The phalanx (pl.: phalanxes or phalanges) was a rectangular mass military formation, usually composed entirely of heavy infantry armed with spears, pikes, sarissas, or similar polearms tightly packed together. The term is particularly used to describe the use of this formation in ancient Greek warfare, although the ancient Greek writers used it to also describe any massed infantry formation, regardless of its equipment. Arrian uses the term in his Array against the Alans when he refers to his legions. In Greek texts, the phalanx may be deployed for battle, on the march, or even camped, thus describing the mass of infantry or cavalry that would deploy in line during battle. They marched forward as one entity.
The term itself, as used today, does not refer to a distinctive military unit or division (e.g., the Roman legion or the contemporary Western-type battalion), but to the type of formation of an army's troops. Therefore, this term does not indicate a standard combat strength or composition but includes the total number of infantry, which is deployed in a single formation known as a "phalanx".
Many spear-armed troops historically fought in what might be termed phalanx-like formations. This article focuses on the use of the military phalanx formation in Ancient Greece, the Hellenistic world, and other ancient states heavily influenced by Greek civilization.
History
The earliest known depiction of a phalanx-like formation occurs in the Sumerian Stele of the Vultures from the 25th century BC. Here the troops seem to have been equipped with spears, helmets, and large shields covering the whole body. Ancient Egyptian infantry were known to have employed similar formations. The first usage of the term phalanx comes from Homer's "φαλαγξ", used to describe hoplites fighting in an organized battle line. Homer used the term to differentiate the formation-based combat from the individual duels so often found in his poems.
Historians have not arrived at a consensus about the relationship between the Greek formation and these predecessors of the hoplites. The principles of shield wall and spear hedge were almost universally known among the armies of major civilizations throughout history, and so the similarities may be related to convergent evolution instead of diffusion.
Traditionally, historians date the origin of the hoplite phalanx of ancient Greece to the 8th century BC in Sparta, but this is under revision. It is perhaps more likely that the formation was devised in the 7th century BC after the introduction of the aspis by the city of Argos, which would have made the formation possible. This is further evidenced by the Chigi vase, dated to 650 BC, identifying hoplites armed with aspis, spear, javelins, and other aspects of the panoply.
Another possible theory as to the birth of Greek phalanx warfare stems from the idea that some of the basic aspects of the phalanx were present in earlier times yet were not fully developed due to the lack of appropriate technology. Two of the basic tactics seen in earlier warfare include the principle of cohesion and the use of large groups of soldiers. This would suggest that the Greek phalanx was rather the culmination and perfection of a slowly developed idea that originated many years earlier. As weaponry and armour advanced through the years in different city-states, the phalanx became complex and effective.
Overview

The hoplite phalanx of the Archaic and Classical periods in Greece c. 800–350 BC was the formation in which the hoplites would line up in ranks in close order. The hoplites would lock their shields together, and the first few ranks of soldiers would project their spears out over the first rank of shields. The phalanx therefore presented a shield wall and a mass of spear points to the enemy, making frontal assaults against it very difficult. It also allowed a higher proportion of the soldiers to be actively engaged in combat at a given time (rather than just those in the front rank).
Battles between two phalanxes usually took place in open, flat plains where it was easier to advance and stay in formation. Rough terrain or hilly regions would have made it difficult to maintain a steady line and would have defeated the purpose of a phalanx. As a result, battles between Greek city-states would not take place in just any location, nor would they be limited to sometimes obvious strategic points. Rather, many times, the two opposing sides would find the most suitable piece of land where the conflict could be settled. Typically, the battle ended with one of the two fighting forces fleeing to safety.
The phalanx usually advanced at a walking pace, although it is possible that they picked up speed during the last several yards. One of the main reasons for this slow approach was to maintain formation. The formation would be rendered useless if the phalanx was lost as the unit approached the enemy and could even become detrimental to the advancing unit, resulting in a weaker formation that was easier for an enemy force to break through. If the hoplites of the phalanx were to pick up speed toward the latter part of the advance, it would have been for the purpose of gaining momentum against the enemy in the initial collision. Herodotus said of the Greeks at the Battle of Marathon: "They were the first Greeks we know of to charge their enemy at a run." Many historians believe that this adaptation was precipitated by their desire to minimize their losses from Persian archery. According to some historians, the opposing sides could collide, possibly breaking many of the spears of the front row and maiming or killing the front part of the unit army due to the collision.
The spears of a phalanx had spiked butts (sauroter). In battle, the back ranks used the sauroter to finish fallen enemy soldiers.
Othismos or "pushing"

The "physical pushing match" theory is one where the battle would rely on the valour of the men in the front line, whilst those in the rear maintained forward pressure on the front ranks with their shields, and the whole formation would consistently press forward trying to break the enemy formation. This is the most widely accepted interpretation of the ancient sources thus when two phalanx formations engaged, the struggle essentially became a pushing match. (The Ancient Greek word φάλαγξ - phalanx - could refer to a tree-trunk or log used as a roller, suggesting an image of physical effort.) Historians such as Victor Davis Hanson point out that it is difficult to account for exceptionally deep phalanx formations unless they were necessary to facilitate the physical pushing depicted by this theory, as those behind the first two ranks could not take part in the actual spear thrusting.
No Greek art ever depicts anything like a phalanx pushing match, so this hypothesis is a product of educated speculation rather than explicit testimony from contemporary sources and is far from being academically resolved. The Greek term for "push" was used in the same metaphorical manner as the English word is (for example it was also used to describe the process of rhetorical arguments) and so does not necessarily describe a literal physical push, although it is possible that it did.
For instance, if Othismos were to accurately describe a physical pushing match, it would be logical to state that the deeper phalanx would always win an engagement since the physical strength of individuals would not compensate for even one additional rank on the enemy side. However, there are numerous examples of shallow phalanxes holding off an opponent. For instance, at Delium in 424 BC, the Athenian left flank, a formation eight men deep, held off a formation of Thebans 25 deep without immediate collapse. It is difficult with the physical pushing model to imagine eight men withstanding the pushing force of 25 opponents for a matter of seconds, let alone half the battle.
Such arguments have led to a wave of counter-criticism to physical shoving theorists. Adrian Goldsworthy, in his article "The Othismos, Myths and Heresies: The nature of Hoplite Battle", argues that the physical pushing match model does not fit with the average casualty figures of hoplite warfare nor the practical realities of moving large formations of men in battle. This debate has yet to be resolved amongst scholars.
Practical difficulties with this theory also include the fact that, in a shoving match, an eight-foot spear is too long to fight effectively or even to parry attacks. Spears enable a formation of men to keep their enemies at a distance, parry attacks aimed at them and their comrades, and give the necessary reach to strike multiple men in the opposite formation. A pushing match would put enemies so close together that a quick stabbing with a knife would kill the front row almost instantly. The crush of men would also prevent the formation from withdrawing or retreating, which would result in much higher casualties than is recorded. The speed at which this would occur would also end the battle very quickly, instead of prolonging it for hours.
Shields

Each individual hoplite carried his shield on his left arm, protecting not only himself but also the soldier to the left. This meant that the men at the extreme right of the phalanx were only half-protected. In battle, opposing phalanxes would try to exploit this weakness by attempting to overlap the enemy's right flank. It also meant that, in battle, a phalanx would tend to drift to the right (as hoplites sought to remain behind the shield of their neighbor). Some groups, such as the Spartans at Nemea, tried to use this phenomenon to their advantage. In this case, the phalanx would sacrifice its left side, which typically consisted of allied troops, in an effort to overtake the enemy from the flank. It is unlikely that this strategy worked very often, as it is not mentioned frequently in ancient Greek literature.
There was a leader in each row of a phalanx, and a rear rank officer, the ouragos (meaning tail-leader), who kept order in the rear. The hoplites had to trust their neighbors to protect them and in turn be willing to protect their neighbors; a phalanx was thus only as strong as its weakest elements. The effectiveness of the phalanx therefore depended on how well the hoplites could maintain this formation in combat and how well they could stand their ground, especially when engaged against another phalanx. For this reason, the formation was deliberately organized to group friends and family close together, thus providing a psychological incentive to support one's fellows, and a disincentive, through shame, to panic or attempt to flee. The more disciplined and courageous the army, the more likely it was to win – often engagements between the various city-states of Greece would be resolved by one side fleeing before the battle. The Greek word dynamis (the "will to fight") expresses the drive that kept hoplites in formation.
Now of those, who dare, abiding one beside another, to advance to the close fray, and the foremost champions, fewer die, and they save the people in the rear; but in men that fear, all excellence is lost. No one could ever in words go through those several ills, which befall a man, if he has been actuated by cowardice. For 'tis grievous to wound in the rear the back of a flying man in hostile war. Shameful too is a corpse lying low in the dust, wounded behind in the back by the point of a spear.
— Tyrtaeus, The War Songs of Tyrtaeus
Hoplite armament
Each hoplite provided his own equipment. The primary hoplite weapon was a spear around 2.4 metres (7.9 ft) in length called a dory. Although accounts of its length vary, it is usually now believed to have been seven to nine feet long (~2.1–2.7 m). It was held one-handed, with the other hand holding the hoplite's shield (aspis). The spearhead was usually a curved leaf shape, while the rear of the spear had a spike called a sauroter ('lizard-killer') which was used to stand the spear in the ground (hence the name). It was also used as a secondary weapon if the main shaft snapped or to kill enemies lying on the ground. This was a common problem, especially for soldiers who were involved in the initial clash with the enemy. Despite the snapping of the spear, hoplites could easily switch to the sauroter without great consequence. The rear ranks used the secondary end to finish off fallen opponents as the phalanx advanced over them.
Throughout the hoplite era, the standard hoplite armour went through many cyclical changes. An Archaic hoplite typically wore a bronze breastplate, a bronze helmet with cheekplates, as well as greaves and other armour. Later, in the classical period, the breastplate became less common, replaced instead with a corselet that some claim was made of linothorax (layers of linen glued together), or perhaps of leather, sometimes covered in whole or in part with overlapping metal scales. Eventually, even greaves became less commonly used, although degrees of heavier armour remained, as attested by Xenophon as late as 401 BC.
These changes reflected the balancing of mobility with protection, especially as cavalry became more prominent in the Peloponnesian War and the need to combat light troops, which were increasingly used to negate the hoplite's role as the primary force in battle. Yet bronze armour remained in some form until the end of the hoplite era. Some archaeologists have pointed out that bronze armour does not actually provide as much protection from direct blows as more extensive corselet padding, and have suggested its continued use was a matter of status for those who could afford it. In the classical Greek dialect, there is no word for swordsmen; yet hoplites also carried either a short sword called the xiphos or a curved sword called the kopis, used as a secondary weapon if the dory was broken or lost. Samples of the xiphos recovered at excavation sites were typically around 60 cm (24 in) in length. These swords were double-edged (or single-edged in the case of the kopis) and could therefore be used as a cutting and thrusting weapon. These short swords were often used to stab or cut at the enemy's neck during close combat.
Hoplites carried a circular shield called an aspis made from wood and covered in bronze, measuring roughly a metre (3.3 feet) in diameter. It spanned from chin to knee and was very heavy: 8–15 kg (18–33 lb). This medium-sized shield (fairly large for the period considering the average male height) was made possible partly by its dish-like shape, which allowed it to be supported with the rim on the shoulder. This was quite an important feature of the shield, especially for the hoplites who remained in the latter ranks. While these soldiers continued to help press forward, they did not have the added burden of holding up their shield. But the circular shield was not without its disadvantages. Despite its mobility, protective curve, and double straps the circular shape created gaps in the shield wall at both its top and bottom. (Top gaps were somewhat reduced by the one or two spears jutting out of the gap. In order to minimize the bottom gaps, thick leather curtains were used but only by an unknown percentage of the hoplites, possibly only in the first row since there were disadvantages as well: considerable weight on an already heavy shield and a certain additional cost.) These gaps left parts of the hoplite exposed to potentially lethal spear thrusts and were a persistent vulnerability for hoplites controlling the front lines.
Phalangite armament
The phalanx of the Ancient Macedonian kingdom and the later Hellenistic successor states was a development of the hoplite phalanx. The "phalangites" were armed with a much longer spear, the sarissa, and less heavily armoured. The sarissa was the pike used by the ancient Macedonian army. Its actual length is unknown, but apparently it was twice as long as the dory. This makes it at least 14 feet (4.3 m), but 18 feet (5.5 m) appears more likely. (The cavalry xyston was 12.5 feet (3.8 m) by comparison.) The great length of the pike was balanced by a counterweight at the rear end, which also functioned as a butt-spike, allowing the sarissa to be planted into the ground. Because of its great length, weight and different balance, a sarissa was wielded two-handed. This meant that the aspis was no longer a practical defence. Instead, the phalangites strapped a smaller pelte shield (usually reserved for peltasts, light skirmishers) to their left forearm. Recent theories, including examination of ancient frescoes depicting full sets of weapons and armor, claim that the shields used were actually larger than the pelte but smaller than the aspis, hanging by leather strap(s) from the left shoulder or from both shoulders. The shield would retain handling straps in the inner curve, to be handled like a (smaller) aspis if the fight progressed to sword-wielding. Although in both shield size assumptions this reduced the shield wall, the extreme length of the spear kept the enemy at a greater distance, as the pikes of the first three to five ranks could all be brought to bear in front of the front row. This pike had to be held underhand, as the shield would have obscured the soldier's vision had it been held overhead. It would also be very hard to remove a sarissa from anything it stuck in (the earth, shields, and soldiers of the opposition) if it were thrust downwards, due to its length. The Macedonian phalanx was much less able to form a shield wall, but the lengthened spears would have compensated for this. Such a phalanx formation also reduced the likelihood that battles would degenerate into a pushing match.
Deployment and combat
A tetrarchia was a unit of four files (8-man columns in tight formation) and a tetrarchès or tetrarch was a commander of four files; a dilochia was a double file and a dilochitès was a double-file leader; a lochos was a single file and a lochagos was a file leader; a dimoiria was a half file and a dimoirites was a half-file leader. Another name for the half file was a hèmilochion with a hèmilochitès being a half-file leader.
Phalanx composition and strength
The basic combat element of the Greek armies was either the stichos ("file", usually 8–16 men strong) or the enomotia ("sworn" and made up by 2–4 stichœ, totaling up to 32 men), both led by a dimœrites who was assisted by a decadarchos and two decasterœ (sing. decasteros). Four to a maximum of 32 enomotiæ (depending on the era in question or the city) formed a lochos led by a lochagos, who in this way was in command of initially a hundred hoplites to a maximum of around five hundred in the late Hellenistic armies. Here, it has to be noted that the military manuals of Asclepiodotus and Aelian use the term lochos to denote a file in the phalanx. A taxis (mora for the Spartans) was the greatest standard hoplitic formation of five to fifteen hundred, led by a strategos (general). The entire army, a total of several taxeis or moræ was led by a generals' council. The commander-in-chief was usually called a polemarchos or a strategos autocrator.
Phalanx front and depth
Hoplite phalanxes usually deployed in ranks of eight men or more deep; the Macedonian phalanxes were usually 16 men deep, sometimes reported to have been arrayed 32 men deep. There are some notable extremes; at the battles of Leuctra and Mantinea, the Theban general Epaminondas arranged the left wing of the phalanx into a "hammerhead" of fifty ranks of elite hoplites deep (see below) and when depth was less important, phalanxes just four deep are recorded, as at the battle of Marathon.
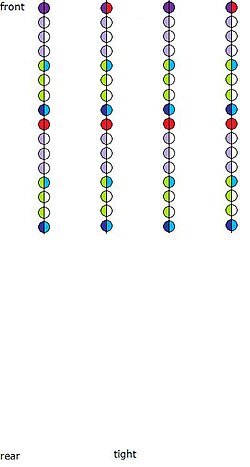
The phalanx depth could vary depending on the needs of the moment and plans of the general. While the phalanx was in march, an eis bathos formation (loose, meaning literally "in depth") was adopted in order to move more freely and maintain order. This was also the initial battle formation as, in addition, it permitted friendly units to pass through whether assaulting or retreating. In this status, the phalanx had twice the normal depth and each hoplite had to occupy about 1.8–2 metres (5 ft 11 in – 6 ft 7 in) in width. When enemy infantry was approaching, a rapid switch to the pycne (spelled also pucne) formation (dense or tight formation) was necessary. In that case, each man's space was halved and the formation depth returned to normal. An even denser formation, the synaspismos or sunaspismos (ultra-tight or locked shields formation), was used when the phalanx was expected to experience extra pressure, intense missile volleys or frontal cavalry charges. In synaspismos, the rank depth was half that of a normal phalanx and the width each man occupied was as small as 0.45 metres (1.5 ft).
Stages of combat
Several stages in hoplite combat can be defined:
Ephodos: The hoplites stop singing their pæanes (battle hymns) and move towards the enemy, gradually picking up pace and momentum. In the instants before impact, war cries (alalagmœ, sing. alalagmos) would be made. Notable war cries were the Athenian (eleleleleu! eleleleleu!) and the Macedonian (alalalalai! alalalalai!) alalagmœ.
Krousis: The opposing phalanxes meet each other almost simultaneously along their front.
Doratismos: Repeated, rapid spear thrusts in order to disrupt the enemy formation. The use of long spears would keep enemies apart as well as allow men in a row to assist their comrades next to them. The prodding could also open up a man to allow a comrade to spear him. Too hard prodding could get a spear stuck in a shield, which would necessitate someone in the back to lend his to the now-disarmed man.
Othismos: Literally "pushing" after most spears have been broken, the hoplites begin to push with their spears and spear shafts against their opponents' shields. This could be the longest phase.
Pararrhexis: Breaching the opposing phalanx, the enemy formation shatters and the battle ends. Cavalry would be used at this point to mop up the scattered enemy.
Tactics

Bottom: the diagonal phalanx utilised by the Thebans under Epaminondas. The strong left wing advanced while the weak right wing retreated or remained stationary.

The early history of the phalanx is largely one of combat between hoplite armies from competing Greek city-states. The usual result was rather identical, inflexible formations pushing against each other until one broke. The potential of the phalanx to achieve something more was demonstrated at Battle of Marathon (490 BC). Facing the much larger army of Darius I, the Athenians thinned out their phalanx and consequently lengthened their front, to avoid being outflanked. However, even a reduced-depth phalanx proved unstoppable to the lightly armed Persian infantry. After routing the Persian wings, the hoplites on the Athenian wings wheeled inwards, destroying the elite troop at the Persian centre, resulting in a crushing victory for Athens. Throughout the Greco-Persian Wars the hoplite phalanx was to prove superior to the Persian infantry (e.g., the battles of Thermopylae and Plataea).
Perhaps the most prominent example of the phalanx's evolution was the oblique order, made famous in the Battle of Leuctra. There, the Theban general Epaminondas thinned out the right flank and centre of his phalanx, and deepened his left flank to an unheard-of fifty men deep. In doing so, Epaminondas reversed the convention by which the right flank of the phalanx was strongest. This allowed the Thebans to assault in strength the elite Spartan troops on the right flank of the opposing phalanx. Meanwhile, the centre and right flank of the Theban line were echeloned back, from the opposing phalanx, keeping the weakened parts of the formation from being engaged. Once the Spartan right had been routed by the Theban left, the remainder of the Spartan line also broke. Thus, by localising the attacking power of the hoplites, Epaminondas was able to defeat an enemy previously thought invincible.
Philip II of Macedon spent several years in Thebes as a hostage, and paid attention to Epaminondas' innovations. On return to his homeland, he raised a revolutionary new infantry force, which was to change the face of the Greek world. Philip's phalangites were the first force of professional soldiers seen in Ancient Greece apart from Sparta. They were armed with longer spears (the sarissa) and were drilled more thoroughly in more evolved, complicated tactics and manoeuvres. More importantly, though, Philip's phalanx was part of a multi-faceted, combined force which included a variety of skirmishers and cavalry, most notably the famous Companion cavalry. The Macedonian phalanx now was used to pin the centre of the enemy line, while cavalry and more mobile infantry struck at the foe's flanks. Its supremacy over the more static armies fielded by the Greek city-states was shown at the Battle of Chaeronea, where Philip II's army crushed the allied Theban and Athenian phalanxes.
Weaknesses
The hoplite phalanx was weakest when facing an enemy fielding lighter and more flexible troops without its own such supporting troops. An example of this would be the Battle of Lechaeum, where an Athenian contingent led by Iphicrates routed an entire Spartan mora (a unit of 500–900 hoplites). The Athenian force had a considerable proportion of light missile troops armed with javelins and bows that wore down the Spartans with repeated attacks, causing disarray in the Spartan ranks and an eventual rout when they spotted Athenian heavy infantry reinforcements trying to flank them by boat.
The Macedonian phalanx had weaknesses similar to its hoplitic predecessor. Theoretically indestructible from the front, its flanks and rear were very vulnerable, and once engaged it may not easily disengage or redeploy to face a threat from those directions. Thus, a phalanx facing non-phalangite formations required some sort of protection on its flanks – lighter or at least more mobile infantry, cavalry, etc. This was shown at the Battle of Magnesia, where, once the Seleucid supporting cavalry elements were driven off, the phalanx was static and unable to go on the offensive against its Roman opponents (although they continued to resist stoutly and attempted a fighting withdrawal under a hail of Roman missiles, until the elephants posted on their flanks panicked and disrupted their formation).
The Macedonian phalanx could also lose its cohesion without proper coordination or while moving through broken terrain; doing so could create gaps between individual blocks/syntagmata, or could prevent a solid front within those sub-units as well, causing other sections of the line to bunch up. In this event, as in the battles of Cynoscephalae and Pydna, the phalanx became vulnerable to attacks by more flexible units – such as Roman legionary centuries, which were able to avoid the sarissae and engage in hand-to-hand combat with the phalangites.
Another important area that must be considered concerns the psychological tendencies of the hoplites. Because the strength of a phalanx depended on the ability of the hoplites to maintain their frontline, it was crucial that a phalanx be able to quickly and efficiently replace fallen soldiers in the front ranks. If a phalanx failed to do this in a structured manner, the opposing phalanx would have an opportunity to breach the line which, many times, would lead to a quick defeat. This then implies that the hoplites ranks closer to the front must be mentally prepared to replace their fallen comrade and adapt to his new position without disrupting the structure of the frontline.
Finally, most of the phalanx-centric armies tended to lack supporting echelons behind the main line of battle. This meant that breaking through the line of battle or compromising one of its flanks often ensured victory.
Classical decline and post-classical use

After reaching its zenith in the conquests of Alexander the Great, the phalanx began a slow decline, as Hellenistic successor states declined. The combined arms tactics used by Alexander and his father were gradually replaced by a return to the simpler frontal charge tactics of the hoplite phalanx. The expense of the supporting arms and cavalry, and the widespread use of mercenaries, caused the Diadochi to rely on phalanx vs. phalanx tactics during the Wars of the Diadochi.
The decline of the Diadochi and the phalanx was linked with the rise of Rome and the Roman legions from the 3rd century BC. The Battle of the Caudine Forks showed the clumsiness of the Roman phalanx against the Samnites. The Romans had originally employed the phalanx themselves but gradually evolved more flexible tactics. The result was the three-line Roman legion of the middle period of the Roman Republic, the Manipular System. Romans used a phalanx for their third military line, the triarii. These were veteran reserve troops armed with the hastae or spear. Rome conquered most of the Hellenistic successor states, along with the various Greek city-states and leagues. As these states ceased to exist, so did the armies which used the traditional phalanx. Subsequently, troops from these regions were equipped, trained and fought using the Roman model.
A phalanx formation called the phoulkon appeared in the late Roman army and Byzantine army. It had characteristics of the classical Greek and Hellenistic phalanxes, but was more flexible. It was used against cavalry more than infantry.
However, the phalanx did not totally disappear. In some battles between the Roman army and Hellenistic phalanxes, such as Pydna (168 BC), Cynoscephalae (197 BC) and Magnesia (190 BC), the phalanx performed well. It even drove back the Roman infantry. However, at Cynoscephalae and Magnesia, failure to defend the flanks of the phalanx led to defeat. At Pydna, the phalanx lost cohesion when pursuing retreating Roman soldiers. This allowed the Romans to penetrate the formation. Then, Roman close combat skills proved decisive. The historian Polybius details the effectiveness of the Roman legion against the phalanx. He deduces that the Romans refused to fight the phalanx where the phalanx was effective, Romans offered battle only when a legion could exploit the clumsiness and immobility of a phalanx.

Spear-armed troops continued to be important elements in many armies until reliable firearms became available. These did not necessarily fight as a phalanx. For example, compare the classical phalanx and late medieval pike formations.
Military historians have suggested that the Scots under William Wallace and Robert the Bruce consciously imitated the Hellenistic phalanx to produce the Scots' schiltron ("hedgehog"). However, long spears might have been used by Picts and others in Scotlands' Early Middle Ages. Prior to 1066, long spear tactics (also found in North Wales) might have been part of irregular warfare in Britain. The Scots used imported French pikes and dynamic tactics at the Battle of Flodden. However, Flodden found the Scots pitted against effective light artillery, while advancing over bad ground. The combination disorganised the Scottish phalanxes and permitted effective attacks by English longbowmen, and soldiers wielding shorter, handier polearms called bills. Some contemporary sources might say that the bills cut off the heads of Scottish pikes.
The pike was briefly reconsidered as a weapon by European armies in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. It could protect riflemen, whose slower rate of fire made them vulnerable. A collapsible pike was invented but never issued. The Confederate Army considered these weapons for the American Civil War. Some were even manufactured but probably were never issued. Pikes were manufactured during World War II as "Croft's Pikes".
While obsolete in military practice, the phalanx remained in use as a metaphor of warriors moving forward as a single united block. This metaphor inspired several 20th-century political movements, notably the Spanish Falange and its ideology of Falangism.