Torrent, also referred to simply as torrent, is a communication protocol for peer-to-peer file sharing (P2P), which enables users to distribute data and electronic files over the Internet in a decentralized manner. The protocol is developed and maintained by Rainberry, Inc., and was first released in 2001.
To send or receive files, users use a BitTorrent client on their Internet-connected computer, which are available for a variety of computing platforms and operating systems, including an official client. BitTorrent trackers provide a list of files available for transfer and allow the client to find peer users, known as "seeds", who may transfer the files. BitTorrent downloading is considered to be faster than HTTP ("direct downloading") and FTP due to the lack of a central server that could limit bandwidth.
BitTorrent is one of the most common protocols for transferring large files, such as digital video files containing TV shows and video clips, or digital audio files. BitTorrent accounted for a third of all internet traffic in 2004, according to a study by Cachelogic. As recently as 2019 BitTorrent remained a significant file sharing protocol according to Sandvine, generating a substantial amount of Internet traffic, with 2.46% of downstream, and 27.58% of upstream traffic, although this share has declined significantly since then.
History
Programmer Bram Cohen, a University at Buffalo alumnus, designed the protocol in April 2001, and released the first available version on 2 July 2001. Cohen and Ashwin Navin founded BitTorrent, Inc. (later renamed Rainberry, Inc.) to further develop the technology in 2004.
The first release of the BitTorrent client had no search engine and no peer exchange. Up until 2005, the only way to share files was by creating a small text file called a "torrent", that they would upload to a torrent index site. The first uploader acted as a seed, and downloaders would initially connect as peers. Those who wish to download the file would download the torrent, which their client would use to connect to a tracker which had a list of the IP addresses of other seeds and peers in the swarm. Once a peer completed a download of the complete file, it could in turn function as a seed. These files contain metadata about the files to be shared and the trackers which keep track of the other seeds and peers.
In 2005, first Vuze and then the BitTorrent client introduced distributed tracking using distributed hash tables which allowed clients to exchange data on swarms directly without the need for a torrent file.
In 2006, peer exchange functionality was added allowing clients to add peers based on the data found on connected nodes.
In 2017, BitTorrent, Inc. released the BitTorrent v2 protocol specification. BitTorrent v2 is intended to work seamlessly with previous versions of the BitTorrent protocol. The main reason for the update was that the old cryptographic hash function, SHA-1, is no longer considered safe from malicious attacks by the developers, and as such, v2 uses SHA-256. To ensure backwards compatibility, the v2 .torrent file format supports a hybrid mode where the torrents are hashed through both the new method and the old method, with the intent that the files will be shared with peers on both v1 and v2 swarms. Another update to the specification is adding a hash tree to speed up time from adding a torrent to downloading files, and to allow more granular checks for file corruption. In addition, each file is now hashed individually, enabling files in the swarm to be deduplicated, so that if multiple torrents include the same files, but seeders are only seeding the file from some, downloaders of the other torrents can still download the file. In addition, file hashes can be displayed on tracker, torrent indexing services, to search for swarms by searching for hashes of files contained in them. These hashes are different from the usual SHA-256 hash of files and can be obtained using tools. Magnet links for v2 also support a hybrid mode to ensure support for legacy clients.
Design

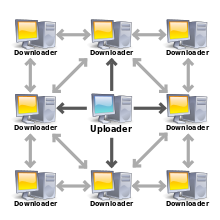
The BitTorrent protocol can be used to reduce the server and network impact of distributing large files. Rather than downloading a file from a single source server, the BitTorrent protocol allows users to join a "swarm" of hosts to upload and download from each other simultaneously. The protocol is an alternative to the older single source, multiple mirror sources technique for distributing data, and can work effectively over networks with lower bandwidth. Using the BitTorrent protocol, several basic computers, such as home computers, can replace large servers while efficiently distributing files to many recipients. This lower bandwidth usage also helps prevent large spikes in internet traffic in a given area, keeping internet speeds higher for all users in general, regardless of whether or not they use the BitTorrent protocol.
The file being distributed is divided into segments called pieces. As each peer receives a new piece of the file, it becomes a source (of that piece) for other peers, relieving the original seed from having to send that piece to every computer or user wishing a copy. With BitTorrent, the task of distributing the file is shared by those who want it; it is entirely possible for the seed to send only a single copy of the file itself and eventually distribute to an unlimited number of peers. Each piece is protected by a cryptographic hash contained in the torrent descriptor. This ensures that any modification of the piece can be reliably detected, and thus prevents both accidental and malicious modifications of any of the pieces received at other nodes. If a node starts with an authentic copy of the torrent descriptor, it can verify the authenticity of the entire file it receives.
Pieces are typically downloaded non-sequentially, and are rearranged into the correct order by the BitTorrent client, which monitors which pieces it needs, and which pieces it has and can upload to other peers. Pieces are of the same size throughout a single download (for example, a 10 MB file may be transmitted as ten 1 MB pieces or as forty 256 KB pieces). Due to the nature of this approach, the download of any file can be halted at any time and be resumed at a later date, without the loss of previously downloaded information, which in turn makes BitTorrent particularly useful in the transfer of larger files. This also enables the client to seek out readily available pieces and download them immediately, rather than halting the download and waiting for the next (and possibly unavailable) piece in line, which typically reduces the overall time of the download. This eventual transition from peers to seeders determines the overall "health" of the file (as determined by the number of times a file is available in its complete form).
The distributed nature of BitTorrent can lead to a flood-like spreading of a file throughout many peer computer nodes. As more peers join the swarm, the likelihood of a successful download by any particular node increases. Relative to traditional Internet distribution schemes, this permits a significant reduction in the original distributor's hardware and bandwidth resource costs. Distributed downloading protocols in general provide redundancy against system problems, reduce dependence on the original distributor, and provide sources for the file which are generally transient and therefore there is no single point of failure as in one way server-client transfers.
Though both ultimately transfer files over a network, a BitTorrent download differs from a one way server-client download (as is typical with an HTTP or FTP request, for example) in several fundamental ways:
- BitTorrent makes many small data requests over different IP connections to different machines, while server-client downloading is typically made via a single TCP connection to a single machine.
- BitTorrent downloads in a random or in a "rarest-first" approach that ensures high availability, while classic downloads are sequential.
Taken together, these differences allow BitTorrent to achieve much lower cost to the content provider, much higher redundancy, and much greater resistance to abuse or to "flash crowds" than regular server software. However, this protection, theoretically, comes at a cost: downloads can take time to rise to full speed because it may take time for enough peer connections to be established, and it may take time for a node to receive sufficient data to become an effective uploader. This contrasts with regular downloads (such as from an HTTP server, for example) that, while more vulnerable to overload and abuse, rise to full speed very quickly, and maintain this speed throughout. In the beginning, BitTorrent's non-contiguous download methods made it harder to support "streaming playback". In 2014, the client Popcorn Time allowed for streaming of BitTorrent video files. Since then, more and more clients are offering streaming options.
Searching
The BitTorrent protocol provides no way to index torrent files. As a result, a comparatively small number of websites have hosted a large majority of torrents, many linking to copyrighted works without the authorization of copyright holders, rendering those sites especially vulnerable to lawsuits. A BitTorrent index is a "list of .torrent files, which typically includes descriptions" and information about the torrent's content. Several types of websites support the discovery and distribution of data on the BitTorrent network. Public torrent-hosting sites such as The Pirate Bay allow users to search and download from their collection of torrent files. Users can typically also upload torrent files for content they wish to distribute. Often, these sites also run BitTorrent trackers for their hosted torrent files, but these two functions are not mutually dependent: a torrent file could be hosted on one site and tracked by another unrelated site. Private host/tracker sites operate like public ones except that they may restrict access to registered users and may also keep track of the amount of data each user uploads and downloads, in an attempt to reduce "leeching".
Web search engines allow the discovery of torrent files that are hosted and tracked on other sites; examples include The Pirate Bay and BTDigg. These sites allow the user to ask for content meeting specific criteria (such as containing a given word or phrase) and retrieve a list of links to torrent files matching those criteria. This list can often be sorted with respect to several criteria, relevance (seeders to leechers ratio) being one of the most popular and useful (due to the way the protocol behaves, the download bandwidth achievable is very sensitive to this value). Metasearch engines allow one to search several BitTorrent indices and search engines at once.
The Tribler BitTorrent client was among the first to incorporate built-in search capabilities. With Tribler, users can find .torrent files held by random peers and taste buddies. It adds such an ability to the BitTorrent protocol using a gossip protocol, somewhat similar to the eXeem network which was shut down in 2005. The software includes the ability to recommend content as well. After a dozen downloads, the Tribler software can roughly estimate the download taste of the user, and recommend additional content.
In May 2007, researchers at Cornell University published a paper proposing a new approach to searching a peer-to-peer network for inexact strings, which could replace the functionality of a central indexing site. A year later, the same team implemented the system as a plugin for Vuze called Cubit and published a follow-up paper reporting its success.
A somewhat similar facility but with a slightly different approach is provided by the BitComet client through its "Torrent Exchange" feature. Whenever two peers using BitComet (with Torrent Exchange enabled) connect to each other they exchange lists of all the torrents (name and info-hash) they have in the Torrent Share storage (torrent files which were previously downloaded and for which the user chose to enable sharing by Torrent Exchange). Thus each client builds up a list of all the torrents shared by the peers it connected to in the current session (or it can even maintain the list between sessions if instructed).
At any time the user can search into that Torrent Collection list for a certain torrent and sort the list by categories. When the user chooses to download a torrent from that list, the .torrent file is automatically searched for (by info-hash value) in the DHT Network and when found it is downloaded by the querying client which can subsequently create and initiate a downloading task.
Downloading and sharing
Users find a torrent of interest on a torrent index site or by using a search engine built into the client, download it, and open it with a BitTorrent client. The client connects to the tracker(s) or seeds specified in the torrent file, from which it receives a list of seeds and peers currently transferring pieces of the file(s). The client connects to those peers to obtain the various pieces. If the swarm contains only the initial seeder, the client connects directly to it, and begins to request pieces. Clients incorporate mechanisms to optimize their download and upload rates.
The effectiveness of this data exchange depends largely on the policies that clients use to determine to whom to send data. Clients may prefer to send data to peers that send data back to them (a "tit for tat" exchange scheme), which encourages fair trading. But strict policies often result in suboptimal situations, such as when newly joined peers are unable to receive any data because they do not have any pieces yet to trade themselves or when two peers with a good connection between them do not exchange data simply because neither of them takes the initiative. To counter these effects, the official BitTorrent client program uses a mechanism called "optimistic unchoking", whereby the client reserves a portion of its available bandwidth for sending pieces to random peers (not necessarily known good partners, or "preferred peers") in hopes of discovering even better partners and to ensure that newcomers get a chance to join the swarm.
Although "swarming" scales well to tolerate "flash crowds" for popular content, it is less useful for unpopular or niche market content. Peers arriving after the initial rush might find the content unavailable and need to wait for the arrival of a "seed" in order to complete their downloads. The seed arrival, in turn, may take long to happen (this is termed the "seeder promotion problem"). Since maintaining seeds for unpopular content entails high bandwidth and administrative costs, this runs counter to the goals of publishers that value BitTorrent as a cheap alternative to a client-server approach. This occurs on a huge scale; measurements have shown that 38% of all new torrents become unavailable within the first month. A strategy adopted by many publishers which significantly increases availability of unpopular content consists of bundling multiple files in a single swarm. More sophisticated solutions have also been proposed; generally, these use cross-torrent mechanisms through which multiple torrents can cooperate to better share content.
Creating and publishing
The peer distributing a data file treats the file as a number of identically sized pieces, usually with byte sizes of a power of 2, and typically between 32 KB and 16 MB each. The peer creates a hash for each piece, using the SHA-1 hash function, and records it in the torrent file. Pieces with sizes greater than 512 KB will reduce the size of a torrent file for a very large payload, but is claimed to reduce the efficiency of the protocol. When another peer later receives a particular piece, the hash of the piece is compared to the recorded hash to test that the piece is error-free. Peers that provide a complete file are called seeders, and the peer providing the initial copy is called the initial seeder. The exact information contained in the torrent file depends on the version of the BitTorrent protocol.
By convention, the name of a torrent file has the suffix .torrent. Torrent files use the Bencode file format, and contain an "announce" section, which specifies the URL of the tracker, and an "info" section, containing (suggested) names for the files, their lengths, the piece length used, and a SHA-1 hash code
for each piece, all of which are used by clients to verify the
integrity of the data they receive. Though SHA-1 has shown signs of
cryptographic weakness, Bram Cohen did not initially consider the risk
big enough for a backward incompatible change to, for example, SHA-3. As of BitTorrent v2 the hash function has been updated to SHA-256.
In the early days, torrent files were typically published to torrent index websites, and registered with at least one tracker. The tracker maintained lists of the clients currently connected to the swarm. Alternatively, in a trackerless system (decentralized tracking) every peer acts as a tracker. Azureus was the first BitTorrent client to implement such a system through the distributed hash table (DHT) method. An alternative and incompatible DHT system, known as Mainline DHT, was released in the Mainline BitTorrent client three weeks later (though it had been in development since 2002) and subsequently adopted by the μTorrent, Transmission, rTorrent, KTorrent, BitComet, and Deluge clients.
After the DHT was adopted, a "private" flag – analogous to the broadcast flag – was unofficially introduced, telling clients to restrict the use of decentralized tracking regardless of the user's desires. The flag is intentionally placed in the info section of the torrent so that it cannot be disabled or removed without changing the identity of the torrent. The purpose of the flag is to prevent torrents from being shared with clients that do not have access to the tracker. The flag was requested for inclusion in the official specification in August 2008, but has not been accepted yet. Clients that have ignored the private flag were banned by many trackers, discouraging the practice.
Anonymity
BitTorrent does not, on its own, offer its users anonymity. One can usually see the IP addresses of all peers in a swarm in one's own client or firewall program. This may expose users with insecure systems to attacks. In some countries, copyright organizations scrape lists of peers, and send takedown notices to the internet service provider of users participating in the swarms of files that are under copyright. In some jurisdictions, copyright holders may launch lawsuits against uploaders or downloaders for infringement, and police may arrest suspects in such cases.
Various means have been used to promote anonymity. For example, the BitTorrent client Tribler makes available a Tor-like onion network, optionally routing transfers through other peers to obscure which client has requested the data. The exit node would be visible to peers in a swarm, but the Tribler organization provides exit nodes. One advantage of Tribler is that clearnet torrents can be downloaded with only a small decrease in download speed from one "hop" of routing.
i2p provides a similar anonymity layer although in that case, one can only download torrents that have been uploaded to the i2p network. The bittorrent client Vuze allows users who are not concerned about anonymity to take clearnet torrents, and make them available on the i2p network.
Most BitTorrent clients are not designed to provide anonymity when used over Tor, and there is some debate as to whether torrenting over Tor acts as a drag on the network.
Private torrent trackers are usually invitation only, and require members to participate in uploading, but have the downside of a single centralized point of failure. Oink's Pink Palace and What.cd are examples of private trackers which have been shut down.
Seedbox services download the torrent files first to the company's servers, allowing the user to direct download the file from there. One's IP address would be visible to the Seedbox provider, but not to third parties.
Virtual private networks encrypt transfers, and substitute a different IP address for the user's, so that anyone monitoring a torrent swarm will only see that address.
Associated technologies
Distributed trackers
On 2 May 2005, Azureus 2.3.0.0 (now known as Vuze) was released, utilizing a distributed database system. This system is a distributed hash table implementation which allows the client to use torrents that do not have a working BitTorrent tracker. A bootstrap server is instead utilized. The following month, BitTorrent, Inc. released version 4.2.0 of the Mainline BitTorrent client, which supported an alternative DHT implementation (popularly known as "Mainline DHT", outlined in a draft on their website) that is incompatible with that of Azureus. In 2014, measurement showed concurrent users of Mainline DHT to be from 10 million to 25 million, with a daily churn of at least 10 million.
Current versions of the official BitTorrent client, μTorrent, BitComet, Transmission and BitSpirit all share compatibility with Mainline DHT. Both DHT implementations are based on Kademlia. As of version 3.0.5.0, Azureus also supports Mainline DHT in addition to its own distributed database through use of an optional application plugin. This potentially allows the Azureus/Vuze client to reach a bigger swarm.
Another idea that has surfaced in Vuze is that of virtual torrents. This idea is based on the distributed tracker approach and is used to describe some web resource. Currently, it is used for instant messaging. It is implemented using a special messaging protocol and requires an appropriate plugin. Anatomic P2P is another approach, which uses a decentralized network of nodes that route traffic to dynamic trackers. Most BitTorrent clients also use peer exchange (PEX) to gather peers in addition to trackers and DHT. Peer exchange checks with known peers to see if they know of any other peers. With the 3.0.5.0 release of Vuze, all major BitTorrent clients now have compatible peer exchange.
Web seeding
Web "seeding" was implemented in 2006 as the ability of BitTorrent clients to download torrent pieces from an HTTP source in addition to the "swarm". The advantage of this feature is that a website may distribute a torrent for a particular file or batch of files and make those files available for download from that same web server; this can simplify long-term seeding and load balancing through the use of existing, cheap, web hosting setups. In theory, this would make using BitTorrent almost as easy for a web publisher as creating a direct HTTP download. In addition, it would allow the "web seed" to be disabled if the swarm becomes too popular while still allowing the file to be readily available. This feature has two distinct specifications, both of which are supported by Libtorrent and the 26+ clients that use it.
The first was created by John "TheSHAD0W" Hoffman, who created BitTornado. This first specification requires running a web service that serves content by info-hash and piece number, rather than filename.
The other specification is created by GetRight authors and can rely on a basic HTTP download space (using byte serving).
In September 2010, a new service named Burnbit was launched which generates a torrent from any URL using webseeding. There are server-side solutions that provide initial seeding of the file from the web server via standard BitTorrent protocol and when the number of external seeders reach a limit, they stop serving the file from the original source.
RSS feeds
A technique called broadcatching combines RSS feeds with the BitTorrent protocol to create a content delivery system, further simplifying and automating content distribution. Steve Gillmor explained the concept in a column for Ziff-Davis in December 2003. The discussion spread quickly among bloggers (Ernest Miller, Chris Pirillo, etc.). In an article entitled Broadcatching with BitTorrent, Scott Raymond explained:
I want RSS feeds of BitTorrent files. A script would periodically check the feed for new items, and use them to start the download. Then, I could find a trusted publisher of an Alias RSS feed, and "subscribe" to all new episodes of the show, which would then start downloading automatically – like the "season pass" feature of the TiVo.
— Scott Raymond, scottraymond.net
The RSS feed will track the content, while BitTorrent ensures content integrity with cryptographic hashing of all data, so feed subscribers will receive uncorrupted content. One of the first and popular software clients (free and open source) for broadcatching is Miro. Other free software clients such as PenguinTV and KatchTV are also now supporting broadcatching. The BitTorrent web-service MoveDigital added the ability to make torrents available to any web application capable of parsing XML through its standard REST-based interface in 2006, though this has since been discontinued. Additionally, Torrenthut is developing a similar torrent API that will provide the same features, and help bring the torrent community to Web 2.0 standards. Alongside this release is a first PHP application built using the API called PEP, which will parse any Really Simple Syndication (RSS 2.0) feed and automatically create and seed a torrent for each enclosure found in that feed.
Throttling and encryption
Since BitTorrent makes up a large proportion of total traffic, some ISPs have chosen to "throttle" (slow down) BitTorrent transfers. For this reason, methods have been developed to disguise BitTorrent traffic in an attempt to thwart these efforts. Protocol header encrypt (PHE) and Message stream encryption/Protocol encryption (MSE/PE) are features of some BitTorrent clients that attempt to make BitTorrent hard to detect and throttle. As of November 2015, Vuze, BitComet, KTorrent, Transmission, Deluge, μTorrent, MooPolice, Halite, qBittorrent, rTorrent, and the latest official BitTorrent client (v6) support MSE/PE encryption.
In August 2007, Comcast was preventing BitTorrent seeding by monitoring and interfering with the communication between peers. Protection against these efforts is provided by proxying the client-tracker traffic via an encrypted tunnel to a point outside of the Comcast network. In 2008, Comcast called a "truce" with BitTorrent, Inc. with the intention of shaping traffic in a protocol-agnostic manner. Questions about the ethics and legality of Comcast's behavior have led to renewed debate about net neutrality in the United States. In general, although encryption can make it difficult to determine what is being shared, BitTorrent is vulnerable to traffic analysis. Thus, even with MSE/PE, it may be possible for an ISP to recognize BitTorrent and also to determine that a system is no longer downloading but only uploading data, and terminate its connection by injecting TCP RST (reset flag) packets.
Multitrackers
Another unofficial feature is an extension to the BitTorrent metadata format proposed by John Hoffman and implemented by several indexing websites. It allows the use of multiple trackers per file, so if one tracker fails, others can continue to support file transfer. It is implemented in several clients, such as BitComet, BitTornado, BitTorrent, KTorrent, Transmission, Deluge, μTorrent, rtorrent, Vuze, and Frostwire. Trackers are placed in groups, or tiers, with a tracker randomly chosen from the top tier and tried, moving to the next tier if all the trackers in the top tier fail.
Torrents with multiple trackers can decrease the time it takes to download a file, but also have a few consequences:
- Poorly implemented clients may contact multiple trackers, leading to more overhead-traffic.
- Torrents from closed trackers suddenly become downloadable by non-members, as they can connect to a seed via an open tracker.
Peer selection
As of December 2008, BitTorrent, Inc. was working with Oversi on new Policy Discover Protocols that query the ISP for capabilities and network architecture information. Oversi's ISP hosted NetEnhancer box is designed to "improve peer selection" by helping peers find local nodes, improving download speeds while reducing the loads into and out of the ISP's network.
Implementations
The BitTorrent specification is free to use and many clients are open source, so BitTorrent clients have been created for all common operating systems using a variety of programming languages. The official BitTorrent client, μTorrent, qBittorrent, Transmission, Vuze, and BitComet are some of the most popular clients.
Some BitTorrent implementations such as MLDonkey and Torrentflux are designed to run as servers. For example, this can be used to centralize file sharing on a single dedicated server which users share access to on the network. Server-oriented BitTorrent implementations can also be hosted by hosting providers at co-located facilities with high bandwidth Internet connectivity (e.g., a datacenter) which can provide dramatic speed benefits over using BitTorrent from a regular home broadband connection. Services such as ImageShack can download files on BitTorrent for the user, allowing them to download the entire file by HTTP once it is finished.
The Opera web browser supports BitTorrent natively. Brave web browser ships with an extension which supports WebTorrent, a BitTorrent-like protocol based on WebRTC instead of UDP and TCP. BitLet allowed users to download Torrents directly from their browser using a Java applet (until browsers removed support for Java applets). An increasing number of hardware devices are being made to support BitTorrent. These include routers and NAS devices containing BitTorrent-capable firmware like OpenWrt. Proprietary versions of the protocol which implement DRM, encryption, and authentication are found within managed clients such as Pando.
Adoption
A growing number of individuals and organizations are using BitTorrent to distribute their own or licensed works (e.g. indie bands distributing digital files of their new songs). Independent adopters report that BitTorrent technology reduces demands on private networking hardware and bandwidth, an essential for non-profit groups with large amounts of internet traffic.
Many major open source and free software projects encourage BitTorrent as well as conventional downloads of their products (via HTTP, FTP etc.) to increase availability and to reduce load on their own servers, especially when dealing with larger files. In addition, some video game installers, especially those whose large size makes them difficult to host due to bandwidth limits, extremely frequent downloads, and unpredictable changes in network traffic, will distribute instead a specialized, stripped down BitTorrent client with enough functionality to download the game from the other running clients and the primary server (which is maintained in case not enough peers are available).
Some uses of BitTorrent for file sharing may violate laws in some jurisdictions (see legislation section).
Popularity and traffic statistics
As of January 2012, BitTorrent is utilized by 150 million active users. Based on this figure, the total number of monthly users may be estimated to more than a quarter of a billion (≈ 250 million). As of February 2013, BitTorrent was responsible for 3.35% of all worldwide bandwidth—more than half of the 6% of total bandwidth dedicated to file sharing. As of 2013, BitTorrent had 15–27 million concurrent users at any time.
Film, video, and music
- BitTorrent Inc. has obtained a number of licenses from Hollywood studios for distributing popular content from their websites.
- Sub Pop Records releases tracks and videos via BitTorrent Inc. to distribute its 1000+ albums. Babyshambles and The Libertines (both bands associated with Pete Doherty) have extensively used torrents to distribute hundreds of demos and live videos. US industrial rock band Nine Inch Nails frequently distributes albums via BitTorrent.
- Podcasting software has integrated BitTorrent to help podcasters deal with the download demands of their MP3 "radio" programs. Specifically, Juice and Miro (formerly known as Democracy Player) support automatic processing of .torrent files from RSS feeds. Similarly, some BitTorrent clients, such as μTorrent, are able to process web feeds and automatically download content found within them.
- DGM Live purchases are provided via BitTorrent.
- VODO, a service which distributes "free-to-share" movies and TV shows via BitTorrent.
Broadcasters
- In 2008, the CBC became the first public broadcaster in North America to make a full show (Canada's Next Great Prime Minister) available for download using BitTorrent.
- The Norwegian Broadcasting Corporation (NRK) has since March 2008 experimented with bittorrent distribution, available online. Only selected works in which NRK owns all royalties are published. Responses have been very positive, and NRK is planning to offer more content.
- The Dutch VPRO broadcasting organization released four documentaries in 2009 and 2010 under a Creative Commons license using the content distribution feature of the Mininova tracker.
Cloud Service Providers
- The Amazon AWS's Simple Storage Service (S3), until April 29, 2021, had supported sharing of bucket objects with BitTorrent protocols. As of June 13, 2020, the feature is only available in service regions launched after May 30, 2016. The feature for the existing customers will be extended for an additional 12 months following the deprecation. After April 29, 2022, BitTorrent clients will no longer connect to Amazon S3.
Software
- Blizzard Entertainment uses BitTorrent (via its Blizzard Battle.net distribution platform, formerly the "Blizzard Downloader") to distribute content and patches for Diablo III, StarCraft II and World of Warcraft, including the games themselves.
- Wargaming uses BitTorrent in their popular titles World of Tanks, World of Warships and World of Warplanes to distribute game updates.
- CCP Games, maker of the space simulation MMORPG Eve Online, has announced that a new launcher will be released that is based on BitTorrent.
- Resilio Sync is a BitTorrent-based folder-syncing tool which can act as an alternative to server-based synchronisation services such as Dropbox.
Government
- The British government used BitTorrent to distribute details about how the tax money of British citizens was spent.
Education
- Florida State University uses BitTorrent to distribute large scientific data sets to its researchers.
- Many universities that have BOINC distributed computing projects have used the BitTorrent functionality of the client-server system to reduce the bandwidth costs of distributing the client-side applications used to process the scientific data. If a BOINC distributed computing application needs to be updated (or merely sent to a user), it can do so with little impact on the BOINC server.
- The developing Human Connectome Project uses BitTorrent to share their open dataset.
- Academic Torrents is a BitTorrent tracker for use by researchers in fields that need to share large datasets.
Others
- Facebook uses BitTorrent to distribute updates to Facebook servers.
- Twitter uses BitTorrent to distribute updates to Twitter servers.
- The Internet Archive added BitTorrent to its file download options for over 1.3 million existing files, and all newly uploaded files, in August 2012. This method is the fastest means of downloading media from the Archive.
By early 2015, AT&T estimated that BitTorrent accounted for 20% of all broadband traffic.
Routers that use network address translation (NAT) must maintain tables of source and destination IP addresses and ports. Because BitTorrent frequently contacts 20–30 servers per second, the NAT tables of some consumer-grade routers are rapidly filled. This is a known cause of some home routers ceasing to work correctly.
Legislation
Although the protocol itself is legal, problems stem from using the protocol to traffic copyright infringing works, since BitTorrent is often used to download otherwise paid content, such as movies and video games. There has been much controversy over the use of BitTorrent trackers. BitTorrent metafiles themselves do not store file contents. Whether the publishers of BitTorrent metafiles violate copyrights by linking to copyrighted works without the authorization of copyright holders is controversial. Various jurisdictions have pursued legal action against websites that host BitTorrent trackers.
As a result the use of BitTorrent may sometimes be limited by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) due to legal or copyright grounds. Users may choose to run seedboxes or virtual private networks (VPNs) to circumvent these restrictions.
High-profile examples include the closing of Suprnova.org, TorrentSpy, LokiTorrent, BTJunkie, Mininova, Oink's Pink Palace and What.cd. BitTorrent search engine The Pirate Bay torrent website, formed by a Swedish group, is noted for the "legal" section of its website in which letters and replies on the subject of alleged copyright infringements are publicly displayed. On 31 May 2006, The Pirate Bay's servers in Sweden were raided by Swedish police on allegations by the MPAA of copyright infringement; however, the tracker was up and running again three days later. In the study used to value NBC Universal in its merger with Comcast, Envisional examined the 10,000 torrent swarms managed by PublicBT which had the most active downloaders. After excluding pornographic and unidentifiable content, it was found that only one swarm offered legitimate content.
In the United States, more than 200,000 lawsuits have been filed for copyright infringement on BitTorrent since 2010. In the United Kingdom, on 30 April 2012, the High Court of Justice ordered five ISPs to block The Pirate Bay.
Security
One concern is the UDP flood attack. BitTorrent implementations often use μTP for their communication. To achieve high bandwidths, the underlying protocol used is UDP, which allows spoofing of source addresses of internet traffic. It has been possible to carry out denial-of-service attacks in a P2P lab environment, where users running BitTorrent clients act as amplifiers for an attack at another service. However this is not always an effective attack because ISPs can check if the source address is correct.
Several studies on BitTorrent found files available for download containing malware. In particular, one small sample indicated that 18% of all executable programs available for download contained malware. Another study claims that as much as 14.5% of BitTorrent downloads contain zero-day malware, and that BitTorrent was used as the distribution mechanism for 47% of all zero-day malware they have found.