In quantum physics, a measurement is the testing or manipulation of a physical system to yield a numerical result. A fundamental feature of quantum theory is that the predictions it makes are probabilistic. The procedure for finding a probability involves combining a quantum state, which mathematically describes a quantum system, with a mathematical representation of the measurement to be performed on that system. The formula for this calculation is known as the Born rule. For example, a quantum particle like an electron can be described by a quantum state that associates to each point in space a complex number called a probability amplitude. Applying the Born rule to these amplitudes gives the probabilities that the electron will be found in one region or another when an experiment is performed to locate it. This is the best the theory can do; it cannot say for certain where the electron will be found. The same quantum state can also be used to make a prediction of how the electron will be moving, if an experiment is performed to measure its momentum instead of its position. The uncertainty principle implies that, whatever the quantum state, the range of predictions for the electron's position and the range of predictions for its momentum cannot both be narrow. Some quantum states imply a near-certain prediction of the result of a position measurement, but the result of a momentum measurement will be highly unpredictable, and vice versa. Furthermore, the fact that nature violates the statistical conditions known as Bell inequalities indicates that the unpredictability of quantum measurement results cannot be explained away as due to ignorance about "hidden variables" within quantum systems.
Measuring a quantum system generally changes the quantum state that describes that system. This is a central feature of quantum mechanics, one that is both mathematically intricate and conceptually subtle. The mathematical tools for making predictions about what measurement outcomes may occur, and how quantum states can change, were developed during the 20th century and make use of linear algebra and functional analysis. Quantum physics has proven to be an empirical success and to have wide-ranging applicability. However, on a more philosophical level, debates continue about the meaning of the measurement concept.
Mathematical formalism
"Observables" as self-adjoint operators
In quantum mechanics, each physical system is associated with a Hilbert space, each element of which represents a possible state of the physical system. The approach codified by John von Neumann represents a measurement upon a physical system by a self-adjoint operator on that Hilbert space termed an "observable". These observables play the role of measurable quantities familiar from classical physics: position, momentum, energy, angular momentum and so on. The dimension of the Hilbert space may be infinite, as it is for the space of square-integrable functions on a line, which is used to define the quantum physics of a continuous degree of freedom. Alternatively, the Hilbert space may be finite-dimensional, as occurs for spin degrees of freedom. Many treatments of the theory focus on the finite-dimensional case, as the mathematics involved is somewhat less demanding. Indeed, introductory physics texts on quantum mechanics often gloss over mathematical technicalities that arise for continuous-valued observables and infinite-dimensional Hilbert spaces, such as the distinction between bounded and unbounded operators; questions of convergence (whether the limit of a sequence of Hilbert-space elements also belongs to the Hilbert space), exotic possibilities for sets of eigenvalues, like Cantor sets; and so forth. These issues can be satisfactorily resolved using spectral theory; the present article will avoid them whenever possible.
Projective measurement
The eigenvectors of a von Neumann observable form an orthonormal basis for the Hilbert space, and each possible outcome of that measurement corresponds to one of the vectors comprising the basis. A density operator is a positive-semidefinite operator on the Hilbert space whose trace is equal to 1. For each measurement that can be defined, the probability distribution over the outcomes of that measurement can be computed from the density operator. The procedure for doing so is the Born rule, which states that
where is the density operator, and is the projection operator onto the basis vector corresponding to the measurement outcome . The average of the eigenvalues of a von Neumann observable, weighted by the Born rule probabilities, is the expectation value of that observable. For an observable , the expectation value given a quantum state is
A density operator that is a rank-1 projection is known as a pure quantum state, and all quantum states that are not pure are designated mixed. Pure states are also known as wavefunctions. Assigning a pure state to a quantum system implies certainty about the outcome of some measurement on that system (i.e., for some outcome ). Any mixed state can be written as a convex combination of pure states, though not in a unique way. The state space of a quantum system is the set of all states, pure and mixed, that can be assigned to it.
The Born rule associates a probability with each unit vector in the Hilbert space, in such a way that these probabilities sum to 1 for any set of unit vectors comprising an orthonormal basis. Moreover, the probability associated with a unit vector is a function of the density operator and the unit vector, and not of additional information like a choice of basis for that vector to be embedded in. Gleason's theorem establishes the converse: all assignments of probabilities to unit vectors (or, equivalently, to the operators that project onto them) that satisfy these conditions take the form of applying the Born rule to some density operator.
Generalized measurement (POVM)
In functional analysis and quantum measurement theory, a positive-operator-valued measure (POVM) is a measure whose values are positive semi-definite operators on a Hilbert space. POVMs are a generalisation of projection-valued measures (PVMs) and, correspondingly, quantum measurements described by POVMs are a generalisation of quantum measurement described by PVMs. In rough analogy, a POVM is to a PVM what a mixed state is to a pure state. Mixed states are needed to specify the state of a subsystem of a larger system (see Schrödinger–HJW theorem); analogously, POVMs are necessary to describe the effect on a subsystem of a projective measurement performed on a larger system. POVMs are the most general kind of measurement in quantum mechanics, and can also be used in quantum field theory. They are extensively used in the field of quantum information.
In the simplest case, of a POVM with a finite number of elements acting on a finite-dimensional Hilbert space, a POVM is a set of positive semi-definite matrices on a Hilbert space that sum to the identity matrix,
In quantum mechanics, the POVM element is associated with the measurement outcome , such that the probability of obtaining it when making a measurement on the quantum state is given by
- ,
where is the trace operator. When the quantum state being measured is a pure state this formula reduces to
- .
State change due to measurement
A measurement upon a quantum system will generally bring about a change of the quantum state of that system. Writing a POVM does not provide the complete information necessary to describe this state-change process. To remedy this, further information is specified by decomposing each POVM element into a product:
The Kraus operators , named for Karl Kraus, provide a specification of the state-change process. They are not necessarily self-adjoint, but the products are. If upon performing the measurement the outcome is obtained, then the initial state is updated to
An important special case is the Lüders rule, named for Gerhart Lüders. If the POVM is itself a PVM, then the Kraus operators can be taken to be the projectors onto the eigenspaces of the von Neumann observable:
If the initial state is pure, and the projectors have rank 1, they can be written as projectors onto the vectors and , respectively. The formula simplifies thus to
This has historically been known as the "reduction of the wave packet" or the "collapse of the wavefunction". The pure state implies a probability-one prediction for any von Neumann observable that has as an eigenvector. Introductory texts on quantum theory often express this by saying that if a quantum measurement is repeated in quick succession, the same outcome will occur both times. This is an oversimplification, since the physical implementation of a quantum measurement may involve a process like the absorption of a photon; after the measurement, the photon does not exist to be measured again.
We can define a linear, trace-preserving, completely positive map, by summing over all the possible post-measurement states of a POVM without the normalisation:
It is an example of a quantum channel, and can be interpreted as expressing how a quantum state changes if a measurement is performed but the result of that measurement is lost.
Examples
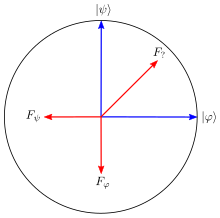
The prototypical example of a finite-dimensional Hilbert space is a qubit, a quantum system whose Hilbert space is 2-dimensional. A pure state for a qubit can be written as a linear combination of two orthogonal basis states and with complex coefficients:
A measurement in the basis will yield outcome with probability and outcome with probability , so by normalization,
An arbitrary state for a qubit can be written as a linear combination of the Pauli matrices, which provide a basis for self-adjoint matrices:
where the real numbers are the coordinates of a point within the unit ball and
POVM elements can be represented likewise, though the trace of a POVM element is not fixed to equal 1. The Pauli matrices are traceless and orthogonal to one another with respect to the Hilbert–Schmidt inner product, and so the coordinates of the state are the expectation values of the three von Neumann measurements defined by the Pauli matrices. If such a measurement is applied to a qubit, then by the Lüders rule, the state will update to the eigenvector of that Pauli matrix corresponding to the measurement outcome. The eigenvectors of are the basis states and , and a measurement of is often called a measurement in the "computational basis." After a measurement in the computational basis, the outcome of a or measurement is maximally uncertain.
A pair of qubits together form a system whose Hilbert space is 4-dimensional. One significant von Neumann measurement on this system is that defined by the Bell basis, a set of four maximally entangled states:

A common and useful example of quantum mechanics applied to a continuous degree of freedom is the quantum harmonic oscillator. This system is defined by the Hamiltonian
where , the momentum operator and the position operator are self-adjoint operators on the Hilbert space of square-integrable functions on the real line. The energy eigenstates solve the time-independent Schrödinger equation:
These eigenvalues can be shown to be given by
and these values give the possible numerical outcomes of an energy measurement upon the oscillator. The set of possible outcomes of a position measurement on a harmonic oscillator is continuous, and so predictions are stated in terms of a probability density function that gives the probability of the measurement outcome lying in the infinitesimal interval from to .
History of the measurement concept
The "old quantum theory"
The old quantum theory is a collection of results from the years 1900–1925 which predate modern quantum mechanics. The theory was never complete or self-consistent, but was rather a set of heuristic corrections to classical mechanics. The theory is now understood as a semi-classical approximation to modern quantum mechanics. Notable results from this period include Planck's calculation of the blackbody radiation spectrum, Einstein's explanation of the photoelectric effect, Einstein and Debye's work on the specific heat of solids, Bohr and van Leeuwen's proof that classical physics cannot account for diamagnetism, Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom and Arnold Sommerfeld's extension of the Bohr model to include relativistic effects.

The Stern–Gerlach experiment, proposed in 1921 and implemented in 1922, became a prototypical example of a quantum measurement having a discrete set of possible outcomes. In the original experiment, silver atoms were sent through a spatially varying magnetic field, which deflected them before they struck a detector screen, such as a glass slide. Particles with non-zero magnetic moment are deflected, due to the magnetic field gradient, from a straight path. The screen reveals discrete points of accumulation, rather than a continuous distribution, owing to the particles' quantized spin.
Transition to the “new” quantum theory
A 1925 paper by Heisenberg, known in English as "Quantum theoretical re-interpretation of kinematic and mechanical relations", marked a pivotal moment in the maturation of quantum physics. Heisenberg sought to develop a theory of atomic phenomena that relied only on "observable" quantities. At the time, and in contrast with the later standard presentation of quantum mechanics, Heisenberg did not regard the position of an electron bound within an atom as "observable". Instead, his principal quantities of interest were the frequencies of light emitted or absorbed by atoms.
The uncertainty principle dates to this period. It is frequently attributed to Heisenberg, who introduced the concept in analyzing a thought experiment where one attempts to measure an electron's position and momentum simultaneously. However, Heisenberg did not give precise mathematical definitions of what the "uncertainty" in these measurements meant. The precise mathematical statement of the position-momentum uncertainty principle is due to Kennard, Pauli, and Weyl, and its generalization to arbitrary pairs of noncommuting observables is due to Robertson and Schrödinger.
Writing and for the self-adjoint operators representing position and momentum respectively, a standard deviation of position can be defined as
and likewise for the momentum:
The Kennard–Pauli–Weyl uncertainty relation is
This inequality means that no preparation of a quantum particle can imply simultaneously precise predictions for a measurement of position and for a measurement of momentum. The Robertson inequality generalizes this to the case of an arbitrary pair of self-adjoint operators and . The commutator of these two operators is
and this provides the lower bound on the product of standard deviations:
Substituting in the canonical commutation relation , an expression first postulated by Max Born in 1925, recovers the Kennard–Pauli–Weyl statement of the uncertainty principle.
The existence of the uncertainty principle naturally raises the question of whether quantum mechanics can be understood as an approximation to a more exact theory. Do there exist "hidden variables", more fundamental than the quantities addressed in quantum theory itself, knowledge of which would allow more exact predictions than quantum theory can provide? A collection of results, most significantly Bell's theorem, have demonstrated that broad classes of such hidden-variable theories are in fact incompatible with quantum physics.
Bell published the theorem now known by his name in 1964, investigating more deeply a thought experiment originally proposed in 1935 by Einstein, Podolsky and Rosen. According to Bell's theorem, if nature actually operates in accord with any theory of local hidden variables, then the results of a Bell test will be constrained in a particular, quantifiable way. If a Bell test is performed in a laboratory and the results are not thus constrained, then they are inconsistent with the hypothesis that local hidden variables exist. Such results would support the position that there is no way to explain the phenomena of quantum mechanics in terms of a more fundamental description of nature that is more in line with the rules of classical physics. Many types of Bell test have been performed in physics laboratories, often with the goal of ameliorating problems of experimental design or set-up that could in principle affect the validity of the findings of earlier Bell tests. This is known as "closing loopholes in Bell tests". To date, Bell tests have found that the hypothesis of local hidden variables is inconsistent with the way that physical systems behave.
Quantum systems as measuring devices
The Robertson–Schrödinger uncertainty principle establishes that when two observables do not commute, there is a tradeoff in predictability between them. The Wigner–Araki–Yanase theorem demonstrates another consequence of non-commutativity: the presence of a conservation law limits the accuracy with which observables that fail to commute with the conserved quantity can be measured. Further investigation in this line led to the formulation of the Wigner–Yanase skew information.
Historically, experiments in quantum physics have often been described in semiclassical terms. For example, the spin of an atom in a Stern–Gerlach experiment might be treated as a quantum degree of freedom, while the atom is regarded as moving through a magnetic field described by the classical theory of Maxwell's equations. But the devices used to build the experimental apparatus are themselves physical systems, and so quantum mechanics should be applicable to them as well. Beginning in the 1950s, Rosenfeld, von Weizsäcker and others tried to develop consistency conditions that expressed when a quantum-mechanical system could be treated as a measuring apparatus. One proposal for a criterion regarding when a system used as part of a measuring device can be modeled semiclassically relies on the Wigner function, a quasiprobability distribution that can be treated as a probability distribution on phase space in those cases where it is everywhere non-negative.
Decoherence
A quantum state for an imperfectly isolated system will generally evolve to be entangled with the quantum state for the environment. Consequently, even if the system's initial state is pure, the state at a later time, found by taking the partial trace of the joint system-environment state, will be mixed. This phenomenon of entanglement produced by system-environment interactions tends to obscure the more exotic features of quantum mechanics that the system could in principle manifest. Quantum decoherence, as this effect is known, was first studied in detail during the 1970s. (Earlier investigations into how classical physics might be obtained as a limit of quantum mechanics had explored the subject of imperfectly isolated systems, but the role of entanglement was not fully appreciated.) A significant portion of the effort involved in quantum computing is to avoid the deleterious effects of decoherence.
To illustrate, let denote the initial state of the system, the initial state of the environment and the Hamiltonian specifying the system-environment interaction. The density operator can be diagonalized and written as a linear combination of the projectors onto its eigenvectors:
Expressing time evolution for a duration by the unitary operator , the state for the system after this evolution is
which evaluates to
The quantities surrounding can be identified as Kraus operators, and so this defines a quantum channel.
Specifying a form of interaction between system and environment can establish a set of "pointer states," states for the system that are (approximately) stable, apart from overall phase factors, with respect to environmental fluctuations. A set of pointer states defines a preferred orthonormal basis for the system's Hilbert space.
Quantum information and computation
Quantum information science studies how information science and its application as technology depend on quantum-mechanical phenomena. Understanding measurement in quantum physics is important for this field in many ways, some of which are briefly surveyed here.
Measurement, entropy, and distinguishability
The von Neumann entropy is a measure of the statistical uncertainty represented by a quantum state. For a density matrix , the von Neumann entropy is
writing in terms of its basis of eigenvectors,
the von Neumann entropy is
This is the Shannon entropy of the set of eigenvalues interpreted as a probability distribution, and so the von Neumann entropy is the Shannon entropy of the random variable defined by measuring in the eigenbasis of . Consequently, the von Neumann entropy vanishes when is pure. The von Neumann entropy of can equivalently be characterized as the minimum Shannon entropy for a measurement given the quantum state , with the minimization over all POVMs with rank-1 elements.
Many other quantities used in quantum information theory also find motivation and justification in terms of measurements. For example, the trace distance between quantum states is equal to the largest difference in probability that those two quantum states can imply for a measurement outcome:
Similarly, the fidelity of two quantum states, defined by
expresses the probability that one state will pass a test for identifying a successful preparation of the other. The trace distance provides bounds on the fidelity via the Fuchs–van de Graaf inequalities:
Quantum circuits

Quantum circuits are a model for quantum computation in which a computation is a sequence of quantum gates followed by measurements. The gates are reversible transformations on a quantum mechanical analog of an n-bit register. This analogous structure is referred to as an n-qubit register. Measurements, drawn on a circuit diagram as stylized pointer dials, indicate where and how a result is obtained from the quantum computer after the steps of the computation are executed. Without loss of generality, one can work with the standard circuit model, in which the set of gates are single-qubit unitary transformations and controlled NOT gates on pairs of qubits, and all measurements are in the computational basis.
Measurement-based quantum computation
Measurement-based quantum computation (MBQC) is a model of quantum computing in which the answer to a question is, informally speaking, created in the act of measuring the physical system that serves as the computer.
Quantum tomography
Quantum state tomography is a process by which, given a set of data representing the results of quantum measurements, a quantum state consistent with those measurement results is computed. It is named by analogy with tomography, the reconstruction of three-dimensional images from slices taken through them, as in a CT scan. Tomography of quantum states can be extended to tomography of quantum channels and even of measurements.
Quantum metrology
Quantum metrology is the use of quantum physics to aid the measurement of quantities that, generally, had meaning in classical physics, such as exploiting quantum effects to increase the precision with which a length can be measured. A celebrated example is the introduction of squeezed light into the LIGO experiment, which increased its sensitivity to gravitational waves.
Laboratory implementations
The range of physical procedures to which the mathematics of quantum measurement can be applied is very broad. In the early years of the subject, laboratory procedures involved the recording of spectral lines, the darkening of photographic film, the observation of scintillations, finding tracks in cloud chambers, and hearing clicks from Geiger counters. Language from this era persists, such as the description of measurement outcomes in the abstract as "detector clicks".
The double-slit experiment is a prototypical illustration of quantum interference, typically described using electrons or photons. The first interference experiment to be carried out in a regime where both wave-like and particle-like aspects of photon behavior are significant was G. I. Taylor's test in 1909. Taylor used screens of smoked glass to attenuate the light passing through his apparatus, to the extent that, in modern language, only one photon would be illuminating the interferometer slits at a time. He recorded the interference patterns on photographic plates; for the dimmest light, the exposure time required was roughly three months. In 1974, the Italian physicists Pier Giorgio Merli, Gian Franco Missiroli, and Giulio Pozzi implemented the double-slit experiment using single electrons and a television tube. A quarter-century later, a team at the University of Vienna performed an interference experiment with buckyballs, in which the buckyballs that passed through the interferometer were ionized by a laser, and the ions then induced the emission of electrons, emissions which were in turn amplified and detected by an electron multiplier.
Modern quantum optics experiments can employ single-photon detectors. For example, in the "BIG Bell test" of 2018, several of the laboratory setups used single-photon avalanche diodes. Another laboratory setup used superconducting qubits. The standard method for performing measurements upon superconducting qubits is to couple a qubit with a resonator in such a way that the characteristic frequency of the resonator shifts according to the state for the qubit, and detecting this shift by observing how the resonator reacts to a probe signal.
Interpretations of quantum mechanics

Despite the consensus among scientists that quantum physics is in practice a successful theory, disagreements persist on a more philosophical level. Many debates in the area known as quantum foundations concern the role of measurement in quantum mechanics. Recurring questions include which interpretation of probability theory is best suited for the probabilities calculated from the Born rule; and whether the apparent randomness of quantum measurement outcomes is fundamental, or a consequence of a deeper deterministic process. Worldviews that present answers to questions like these are known as "interpretations" of quantum mechanics; as the physicist N. David Mermin once quipped, "New interpretations appear every year. None ever disappear."
A central concern within quantum foundations is the "quantum measurement problem," though how this problem is delimited, and whether it should be counted as one question or multiple separate issues, are contested topics. Of primary interest is the seeming disparity between apparently distinct types of time evolution. Von Neumann declared that quantum mechanics contains "two fundamentally different types" of quantum-state change. First, there are those changes involving a measurement process, and second, there is unitary time evolution in the absence of measurement. The former is stochastic and discontinuous, writes von Neumann, and the latter deterministic and continuous. This dichotomy has set the tone for much later debate. Some interpretations of quantum mechanics find the reliance upon two different types of time evolution distasteful and regard the ambiguity of when to invoke one or the other as a deficiency of the way quantum theory was historically presented. To bolster these interpretations, their proponents have worked to derive ways of regarding "measurement" as a secondary concept and deducing the seemingly stochastic effect of measurement processes as approximations to more fundamental deterministic dynamics. However, consensus has not been achieved among proponents of the correct way to implement this program, and in particular how to justify the use of the Born rule to calculate probabilities. Other interpretations regard quantum states as statistical information about quantum systems, thus asserting that abrupt and discontinuous changes of quantum states are not problematic, simply reflecting updates of the available information. Of this line of thought, Bell asked, "Whose information? Information about what?" Answers to these questions vary among proponents of the informationally-oriented interpretations.

























































![{\displaystyle [A,B]=AB-BA,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b2a47259b42e63c048c65f67d304404867841951)
![{\displaystyle \sigma _{A}\sigma _{B}\geq \left|{\frac {1}{2i}}\langle [A,B]\rangle \right|={\frac {1}{2}}\left|\langle [A,B]\rangle \right|.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d15f644ab43a23f762c87886b1ae050f83b001ba)
![{\displaystyle [{x},{p}]=i\hbar }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d7dad6e853b68a93aa6607b63a3a08cfc24d6088)






![{\displaystyle \rho _{S}'={\rm {tr}}_{E}U\left[\rho _{S}\otimes \left(\sum _{i}p_{i}|\psi _{i}\rangle \langle \psi _{i}|\right)\right]U^{\dagger },}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/04f34a1930a48d600509e418c6bd2616f2bfe784)




![{\displaystyle {\frac {1}{2}}||\rho -\sigma ||=\max _{0\leq E\leq I}[{\rm {tr}}(E\rho )-{\rm {tr}}(E\sigma )].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/546b08be0062e916339e9e0efc9f88b40e8553a7)


