, engaging in wars against the Gros Ventres alongside them, and later fighting the Blackfoot. A Plains people, they went no further north than the North Saskatchewan River and purchased a great deal of European trade goods through Cree middlemen from the Hudson's Bay Company. The lifestyle of this group was semi-nomadic, and they followed the herds of bison during the warmer months. They traded with European traders, and worked with the Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara tribes.
In the earliest oral history, the Algonquins were from the Atlantic coast. Together with other Anicinàpek, they arrived at the "First Stopping Place" near Montreal. While the other Anicinàpe peoples continued their journey up the St. Lawrence River, the Algonquins settled along the Ottawa River (Kitcisìpi), an important highway for commerce, cultural exchange, and transportation. A distinct Algonquin identity, though, was not realized until after the dividing of the Anicinàpek at the "Third Stopping Place", estimated at 2,000 years ago near present-day Detroit.
According to their tradition, and from recordings in birch bark scrolls (wiigwaasabak), Ojibwe (an Algonquian-speaking people) came from the eastern areas of North America, or Turtle Island, and from along the east coast. They traded widely across the continent for thousands of years and knew of the canoe routes west and a land route to the west coast. According to the oral history, seven great miigis (radiant/iridescent) beings appeared to the peoples in the Waabanakiing to teach the peoples of the mide way of life. One of the seven great miigis beings was too spiritually powerful and killed the peoples in the Waabanakiing when the people were in its presence. The six great miigis beings remained to teach while the one returned into the ocean. The six great miigis beings then established doodem (clans) for the peoples in the east. Of these doodem, the five original Anishinaabe doodem were the Wawaazisii (Bullhead), Baswenaazhi (Echo-maker, i.e., Crane), Aan'aawenh (Pintail Duck), Nooke (Tender, i.e., Bear) and Moozoonsii (Little Moose), then these six miigis beings returned into the ocean as well. If the seventh miigis being stayed, it would have established the Thunderbird doodem.
The Nuu-chah-nulth are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast. The term Nuu-chah-nulth is used to describe fifteen separate but related First Nations, such as the Tla-o-qui-aht First Nations, Ehattesaht First Nation and Hesquiaht First Nation whose traditional home is on the west coast of Vancouver Island. In pre-contact and early post-contact times, the number of nations was much greater, but smallpox and other consequences of contact resulted in the disappearance of groups, and the absorption of others into neighbouring groups. The Nuu-chah-nulth are relations of the Kwakwaka'wakw, the Haisla, and the Ditidaht. The Nuu-chah-nulth language is part of the Wakashan language group.
In 1999 the discovery of the body of Kwäday Dän Ts'ìnchi provided archaeologists with significant information on indigenous tribal life prior to extensive European contact. Kwäday Dän Ts'ìnchi (meaning "Long Ago Person Found" in Southern Tutchone), or "Canadian Ice Man", is a naturally mummified body that a group of hunters found in Tatshenshini-Alsek Provincial Park in British Columbia. Radiocarbon dating of artifacts found with the body placed the age of the find between 1450 AD and 1700 AD. Genetic testing showed that he was a member of the Champagne and Aishihik First Nations.
European contact
Aboriginal people in Canada interacted with Europeans as far back as 1000 AD, but prolonged contact came only after Europeans established permanent settlements in the 17th and 18th centuries. European written accounts noted friendliness on the part of the First Nations, who profited in trade with Europeans. Such trade strengthened the more organized political entities such as the Iroquois Confederation. The Aboriginal population is estimated to have been between 200,000 and two million in the late 15th century. The effect of European colonization was a 40 to 80 percent Aboriginal population decrease post-contact. This is attributed to various factors, including repeated outbreaks of European infectious diseases such as influenza, measles and smallpox (to which they had not developed immunity), inter-nation conflicts over the fur trade, conflicts with colonial authorities and settlers and loss of land and a subsequent loss of nation self-suffiency. For example, during the late 1630s, smallpox killed more than half of the Huron, who controlled most of the early fur trade in what became Canada. Reduced to fewer than 10,000 people, the Huron Wendat were attacked by the Iroquois, their traditional enemies. In the Maritimes, the Beothuk disappeared entirely.
There are reports of contact made before Christopher Columbus between the first peoples and those from other continents. Even in Columbus' time there was much speculation that other Europeans had made the trip in ancient or contemporary times; Gonzalo Fernández de Oviedo y Valdés records accounts of these in his General y natural historia de las Indias of 1526, which includes biographical information on Columbus. Aboriginal first contact period is not well defined. The earliest accounts of contact occurred in the late 10th century, between the Beothuk and Norsemen. According to the Sagas of Icelanders, the first European to see what is now Canada was Bjarni Herjólfsson, who was blown off course en route from Iceland to Greenland in the summer of 985 or 986 CE. The first European explorers and settlers of what is now Canada relied on the First Nations peoples, for resources and trade to sustain a living. The first written accounts of interaction show a predominantly Old world bias, labelling the indigenous peoples as "savages", although the indigenous peoples were organized and self-sufficient. In the early days of contact, the First Nations and Inuit populations welcomed the Europeans, assisting them in living off the land and joining forces with the French and British in their various battles. It was not until the colonial and imperial forces of Britain and France established dominant settlements and, no longer needing the help of the First Nations people, began to break treaties and force them off the land that the antagonism between the two groups grew.
16th–18th centuries
The Portuguese Crown claimed that it had territorial rights in the area visited by Cabot. In 1493 Pope Alexander VI – assuming international jurisdiction – had divided lands discovered in America between Spain and Portugal. The next year, in the Treaty of Tordesillas, these two kingdoms decided to draw the dividing line running north–south, 370 leagues (from 1,500 to 2,200 km (930 to 1,370 mi) approximately depending on the league used) west of the Cape Verde Islands. Land to the west would be Spanish, to the east Portuguese. Given the uncertain geography of the day, this seemed to give the "new founde isle" to Portugal. On the 1502 Cantino map, Newfoundland appears on the Portuguese side of the line (as does Brazil). An expedition captured about 60 Aboriginal people as slaves who were said to "resemble gypsies in colour, features, stature and aspect; are clothed in the skins of various animals ...They are very shy and gentle, but well formed in arms and legs and shoulders beyond description ...." Some captives, sent by Gaspar Corte-Real, reached Portugal. The others drowned, with Gaspar, on the return voyage. Gaspar's brother, Miguel Corte-Real, went to look for him in 1502, but also failed to return.
In 1604 King Henry IV of France granted Pierre Dugua, Sieur de Mons a fur-trade monopoly. Dugua led his first colonization expedition to an island located near to the mouth of the St. Croix River. Samuel de Champlain, his geographer, promptly carried out a major exploration of the northeastern coastline of what is now the United States. Under Samuel de Champlain, the Saint Croix settlement moved to Port Royal (today's Annapolis Royal, Nova Scotia), a new site across the Bay of Fundy, on the shore of the Annapolis Basin, an inlet in western Nova Scotia. Acadia became France's most successful colony to that time. The cancellation of Dugua's fur monopoly in 1607 ended the Port Royal settlement. Champlain persuaded First Nations to allow him to settle along the St. Lawrence, where in 1608 he would found France's first permanent colony in Canada at Quebec City. The colony of Acadia grew slowly, reaching a population of about 5,000 by 1713. New France had cod-fishery coastal communities, and farm economies supported communities along the St. Lawrence River. French voyageurs travelled deep into the hinterlands (of what is today Quebec, Ontario, and Manitoba, as well as what is now the American Midwest and the Mississippi Valley), trading with First Nations as they went – guns, gunpowder, cloth, knives, and kettles for beaver furs. The fur trade kept the interest in France's overseas colonies alive, yet only encouraged a small colonial population, as minimal labour was required. The trade also discouraged the development of agriculture, the surest foundation of a colony in the New World.
The Métis
The Métis (from French métis – "mixed") are descendants of unions between Cree, Ojibwe, Algonquin, Saulteaux, Menominee and other First Nations in the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries and Europeans, mainly French. The Métis were historically the children of French fur traders and Nehiyaw women or, from unions of English or Scottish traders and Northern Dene women (Anglo-Métis). The Métis spoke or still speak either Métis French or a mixed language called Michif. Michif, Mechif or Métchif is a phonetic spelling of the Métis pronunciation of Métif, a variant of Métis. The Métis as of 2013 predominantly speak English, with French a strong second language, as well as numerous Aboriginal tongues. Métis French is best preserved in Canada, Michif in the United States, notably in the Turtle Mountain Indian Reservation of North Dakota, where Michif is the official language of the Métis that reside on this Chippewa reservation. The encouragement and use of Métis French and Michif is growing due to outreach within the five provincial Métis councils after at least a generation of steep decline. Canada's Indian and Northern Affairs define Métis to be those persons of mixed First Nation and European ancestry.
Colonial wars
Allied with the French, the first nations of the Wabanaki Confederacy of Acadia fought six colonial wars against the British and their native allies (See the French and Indian Wars, Father Rale's War and Father Le Loutre's War). In the second war, Queen Anne's War, the British conquered Acadia (1710). The sixth and final colonial war between the nations of France and Great Britain (1754–1763), resulted in the French giving up their claims and the British claimed the lands of Canada.
In this final war, the Franco-Indian alliance brought together Americans, First Nations and the French, centred on the Great Lakes and the Illinois Country. The alliance involved French settlers on the one side, and on the other side were the Abenaki, Odawa, Menominee, Ho-Chunk (Winnebago), Mississaugas, Illiniwek, Huron-Petun, Potawatomi etc. It allowed the French and the Indians to form a haven in the middle-Ohio valley before the open conflict between the European powers erupted.
In the Royal Proclamation of 1763, the British recognized the treaty rights of the indigenous populations and resolved to only settle those areas purchased lawfully from the indigenous peoples. Treaties and land purchases were made in several cases by the British, but the lands of several indigenous nations remain unceded and/or unresolved.
Slavery
First Nations routinely captured slaves from neighbouring tribes. Sources report that the conditions under which First Nations slaves lived could be brutal, with the Makah tribe practicing death by starvation as punishment and Pacific coast tribes routinely performing ritualized killings of slaves as part of social ceremonies into the mid-1800s. Slave-owning tribes of the fishing societies, such as the Yurok and Haida lived along the coast from what is now Alaska to California. Fierce warrior indigenous slave-traders of the Pacific Northwest Coast raided as far south as California. Slavery was hereditary, the slaves and their descendants being considered prisoners of war. Some tribes in British Columbia continued to segregate and ostracize the descendants of slaves as late as the 1970s. Among Pacific Northwest tribes about a quarter of the population were slaves.
The citizens of New France received slaves as gifts from their allies among First Nations peoples. Slaves were prisoners taken in raids against the villages of the Fox nation, a tribe that was an ancient rival of the Miami people and their Algonquian allies. Native (or "pani", a corruption of Pawnee) slaves were much easier to obtain and thus more numerous than African slaves in New France, but were less valued. The average native slave died at 18, and the average African slave died at 25 (the average European could expect to live until the age of 35). By 1790 the abolition movement was gaining ground in Canada and the ill intent of slavery was evidenced by an incident involving a slave woman being violently abused by her slave owner on her way to being sold in the United States. The Act Against Slavery of 1793 legislated the gradual abolition of slavery: no slaves could be imported; slaves already in the province would remain enslaved until death, no new slaves could be brought into Upper Canada, and children born to female slaves would be slaves but must be freed at age 25. The Act remained in force until 1833 when the British Parliament's Slavery Abolition Act finally abolished slavery in all parts of the British Empire. Historian Marcel Trudel has documented 4,092 recorded slaves throughout Canadian history, of which 2,692 were Aboriginal people, owned by the French, and 1,400 blacks owned by the British, together owned by approximately 1,400 masters. Trudel also noted 31 marriages took place between French colonists and Aboriginal slaves.
1775–1815
British agents worked to make the First Nations into military allies of the British, providing supplies, weapons, and encouragement. During the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783) most of the tribes supported the British. In 1779, the Americans launched a campaign to burn the villages of the Iroquois in New York State. The refugees fled to Fort Niagara and other British posts, and remained permanently in Canada. Although the British ceded the Old Northwest to the United States in the Treaty of Paris in 1783, it kept fortifications and trading posts in the region until 1795. The British then evacuated American territory, but operated trading posts in British territory, providing weapons and encouragement to tribes that were resisting American expansion into such areas as Ohio, Indiana, Michigan, Illinois and Wisconsin. Officially, the British agents discouraged any warlike activities or raids on American settlements, but the Americans became increasingly angered, and this became one of the causes of the War of 1812.
In the war, the great majority of First Nations supported the British, and many fought under the aegis of Tecumseh. But Tecumseh died in battle in 1813 and the Indian coalition collapsed. The British had long wished to create a neutral Indian state in the American Old Northwest, and made this demand as late as 1814 at the peace negotiations at Ghent. The Americans rejected the idea, the British dropped it, and Britain's Indian allies lost British support. In addition, the Indians were no longer able to gather furs in American territory. Abandoned by their powerful sponsor, Great Lakes-area natives ultimately assimilated into American society, migrated to the west or to Canada, or were relocated onto reservations in Michigan and Wisconsin. Historians have unanimously agreed that the Indians were the major losers in the War of 1812.
19th century
Living conditions for Indigenous people in the prairie regions deteriorated quickly. Between 1875 and 1885, settlers and hunters of European descent contributed to hunting the North American bison almost to extinction; the construction of the Canadian Pacific Railway brought large numbers of European settlers west who encroached on Indigenous territory. European Canadians established governments, police forces, and courts of law with different foundations from indigenous practices. Various epidemics continued to devastate Indigenous communities. All of these factors had a profound effect on Indigenous people, particularly those from the plains who had relied heavily on bison for food and clothing. Most of those nations that agreed to treaties had negotiated for a guarantee of food and help to begin farming. Just as the bison disappeared (the last Canadian hunt was in 1879), Lieutenant-Governor Edgar Dewdney cut rations to indigenous people in an attempt to reduce government costs. Between 1880 and 1885, approximately 3,000 Indigenous people starved to death in the North-Western Territory/Northwest Territories.
Offended by the concepts of the treaties, Cree chiefs resisted them. Big Bear refused to sign Treaty 6 until starvation among his people forced his hand in 1882. His attempts to unite Indigenous nations made progress. In 1884 the Métis (including the Anglo-Métis) asked Louis Riel to return from the United States, where he had fled after the Red River Rebellion, to appeal to the government on their behalf. The government gave a vague response. In March 1885, Riel, Gabriel Dumont, Honoré Jackson (a.k.a. Will Jackson), Crowfoot, Chief of the Blackfoot First Nation and Chief Poundmaker, who after the 1876 negotiations of Treaty 6 split off to form his band. Together, they set up the Provisional Government of Saskatchewan, believing that they could influence the federal government in the same way as they had in 1869. The North-West Rebellion of 1885 was a brief and unsuccessful uprising by the Métis people of the District of Saskatchewan under Louis Riel against the Dominion of Canada, which they believed had failed to address their concerns for the survival of their people. In 1884, 2,000 Cree from reserves met near Battleford to organise into a large, cohesive resistance. Discouraged by the lack of government response but encouraged by the efforts of the Métis at armed rebellion, Wandering Spirit and other young militant Cree attacked the small town of Frog Lake, killing Thomas Quinn, the hated Indian Agent and eight others. Although Big Bear actively opposed the attacks, he was charged and tried for treason and sentenced to three years in prison. After the Red River Rebellion of 1869–1870, Métis moved from Manitoba to the District of Saskatchewan, where they founded a settlement at Batoche on the South Saskatchewan River.
In Manitoba settlers from Ontario began to arrive. They pushed for land to be allotted in the square concession system of English Canada, rather than the seigneurial system of strips reaching back from a river which the Métis were familiar with in their French-Canadian culture. The buffalo were being hunted to extinction by the Hudson's Bay Company and other hunters, as for generations the Métis had depended on them as a chief source of food.
Colonization and assimilation
The history of colonization is complex, varied according to the time and place. France and Britain were the main colonial powers involved, though the United States also began to extend its territory at the expense of indigenous people as well.
From the late 18th century, European Canadians encouraged First Nations to assimilate into the European-based culture, referred to as "Canadian culture". The assumption was that this was the "correct" culture because the Canadians of European descent saw themselves as dominant, and technologically, politically and culturally superior. There was resistance against this assimilation and many businesses denied European practices. The Tecumseh Wigwam of Toronto, for example, did not adhere to the widely practiced Lord's Day observance, making it a popular spot, especially on Sundays. These attempts reached a climax in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Founded in the 19th century, the Canadian Indian residential school system was intended to force the assimilation of Aboriginal and First Nations people into European-Canadian society. The purpose of the schools, which separated children from their families, has been described by commentators as "killing the Indian in the child."
Funded under the Indian Act by Indian and Northern Affairs Canada, a branch of the federal government, the schools were run by churches of various denominations – about 60% by Roman Catholics, and 30% by the Anglican Church of Canada and the United Church of Canada, along with its pre-1925 predecessors, Presbyterian, Congregationalist and Methodist churches.
The attempt to force assimilation involved punishing children for speaking their own languages or practicing their own faiths, leading to allegations in the 20th century of cultural genocide and ethnocide. There was widespread physical and sexual abuse. Overcrowding, poor sanitation, and a lack of medical care led to high rates of tuberculosis, and death rates of up to 69%. Details of the mistreatment of students had been published numerous times throughout the 20th century, but following the closure of the schools in the 1960s, the work of indigenous activists and historians led to a change in the public perception of the residential school system, as well as official government apologies, and a (controversial) legal settlement.
Colonization had a significant impact on First Nations diet and health. According to the historian Mary-Ellen Kelm, "inadequate reserve allocations, restrictions on the food fishery, overhunting, and over-trapping" alienated First Nations from their traditional way of life, which undermined their physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual health.
20th century
As Canadian ideas of progress evolved around the start of the 20th century, the federal Indian policy was directed at removing Indigenous people from their communal lands and encouraging assimilation. Amendments to the Indian Act in 1905 and 1911 made it easier for the government to expropriate reserve lands from First Nations. The government sold nearly half of the Blackfoot reserve in Alberta to settlers.
When the Kainai (Blood) Nation refused to accept the sale of their lands in 1916 and 1917, the Department of Indian Affairs held back funding necessary for farming until they relented. In British Columbia, the McKenna–McBride Royal Commission was created in 1912 to settle disputes over reserve lands in the province. The claims of Indigenous people were ignored, and the commission allocated new, less valuable lands (reserves) for First Nations.
Those nations who managed to maintain their ownership of good lands often farmed successfully. Indigenous people living near the Cowichan and Fraser rivers, and those from Saskatchewan managed to produce good harvests. Since 1881, those First Nations people living in the prairie provinces required permits from Indian Agents to sell any of their produce. Later the government created a pass system in the old Northwest Territories that required indigenous people to seek written permission from an Indian Agent before leaving their reserves for any length of time. Indigenous people regularly defied those laws, as well as bans on Sun Dances and potlatches, in an attempt to practice their culture.
The 1930 Constitution Act or Natural Resources Acts was part of a shift acknowledging indigenous rights. It enabled provincial control of Crown land and allowed Provincial laws regulating game to apply to Indians, but it also ensured that "Indians shall have the right ... of hunting, trapping and fishing game and fish for food at all seasons of the year on all unoccupied Crown lands and on any other lands to which the said Indians may have a right of access."
First and Second World Wars
More than 6,000 First Nations, Inuit and Métis served with British forces during First World War and Second World War. A generation of young native men fought on the battlefields of Europe during the Great War and approximately 300 of them died there. When Canada declared war on Germany on September 10, 1939, the native community quickly responded to volunteer. Four years later, in May 1943, the government declared that, as British subjects, all able Indian men of military age could be called up for training and service in Canada or overseas.
Late 20th century
Following the end of the Second World War, laws concerning First Nations in Canada began to change, albeit slowly. The federal prohibition of potlatch and Sun Dance ceremonies ended in 1951. Provincial governments began to accept the right of Indigenous people to vote. In June 1956, section 9 of the Citizenship Act was amended to grant formal citizenship to Status Indians and Inuit, retroactively as of January 1947.
In 1960, First Nations people received the right to vote in federal elections without forfeiting their Indian status. By comparison, Native Americans in the United States had been allowed to vote since the 1920s.
1969 White Paper
In his 1969 White Paper, then-Minister of Indian Affairs, Jean Chrétien, proposed the abolition of the Indian Act of Canada, the rejection of Aboriginal land claims, and the assimilation of First Nations people into the Canadian population with the status of "other ethnic minorities" rather than as a distinct group.
Harold Cardinal and the Indian Chiefs of Alberta responded with a document entitled "Citizens Plus" but commonly known as the "Red Paper". In it, they explained Status Indians' widespread opposition to Chrétien's proposal. Prime Minister Pierre Trudeau and the Liberals began to back away from the 1969 White Paper, particularly after the Calder case decision in 1973. After the Canadian Supreme Court recognized that indigenous rights and treaty rights were not extinguished, a process was begun to resolve land claims and treaty rights and is ongoing today.
Health transfer policy
In 1970, severe mercury poisoning, called Ontario Minamata disease, was discovered among Asubpeeschoseewagong First Nation and Wabaseemoong Independent Nations people, who lived near Dryden, Ontario. There was extensive mercury pollution caused by Dryden Chemicals Company's waste water effluent in the Wabigoon-English River system. Because local fish were no longer safe to eat, the Ontario provincial government closed the commercial fisheries run by the First Nation people and ordered them to stop eating local fish. Previously it had made up the majority of their diet. In addition to the acute mercury poisoning in northwestern Ontario, Aamjiwnaang First Nation people near Sarnia, Ontario, experienced a wide range of chemical effects, including severe mercury poisoning. They suffered low birth rates, skewed birth-gender ratio, and health effects among the population. This led to legislation and eventually the Indian Health Transfer Policy that provided a framework for the assumption of control of health services by First Nations people, and set forth a developmental approach to transfer centred on the concept of self-determination in health. Through this process, the decision to enter into transfer discussions with Health Canada rests with each community. Once involved in transfer, communities are able to take control of health programme responsibilities at a pace determined by their individual circumstances and health management capabilities.
The capacity, experience and relationships developed by First Nations as a result of health transfer was a factor that assisted the creation of the First Nations Health Authority in British Columbia.
Elijah Harper and the Meech Lake Accord
In 1981, Elijah Harper, a Cree from Red Sucker Lake, Manitoba, became the first "Treaty Indian" in Manitoba to be elected as a member of the Legislative Assembly of Manitoba. In 1990, Harper achieved national fame by holding an eagle feather as he refused to accept the Meech Lake Accord, a constitutional amendment package negotiated to gain Quebec's acceptance of the Constitution Act, 1982, but also one that did not address any First Nations grievances. The accord was negotiated in 1987 without the input of Canada's Aboriginal peoples. The third, final constitutional conference on Aboriginal peoples was also unsuccessful. The Manitoba assembly was required to unanimously consent to a motion allowing it to hold a vote on the accord, because of a procedural rule. Twelve days before the ratification deadline for the Accord, Harper began a filibuster that prevented the assembly from ratifying the accord. Because Meech Lake failed in Manitoba, the proposed constitutional amendment failed. Harper also opposed the Charlottetown Accord in 1992, even though Assembly of First Nations Chief Ovide Mercredi supported it.
Women's status and Bill C-31
According to the Indian Act, status Indian women who married men who were not status Indians lost their treaty status, and their children would not get status. However, in the reverse situation, if a status Indian man married a woman who was not a status Indian, the man would keep his status and his children would also receive treaty status. In the 1970s, the Indian Rights for Indian Women and Native Women's Association of Canada groups campaigned against this policy because it discriminated against women and failed to fulfill treaty promises. They successfully convinced the federal government to change the section of the act with the adoption of Bill C-31 on June 28, 1985. Women who had lost their status and children who had been excluded were then able to register and gain official Indian status. Despite these changes, status Indian women who married men who were not status Indians could pass their status on only one generation: their children would gain status, but (without a marriage to a full-status Indian) their grandchildren would not. A status Indian man who married a woman who was not a status Indian retained status as did his children, but his wife did not gain status, nor did his grandchildren.
Bill C-31 also gave elected bands the power to regulate who was allowed to reside on their reserves and to control development on their reserves. It abolished the concept of "enfranchisement" by which First Nations people could gain certain rights by renouncing their Indian status.
Erasmus–Dussault commission
In 1991, Prime Minister Brian Mulroney created the Royal Commission on Aboriginal Peoples chaired by René Dussault and Georges Erasmus. Their 1996 report proposed the creation of a government for (and by) the First Nations that would be responsible within its own jurisdiction, and with which the federal government would speak on a "Nation-to-Nation" basis. This proposal offered a far different way of doing politics than the traditional policy of assigning First Nations matters under the jurisdiction of the Indian and Northern Affairs, managed by one minister of the federal cabinet. The report also recommended providing the governments of the First Nations with up to $2 billion every year until 2010, in order to reduce the economic gap between the First Nations and the rest of the Canadian citizenry. The money would represent an increase of at least 50% to the budget of Indian and Northern Affairs. The report engaged First Nations leaders to think of ways to cope with the challenging issues their people were facing, so the First Nations could take their destiny into their own hands.
The federal government, then headed by Jean Chrétien, responded to the report a year later by officially presenting its apologies for the forced acculturation the federal government had imposed on the First Nations, and by offering an "initial" provision of $350 million.
In the spirit of the Eramus–Dussault commission, tripartite (federal, provincial, and First Nations) accords have been signed since the report was issued. Several political crises between different provincial governments and different bands of the First Nations also occurred in the late 20th century, notably the Oka Crisis, Ipperwash Crisis, Burnt Church Crisis, and the Gustafsen Lake standoff.
Early 21st century
In 2001, the Quebec government, the federal government, and the Cree Nation signed "La Paix des Braves" (The Peace of the Braves, a reference to the 1701 peace treaty between the French and the Iroquois League). The agreement allowed Hydro-Québec to exploit the province's hydroelectric resources in exchange for an allocation of $3.5 billion to be given to the government of the Cree Nation. Later, the Inuit of northern Quebec (Nunavik) joined in the agreement.
In 2005, the leaders of the First Nations, various provincial governments, and the federal government produced an agreement called the Kelowna Accord, which would have yielded $5 billion over 10 years, but the new federal government of Stephen Harper (2006) did not follow through on the working paper. First Nations, along with the Métis and the Inuit, have claimed to receive inadequate funding for education, and allege their rights have been overlooked. James Bartleman, Lieutenant Governor of Ontario from 2002 to 2007, listed the encouragement of indigenous young people as one of his key priorities. During his term, he launched initiatives to promote literacy and bridge-building. Bartleman was the first Aboriginal person to be lieutenant governor in Ontario.
In 2006, 76 First Nations communities had boil-water advisory conditions. In late 2005, the drinking water crisis of the Kashechewan First Nation received national media attention when E. coli was discovered in their water supply system, following two years of living under a boil-water advisory. The drinking water was supplied by a new treatment plant built in March 1998. The cause of the tainted water was a plugged chlorine injector that was not discovered by local operators, who were not qualified to be running the treatment plant. When officials arrived and fixed the problem, chlorine levels were around 1.7 mg/l, which was blamed for skin disorders such as impetigo and scabies. An investigation led by Health Canada revealed that skin disorders were likely due to living in squalor. The evacuation of Kashechewan was largely viewed by Canadians as a cry for help for other underlying social and economic issues that Aboriginal people in Canada face.
On June 29, 2007, Canadian Aboriginal groups held countrywide protests aimed at ending First Nations poverty, dubbed the Aboriginal Day of Action. The demonstrations were largely peaceful, although groups disrupted transportation with blockades or bonfires; a stretch of the Highway 401 was shut down, as was the Canadian National Railway's line between Toronto and Montreal.
The Idle No More protest movement originated among the Aboriginals in Canada and their non-Aboriginal supporters in Canada, and to a lesser extent, internationally. It consisted of a number of political actions worldwide, inspired in part by the hunger strike of Attawapiskat First Nation Chief Theresa Spence and further coordinated via social media. A reaction to alleged abuses of indigenous treaty rights by the federal government, the movement took particular issue with the omnibus bill Bill C-45.
Canadian Crown and First Nations relations
The relationship between the Canadian Crown and the First Nations, Inuit, and Métis peoples stretches back to the first interactions between European colonialists and North American indigenous people. Over centuries of interaction, treaties were established, and First Nations have, like the Māori and the Treaty of Waitangi in New Zealand, come to generally view these agreements as being between them and the Crown of Canada, and not the ever-changing governments.
The associations exist between the Aboriginal peoples and the reigning monarch of Canada; as was stated in the proposed First Nations – Federal Crown Political Accord: "cooperation will be a cornerstone for partnership between Canada and First Nations, wherein Canada is the short-form reference to Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada". These relations are governed by the established treaties; the Supreme Court stated that treaties "served to reconcile pre-existing Aboriginal sovereignty with assumed Crown sovereignty, and to define Aboriginal rights", and the First Nations saw these agreements as meant to last "as long as the sun shines, grass grows and rivers flow".
Taxation
Although taxes are not specifically addressed in the written terms of any treaties, assurances regarding taxation were clearly offered when at least some treaties were negotiated.
The various statutory exemptions from taxation are established under the Indian Act, which reads:
- 87(1). Notwithstanding any other Act of Parliament or any Act of the legislature of a province ... the following property is exempt from taxation
- (a) the interest of an Indian or a band in reserve lands or surrendered lands; and
- (b) the personal property of an Indian or a band situated on a reserve.
- 87(2). No Indian or band is subject to taxation in respect of the ownership, occupation, possession or use of any property mentioned in paragraph (1)(a) or (b) or is otherwise subject to taxation in respect of any such property.
Many scholars believe these exemptions serve to oppress Aboriginal peoples by allowing conservative-minded courts to impart their own (sometimes discriminatory) views into the Aboriginal taxation jurisprudence. As one professor wrote:
[Because] income-generating activity in the "commercial mainstream" contrasts with income-generating activity that is "intimately connected to" the reserve ... [the] Tax Court of Canada implie[s] that the "traditional way of life" of Aboriginal peoples d[oes] not embrace "economic aspects" ... beyond a subsistence economy. [footnotes omitted]
Political organization
Self-government has given chiefs and their councils powers which combine those of a province, school board, health board and municipality. Councils are also largely self-regulating regarding utilities, environmental protection, natural resources, building codes, etc. There is concern that this wide-ranging authority, concentrated in a single council, might be a cause of the dysfunctional governments experienced by many First Nations.
The Assembly of First Nations (AFN) is a body of First Nations leaders in Canada. The aims of the organization are to protect the rights, treaty obligations, ceremonies, and claims of citizens of the First Nations in Canada.
After the failures of the League of Indians in Canada in the interwar period and the North American Indian Brotherhood in two decades following the Second World War, the Aboriginal peoples of Canada organised themselves once again in the early 1960s. The National Indian Council was created in 1961 to represent Indigenous people, including treaty/status Indians, non-status people, the Métis people, though not the Inuit. This organization collapsed in 1968 as the three groups failed to act as one, so the non-status and Métis groups formed the Native Council of Canada and treaty/status groups formed the National Indian Brotherhood (NIB), an umbrella group for provincial and territorial First Nations organizations.
Culture
National Indigenous Peoples Day, formerly National Aboriginal Day, June 21, recognizes the cultures and contributions of Aboriginal peoples of Canada. There are currently over 600 recognized First Nations governments or bands encompassing 1,172,790 people spread across Canada with distinctive Aboriginal cultures, languages, art, and music.
Languages
Today, there are over thirty different languages spoken by indigenous people, most of which are spoken only in Canada. Many are in decline. Those with the most speakers include Anishinaabe and Cree (together totalling up to 150,000 speakers); Inuktitut with about 29,000 speakers in the Northwest Territories, Nunavut, Nunavik (Northern Quebec), and Nunatsiavut (Northern Labrador); and Mi'kmaq, with around 8,500 speakers, mostly in Eastern Canada. Many Aboriginal peoples have lost their native languages and often all but surviving elders speak English or French as their first language.
Two of Canada's territories give official status to native languages. In Nunavut, Inuktitut and Inuinnaqtun are official languages alongside English and French, and Inuktitut is a common vehicular language in government. In the Northwest Territories, the Official Languages Act declares that there are eleven different languages: Chipewyan, Cree, English, French, Gwich'in, Inuinnaqtun, Inuktitut, Inuvialuktun, North Slavey, South Slavey and Tłįchǫ. Besides English and French, these languages are not vehicular in government; official status entitles citizens to receive services in them on request and to deal with the government in them.
Art
First Nations were producing art for thousands of years before the arrival of European settler colonists and the eventual establishment of Canada as a nation state. Like the peoples who produced them, indigenous art traditions spanned territories across North America. Indigenous art traditions are organized by art historians according to cultural, linguistic or regional groups: Northwest Coast, Plateau, Plains, Eastern Woodlands, Subarctic, and Arctic.
Art traditions vary enormously amongst and within these diverse groups. Indigenous art with a focus on portability and the body is distinguished from European traditions and its focus on architecture. Indigenous visual art may be used in conjunction with other arts. Shamans' masks and rattles are used ceremoniously in dance, storytelling and music. Artworks preserved in museum collections date from the period after European contact and show evidence of the creative adoption and adaptation of European trade goods such as metal and glass beads. During the 19th and the first half of the 20th century the Canadian government pursued an active policy of forced and cultural assimilation toward indigenous peoples. The Indian Act banned manifestations of the Sun Dance, the Potlatch, and works of art depicting them.
It was not until the 1950s and 1960s that indigenous artists such as Mungo Martin, Bill Reid and Norval Morrisseau began to publicly renew and re-invent indigenous art traditions. Currently there are indigenous artists practising in all media in Canada and two indigenous artists, Edward Poitras and Rebecca Belmore, have represented Canada at the Venice Biennale in 1995 and 2005 respectively.
Music
The First Nations peoples of Canada comprise diverse ethnic groups, each with their own musical traditions. There are general similarities in the music, but is usually social (public) or ceremonial (private). Public, social music may be dance music accompanied by rattles and drums. Private, ceremonial music includes vocal songs with accompaniment on percussion, used to mark occasions like Midewiwin ceremonies and Sun Dances.
Traditionally, Aboriginal peoples used the materials at hand to make their instruments for centuries before Europeans immigrated to Canada. First Nations people made gourds and animal horns into rattles, which were elaborately carved and beautifully painted. In woodland areas, they made horns of birch bark and drumsticks of carved antlers and wood. Traditional percussion instruments such as drums were generally made of carved wood and animal hides. These musical instruments provide the background for songs, and songs are the background for dances. Traditional First Nations people consider song and dance to be sacred. For years after Europeans came to Canada, First Nations people were forbidden to practice their ceremonies.
Demographics
In the 20th century, the First Nations population of Canada increased tenfold. Between 1900 and 1950 the population grew only by 29% but after the 1960s the infant mortality level on reserves dropped and the population grew by 161%. Since the 1980s, the number of First Nations babies more than doubled and currently almost half of the First Nations population is under the age of 25. As a result, the First Nations population of Canada is expected to increase in the coming decades.
In 2016, there were 1,673,785 Aboriginal people in Canada, accounting for 4.9% of the total population. This was up from 3.8% in 2006.
There are distinct First Nations in Canada, originating across the country. Indian reserves, established in Canadian law by treaties such as Treaty 7, are the very limited contemporary lands of First Nations recognized by the non-indigenous governments. A few reserves exist within cities, such as the Opawikoscikan Reserve in Prince Albert, Wendake in Quebec City or Enoch Cree Nation 135 in the Edmonton Metropolitan Region. There are more reserves in Canada than there are First Nations, as First Nations were ceded multiple reserves by treaty.
First Nations can be grouped into cultural areas based on their ancestors' primary lifeway, or occupation, at the time of European contact. These culture areas correspond closely with physical and ecological regions of Canada.
Ethnographers commonly classify indigenous peoples of the Americas in the United States and Canada into ten geographical regions with shared cultural traits (called cultural areas). The Canadian (in whole or in part) regions are Arctic, Subarctic, Northeast Woodlands, Plains, and Plateau. See the individual article on each tribe, band society or First Nation.
The Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast communities centred around ocean and river fishing; in the interior of British Columbia, hunting and gathering and river fishing. In both of these areas, salmon was of chief importance. For the people of the plains, bison hunting was the primary activity. In the subarctic forest, other species such as the moose were more important. For peoples near the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence River, shifting agriculture was practised, including the raising of maize, beans, and squash.
Today, Aboriginal people work in a variety of occupations and live outside their ancestral homes. The traditional cultures of their ancestors, shaped by nature, still exert a strong influence on their culture, from spirituality to political attitudes.
Contemporary issues
First Nations peoples face a number of problems to a greater degree than Canadians overall, some with living conditions comparable to developing countries like Haiti. Indigenous peoples have higher rates of unemployment, rates of incarceration, substance abuse, health problems, homelessness, fetal alcohol syndrome, lower levels of education and higher levels of poverty.
Residential schools
Canada's federal residential school system began in the mid-1870s, building upon a patchwork of boarding schools established and operated by various Christian denominations. Member of Parliament for Assiniboia West, Nicholas Flood Davin, produced a report, known generally as the Davin Report, that recommended the establishment of a school system similar to that being created in the United States. One of its chief goals was to remove Aboriginal children from "the influence of the wigwam", which he claimed was stronger than that of existing day schools, and keep them instead "constantly within the circle of civilized conditions". While the history of the Indian Residential School system (IRS) is a checkered one, much criticism has been levelled at both the system and those who established and supported it. Neglect and poor nutrition were often what Aboriginal children experienced, particularly in the early decades of the system's operation. The stripping away of traditional native culture—sometimes referred to as "cultural genocide"—is another charge levelled at the residential schools. In many schools, students were not allowed to speak their Indigenous languages or practice any of their own customs, and thus lost their sense of identity, inevitably driving a cultural wedge between children and their family.
By 1920, attendance at some sort of school was mandatory for Aboriginal children in Canada. The Indian Act made education compulsory, and where there were no federal days schools—or, in later decades, a provincial public school—a residential school was the only choice. Enrolment statistics indicate that between 20% and 30% of Aboriginal children during the history of the IRS system attended a residential school for at least a year, and many were enrolled for ten years or more. In some cases, children could return home on weekends and holidays, but for those in schools established far away from remote communities, this was not possible.
The removal of children from their families and communities brought short and long term harm to many native communities. While many schools had infirmaries and provided medical care in later decades, abuse of various kinds and crowded conditions in the first decades of the IRS history led to poor health and even death for a percentage of those enrolled. It has been argued that the psychological and emotional trauma resulting from both the abuse and the removal of the children from their families and culture has resulted in substance abuse, greater domestic violence, unemployability, and increased rates of suicide. In many cases, children leaving residential schools found themselves at an intersection of cultures, where they were no longer comfortable within their own cultures, yet not accepted into mainstream Canadian culture. Former students are now routinely referred to as "survivors".
Not all Aboriginal children attended residential schools. During the period in which the schools operated, more than a third of indigenous children attended federal day schools, and about a third received no schooling at all. It is however the residential school system that receives much of the blame for the various problems and challenges facing Canada's indigenous people today. During the years in which the residential schools operated, they were regarded by most Canadians as a sensible and beneficial solution to native education, and in some cases, Aboriginal communities specifically requested that a residential school be built. When the system began to closing down in the 1960s, a significant number of communities asked that their school remain open.
The last Canadian residential school to close was Gordon Indian Residential School in Saskatchewan, founded in 1889, and closed in 1996.
The Christian denominations that operated the schools on behalf of the federal government have expressed regret and issued apologies for their part in a system that harmed many indigenous children. In 2008, the government issued an official apology to the students who were forced to attend the residential schools and their families.
In June 2015, the federally-established Truth and Reconciliation Commission, charged with investigating and reporting on the residential school system, issued its summary report, and in December of the same year, its final report. Chief Commissioner, Judge Murray Sinclair, has publicly declared the residential school system a deliberate act of cultural genocide against First Nations peoples. In its report, the commission submitted 94 recommendations to the Canadian government, recommendations which, if implemented, would substantially improve indigenous race relations, increase quality of life for survivors and extended families, and help undo the damage caused by residential schools. While the Liberal government, under Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, has committed itself to improving the lives of Canada's indigenous people, and specifically to implementing the TRC recommendations, some of those recommendations may be beyond the power of the Canadian government. The countless research documents assembled by the TRC will be archived in a special repository at the University of Manitoba.
Employment
The income of women with status living off-reserve was on average $13,870 a year, according to a 1996 Canadian census. This is about $5500 less than non-Indigenous women, such as Inuit and Métis women, which recorded slightly higher average annual incomes; regardless of the small discrepancy, all of which are substantially less than Statistics Canada's estimated amount of which an individual living in a large Canadian city would require to meet their needs. It is not unlikely for Aboriginal women living in poverty to not only tend to their own needs, but often tend to the needs of their elderly parents, care for loved ones in ill-health, as well as raising children; all of which is often supported only on a single income. It is believed that homelessness and inadequate shelter are widespread problems facing Aboriginal families, in all settings.
Self governance
A paramount conclusion by the Royal Commission on Aboriginal Peoples is that the repeated assaults on the culture and collective identity of the Aboriginal people has resulted in a weakened foundation of Aboriginal society and has contributed to the alienation that inevitably drives some to self-destructive and antisocial behaviour. The social problems among Aboriginal people are, in large measure, a legacy of history.
Crime and incarceration
Aboriginals are also more likely to be the victims of crime. This is particularly true in the younger population (aged 15–34), where acts of violence are two and a half times more likely to occur than in the older population. Domestic violence and sexual abuse against children is more prevalent in the Aboriginal population with sexual abuse affecting 25–50% of Aboriginal female children versus 20–25% of female children in the general population. Children who come from homes with a history of violence are at a greater risk of becoming the perpetrators of violence later in life. This is especially true of males.
As of 2007, 17% of incarcerated individuals in Canada were of Aboriginal descent, despite representing only 2.7% of the general population. This is a sixfold increase in rates of incarceration within the Aboriginal population as opposed to the general Canadian population. There are many reasons for the over-representation of Aboriginals within the Canadian justice system. Lack of education, poverty, unemployment and abuse all lead to higher crime rates. Also, statistically, Aboriginals have a greater chance of conviction and subsequently, incarceration once convicted. They are also much less likely to receive parole during their sentence.
Health
The Canadian federal government is responsible for health and social services on the reserve and in Inuit communities, while the provincial and territorial governments provide services elsewhere. The divide between each level of government has led to a gap in services for Aboriginal people living off-reserve and in Canadian towns and cities. Although Aboriginal people living off-reserve have access to the programs and services designed for the general population, these programs and services do not address the specific needs of Aboriginal people, nor is it delivered in a culturally appropriate way. It has not been until recently that the Canadian federal government had to increase recognition to the needs for programs and services for Aboriginal people in predominantly non-Aboriginal communities. It is however funding that lags the growth of urban Aboriginal populations and the uncoordinated delivery of services through various government departments would also pose as a barrier. The federal Interlocutor for Métis and Non-Status Indians pointed out that in 2003 almost 90 percent of the funding for programs designed for Aboriginal peoples is spent on reserves, while off-reserve programs for Aboriginal people are delivered through just 22 federal departments, as well as other provincial and territorial agencies. The federal subcommittee on Indigenous child welfare described a "jurisdictional web" in which there is little to no coordination with or between municipal, provincial and federal levels of government.
The health care services available to Aboriginal people is rarely delivered in a culturally sensitive approach. It is the constant cast of "the other" by the settler Canadian population that contaminates the delivery of such necessary services to Aboriginal peoples. It was argued by Ontario finance minister Jim Flaherty in 1992 that the Canadian government could boost health-care funding for "real people in real towns" by cutting the bureaucracy that serves only Aboriginal peoples. These types of statements, especially made by people often heard by a greater audience, are said to have detrimental and influential effects on the overall attitudes of settler population folks, as well as Aboriginal peoples.
Diabetes
There are marked differences between the epidemiology of diabetes in First Nation population compared to the general population. Reasons for the different rate of Type 2 Diabetes between First Nation and the general population include a complex combination of environmental (lifestyle, diet, poverty) and genetic and biological factors (e.g. thrifty genotype hypothesis, thrifty phenotype) – though to what extent each factor plays a role is still not clear.
The Aboriginal population in Canada (First Nations, Inuit and Métis) have a significantly higher prevalence rate of diabetes than the non-Aboriginal population. Age-standardized rates show that the prevalence of diabetes among First Nations individuals living on-reserve is 17.2%; First Nations individuals living off-reserve is 10.3%; Métis individuals 7.3%; and non-Aboriginal peoples at 5.0%. It is important to note that Aboriginal individuals are generally diagnosed at a younger age than non-Aboriginal individuals, and Aboriginal females experience higher rates of gestational diabetes than non-Aboriginal females. The complications and prevalence of diabetes are seen among the Aboriginal population more often than non-Aboriginal population. These may be attributed to the socio-cultural, biological, environmental and lifestyle changes seen in the First Nations, Inuit, and Métis populations, which have been most especially prevalent in the last half century, all of which contributing significantly to the increased rates of diabetes and the complications associated among the Aboriginal population.
Substance-use disorders
First Nations in Canada engage in a disproportionate amount of substance abuse. In Vancouver, Indigenous people were faced with almost 18 per cent of drug charges, but are just 2.2 per cent of the city's population. A much higher proportion of First Nations people engage in heavy drinking weekly (16%) as opposed to the general population (8%). 19% of First Nations also reported cocaine and opiates use, higher than 13% of the general Canadian population that reported using opioids.
Life expectancy
Life expectancy at birth is significantly lower for First Nations babies than for babies in the Canadian population as a whole. As of 2001, Indian and Northern Affairs Canada estimates First Nations life expectancy to be 8.1 years shorter for males and 5.5 years shorter for females. Where females in the general population had a life expectancy at birth of 82 years, First Nations females had a life expectancy of 76 years. In males the life expectancy for First Nations individuals was 69 years as opposed to 77 in the general population. The reasons behind the lower life expectancy for First Nations individuals are varied and complex; however, social determinants of health are thought to play a large part.
Suicide
Overall, First Nations individuals have some of the highest rates of suicide globally. Suicide rates are more than twice the sex-specific rate and also three times the age-specific rates of non-Aboriginal Canadians. Residential Aboriginals between ages 10 and 29 show an elevated suicide risk as compared to non-residential Aboriginals by 5–6 times. One theory for the increased incidences of suicide within Aboriginal populations as compared to the general Canadian population is called acculturation stress which results from the intersection of multiple cultures within one's life. This leads to differing expectations and cultural clashes within the community, the family and the individual. At the community level, a general economic disadvantage is seen, exacerbated by unemployment and low education levels, leading to poverty, political disempowerment and community disorganization. The family suffers through a loss of tradition as they attempt to assimilate into mainstream Canadian culture. These lead to low self-esteem in the individual as First Nations culture and tradition are marginalized affecting one's sense of self-identity. These factors combine to create a world where First Nations individuals feel they cannot identify completely as Aboriginal, nor can they fully identify as mainstream Canadians. When that balance cannot be found, many (particularly youths) turn to suicide as a way out.
Drinking water
400 First Nations communities in Canada had some kind of water problem between 2004 and 2014. The residents of Neskantaga First Nation in Ontario have had a boil-water advisory since 1995. In 2015, newly elected Prime Minister Justin Trudeau promised to solve the drinking water problem within five years, by investing $1.8 billion. As of October 2021, long-term boil water advisories are still present in 32 First Nations drinking water systems.
Land claims
Across Canada, many First Nations have not signed treaties with the Canadian Crown. Many First Nations are in the process of negotiating a modern treaty, which would grant them treaty rights. Some First Nation bands are also trying to resolve their historical grievances with the Canadian government. These grievances often originate from a breach of treaty obligations or of the Indian Act by the government of Canada. They can also involve mismanagement of indigenous land or assets by the Crown.
Missing and murdered women
Across Canada, there has been a large number of missing and murdered Aboriginal women since 1980. 16% of female murder victims and 12% of missing women have been Aboriginal, while demographically they constitute only 4% of the overall female population. This amounts to almost 1,200 Aboriginal females either missing or murdered in just over 30 years.
In 2014 the Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP) released Missing and Murdered Aboriginal Women: A National Operational Review. This publication documents the official findings of this demographic as well as advises for future change. It finds that there are 164 Aboriginal women still missing and 1,017 murdered, making for a total of 1,181. "There are 225 unsolved cases of either missing or murdered Aboriginal females: 105 missing for more than 30 days as of November 4, 2013, whose cause of disappearance was categorized as 'unknown' or 'foul play suspected' and 120 unsolved homicides between 1980 and 2012." Indigenous women in Canada are overrepresented among the missing and murdered females in Canada. Additionally, there are shared characteristics among these cases: most of the murders were committed by men and were someone the victim knew, either a partner or an acquaintance. "Aboriginal women between the ages of 25 and 44 are 5 times more likely than other women of the same age to die as a result of violence." These statistics portray the severity and prevalence of violence against indigenous women in Canada.
Self-governance and preservation of indigenous territories become increasingly difficult as natural resources continue to be exploited by foreign companies. Projects such as "mining, logging, hydroelectric construction, large-scale export oriented agribusiness or oil exploration" are usually coupled with environmental degradation and occasionally violence and militarization." Many scholars go so far as to link the proliferation of global neoliberalism with a rise in violence. Women's concerns are nearly always pushed aside, to be addressed later; their safety is therefore often compromised and not deemed priority. Privatization of public services and reduction in the universality of health care produces negative repercussions for those of lower socioeconomic status in rural locations; these downsides are magnified for female Aboriginals.
Missing and murdered men
Approximately 2,500 aboriginal people were murdered in Canada between 1982 and 2011, out of 15,000 murders in Canada overall. Of the 2,500 murdered aboriginal Canadians, fully 71 per cent — 1,750 — were male.
According to summaries of seven consultation sessions posted to a government website, the desire to dedicate some attention to violence against indigenous men and boys has come up at four of the meetings.
These calls to extend the scope of the inquiry to include missing and murdered aboriginal people of all genders have met with resistance and been criticized as detracting from the current focus on the issue of missing and murdered aboriginal women. Barbara Bailey, who was on the UN team that visited Canada in 2013 to investigate the violence, has said, "I think to detract now would really be a tragedy. Let's fix that problem first and then we can begin to see what else is out there."
Speaking on the matter, Minister of Indigenous Affairs, Carolyn Bennett has said, "Our mandate now is to get to the bottom of the tragedy of missing and murdered indigenous women and girls in Canada", citing sexism as being of specific concern. Dawn Lavell-Harvard, the president of the Native Women's Association of Canada, has also weighed in on the issue by saying, "Absolutely [men] deserve the same amount of attention, just not necessarily in the same forum", neither that forum nor an equal level of attention have yet to materialize.