

Surveillance is the monitoring of behavior, many activities, or information for the purpose of information gathering, influencing, managing or directing. This can include observation from a distance by means of electronic equipment, such as closed-circuit television (CCTV), or interception of electronically transmitted information like Internet traffic. It can also include simple technical methods, such as human intelligence gathering and postal interception.
Surveillance is used by citizens, for instance for protecting their neighborhoods. It is widely used by governments for intelligence gathering, including espionage, prevention of crime, the protection of a process, person, group or object, or the investigation of crime. It is also used by criminal organizations to plan and commit crimes, and by businesses to gather intelligence on criminals, their competitors, suppliers or customers. Religious organizations charged with detecting heresy and heterodoxy may also carry out surveillance. Auditors carry out a form of surveillance.
A byproduct of surveillance is that it can unjustifiably violate people's privacy and is often criticized by civil liberties activists. Democracies may have laws that seek to restrict governmental and private use of surveillance, whereas authoritarian governments seldom have any domestic restrictions.
Espionage is by definition covert and typically illegal according to the rules of the observed party, whereas most types of surveillance are overt and are considered legal or legitimate by state authorities. International espionage seems to be common among all types of countries.
Methods
Computer

The vast majority of computer surveillance involves the monitoring of data and traffic on the Internet. In the United States for example, under the Communications Assistance For Law Enforcement Act, all phone calls and broadband Internet traffic (emails, web traffic, instant messaging, etc.) are required to be available for unimpeded real-time monitoring by federal law enforcement agencies.
There is far too much data on the Internet for human investigators to manually search through all of it. Therefore, automated Internet surveillance computers sift through the vast amount of intercepted Internet traffic to identify and report to human investigators the traffic that is considered interesting or suspicious. This process is regulated by targeting certain "trigger" words or phrases, visiting certain types of web sites, or communicating via email or online chat with suspicious individuals or groups. Billions of dollars per year are spent by agencies, such as the NSA, the FBI and the now-defunct Information Awareness Office, to develop, purchase, implement, and operate systems such as Carnivore, NarusInsight, and ECHELON to intercept and analyze all of this data to extract only the information which is useful to law enforcement and intelligence agencies.
Computers can be a surveillance target because of the personal data stored on them. If someone is able to install software, such as the FBI's Magic Lantern and CIPAV, on a computer system, they can easily gain unauthorized access to this data. Such software could be installed physically or remotely. Another form of computer surveillance, known as van Eck phreaking, involves reading electromagnetic emanations from computing devices in order to extract data from them at distances of hundreds of meters. The NSA runs a database known as "Pinwale", which stores and indexes large numbers of emails of both American citizens and foreigners. Additionally, the NSA runs a program known as PRISM, which is a data mining system that gives the United States government direct access to information from technology companies. Through accessing this information, the government is able to obtain search history, emails, stored information, live chats, file transfers, and more. This program generated huge controversies in regards to surveillance and privacy, especially from U.S. citizens.
Telephones
The official and unofficial tapping of telephone lines is widespread. In the United States for instance, the Communications Assistance For Law Enforcement Act (CALEA) requires that all telephone and VoIP communications be available for real-time wiretapping by Federal law enforcement and intelligence agencies. Two major telecommunications companies in the U.S.—AT&T Inc. and Verizon—have contracts with the FBI, requiring them to keep their phone call records easily searchable and accessible for Federal agencies, in return for $1.8 million per year. Between 2003 and 2005, the FBI sent out more than 140,000 "National Security Letters" ordering phone companies to hand over information about their customers' calling and Internet histories. About half of these letters requested information on U.S. citizens.
Human agents are not required to monitor most calls. Speech-to-text software creates machine-readable text from intercepted audio, which is then processed by automated call-analysis programs, such as those developed by agencies such as the Information Awareness Office, or companies such as Verint, and Narus, which search for certain words or phrases, to decide whether to dedicate a human agent to the call.
Law enforcement and intelligence services in the United Kingdom and the United States possess technology to activate the microphones in cell phones remotely, by accessing phones' diagnostic or maintenance features in order to listen to conversations that take place near the person who holds the phone.
The StingRay tracker is an example of one of these tools used to monitor cell phone usage in the United States and the United Kingdom. Originally developed for counterterrorism purposes by the military, they work by broadcasting powerful signals that cause nearby cell phones to transmit their IMSI number, just as they would to normal cell phone towers. Once the phone is connected to the device, there is no way for the user to know that they are being tracked. The operator of the stingray is able to extract information such as location, phone calls, and text messages, but it is widely believed that the capabilities of the StingRay extend much further. A lot of controversy surrounds the StingRay because of its powerful capabilities and the secrecy that surrounds it.
Mobile phones are also commonly used to collect location data. The geographical location of a mobile phone (and thus the person carrying it) can be determined easily even when the phone is not being used, using a technique known as multilateration to calculate the differences in time for a signal to travel from the cell phone to each of several cell towers near the owner of the phone. The legality of such techniques has been questioned in the United States, in particular whether a court warrant is required. Records for one carrier alone (Sprint), showed that in a given year federal law enforcement agencies requested customer location data 8 million times.

In response to customers' privacy concerns in the post Edward Snowden era, Apple's iPhone 6 has been designed to disrupt investigative wiretapping efforts. The phone encrypts e-mails, contacts, and photos with a code generated by a complex mathematical algorithm that is unique to an individual phone, and is inaccessible to Apple. The encryption feature on the iPhone 6 has drawn criticism from FBI director James B. Comey and other law enforcement officials since even lawful requests to access user content on the iPhone 6 will result in Apple supplying "gibberish" data that requires law enforcement personnel to either break the code themselves or to get the code from the phone's owner. Because the Snowden leaks demonstrated that American agencies can access phones anywhere in the world, privacy concerns in countries with growing markets for smart phones have intensified, providing a strong incentive for companies like Apple to address those concerns in order to secure their position in the global market.
Apple has made several moves to emphasize their concern for privacy, in order to appeal to more consumers. In 2011, Apple stopped the use of permanent device identifiers, and in 2019, they banned the ability of third parties to track on children’s apps.
Although the CALEA requires telecommunication companies to build into their systems the ability to carry out a lawful wiretap, the law has not been updated to address the issue of smart phones and requests for access to e-mails and metadata. The Snowden leaks show that the NSA has been taking advantage of this ambiguity in the law by collecting metadata on "at least hundreds of millions" of "incidental" targets from around the world. The NSA uses an analytic tool known as CO-TRAVELER in order to track people whose movements intersect and to find any hidden connections with persons of interest.
The Snowden leaks have also revealed that the British Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ) can access information collected by the NSA on American citizens. Once the data has been collected, the GCHQ can hold on to it for up to two years. The deadline can be extended with the permission of a "senior UK official".
Cameras


Surveillance cameras, or security cameras, are video cameras used for the purpose of observing an area. They are often connected to a recording device or IP network, and may be watched by a security guard or law enforcement officer. Cameras and recording equipment used to be relatively expensive and required human personnel to monitor camera footage, but analysis of footage has been made easier by automated software that organizes digital video footage into a searchable database, and by video analysis software (such as VIRAT and HumanID). The amount of footage is also drastically reduced by motion sensors which record only when motion is detected. With cheaper production techniques, surveillance cameras are simple and inexpensive enough to be used in home security systems, and for everyday surveillance. Video cameras are one of the most common methods of surveillance.
As of 2016, there are about 350 million surveillance cameras worldwide. About 65% of these cameras are installed in Asia. The growth of CCTV has been slowing in recent years. In 2018, China was reported to have a huge surveillance network of over 170 million CCTV cameras with 400 million new cameras expected to be installed in the next three years, many of which use facial recognition technology.
In the United States, the Department of Homeland Security awards billions of dollars per year in Homeland Security grants for local, state, and federal agencies to install modern video surveillance equipment. For example, the city of Chicago, Illinois, recently used a $5.1 million Homeland Security grant to install an additional 250 surveillance cameras, and connect them to a centralized monitoring center, along with its preexisting network of over 2000 cameras, in a program known as Operation Virtual Shield. Speaking in 2009, Chicago Mayor Richard Daley announced that Chicago would have a surveillance camera on every street corner by 2016. New York City received a $350 million grant towards the development of the Domain Awareness System, which is an interconnected system of sensors including 18,000 CCTV cameras used for continual surveillance of the city by both police officers and artificial intelligence systems.
In the United Kingdom, the vast majority of video surveillance cameras are not operated by government bodies, but by private individuals or companies, especially to monitor the interiors of shops and businesses. According to 2011 Freedom of Information Act requests, the total number of local government operated CCTV cameras was around 52,000 over the entirety of the UK. The prevalence of video surveillance in the UK is often overstated due to unreliable estimates being requoted; for example one report in 2002 extrapolated from a very small sample to estimate the number of cameras in the UK at 4.2 million (of which 500,000 were in Greater London). More reliable estimates put the number of private and local government operated cameras in the United Kingdom at around 1.85 million in 2011.
In the Netherlands, one example city where there are cameras is The Hague. There, cameras are placed in city districts in which the most illegal activity is concentrated. Examples are the red-light districts and the train stations.
As part of China's Golden Shield Project, several U.S. corporations, including IBM, General Electric, and Honeywell, have been working closely with the Chinese government to install millions of surveillance cameras throughout China, along with advanced video analytics and facial recognition software, which will identify and track individuals everywhere they go. They will be connected to a centralized database and monitoring station, which will, upon completion of the project, contain a picture of the face of every person in China: over 1.3 billion people. Lin Jiang Huai, the head of China's "Information Security Technology" office (which is in charge of the project), credits the surveillance systems in the United States and the U.K. as the inspiration for what he is doing with the Golden Shield Project.

The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is funding a research project called Combat Zones That See that will link up cameras across a city to a centralized monitoring station, identify and track individuals and vehicles as they move through the city, and report "suspicious" activity (such as waving arms, looking side-to-side, standing in a group, etc.).
At Super Bowl XXXV in January 2001, police in Tampa, Florida, used Identix's facial recognition software, FaceIt, to scan the crowd for potential criminals and terrorists in attendance at the event (it found 19 people with pending arrest warrants).
Governments often initially claim that cameras are meant to be used for traffic control, but many of them end up using them for general surveillance. For example, Washington, D.C. had 5,000 "traffic" cameras installed under this premise, and then after they were all in place, networked them all together and then granted access to the Metropolitan Police Department, so they could perform "day-to-day monitoring".
The development of centralized networks of CCTV cameras watching public areas – linked to computer databases of people's pictures and identity (biometric data), able to track people's movements throughout the city, and identify whom they have been with – has been argued by some to present a risk to civil liberties. Trapwire is an example of such a network.
Social network analysis

One common form of surveillance is to create maps of social networks based on data from social networking sites such as Facebook, MySpace, Twitter as well as from traffic analysis information from phone call records such as those in the NSA call database, and others. These social network "maps" are then data mined to extract useful information such as personal interests, friendships & affiliations, wants, beliefs, thoughts, and activities.
Many U.S. government agencies such as the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), the National Security Agency (NSA), and the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) are investing heavily in research involving social network analysis. The intelligence community believes that the biggest threat to U.S. power comes from decentralized, leaderless, geographically dispersed groups of terrorists, subversives, extremists, and dissidents. These types of threats are most easily countered by finding important nodes in the network, and removing them. To do this requires a detailed map of the network.
Jason Ethier of Northeastern University, in his study of modern social network analysis, said the following of the Scalable Social Network Analysis Program developed by the Information Awareness Office:
The purpose of the SSNA algorithms program is to extend techniques of social network analysis to assist with distinguishing potential terrorist cells from legitimate groups of people.... In order to be successful SSNA will require information on the social interactions of the majority of people around the globe. Since the Defense Department cannot easily distinguish between peaceful citizens and terrorists, it will be necessary for them to gather data on innocent civilians as well as on potential terrorists.
— Jason Ethier
AT&T developed a programming language called "Hancock", which is able to sift through enormous databases of phone call and Internet traffic records, such as the NSA call database, and extract "communities of interest"—groups of people who call each other regularly, or groups that regularly visit certain sites on the Internet. AT&T originally built the system to develop "marketing leads", but the FBI has regularly requested such information from phone companies such as AT&T without a warrant, and, after using the data, stores all information received in its own databases, regardless of whether or not the information was ever useful in an investigation.
Some people believe that the use of social networking sites is a form of "participatory surveillance", where users of these sites are essentially performing surveillance on themselves, putting detailed personal information on public websites where it can be viewed by corporations and governments. In 2008, about 20% of employers reported using social networking sites to collect personal data on prospective or current employees.
Biometric

Biometric surveillance is a technology that measures and analyzes human physical and/or behavioral characteristics for authentication, identification, or screening purposes. Examples of physical characteristics include fingerprints, DNA, and facial patterns. Examples of mostly behavioral characteristics include gait (a person's manner of walking) or voice.
Facial recognition is the use of the unique configuration of a person's facial features to accurately identify them, usually from surveillance video. Both the Department of Homeland Security and DARPA are heavily funding research into facial recognition systems. The Information Processing Technology Office ran a program known as Human Identification at a Distance which developed technologies that are capable of identifying a person at up to 500 ft (150 m) by their facial features.
Another form of behavioral biometrics, based on affective computing, involves computers recognizing a person's emotional state based on an analysis of their facial expressions, how fast they are talking, the tone and pitch of their voice, their posture, and other behavioral traits. This might be used for instance to see if a person's behavior is suspect (looking around furtively, "tense" or "angry" facial expressions, waving arms, etc.).
A more recent development is DNA profiling, which looks at some of the major markers in the body's DNA to produce a match. The FBI is spending $1 billion to build a new biometric database, which will store DNA, facial recognition data, iris/retina (eye) data, fingerprints, palm prints, and other biometric data of people living in the United States. The computers running the database are contained in an underground facility about the size of two American football fields.
The Los Angeles Police Department is installing automated facial recognition and license plate recognition devices in its squad cars, and providing handheld face scanners, which officers will use to identify people while on patrol.
Facial thermographs are in development, which allow machines to identify certain emotions in people such as fear or stress, by measuring the temperature generated by blood flow to different parts of the face. Law enforcement officers believe that this has potential for them to identify when a suspect is nervous, which might indicate that they are hiding something, lying, or worried about something.
In his paper in Ethics and Information Technology, Avi Marciano maps the harms caused by biometric surveillance, traces their theoretical origins, and brings these harms together in one integrative framework to elucidate their cumulative power. Marciano proposes four types of harms: Unauthorized use of bodily information, denial or limitation of access to physical spaces, bodily social sorting, and symbolic ineligibility through construction of marginality and otherness. Biometrics' social power, according to Marciano, derives from three main features: their complexity as "enigmatic technologies", their objective-scientific image, and their increasing agency, particularly in the context of automatic decision-making.
Aerial

Aerial surveillance is the gathering of surveillance, usually visual imagery or video, from an airborne vehicle—such as an unmanned aerial vehicle, helicopter, or spy plane. Military surveillance aircraft use a range of sensors (e.g. radar) to monitor the battlefield.
Digital imaging technology, miniaturized computers, and numerous other technological advances over the past decade have contributed to rapid advances in aerial surveillance hardware such as micro-aerial vehicles, forward-looking infrared, and high-resolution imagery capable of identifying objects at extremely long distances. For instance, the MQ-9 Reaper, a U.S. drone plane used for domestic operations by the Department of Homeland Security, carries cameras that are capable of identifying an object the size of a milk carton from altitudes of 30,000 feet (9.1 km), and has forward-looking infrared devices that can detect the heat from a human body at distances of up to 60 kilometers (37 mi). In an earlier instance of commercial aerial surveillance, the Killington Mountain ski resort hired 'eye in the sky' aerial photography of its competitors' parking lots to judge the success of its marketing initiatives as it developed starting in the 1950s.

The United States Department of Homeland Security is in the process of testing UAVs to patrol the skies over the United States for the purposes of critical infrastructure protection, border patrol, "transit monitoring", and general surveillance of the U.S. population. Miami-Dade police department ran tests with a vertical take-off and landing UAV from Honeywell, which is planned to be used in SWAT operations. Houston's police department has been testing fixed-wing UAVs for use in "traffic control".
The United Kingdom, as well, is working on plans to build up a fleet of surveillance UAVs ranging from micro-aerial vehicles to full-size drones, to be used by police forces throughout the U.K.
In addition to their surveillance capabilities, MAVs are capable of carrying tasers for "crowd control", or weapons for killing enemy combatants.
Programs such as the Heterogeneous Aerial Reconnaissance Team program developed by DARPA have automated much of the aerial surveillance process. They have developed systems consisting of large teams drone planes that pilot themselves, automatically decide who is "suspicious" and how to go about monitoring them, coordinate their activities with other drones nearby, and notify human operators if something suspicious is occurring. This greatly increases the amount of area that can be continuously monitored, while reducing the number of human operators required. Thus a swarm of automated, self-directing drones can automatically patrol a city and track suspicious individuals, reporting their activities back to a centralized monitoring station. In addition, researchers also investigate possibilities of autonomous surveillance by large groups of micro aerial vehicles stabilized by decentralized bio-inspired swarming rules.
Corporate
Corporate surveillance is the monitoring of a person or group's behavior by a corporation. The data collected is most often used for marketing purposes or sold to other corporations, but is also regularly shared with government agencies. It can be used as a form of business intelligence, which enables the corporation to better tailor their products and/or services to be desirable by their customers. Although there is a common belief that monitoring can increase productivity, it can also create consequences such as increasing chances of deviant behavior and creating punishments that are not equitable to their actions. Additionally, monitoring can cause resistance and backlash because it insinuates an employer's suspicion and lack of trust.
Data mining and profiling
Data mining is the application of statistical techniques and programmatic algorithms to discover previously unnoticed relationships within the data. Data profiling in this context is the process of assembling information about a particular individual or group in order to generate a profile — that is, a picture of their patterns and behavior. Data profiling can be an extremely powerful tool for psychological and social network analysis. A skilled analyst can discover facts about a person that they might not even be consciously aware of themselves.
Economic (such as credit card purchases) and social (such as telephone calls and emails) transactions in modern society create large amounts of stored data and records. In the past, this data was documented in paper records, leaving a "paper trail", or was simply not documented at all. Correlation of paper-based records was a laborious process—it required human intelligence operators to manually dig through documents, which was time-consuming and incomplete, at best.
But today many of these records are electronic, resulting in an "electronic trail". Every use of a bank machine, payment by credit card, use of a phone card, call from home, checked out library book, rented video, or otherwise complete recorded transaction generates an electronic record. Public records—such as birth, court, tax and other records—are increasingly being digitized and made available online. In addition, due to laws like CALEA, web traffic and online purchases are also available for profiling. Electronic record-keeping makes data easily collectable, storable, and accessible—so that high-volume, efficient aggregation and analysis is possible at significantly lower costs.
Information relating to many of these individual transactions is often easily available because it is generally not guarded in isolation, since the information, such as the title of a movie a person has rented, might not seem sensitive. However, when many such transactions are aggregated they can be used to assemble a detailed profile revealing the actions, habits, beliefs, locations frequented, social connections, and preferences of the individual. This profile is then used, by programs such as ADVISE and TALON, to determine whether the person is a military, criminal, or political threat.
In addition to its own aggregation and profiling tools, the government is able to access information from third parties — for example, banks, credit companies or employers, etc. — by requesting access informally, by compelling access through the use of subpoenas or other procedures, or by purchasing data from commercial data aggregators or data brokers. The United States has spent $370 million on its 43 planned fusion centers, which are national network of surveillance centers that are located in over 30 states. The centers will collect and analyze vast amounts of data on U.S. citizens. It will get this data by consolidating personal information from sources such as state driver's licensing agencies, hospital records, criminal records, school records, credit bureaus, banks, etc. – and placing this information in a centralized database that can be accessed from all of the centers, as well as other federal law enforcement and intelligence agencies.
Under United States v. Miller (1976), data held by third parties is generally not subject to Fourth Amendment warrant requirements.
Human operatives
A tail may surreptitiously track and report on the movements and contacts of a person of interest. Such following by one or more people may provide useful in formation in relatively densely populated urban environments.
Organizations that have enemies who wish to gather information about the groups' members or activities face the issue of potential infiltration.
In addition to operatives' infiltrating an organization, the surveilling party may exert pressure on certain members of the target organization to act as informants (i.e., to disclose the information they hold on the organization and its members).
Fielding operatives is very expensive, and governments with wide-reaching electronic surveillance tools at their disposal, rather than gathering the sort of information which operatives can provide, may use less problematic forms of surveillance - such as those mentioned above. Nevertheless, the use of human infiltrators remains common. For instance, in 2007 documents surfaced showing that the FBI planned to field a total of 15,000 undercover agents and informants in response to an anti-terrorism directive (issued by President George W. Bush in 2004) that ordered intelligence and law-enforcement agencies to increase their HUMINT capabilities.
Satellite imagery
On May 25, 2007, the U.S. Director of National Intelligence Michael McConnell authorized the National Applications Office (NAO) of the Department of Homeland Security to allow local, state, and domestic Federal agencies to access imagery from military intelligence Reconnaissance satellites and Reconnaissance aircraft sensors which can now be used to observe the activities of U.S. citizens. The satellites and aircraft sensors will be able to penetrate cloud cover, detect chemical traces, and identify objects in buildings and "underground bunkers", and will provide real-time video at much higher resolutions than the still-images produced by programs such as Google Earth.
Identification and credentials

One of the simplest forms of identification is the carrying of credentials. Some nations have an identity card system to aid identification, whilst others are considering it but face public opposition. Other documents, such as passports, driver's licenses, library cards, banking or credit cards are also used to verify identity.
If the form of the identity card is "machine-readable", usually using an encoded magnetic stripe or identification number (such as a Social Security number), it corroborates the subject's identifying data. In this case it may create an electronic trail when it is checked and scanned, which can be used in profiling, as mentioned above.
Wireless Tracking
This section refers to methods that involve the monitoring of tracking devices through the aid of wireless signals.
Mobile phones
Mobile carrier antennas are also commonly used to collect geolocation data on mobile phones. The geographical location of a powered mobile phone (and thus the person carrying it) can be determined easily (whether it is being used or not), using a technique known as multilateration to calculate the differences in time for a signal to travel from the cell phone to each of several cell towers near the owner of the phone. Dr. Victor Kappeler of Eastern Kentucky University indicates that police surveillance is a strong concern, stating the following statistics from 2013:
Of the 321,545 law enforcement requests made to Verizon, 54,200 of these requests were for "content" or "location" information—not just cell phone numbers or IP addresses. Content information included the actual text of messages, emails and the wiretapping of voice or messaging content in real-time.
A comparatively new off-the-shelf surveillance device is an IMSI-catcher, a telephone eavesdropping device used to intercept mobile phone traffic and track the movement of mobile phone users. Essentially a "fake" mobile tower acting between the target mobile phone and the service provider's real towers, it is considered a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack. IMSI-catchers are used in some countries by law enforcement and intelligence agencies, but their use has raised significant civil liberty and privacy concerns and is strictly regulated in some countries.
In March 2020, British daily The Guardian, based on the claims of a whistleblower, accused the government of Saudi Arabia of exploiting global mobile telecom network weaknesses to spy on its citizens traveling around the United States. The data shared by the whistleblower in support of the claims, showed that a systematic spying campaign was being run by the kingdom exploiting the flaws of SS7, a global messaging system. The data showed that millions of secret tracking commands originated from Saudi in a duration of four-months, starting from November 2019.
RFID tagging
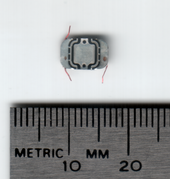
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tagging is the use of very small electronic devices (called "RFID tags") which are applied to or incorporated into a product, animal, or person for the purpose of identification and tracking using radio waves. The tags can be read from several meters away. They are extremely inexpensive, costing a few cents per piece, so they can be inserted into many types of everyday products without significantly increasing the price, and can be used to track and identify these objects for a variety of purposes.
Some companies appear to be "tagging" their workers by incorporating RFID tags in employee ID badges. Workers in U.K. considered strike action in protest of having themselves tagged; they felt that it was dehumanizing to have all of their movements tracked with RFID chips. Some critics have expressed fears that people will soon be tracked and scanned everywhere they go. On the other hand, RFID tags in newborn baby ID bracelets put on by hospitals have foiled kidnappings.
In a 2003 editorial, CNET News.com's chief political correspondent, Declan McCullagh, speculated that, soon, every object that is purchased, and perhaps ID cards, will have RFID devices in them, which would respond with information about people as they walk past scanners (what type of phone they have, what type of shoes they have on, which books they are carrying, what credit cards or membership cards they have, etc.). This information could be used for identification, tracking, or targeted marketing. As of 2021, this has largely not come to pass.
RFID tagging on humans

A human microchip implant is an identifying integrated circuit device or RFID transponder encased in silicate glass and implanted in the body of a human being. A subdermal implant typically contains a unique ID number that can be linked to information contained in an external database, such as personal identification, medical history, medications, allergies, and contact information.
Several types of microchips have been developed in order to control and monitor certain types of people, such as criminals, political figures and spies, a "killer" tracking chip patent was filed at the German Patent and Trademark Office (DPMA) around May 2009.
Verichip is an RFID device produced by a company called Applied Digital Solutions (ADS). Verichip is slightly larger than a grain of rice, and is injected under the skin. The injection reportedly feels similar to receiving a shot. The chip is encased in glass, and stores a "VeriChip Subscriber Number" which the scanner uses to access their personal information, via the Internet, from Verichip Inc.'s database, the "Global VeriChip Subscriber Registry". Thousands of people have already had them inserted. In Mexico, for example, 160 workers at the Attorney General's office were required to have the chip injected for identity verification and access control purposes.
Implantable microchips have also been used in healthcare settings, but ethnographic researchers have identified a number of ethical problems with such uses; these problems include unequal treatment, diminished trust, and possible endangerment of patients.
Radar
Perimeter surveillance radar (PSR) is a class of radar sensors that monitor activity surrounding or on critical infrastructure areas such as airports, seaports, military installations, national borders, refineries and other critical industry and the like. Such radars are characterized by their ability to detect movement at ground level of targets such as an individual walking or crawling towards a facility. Such radars typically have ranges of several hundred metres to over 10 kilometres.
Alternate technologies include laser-based systems. These have the potential for very high target position accuracy, however they are less effective in the presence of fog and other obscurants.Geolocation devices
Global Positioning System

In the U.S., police have planted hidden GPS tracking devices in people's vehicles to monitor their movements, without a warrant. In early 2009, they were arguing in court that they have the right to do this.
Several cities are running pilot projects to require parolees to wear GPS devices to track their movements when they get out of prison.
Devices
Covert listening devices and video devices, or "bugs", are hidden electronic devices which are used to capture, record, and/or transmit data to a receiving party such as a law enforcement agency.
The U.S. has run numerous domestic intelligence operations, such as COINTELPRO, which have bugged the homes, offices, and vehicles of thousands of U.S. citizens, usually political activists, subversives, and criminals.
Law enforcement and intelligence services in the U.K. and the United States possess technology to remotely activate the microphones in cell phones, by accessing the phone's diagnostic/maintenance features, in order to listen to conversations that take place nearby the person who holds the phone.
Postal services
As more people use faxes and e-mail the significance of surveilling the postal system is decreasing, in favor of Internet and telephone surveillance. But interception of post is still an available option for law enforcement and intelligence agencies, in certain circumstances. This is not a common practice, however, and entities like the US Army require high levels of approval to conduct.
The U.S. Central Intelligence Agency and Federal Bureau of Investigation have performed twelve separate mail-opening campaigns targeted towards U.S. citizens. In one of these programs, more than 215,000 communications were intercepted, opened, and photographed.
Stakeout
A stakeout is the coordinated surveillance of a location or person. Stakeouts are generally performed covertly and for the purpose of gathering evidence related to criminal activity. The term derives from the practice by land surveyors of using survey stakes to measure out an area before the main building project begins.
Internet of things
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a term that refers to the future of technology in which data can be collected without human and computer interaction. IoTs can be used for identification, monitoring, location tracking, and health tracking. While IoTs have the benefit of being a time-saving tool that makes activities simpler, they raise the concern of government surveillance and privacy regarding how data will be used.
Controversy

Support
Supporters of surveillance systems believe that these tools can help protect society from terrorists and criminals. They argue that surveillance can reduce crime by three means: by deterrence, by observation, and by reconstruction. Surveillance can deter by increasing the chance of being caught, and by revealing the modus operandi. This requires a minimal level of invasiveness.
Another method on how surveillance can be used to fight criminal activity is by linking the information stream obtained from them to a recognition system (for instance, a camera system that has its feed run through a facial recognition system). This can for instance auto-recognize fugitives and direct police to their location.
A distinction here has to be made however on the type of surveillance employed. Some people that support video surveillance in city streets may not support indiscriminate telephone taps and vice versa. Besides the types, the way in which this surveillance is done also matters a lot; i.e. indiscriminate telephone taps are supported by much fewer people than say telephone taps done only to people suspected of engaging in illegal activities.
Surveillance can also be used to give human operatives a tactical advantage through improved situational awareness, or through the use of automated processes, i.e. video analytics. Surveillance can help reconstruct an incident and prove guilt through the availability of footage for forensics experts. Surveillance can also influence subjective security if surveillance resources are visible or if the consequences of surveillance can be felt.
Some of the surveillance systems (such as the camera system that has its feed run through a facial recognition system mentioned above) can also have other uses besides countering criminal activity. For instance, it can help in retrieving runaway children, abducted or missing adults and mentally disabled people. Other supporters simply believe that there is nothing that can be done about the loss of privacy, and that people must become accustomed to having no privacy. As Sun Microsystems CEO Scott McNealy said: "You have zero privacy anyway. Get over it."
Another common argument is: "If you aren't doing something wrong then you don't have anything to fear." That is, one does not have a right to privacy regarding illegal activities, while those following the law suffer no harm from surveillance and so have no standing to object to it. Beyond the heroically self-serving identification of what is wrong with what is illegal, the ethical fly in this ointment is the tacit premise that the individual has no duty to preserve the health of the state--the antithesis of the principle that only the consent of the governed can adequately serve as the moral foundation of a (just) state and warrant the vast gulf between its power (and agency) and that of the individual.
Opposition


With the advent of programs such as the Total Information Awareness program and ADVISE, technologies such as high speed surveillance computers and biometrics software, and laws such as the Communications Assistance for Law Enforcement Act, governments now possess an unprecedented ability to monitor the activities of their subjects. Many civil rights and privacy groups, such as the Electronic Frontier Foundation and American Civil Liberties Union, have expressed concern that by allowing continual increases in government surveillance of citizens we will end up in a mass surveillance society, with extremely limited, or non-existent political and/or personal freedoms. Fears such as this have led to numerous lawsuits such as Hepting v. AT&T.
Some critics state that the claim made by supporters should be modified to read: "As long as we do what we're told, we have nothing to fear.". For instance, a person who is part of a political group which opposes the policies of the national government, might not want the government to know their names and what they have been reading, so that the government cannot easily subvert their organization, arrest, or kill them. Other critics state that while a person might not have anything to hide right now, the government might later implement policies that they do wish to oppose, and that opposition might then be impossible due to mass surveillance enabling the government to identify and remove political threats. Further, other critics point to the fact that most people do have things to hide. For example, if a person is looking for a new job, they might not want their current employer to know this. Also if an employer wishes total privacy to watch over their own employee and secure their financial information it may become impossible, and they may not wish to hire those under surveillance.
In December 2017, the Government of China took steps to oppose widespread surveillance by security-company cameras, webcams, and IP cameras after tens-of-thousands were made accessible for internet viewing by IT company Qihoo
Totalitarianism

Programs such as the Total Information Awareness program, and laws such as the Communications Assistance For Law Enforcement Act have led many groups to fear that society is moving towards a state of mass surveillance with severely limited personal, social, political freedoms, where dissenting individuals or groups will be strategically removed in COINTELPRO-like purges.
Kate Martin, of the Center For National Security Studies said of the use of military spy satellites being used to monitor the activities of U.S. citizens: "They are laying the bricks one at a time for a police state."
Some point to the blurring of lines between public and private places, and the privatization of places traditionally seen as public (such as shopping malls and industrial parks) as illustrating the increasing legality of collecting personal information. Traveling through many public places such as government offices is hardly optional for most people, yet consumers have little choice but to submit to companies' surveillance practices. Surveillance techniques are not created equal; among the many biometric identification technologies, for instance, face recognition requires the least cooperation. Unlike automatic fingerprint reading, which requires an individual to press a finger against a machine, this technique is subtle and requires little to no consent.
Psychological/social effects
Some critics, such as Michel Foucault, believe that in addition to its obvious function of identifying and capturing individuals who are committing undesirable acts, surveillance also functions to create in everyone a feeling of always being watched, so that they become self-policing. This allows the State to control the populace without having to resort to physical force, which is expensive and otherwise problematic.
With the development of digital technology, individuals have become increasingly perceptible to one another, as surveillance becomes virtual. Online surveillance is the utilization of the internet to observe one's activity. Corporations, citizens, and governments participate in tracking others' behaviours for motivations that arise out of business relations, to curiosity, to legality. In her book Superconnected, Mary Chayko differentiates between two types of surveillance: vertical and horizontal. Vertical surveillance occurs when there is a dominant force, such as the government that is attempting to control or regulate the actions of a given society. Such powerful authorities often justify their incursions as a means to protect society from threats of violence or terrorism. Some individuals question when this becomes an infringement on civil rights.
Horizontal diverges from vertical surveillance as the tracking shifts from an authoritative source to an everyday figure, such as a friend, coworker, or stranger that is interested in one's mundane activities. Individuals leave traces of information when they are online that reveal their interests and desires of which others observe. While this can allow people to become interconnected and develop social connections online, it can also increase potential risk to harm, such as cyberbullying or censoring/stalking by strangers, reducing privacy.
In addition, Simone Browne argues that surveillance wields an immense racializing quality such that it operates as "racializing surveillance." Browne uses racializing surveillance to refer to moments when enactments of surveillance are used to reify boundaries, borders, and bodies along racial lines and where the outcome is discriminatory treatment of those who are negatively racialized by such surveillance. Browne argues racializing surveillance pertains to policing what is "in or out of place."
Privacy
Numerous civil rights groups and privacy groups oppose surveillance as a violation of people's right to privacy. Such groups include: Electronic Privacy Information Center, Electronic Frontier Foundation, American Civil Liberties Union and Privacy International.
There have been several lawsuits such as Hepting v. AT&T and EPIC v. Department of Justice by groups or individuals, opposing certain surveillance activities.
Legislative proceedings such as those that took place during the Church Committee, which investigated domestic intelligence programs such as COINTELPRO, have also weighed the pros and cons of surveillance.
Court cases
People vs. Diaz (2011) was a court case in the realm of cell phone privacy, even though the decision was later overturned. In this case, Gregory Diaz was arrested during a sting operation for attempting to sell ecstasy. During his arrest, police searched Diaz's phone and found more incriminating evidence including SMS text messages and photographs depicting illicit activities. During his trial, Diaz attempted to have the information from his cell phone removed from evidence, but the courts deemed it as lawful and Diaz's appeal was denied on the California State Court level and, later, the Supreme Court level. Just three short years after, this decision was overturned in the case Riley vs. California (2014).
Riley vs. California (2014) was a U.S. Supreme Court case in which a man was arrested for his involvement in a drive-by shooting. A few days after the shooting the police made an arrest of the suspect (Riley), and, during the arrest, the police searched him. However, this search was not only of Riley's person, but also the police opened and searched his cell phone, finding pictures of other weapons, drugs, and of Riley showing gang signs. In court, the question arose whether searching the phone was lawful or if the search was protected by the 4th amendment of the constitution. The decision held that the search of Riley's cell phone during the arrest was illegal, and that it was protected by the 4th Amendment.
Countersurveillance, inverse surveillance, sousveillance
Countersurveillance is the practice of avoiding surveillance or making surveillance difficult. Developments in the late twentieth century have caused counter surveillance to dramatically grow in both scope and complexity, such as the Internet, increasing prevalence of electronic security systems, high-altitude (and possibly armed) UAVs, and large corporate and government computer databases. Other examples include encrypted messenger apps such as Signal and privacy cryptocurrencies such as Monero and ZCash.
Inverse surveillance is the practice of the reversal of surveillance on other individuals or groups (e.g., citizens photographing police). Well-known examples include George Holliday's recording of the Rodney King beating and the organization Copwatch, which attempts to monitor police officers to prevent police brutality. Counter-surveillance can be also used in applications to prevent corporate spying, or to track other criminals by certain criminal entities. It can also be used to deter stalking methods used by various entities and organizations.
Sousveillance is inverse surveillance, involving the recording by private individuals, rather than government or corporate entities.



