Glass is a non-crystalline solid that is often transparent, brittle and chemically inert. It has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics.
Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of the molten form; some glasses such as volcanic glass are naturally occurring. The most familiar, and historically the oldest, types of manufactured glass are "silicate glasses" based on the chemical compound silica (silicon dioxide, or quartz), the primary constituent of sand. Soda–lime glass, containing around 70% silica, accounts for around 90% of manufactured glass. The term glass, in popular usage, is often used to refer only to this type of material, although silica-free glasses often have desirable properties for applications in modern communications technology. Some objects, such as drinking glasses and eyeglasses, are so commonly made of silicate-based glass that they are simply called by the name of the material.
Despite being brittle, buried silicate glass will survive for very long periods if not disturbed, and many examples of glass fragments exist from early glassmaking cultures. Archaeological evidence suggests glassmaking dates back to at least 3,600 BC in Mesopotamia, Egypt, or Syria. The earliest known glass objects were beads, perhaps created accidentally during metalworking or the production of faience. Due to its ease of formability into any shape, glass has been traditionally used for vessels, such as bowls, vases, bottles, jars and drinking glasses. In its most solid forms, it has also been used for paperweights and marbles. Glass can be coloured by adding metal salts or painted and printed with vitreous enamels, leading to its use in stained glass windows and other glass art objects. The refractive, reflective and transmission properties of glass make glass suitable for manufacturing optical lenses, prisms, and optoelectronics materials. Extruded glass fibres have application as optical fibres in communications networks, thermal insulating material when matted as glass wool so as to trap air, or in glass-fibre reinforced plastic (fibreglass).
Microscopic structure
The standard definition of a glass (or vitreous solid) is a solid formed by rapid melt quenching. However, the term "glass" is often defined in a broader sense, to describe any non-crystalline (amorphous) solid that exhibits a glass transition when heated towards the liquid state.
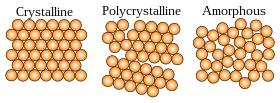
Glass is an amorphous solid. Although the atomic-scale structure of glass shares characteristics of the structure of a supercooled liquid, glass exhibits all the mechanical properties of a solid. As in other amorphous solids, the atomic structure of a glass lacks the long-range periodicity observed in crystalline solids. Due to chemical bonding constraints, glasses do possess a high degree of short-range order with respect to local atomic polyhedra. The notion that glass flows to an appreciable extent over extended periods of time well below the glass transition temperature is not supported by empirical research or theoretical analysis (see viscosity in solids). Though atomic motion at glass surfaces can be observed, and a viscosity on the order of 1017–1018 Pa s can be measured in glass, such a high value reinforces the fact that glass would not change shape appreciably over even large periods of time.
Formation from a supercooled liquid
What is the nature of the transition between a fluid or regular solid and a glassy phase? "The deepest and most interesting unsolved problem in solid state theory is probably the theory of the nature of glass and the glass transition." —P.W. Anderson
For melt quenching, if the cooling is sufficiently rapid (relative to the characteristic crystallization time) then crystallization is prevented and instead the disordered atomic configuration of the supercooled liquid is frozen into the solid state at Tg. The tendency for a material to form a glass while quenched is called glass-forming ability. This ability can be predicted by the rigidity theory. Generally, a glass exists in a structurally metastable state with respect to its crystalline form, although in certain circumstances, for example in atactic polymers, there is no crystalline analogue of the amorphous phase.
Glass is sometimes considered to be a liquid due to its lack of a first-order phase transition where certain thermodynamic variables such as volume, entropy and enthalpy are discontinuous through the glass transition range. The glass transition may be described as analogous to a second-order phase transition where the intensive thermodynamic variables such as the thermal expansivity and heat capacity are discontinuous. However, the equilibrium theory of phase transformations does not hold for glass, and hence the glass transition cannot be classed as one of the classical equilibrium phase transformations in solids.
Occurrence in nature
Glass can form naturally from volcanic magma. Obsidian is a common volcanic glass with high silica (SiO2) content formed when felsic lava extruded from a volcano cools rapidly. Impactite is a form of glass formed by the impact of a meteorite, where Moldavite (found in central and eastern Europe), and Libyan desert glass (found in areas in the eastern Sahara, the deserts of eastern Libya and western Egypt) are notable examples. Vitrification of quartz can also occur when lightning strikes sand, forming hollow, branching rootlike structures called fulgurites. Trinitite is a glassy residue formed from the desert floor sand at the Trinity nuclear bomb test site. Edeowie glass, found in South Australia, is proposed to originate from Pleistocene grassland fires, lightning strikes, or hypervelocity impact by one or several asteroids or comets.
A piece of volcanic obsidian glass
Tube fulgurites
Trinitite, a glass made by the Trinity nuclear-weapon test
History
Naturally occurring obsidian glass was used by Stone Age societies as it fractures along very sharp edges, making it ideal for cutting tools and weapons. Glassmaking dates back at least 6000 years, long before humans had discovered how to smelt iron. Archaeological evidence suggests that the first true synthetic glass was made in Lebanon and the coastal north Syria, Mesopotamia or ancient Egypt. The earliest known glass objects, of the mid-third millennium BC, were beads, perhaps initially created as accidental by-products of metalworking (slags) or during the production of faience, a pre-glass vitreous material made by a process similar to glazing. Early glass was rarely transparent and often contained impurities and imperfections, and is technically faience rather than true glass, which did not appear until the 15th century BC. However, red-orange glass beads excavated from the Indus Valley Civilization dated before 1700 BC (possibly as early as 1900 BC) predate sustained glass production, which appeared around 1600 BC in Mesopotamia and 1500 BC in Egypt. During the Late Bronze Age there was a rapid growth in glassmaking technology in Egypt and Western Asia. Archaeological finds from this period include coloured glass ingots, vessels, and beads. Much early glass production relied on grinding techniques borrowed from stoneworking, such as grinding and carving glass in a cold state.
The term glass developed in the late Roman Empire. It was in the Roman glassmaking centre at Trier (located in current-day Germany) that the late-Latin term glesum originated, probably from a Germanic word for a transparent, lustrous substance. Glass objects have been recovered across the Roman Empire in domestic, funerary, and industrial contexts, as well as trade items in marketplaces in distant provinces. Examples of Roman glass have been found outside of the former Roman Empire in China, the Baltics, the Middle East, and India. The Romans perfected cameo glass, produced by etching and carving through fused layers of different colours to produce a design in relief on the glass object.
In post-classical West Africa, Benin was a manufacturer of glass and glass beads. Glass was used extensively in Europe during the Middle Ages. Anglo-Saxon glass has been found across England during archaeological excavations of both settlement and cemetery sites. From the 10th century onwards, glass was employed in stained glass windows of churches and cathedrals, with famous examples at Chartres Cathedral and the Basilica of Saint-Denis. By the 14th century, architects were designing buildings with walls of stained glass such as Sainte-Chapelle, Paris, (1203–1248) and the East end of Gloucester Cathedral. With the change in architectural style during the Renaissance period in Europe, the use of large stained glass windows became much less prevalent, although stained glass had a major revival with Gothic Revival architecture in the 19th century.
During the 13th century, the island of Murano, Venice, became a centre for glass making, building on medieval techniques to produce colourful ornamental pieces in large quantities. Murano glass makers developed the exceptionally clear colourless glass cristallo, so called for its resemblance to natural crystal, which was extensively used for windows, mirrors, ships' lanterns, and lenses. In the 13th, 14th, and 15th centuries, enamelling and gilding on glass vessels was perfected in Egypt and Syria. Towards the end of the 17th century, Bohemia became an important region for glass production, remaining so until the start of the 20th century. By the 17th century, glass in the Venetian tradition was also being produced in England. In about 1675, George Ravenscroft invented lead crystal glass, with cut glass becoming fashionable in the 18th century. Ornamental glass objects became an important art medium during the Art Nouveau period in the late 19th century.
Throughout the 20th century, new mass production techniques led to widespread availability of glass in much larger amounts, making it practical as a building material and enabling new applications of glass. In the 1920s a mould-etch process was developed, in which art was etched directly into the mould, so that each cast piece emerged from the mould with the image already on the surface of the glass. This reduced manufacturing costs and, combined with a wider use of coloured glass, led to cheap glassware in the 1930s, which later became known as Depression glass. In the 1950s, Pilkington Bros., England, developed the float glass process, producing high-quality distortion-free flat sheets of glass by floating on molten tin. Modern multi-story buildings are frequently constructed with curtain walls made almost entirely of glass. Laminated glass has been widely applied to vehicles for windscreens. Optical glass for spectacles has been used since the Middle Ages. The production of lenses has become increasingly proficient, aiding astronomers as well as having other application in medicine and science. Glass is also employed as the aperture cover in many solar energy collectors.
In the 21st century, glass manufacturers have developed different brands of chemically strengthened glass for widespread application in touchscreens for smartphones, tablet computers, and many other types of information appliances. These include Gorilla Glass, developed and manufactured by Corning, AGC Inc.'s Dragontrail and Schott AG's Xensation.
Physical properties
Optical
Glass is in widespread use in optical systems due to its ability to refract, reflect, and transmit light following geometrical optics. The most common and oldest applications of glass in optics are as lenses, windows, mirrors, and prisms. The key optical properties refractive index, dispersion, and transmission, of glass are strongly dependent on chemical composition and, to a lesser degree, its thermal history. Optical glass typically has a refractive index of 1.4 to 2.4, and an Abbe number (which characterises dispersion) of 15 to 100. Refractive index may be modified by high-density (refractive index increases) or low-density (refractive index decreases) additives.
Glass transparency results from the absence of grain boundaries which diffusely scatter light in polycrystalline materials. Semi-opacity due to crystallization may be induced in many glasses by maintaining them for a long period at a temperature just insufficient to cause fusion. In this way, the crystalline, devitrified material, known as Réaumur's glass porcelain is produced. Although generally transparent to visible light, glasses may be opaque to other wavelengths of light. While silicate glasses are generally opaque to infrared wavelengths with a transmission cut-off at 4 μm, heavy-metal fluoride and chalcogenide glasses are transparent to infrared wavelengths of 7 to 18 μm. The addition of metallic oxides results in different coloured glasses as the metallic ions will absorb wavelengths of light corresponding to specific colours.
Other
In the manufacturing process, glasses can be poured, formed, extruded and moulded into forms ranging from flat sheets to highly intricate shapes. The finished product is brittle but can be laminated or tempered to enhance durability. Glass is typically inert, resistant to chemical attack, and can mostly withstand the action of water, making it an ideal material for the manufacture of containers for foodstuffs and most chemicals. Nevertheless, although usually highly resistant to chemical attack, glass will corrode or dissolve under some conditions. The materials that make up a particular glass composition have an effect on how quickly the glass corrodes. Glasses containing a high proportion of alkali or alkaline earth elements are more susceptible to corrosion than other glass compositions.
The density of glass varies with chemical composition with values ranging from 2.2 grams per cubic centimetre (2,200 kg/m3) for fused silica to 7.2 grams per cubic centimetre (7,200 kg/m3) for dense flint glass. Glass is stronger than most metals, with a theoretical tensile strength for pure, flawless glass estimated at 14 to 35 gigapascals (2,000,000 to 5,100,000 psi) due to its ability to undergo reversible compression without fracture. However, the presence of scratches, bubbles, and other microscopic flaws lead to a typical range of 14 to 175 megapascals (2,000 to 25,400 psi) in most commercial glasses. Several processes such as toughening can increase the strength of glass. Carefully drawn flawless glass fibres can be produced with strength of up to 11.5 gigapascals (1,670,000 psi).
Reputed flow
The observation that old windows are sometimes found to be thicker at the bottom than at the top is often offered as supporting evidence for the view that glass flows over a timescale of centuries, the assumption being that the glass has exhibited the liquid property of flowing from one shape to another. This assumption is incorrect, as once solidified, glass stops flowing. The sags and ripples observed in old glass were already there the day it was made; manufacturing processes used in the past produced sheets with imperfect surfaces and non-uniform thickness (the near-perfect float glass used today only became widespread in the 1960s).
A 2017 study computed the rate of flow of the medieval glass used in Westminster Abbey from the year 1268. The study found that the room temperature viscosity of this glass was roughly 1024 Pa·s which is about 1016 times less viscous than a previous estimate made in 1998, which focused on soda-lime silicate glass. Even with this lower viscosity, the study authors calculated that the maximum flow rate of medieval glass is 1nm per billion years, making it impossible to observe in a human timescale.
Types
Silicate
Silicon dioxide (SiO2) is a common fundamental constituent of glass. Fused quartz is a glass made from chemically pure silica. It has very low thermal expansion and excellent resistance to thermal shock, being able to survive immersion in water while red hot, resists high temperatures (1000–1500 °C) and chemical weathering, and is very hard. It is also transparent to a wider spectral range than ordinary glass, extending from the visible further into both the UV and IR ranges, and is sometimes used where transparency to these wavelengths is necessary. Fused quartz is used for high-temperature applications such as furnace tubes, lighting tubes, melting crucibles, etc. However, its high melting temperature (1723 °C) and viscosity make it difficult to work with. Therefore, normally, other substances (fluxes) are added to lower the melting temperature and simplify glass processing.
Soda–lime
Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3, "soda") is a common additive and acts to lower the glass-transition temperature. However, sodium silicate is water-soluble, so lime (CaO, calcium oxide, generally obtained from limestone), along with magnesium oxide (MgO), and aluminium oxide (Al2O3), are commonly added to improve chemical durability. Soda–lime glasses (Na2O) + lime (CaO) + magnesia (MgO) + alumina (Al2O3) account for over 75% of manufactured glass, containing about 70 to 74% silica by weight. Soda–lime–silicate glass is transparent, easily formed, and most suitable for window glass and tableware. However, it has a high thermal expansion and poor resistance to heat. Soda–lime glass is typically used for windows, bottles, light bulbs, and jars.
Borosilicate
Borosilicate glasses (e.g. Pyrex, Duran) typically contain 5–13% boron trioxide (B2O3). Borosilicate glasses have fairly low coefficients of thermal expansion (7740 Pyrex CTE is 3.25×10−6/°C as compared to about 9×10−6/°C for a typical soda–lime glass). They are, therefore, less subject to stress caused by thermal expansion and thus less vulnerable to cracking from thermal shock. They are commonly used for e.g. labware, household cookware, and sealed beam car head lamps.
Lead
The addition of lead(II) oxide into silicate glass lowers melting point and viscosity of the melt. The high density of lead glass (silica + lead oxide (PbO) + potassium oxide (K2O) + soda (Na2O) + zinc oxide (ZnO) + alumina) results in a high electron density, and hence high refractive index, making the look of glassware more brilliant and causing noticeably more specular reflection and increased optical dispersion. Lead glass has a high elasticity, making the glassware more workable and giving rise to a clear "ring" sound when struck. However, lead glass cannot withstand high temperatures well. Lead oxide also facilitates solubility of other metal oxides and is used in coloured glass. The viscosity decrease of lead glass melt is very significant (roughly 100 times in comparison with soda glass); this allows easier removal of bubbles and working at lower temperatures, hence its frequent use as an additive in vitreous enamels and glass solders. The high ionic radius of the Pb2+ ion renders it highly immobile and hinders the movement of other ions; lead glasses therefore have high electrical resistance, about two orders of magnitude higher than soda–lime glass (108.5 vs 106.5 Ω⋅cm, DC at 250 °C).
Aluminosilicate
Aluminosilicate glass typically contains 5–10% alumina (Al2O3). Aluminosilicate glass tends to be more difficult to melt and shape compared to borosilicate compositions, but has excellent thermal resistance and durability. Aluminosilicate glass is extensively used for fiberglass, used for making glass-reinforced plastics (boats, fishing rods, etc.), top-of-stove cookware, and halogen bulb glass.
Other oxide additives
The addition of barium also increases the refractive index. Thorium oxide gives glass a high refractive index and low dispersion and was formerly used in producing high-quality lenses, but due to its radioactivity has been replaced by lanthanum oxide in modern eyeglasses. Iron can be incorporated into glass to absorb infrared radiation, for example in heat-absorbing filters for movie projectors, while cerium(IV) oxide can be used for glass that absorbs ultraviolet wavelengths. Fluorine lowers the dielectric constant of glass. Fluorine is highly electronegative and lowers the polarizability of the material. Fluoride silicate glasses are used in manufacture of integrated circuits as an insulator.
Glass-ceramics
Glass-ceramic materials contain both non-crystalline glass and crystalline ceramic phases. They are formed by controlled nucleation and partial crystallisation of a base glass by heat treatment. Crystalline grains are often embedded within a non-crystalline intergranular phase of grain boundaries. Glass-ceramics exhibit advantageous thermal, chemical, biological, and dielectric properties as compared to metals or organic polymers.
The most commercially important property of glass-ceramics is their imperviousness to thermal shock. Thus, glass-ceramics have become extremely useful for countertop cooking and industrial processes. The negative thermal expansion coefficient (CTE) of the crystalline ceramic phase can be balanced with the positive CTE of the glassy phase. At a certain point (~70% crystalline) the glass-ceramic has a net CTE near zero. This type of glass-ceramic exhibits excellent mechanical properties and can sustain repeated and quick temperature changes up to 1000 °C.
Fibreglass
Fibreglass (also called glass fibre reinforced plastic, GRP) is a composite material made by reinforcing a plastic resin with glass fibres. It is made by melting glass and stretching the glass into fibres. These fibres are woven together into a cloth and left to set in a plastic resin. Fibreglass has the properties of being lightweight and corrosion resistant, and is a good insulator enabling its use as building insulation material and for electronic housing for consumer products. Fibreglass was originally used in the United Kingdom and United States during World War II to manufacture radomes. Uses of fibreglass include building and construction materials, boat hulls, car body parts, and aerospace composite materials.
Glass-fibre wool is an excellent thermal and sound insulation material, commonly used in buildings (e.g. attic and cavity wall insulation), and plumbing (e.g. pipe insulation), and soundproofing. It is produced by forcing molten glass through a fine mesh by centripetal force, and breaking the extruded glass fibres into short lengths using a stream of high-velocity air. The fibres are bonded with an adhesive spray and the resulting wool mat is cut and packed in rolls or panels.
Non-silicate
Besides common silica-based glasses many other inorganic and organic materials may also form glasses, including metals, aluminates, phosphates, borates, chalcogenides, fluorides, germanates (glasses based on GeO2), tellurites (glasses based on TeO2), antimonates (glasses based on Sb2O3), arsenates (glasses based on As2O3), titanates (glasses based on TiO2), tantalates (glasses based on Ta2O5), nitrates, carbonates, plastics, acrylic, and many other substances. Some of these glasses (e.g. Germanium dioxide (GeO2, Germania), in many respects a structural analogue of silica, fluoride, aluminate, phosphate, borate, and chalcogenide glasses) have physico-chemical properties useful for their application in fibre-optic waveguides in communication networks and other specialised technological applications.
Silica-free glasses may often have poor glass forming tendencies. Novel techniques, including containerless processing by aerodynamic levitation (cooling the melt whilst it floats on a gas stream) or splat quenching (pressing the melt between two metal anvils or rollers), may be used to increase cooling rate, or to reduce crystal nucleation triggers.
Amorphous metals
In the past, small batches of amorphous metals with high surface area configurations (ribbons, wires, films, etc.) have been produced through the implementation of extremely rapid rates of cooling. Amorphous metal wires have been produced by sputtering molten metal onto a spinning metal disk.
A number of alloys have been produced in layers with thickness exceeding 1 millimeter. These are known as bulk metallic glasses (BMG). Liquidmetal Technologies sell a number of zirconium-based BMGs.
Batches of amorphous steel have also been produced that demonstrate mechanical properties far exceeding those found in conventional steel alloys.
Experimental evidence indicates that the system Al-Fe-Si may undergo a first-order transition to an amorphous form (dubbed "q-glass") on rapid cooling from the melt. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images indicate that q-glass nucleates from the melt as discrete particles with a uniform spherical growth in all directions. While x-ray diffraction reveals the isotropic nature of q-glass, a nucleation barrier exists implying an interfacial discontinuity (or internal surface) between the glass and melt phases.
Polymers
Important polymer glasses include amorphous and glassy pharmaceutical compounds. These are useful because the solubility of the compound is greatly increased when it is amorphous compared to the same crystalline composition. Many emerging pharmaceuticals are practically insoluble in their crystalline forms. Many polymer thermoplastics familiar from everyday use are glasses. For many applications, like glass bottles or eyewear, polymer glasses (acrylic glass, polycarbonate or polyethylene terephthalate) are a lighter alternative to traditional glass.
Molecular liquids and molten salts
Molecular liquids, electrolytes, molten salts, and aqueous solutions are mixtures of different molecules or ions that do not form a covalent network but interact only through weak van der Waals forces or through transient hydrogen bonds. In a mixture of three or more ionic species of dissimilar size and shape, crystallization can be so difficult that the liquid can easily be supercooled into a glass. Examples include LiCl:RH2O (a solution of lithium chloride salt and water molecules) in the composition range 4<R<8. sugar glass, or Ca0.4K0.6(NO3)1.4. Glass electrolytes in the form of Ba-doped Li-glass and Ba-doped Na-glass have been proposed as solutions to problems identified with organic liquid electrolytes used in modern lithium-ion battery cells.
Production
Following the glass batch preparation and mixing, the raw materials are transported to the furnace. Soda–lime glass for mass production is melted in glass melting furnaces. Smaller scale furnaces for specialty glasses include electric melters, pot furnaces, and day tanks. After melting, homogenization and refining (removal of bubbles), the glass is formed. Flat glass for windows and similar applications is formed by the float glass process, developed between 1953 and 1957 by Sir Alastair Pilkington and Kenneth Bickerstaff of the UK's Pilkington Brothers, who created a continuous ribbon of glass using a molten tin bath on which the molten glass flows unhindered under the influence of gravity. The top surface of the glass is subjected to nitrogen under pressure to obtain a polished finish. Container glass for common bottles and jars is formed by blowing and pressing methods. This glass is often slightly modified chemically (with more alumina and calcium oxide) for greater water resistance.
Once the desired form is obtained, glass is usually annealed for the removal of stresses and to increase the glass's hardness and durability. Surface treatments, coatings or lamination may follow to improve the chemical durability (glass container coatings, glass container internal treatment), strength (toughened glass, bulletproof glass, windshields), or optical properties (insulated glazing, anti-reflective coating).
New chemical glass compositions or new treatment techniques can be initially investigated in small-scale laboratory experiments. The raw materials for laboratory-scale glass melts are often different from those used in mass production because the cost factor has a low priority. In the laboratory mostly pure chemicals are used. Care must be taken that the raw materials have not reacted with moisture or other chemicals in the environment (such as alkali or alkaline earth metal oxides and hydroxides, or boron oxide), or that the impurities are quantified (loss on ignition). Evaporation losses during glass melting should be considered during the selection of the raw materials, e.g., sodium selenite may be preferred over easily evaporating selenium dioxide (SeO2). Also, more readily reacting raw materials may be preferred over relatively inert ones, such as aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3) over alumina (Al2O3). Usually, the melts are carried out in platinum crucibles to reduce contamination from the crucible material. Glass homogeneity is achieved by homogenizing the raw materials mixture (glass batch), by stirring the melt, and by crushing and re-melting the first melt. The obtained glass is usually annealed to prevent breakage during processing.
Colour
Colour in glass may be obtained by addition of homogenously distributed electrically charged ions (or colour centres). While ordinary soda–lime glass appears colourless in thin section, iron(II) oxide (FeO) impurities produce a green tint in thick sections. Manganese dioxide (MnO2), which gives glass a purple colour, may be added to remove the green tint given by FeO. FeO and chromium(III) oxide (Cr2O3) additives are used in the production of green bottles. Iron (III) oxide, on the other-hand, produces yellow or yellow-brown glass. Low concentrations (0.025 to 0.1%) of cobalt oxide (CoO) produces rich, deep blue cobalt glass. Chromium is a very powerful colourising agent, yielding dark green. Sulphur combined with carbon and iron salts produces amber glass ranging from yellowish to almost black. A glass melt can also acquire an amber colour from a reducing combustion atmosphere. Cadmium sulfide produces imperial red, and combined with selenium can produce shades of yellow, orange, and red. The additive Copper(II) oxide (CuO) produces a turquoise colour in glass, in contrast to Copper(I) oxide (Cu2O) which gives a dull brown-red colour.
Iron(II) oxide and chromium(III) oxide additives are often used in the production of green bottles.
Cobalt oxide produces rich, deep blue glass, such as Bristol blue glass.
Different oxide additives produce the different colours in glass: turquoise (Copper(II) oxide), purple (Manganese dioxide), and red (Cadmium sulfide).
Uses
Architecture and windows
Soda–lime sheet glass is typically used as transparent glazing material, typically as windows in external walls of buildings. Float or rolled sheet glass products is cut to size either by scoring and snapping the material, laser cutting, water jets, or diamond bladed saw. The glass may be thermally or chemically tempered (strengthened) for safety and bent or curved during heating. Surface coatings may be added for specific functions such as scratch resistance, blocking specific wavelengths of light (e.g. infrared or ultraviolet), dirt-repellence (e.g. self-cleaning glass), or switchable electrochromic coatings.
Structural glazing systems represent one of the most significant architectural innovations of modern times, where glass buildings now often dominate skylines of many modern cities. These systems use stainless steel fittings countersunk into recesses in the corners of the glass panels allowing strengthened panes to appear unsupported creating a flush exterior. Structural glazing systems have their roots in iron and glass conservatories of the nineteenth century
Tableware
Glass is an essential component of tableware and is typically used for water, beer and wine drinking glasses. Wine glasses are typically stemware, i.e. goblets formed from a bowl, stem, and foot. Crystal or Lead crystal glass may be cut and polished to produce decorative drinking glasses with gleaming facets. Other uses of glass in tableware include decanters, jugs, plates, and bowls.
Packaging
The inert and impermeable nature of glass makes it a stable and widely used material for food and drink packaging as glass bottles and jars. Most container glass is soda–lime glass, produced by blowing and pressing techniques. Container glass has a lower magnesium oxide and sodium oxide content than flat glass, and a higher silica, calcium oxide, and aluminum oxide content. Its higher content of water-insoluble oxides imparts slightly higher chemical durability against water, which is advantageous for storing beverages and food. Glass packaging is sustainable, readily recycled, reusable and refillable.
For electronics applications, glass can be used as a substrate in the manufacture of integrated passive devices, thin-film bulk acoustic resonators, and as a hermetic sealing material in device packaging, including very thin solely glass based encapsulation of integrated circuits and other semiconductors in high manufacturing volumes.
Laboratories
Glass is an important material in scientific laboratories for the manufacture of experimental apparatus because it is relatively cheap, readily formed into required shapes for experiment, easy to keep clean, can withstand heat and cold treatment, is generally non-reactive with many reagents, and its transparency allows for the observation of chemical reactions and processes. Laboratory glassware applications include flasks, petri dishes, test tubes, pipettes, graduated cylinders, glass lined metallic containers for chemical processing, fractionation columns, glass pipes, Schlenk lines, gauges, and thermometers. Although most standard laboratory glassware has been mass-produced since the 1920s, scientists still employ skilled glassblowers to manufacture bespoke glass apparatus for their experimental requirements.
A Vigreux column in a laboratory setup
A Schlenk line with four ports
Erlenmeyer flask
Optics
Glass is a ubiquitous material in optics by virtue of its ability to refract, reflect, and transmit light. These and other optical properties can be controlled by varying chemical compositions, thermal treatment, and manufacturing techniques. The many applications of glass in optics includes glasses for eyesight correction, imaging optics (e.g. lenses and mirrors in telescopes, microscopes, and cameras), fibre optics in telecommunications technology, and integrated optics. Microlenses and gradient-index optics (where the refractive index is non-uniform) find application in e.g. reading optical discs, laser printers, photocopiers, and laser diodes.
Art
Glass as art dates to least 1300 BC shown as an example of natural glass found in Tutankhamun's pectoral, which also contained vitreous enamel, that is to say, melted coloured glass used on a metal backing. Enamelled glass, the decoration of glass vessels with coloured glass paints, has existed since 1300 BC, and was prominent in the early 20th century with Art Nouveau glass and that of the House of Fabergé in St. Petersburg, Russia. Both techniques were used in stained glass, which reached its height roughly from 1000 to 1550, before a revival in the 19th century.
The 19th century saw a revival in ancient glassmaking techniques including cameo glass, achieved for the first time since the Roman Empire, initially mostly for pieces in a neo-classical style. The Art Nouveau movement made great use of glass, with René Lalique, Émile Gallé, and Daum of Nancy in the first French wave of the movement, producing coloured vases and similar pieces, often in cameo glass or in lustre glass techniques.
Louis Comfort Tiffany in America specialised in stained glass, both secular and religious, in panels and his famous lamps. The early 20th-century saw the large-scale factory production of glass art by firms such as Waterford and Lalique. Small studios may hand-produce glass artworks. Techniques for producing glass art include blowing, kiln-casting, fusing, slumping, pâte de verre, flame-working, hot-sculpting and cold-working. Cold work includes traditional stained glass work and other methods of shaping glass at room temperature. Objects made out of glass include vessels, paperweights, marbles, beads, sculptures and installation art.