|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

The uncertainty principle, also known as Heisenberg's indeterminacy principle, is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics. It states that there is a limit to the precision with which certain pairs of physical properties, such as position and momentum, can be simultaneously known. In other words, the more accurately one property is measured, the less accurately the other property can be known.
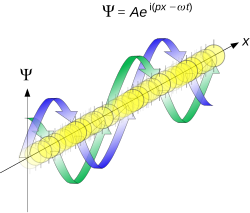
More formally, the uncertainty principle is any of a variety of mathematical inequalities asserting a fundamental limit to the product of the accuracy of certain related pairs of measurements on a quantum system, such as position, x, and momentum, p. Such paired-variables are known as complementary variables or canonically conjugate variables.
First introduced in 1927 by German physicist Werner Heisenberg, the formal inequality relating the standard deviation of position σx and the standard deviation of momentum σp was derived by Earle Hesse Kennard later that year and by Hermann Weyl in 1928:
where is the reduced Planck constant.
The quintessentially quantum mechanical uncertainty principle comes in many forms other than position–momentum. The energy–time relationship is widely used to relate quantum state lifetime to measured energy widths but its formal derivation is fraught with confusing issues about the nature of time. The basic principle has been extended in numerous directions; it must be considered in many kinds of fundamental physical measurements.
Position-momentum
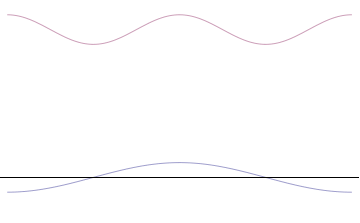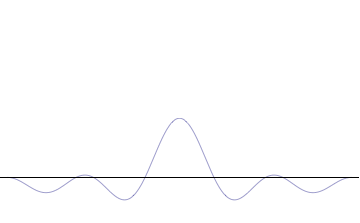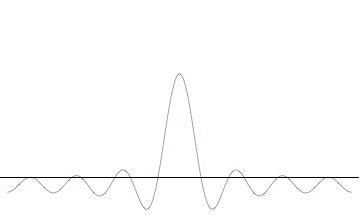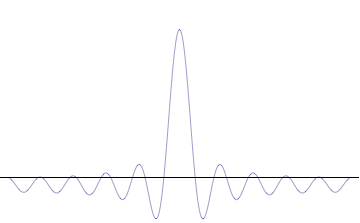
It is vital to illustrate how the principle applies to relatively intelligible physical situations since it is indiscernible on the macroscopic scales that humans experience. Two alternative frameworks for quantum physics offer different explanations for the uncertainty principle. The wave mechanics picture of the uncertainty principle is more visually intuitive, but the more abstract matrix mechanics picture formulates it in a way that generalizes more easily.
Mathematically, in wave mechanics, the uncertainty relation between position and momentum arises because the expressions of the wavefunction in the two corresponding orthonormal bases in Hilbert space are Fourier transforms of one another (i.e., position and momentum are conjugate variables). A nonzero function and its Fourier transform cannot both be sharply localized at the same time. A similar tradeoff between the variances of Fourier conjugates arises in all systems underlain by Fourier analysis, for example in sound waves: A pure tone is a sharp spike at a single frequency, while its Fourier transform gives the shape of the sound wave in the time domain, which is a completely delocalized sine wave. In quantum mechanics, the two key points are that the position of the particle takes the form of a matter wave, and momentum is its Fourier conjugate, assured by the de Broglie relation p = ħk, where k is the wavenumber.
In matrix mechanics, the mathematical formulation of quantum mechanics, any pair of non-commuting self-adjoint operators representing observables are subject to similar uncertainty limits. An eigenstate of an observable represents the state of the wavefunction for a certain measurement value (the eigenvalue). For example, if a measurement of an observable A is performed, then the system is in a particular eigenstate Ψ of that observable. However, the particular eigenstate of the observable A need not be an eigenstate of another observable B: If so, then it does not have a unique associated measurement for it, as the system is not in an eigenstate of that observable.
Visualization
The uncertainty principle can be visualized using the position- and momentum-space wavefunctions for one spinless particle with mass in one dimension.
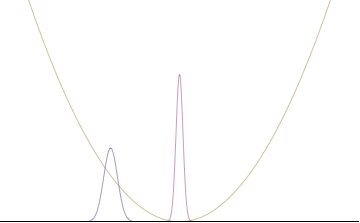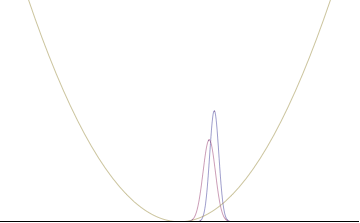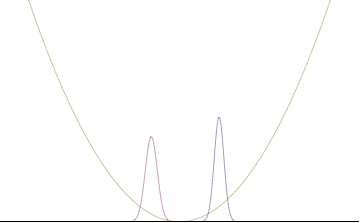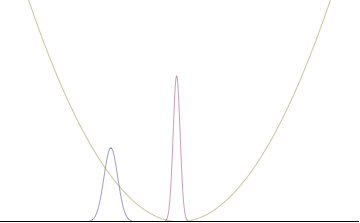
The more localized the position-space wavefunction, the more likely the particle is to be found with the position coordinates in that region, and correspondingly the momentum-space wavefunction is less localized so the possible momentum components the particle could have are more widespread. Conversely, the more localized the momentum-space wavefunction, the more likely the particle is to be found with those values of momentum components in that region, and correspondingly the less localized the position-space wavefunction, so the position coordinates the particle could occupy are more widespread. These wavefunctions are Fourier transforms of each other: mathematically, the uncertainty principle expresses the relationship between conjugate variables in the transform.

Left: If wavelength λ is unknown, so are momentum p, wave-vector k and energy E (de Broglie relations). As the particle is more localized in position space, Δx is smaller than for Δpx.
Right: If λ is known, so are p, k, and E. As the particle is more localized in momentum space, Δp is smaller than for Δx.
Wave mechanics interpretation
According to the de Broglie hypothesis, every object in the universe is associated with a wave. Thus every object, from an elementary particle to atoms, molecules and on up to planets and beyond are subject to the uncertainty principle.
The time-independent wave function of a single-moded plane wave of wavenumber k0 or momentum p0 is
The Born rule states that this should be interpreted as a probability density amplitude function in the sense that the probability of finding the particle between a and b is
In the case of the single-mode plane wave, is 1 if and 0 otherwise. In other words, the particle position is extremely uncertain in the sense that it could be essentially anywhere along the wave packet.
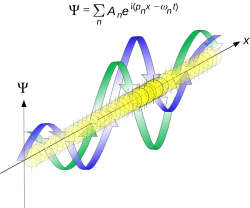
On the other hand, consider a wave function that is a sum of many waves, which we may write as where An represents the relative contribution of the mode pn to the overall total. The figures to the right show how with the addition of many plane waves, the wave packet can become more localized. We may take this a step further to the continuum limit, where the wave function is an integral over all possible modes with representing the amplitude of these modes and is called the wave function in momentum space. In mathematical terms, we say that is the Fourier transform of and that x and p are conjugate variables. Adding together all of these plane waves comes at a cost, namely the momentum has become less precise, having become a mixture of waves of many different momenta.
One way to quantify the precision of the position and momentum is the standard deviation σ. Since is a probability density function for position, we calculate its standard deviation.
The precision of the position is improved, i.e. reduced σx, by using many plane waves, thereby weakening the precision of the momentum, i.e. increased σp. Another way of stating this is that σx and σp have an inverse relationship or are at least bounded from below. This is the uncertainty principle, the exact limit of which is the Kennard bound.
We are interested in the variances of position and momentum, defined as
Without loss of generality, we will assume that the means vanish, which just amounts to a shift of the origin of our coordinates. (A more general proof that does not make this assumption is given below.) This gives us the simpler form
The function can be interpreted as a vector in a function space. We can define an inner product for a pair of functions u(x) and v(x) in this vector space: where the asterisk denotes the complex conjugate.
With this inner product defined, we note that the variance for position can be written as
We can repeat this for momentum by interpreting the function as a vector, but we can also take advantage of the fact that and are Fourier transforms of each other. We evaluate the inverse Fourier transform through integration by parts: where in the integration by parts, the cancelled term vanishes because the wave function vanishes at infinity, and the final two integrations re-assert the Fourier transforms. Often the term is called the momentum operator in position space. Applying Parseval's theorem, we see that the variance for momentum can be written as
The Cauchy–Schwarz inequality asserts that
The modulus squared of any complex number z can be expressed as we let and and substitute these into the equation above to get
All that remains is to evaluate these inner products.
Plugging this into the above inequalities, we get or taking the square root
with equality if and only if p and x are linearly dependent. Note that the only physics involved in this proof was that and are wave functions for position and momentum, which are Fourier transforms of each other. A similar result would hold for any pair of conjugate variables.
Matrix mechanics interpretation
(Ref [11])
In matrix mechanics, observables such as position and momentum are represented by self-adjoint operators. When considering pairs of observables, an important quantity is the commutator. For a pair of operators  and , one defines their commutator as In the case of position and momentum, the commutator is the canonical commutation relation
The physical meaning of the non-commutativity can be understood by considering the effect of the commutator on position and momentum eigenstates. Let be a right eigenstate of position with a constant eigenvalue x0. By definition, this means that Applying the commutator to yields where Î is the identity operator.
Suppose, for the sake of proof by contradiction, that is also a right eigenstate of momentum, with constant eigenvalue p0. If this were true, then one could write On the other hand, the above canonical commutation relation requires that This implies that no quantum state can simultaneously be both a position and a momentum eigenstate.
When a state is measured, it is projected onto an eigenstate in the basis of the relevant observable. For example, if a particle's position is measured, then the state amounts to a position eigenstate. This means that the state is not a momentum eigenstate, however, but rather it can be represented as a sum of multiple momentum basis eigenstates. In other words, the momentum must be less precise. This precision may be quantified by the standard deviations,
As in the wave mechanics interpretation above, one sees a tradeoff between the respective precisions of the two, quantified by the uncertainty principle.
Quantum harmonic oscillator stationary states
Consider a one-dimensional quantum harmonic oscillator. It is possible to express the position and momentum operators in terms of the creation and annihilation operators:
Using the standard rules for creation and annihilation operators on the energy eigenstates, the variances may be computed directly, The product of these standard deviations is then
In particular, the above Kennard bound is saturated for the ground state n=0, for which the probability density is just the normal distribution.
Quantum harmonic oscillators with Gaussian initial condition
In a quantum harmonic oscillator of characteristic angular frequency ω, place a state that is offset from the bottom of the potential by some displacement x0 as where Ω describes the width of the initial state but need not be the same as ω. Through integration over the propagator, we can solve for the full time-dependent solution. After many cancelations, the probability densities reduce to where we have used the notation to denote a normal distribution of mean μ and variance σ2. Copying the variances above and applying trigonometric identities, we can write the product of the standard deviations as
From the relations we can conclude the following (the right most equality holds only when Ω = ω):
Coherent states
A coherent state is a right eigenstate of the annihilation operator, which may be represented in terms of Fock states as
In the picture where the coherent state is a massive particle in a quantum harmonic oscillator, the position and momentum operators may be expressed in terms of the annihilation operators in the same formulas above and used to calculate the variances, Therefore, every coherent state saturates the Kennard bound with position and momentum each contributing an amount in a "balanced" way. Moreover, every squeezed coherent state also saturates the Kennard bound although the individual contributions of position and momentum need not be balanced in general.
Particle in a box
Consider a particle in a one-dimensional box of length . The eigenfunctions in position and momentum space are and where and we have used the de Broglie relation . The variances of and can be calculated explicitly:
The product of the standard deviations is therefore For all , the quantity is greater than 1, so the uncertainty principle is never violated. For numerical concreteness, the smallest value occurs when , in which case
Constant momentum

Assume a particle initially has a momentum space wave function described by a normal distribution around some constant momentum p0 according to where we have introduced a reference scale , with describing the width of the distribution—cf. nondimensionalization. If the state is allowed to evolve in free space, then the time-dependent momentum and position space wave functions are
Since and , this can be interpreted as a particle moving along with constant momentum at arbitrarily high precision. On the other hand, the standard deviation of the position is such that the uncertainty product can only increase with time as
Energy–time uncertainty principle
Energy spectrum line-width vs lifetime
An energy–time uncertainty relation like has a long, controversial history; the meaning of and varies and different formulations have different arenas of validity. However, one well-known application is both well established and experimentally verified: the connection between the life-time of a resonance state, and its energy width : In particle-physics, widths from experimental fits to the Breit–Wigner energy distribution are used to characterize the lifetime of quasi-stable or decaying states.
An informal, heuristic meaning of the principle is the following: A state that only exists for a short time cannot have a definite energy. To have a definite energy, the frequency of the state must be defined accurately, and this requires the state to hang around for many cycles, the reciprocal of the required accuracy. For example, in spectroscopy, excited states have a finite lifetime. By the time–energy uncertainty principle, they do not have a definite energy, and, each time they decay, the energy they release is slightly different. The average energy of the outgoing photon has a peak at the theoretical energy of the state, but the distribution has a finite width called the natural linewidth. Fast-decaying states have a broad linewidth, while slow-decaying states have a narrow linewidth. The same linewidth effect also makes it difficult to specify the rest mass of unstable, fast-decaying particles in particle physics. The faster the particle decays (the shorter its lifetime), the less certain is its mass (the larger the particle's width).
Time in quantum mechanics
The concept of "time" in quantum mechanics offers many challenges. There is no quantum theory of time measurement; relativity is both fundamental to time and difficult to include in quantum mechanics. While position and momentum are associated with a single particle, time is a system property: it has no operator needed for the Robertson–Schrödinger relation. The mathematical treatment of stable and unstable quantum systems differ. These factors combine to make energy–time uncertainty principles controversial.
Three notions of "time" can be distinguished: external, intrinsic, and observable. External or laboratory time is seen by the experimenter; intrinsic time is inferred by changes in dynamic variables, like the hands of a clock or the motion of a free particle; observable time concerns time as an observable, the measurement of time-separated events.
An external-time energy–time uncertainty principle might say that measuring the energy of a quantum system to an accuracy requires a time interval . However, Yakir Aharonov and David Bohm have shown that, in some quantum systems, energy can be measured accurately within an arbitrarily short time: external-time uncertainty principles are not universal.
Intrinsic time is the basis for several formulations of energy–time uncertainty relations, including the Mandelstam–Tamm relation discussed in the next section. A physical system with an intrinsic time closely matching the external laboratory time is called a "clock".
Observable time, measuring time between two events, remains a challenge for quantum theories; some progress has been made using positive operator-valued measure concepts.
Mandelstam–Tamm
In 1945, Leonid Mandelstam and Igor Tamm derived a non-relativistic time–energy uncertainty relation as follows. From Heisenberg mechanics, the generalized Ehrenfest theorem for an observable B without explicit time dependence, represented by a self-adjoint operator relates time dependence of the average value of to the average of its commutator with the Hamiltonian:
The value of is then substituted in the Robertson uncertainty relation for the energy operator and : giving (whenever the denonminator is nonzero). While this is a universal result, it depends upon the observable chosen and that the deviations and are computed for a particular state. Identifying and the characteristic time gives an energy–time relationship Although has the dimension of time, it is different from the time parameter t that enters the Schrödinger equation. This can be interpreted as time for which the expectation value of the observable, changes by an amount equal to one standard deviation. Examples:
- The time a free quantum particle passes a point in space is more uncertain as the energy of the state is more precisely controlled: Since the time spread is related to the particle position spread and the energy spread is related to the momentum spread, this relation is directly related to position–momentum uncertainty.
- A Delta particle, a quasistable composite of quarks related to protons and neutrons, has a lifetime of 10−23 s, so its measured mass equivalent to energy, 1232 MeV/c2, varies by ±120 MeV/c2; this variation is intrinsic and not caused by measurement errors.
- Two energy states with energies superimposed to create a composite state
- The probability amplitude of this state has a time-dependent interference term:
- The oscillation period varies inversely with the energy difference: .
Each example has a different meaning for the time uncertainty, according to the observable and state used.
Quantum field theory
Some formulations of quantum field theory uses temporary electron–positron pairs in its calculations called virtual particles. The mass-energy and lifetime of these particles are related by the energy–time uncertainty relation. The energy of a quantum systems is not known with enough precision to limit their behavior to a single, simple history. Thus the influence of all histories must be incorporated into quantum calculations, including those with much greater or much less energy than the mean of the measured/calculated energy distribution.
The energy–time uncertainty principle does not temporarily violate conservation of energy; it does not imply that energy can be "borrowed" from the universe as long as it is "returned" within a short amount of time. The energy of the universe is not an exactly known parameter at all times. When events transpire at very short time intervals, there is uncertainty in the energy of these events.
Intrinsic quantum uncertainty
Historically, the uncertainty principle has been confused with a related effect in physics, called the observer effect, which notes that measurements of certain systems cannot be made without affecting the system, that is, without changing something in a system. Heisenberg used such an observer effect at the quantum level (see below) as a physical "explanation" of quantum uncertainty. It has since become clearer, however, that the uncertainty principle is inherent in the properties of all wave-like systems, and that it arises in quantum mechanics simply due to the matter wave nature of all quantum objects. Thus, the uncertainty principle actually states a fundamental property of quantum systems and is not a statement about the observational success of current technology.
Mathematical formalism
Starting with Kennard's derivation of position-momentum uncertainty, Howard Percy Robertson developed a formulation for arbitrary Hermitian operator operators expressed in terms of their standard deviation where the brackets indicate an expectation value. For a pair of operators and , define their commutator as
and the Robertson uncertainty relation is given by
Erwin Schrödinger showed how to allow for correlation between the operators, giving a stronger inequality, known as the Robertson-Schrödinger uncertainty relation,
where the anticommutator, is used.
The derivation shown here incorporates and builds off of those shown in Robertson, Schrödinger and standard textbooks such as Griffiths. For any Hermitian operator , based upon the definition of variance, we have we let and thus
Similarly, for any other Hermitian operator in the same state for
The product of the two deviations can thus be expressed as
| (1) |
In order to relate the two vectors and , we use the Cauchy–Schwarz inequality which is defined as and thus Equation (1) can be written as
| (2) |
Since is in general a complex number, we use the fact that the modulus squared of any complex number is defined as , where is the complex conjugate of . The modulus squared can also be expressed as
| (3) |
we let and and substitute these into the equation above to get
| (4) |
The inner product is written out explicitly as and using the fact that and are Hermitian operators, we find
Similarly it can be shown that
Thus, we have and
We now substitute the above two equations above back into Eq. (4) and get
Substituting the above into Equation (2) we get the Schrödinger uncertainty relation
This proof has an issue related to the domains of the operators involved. For the proof to make sense, the vector has to be in the domain of the unbounded operator , which is not always the case. In fact, the Robertson uncertainty relation is false if is an angle variable and is the derivative with respect to this variable. In this example, the commutator is a nonzero constant—just as in the Heisenberg uncertainty relation—and yet there are states where the product of the uncertainties is zero. (See the counterexample section below.) This issue can be overcome by using a variational method for the proof, or by working with an exponentiated version of the canonical commutation relations.
Note that in the general form of the Robertson–Schrödinger uncertainty relation, there is no need to assume that the operators and are self-adjoint operators. It suffices to assume that they are merely symmetric operators. (The distinction between these two notions is generally glossed over in the physics literature, where the term Hermitian is used for either or both classes of operators. See Chapter 9 of Hall's book for a detailed discussion of this important but technical distinction.)
Mixed states
The Robertson–Schrödinger uncertainty relation may be generalized in a straightforward way to describe mixed states.
The Maccone–Pati uncertainty relations
The Robertson–Schrödinger uncertainty relation can be trivial if the state of the system is chosen to be eigenstate of one of the observable. The stronger uncertainty relations proved by Lorenzo Maccone and Arun K. Pati give non-trivial bounds on the sum of the variances for two incompatible observables. (Earlier works on uncertainty relations formulated as the sum of variances include, e.g., Ref. due to Yichen Huang.) For two non-commuting observables and the first stronger uncertainty relation is given by where , , is a normalized vector that is orthogonal to the state of the system and one should choose the sign of to make this real quantity a positive number.
The second stronger uncertainty relation is given by where is a state orthogonal to . The form of implies that the right-hand side of the new uncertainty relation is nonzero unless is an eigenstate of . One may note that can be an eigenstate of without being an eigenstate of either or . However, when is an eigenstate of one of the two observables the Heisenberg–Schrödinger uncertainty relation becomes trivial. But the lower bound in the new relation is nonzero unless is an eigenstate of both.
Improving the Robertson–Schrödinger uncertainty relation based on decompositions of the density matrix
The Robertson–Schrödinger uncertainty can be improved noting that it must hold for all components in any decomposition of the density matrix given as Here, for the probabilities and hold. Then, using the relation for , it follows that where the function in the bound is defined The above relation very often has a bound larger than that of the original Robertson–Schrödinger uncertainty relation. Thus, we need to calculate the bound of the Robertson–Schrödinger uncertainty for the mixed components of the quantum state rather than for the quantum state, and compute an average of their square roots. The following expression is stronger than the Robertson–Schrödinger uncertainty relation where on the right-hand side there is a concave roof over the decompositions of the density matrix. The improved relation above is saturated by all single-qubit quantum states.
With similar arguments, one can derive a relation with a convex roof on the right-hand side where denotes the quantum Fisher information and the density matrix is decomposed to pure states as The derivation takes advantage of the fact that the quantum Fisher information is the convex roof of the variance times four.
A simpler inequality follows without a convex roof which is stronger than the Heisenberg uncertainty relation, since for the quantum Fisher information we have while for pure states the equality holds.
Phase space
In the phase space formulation of quantum mechanics, the Robertson–Schrödinger relation follows from a positivity condition on a real star-square function. Given a Wigner function with star product ★ and a function f, the following is generally true:
Choosing , we arrive at
Since this positivity condition is true for all a, b, and c, it follows that all the eigenvalues of the matrix are non-negative.
The non-negative eigenvalues then imply a corresponding non-negativity condition on the determinant, or, explicitly, after algebraic manipulation,
Examples
Since the Robertson and Schrödinger relations are for general operators, the relations can be applied to any two observables to obtain specific uncertainty relations. A few of the most common relations found in the literature are given below.
- Position–linear momentum uncertainty relation: for the position and linear momentum operators, the canonical commutation relation implies the Kennard inequality from above:
- Angular momentum uncertainty relation: For two orthogonal components of the total angular momentum operator of an object: where i, j, k are distinct, and Ji denotes angular momentum along the xi axis. This relation implies that unless all three components vanish together, only a single component of a system's angular momentum can be defined with arbitrary precision, normally the component parallel to an external (magnetic or electric) field. Moreover, for , a choice , , in angular momentum multiplets, ψ = |j, m⟩, bounds the Casimir invariant (angular momentum squared, ) from below and thus yields useful constraints such as j(j + 1) ≥ m(m + 1), and hence j ≥ m, among others.
- For the number of electrons in a superconductor and the phase of its Ginzburg–Landau order parameter
Limitations
The derivation of the Robertson inequality for operators and requires and to be defined. There are quantum systems where these conditions are not valid. One example is a quantum particle on a ring, where the wave function depends on an angular variable in the interval . Define "position" and "momentum" operators and by and with periodic boundary conditions on . The definition of depends the range from 0 to . These operators satisfy the usual commutation relations for position and momentum operators, . More precisely, whenever both and are defined, and the space of such is a dense subspace of the quantum Hilbert space.
Now let be any of the eigenstates of , which are given by . These states are normalizable, unlike the eigenstates of the momentum operator on the line. Also the operator is bounded, since ranges over a bounded interval. Thus, in the state , the uncertainty of is zero and the uncertainty of is finite, so that The Robertson uncertainty principle does not apply in this case: is not in the domain of the operator , since multiplication by disrupts the periodic boundary conditions imposed on .
For the usual position and momentum operators and on the real line, no such counterexamples can occur. As long as and are defined in the state , the Heisenberg uncertainty principle holds, even if fails to be in the domain of or of .
Additional uncertainty relations
Heisenberg limit
In quantum metrology, and especially interferometry, the Heisenberg limit is the optimal rate at which the accuracy of a measurement can scale with the energy used in the measurement. Typically, this is the measurement of a phase (applied to one arm of a beam-splitter) and the energy is given by the number of photons used in an interferometer. Although some claim to have broken the Heisenberg limit, this reflects disagreement on the definition of the scaling resource. Suitably defined, the Heisenberg limit is a consequence of the basic principles of quantum mechanics and cannot be beaten, although the weak Heisenberg limit can be beaten.
Systematic and statistical errors
The inequalities above focus on the statistical imprecision of observables as quantified by the standard deviation . Heisenberg's original version, however, was dealing with the systematic error, a disturbance of the quantum system produced by the measuring apparatus, i.e., an observer effect.
If we let represent the error (i.e., inaccuracy) of a measurement of an observable A and the disturbance produced on a subsequent measurement of the conjugate variable B by the former measurement of A, then the inequality proposed by Ozawa−encompassing both systematic and statistical errors—holds:
Heisenberg's uncertainty principle, as originally described in the 1927 formulation, mentions only the first term of Ozawa inequality, regarding the systematic error. Using the notation above to describe the error/disturbance effect of sequential measurements (first A, then B), it could be written as
The formal derivation of the Heisenberg relation is possible but far from intuitive. It was not proposed by Heisenberg, but formulated in a mathematically consistent way only in recent years. Also, it must be stressed that the Heisenberg formulation is not taking into account the intrinsic statistical errors and . There is increasing experimental evidence that the total quantum uncertainty cannot be described by the Heisenberg term alone, but requires the presence of all the three terms of the Ozawa inequality.
Using the same formalism, it is also possible to introduce the other kind of physical situation, often confused with the previous one, namely the case of simultaneous measurements (A and B at the same time):
The two simultaneous measurements on A and B are necessarily unsharp or weak.
It is also possible to derive an uncertainty relation that, as the Ozawa's one, combines both the statistical and systematic error components, but keeps a form very close to the Heisenberg original inequality. By adding Robertson
and Ozawa relations we obtain The four terms can be written as: Defining: as the inaccuracy in the measured values of the variable A and as the resulting fluctuation in the conjugate variable B, Kazuo Fujikawa established an uncertainty relation similar to the Heisenberg original one, but valid both for systematic and statistical errors:
Quantum entropic uncertainty principle
For many distributions, the standard deviation is not a particularly natural way of quantifying the structure. For example, uncertainty relations in which one of the observables is an angle has little physical meaning for fluctuations larger than one period. Other examples include highly bimodal distributions, or unimodal distributions with divergent variance.
A solution that overcomes these issues is an uncertainty based on entropic uncertainty instead of the product of variances. While formulating the many-worlds interpretation of quantum mechanics in 1957, Hugh Everett III conjectured a stronger extension of the uncertainty principle based on entropic certainty. This conjecture, also studied by I. I. Hirschman and proven in 1975 by W. Beckner and by Iwo Bialynicki-Birula and Jerzy Mycielski is that, for two normalized, dimensionless Fourier transform pairs f(a) and g(b) where
- and
the Shannon information entropies and are subject to the following constraint,
where the logarithms may be in any base.
The probability distribution functions associated with the position wave function ψ(x) and the momentum wave function φ(x) have dimensions of inverse length and momentum respectively, but the entropies may be rendered dimensionless by where x0 and p0 are some arbitrarily chosen length and momentum respectively, which render the arguments of the logarithms dimensionless. Note that the entropies will be functions of these chosen parameters. Due to the Fourier transform relation between the position wave function ψ(x) and the momentum wavefunction φ(p), the above constraint can be written for the corresponding entropies as
where h is the Planck constant.
Depending on one's choice of the x0 p0 product, the expression may be written in many ways. If x0 p0 is chosen to be h, then
If, instead, x0 p0 is chosen to be ħ, then
If x0 and p0 are chosen to be unity in whatever system of units are being used, then where h is interpreted as a dimensionless number equal to the value of the Planck constant in the chosen system of units. Note that these inequalities can be extended to multimode quantum states, or wavefunctions in more than one spatial dimension.
The quantum entropic uncertainty principle is more restrictive than the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. From the inverse logarithmic Sobolev inequalities (equivalently, from the fact that normal distributions maximize the entropy of all such with a given variance), it readily follows that this entropic uncertainty principle is stronger than the one based on standard deviations, because
In other words, the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, is a consequence of the quantum entropic uncertainty principle, but not vice versa. A few remarks on these inequalities. First, the choice of base e is a matter of popular convention in physics. The logarithm can alternatively be in any base, provided that it be consistent on both sides of the inequality. Second, recall the Shannon entropy has been used, not the quantum von Neumann entropy. Finally, the normal distribution saturates the inequality, and it is the only distribution with this property, because it is the maximum entropy probability distribution among those with fixed variance (cf. here for proof).
| Entropic uncertainty of the normal distribution |
|---|
A measurement apparatus will have a finite resolution set by the discretization of its possible outputs into bins, with the probability of lying within one of the bins given by the Born rule. We will consider the most common experimental situation, in which the bins are of uniform size. Let δx be a measure of the spatial resolution. We take the zeroth bin to be centered near the origin, with possibly some small constant offset c. The probability of lying within the jth interval of width δx is
To account for this discretization, we can define the Shannon entropy of the wave function for a given measurement apparatus as
Under the above definition, the entropic uncertainty relation is
Here we note that δx δp/h is a typical infinitesimal phase space volume used in the calculation of a partition function. The inequality is also strict and not saturated. Efforts to improve this bound are an active area of research.
| Normal distribution example |
|---|
| Sinc function example |
|---|
Uncertainty relation with three angular momentum components
For a particle of spin- the following uncertainty relation holds where are angular momentum components. The relation can be derived from and The relation can be strengthened as where is the quantum Fisher information.
Harmonic analysis
In the context of harmonic analysis, a branch of mathematics, the uncertainty principle implies that one cannot at the same time localize the value of a function and its Fourier transform. To wit, the following inequality holds,
Further mathematical uncertainty inequalities, including the above entropic uncertainty, hold between a function f and its Fourier transform ƒ̂:
Signal processing
In the context of signal processing, and in particular time–frequency analysis, uncertainty principles are referred to as the Gabor limit, after Dennis Gabor, or sometimes the Heisenberg–Gabor limit. The basic result, which follows from "Benedicks's theorem", below, is that a function cannot be both time limited and band limited (a function and its Fourier transform cannot both have bounded domain)—see bandlimited versus timelimited. More accurately, the time-bandwidth or duration-bandwidth product satisfies where and are the standard deviations of the time and frequency energy or power (i.e. squared) representations respectively. The minimum is attained for a Gaussian-shaped pulse (Gabor wavelet) [For the un-squared Gaussian (i.e. signal amplitude) and its un-squared Fourier transform magnitude ; squaring reduces each by a factor .] Another common measure is the product of the time and frequency full width at half maximum (of the power/energy), which for the Gaussian equals (see bandwidth-limited pulse).
Stated alternatively, "One cannot simultaneously sharply localize a signal (function f) in both the time domain and frequency domain (ƒ̂, its Fourier transform)".
When applied to filters, the result implies that one cannot achieve high temporal resolution and frequency resolution at the same time; a concrete example are the resolution issues of the short-time Fourier transform—if one uses a wide window, one achieves good frequency resolution at the cost of temporal resolution, while a narrow window has the opposite trade-off.
Alternate theorems give more precise quantitative results, and, in time–frequency analysis, rather than interpreting the (1-dimensional) time and frequency domains separately, one instead interprets the limit as a lower limit on the support of a function in the (2-dimensional) time–frequency plane. In practice, the Gabor limit limits the simultaneous time–frequency resolution one can achieve without interference; it is possible to achieve higher resolution, but at the cost of different components of the signal interfering with each other.
As a result, in order to analyze signals where the transients are important, the wavelet transform is often used instead of the Fourier.
Discrete Fourier transform
Let be a sequence of N complex numbers and be its discrete Fourier transform.
Denote by the number of non-zero elements in the time sequence and by the number of non-zero elements in the frequency sequence . Then,
This inequality is sharp, with equality achieved when x or X is a Dirac mass, or more generally when x is a nonzero multiple of a Dirac comb supported on a subgroup of the integers modulo N (in which case X is also a Dirac comb supported on a complementary subgroup, and vice versa).
More generally, if T and W are subsets of the integers modulo N, let denote the time-limiting operator and band-limiting operators, respectively. Then where the norm is the operator norm of operators on the Hilbert space of functions on the integers modulo N. This inequality has implications for signal reconstruction.
When N is a prime number, a stronger inequality holds: Discovered by Terence Tao, this inequality is also sharp.
Benedicks's theorem
Amrein–Berthier and Benedicks's theorem intuitively says that the set of points where f is non-zero and the set of points where ƒ̂ is non-zero cannot both be small.
Specifically, it is impossible for a function f in L2(R) and its Fourier transform ƒ̂ to both be supported on sets of finite Lebesgue measure. A more quantitative version is
One expects that the factor CeC|S||Σ| may be replaced by CeC(|S||Σ|)1/d, which is only known if either S or Σ is convex.
Hardy's uncertainty principle
The mathematician G. H. Hardy formulated the following uncertainty principle: it is not possible for f and ƒ̂ to both be "very rapidly decreasing". Specifically, if f in is such that and ( an integer), then, if ab > 1, f = 0, while if ab = 1, then there is a polynomial P of degree ≤ N such that
This was later improved as follows: if is such that then where P is a polynomial of degree (N − d)/2 and A is a real d × d positive definite matrix.
This result was stated in Beurling's complete works without proof and proved in Hörmander (the case ) and Bonami, Demange, and Jaming for the general case. Note that Hörmander–Beurling's version implies the case ab > 1 in Hardy's Theorem while the version by Bonami–Demange–Jaming covers the full strength of Hardy's Theorem. A different proof of Beurling's theorem based on Liouville's theorem appeared in ref.
A full description of the case ab < 1 as well as the following extension to Schwartz class distributions appears in ref.
Theorem — If a tempered distribution is such that and then for some convenient polynomial P and real positive definite matrix A of type d × d.
History
In 1925 Heisenberg published the Umdeutung (reinterpretation) paper where he showed that central aspect of quantum theory was the non-commutativity: the theory implied that the relative order of position and momentum measurement was significant. Working with Max Born and Pascual Jordan, he continued to develop matrix mechanics, that would become the first modern quantum mechanics formulation.

In March 1926, working in Bohr's institute, Heisenberg realized that the non-commutativity implies the uncertainty principle. Writing to Wolfgang Pauli in February 1927, he worked out the basic concepts.
In his celebrated 1927 paper "Über den anschaulichen Inhalt der quantentheoretischen Kinematik und Mechanik" ("On the Perceptual Content of Quantum Theoretical Kinematics and Mechanics"), Heisenberg established this expression as the minimum amount of unavoidable momentum disturbance caused by any position measurement, but he did not give a precise definition for the uncertainties Δx and Δp. Instead, he gave some plausible estimates in each case separately. His paper gave an analysis in terms of a microscope that Bohr showed was incorrect; Heisenberg included an addendum to the publication.
In his 1930 Chicago lecture he refined his principle:
| (A1) |
Later work broadened the concept. Any two variables that do not commute cannot be measured simultaneously—the more precisely one is known, the less precisely the other can be known. Heisenberg wrote:
It can be expressed in its simplest form as follows: One can never know with perfect accuracy both of those two important factors which determine the movement of one of the smallest particles—its position and its velocity. It is impossible to determine accurately both the position and the direction and speed of a particle at the same instant.
Kennard in 1927 first proved the modern inequality:
| (A2) |
where ħ = h/2π, and σx, σp are the standard deviations of position and momentum. (Heisenberg only proved relation (A2) for the special case of Gaussian states.) In 1929 Robertson generalized the inequality to all observables and in 1930 Schrödinger extended the form to allow non-zero covariance of the operators; this result is referred to as Robertson-Schrödinger inequality.
Terminology and translation
Throughout the main body of his original 1927 paper, written in German, Heisenberg used the word "Ungenauigkeit", to describe the basic theoretical principle. Only in the endnote did he switch to the word "Unsicherheit". Later on, he always used "Unbestimmtheit". When the English-language version of Heisenberg's textbook, The Physical Principles of the Quantum Theory, was published in 1930, however, only the English word "uncertainty" was used, and it became the term in the English language.
Heisenberg's microscope

The principle is quite counter-intuitive, so the early students of quantum theory had to be reassured that naive measurements to violate it were bound always to be unworkable. One way in which Heisenberg originally illustrated the intrinsic impossibility of violating the uncertainty principle is by using the observer effect of an imaginary microscope as a measuring device.
He imagines an experimenter trying to measure the position and momentum of an electron by shooting a photon at it.
- Problem 1 – If the photon has a short wavelength, and therefore, a large momentum, the position can be measured accurately. But the photon scatters in a random direction, transferring a large and uncertain amount of momentum to the electron. If the photon has a long wavelength and low momentum, the collision does not disturb the electron's momentum very much, but the scattering will reveal its position only vaguely.
- Problem 2 – If a large aperture is used for the microscope, the electron's location can be well resolved (see Rayleigh criterion); but by the principle of conservation of momentum, the transverse momentum of the incoming photon affects the electron's beamline momentum and hence, the new momentum of the electron resolves poorly. If a small aperture is used, the accuracy of both resolutions is the other way around.
The combination of these trade-offs implies that no matter what photon wavelength and aperture size are used, the product of the uncertainty in measured position and measured momentum is greater than or equal to a lower limit, which is (up to a small numerical factor) equal to the Planck constant. Heisenberg did not care to formulate the uncertainty principle as an exact limit, and preferred to use it instead, as a heuristic quantitative statement, correct up to small numerical factors, which makes the radically new noncommutativity of quantum mechanics inevitable.
Critical reactions
The Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics and Heisenberg's uncertainty principle were, in fact, initially seen as twin targets by detractors. According to the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics, there is no fundamental reality that the quantum state describes, just a prescription for calculating experimental results. There is no way to say what the state of a system fundamentally is, only what the result of observations might be.
Albert Einstein believed that randomness is a reflection of our ignorance of some fundamental property of reality, while Niels Bohr believed that the probability distributions are fundamental and irreducible, and depend on which measurements we choose to perform. Einstein and Bohr debated the uncertainty principle for many years.
Ideal detached observer
Wolfgang Pauli called Einstein's fundamental objection to the uncertainty principle "the ideal of the detached observer" (phrase translated from the German):
"Like the moon has a definite position" Einstein said to me last winter, "whether or not we look at the moon, the same must also hold for the atomic objects, as there is no sharp distinction possible between these and macroscopic objects. Observation cannot create an element of reality like a position, there must be something contained in the complete description of physical reality which corresponds to the possibility of observing a position, already before the observation has been actually made." I hope, that I quoted Einstein correctly; it is always difficult to quote somebody out of memory with whom one does not agree. It is precisely this kind of postulate which I call the ideal of the detached observer.
— Letter from Pauli to Niels Bohr, February 15, 1955
Einstein's slit
The first of Einstein's thought experiments challenging the uncertainty principle went as follows:
Consider a particle passing through a slit of width d. The slit introduces an uncertainty in momentum of approximately h/d because the particle passes through the wall. But let us determine the momentum of the particle by measuring the recoil of the wall. In doing so, we find the momentum of the particle to arbitrary accuracy by conservation of momentum.
Bohr's response was that the wall is quantum mechanical as well, and that to measure the recoil to accuracy Δp, the momentum of the wall must be known to this accuracy before the particle passes through. This introduces an uncertainty in the position of the wall and therefore the position of the slit equal to h/Δp, and if the wall's momentum is known precisely enough to measure the recoil, the slit's position is uncertain enough to disallow a position measurement.
A similar analysis with particles diffracting through multiple slits is given by Richard Feynman.
Einstein's box
Bohr was present when Einstein proposed the thought experiment which has become known as Einstein's box. Einstein argued that "Heisenberg's uncertainty equation implied that the uncertainty in time was related to the uncertainty in energy, the product of the two being related to the Planck constant." Consider, he said, an ideal box, lined with mirrors so that it can contain light indefinitely. The box could be weighed before a clockwork mechanism opened an ideal shutter at a chosen instant to allow one single photon to escape. "We now know, explained Einstein, precisely the time at which the photon left the box." "Now, weigh the box again. The change of mass tells the energy of the emitted light. In this manner, said Einstein, one could measure the energy emitted and the time it was released with any desired precision, in contradiction to the uncertainty principle."
Bohr spent a sleepless night considering this argument, and eventually realized that it was flawed. He pointed out that if the box were to be weighed, say by a spring and a pointer on a scale, "since the box must move vertically with a change in its weight, there will be uncertainty in its vertical velocity and therefore an uncertainty in its height above the table. ... Furthermore, the uncertainty about the elevation above the Earth's surface will result in an uncertainty in the rate of the clock," because of Einstein's own theory of gravity's effect on time. "Through this chain of uncertainties, Bohr showed that Einstein's light box experiment could not simultaneously measure exactly both the energy of the photon and the time of its escape."
EPR paradox for entangled particles
In 1935, Einstein, Boris Podolsky and Nathan Rosen published an analysis of spatially separated entangled particles (EPR paradox). According to EPR, one could measure the position of one of the entangled particles and the momentum of the second particle, and from those measurements deduce the position and momentum of both particles to any precision, violating the uncertainty principle. In order to avoid such possibility, the measurement of one particle must modify the probability distribution of the other particle instantaneously, possible violating the principle of locality.
In 1964, John Stewart Bell showed that this assumption can be falsified, since it would imply a certain inequality between the probabilities of different experiments. Experimental results confirm the predictions of quantum mechanics, ruling out EPR basic assumption of local hidden variables.
Popper's criticism
Science philosopher Karl Popper approached the problem of indeterminacy as a logician and metaphysical realist. He disagreed with the application of the uncertainty relations to individual particles rather than to ensembles of identically prepared particles, referring to them as "statistical scatter relations". In this statistical interpretation, a particular measurement may be made to arbitrary precision without invalidating the quantum theory.
In 1934, Popper published Zur Kritik der Ungenauigkeitsrelationen (Critique of the Uncertainty Relations) in Naturwissenschaften, and in the same year Logik der Forschung (translated and updated by the author as The Logic of Scientific Discovery in 1959), outlining his arguments for the statistical interpretation. In 1982, he further developed his theory in Quantum theory and the schism in Physics, writing:
[Heisenberg's] formulae are, beyond all doubt, derivable statistical formulae of the quantum theory. But they have been habitually misinterpreted by those quantum theorists who said that these formulae can be interpreted as determining some upper limit to the precision of our measurements.
Popper proposed an experiment to falsify the uncertainty relations, although he later withdrew his initial version after discussions with Carl Friedrich von Weizsäcker, Heisenberg, and Einstein; Popper sent his paper to Einstein and it may have influenced the formulation of the EPR paradox.
Free will
Some scientists including Arthur Compton and Martin Heisenberg have suggested that the uncertainty principle, or at least the general probabilistic nature of quantum mechanics, could be evidence for the two-stage model of free will. One critique, however, is that apart from the basic role of quantum mechanics as a foundation for chemistry, nontrivial biological mechanisms requiring quantum mechanics are unlikely, due to the rapid decoherence time of quantum systems at room temperature. Proponents of this theory commonly say that this decoherence is overcome by both screening and decoherence-free subspaces found in biological cells.
Thermodynamics
There is reason to believe that violating the uncertainty principle also strongly implies the violation of the second law of thermodynamics. See Gibbs paradox.
Rejection of the principle
Uncertainty principles relate quantum particles–electrons for example–to classical concepts–position and momentum. This presumes quantum particles have position and momentum. Edwin C. Kemble pointed out in 1937 that such properties cannot be experimentally verified and assuming they exist gives rise to many contradictions; similarly Rudolf Haag notes that position in quantum mechanics is an attribute of an interaction, say between an electron and a detector, not an intrinsic property. From this point of view the uncertainty principle is not a fundamental quantum property but a concept "carried over from the language of our ancestors" as Kemble says.



![{\displaystyle \operatorname {P} [a\leq X\leq b]=\int _{a}^{b}|\psi (x)|^{2}\,\mathrm {d} x~.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f8852ff1f2e7c518fce8dfbb77f8e8a7920c63f3)














![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}g(x)&={\frac {1}{\sqrt {2\pi \hbar }}}\cdot \int _{-\infty }^{\infty }{\tilde {g}}(p)\cdot e^{ipx/\hbar }\,dp\\&={\frac {1}{\sqrt {2\pi \hbar }}}\int _{-\infty }^{\infty }p\cdot \varphi (p)\cdot e^{ipx/\hbar }\,dp\\&={\frac {1}{2\pi \hbar }}\int _{-\infty }^{\infty }\left[p\cdot \int _{-\infty }^{\infty }\psi (\chi )e^{-ip\chi /\hbar }\,d\chi \right]\cdot e^{ipx/\hbar }\,dp\\&={\frac {i}{2\pi }}\int _{-\infty }^{\infty }\left[{\cancel {\left.\psi (\chi )e^{-ip\chi /\hbar }\right|_{-\infty }^{\infty }}}-\int _{-\infty }^{\infty }{\frac {d\psi (\chi )}{d\chi }}e^{-ip\chi /\hbar }\,d\chi \right]\cdot e^{ipx/\hbar }\,dp\\&={\frac {-i}{2\pi }}\int _{-\infty }^{\infty }\int _{-\infty }^{\infty }{\frac {d\psi (\chi )}{d\chi }}e^{-ip\chi /\hbar }\,d\chi \,e^{ipx/\hbar }\,dp\\&=-i{\sqrt {\frac {\hbar }{2\pi }}}\int _{-\infty }^{\infty }{\frac {d\psi (\chi )}{d\chi }}e^{-ip\chi /\hbar }\,d\chi \\&=\left(-i\hbar {\frac {d}{dx}}\right)\cdot \psi (x),\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e49cf162e038b87ed80c4e5d59c54ac173001db5)








![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\langle f\mid g\rangle -\langle g\mid f\rangle ={}&\int _{-\infty }^{\infty }\psi ^{*}(x)\,x\cdot \left(-i\hbar {\frac {d}{dx}}\right)\,\psi (x)\,dx\\&{}-\int _{-\infty }^{\infty }\psi ^{*}(x)\,\left(-i\hbar {\frac {d}{dx}}\right)\cdot x\,\psi (x)\,dx\\={}&i\hbar \cdot \int _{-\infty }^{\infty }\psi ^{*}(x)\left[\left(-x\cdot {\frac {d\psi (x)}{dx}}\right)+{\frac {d(x\psi (x))}{dx}}\right]\,dx\\={}&i\hbar \cdot \int _{-\infty }^{\infty }\psi ^{*}(x)\left[\left(-x\cdot {\frac {d\psi (x)}{dx}}\right)+\psi (x)+\left(x\cdot {\frac {d\psi (x)}{dx}}\right)\right]\,dx\\={}&i\hbar \cdot \int _{-\infty }^{\infty }\psi ^{*}(x)\psi (x)\,dx\\={}&i\hbar \cdot \int _{-\infty }^{\infty }|\psi (x)|^{2}\,dx\\={}&i\hbar \end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d4ddead3f7e2d237c2ad9bb5258ad66a9d92c599)



![{\displaystyle [{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}]={\hat {A}}{\hat {B}}-{\hat {B}}{\hat {A}}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3133da214f8f0fcf1ba11e907cfd121a2179b1b4)
![{\displaystyle [{\hat {x}},{\hat {p}}]=i\hbar .}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/fee0861ae7784cb51a1b43f6c51735c22c23274e)


![{\displaystyle [{\hat {x}},{\hat {p}}]|\psi \rangle =({\hat {x}}{\hat {p}}-{\hat {p}}{\hat {x}})|\psi \rangle =({\hat {x}}-x_{0}{\hat {I}}){\hat {p}}\,|\psi \rangle =i\hbar |\psi \rangle ,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8255257353e4743e966c106dea5674689ed04690)

![{\displaystyle [{\hat {x}},{\hat {p}}]|\psi \rangle =i\hbar |\psi \rangle \neq 0.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/04d341bbd1c29d8f96a5ce5ad6e2cf856d1b1f40)





















































![{\displaystyle {\frac {d\langle {\hat {B}}\rangle }{dt}}={\frac {i}{\hbar }}\langle [{\hat {H}},{\hat {B}}]\rangle .}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/92bca95fec448b2e3291ae56caf76d1796e6c02f)
![{\displaystyle \langle [{\hat {H}},{\hat {B}}]\rangle }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/42ce91773492f7d6bdcd2ce0ad93cb92f38c1287)

![{\displaystyle \sigma _{H}\sigma _{B}\geq \left|{\frac {1}{2i}}\langle [{\hat {H}},{\hat {B}}]\rangle \right|,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/48c8d45afe6c1f61a750dbb97358c10dde03f8fb)


















![{\displaystyle [{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}]={\hat {A}}{\hat {B}}-{\hat {B}}{\hat {A}},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9814a77ea436e956fd7abaad7b5906457037b565)
![{\displaystyle \sigma _{A}\sigma _{B}\geq \left|{\frac {1}{2i}}\langle [{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}]\rangle \right|={\frac {1}{2}}\left|\langle [{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}]\rangle \right|,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2e237cc47d6a6ffaf614f696672356c362f84ac0)
![{\displaystyle \sigma _{A}^{2}\sigma _{B}^{2}\geq \left|{\frac {1}{2}}\langle \{{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}\}\rangle -\langle {\hat {A}}\rangle \langle {\hat {B}}\rangle \right|^{2}+\left|{\frac {1}{2i}}\langle [{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}]\rangle \right|^{2},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/81d7a893fe43757553fb6a3e5a51cdb83290aadd)



















![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\langle f\mid g\rangle &=\langle \Psi |({\hat {A}}-\langle {\hat {A}}\rangle )({\hat {B}}-\langle {\hat {B}}\rangle )\Psi \rangle \\[4pt]&=\langle \Psi \mid ({\hat {A}}{\hat {B}}-{\hat {A}}\langle {\hat {B}}\rangle -{\hat {B}}\langle {\hat {A}}\rangle +\langle {\hat {A}}\rangle \langle {\hat {B}}\rangle )\Psi \rangle \\[4pt]&=\langle \Psi \mid {\hat {A}}{\hat {B}}\Psi \rangle -\langle \Psi \mid {\hat {A}}\langle {\hat {B}}\rangle \Psi \rangle -\langle \Psi \mid {\hat {B}}\langle {\hat {A}}\rangle \Psi \rangle +\langle \Psi \mid \langle {\hat {A}}\rangle \langle {\hat {B}}\rangle \Psi \rangle \\[4pt]&=\langle {\hat {A}}{\hat {B}}\rangle -\langle {\hat {A}}\rangle \langle {\hat {B}}\rangle -\langle {\hat {A}}\rangle \langle {\hat {B}}\rangle +\langle {\hat {A}}\rangle \langle {\hat {B}}\rangle \\[4pt]&=\langle {\hat {A}}{\hat {B}}\rangle -\langle {\hat {A}}\rangle \langle {\hat {B}}\rangle .\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e8c0c05428ab53be785878d1546c265c45c6e755)

![{\displaystyle \langle f\mid g\rangle -\langle g\mid f\rangle =\langle {\hat {A}}{\hat {B}}\rangle -\langle {\hat {A}}\rangle \langle {\hat {B}}\rangle -\langle {\hat {B}}{\hat {A}}\rangle +\langle {\hat {A}}\rangle \langle {\hat {B}}\rangle =\langle [{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}]\rangle }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/eaf12a5caf8e73c4e1cfdfbbf3ebb1c3e32e7e0f)

![{\displaystyle |\langle f\mid g\rangle |^{2}={\Big (}{\frac {1}{2}}\langle \{{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}\}\rangle -\langle {\hat {A}}\rangle \langle {\hat {B}}\rangle {\Big )}^{2}+{\Big (}{\frac {1}{2i}}\langle [{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}]\rangle {\Big )}^{2}\,.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/074cd206c3b6789fd747fa2efa892ea596651470)
![{\displaystyle \sigma _{A}\sigma _{B}\geq {\sqrt {{\Big (}{\frac {1}{2}}\langle \{{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}\}\rangle -\langle {\hat {A}}\rangle \langle {\hat {B}}\rangle {\Big )}^{2}+{\Big (}{\frac {1}{2i}}\langle [{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}]\rangle {\Big )}^{2}}}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/96a2a724edaa3e9b3e175f7de8158b796bef58c0)

![{\displaystyle \sigma _{A}^{2}\sigma _{B}^{2}\geq \left|{\frac {1}{2}}\operatorname {tr} (\rho \{A,B\})-\operatorname {tr} (\rho A)\operatorname {tr} (\rho B)\right|^{2}+\left|{\frac {1}{2i}}\operatorname {tr} (\rho [A,B])\right|^{2}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c8271822251517d5a4e6879ea287fd36556a95e8)


![{\displaystyle \sigma _{A}^{2}+\sigma _{B}^{2}\geq \pm i\langle \Psi \mid [A,B]|\Psi \rangle +\mid \langle \Psi \mid (A\pm iB)\mid {\bar {\Psi }}\rangle |^{2},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/fe87035b4463c5578ccda71d74b8e7c9fd627515)




![{\displaystyle \pm i\langle \Psi \mid [A,B]\mid \Psi \rangle }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3a34a5250780e2a23b4befafff39d5522cc8266c)









![{\displaystyle \sigma _{A}^{2}\sigma _{B}^{2}\geq \left[\sum _{k}p_{k}L(\varrho _{k})\right]^{2},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/fe2197885d47337c2e848acc051efdea71b02870)
![{\displaystyle L(\varrho )={\sqrt {\left|{\frac {1}{2}}\operatorname {tr} (\rho \{A,B\})-\operatorname {tr} (\rho A)\operatorname {tr} (\rho B)\right|^{2}+\left|{\frac {1}{2i}}\operatorname {tr} (\rho [A,B])\right|^{2}}}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9217563cc15d7b37797888126f4b4c44b7f19c08)
![{\displaystyle \sigma _{A}^{2}\sigma _{B}^{2}\geq \left[\max _{p_{k},\varrho _{k}}\sum _{k}p_{k}L(\varrho _{k})\right]^{2},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/98f249b302c95aa4be14de7ec6f82ffb5f169d5e)
![{\displaystyle \sigma _{A}^{2}F_{Q}[\varrho ,B]\geq 4\left[\min _{p_{k},\Psi _{k}}\sum _{k}p_{k}L(\vert \Psi _{k}\rangle \langle \Psi _{k}\vert )\right]^{2}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/58902ccc3a0b70047c4db2a60db2c59e012fd34f)
![{\displaystyle F_{Q}[\varrho ,B]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7022310dbb24400e5c70f2a78e6f35633b161a2a)

![{\displaystyle \sigma _{A}^{2}F_{Q}[\varrho ,B]\geq \vert \langle i[A,B]\rangle \vert ^{2},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c25345e515fab68aaa473847b0f644f1d1b0965a)
![{\displaystyle F_{Q}[\varrho ,B]\leq 4\sigma _{B},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/76b697790877dcd32b480f16ef3565113c062e83)






![{\displaystyle [{\hat {x}},{\hat {p}}]=i\hbar }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/42dbbd0db710385288536bcf4f4a1b7cceb75d9a)


![{\displaystyle [J_{x},J_{y}]=i\hbar \varepsilon _{xyz}J_{z}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/92feb40a1e1bb732beffa55c687ccfbcec8ff007)







![{\displaystyle [0,2\pi ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/348d40bf3f8b7e1c00c4346440d7e2e4f0cc9b91)
![{\displaystyle {\hat {A}}\psi (\theta )=\theta \psi (\theta ),\quad \theta \in [0,2\pi ],}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f85b2a63d69030bd4deabafe7641563413b8ec23)


![{\displaystyle [{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}]=i\hbar }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ac8c6748f07eed66c5b329fcebdb8ca9d859ff71)














![{\displaystyle \varepsilon _{A}\,\eta _{B}+\varepsilon _{A}\,\sigma _{B}+\sigma _{A}\,\eta _{B}\,\geq \,{\frac {1}{2}}\,\left|{\Bigl \langle }{\bigl [}{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}{\bigr ]}{\Bigr \rangle }\right|}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e07b031a15d10a6380f7ee47da5c5c1dfb93e31a)
![{\displaystyle \varepsilon _{A}\,\eta _{B}\,\geq \,{\frac {1}{2}}\,\left|{\Bigl \langle }{\bigl [}{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}{\bigr ]}{\Bigr \rangle }\right|}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/28d08057de34306115c996b9943fb0603282befc)

![{\displaystyle \varepsilon _{A}\,\varepsilon _{B}\,\geq \,{\frac {1}{2}}\,\left|{\Bigl \langle }{\bigl [}{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}{\bigr ]}{\Bigr \rangle }\right|}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8f93231686a00ca50485a5eccdadddfbc4f6b2c3)
![{\displaystyle \sigma _{A}\,\sigma _{B}\,\geq \,{\frac {1}{2}}\,\left|{\Bigl \langle }{\bigl [}{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}{\bigr ]}{\Bigr \rangle }\right|}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1606cabaad53903e8110417fff05ebda20a2dd41)
![{\displaystyle \varepsilon _{A}\eta _{B}+\varepsilon _{A}\,\sigma _{B}+\sigma _{A}\,\eta _{B}+\sigma _{A}\sigma _{B}\geq \left|{\Bigl \langle }{\bigl [}{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}{\bigr ]}{\Bigr \rangle }\right|.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/99801a6fd6e9d9f36223cce7aba8a30cf39e6230)
![{\displaystyle (\varepsilon _{A}+\sigma _{A})\,(\eta _{B}+\sigma _{B})\,\geq \,\left|{\Bigl \langle }{\bigl [}{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}{\bigr ]}{\Bigr \rangle }\right|.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8ec1acc4af7b675c838b09fc719057c5d16819c4)


![{\displaystyle {\bar {\varepsilon }}_{A}\,{\bar {\eta }}_{B}\,\geq \,\left|{\Bigl \langle }{\bigl [}{\hat {A}},{\hat {B}}{\bigr ]}{\Bigr \rangle }\right|}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bb507c6e7fa92a94bfb07f979999ccbb5ac7450a)














![{\displaystyle \operatorname {P} [x_{j}]=\int _{(j-1/2)\delta x-c}^{(j+1/2)\delta x-c}|\psi (x)|^{2}\,dx}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b7c173529c81593fd8c2e56a4e1af15f369c365c)
![{\displaystyle H_{x}=-\sum _{j=-\infty }^{\infty }\operatorname {P} [x_{j}]\ln \operatorname {P} [x_{j}].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/25c2fd9ede05e0615e6eff1a8f2ace626debd818)






![{\displaystyle \sigma _{J_{x}}^{2}+\sigma _{J_{y}}^{2}+F_{Q}[\varrho ,J_{z}]/4\geq j,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d8a1b42fce2b1dd5c19fff569af0ffa3207ed373)
![{\displaystyle F_{Q}[\varrho ,J_{z}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7f630b4c044755b6f4d96b917992e2c23910f7b9)


































