Overview



Tax policy is the mechanism through which market results are redistributed, affecting after-tax inequality. The provisions of the United States Internal Revenue Code regarding income taxes and estate taxes have undergone significant changes under both Republican and Democratic administrations and Congresses since 1964. Since the Johnson Administration, the top marginal income tax rates have been reduced from 91% for the wealthiest Americans in 1963, to a low of 35% under George W Bush, rising recently to 39.6% (or in some cases 43.4%) in 2013 under the Obama Administration. Capital gains taxes have also decreased over the last several years, and have experienced a more punctuated evolution than income taxes as significant and frequent changes to these rates occurred from 1981 to 2011. Both estate and inheritance taxes have been steadily declining since the 1990s. Economic inequality in the United States has been steadily increasing since the 1980s as well and economists such as Paul Krugman, Joseph Stiglitz, and Peter Orszag, politicians like Barack Obama and Paul Ryan, and media entities have engaged in debates and accusations over the role of tax policy changes in perpetuating economic inequality.
Tax expenditures (i.e., deductions, exemptions, and preferential tax rates) represent a major driver of inequality, as the top 20% get roughly 50% of the benefit from them, with the top 1% getting 17% of the benefit. For example, a 2011 Congressional Research Service report stated, "Changes in capital gains and dividends were the largest contributor to the increase in the overall income inequality." CBO estimated tax expenditures would be $1.5 trillion in fiscal year 2017, approximately 8% GDP; for scale, the budget deficit historically has averaged around 3% GDP.
Scholarly and popular literature exists on this topic with numerous works on both sides of the debate. The work of Emmanuel Saez, for example, has concerned the role of American tax policy in aggregating wealth into the richest households in recent years while Thomas Sowell and Gary Becker maintain that education, globalization, and market forces are the root causes of income and overall economic inequality. The Revenue Act of 1964 and the "Bush Tax Cuts" coincide with the rising economic inequality in the United States both by socioeconomic class and race.
Changes in economic inequality

Income inequality
Economists and related experts have described America's growing income inequality as "deeply worrying", unjust, a danger to democracy/social stability, and a sign of national decline. Yale professor Robert Shiller, who was among three Americans who won the Nobel prize for economics in 2013, said after receiving the award, "The most important problem that we are facing now today, I think, is rising inequality in the United States and elsewhere in the world."
Inequality in land and income ownership is negatively correlated with subsequent economic growth. A strong demand for redistribution may occur in societies where a large section of the population does not have access to the productive resources of the economy. Voters may internalize such issues. High unemployment rates have a significant negative effect when interacting with increases in inequality. Increasing inequality harms growth in countries with high levels of urbanization. High and persistent unemployment also has a negative effect on subsequent long-run economic growth. Unemployment may seriously harm growth because it is a waste of resources, generates redistributive pressures and distortions, depreciates existing human capital and deters its accumulation, drives people to poverty, results in liquidity constraints that limit labor mobility, and because it erodes individual self-esteem and promotes social dislocation, unrest and conflict. Policies to control unemployment and reduce its inequality-associated effects can strengthen long-run growth.
Gini coefficient
The Gini Coefficient, a statistical measurement of the inequality present in a nation's income distribution developed by Italian statistician and sociologist Corrado Gini, for the United States has increased over the last few decades. The closer the Gini Coefficient is to one, the closer its income distribution is to absolute inequality. In 2007, the United Nations approximated the United States' Gini Coefficient at 41% while the CIA Factbook placed the coefficient at 45%. The United States' Gini Coefficient was below 40% in 1964 and slightly declined through the 1970s. However, around 1981, the Gini Coefficient began to increase and rose steadily through the 2000s.
Wealth distribution
Wealth, in economic terms, is defined as the value of an individual's or household's total assets minus his or its total liabilities. The components of wealth include assets, both monetary and non-monetary, and income. Wealth is accrued over time by savings and investment. Levels of savings and investment are determined by an individual's or a household's consumption, the market real interest rate, and income. Individuals and households with higher incomes are more capable of saving and investing because they can set aside more of their disposable income to it while still optimizing their consumption functions. It is more difficult for lower-income individuals and households to save and invest because they need to use a higher percentage of their income for fixed and variable costs thus leaving them with a more limited amount of disposable income to optimize their consumption. Accordingly, a natural wealth gap exists in any market as some workers earn higher wages and thus are able to divert more income towards savings and investment which build wealth.
The wealth gap in the United States is large and the large majority of net worth and financial wealth is concentrated in a relatively very small percentage of the population. Sociologist and University of California-Santa Cruz professor G. William Domhoff writes that "numerous studies show that the wealth distribution has been extremely concentrated throughout American history" and that "most Americans (high income or low income, female or male, young or old, Republican or Democrat) have no idea just how concentrated the wealth distribution actually is." In 2007, the top 1% of households owned 34.6% of all privately held wealth and the next 19% possessed 50.5% of all privately held wealth. Taken together, 20% of Americans controlled 85.1% of all privately held wealth in the country. In the same year, the top 1% of households also possessed 42.7% of all financial wealth and the top 19% owned 50.3% of all financial wealth in the country. Together, the top 20% of households owned 93% of the financial wealth in the United States. Financial wealth is defined as "net worth minus net equity in owner-occupied housing." In real money terms and not just percentage share of wealth, the wealth gap between the top 1% and the other quartiles of the population is immense. The average wealth of households in the top 1% of the population was $13.977 million in 2009. This is fives times as large as the average household wealth for the next four percent (average household wealth of $2.7 million), fifteen times as large as the average household wealth for the next five percent (average household wealth of $908,000), and twenty-nine times the size of the average household wealth of the next ten percent of the population (average household wealth of $477,000) in the same year. Comparatively, the average household wealth of the lowest quartile was -$27,000 and the average household wealth of the second quartile (bottom 20-40th percentile of the population) was $5,000. The middle class, the middle quartile of the population, has an average household wealth level of $65,000.
According to the Congressional Budget Office, the real, or inflation-adjusted, after-tax earnings of the wealthiest one percent of Americans grew by 275% from 1979 to 2007. Simultaneously, the real, after-tax earnings of the bottom twenty percent of wage earnings in the United States grew 18%. The difference in the growth of real income of the top 1% and the bottom 20% of Americans was 257%. The average increase in real, after-tax income for all U.S. households during this time period was 62% which is slightly below the real, after-tax income growth rate of 65% experienced by the top 20% of wage earners, not accounting for the top 1%. Data aggregated and analyzed by Robert B. Reich, Thomas Piketty, and Emmanuel Saez and released in a New York Times article written by Bill Marsh shows that real wages for production and non-supervisory workers, which account for 82% of the U.S. workforce, increased by 100% from 1947 to 1979 but then increased by only 8% from 1979–2009. Their data also shows that the bottom fifth experienced a 122% growth rate in wages from 1947 to 1979 but then experienced a negative growth rate of 4% in their real wages from 1979–2009. The real wages of the top fifth rose by 99% and then 55% during the same periods, respectively. Average real hourly wages have also increased by a significantly larger rate for the top 20% than they have for the bottom 20%. Real family income for the bottom 20% increased by 7.4% from 1979 to 2009 while it increased by 49% for the top 20% and increased by 22.7% for the second top fifth of American families. As of 2007, the United Nations estimated the ratio of average income for the top 10% to the bottom 10% of Americans, via the Gini Coefficient, as 15.9:1. The ratio of average income for the top 20% to the bottom 20% in the same year and using the same index was 8.4:1. According to these UN statistics, the United States has the third highest disparity between the average income of the top 10% and 20% to the bottom 10% and bottom 20% of the population, respectively, of the OECD (Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development) countries. Only Chile and Mexico have larger average income disparities between the top 10% and bottom 10% of the population with 26:1 and 23:1, respectively. Consequently, the United States has the fourth highest Gini Coefficient of the OECD countries at 40.8% which is lower than Chile's (52%), Mexico's (51%), and just lower than Turkey's (42%).
Tax structure
A 2011 Congressional Research Service report stated, "Changes in capital gains and dividends were the largest contributor to the increase in the overall income inequality. Taxes were less progressive in 2006 than in 1996, and consequently, tax policy also contributed to the increase in income inequality between 1996 and 2006. But overall income inequality would likely have increased even in the absence of tax policy changes." Since 1964, the U.S. income tax, including the capital gains tax, has become less progressive (although recent changes have made the federal tax code the most progressive since 1979). The estate tax, a highly progressive tax, has also been reduced over the last decades.
A progressive tax code is believed to mitigate the effects of recessions by taking a smaller percentage of income from lower-income consumers than from other consumers in the economy so they can spend more of their disposable income on consumption and thus restore equilibrium. This is known as an automatic stabilizer as it does not need Congressional action such as legislation. It also mitigates inflation by taking more money from the wealthiest consumers so their large level of consumption does not create demand-driven inflation.
Wealth distribution in the United States by net worth (2007). The net wealth of many people in the lowest 20% is negative because of debt. By 2014 the wealth gap deepened.
One argument against the view that tax policy increases income inequality is analysis of the overall share of wealth controlled by the top 1%.
Income tax
The Revenue Act of 1964 was the first bill of the Post-World War II era to reduce marginal income tax rates. This reform, which was proposed under John F. Kennedy but passed under Lyndon Johnson, reduced the top marginal income (annual income of $2.9 million+ adjusted for inflation) tax rate from 91% (for tax year 1963) to 77% (for tax year 1964) and 70% (for tax year 1965) for annual incomes of $1.4 million+. It was the first tax legislation to reduce the top end of the marginal income tax rate distribution since 1924. The top marginal income tax rate had been 91% since 1946 and had not been below 70% since 1936. The "Bush Tax Cuts," which are the popularly known names of the Economic Growth and Tax Relief Reconciliation Act of 2001 and the Jobs and Growth Tax Relief Reconciliation Act of 2003 passed during President George W. Bush's first term, reduced the top marginal income tax rate from 38.6% (annual income at $382,967+ adjusted for inflation) to 35%. These rates were continued under the Obama Administration and will extend through 2013. The number of income tax brackets declined during this time period as well but several years, particularly after 1992, saw an increase in the number of income tax brackets. In 1964, there were 26 income tax brackets. The number of brackets was reduced to 16 by 1981 and then collapsed into 13 brackets after passage of the Economic Recovery Tax Act of 1981. Five years later, the 13 income tax brackets were collapsed into five under the Reagan Administration. By the end of the G. H. W. Bush administration in 1992, the number of income tax brackets had reached an all-time low of three but President Bill Clinton oversaw a reconfiguration of the brackets that increased the number to five in 1993. The current number of income tax brackets, as of 2011, is six which is the number of brackets configured under President George W. Bush.
The NYT reported in July 2018 that: "The top-earning 1 percent of households — those earning more than $607,000 a year — will pay a combined $111 billion less this year in federal taxes than they would have if the laws had remained unchanged since 2000. That's an enormous windfall. It's more, in total dollars, than the tax cut received over the same period by the entire bottom 60 percent of earners." This represents the tax cuts for the top 1% from the Bush tax cuts and Trump tax cuts, partially offset by the tax increases on the top 1% by Obama.
Effective tax rates

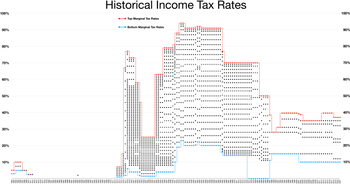
Ronald Reagan made very large reductions in the nominal marginal income tax rates with his Tax Reform Act of 1986, which did not make a similarly large reduction in the effective tax rate on marginal incomes. Noah writes in his ten part series entitled "The Great Divergence," that "in 1979, the effective tax rate on the top 0.01 percent was 42.9 percent, according to the Congressional Budget Office, but by Reagan's last year in office it was 32.2%." This effective rate held steadily until the first few years of the Clinton presidency when it increased to a peak high of 41%. However, it fell back down to the low 30s by his second term in the White House. This percentage reduction in the effective marginal income tax rate for the wealthiest Americans, 9%, is not a very large decrease in their tax burden, according to Noah, especially in comparison to the 20% drop in nominal rates from 1980 to 1981 and the 15% drop in nominal rates from 1986 to 1987. In addition to this small reduction on the income taxes of the wealthiest taxpayers in America, Noah discovered that the effective income tax burden for the bottom 20% of wage earners was 8% in 1979 and dropped to 6.4% under the Clinton Administration. This effective rate further dropped under the George W. Bush Administration. Under Bush, the rate decreased from 6.4% to 4.3%. Reductions in the effective income tax burden on the poor coinciding with modest reductions in the effective income tax rate on the wealthiest 0.01% of tax payers could not have been the driving cause of increased income inequality that began in the 1980s. These figures are similar to an analysis of effective federal tax rates from 1979-2005 by the Congressional Budget Office. The figures show a decrease in the total effective tax rate from 37.0% in 1979 to 29% in 1989. The effective individual income tax rate dropped from 21.8% to 19.9% in 1989. However, by 2010, the top 1 percent of all households an average federal tax rate of 29.4 percent, with 2013 rates to be significantly higher.
Capital gains tax

Capital gains are profits from investments in capital assets such as bonds, stocks, and real estate. These gains are taxed, for individuals, as ordinary income when held for less than one year which means that they have the same marginal tax rate as the marginal income tax rate of their recipient. This is known as the capital gains tax rate on a short-term capital gains. Accordingly, the capital gains tax rate for short-term capital gains paid by an individual is equal to the marginal income tax rate of that individual. The tax rate then decreases once the capital gain becomes a long-term capital gain, or is held for 1 year or more.
In 1964, the effective capital gains tax rate was 25%. This means that the actual tax percentage of all capital gains realized in the U.S. in 1964 was 25% as opposed to the nominal capital gains tax rate, or the percentage that would have been collected by the government prior to deductions and evasions. This effective rate held constant until a small rise in 1968 up to 26.9% and then began steadily increasing until it peaked at 39.875% in 1978. This top rate then fell to 28% in 1979 and further dropped to 20% in 1982. This top capital gains rate held until 1986 when the Tax Reform Act of 1986 re-raised it to 28% and 33% for all individuals subject to phase-outs. The Tax Reform Act of 1986 shifted capital gains to income for the first time thus establishing equal short-term capital gains taxes and marginal income tax rates. The top rate of 28%, not taking into account taxpayers under the stipulations of a phase-out, remained until 1997, despite increases in marginal income tax rates, when it was lowered to 28%. Starting in May 1997, however, long-term capital gains were divided into multiple subgroups based on the duration of time investors held them. Each new subgroup had a different tax rate. This effectively reduced the top capital gains tax rate on a long-term capital good held for over 1 year from 28% to 20%. These multiple subgroups were reorganized into less than one year, one to five years, and five years or more and were in place from 1998 to 2003. In 2003, the divisions reverted to the less than one year and more than one year categories until 2011 when then reverted to the three divisions first implemented in 1998. This rate, 20%, remained until 2003 when it was further reduced to 15%. The 15% long-term capital gains tax rate was then changed back to its 1997 rate of 20% in 2011. Capital gains taxes for the bottom two and top two income tax brackets have changed significantly since the late 1980s. The short-term and long-term capital gains tax rates for the bottom two tax rates, 15% and 28%, respectively, were equal to those tax payers' marginal income tax rates from 1988 until 1997. In 1997, the capital gains tax rates for the bottom two income tax brackets were reduced to 10% and 20% for the 15% and 28% income tax brackets, respectively. These rates remained until 2001. President Bush made additional changes to the capital gains tax rates for the bottom two income tax brackets in 2001, which were lowered from 15% and 28% to 10% and 15%, respectively, by lowering the tax on long-term capital gains held for more than five years from 10% to 8%. He also reduced the tax on short-term capital gains from 28% to 15% for the 15% tax bracket as well as lowered the tax on long-term capital goods from 20% to 10%. In 2003, the capital gains tax on long-term capital goods decreased from 10% to 5% for both of the bottom two tax brackets (10% and 15%). In 2008, these same rates were dropped to 0% but were restored to the 2003 rates in 2011 under President Obama via the extension of the Bush Tax Cuts.
Overall, capital gains tax rates decreased significantly for both the bottom two and the top two income tax brackets. The top two income tax brackets have had a net decrease in their long-term capital gains tax rates of 13% since 1988, while the lowest two income tax brackets' long-term capital gains tax rates have changed by 10% and 13%, respectively, in that time. The difference between income and long-term capital gains taxes for the top two income tax brackets (5% in 1988 and 18% and 20%, respectively, in 2011), however, is larger than the difference between the income and long-term capital gains tax rates for the bottom two income tax brackets (0% in 1988 and 5% and 10%, respectively, in 2011). As of the 2013 tax year, all investment income for high earning households will be subject to a 3.8% surtax bringing the top capital gains rate to 23.8%.
Gift tax
The inheritance tax, which is also known as the "gift tax", has been altered in the Post-World War II era as well. First established in 1932 as a means to raise tax revenue from the wealthiest Americans, the inheritance tax was put at a nominal rate of 25% points lower than the estate tax which meant its effective rate was 18.7%. Its exemption, up to $50,000, was the same as the estate tax exemption. Under current law, individuals can give gifts of up to $13,000 without incurring a tax and couples can poll their gift together to give a gift of up to $26,000 a year without incurring a tax. The lifetime gift tax exemption is $5 million which is the same amount as the estate tax exemption. These two exemptions are directly tied to each other as the amount exempted from one reduces the amount that can be exempted from the other at a 1:1 ratio. The inheritance/gift tax generally affects a very small percentage of the population as most citizens do not inherit anything from their deceased relatives in any given year. In 2000, the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland published a report that found that 1.6% of Americans received an inheritance of $100,000 or more and an additional 1.1% received an inheritance worth $50,000 to $100,000 while 91.9% of Americans did not receive an inheritance. A 2010 report conducted by Citizens for Tax Justice found that only 0.6% of the population would pass on an inheritance in the event of death in that fiscal year. Accordingly, data shows that inheritance taxes are a tax almost exclusively on the wealthy. In 1986, Congress enacted legislation to prevent trust funds of wealthy individuals from skipping a generation before taxes had to be paid on the inheritance.
Estate tax
Estate taxes, while affecting more taxpayers than inheritance taxes, do not affect many Americans and are also considered to be a tax aimed at the wealthy. In 2007, all of the state governments combined collected $22 billion in tax receipts from estate taxes and these taxes affected less than 5% of the population including less than 1% of citizens in every state. In 2004, the average tax burden of the federal estate tax was 0% for the bottom 80% of the population by household. The average tax burden of the estate tax for the top 20% was $1,362. The table below gives a general impression of the spread of estate taxes by income. A certain dollar amount of every estate can be exempted from tax, however. For example, if the government allows an exemption of up to $2 million on an estate then the tax on a $4 million estate would only be paid on $2 million worth of that estate, not all $4 million. This reduces the effective estate tax rate. In 2001, the "exclusion" amount on estates was $675,000 and the top tax rate was 55%. The exclusion amount steadily increased to $3.5 million by 2009 while the tax rate dropped to 45% when it was temporarily repealed in 2010. The estate tax was reinstated in 2011 with a further increased cap of $5 million for individuals and $10 million for couples filing jointly and a reduced rate of 35%. The "step-up basis" of estate tax law allows a recipient of an estate or portion of an estate to have a tax basis in the property equal to the market value of the property. This enables recipients of an estate to sell it at market value without having paid any tax on it. According to the Congressional Budget Office, this exemption costs the federal government $715 billion a year.
Sales tax
Sales taxes are taxes placed on the sale or lease of goods and services in the United States. While no national general sales tax exists, the federal government levies several national selective sales taxes. States also may levy selective sales taxes on the sale or lease of particular goods or services. States may also delegate to local governments the authority to impose additional general or selective sales taxes.
Tax expenditures

The term "tax expenditures" refers to income exclusions, deductions, preferential rates, and credits that reduce revenues for any given level of tax rates in the individual, payroll, and corporate income tax systems. Like conventional spending, they contribute to the federal budget deficit. They also influence choices about working, saving, and investing, and affect the distribution of income. The amount of reduced federal revenues are significant, estimated by CBO at nearly 8% GDP or about $1.5 trillion in 2017, for scale roughly half the revenue collected by the government and nearly three times as large as the budget deficit. Since eliminating a tax expenditure changes economic behavior, the amount of additional revenue that would be generated is somewhat less than the estimated size of the tax expenditure.
CBO reported that the following were among the largest individual (non-corporate) tax expenditures in 2013:
- The exclusion from workers' taxable income of employers' contributions for health care, health insurance premiums, and premiums for long-term care insurance ($248B);
- The exclusion of contributions to and the earnings of pension funds such as 401k plans ($137B);
- Preferential tax rates on dividends and long-term capital gains ($161B); and
- The deductions for state and local taxes ($77B), mortgage interest ($70B) and charitable contributions ($39B).
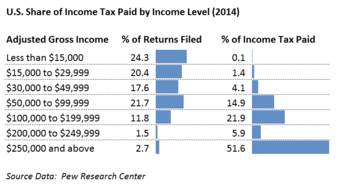
In 2013, CBO estimated that more than half of the combined benefits of 10 major tax expenditures would apply to households in the top 20% income group, and that 17% of the benefit would go to the top 1% households. The top 20% of income earners pay about 70% of federal income taxes, excluding payroll taxes. For scale, 50% of the $1.5 trillion in tax expenditures in 2016 was $750 billion, while the U.S. budget deficit was approximately $600 billion. In other words, eliminating the tax expenditures for the top 20% might balance the budget over the short-term, depending on economic feedback effects.
Credits and exemptions
Education
Economist Gary Becker has described educational attainment as the root of economic mobility. The United States offers several tax incentives for education, such as the American Opportunity Tax Credit and Hope credit along with tax exemptions for scholarships and grants. Those who do not qualify for such aid can obtain a low-interest student loan, which may be subsidized based on financial need, and tuition can often be deducted from the federal income tax. Such loans were created with the goal of encouraging greater social mobility and equality of opportunity.
According to Becker, the rise in returns on investments in human capital is beneficial and desirable to society because it increases productivity and standards of living. However, the cost for college tuition has increased significantly faster than inflation, leading the United States to have one of the most expensive higher education systems in the world. It has been suggested that tax policy could be used to help reduce these costs, by taxing the endowment income of universities and linking the endowment tax to tuition rates. The United States spends about 7.3% of GDP ($1.1 trillion in 2011 - public and private, all levels) annually on education, with 70% funded publicly through varying levels of federal, state, and local taxation.
Healthcare
The United States tax code includes deductions and penalties with regard to health insurance coverage. The number of uninsured in the United States, many of whom are the working poor or unemployed, are one of the primary concerns raised by advocates of health care reform. The costs of treating the uninsured must often be absorbed by providers as charity care, passed on to the insured via cost shifting and higher health insurance premiums, or paid by taxpayers through higher taxes. The federal income tax offers employers a deduction for amounts contributed health care plans.
In 2014, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act encourages states to expand Medicaid for low income households, funded by additional federal taxes. Some of the taxes specifically target wealthier households. Income from self-employment and wages of single individuals in excess of $200,000 annually will be subject to an additional tax of 0.9%. The threshold amount is $250,000 for a married couple filing jointly (threshold applies to joint compensation of the two spouses), or $125,000 for a married person filing separately. In addition, a Medicare tax of 3.8% will apply to unearned income, specifically the lesser of net investment income or the amount by which adjusted gross income exceeds $200,000 ($250,000 for a married couple filing jointly; $125,000 for a married person filing separately.)
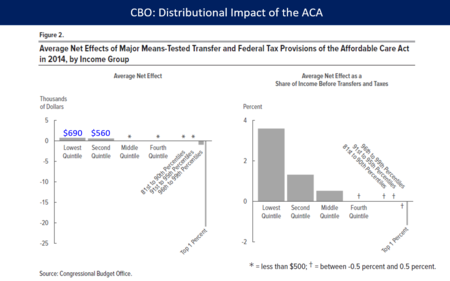
In March 2018, the CBO reported that the ACA had reduced income inequality in 2014, saying that the law led the lowest and second quintiles (the bottom 40%) to receive an average of an additional $690 and $560 respectively while causing households in the top 1% to pay an additional $21,000 due mostly to the net investment income tax and the additional Medicare tax. The law placed relatively little burden on households in the top quintile (top 20%) outside of the top 1%.
Compression and divergence in tax code changes
Princeton economics professor, Nobel laureate, and John Bates Clarke Award winner Paul Krugman argues that politics not economic conditions have made income inequality in the United States "unique" and to a degree that "other advanced countries have not seen." According to Krugman, government action can either compress or widen income inequality through tax policy and other redistributive or transfer policies. Krugman illustrates this point by describing "The Great Compression" and "The Great Divergence." He states that the end of the Great Depression to the end of World War II, from 1939–1946, saw a rapid narrowing of the spread of the income distribution in America which effectively created the middle class. Krugman calls this economic time period "The Great Compression" because the income distribution was compressed. He attributes this phenomenon to intrinsically equalizing economic policy such as increased tax rates on the wealthy, higher corporate tax rates, a pro-union organizing environment, minimum wage, Social Security, unemployment insurance, and "extensive government controls on the economy that were used in a way that tended to equalize incomes." This "artificial[ly]" created middle class endured due to the creation of middle class institutions, norms, and expectations that promoted income equality. Krugman believes this period ends in 1980, which he points out as being "interesting" because it was when "Reagan came to the White House." From 1980 to the present, Krugman believes income inequality was uniquely shaped by the political environment and not the global economic environment. For example, the U.S. and Canada both had approximately 30% of its workers in unions during the 1960s. However, by 2010, around 25% of Canadian workers were still unionized while 11% of American workers were unionized. Krugman blames Reagan for this rapid decline in unionization because he "declared open season on unions" while the global market clearly made room for unions as Canada's high union rate proves. Contrary to the arguments made by Chicago economists such as Gary Becker, Krugman points out that while the wealth gap between the college educated and non-college educated continues to grow, the largest rise in income inequality is between the well-educated-college graduates and college graduates, and not between college graduates and non-college graduates. The average high school teacher, according to Krugman, has a post-graduate degree which is a comparable level of education to a hedge fund manager whose income is several times that of the average high school teacher. In 2006, the "highest paid hedge fund manager in the United States made an amount equal to the salaries of all 80,000 New York City school teachers for the next three years." Accordingly, Krugman believes that education and a shifting global market are not the sole causes of increased income inequalities since the 1980s but rather that politics and the implementation of conservative ideology has aggregated wealth to the rich. Some of these political policies include the Reagan tax cuts in 1981 and 1986.
Nobel laureate Joseph Stiglitz asserts in a Vanity Fair article published in May 2011 entitled "Of the 1%, by the 1%, for the 1%" that "preferential tax treatment for special interests" has helped increase income inequality in the United States as well as reduced the efficiency of the market. He specifically points to the reduction in capital gains over the last few years, which are "how the rich receive a large portion of their income," as giving the wealthy a "free ride." Stiglitz criticizes the "marginal productivity theory" saying that the largest gains in wages are going toward in his opinion, less than worthy occupations such as finance whose effects have been "massively negative." Accordingly, if income inequality is predominately explained by rising marginal productivity of the educated then why are financiers, who are responsible for bringing the U.S. economy "to the brink of ruin."
Thomas Piketty and Emmanuel Saez wrote in their work "Income Inequality in the United States,1913–1998" that "top income and wages shares(in the United States) display a U-shaped pattern over the century" and "that the large shocks that capital owners experienced during the Great Depression and World War II have had a permanent effect on top capital incomes...that steep progressive income and estate taxation may have prevented large fortunes from recovery form the shocks." Saez and Piketty argue that the "working rich" are now at the top of the income ladder in the United States and their wealth far out-paces the rest of the country. Piketty and Saez plotted the percentage share of total income accrued by the top 1%, top 5%, and the top 10% of wage earners in the United States from 1913-2008. According to their data, the top 1% controlled 10% of the total income while the top 5% owned approximately 13% and the top 10% possessed around 12% of total income. By 1984, the percentage of total income owned by the top 1% rose from 10% to 16% while income shares of the top 5% and top 10% controlled 13.5% and 12%, respectively. The growth in income for the top 1% then rose up to 22% by 1998 while the income growth rates for the top 5% and top 10% remained constant (15% total share of income and 12% total share of income, respectively). The percentage share of total income owned by the top 1% fell to 16% during the post-9/11 recession but then re-rose to its 1998 level by 2008. In 2008, the wealth gap in terms of percentage of total income in the United States between the top 1% and 5% was 7% and the gap between the top 1% and top 10% was 9%. This is an 11% reversal from the respective percentage shares of income held by these groups in 1963. Income inequality clearly accelerated beginning in the 1980s.
Larry Bartels, a Princeton political scientist and the author of Unequal Democracy, argues that federal tax policy since 1964 and starting even before that has increased economic inequality in the United States. He states that the real income growth rate for low and middle class workers is significantly smaller under Republican administrations than it is under Democratic administrations while the real income growth rate for the upper class is much larger under Republican administrations than it is for Democratic administrations. He finds that from 1948 to 2005, pre-tax real income growth for the bottom 20% grew by 1.42% while pre-tax real income growth for the top 20% grew by 2%. Under the Democratic administrations in this time period, (Truman, Kennedy, Johnson, Carter, and Clinton) the pre-tax real income growth rate for the bottom 20% was 2.64% while the pre-tax real income growth rate for the top 20% was 2.12%. During the Republican administrations of this time period (Eisenhower, Nixon, Ford, Reagan, G. H. W. Bush, and G. W. Bush), the pre-tax real income growth rate was 0.43% for the bottom 20% and 1.90% for the top 20%. The disparity under Democratic presidents in this time period between the top and bottom 20% pre-tax real income growth rate was -0.52% while the disparity under Republican presidents was 1.47%. The pre-tax real income growth rate for the wealthiest 40%, 60%, and 80% of population was higher under the Democratic administrations than it was under the Republican administrations in this time period. The United States was more equal and growing wealthier, based on income, under Democratic Presidents from 1948-2005 than it was under Republican Presidents in the same time period. Additionally, Bartels believes that the reduction and the temporary repeal of the estate tax also increased income inequality by benefiting almost exclusively the wealthiest in America.
According to a working paper released by the Society for the Study of Economic Inequality entitled "Tax policy and income inequality in the U.S.,1978—2009: A decomposition approach," tax policy can either exacerbate or curtail economic inequality. This article argues that tax policy reforms passed under Republican administrations since 1979 have increased economic inequality while Democratic administrations during the same time period have reduced economic inequality. The net vector movement of tax reforms on economic inequality since 1979 is essentially zero as the opposing policies neutralized each other.
Policy responses
Public policy responses addressing causes and effects of income inequality include: progressive tax incidence adjustments, strengthening social safety net provisions such as Aid to Families with Dependent Children, welfare, the food stamp program, Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid, increasing and reforming higher education subsidies, increasing infrastructure spending, and placing limits on and taxing rent-seeking.
Taxes on the wealthy
The Congressional Budget Office reported that less progressive tax and transfer policies contributed to an increase in after-tax income inequality between 1979 and 2007. This indicates that more progressive income tax policies (e.g., higher income taxes on the wealthy and a higher earned-income tax credit) would reduce after-tax income inequality.
In their World Inequality Report published in December 2017, Piketty, Saez and coauthors revealed that in "Russia and the United States, the rise in wealth inequality has been extreme, whereas in Europe it has been more moderate." They reported that the tax system in the United States, along with "massive educational inequalities", have grown "less progressive despite a surge in top labor compensation since the 1980s, and in top capital incomes in the 2000s."[66]: 10 The "top 1% income share was close to 10% in the [US and Europe] in 1980, it rose only slightly to 12% in 2016 in Western Europe [where taxation and education policies are more progressive] while it shot up to 20% in the United States." The "bottom 50% income share decreased from more than 20% in 1980 to 13% in 2016." In 2012, the economists Emmanuel Saez and Thomas Piketty had recommended much higher top marginal tax rates on the wealthy, up to 50 percent, 70 percent or even 90 percent.
Ralph Nader, Jeffrey Sachs, the United Front Against Austerity, among others, call for a financial transactions tax (also known as the Robin Hood tax) to bolster the social safety net and the public sector.
The Pew Center reported in January 2014 that 54% of Americans supported raising taxes on the wealthy and corporations to expand aid to the poor. By party, 29% of Republicans and 75% of Democrats supported this action.
Senator Elizabeth Warren proposed an annual tax on wealth in January 2019, specifically a 2% tax for wealth over $50 million and another 1% surcharge on wealth over $1 billion. Wealth is defined as including all asset classes, including financial assets and real estate. Economists Emmanuel Saez and Gabriel Zucman estimated that about 75,000 households (less than 0.1%) would pay the tax. The tax would raise around $2.75 trillion over 10 years, roughly 1% GDP on average per year. This would raise the total tax burden for those subject to the wealth tax from 3.2% relative to their wealth under current law to about 4.3% on average, versus the 7.2% for the bottom 99% families. For scale, the federal budget deficit in 2018 was 3.9% GDP and is expected to rise towards 5% GDP over the next decade. The plan received both praise and criticism. Two billionaires, Michael Bloomberg and Howard Schultz, criticized the proposal as "unconstitutional" and "ridiculous," respectively. Warren was not surprised by this reaction, stating: "Another billionaire who thinks that billionaires shouldn't pay more in taxes." Economist Paul Krugman wrote in January 2019 that polls indicate the idea of taxing the rich more is very popular.
Senators Charles Schumer and Bernie Sanders advocated limiting stock buybacks in January 2019. They explained that from 2008-2017, 466 of the S&P 500 companies spent $4 trillion on stock buybacks, about 50% of profits, with another 40% going to dividends. During 2018 alone, a record $1 trillion was spent on buybacks. Stock buybacks shift wealth upwards, because the top 1% own about 40% of shares and the top 10% own about 85%. Further, corporations directing profits to shareholders are not reinvesting the money in the firm or paying workers more. They wrote: "If corporations continue to purchase their own stock at this rate, income disparities will continue to grow, productivity will suffer, the long-term strength of companies will diminish — and the American worker will fall further behind." Their proposed legislation would prohibit buybacks unless the corporation has taken other steps first, such as paying workers more, providing more benefits such as healthcare and pensions, and investing in the community. To prevent corporations from shifting from buybacks to dividends, they proposed limiting dividends, perhaps by taking action through the tax code.

