Depending on the particular implementation, e-voting may use standalone electronic voting machines (also called EVM) or computers connected to the Internet (online voting). It may encompass a range of Internet services, from basic transmission of tabulated results to full-function online voting through common connectable household devices. The degree of automation may be limited to marking a paper ballot, or may be a comprehensive system of vote input, vote recording, data encryption and transmission to servers, and consolidation and tabulation of election results.
A worthy e-voting system must perform most of these tasks while complying with a set of standards established by regulatory bodies, and must also be capable to deal successfully with strong requirements associated with security, accuracy, integrity, swiftness, privacy, auditability, accessibility, cost-effectiveness, scalability and ecological sustainability.
Electronic voting technology can include punched cards, optical scan voting systems and specialized voting kiosks (including self-contained direct-recording electronic voting systems, or DRE). It can also involve transmission of ballots and votes via telephones, private computer networks, or the Internet.
In general, two main types of e-voting can be identified:
- e-voting which is physically supervised by representatives of governmental or independent electoral authorities (e.g. electronic voting machines located at polling stations);
- remote e-voting via the Internet (also called i-voting) where the voter submits his or her vote electronically to the election authorities, from any location.
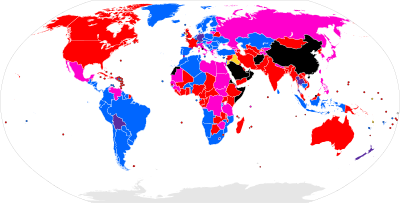
Electronic voting systems are used everywhere in many countries across the whole world, incl. Argentina, Australia, Bangladesh, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, France, Germany, India, Italy, Japan, Kazakhstan, South Korea, Malaysia, the Netherlands, Norway, Pakistan, the Philippines, Spain, Switzerland, Thailand, the United Kingdom and the United States.
Benefits
Electronic voting technology intends to speed the counting of ballots, reduce the cost of paying staff to count votes manually and can provide improved accessibility for disabled voters. Also in the long term, expenses are expected to decrease. Results can be reported and published faster. Voters save time and cost by being able to vote independently from their location. This may increase overall voter turnout. The citizen groups benefiting most from electronic elections are the ones living abroad, citizens living in rural areas far away from polling stations and the disabled with mobility impairments.
Concerns
It has been demonstrated that as voting systems become more complex and include software, different methods of election fraud become possible. Others also challenge the use of electronic voting from a theoretical point of view, arguing that humans are not equipped for verifying operations occurring within an electronic machine and that because people cannot verify these operations, the operations cannot be trusted. Furthermore, some computing experts have argued for the broader notion that people cannot trust any programming they did not author.
The use of electronic voting in elections remains a contentious issue. Some countries such as Netherlands and Germany have stopped using it after it was shown to be unreliable, while the Indian Election commission recommends it. The involvement of numerous stakeholders including companies that manufacture these machines as well as political parties that stand to gain from rigging complicates this further.
Critics of electronic voting, including security analyst Bruce Schneier, note that "computer security experts are unanimous on what to do (some voting experts disagree, but it is the computer security experts who need to be listened to; the problems here are with the computer, not with the fact that the computer is being used in a voting application)... DRE machines must have a voter-verifiable paper audit trails... Software used on DRE machines must be open to public scrutiny" to ensure the accuracy of the voting system. Verifiable ballots are necessary because computers can and do malfunction, and because voting machines can be compromised.
Many insecurities have been found in commercial voting machines, such as using a default administration password. Cases have also been reported of machines making unpredictable, inconsistent errors. Key issues with electronic voting are therefore the openness of a system to public examination from outside experts, the creation of an authenticatable paper record of votes cast and a chain of custody for records. And, there is a risk that commercial voting machines results are changed by the company providing the machine. There is no guarantee that results are collected and reported accurately.
There has been contention, especially in the United States, that electronic voting, especially DRE voting, could facilitate electoral fraud and may not be fully auditable. In addition, electronic voting has been criticised as unnecessary and expensive to introduce. While countries like India continue to use electronic voting, several countries have cancelled e-voting systems or decided against a large-scale rollout, notably the Netherlands, Ireland, Germany and the United Kingdom due to issues in reliability of EVMs.
Moreover, people without internet access and/or the skills to use it are excluded from the service. The so-called digital divide describes the gap between those who have access to the internet and those who do not. Depending on the country or even regions in a country the gap differs. This concern is expected to become less important in future since the number of internet users tends to increase.
The main psychological issue is trust. Voters fear that their vote could be changed by a virus on their PC or during transmission to governmental servers.
Expenses for the installation of an electronic voting system are high. For some governments they may be too high so that they do not invest. This aspect is even more important if it is not sure whether electronic voting is a long-term solution.
New South Wales 2021 iVote failures
During the 2021 NSW Local Government Elections the online voting system "iVote" had technical issues that caused some access problems for some voters. Analysis done of these failures indicated a significant chance of the outages having impacted on the electoral results for the final positions. In the Kempsey ward, where the margin between the last elected and first non-elected candidates was only 69 votes, the electoral commission determined that the outage caused a 60% chance that the wrong final candidate was elected. Singleton had a 40% chance of having elected the wrong councillor, Shellharbour was a 7% chance and two other races were impacted by a sub-1% chance of having elected the wrong candidate. The NSW Supreme Court ordered the elections in Kempsey, Singleton and Shellharbour Ward A to be re-run. In the 2022 Kempsey re-vote the highest placed non-elected candidate from 2021, Dean Saul, was instead one of the first councillors elected. This failure caused the NSW Government to suspend the iVote system from use in the 2023 New South Wales state election.
Types of system
Electronic voting machines
Electronic voting systems for electorates have been in use since the 1960s when punched card systems debuted. Their first widespread use was in the US where 7 counties switched to this method for the 1964 presidential election. The newer optical scan voting systems allow a computer to count a voter's mark on a ballot. DRE voting machines which collect and tabulate votes in a single machine, are used by all voters in all elections in Brazil and India, and also on a large scale in Venezuela and the United States. They have been used on a large scale in the Netherlands but have been decommissioned after public concerns. In Brazil, the use of DRE voting machines has been associated with a decrease in error-ridden and uncounted votes, promoting a larger enfranchisement of mainly less educated people in the electoral process, shifting government spending toward public healthcare, particularly beneficial to the poor.
Paper-based electronic voting system

Paper-based voting systems originated as a system where votes are cast and counted by hand, using paper ballots. With the advent of electronic tabulation came systems where paper cards or sheets could be marked by hand, but counted electronically. These systems included punched card voting, marksense and later digital pen voting systems.
These systems can include a ballot marking device or electronic ballot marker that allows voters to make their selections using an electronic input device, usually a touch screen system similar to a DRE. Systems including a ballot marking device can incorporate different forms of assistive technology. In 2004, Open Voting Consortium demonstrated the 'Dechert Design', a General Public License open source paper ballot printing system with open source bar codes on each ballot.
Direct-recording electronic (DRE) voting system
A direct-recording electronic (DRE) voting machine records votes by means of a ballot display provided with mechanical or electro-optical components that can be activated by the voter (typically buttons or a touchscreen); that processes data with computer software; and that records voting data and ballot images in memory components. After the election it produces a tabulation of the voting data stored in a removable memory component and as a printed copy. The system may also provide a means for transmitting individual ballots or vote totals to a central location for consolidating and reporting results from precincts at the central location. These systems use a precinct count method that tabulates ballots at the polling place. They typically tabulate ballots as they are cast and print the results after the close of polling.
In 2002, in the United States, the Help America Vote Act mandated that one handicapped accessible voting system be provided per polling place, which most jurisdictions have chosen to satisfy with the use of DRE voting machines, some switching entirely over to DRE. In 2004, 28.9% of the registered voters in the United States used some type of direct recording electronic voting system, up from 7.7% in 1996.

In 2004, India adopted Electronic Voting Machines (EVM) for its elections to its parliament with 380 million voters casting their ballots using more than one million voting machines. The Indian EVMs are designed and developed by two government-owned defence equipment manufacturing units, Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) and Electronics Corporation of India Limited (ECIL). Both systems are identical, and are developed to the specifications of Election Commission of India. The system is a set of two devices running on 7.5 volt batteries. One device, the voting Unit is used by the voter, and another device called the control unit is operated by the electoral officer. Both units are connected by a five-metre cable. The voting unit has a blue button for each candidate. The unit can hold 16 candidates, but up to four units can be chained, to accommodate 64 candidates. The control unit has three buttons on the surface – one button to release a single vote, one button to see the total number of votes cast till now, and one button to close the election process. The result button is hidden and sealed. It cannot be pressed unless the close button has already been pressed. A controversy was raised when the voting machine malfunctioned which was shown in Delhi assembly. On 9 April 2019, the Supreme Court ordered the ECI to increase voter-verified paper audit trail (VVPAT) slips vote count to five randomly selected EVMs per assembly constituency, which means ECI has to count VVPAT slips of 20,625 EVMs before it certifies the final election results.
Public network DRE voting system
A public network DRE voting system is an election system that uses electronic ballots and transmits vote data from the polling place to another location over a public network. Vote data may be transmitted as individual ballots as they are cast, periodically as batches of ballots throughout the election day, or as one batch at the close of voting. Public network DRE voting system can utilize either precinct count or central count method. The central count method tabulates ballots from multiple precincts at a central location.
Online voting

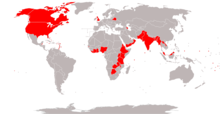
Internet voting systems have gained popularity and have been used for government and membership organization elections and referendums in Estonia, and Switzerland as well as municipal elections in Canada and party primary elections in the United States and France. Internet voting has also been widely used in sub-national participatory budgeting processes, including in Brazil, France, United States, Portugal and Spain.
Security experts have found security problems in every attempt at online voting, including systems in Australia, Estonia, Switzerland, Russia, and the United States.
It has been argued political parties that have more support from the less fortunate—who are unfamiliar with the Internet—may suffer in the elections due to e-voting, which tends to increase voting in the upper/middle class. It is unsure as to whether narrowing the digital divide would promote equal voting opportunities for people across various social, economic, and ethnic backgrounds. In the long run, this is contingent not only on internet accessibility but also depends on people's level of familiarity with the Internet.
The effects of internet voting on overall voter turnout are unclear. A 2017 study of online voting in two Swiss cantons found that it had no effect on turnout, and a 2009 study of Estonia's national election found similar results. To the contrary, however, the introduction of online voting in municipal elections in the Canadian province of Ontario resulted in an average increase in turnout of around 3.5 percentage points. Similarly, a further study of the Swiss case found that while online voting did not increase overall turnout, it did induce some occasional voters to participate who would have abstained were online voting not an option.
A paper on “remote electronic voting and turnout in the Estonian 2007 parliamentary elections” showed that rather than eliminating inequalities, e-voting might have enhanced the digital divide between higher and lower socioeconomic classes. People who lived greater distances from polling areas voted at higher levels with this service now available. The 2007 Estonian elections yielded a higher voter turnout from those who lived in higher income regions and who received formal education. Still regarding the Estonian Internet voting system, it was proved to be more cost-efficient than the rest of the voting systems offered in 2017 local elections.
| Voting system | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|
| Advance voting in county centres | 5.48 | 5.92 |
| Advance voting in ordinary polling stations | 16.24 | 17.36 |
| Early voting in county centres | 5.83 | 6.30 |
| Election day voting in county centres | 4.97 | 5.58 |
| Election day voting in ordinary polling stations | 2.83 | 3.01 |
| Internet voting | 2.17 | 2.26 |
Electronic voting is perceived to be favored moreover by a certain demographic, namely the younger generation such as Generation X and Y voters. However, in recent elections about a quarter of e-votes were cast by the older demographic, such as individuals over the age of 55. Including this, about 20% of e-votes came from voters between the ages of 45 and 54. This goes to show that e-voting is not supported exclusively by the younger generations, but finding some popularity amongst Gen X and Baby Boomers as well. In terms of electoral results as well, the expectation that online voting would favor younger candidates has not been borne out in the data, with mayors in Ontario, Canada who were elected in online elections actually being slightly older on average than those elected by pencil and paper.
Online voting is widely used privately for shareholder votes, and other private organizations. The election management companies do not promise accuracy or privacy. In fact one company uses an individual's past votes for research, and to target ads.
Corporations and organizations routinely use Internet voting to elect officers and board members and for other proxy elections. Internet voting systems have been used privately in many modern nations and publicly in the United States, the UK, Switzerland and Estonia. In Switzerland, where it is already an established part of local referendums, voters get their passwords to access the ballot through the postal service. Most voters in Estonia can cast their vote in local and parliamentary elections, if they want to, via the Internet, as most of those on the electoral roll have access to an e-voting system, the largest run by any European Union country. It has been made possible because most Estonians carry a national identity card equipped with a computer-readable microchip and it is these cards which they use to get access to the online ballot. All a voter needs is a computer, an electronic card reader, their ID card and its PIN, and they can vote from anywhere in the world. Estonian e-votes can only be cast during the days of advance voting. On election day itself people have to go to polling stations and fill in a paper ballot.
Hybrid systems
There are also hybrid systems that include an electronic ballot marking device (usually a touch screen system similar to a DRE) or other assistive technology to print a voter verified paper audit trail, then use a separate machine for electronic tabulation. Hybrid voting often includes both e-voting and mail-in paper ballots.
Internet voting can use remote locations (voting from any Internet capable computer) or can use traditional polling locations with voting booths consisting of Internet connected voting systems.
Analysis

Electronic voting systems may offer advantages compared to other voting techniques. An electronic voting system can be involved in any one of a number of steps in the setup, distributing, voting, collecting, and counting of ballots, and thus may or may not introduce advantages into any of these steps. Potential disadvantages exist as well including the potential for flaws or weakness in any electronic component.
Charles Stewart of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology estimates that 1 million more ballots were counted in the 2004 US presidential election than in 2000 because electronic voting machines detected votes that paper-based machines would have missed.
In May 2004 the U.S. Government Accountability Office released a report titled "Electronic Voting Offers Opportunities and Presents Challenges", analyzing both the benefits and concerns created by electronic voting. A second report was released in September 2005 detailing some of the concerns with electronic voting, and ongoing improvements, titled "Federal Efforts to Improve Security and Reliability of Electronic Voting Systems Are Under Way, but Key Activities Need to Be Completed".
Electronic ballots
Electronic voting systems may use electronic ballot to store votes in computer memory. Systems which use them exclusively are called DRE voting systems. When electronic ballots are used there is no risk of exhausting the supply of ballots. Additionally, these electronic ballots remove the need for printing of paper ballots, a significant cost. When administering elections in which ballots are offered in multiple languages (in some areas of the United States, public elections are required by the National Voting Rights Act of 1965), electronic ballots can be programmed to provide ballots in multiple languages for a single machine. The advantage with respect to ballots in different languages appears to be unique to electronic voting. For example, King County, Washington's demographics require them under U.S. federal election law to provide ballot access in Chinese. With any type of paper ballot, the county has to decide how many Chinese-language ballots to print, how many to make available at each polling place, etc. Any strategy that can assure that Chinese-language ballots will be available at all polling places is certain, at the very least, to result in a significant number of wasted ballots. (The situation with lever machines would be even worse than with paper: the only apparent way to reliably meet the need would be to set up a Chinese-language lever machine at each polling place, few of which would be used at all.)
Critics argue the need for extra ballots in any language can be mitigated by providing a process to print ballots at voting locations. They argue further, the cost of software validation, compiler trust validation, installation validation, delivery validation and validation of other steps related to electronic voting is complex and expensive, thus electronic ballots are not guaranteed to be less costly than printed ballots.
Accessibility

Electronic voting machines can be made fully accessible for persons with disabilities. Punched card and optical scan machines are not fully accessible for the blind or visually impaired, and lever machines can be difficult for voters with limited mobility and strength. Electronic machines can use headphones, sip and puff, foot pedals, joy sticks and other adaptive technology to provide the necessary accessibility.
Organizations such as the Verified Voting Foundation have criticized the accessibility of electronic voting machines and advocate alternatives. Some disabled voters (including the visually impaired) could use a tactile ballot, a ballot system using physical markers to indicate where a mark should be made, to vote a secret paper ballot. These ballots can be designed identically to those used by other voters. However, other disabled voters (including voters with dexterity disabilities) could be unable to use these ballots.
Cryptographic verification
The concept of election verifiability through cryptographic solutions has emerged in the academic literature to introduce transparency and trust in electronic voting systems. It allows voters and election observers to verify that votes have been recorded, tallied and declared correctly, in a manner independent from the hardware and software running the election. Three aspects of verifiability are considered: individual, universal, and eligibility. Individual verifiability allows a voter to check that her own vote is included in the election outcome, universal verifiability allows voters or election observers to check that the election outcome corresponds to the votes cast, and eligibility verifiability allows voters and observers to check that each vote in the election outcome was cast by a uniquely registered voter.
Voter intent
Electronic voting machines are able to provide immediate feedback to the voter detecting such possible problems as undervoting and overvoting which may result in a spoiled ballot. This immediate feedback can be helpful in successfully determining voter intent.
Transparency
It has been alleged by groups such as the UK-based Open Rights Group that a lack of testing, inadequate audit procedures, and insufficient attention given to system or process design with electronic voting leaves "elections open to error and fraud".
In 2009, the Federal Constitutional Court of Germany found that when using voting machines the "verification of the result must be possible by the citizen reliably and without any specialist knowledge of the subject." The DRE Nedap-computers used till then did not fulfill that requirement. The decision did not ban electronic voting as such, but requires all essential steps in elections to be subject to public examinability.
In 2013, The California Association of Voting Officials was formed to maintain efforts toward publicly owned General Public License open source voting systems
Coercion evidence
In 2013, researchers from Europe proposed that the electronic voting systems should be coercion evident. There should be a public evidence of the amount of coercion that took place in a particular elections. An internet voting system called "Caveat Coercitor" shows how coercion evidence in voting systems can be achieved.
Audit trails
A fundamental challenge with any voting machine is to produce evidence that the votes were recorded as cast and tabulated as recorded. Election results produced by voting systems that rely on voter-marked paper ballots can be verified with manual hand counts (either valid sampling or full recounts). Paperless ballot voting systems must support auditability in different ways. An independently auditable system, sometimes called an Independent Verification, can be used in recounts or audits. These systems can include the ability for voters to verify how their votes were cast or enable officials to verify that votes were tabulated correctly.
A discussion draft argued by researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) states, "Simply put, the DRE architecture’s inability to provide for independent audits of its electronic records makes it a poor choice for an environment in which detecting errors and fraud is important." The report does not represent the official position of NIST, and misinterpretations of the report has led NIST to explain that "Some statements in the report have been misinterpreted. The draft report includes statements from election officials, voting system vendors, computer scientists and other experts in the field about what is potentially possible in terms of attacks on DREs. However, these statements are not report conclusions."

Various technologies can be used to assure DRE voters that their votes were cast correctly, and allow officials to detect possible fraud or malfunction, and to provide a means to audit the tabulated results. Some systems include technologies such as cryptography (visual or mathematical), paper (kept by the voter or verified and left with election officials), audio verification, and dual recording or witness systems (other than with paper).
Dr. Rebecca Mercuri, the creator of the Voter Verified Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT) concept (as described in her Ph.D. dissertation in October 2000 on the basic voter verifiable ballot system), proposes to answer the auditability question by having the voting machine print a paper ballot or other paper facsimile that can be visually verified by the voter before being entered into a secure location. Subsequently, this is sometimes referred to as the "Mercuri method." To be truly voter-verified, the record itself must be verified by the voter and able to be done without assistance, such as visually or audibly. If the voter must use a bar-code scanner or other electronic device to verify, then the record is not truly voter-verifiable, since it is actually the electronic device that is verifying the record for the voter. VVPAT is the form of Independent Verification most commonly found in elections in the United States and other countries such as Venezuela.
End-to-end auditable voting systems can provide the voter with a receipt that can be taken home. This receipt does not allow voters to prove to others how they voted, but it does allow them to verify that the system detected their vote correctly. End-to-end (E2E) systems include Punchscan, ThreeBallot and Prêt à Voter. Scantegrity is an add-on that extends current optical scan voting systems with an E2E layer. The city of Takoma Park, Maryland used Scantegrity II for its November 2009 election.
Systems that allow the voter to prove how they voted are never used in U.S. public elections, and are outlawed by most state constitutions. The primary concerns with this solution are voter intimidation and vote selling.
An audit system can be used in measured random recounts to detect possible malfunction or fraud. With the VVPAT method, the paper ballot is often treated as the official ballot of record. In this scenario, the ballot is primary and the electronic records are used only for an initial count. In any subsequent recounts or challenges, the paper, not the electronic ballot, would be used for tabulation. Whenever a paper record serves as the legal ballot, that system will be subject to the same benefits and concerns as any paper ballot system.
To successfully audit any voting machine, a strict chain of custody is required.
The solution was first demonstrated (New York City, March 2001) and used (Sacramento, California 2002) by AVANTE International Technology, Inc.. In 2004 Nevada was the first state to successfully implement a DRE voting system that printed an electronic record. The $9.3 million voting system provided by Sequoia Voting Systems included more than 2,600 AVC EDGE touchscreen DREs equipped with the VeriVote VVPAT component. The new systems, implemented under the direction of then Secretary of State Dean Heller replaced largely punched card voting systems and were chosen after feedback was solicited from the community through town hall meetings and input solicited from the Nevada Gaming Control Board.
Hardware

Inadequately secured hardware can be subject to physical tampering. Some critics, such as the group "Wij vertrouwen stemcomputers niet" ("We do not trust voting machines"), charge that, for instance, foreign hardware could be inserted into the machine, or between the user and the central mechanism of the machine itself, using a man in the middle attack technique, and thus even sealing DRE machines may not be sufficient protection. This claim is countered by the position that review and testing procedures can detect fraudulent code or hardware, if such things are present, and that a thorough, verifiable chain of custody would prevent the insertion of such hardware or software. Security seals are commonly employed in an attempt to detect tampering, but testing by Argonne National Laboratory and others demonstrates that existing seals can usually be quickly defeated by a trained person using low-tech methods.
Software
Security experts, such as Bruce Schneier, have demanded that voting machine source code should be publicly available for inspection. Others have also suggested publishing voting machine software under a free software license as is done in Australia.
Testing and certification
One method to detect errors with voting machines is parallel testing, which are conducted on the Election Day with randomly picked machines. The ACM published a study showing that, to change the outcome of the 2000 U.S. Presidential election, only 2 votes in each precinct would have needed to be changed.
Cost
Cost of having electronic machines receive the voter's choices, print a ballot and scan the ballots to tally results is higher than the cost of printing blank ballots, having voters mark them directly (with machine-marking only when voters want it) and scanning ballots to tally results, according to studies in Georgia, New York and Pennsylvania.
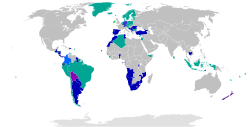
Adoption worldwide
Electronic voting by country varies and may include voting machines in polling places, centralized tallying of paper ballots, and internet voting. Many countries use centralized tallying. Some also use electronic voting machines in polling places. Very few use internet voting. Several countries have tried electronic approaches and stopped because of difficulties or concerns about security and reliability.
Electronic voting requires capital spending every few years to update equipment, as well as annual spending for maintenance, security, and supplies. If it works well, its speed can be an advantage where many contests are on each ballot. Hand-counting is more feasible in parliamentary systems where each level of government is elected at different times, and only one contest is on each ballot, for the national or regional member of parliament, or for a local council member.
Polling place electronic voting or Internet voting examples have taken place in Australia, Belgium, Brazil, Estonia, France, Germany, India, Italy, Namibia, the Netherlands ( Rijnland Internet Election System), Norway, Peru, Switzerland, the UK, Venezuela, Pakistan and the Philippines.In popular culture
In the 2006 film Man of the Year starring Robin Williams, the character played by Williams—a comedic host of political talk show—wins the election for President of the United States when a software error in the electronic voting machines produced by the fictional manufacturer Delacroy causes votes to be tallied inaccurately.
In Runoff, a 2007 novel by Mark Coggins, a surprising showing by the Green Party candidate in a San Francisco Mayoral election forces a runoff between him and the highly favored establishment candidate—a plot line that closely parallels the actual results of the 2003 election. When the private-eye protagonist of the book investigates at the behest of a powerful Chinatown businesswoman, he determines that the outcome was rigged by someone who defeated the security on the city's newly installed e-voting system.
"Hacking Democracy" is a 2006 documentary film shown on HBO. Filmed over three years, it documents American citizens investigating anomalies and irregularities with electronic voting systems that occurred during America's 2000 and 2004 elections, especially in Volusia County, Florida. The film investigates the flawed integrity of electronic voting machines, particularly those made by Diebold Election Systems and culminates in the hacking of a Diebold election system in Leon County, Florida.
The central conflict in the MMO video game Infantry resulted from the global institution of direct democracy through the use of personal voting devices sometime in the 22nd century AD. The practice gave rise to a 'voting class' of citizens composed mostly of homemakers and retirees who tended to be at home all day. Because they had the most free time to participate in voting, their opinions ultimately came to dominate politics.