
In physics, mass–energy equivalence is the relationship between mass and energy in a system's rest frame, where the two quantities differ only by a multiplicative constant and the units of measurement. The principle is described by the physicist Albert Einstein's formula: . In a reference frame where the system is moving, its relativistic energy and relativistic mass (instead of rest mass) obey the same formula.
The formula defines the energy E of a particle in its rest frame as the product of mass (m) with the speed of light squared (c2). Because the speed of light is a large number in everyday units (approximately 300000 km/s or 186000 mi/s), the formula implies that a small amount of "rest mass", measured when the system is at rest, corresponds to an enormous amount of energy, which is independent of the composition of the matter.
Rest mass, also called invariant mass, is a fundamental physical property that is independent of momentum, even at extreme speeds approaching the speed of light. Its value is the same in all inertial frames of reference. Massless particles such as photons have zero invariant mass, but massless free particles have both momentum and energy.
The equivalence principle implies that when energy is lost in chemical reactions, nuclear reactions, and other energy transformations, the system will also lose a corresponding amount of mass. The energy, and mass, can be released to the environment (outside of the system being considered) as radiant energy, such as light, or as thermal energy. The principle is fundamental to many fields of physics, including nuclear and particle physics.
Mass–energy equivalence arose from special relativity as a paradox described by the French polymath Henri Poincaré (1854–1912). Einstein was the first to propose the equivalence of mass and energy as a general principle and a consequence of the symmetries of space and time. The principle first appeared in "Does the inertia of a body depend upon its energy-content?", one of his annus mirabilis papers, published on 21 November 1905. The formula and its relationship to momentum, as described by the energy–momentum relation, were later developed by other physicists.
Description
| Special relativity |
|---|
 |
Mass–energy equivalence states that all objects having mass, or massive objects, have a corresponding intrinsic energy, even when they are stationary. In the rest frame of an object, where by definition it is motionless and so has no momentum, the mass and energy are equal or they differ only by a constant factor, the speed of light squared (c2). In Newtonian mechanics, a motionless body has no kinetic energy, and it may or may not have other amounts of internal stored energy, like chemical energy or thermal energy, in addition to any potential energy it may have from its position in a field of force. These energies tend to be much smaller than the mass of the object multiplied by c2, which is on the order of 1017 joules for a mass of one kilogram. Due to this principle, the mass of the atoms that come out of a nuclear reaction is less than the mass of the atoms that go in, and the difference in mass shows up as heat and light with the same equivalent energy as the difference. In analyzing these extreme events, Einstein's formula can be used with E as the energy released (removed), and m as the change in mass.
In relativity, all the energy that moves with an object (i.e., the energy as measured in the object's rest frame) contributes to the total mass of the body, which measures how much it resists acceleration. If an isolated box of ideal mirrors could contain light, the individually massless photons would contribute to the total mass of the box by the amount equal to their energy divided by c2. For an observer in the rest frame, removing energy is the same as removing mass and the formula m = E/c2 indicates how much mass is lost when energy is removed. In the same way, when any energy is added to an isolated system, the increase in the mass is equal to the added energy divided by c2.
Mass in special relativity
An object moves at different speeds in different frames of reference, depending on the motion of the observer. This implies the kinetic energy, in both Newtonian mechanics and relativity, is 'frame dependent', so that the amount of relativistic energy that an object is measured to have depends on the observer. The relativistic mass of an object is given by the relativistic energy divided by c2. Because the relativistic mass is exactly proportional to the relativistic energy, relativistic mass and relativistic energy are nearly synonymous; the only difference between them is the units. The rest mass or invariant mass of an object is defined as the mass an object has in its rest frame, when it is not moving with respect to the observer. Physicists typically use the term mass, though experiments have shown an object's gravitational mass depends on its total energy and not just its rest mass. The rest mass is the same for all inertial frames, as it is independent of the motion of the observer, it is the smallest possible value of the relativistic mass of the object. Because of the attraction between components of a system, which results in potential energy, the rest mass is almost never additive; in general, the mass of an object is not the sum of the masses of its parts. The rest mass of an object is the total energy of all the parts, including kinetic energy, as observed from the center of momentum frame, and potential energy. The masses add up only if the constituents are at rest (as observed from the center of momentum frame) and do not attract or repel, so that they do not have any extra kinetic or potential energy. Massless particles are particles with no rest mass, and therefore have no intrinsic energy; their energy is due only to their momentum.
Relativistic mass
Relativistic mass depends on the motion of the object, so that different observers in relative motion see different values for it. The relativistic mass of a moving object is larger than the relativistic mass of an object at rest, because a moving object has kinetic energy. If the object moves slowly, the relativistic mass is nearly equal to the rest mass and both are nearly equal to the classical inertial mass (as it appears in Newton's laws of motion). If the object moves quickly, the relativistic mass is greater than the rest mass by an amount equal to the mass associated with the kinetic energy of the object. Massless particles also have relativistic mass derived from their kinetic energy, equal to their relativistic energy divided by c2, or mrel = E/c2. The speed of light is one in a system where length and time are measured in natural units and the relativistic mass and energy would be equal in value and dimension. As it is just another name for the energy, the use of the term relativistic mass is redundant and physicists generally reserve mass to refer to rest mass, or invariant mass, as opposed to relativistic mass. A consequence of this terminology is that the mass is not conserved in special relativity, whereas the conservation of momentum and conservation of energy are both fundamental laws.
Conservation of mass and energy
The Conservation of energy is a universal principle in physics and holds for any interaction, along with the conservation of momentum. The classical conservation of mass, in contrast, is violated in certain relativistic settings. This concept has been experimentally proven in a number of ways, including the conversion of mass into kinetic energy in nuclear reactions and other interactions between elementary particles. While modern physics has discarded the expression 'conservation of mass', in older terminology a relativistic mass can also be defined to be equivalent to the energy of a moving system, allowing for a conservation of relativistic mass. Mass conservation breaks down when the energy associated with the mass of a particle is converted into other forms of energy, such as kinetic energy, thermal energy, or radiant energy.
Massless particles
Massless particles have zero rest mass. The Planck–Einstein relation for the energy for photons is given by the equation E = hf, where h is the Planck constant and f is the photon frequency. This frequency and thus the relativistic energy are frame-dependent. If an observer runs away from a photon in the direction the photon travels from a source, and it catches up with the observer, the observer sees it as having less energy than it had at the source. The faster the observer is traveling with regard to the source when the photon catches up, the less energy the photon would be seen to have. As an observer approaches the speed of light with regard to the source, the redshift of the photon increases, according to the relativistic Doppler effect. The energy of the photon is reduced and as the wavelength becomes arbitrarily large, the photon's energy approaches zero, because of the massless nature of photons, which does not permit any intrinsic energy.
Composite systems
For closed systems made up of many parts, like an atomic nucleus, planet, or star, the relativistic energy is given by the sum of the relativistic energies of each of the parts, because energies are additive in these systems. If a system is bound by attractive forces, and the energy gained in excess of the work done is removed from the system, then mass is lost with this removed energy. The mass of an atomic nucleus is less than the total mass of the protons and neutrons that make it up. This mass decrease is also equivalent to the energy required to break up the nucleus into individual protons and neutrons. This effect can be understood by looking at the potential energy of the individual components. The individual particles have a force attracting them together, and forcing them apart increases the potential energy of the particles in the same way that lifting an object up on earth does. This energy is equal to the work required to split the particles apart. The mass of the Solar System is slightly less than the sum of its individual masses.
For an isolated system of particles moving in different directions, the invariant mass of the system is the analog of the rest mass, and is the same for all observers, even those in relative motion. It is defined as the total energy (divided by c2) in the center of momentum frame. The center of momentum frame is defined so that the system has zero total momentum; the term center of mass frame is also sometimes used, where the center of mass frame is a special case of the center of momentum frame where the center of mass is put at the origin. A simple example of an object with moving parts but zero total momentum is a container of gas. In this case, the mass of the container is given by its total energy (including the kinetic energy of the gas molecules), since the system's total energy and invariant mass are the same in any reference frame where the momentum is zero, and such a reference frame is also the only frame in which the object can be weighed. In a similar way, the theory of special relativity posits that the thermal energy in all objects, including solids, contributes to their total masses, even though this energy is present as the kinetic and potential energies of the atoms in the object, and it (in a similar way to the gas) is not seen in the rest masses of the atoms that make up the object. Similarly, even photons, if trapped in an isolated container, would contribute their energy to the mass of the container. Such extra mass, in theory, could be weighed in the same way as any other type of rest mass, even though individually photons have no rest mass. The property that trapped energy in any form adds weighable mass to systems that have no net momentum is one of the consequences of relativity. It has no counterpart in classical Newtonian physics, where energy never exhibits weighable mass.
Relation to gravity
Physics has two concepts of mass, the gravitational mass and the inertial mass. The gravitational mass is the quantity that determines the strength of the gravitational field generated by an object, as well as the gravitational force acting on the object when it is immersed in a gravitational field produced by other bodies. The inertial mass, on the other hand, quantifies how much an object accelerates if a given force is applied to it. The mass–energy equivalence in special relativity refers to the inertial mass. However, already in the context of Newtonian gravity, the weak equivalence principle is postulated: the gravitational and the inertial mass of every object are the same. Thus, the mass–energy equivalence, combined with the weak equivalence principle, results in the prediction that all forms of energy contribute to the gravitational field generated by an object. This observation is one of the pillars of the general theory of relativity.
The prediction that all forms of energy interact gravitationally has been subject to experimental tests. One of the first observations testing this prediction, called the Eddington experiment, was made during the Solar eclipse of May 29, 1919. During the solar eclipse, the English astronomer and physicist Arthur Eddington observed that the light from stars passing close to the Sun was bent. The effect is due to the gravitational attraction of light by the Sun. The observation confirmed that the energy carried by light indeed is equivalent to a gravitational mass. Another seminal experiment, the Pound–Rebka experiment, was performed in 1960. In this test a beam of light was emitted from the top of a tower and detected at the bottom. The frequency of the light detected was higher than the light emitted. This result confirms that the energy of photons increases when they fall in the gravitational field of the Earth. The energy, and therefore the gravitational mass, of photons is proportional to their frequency as stated by the Planck's relation.
Efficiency
In some reactions, matter particles can be destroyed and their associated energy released to the environment as other forms of energy, such as light and heat. One example of such a conversion takes place in elementary particle interactions, where the rest energy is transformed into kinetic energy. Such conversions between types of energy happen in nuclear weapons, in which the protons and neutrons in atomic nuclei lose a small fraction of their original mass, though the mass lost is not due to the destruction of any smaller constituents. Nuclear fission allows a tiny fraction of the energy associated with the mass to be converted into usable energy such as radiation; in the decay of the uranium, for instance, about 0.1% of the mass of the original atom is lost. In theory, it should be possible to destroy matter and convert all of the rest-energy associated with matter into heat and light, but none of the theoretically known methods are practical. One way to harness all the energy associated with mass is to annihilate matter with antimatter. Antimatter is rare in our universe, however, and the known mechanisms of production require more usable energy than would be released in annihilation. CERN estimated in 2011 that over a billion times more energy is required to make and store antimatter than could be released in its annihilation.
As most of the mass which comprises ordinary objects resides in protons and neutrons, converting all the energy of ordinary matter into more useful forms requires that the protons and neutrons be converted to lighter particles, or particles with no mass at all. In the Standard Model of particle physics, the number of protons plus neutrons is nearly exactly conserved. Despite this, Gerard 't Hooft showed that there is a process that converts protons and neutrons to antielectrons and neutrinos. This is the weak SU(2) instanton proposed by the physicists Alexander Belavin, Alexander Markovich Polyakov, Albert Schwarz, and Yu. S. Tyupkin. This process, can in principle destroy matter and convert all the energy of matter into neutrinos and usable energy, but it is normally extraordinarily slow. It was later shown that the process occurs rapidly at extremely high temperatures that would only have been reached shortly after the Big Bang.
Many extensions of the standard model contain magnetic monopoles, and in some models of grand unification, these monopoles catalyze proton decay, a process known as the Callan–Rubakov effect. This process would be an efficient mass–energy conversion at ordinary temperatures, but it requires making monopoles and anti-monopoles, whose production is expected to be inefficient. Another method of completely annihilating matter uses the gravitational field of black holes. The British theoretical physicist Stephen Hawking theorized it is possible to throw matter into a black hole and use the emitted heat to generate power. According to the theory of Hawking radiation, however, larger black holes radiate less than smaller ones, so that usable power can only be produced by small black holes.
Extension for systems in motion
Unlike a system's energy in an inertial frame, the relativistic energy () of a system depends on both the rest mass () and the total momentum of the system. The extension of Einstein's equation to these systems is given by:
or
where the term represents the square of the Euclidean norm (total vector length) of the various momentum vectors in the system, which reduces to the square of the simple momentum magnitude, if only a single particle is considered. This equation is called the energy–momentum relation and reduces to when the momentum term is zero. For photons where , the equation reduces to .
Low-speed expansion
Using the Lorentz factor, γ, the energy–momentum can be rewritten as E = γmc2 and expanded as a power series:
For speeds much smaller than the speed of light, higher-order terms in this expression get smaller and smaller because v/c is small. For low speeds, all but the first two terms can be ignored:
In classical mechanics, both the m0c2 term and the high-speed corrections are ignored. The initial value of the energy is arbitrary, as only the change in energy can be measured and so the m0c2 term is ignored in classical physics. While the higher-order terms become important at higher speeds, the Newtonian equation is a highly accurate low-speed approximation; adding in the third term yields:
- .
The difference between the two approximations is given by , a number very small for everyday objects. In 2018 NASA announced the Parker Solar Probe was the fastest ever, with a speed of 153,454 miles per hour (68,600 m/s). The difference between the approximations for the Parker Solar Probe in 2018 is , which accounts for an energy correction of four parts per hundred million. The gravitational constant, in contrast, has a standard relative uncertainty of about .
Applications
Application to nuclear physics

The nuclear binding energy is the minimum energy that is required to disassemble the nucleus of an atom into its component parts. The mass of an atom is less than the sum of the masses of its constituents due to the attraction of the strong nuclear force. The difference between the two masses is called the mass defect and is related to the binding energy through Einstein's formula. The principle is used in modeling nuclear fission reactions, and it implies that a great amount of energy can be released by the nuclear fission chain reactions used in both nuclear weapons and nuclear power.
A water molecule weighs a little less than two free hydrogen atoms and an oxygen atom. The minuscule mass difference is the energy needed to split the molecule into three individual atoms (divided by c2), which was given off as heat when the molecule formed (this heat had mass). Similarly, a stick of dynamite in theory weighs a little bit more than the fragments after the explosion; in this case the mass difference is the energy and heat that is released when the dynamite explodes. Such a change in mass may only happen when the system is open, and the energy and mass are allowed to escape. Thus, if a stick of dynamite is blown up in a hermetically sealed chamber, the mass of the chamber and fragments, the heat, sound, and light would still be equal to the original mass of the chamber and dynamite. If sitting on a scale, the weight and mass would not change. This would in theory also happen even with a nuclear bomb, if it could be kept in an ideal box of infinite strength, which did not rupture or pass radiation. Thus, a 21.5 kiloton (9×1013 joule) nuclear bomb produces about one gram of heat and electromagnetic radiation, but the mass of this energy would not be detectable in an exploded bomb in an ideal box sitting on a scale; instead, the contents of the box would be heated to millions of degrees without changing total mass and weight. If a transparent window passing only electromagnetic radiation were opened in such an ideal box after the explosion, and a beam of X-rays and other lower-energy light allowed to escape the box, it would eventually be found to weigh one gram less than it had before the explosion. This weight loss and mass loss would happen as the box was cooled by this process, to room temperature. However, any surrounding mass that absorbed the X-rays (and other "heat") would gain this gram of mass from the resulting heating, thus, in this case, the mass "loss" would represent merely its relocation.
Practical examples
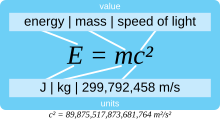
Einstein used the centimetre–gram–second system of units (cgs), but the formula is independent of the system of units. In natural units, the numerical value of the speed of light is set to equal 1, and the formula expresses an equality of numerical values: E = m. In the SI system (expressing the ratio E/m in joules per kilogram using the value of c in metres per second):
- E/m = c2 = (299792458 m/s)2 = 89875517873681764 J/kg (≈ 9.0 × 1016 joules per kilogram).
So the energy equivalent of one kilogram of mass is
- 89.9 petajoules
- 25.0 billion kilowatt-hours (≈ 25,000 GW·h)
- 21.5 trillion kilocalories (≈ 21 Pcal)
- 85.2 trillion BTUs
- 0.0852 quads
or the energy released by combustion of the following:
- 21 500 kilotons of TNT-equivalent energy (≈ 21 Mt)
- 2630000000 litres or 695000000 US gallons of automotive gasoline
Any time energy is released, the process can be evaluated from an E = mc2 perspective. For instance, the "Gadget"-style bomb used in the Trinity test and the bombing of Nagasaki had an explosive yield equivalent to 21 kt of TNT. About 1 kg of the approximately 6.15 kg of plutonium in each of these bombs fissioned into lighter elements totaling almost exactly one gram less, after cooling. The electromagnetic radiation and kinetic energy (thermal and blast energy) released in this explosion carried the missing gram of mass.
Whenever energy is added to a system, the system gains mass, as shown when the equation is rearranged:
- A spring's mass increases whenever it is put into compression or tension. Its mass increase arises from the increased potential energy stored within it, which is bound in the stretched chemical (electron) bonds linking the atoms within the spring.
- Raising the temperature of an object (increasing its thermal energy) increases its mass. For example, consider the world's primary mass standard for the kilogram, made of platinum and iridium. If its temperature is allowed to change by 1 °C, its mass changes by 1.5 picograms (1 pg = 1×10−12 g).
- A spinning ball has greater mass than when it is not spinning. Its increase of mass is exactly the equivalent of the mass of energy of rotation, which is itself the sum of the kinetic energies of all the moving parts of the ball. For example, the Earth itself is more massive due to its rotation, than it would be with no rotation. The rotational energy of the Earth is greater than 1024 Joules, which is over 107 kg.
History
While Einstein was the first to have correctly deduced the mass–energy equivalence formula, he was not the first to have related energy with mass, though nearly all previous authors thought that the energy that contributes to mass comes only from electromagnetic fields. Once discovered, Einstein's formula was initially written in many different notations, and its interpretation and justification was further developed in several steps.
Developments prior to Einstein

Eighteenth century theories on the correlation of mass and energy included that devised by the English scientist Isaac Newton in 1717, who speculated that light particles and matter particles were interconvertible in "Query 30" of the Opticks, where he asks: "Are not the gross bodies and light convertible into one another, and may not bodies receive much of their activity from the particles of light which enter their composition?" Swedish scientist and theologian Emanuel Swedenborg, in his Principia of 1734 theorized that all matter is ultimately composed of dimensionless points of "pure and total motion". He described this motion as being without force, direction or speed, but having the potential for force, direction and speed everywhere within it.
During the nineteenth century there were several speculative attempts to show that mass and energy were proportional in various ether theories. In 1873 the Russian physicist and mathematician Nikolay Umov pointed out a relation between mass and energy for ether in the form of Е = kmc2, where 0.5 ≤ k ≤ 1. The writings of the English engineer Samuel Tolver Preston, and a 1903 paper by the Italian industrialist and geologist Olinto De Pretto, presented a mass–energy relation. Italian mathematician and math historian Umberto Bartocci observed that there were only three degrees of separation linking De Pretto to Einstein, concluding that Einstein was probably aware of De Pretto's work. Preston and De Pretto, following physicist Georges-Louis Le Sage, imagined that the universe was filled with an ether of tiny particles that always move at speed c. Each of these particles has a kinetic energy of mc2 up to a small numerical factor. The nonrelativistic kinetic energy formula did not always include the traditional factor of 1/2, since German polymath Gottfried Leibniz introduced kinetic energy without it, and the 1/2 is largely conventional in prerelativistic physics. By assuming that every particle has a mass that is the sum of the masses of the ether particles, the authors concluded that all matter contains an amount of kinetic energy either given by E = mc2 or 2E = mc2 depending on the convention. A particle ether was usually considered unacceptably speculative science at the time, and since these authors did not formulate relativity, their reasoning is completely different from that of Einstein, who used relativity to change frames.
In 1905, independently of Einstein, French polymath Gustave Le Bon speculated that atoms could release large amounts of latent energy, reasoning from an all-encompassing qualitative philosophy of physics.
Electromagnetic mass
There were many attempts in the 19th and the beginning of the 20th century—like those of British physicists J. J. Thomson in 1881 and Oliver Heaviside in 1889, and George Frederick Charles Searle in 1897, German physicists Wilhelm Wien in 1900 and Max Abraham in 1902, and the Dutch physicist Hendrik Antoon Lorentz in 1904—to understand how the mass of a charged object depends on the electrostatic field. This concept was called electromagnetic mass, and was considered as being dependent on velocity and direction as well. Lorentz in 1904 gave the following expressions for longitudinal and transverse electromagnetic mass:
- ,
where
Another way of deriving a type of electromagnetic mass was based on the concept of radiation pressure. In 1900, French polymath Henri Poincaré associated electromagnetic radiation energy with a "fictitious fluid" having momentum and mass
By that, Poincaré tried to save the center of mass theorem in Lorentz's theory, though his treatment led to radiation paradoxes.
Austrian physicist Friedrich Hasenöhrl showed in 1904 that electromagnetic cavity radiation contributes the "apparent mass"
to the cavity's mass. He argued that this implies mass dependence on temperature as well.
Einstein: mass–energy equivalence

Einstein did not write the exact formula E = mc2 in his 1905 Annus Mirabilis paper "Does the Inertia of an object Depend Upon Its Energy Content?"; rather, the paper states that if a body gives off the energy L by emitting light, its mass diminishes by L/c2. This formulation relates only a change Δm in mass to a change L in energy without requiring the absolute relationship. The relationship convinced him that mass and energy can be seen as two names for the same underlying, conserved physical quantity. He has stated that the laws of conservation of energy and conservation of mass are "one and the same". Einstein elaborated in a 1946 essay that "the principle of the conservation of mass… proved inadequate in the face of the special theory of relativity. It was therefore merged with the energy conservation principle—just as, about 60 years before, the principle of the conservation of mechanical energy had been combined with the principle of the conservation of heat [thermal energy]. We might say that the principle of the conservation of energy, having previously swallowed up that of the conservation of heat, now proceeded to swallow that of the conservation of mass—and holds the field alone."
Mass–velocity relationship

In developing special relativity, Einstein found that the kinetic energy of a moving body is
with v the velocity, m0 the rest mass, and γ the Lorentz factor.
He included the second term on the right to make sure that for small velocities the energy would be the same as in classical mechanics, thus satisfying the correspondence principle:
Without this second term, there would be an additional contribution in the energy when the particle is not moving.
Einstein's view on mass
Einstein, following Lorentz and Abraham, used velocity- and direction-dependent mass concepts in his 1905 electrodynamics paper and in another paper in 1906. In Einstein's first 1905 paper on E = mc2, he treated m as what would now be called the rest mass, and it has been noted that in his later years he did not like the idea of "relativistic mass".
In older physics terminology, relativistic energy is used in lieu of relativistic mass and the term "mass" is reserved for the rest mass. Historically, there has been considerable debate over the use of the concept of "relativistic mass" and the connection of "mass" in relativity to "mass" in Newtonian dynamics. One view is that only rest mass is a viable concept and is a property of the particle; while relativistic mass is a conglomeration of particle properties and properties of spacetime. Another view, attributed to Norwegian physicist Kjell Vøyenli, is that the Newtonian concept of mass as a particle property and the relativistic concept of mass have to be viewed as embedded in their own theories and as having no precise connection.
Einstein's 1905 derivation
Already in his relativity paper "On the electrodynamics of moving bodies", Einstein derived the correct expression for the kinetic energy of particles:
- .
Now the question remained open as to which formulation applies to bodies at rest. This was tackled by Einstein in his paper "Does the inertia of a body depend upon its energy content?", one of his Annus Mirabilis papers. Here, Einstein used V to represent the speed of light in vacuum and L to represent the energy lost by a body in the form of radiation. Consequently, the equation E = mc2 was not originally written as a formula but as a sentence in German saying that "if a body gives off the energy L in the form of radiation, its mass diminishes by L/V2." A remark placed above it informed that the equation was approximated by neglecting "magnitudes of fourth and higher orders" of a series expansion. Einstein used a body emitting two light pulses in opposite directions, having energies of E0 before and E1 after the emission as seen in its rest frame. As seen from a moving frame, this becomes H0 and H1. Einstein obtained, in modern notation:
- .
He then argued that H − E can only differ from the kinetic energy K by an additive constant, which gives
- .
Neglecting effects higher than third order in v/c after a Taylor series expansion of the right side of this yields:
Einstein concluded that the emission reduces the body's mass by E/c2, and that the mass of a body is a measure of its energy content.
The correctness of Einstein's 1905 derivation of E = mc2 was criticized by German theoretical physicist Max Planck in 1907, who argued that it is only valid to first approximation. Another criticism was formulated by American physicist Herbert Ives in 1952 and the Israeli physicist Max Jammer in 1961, asserting that Einstein's derivation is based on begging the question. Other scholars, such as American and Chilean philosophers John Stachel and Roberto Torretti, have argued that Ives' criticism was wrong, and that Einstein's derivation was correct. American physics writer Hans Ohanian, in 2008, agreed with Stachel/Torretti's criticism of Ives, though he argued that Einstein's derivation was wrong for other reasons.
Relativistic center-of-mass theorem of 1906
Like Poincaré, Einstein concluded in 1906 that the inertia of electromagnetic energy is a necessary condition for the center-of-mass theorem to hold. On this occasion, Einstein referred to Poincaré's 1900 paper and wrote: "Although the merely formal considerations, which we will need for the proof, are already mostly contained in a work by H. Poincaré2, for the sake of clarity I will not rely on that work." In Einstein's more physical, as opposed to formal or mathematical, point of view, there was no need for fictitious masses. He could avoid the perpetual motion problem because, on the basis of the mass–energy equivalence, he could show that the transport of inertia that accompanies the emission and absorption of radiation solves the problem. Poincaré's rejection of the principle of action–reaction can be avoided through Einstein's E = mc2, because mass conservation appears as a special case of the energy conservation law.
Further developments
There were several further developments in the first decade of the twentieth century. In May 1907, Einstein explained that the expression for energy ε of a moving mass point assumes the simplest form when its expression for the state of rest is chosen to be ε0 = μV2 (where μ is the mass), which is in agreement with the "principle of the equivalence of mass and energy". In addition, Einstein used the formula μ = E0/V2, with E0 being the energy of a system of mass points, to describe the energy and mass increase of that system when the velocity of the differently moving mass points is increased. Max Planck rewrote Einstein's mass–energy relationship as M = E0 + pV0/c2 in June 1907, where p is the pressure and V0 the volume to express the relation between mass, its latent energy, and thermodynamic energy within the body. Subsequently, in October 1907, this was rewritten as M0 = E0/c2 and given a quantum interpretation by German physicist Johannes Stark, who assumed its validity and correctness. In December 1907, Einstein expressed the equivalence in the form M = μ + E0/c2 and concluded: "A mass μ is equivalent, as regards inertia, to a quantity of energy μc2. […] It appears far more natural to consider every inertial mass as a store of energy." American physical chemists Gilbert N. Lewis and Richard C. Tolman used two variations of the formula in 1909: m = E/c2 and m0 = E0/c2, with E being the relativistic energy (the energy of an object when the object is moving), E0 is the rest energy (the energy when not moving), m is the relativistic mass (the rest mass and the extra mass gained when moving), and m0 is the rest mass. The same relations in different notation were used by Lorentz in 1913 and 1914, though he placed the energy on the left-hand side: ε = Mc2 and ε0 = mc2, with ε being the total energy (rest energy plus kinetic energy) of a moving material point, ε0 its rest energy, M the relativistic mass, and m the invariant mass.
In 1911, German physicist Max von Laue gave a more comprehensive proof of M0 = E0/c2 from the stress–energy tensor, which was later generalized by German mathematician Felix Klein in 1918.
Einstein returned to the topic once again after World War II and this time he wrote E = mc2 in the title of his article intended as an explanation for a general reader by analogy.
Alternative version
An alternative version of Einstein's thought experiment was proposed by American theoretical physicist Fritz Rohrlich in 1990, who based his reasoning on the Doppler effect. Like Einstein, he considered a body at rest with mass M. If the body is examined in a frame moving with nonrelativistic velocity v, it is no longer at rest and in the moving frame it has momentum P = Mv. Then he supposed the body emits two pulses of light to the left and to the right, each carrying an equal amount of energy E/2. In its rest frame, the object remains at rest after the emission since the two beams are equal in strength and carry opposite momentum. However, if the same process is considered in a frame that moves with velocity v to the left, the pulse moving to the left is redshifted, while the pulse moving to the right is blue shifted. The blue light carries more momentum than the red light, so that the momentum of the light in the moving frame is not balanced: the light is carrying some net momentum to the right. The object has not changed its velocity before or after the emission. Yet in this frame it has lost some right-momentum to the light. The only way it could have lost momentum is by losing mass. This also solves Poincaré's radiation paradox. The velocity is small, so the right-moving light is blueshifted by an amount equal to the nonrelativistic Doppler shift factor 1 − v/c. The momentum of the light is its energy divided by c, and it is increased by a factor of v/c. So the right-moving light is carrying an extra momentum ΔP given by:
The left-moving light carries a little less momentum, by the same amount ΔP. So the total right-momentum in both light pulses is twice ΔP. This is the right-momentum that the object lost.
The momentum of the object in the moving frame after the emission is reduced to this amount:
So the change in the object's mass is equal to the total energy lost divided by c2. Since any emission of energy can be carried out by a two-step process, where first the energy is emitted as light and then the light is converted to some other form of energy, any emission of energy is accompanied by a loss of mass. Similarly, by considering absorption, a gain in energy is accompanied by a gain in mass.
Radioactivity and nuclear energy

It was quickly noted after the discovery of radioactivity in 1897 that the total energy due to radioactive processes is about one million times greater than that involved in any known molecular change, raising the question of where the energy comes from. After eliminating the idea of absorption and emission of some sort of Lesagian ether particles, the existence of a huge amount of latent energy, stored within matter, was proposed by New Zealand physicist Ernest Rutherford and British radiochemist Frederick Soddy in 1903. Rutherford also suggested that this internal energy is stored within normal matter as well. He went on to speculate in 1904: "If it were ever found possible to control at will the rate of disintegration of the radio-elements, an enormous amount of energy could be obtained from a small quantity of matter."
Einstein's equation does not explain the large energies released in radioactive decay, but can be used to quantify them. The theoretical explanation for radioactive decay is given by the nuclear forces responsible for holding atoms together, though these forces were still unknown in 1905. The enormous energy released from radioactive decay had previously been measured by Rutherford and was much more easily measured than the small change in the gross mass of materials as a result. Einstein's equation, by theory, can give these energies by measuring mass differences before and after reactions, but in practice, these mass differences in 1905 were still too small to be measured in bulk. Prior to this, the ease of measuring radioactive decay energies with a calorimeter was thought possibly likely to allow measurement of changes in mass difference, as a check on Einstein's equation itself. Einstein mentions in his 1905 paper that mass–energy equivalence might perhaps be tested with radioactive decay, which was known by then to release enough energy to possibly be "weighed," when missing from the system. However, radioactivity seemed to proceed at its own unalterable pace, and even when simple nuclear reactions became possible using proton bombardment, the idea that these great amounts of usable energy could be liberated at will with any practicality, proved difficult to substantiate. Rutherford was reported in 1933 to have declared that this energy could not be exploited efficiently: "Anyone who expects a source of power from the transformation of the atom is talking moonshine."
This outlook changed dramatically in 1932 with the discovery of the neutron and its mass, allowing mass differences for single nuclides and their reactions to be calculated directly, and compared with the sum of masses for the particles that made up their composition. In 1933, the energy released from the reaction of lithium-7 plus protons giving rise to two alpha particles, allowed Einstein's equation to be tested to an error of ±0.5%. However, scientists still did not see such reactions as a practical source of power, due to the energy cost of accelerating reaction particles. After the very public demonstration of huge energies released from nuclear fission after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945, the equation E = mc2 became directly linked in the public eye with the power and peril of nuclear weapons. The equation was featured on page 2 of the Smyth Report, the official 1945 release by the US government on the development of the atomic bomb, and by 1946 the equation was linked closely enough with Einstein's work that the cover of Time magazine prominently featured a picture of Einstein next to an image of a mushroom cloud emblazoned with the equation. Einstein himself had only a minor role in the Manhattan Project: he had cosigned a letter to the U.S. president in 1939 urging funding for research into atomic energy, warning that an atomic bomb was theoretically possible. The letter persuaded Roosevelt to devote a significant portion of the wartime budget to atomic research. Without a security clearance, Einstein's only scientific contribution was an analysis of an isotope separation method in theoretical terms. It was inconsequential, on account of Einstein not being given sufficient information to fully work on the problem.
While E = mc2 is useful for understanding the amount of energy potentially released in a fission reaction, it was not strictly necessary to develop the weapon, once the fission process was known, and its energy measured at 200 MeV (which was directly possible, using a quantitative Geiger counter, at that time). The physicist and Manhattan Project participant Robert Serber noted that somehow "the popular notion took hold long ago that Einstein's theory of relativity, in particular his famous equation E = mc2, plays some essential role in the theory of fission. Einstein had a part in alerting the United States government to the possibility of building an atomic bomb, but his theory of relativity is not required in discussing fission. The theory of fission is what physicists call a non-relativistic theory, meaning that relativistic effects are too small to affect the dynamics of the fission process significantly." There are other views on the equation's importance to nuclear reactions. In late 1938, the Austrian-Swedish and British physicists Lise Meitner and Otto Robert Frisch—while on a winter walk during which they solved the meaning of Hahn's experimental results and introduced the idea that would be called atomic fission—directly used Einstein's equation to help them understand the quantitative energetics of the reaction that overcame the "surface tension-like" forces that hold the nucleus together, and allowed the fission fragments to separate to a configuration from which their charges could force them into an energetic fission. To do this, they used packing fraction, or nuclear binding energy values for elements. These, together with use of E = mc2 allowed them to realize on the spot that the basic fission process was energetically possible.









![{\displaystyle E=m_{0}c^{2}\left[1+{\frac {1}{2}}\left({\frac {v}{c}}\right)^{2}+{\frac {3}{8}}\left({\frac {v}{c}}\right)^{4}+{\frac {5}{16}}\left({\frac {v}{c}}\right)^{6}+\ldots \right].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/81c7043d5fccc00eff27036f20854c4c72874189)






















