| Black Death | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Disease | Bubonic plague |
| Location | Eurasia and North Africa |
| Date | 1346–1353 |
Deaths | 25,000,000 – 50,000,000 (estimated) |
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as 50 million people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. The disease is caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis and spread by fleas and through the air. One of the most significant events in European history, the Black Death had far-reaching population, economic, and cultural impacts. It was the beginning of the second plague pandemic. The plague created religious, social and economic upheavals, with profound effects on the course of European history.
The origin of the Black Death is disputed. Genetic analysis suggests Yersinia pestis bacteria evolved approximately 7,000 years ago, at the beginning of the Neolithic, with flea-mediated strains emerging around 3,800 years ago during the late Bronze Age. The immediate territorial origins of the Black Death and its outbreak remain unclear, with some evidence pointing towards Central Asia, China, the Middle East, and Europe. The pandemic was reportedly first introduced to Europe during the siege of the Genoese trading port of Kaffa in Crimea by the Golden Horde army of Jani Beg in 1347. From Crimea, it was most likely carried by fleas living on the black rats that travelled on Genoese ships, spreading through the Mediterranean Basin and reaching North Africa, West Asia, and the rest of Europe via Constantinople, Sicily, and the Italian Peninsula. There is evidence that once it came ashore, the Black Death mainly spread from person-to-person as pneumonic plague, thus explaining the quick inland spread of the epidemic, which was faster than would be expected if the primary vector was rat fleas causing bubonic plague. In 2022, it was discovered that there was a sudden surge of deaths in what is today Kyrgyzstan from the Black Death in the late 1330s; when combined with genetic evidence, this implies that the initial spread may have been unrelated to the 14th century Mongol conquests previously postulated as the cause.
The Black Death was the second great natural disaster to strike Europe during the Late Middle Ages (the first one being the Great Famine of 1315–1317) and is estimated to have killed 30% to 60% of the European population, as well as approximately 33% of the population of the Middle East. There were further outbreaks throughout the Late Middle Ages and, also due to other contributing factors (the Crisis of the Late Middle Ages), the European population did not regain its 14th century level until the 16th century. Outbreaks of the plague recurred around the world until the early 19th century.
Names
European writers contemporary with the plague described the disease in Latin as pestis or pestilentia, 'pestilence'; epidemia, 'epidemic'; mortalitas, 'mortality'. In English prior to the 18th century, the event was called the "pestilence" or "great pestilence", "the plague" or the "great death".Subsequent to the pandemic "the furste moreyn" (first murrain) or "first pestilence" was applied, to distinguish the mid-14th century phenomenon from other infectious diseases and epidemics of plague.
The 1347 pandemic plague was not referred to specifically as "black" in the time of occurrence in any European language, though the expression "black death" had occasionally been applied to fatal disease beforehand. "Black death" was not used to describe the plague pandemic in English until the 1750s; the term is first attested in 1755, where it translated Danish: den sorte død, lit. 'the black death'. This expression as a proper name for the pandemic had been popularized by Swedish and Danish chroniclers in the 15th and early 16th centuries, and in the 16th and 17th centuries was transferred to other languages as a calque: Icelandic: svarti dauði, German: der schwarze Tod, and French: la mort noire. Previously, most European languages had named the pandemic a variant or calque of the Latin: magna mortalitas, lit. 'Great Death'.
The phrase 'black death' – describing Death as black – is very old. Homer used it in the Odyssey to describe the monstrous Scylla, with her mouths "full of black Death" (Ancient Greek: πλεῖοι μέλανος Θανάτοιο, romanized: pleîoi mélanos Thanátoio). Seneca the Younger may have been the first to describe an epidemic as 'black death', (Latin: mors atra) but only in reference to the acute lethality and dark prognosis of disease. The 12th–13th century French physician Gilles de Corbeil had already used atra mors to refer to a "pestilential fever" (febris pestilentialis) in his work On the Signs and Symptoms of Diseases (De signis et symptomatibus aegritudium). The phrase mors nigra, 'black death', was used in 1350 by Simon de Covino (or Couvin), a Belgian astronomer, in his poem "On the Judgement of the Sun at a Feast of Saturn" (De judicio Solis in convivio Saturni), which attributes the plague to an astrological conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn. His use of the phrase is not connected unambiguously with the plague pandemic of 1347 and appears to refer to the fatal outcome of disease.
The historian Cardinal Francis Aidan Gasquet wrote about the Great Pestilence in 1893 and suggested that it had been "some form of the ordinary Eastern or bubonic plague". In 1908, Gasquet said use of the name atra mors for the 14th-century epidemic first appeared in a 1631 book on Danish history by J. I. Pontanus: "Commonly and from its effects, they called it the black death" (Vulgo & ab effectu atram mortem vocitabant).
Previous plague epidemics

Research from 2017 suggests plague first infected humans in Europe and Asia in the Late Neolithic-Early Bronze Age. Research in 2018 found evidence of Yersinia pestis in an ancient Swedish tomb, which may have been associated with the "Neolithic decline" around 3000 BCE, in which European populations fell significantly. This Y. pestis may have been different from more modern types, with bubonic plague transmissible by fleas first known from Bronze Age remains near Samara.
The symptoms of bubonic plague are first attested in a fragment of Rufus of Ephesus preserved by Oribasius; these ancient medical authorities suggest bubonic plague had appeared in the Roman Empire before the reign of Trajan, six centuries before arriving at Pelusium in the reign of Justinian I. In 2013, researchers confirmed earlier speculation that the cause of the Plague of Justinian (541–549 CE, with recurrences until 750) was Y. pestis. This is known as the first plague pandemic. In 610, the Chinese physician Chao Yuanfang described a "malignant bubo" "coming in abruptly with high fever together with the appearance of a bundle of nodes beneath the tissue." The Chinese physician Sun Simo who died in 652 also mentioned a "malignant bubo" and plague that was common in Lingnan (Guangzhou). Ole Jørgen Benedictow believes that this indicates it was an offshoot of the first plague pandemic which made its way eastward to Chinese territory by around 600.
14th-century plague
Causes
Early theory
A report by the Medical Faculty of Paris stated that a conjunction of planets had caused "a great pestilence in the air" (miasma theory). Muslim religious scholars taught that the pandemic was a "martyrdom and mercy" from God, assuring the believer's place in paradise. For non-believers, it was a punishment.ome Muslim doctors cautioned against trying to prevent or treat a disease sent by God. Others adopted preventive measures and treatments for plague used by Europeans. These Muslim doctors also depended on the writings of the ancient Greeks.
Predominant modern theory
Due to climate change in Asia, rodents began to flee the dried-out grasslands to more populated areas, spreading the disease. The plague disease, caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis, is enzootic (commonly present) in populations of fleas carried by ground rodents, including marmots, in various areas, including Central Asia, Kurdistan, West Asia, North India, Uganda, and the western United States.
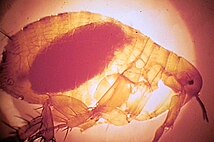
Y. pestis was discovered by Alexandre Yersin, a pupil of Louis Pasteur, during an epidemic of bubonic plague in Hong Kong in 1894; Yersin also proved this bacterium was present in rodents and suggested the rat was the main vehicle of transmission. The mechanism by which Y. pestis is usually transmitted was established in 1898 by Paul-Louis Simond and was found to involve the bites of fleas whose midguts had become obstructed by replicating Y. pestis several days after feeding on an infected host. This blockage starves the fleas, drives them to aggressive feeding behaviour, and causes them to try to clear the blockage via regurgitation, resulting in thousands of plague bacteria flushing into the feeding site and infecting the host. The bubonic plague mechanism was also dependent on two populations of rodents: one resistant to the disease, which act as hosts, keeping the disease endemic, and a second that lacks resistance. When the second population dies, the fleas move on to other hosts, including people, thus creating a human epidemic.
DNA evidence

Definitive confirmation of the role of Y. pestis arrived in 2010 with a publication in PLOS Pathogens by Haensch et al. They assessed the presence of DNA/RNA with polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques for Y. pestis from the tooth sockets in human skeletons from mass graves in northern, central and southern Europe that were associated archaeologically with the Black Death and subsequent resurgences. The authors concluded that this new research, together with prior analyses from the south of France and Germany, "ends the debate about the cause of the Black Death, and unambiguously demonstrates that Y. pestis was the causative agent of the epidemic plague that devastated Europe during the Middle Ages". In 2011 these results were further confirmed with genetic evidence derived from Black Death victims in the East Smithfield burial site in England. Schuenemann et al. concluded in 2011 "that the Black Death in medieval Europe was caused by a variant of Y. pestis that may no longer exist".
Later in 2011, Bos et al. reported in Nature the first draft genome of Y. pestis from plague victims from the same East Smithfield cemetery and indicated that the strain that caused the Black Death is ancestral to most modern strains of Y. pestis.
Later genomic papers have further confirmed the phylogenetic placement of the Y. pestis strain responsible for the Black Death as both the ancestor of later plague epidemics—including the third plague pandemic—and the descendant of the strain responsible for the Plague of Justinian. In addition, plague genomes from prehistory have been recovered.
DNA taken from 25 skeletons from 14th-century London showed that plague is a strain of Y. pestis almost identical to that which hit Madagascar in 2013. Further DNA evidence also proves the role of Y. pestis and traces the source to the Tian Shan mountains in Kyrgyzstan.
Alternative explanations
Researchers are hampered by a lack of reliable statistics from this period. Most work has been done on the spread of the disease in England, where estimates of overall population at the start of the plague vary by over 100%, as no census was undertaken in England between the time of publication of the Domesday Book of 1086 and the poll tax of the year 1377. Estimates of plague victims are usually extrapolated from figures for the clergy.
Mathematical modelling is used to match the spreading patterns and the means of transmission. In 2018 researchers suggested an alternative model in which "the disease was spread from human fleas and body lice to other people". The second model claims to better fit the trends of the plague's death toll, as the rat-flea-human hypothesis would have produced a delayed but very high spike in deaths, contradicting historical death data.
Lars Walløe argued that these authors "take it for granted that Simond's infection model, black rat → rat flea → human, which was developed to explain the spread of plague in India, is the only way an epidemic of Yersinia pestis infection could spread". Similarly, Monica Green has argued that greater attention is needed to the range of (especially non-commensal) animals that might be involved in the transmission of plague.
Archaeologist Barney Sloane has argued that there is insufficient evidence of the extinction of numerous rats in the archaeological record of the medieval waterfront in London, and that the disease spread too quickly to support the thesis that Y. pestis was spread from fleas on rats; he argues that transmission must have been person to person. This theory is supported by research in 2018 which suggested transmission was more likely by body lice and fleas during the second plague pandemic.
Summary
Academic debate continues, but no single alternative explanation for the plague's spread has achieved widespread acceptance. Many scholars arguing for Y. pestis as the major agent of the pandemic suggest that its extent and symptoms can be explained by a combination of bubonic plague with other diseases, including typhus, smallpox, and respiratory infections. In addition to the bubonic infection, others point to additional septicemic and pneumonic forms of plague, which lengthen the duration of outbreaks throughout the seasons and help account for its high mortality rate and additional recorded symptoms. In 2014, Public Health England announced the results of an examination of 25 bodies exhumed in the Clerkenwell area of London, as well as of wills registered in London during the period, which supported the pneumonic hypothesis. Currently, while osteoarcheologists have conclusively verified the presence of Y. pestis bacteria in burial sites across northern Europe through examination of bones and dental pulp, no other epidemic pathogen has been discovered to bolster the alternative explanations.
Transmission
Lack of hygiene
The importance of hygiene was not recognized until the 19th century and the germ theory of disease. Until then streets were usually unhygienic, with live animals and human parasites facilitating the spread of transmissible disease.
By the early 14th century, so much filth had collected inside urban Europe that French and Italian cities were naming streets after human waste. In medieval Paris, several street names were inspired by merde, the French word for "shit". There were rue Merdeux, rue Merdelet, rue Merdusson, rue des Merdons and rue Merdiere—as well as a rue du Pipi. Pigs, cattle, chickens, geese, goats and horses roamed the streets of medieval London and Paris.
Medieval homeowners were supposed to police their housefronts, including removing animal dung, but most urbanites were careless. William E. Cosner, a resident of the London suburb of Farringdon Without, received a complaint alleging that "men could not pass [by his house] for the stink [of] . . . horse dung and horse piss." One irate Londoner complained that the runoff from the local slaughterhouse had made his garden "stinking and putrid", while another charged that the blood from slain animals flooded nearby streets and lanes, "making a foul corruption and abominable sight to all dwelling near." In much of medieval Europe, sanitation legislation consisted of an ordinance requiring homeowners to shout, "Look out below!" three times before dumping a full chamber pot into the street.
Early Christians considered bathing a temptation. With this danger in mind, St. Benedict declared, "To those who are well, and especially to the young, bathing shall seldom be permitted." St. Agnes took the injunction to heart and died without ever bathing.
Territorial origins
According to a team of medical geneticists led by Mark Achtman, Yersinia pestis "evolved in or near China" over 2,600 years ago. Later research by a team led by Galina Eroshenko placed its origins more specifically in the Tian Shan mountains on the border between Kyrgyzstan and China. However more recent research notes that the previous sampling contained East Asian bias and that sampling since then has discovered strains of Y. pestis in the Caucasus region previously thought to be restricted to China. There is also no physical or specific textual evidence of the Black Death in 14th century China. As a result, China's place in the sequence of the plague's spread is still debated to this day. According to Charles Creighton, records of epidemics in 14th-century China suggest nothing more than typhus and major Chinese outbreaks of epidemic disease post-date the European epidemic by several years. The earliest Chinese descriptions of the bubonic plague do not appear until the 1640s.
Nestorian gravesites dating from 1338 to 1339 near Issyk-Kul have inscriptions referring to plague, which has led some historians and epidemiologists to think they mark the outbreak of the epidemic; this is supported by recent direct findings of Y. pestis DNA in teeth samples from graves in the area with inscriptions referring to "pestilence" as the cause of death. Epidemics killed an estimated 25 million across Asia during the fifteen years before the Black Death reached Constantinople in 1347.
The evidence does not suggest, at least at present, that these mortality crises were caused by plague. Although some scholars, including McNeill and Cao, see the 1333 outbreak as a prelude to the outbreaks in Europe from the late 1340s to the early 1350s, scholars of the Yuan and Ming periods remain skeptical about such an interpretation. Nonetheless, the remarkably high mortality rates during the Datong mortality should discourage us from rejecting the possibility of localized/regional outbreaks of plague in different parts of China, albeit differing in scale from, and unrelated to, the pandemic mortality of the Black Death. What we lack is any indication of a plague pandemic that engulfed vast territories of the Yuan Empire and later moved into western Eurasia through Central Asia.
— Philip Slavin
According to John Norris, evidence from Issyk-Kul indicates a small sporadic outbreak characteristic of transmission from rodents to humans with no wide-scale impact. According to Achtman, the dating of the plague suggests that it was not carried along the Silk Road, and its widespread appearance in that region probably postdates the European outbreak. Additionally, the Silk Road had already been heavily disrupted before the spread of the Black Death; Western and Middle Eastern traders found it difficult to trade on the Silk Road by 1325 and impossible by 1340, making its role in the spread of plague less likely. There are no records of the symptoms of the Black Death from Mongol sources or writings from travelers east of the Black Sea prior to the Crimean outbreak in 1346.
Others still favor an origin in China. The theory of Chinese origin implicates the Silk Road, the disease possibly spreading alongside Mongol armies and traders, or possibly arriving via ship—however, this theory is still contested. It is speculated that rats aboard Zheng He's ships in the 15th century may have carried the plague to Southeast Asia, India, and Africa.
Research on the Delhi Sultanate and the Yuan dynasty shows no evidence of any serious epidemic in fourteenth-century India and no specific evidence of plague in 14th-century China, suggesting that the Black Death may not have reached these regions. Ole Benedictow argues that since the first clear reports of the Black Death come from Kaffa, the Black Death most likely originated in the nearby plague focus on the northwestern shore of the Caspian Sea.
Demographic historians estimate that China's population fell by at least 15 per cent, and perhaps as much as a third, between 1340 and 1370. This population loss coincided with the Black Death that ravaged Europe and much of the Islamic world in 1347–52. However, there is a conspicuous lack of evidence for pandemic disease on the scale of the Black Death in China at this time. War and famine – and the diseases that typically accompanied them – probably were the main causes of mortality in the final decades of Mongol rule.
— Richard von Glahn
Monica Green suggests that other parts of Eurasia outside the west do not contain the same evidence of the Black Death, because there were actually four strains of Yersinia pestis that became predominant in different parts of the world. Mongol records of illness such as food poisoning may have been referring to the Black Death. Another theory is that the plague originated near Europe and cycled through the Mediterranean, Northern Europe and Russia before making its way to China. Other historians, such as John Norris and Ole Benedictaw, believe the plague likely originated in Europe or the Middle East, and never reached China. Norris specifically argues for an origin in Kurdistan rather than Central Asia.
European outbreak
The seventh year after it began, it came to England and first began in the towns and ports joining on the seacoasts, in Dorsetshire, where, as in other counties, it made the country quite void of inhabitants so that there were almost none left alive. ... But at length it came to Gloucester, yea even to Oxford and to London, and finally it spread over all England and so wasted the people that scarce the tenth person of any sort was left alive.
Plague was reportedly first introduced to Europe via Genoese traders from their port city of Kaffa in the Crimea in 1347. During a protracted siege of the city in 1345–1346, the Mongol Golden Horde army of Jani Beg—whose mainly Tatar troops were suffering from the disease—catapulted infected corpses over the city walls of Kaffa to infect the inhabitants, though it is also likely that infected rats travelled across the siege lines to spread the epidemic to the inhabitants. As the disease took hold, Genoese traders fled across the Black Sea to Constantinople, where the disease first arrived in Europe in summer 1347.
The epidemic there killed the 13-year-old son of the Byzantine emperor, John VI Kantakouzenos, who wrote a description of the disease modelled on Thucydides's account of the 5th century BCE Plague of Athens, noting the spread of the Black Death by ship between maritime cities. Nicephorus Gregoras, while writing to Demetrios Kydones, described the rising death toll, the futility of medicine, and the panic of the citizens. The first outbreak in Constantinople lasted a year, but the disease recurred ten times before 1400.
Carried by twelve Genoese galleys, plague arrived by ship in Sicily in October 1347; the disease spread rapidly all over the island. Galleys from Kaffa reached Genoa and Venice in January 1348, but it was the outbreak in Pisa a few weeks later that was the entry point into northern Italy. Towards the end of January, one of the galleys expelled from Italy arrived in Marseilles.
From Italy, the disease spread northwest across Europe, striking France, Spain, Portugal, and England by June 1348, then spreading east and north through Germany, Scotland and Scandinavia from 1348 to 1350. It was introduced into Norway in 1349 when a ship landed at Askøy, then spread to Bjørgvin (modern Bergen). Finally, it spread to northern Russia in 1352 and reached Moscow in 1353. Plague was less common in parts of Europe with less-established trade relations, including the majority of the Basque Country, isolated parts of Belgium and the Netherlands, and isolated Alpine villages throughout the continent.
According to some epidemiologists, periods of unfavorable weather decimated plague-infected rodent populations, forcing their fleas onto alternative hosts, inducing plague outbreaks which often peaked in the hot summers of the Mediterranean and during the cool autumn months of the southern Baltic region. Among many other culprits of plague contagiousness, pre-existing malnutrition weakened the immune response, contributing to an immense decline in European population.
West Asian and North African outbreak
The disease struck various regions in the Middle East and North Africa during the pandemic, leading to serious depopulation and permanent change in both economic and social structures.
By autumn 1347, plague had reached Alexandria in Egypt, transmitted by sea from Constantinople via a single merchant ship carrying slaves. By late summer 1348, it reached Cairo, capital of the Mamluk Sultanate, cultural center of the Islamic world, and the largest city in the Mediterranean Basin; the Bahriyya child sultan an-Nasir Hasan fled and more than a third of the 600,000 residents died. The Nile was choked with corpses despite Cairo having a medieval hospital, the late 13th-century bimaristan of the Qalawun complex. The historian al-Maqrizi described the abundant work for grave-diggers and practitioners of funeral rites; plague recurred in Cairo more than fifty times over the following one and a half centuries.
During 1347, the disease travelled eastward to Gaza by April; by July it had reached Damascus, and in October plague had broken out in Aleppo. That year, in the territory of modern Lebanon, Syria, Israel, and Palestine, the cities of Ascalon, Acre, Jerusalem, Sidon, and Homs were all infected. In 1348–1349, the disease reached Antioch. The city's residents fled to the north, but most of them ended up dying during the journey. Within two years, the plague had spread throughout the Islamic world, from Arabia across North Africa.
The pandemic spread westwards from Alexandria along the African coast, while in April 1348 Tunis was infected by ship from Sicily. Tunis was then under attack by an army from Morocco; this army dispersed in 1348 and brought the contagion with them to Morocco, whose epidemic may also have been seeded from the Islamic city of Almería in al-Andalus.
Mecca became infected in 1348 by pilgrims performing the Hajj. In 1351 or 1352, the Rasulid sultan of the Yemen, al-Mujahid Ali, was released from Mamluk captivity in Egypt and carried plague with him on his return home. During 1349, records show the city of Mosul suffered a massive epidemic, and the city of Baghdad experienced a second round of the disease.
Signs and symptoms


Bubonic plague
Symptoms of the plague include fever of 38–41 °C (100–106 °F), headaches, painful aching joints, nausea and vomiting, and a general feeling of malaise. Left untreated, 80% of victims die within eight days.
Contemporary accounts of the pandemic are varied and often imprecise. The most commonly noted symptom was the appearance of buboes (or gavocciolos) in the groin, neck and armpits, which oozed pus and bled when opened. Boccaccio's description:
In men and women alike it first betrayed itself by the emergence of certain tumours in the groin or armpits, some of which grew as large as a common apple, others as an egg ... From the two said parts of the body this deadly gavocciolo soon began to propagate and spread itself in all directions indifferently; after which the form of the malady began to change, black spots or livid making their appearance in many cases on the arm or the thigh or elsewhere, now few and large, now minute and numerous. As the gavocciolo had been and still was an infallible token of approaching death, such also were these spots on whomsoever they showed themselves.
This was followed by acute fever and vomiting of blood. Most people died two to seven days after initial infection. Freckle-like spots and rashes, which may have been caused by flea-bites, were identified as another potential sign of plague.
Pneumonic plague
Lodewijk Heyligen, whose master Cardinal Giovanni Colonna died of plague in 1348, noted a distinct form of the disease, pneumonic plague, that infected the lungs and led to respiratory problems. Symptoms include fever, cough and blood-tinged sputum. As the disease progresses, sputum becomes free-flowing and bright red. Pneumonic plague has a mortality rate of 90–95%.
Septicemic plague
Septicemic plague is the least common of the three forms, with an untreated mortality rate near 100%. Symptoms are high fevers and purple skin patches (purpura due to disseminated intravascular coagulation). In cases of pneumonic and particularly septicemic plague, the progress of the disease is so rapid that there would often be no time for the development of the enlarged lymph nodes that were noted as buboes.
Consequences
Deaths

There are no exact figures for the death toll; the rate varied widely by locality. Urban centers with higher populations suffered longer periods of abnormal mortality. Some estimate that it may have killed between 75,000,000 and 200,000,000 people in Eurasia. A study published in 2022 of pollen samples across Europe from 1250 to 1450 was used to estimate changes in agricultural output before and after the Black Death. The authors found great variability in different regions, with evidence for high mortality in areas of Scandinavia, France, western Germany, Greece, and central Italy, but uninterrupted agricultural growth in central and eastern Europe, Iberia, and Ireland. The authors concluded that "the pandemic was immensely destructive in some areas, but in others it had a far lighter touch ... [the study methodology] invalidates histories of the Black Death that assume Y. pestis was uniformly prevalent, or nearly so, across Europe and that the pandemic had a devastating demographic impact everywhere."
The Black Death killed, by various estimations, from 25 to 60% of Europe's population. Robert Gottfried writes that as early as 1351, "agents for Pope Clement VI calculated the number of dead in Christian Europe at 23,840,000. With a preplague population of about 75 million, Clement's figure accounts for mortality of 31%-a rate about midway between the 50% mortality estimated for East Anglia, Tuscany, and parts of Scandinavia, and the less-than-15% morbidity for Bohemia and Galicia. And it is unerringly close to Froissart's claim that "a third of the world died," a measurement probably drawn from St. John's figure of mortality from plague in the Book of Revelation, a favorite medieval source of information." Ole J. Benedictow proposes 60% mortality rate for Europe as a whole based on available data, with up to 80% based on poor nutritional conditions in the 14th century. According to medieval historian Philip Daileader, it is likely that over four years, 45–50% of the European population died of plague.
The overwhelming number of deaths in Europe sometimes made mass burials necessary, and some sites had hundreds or thousands of bodies. The mass burial sites that have been excavated have allowed archaeologists to continue interpreting and defining the biological, sociological, historical, and anthropological implications of the Black Death. The mortality rate of the Black Death in the 14th century was far greater than the worst 20th-century outbreaks of Y. pestis plague, which occurred in India and killed as much as 3% of the population of certain cities.
In 1348, the disease spread so rapidly that nearly a third of the European population perished before any physicians or government authorities had time to reflect upon its origins. In crowded cities, it was not uncommon for as much as 50% of the population to die. Half of Paris' population of 100,000 people died. In Italy, the population of Florence was reduced from between 110,000 and 120,000 inhabitants in 1338 to 50,000 in 1351. At least 60% of the population of Hamburg and Bremen perished, and a similar percentage of Londoners may have died from the disease as well, leaving a death toll of approximately 62,000 between 1346 and 1353. Florence's tax records suggest that 80% of the city's population died within four months in 1348. Before 1350, there were about 170,000 settlements in Germany, and this was reduced by nearly 40,000 by 1450. The disease bypassed some areas, with the most isolated areas being less vulnerable to contagion. Plague did not appear in Flanders until the turn of the 15th century, and the impact was less severe on the populations of Hainaut, Finland, northern Germany, and areas of Poland. Monks, nuns, and priests were especially hard-hit since they cared for people ill with the plague. The level of mortality in the rest of Eastern Europe was likely similar to that of Western Europe in the first outbreak, with descriptions suggesting a similar effect on Russian towns, and the cycles of plague in Russia being roughly equivalent.

In 1382, the physician to the Avignon Papacy, Raimundo Chalmel de Vinario (Latin: Magister Raimundus, lit. 'Master Raymond'), observed the decreasing mortality rate of successive outbreaks of plague in 1347–1348, 1362, 1371 and 1382 in his treatise On Epidemics (De epidemica). In the first outbreak, two thirds of the population contracted the illness and most patients died; in the next, half the population became ill but only some died; by the third, a tenth were affected and many survived; while by the fourth occurrence, only one in twenty people were sickened and most of them survived. By the 1380s in Europe, the plague predominantly affected children. Chalmel de Vinario recognised that bloodletting was ineffective (though he continued to prescribe bleeding for members of the Roman Curia, whom he disliked), and said that all true cases of plague were caused by astrological factors and were incurable; he was never able to effect a cure.
The populations of some Italian cities, notably Florence, did not regain their pre-14th century size until the 19th century. Italian chronicler Agnolo di Tura recorded his experience from Siena, where plague arrived in May 1348:
Father abandoned child, wife husband, one brother another; for this illness seemed to strike through the breath and sight. And so they died. And none could be found to bury the dead for money or friendship. Members of a household brought their dead to a ditch as best they could, without priest, without divine offices ... great pits were dug and piled deep with the multitude of dead. And they died by the hundreds both day and night ... And as soon as those ditches were filled more were dug ... And I, Agnolo di Tura ... buried my five children with my own hands. And there were also those who were so sparsely covered with earth that the dogs dragged them forth and devoured many bodies throughout the city. There was no one who wept for any death, for all awaited death. And so many died that all believed it was the end of the world.
The most widely accepted estimate for the Middle East, including Iraq, Iran, and Syria, during this time, is for a death toll of about a third of the population. The Black Death killed about 40% of Egypt's population. In Cairo, with a population numbering as many as 600,000, and possibly the largest city west of China, between one third and 40% of the inhabitants died within eight months. By the 18th century, the population of Cairo was halved from its numbers in 1347.
Economic
It has been suggested that the Black Death, like other outbreaks through history, disproportionately affected the poorest people and those already in worse physical condition than the wealthier citizens.
But along with population decline from the pandemic, wages soared in response to a subsequent labour shortage. In some places rents collapsed (e.g., lettings "used to bring in £5, and now but £1.")
However, many labourers, artisans, and craftsmen—those living from money-wages alone—suffered a reduction in real incomes owing to rampant inflation. Landowners were also pushed to substitute monetary rents for labour services in an effort to keep tenants. Taxes and tithes became difficult to collect, with living poor refusing to cover the share of the rich deceased, because many properties were empty and unfarmed, and because tax-collectors, where they could be employed, refused to go to plague spots.
The trade disruptions in the Mongol Empire caused by the Black Death was one of the reasons for its collapse.
Environmental
A study performed by Thomas Van Hoof of the Utrecht University suggests that the innumerable deaths brought on by the pandemic cooled the climate by freeing up land and triggering reforestation. This may have led to the Little Ice Age.
Persecutions

Renewed religious fervor and fanaticism increased in the wake of the Black Death. Some Europeans targeted "various groups such as Jews, friars, foreigners, beggars, pilgrims", lepers, and Romani, blaming them for the crisis. Lepers, and others with skin diseases such as acne or psoriasis, were killed throughout Europe.
Because 14th-century healers and governments were at a loss to explain or stop the disease, Europeans turned to astrological forces, earthquakes and the poisoning of wells by Jews as possible reasons for outbreaks. Many believed the epidemic was a punishment by God for their sins, and could be relieved by winning God's forgiveness.
There were many attacks against Jewish communities. In the Strasbourg massacre of February 1349, about 2,000 Jews were murdered. In August 1349, the Jewish communities in Mainz and Cologne were annihilated. By 1351, 60 major and 150 smaller Jewish communities had been destroyed. During this period many Jews relocated to Poland, where they received a welcome from King Casimir the Great.
Social

One theory that has been advanced is that the Black Death's devastation of Florence, between 1348 and 1350, resulted in a shift in the world view of people in 14th-century Italy that ultimately led to the Renaissance. Italy was particularly badly hit by the pandemic, and the resulting familiarity with death may have caused thinkers to dwell more on their lives on Earth, rather than on spirituality and the afterlife. It has also been argued that the Black Death prompted a new wave of piety, manifested in the sponsorship of religious works of art.
This does not fully explain why the Renaissance occurred in Italy in the 14th century; the Renaissance's emergence was most likely the result of the complex interaction of the above factors, in combination with an influx of Greek scholars after the fall of the Byzantine Empire. As a result of the drastic reduction in the populace the value of the working class increased, and commoners came to enjoy more freedom. To answer the increased need for labour, workers travelled in search of the most favorable position economically.
Prior to the emergence of the Black Death, the continent was considered a feudalistic society, composed of fiefs and city-states frequently managed by the Catholic Church. The pandemic completely restructured both religion and political forces; survivors began to turn to other forms of spirituality and the power dynamics of the fiefs and city-states crumbled. The survivors of the pandemic found not only that the prices of food were lower but also that lands were more abundant, and many of them inherited property from their dead relatives, and this probably contributed to the destabilization of feudalism.
The word "quarantine" has its roots in this period, though the practice of isolating people to prevent the spread of disease is older. In the city-state of Ragusa (modern Dubrovnik, Croatia), a thirty-day isolation period was implemented in 1377 for new arrivals to the city from plague-affected areas. The isolation period was later extended to forty days, and given the name "quarantino" from the Italian word for "forty".
All institutions were affected. Smaller monasteries and convents became unviable and closed. Up to half parish churches lost their priest, apart from the parishioners. Religious sensibilities changed:
"[...]looking back into the past, the history of the Church during the Middle Ages in England appears one continuous and stately progress. It is much nearer to the truth to say that in 1351 the whole ecclesiastical system was wholly disorganised, or, indeed, more than half ruined, and that everything had to be built up anew.[...] To secure the most necessary public ministrations of the rites of religion the most inadequately-prepared subjects had to be accepted, and even these could be obtained only in insufficient numbers.[...]The immediate effect on the people was a religious paralysis. Instead of turning men to God the scourge turned them to despair[...] In time the religious sense and feeling revived, but in many respects it took a new tone, and its manifestations ran in new channels[...]characterised by a devotional and more self-reflective cast than previously.[...]
The new religious spirit found outward expression in the multitude of guilds which sprang into existence at this time, in the remarkable and almost, as it may seem to some, extravagant development of certain pious practices, in the singular spread of a more personal devotion to the Blessed Sacrament, to the Blessed Virgin, to the Five Wounds, to the Holy Name, and other such manifestations of a more tender or more familiar piety.[...]At the close of the fourteenth century and during the course of the fifteenth the supply of ornaments, furniture, plate, statues painted or in highly decked "coats," with which the churches were literally encumbered as time went on, proved a striking contrast to the comparative simplicity which characterised former days, as witnessed by a comparison of inventories.[...]
In fact, the fifteenth century witnessed the beginnings of a great middle-class movement, which can be distinctly traced to the effect of the great pestilence[...]— Cardinal Francis Aidan Gasquet
Recurrences
Second plague pandemic


The plague repeatedly returned to haunt Europe and the Mediterranean throughout the 14th to 17th centuries. According to Jean-Noël Biraben, the plague was present somewhere in Europe in every year between 1346 and 1671 (although some researchers have cautions about the uncritical use of Biraben's data). The second pandemic was particularly widespread in the following years: 1360–1363; 1374; 1400; 1438–1439; 1456–1457; 1464–1466; 1481–1485; 1500–1503; 1518–1531; 1544–1548; 1563–1566; 1573–1588; 1596–1599; 1602–1611; 1623–1640; 1644–1654; and 1664–1667. Subsequent outbreaks, though severe, marked the plague's retreat from most of Europe (18th century) and North Africa (19th century).
Historian George Sussman argued that the plague had not occurred in East Africa until the 20th century. However, other sources suggest that the second pandemic did indeed reach sub-Saharan Africa.
According to historian Geoffrey Parker, "France alone lost almost a million people to the plague in the epidemic of 1628–31." In the first half of the 17th century, a plague killed some 1.7 million people in Italy. More than 1.25 million deaths resulted from the extreme incidence of plague in 17th-century Spain.
The Black Death ravaged much of the Islamic world. Plague could be found in the Islamic world almost every year between 1500 and 1850. Sometimes the outbreaks affected small areas, while other outbreaks affected multiple regions. Plague repeatedly struck the cities of North Africa. Algiers lost 30,000–50,000 inhabitants to it in 1620–1621, and again in 1654–1657, 1665, 1691, and 1740–1742. Cairo suffered more than fifty plague epidemics within 150 years from the plague's first appearance, with the final outbreak of the second pandemic there in the 1840s. Plague remained a major event in Ottoman society until the second quarter of the 19th century. Between 1701 and 1750, thirty-seven larger and smaller epidemics were recorded in Constantinople, and an additional thirty-one between 1751 and 1800. Baghdad has suffered severely from visitations of the plague, and sometimes two-thirds of its population died.
Third plague pandemic

The third plague pandemic (1855–1859) started in China in the mid-19th century, spreading to all inhabited continents and killing 10 million people in India alone. The investigation of the pathogen that caused the 19th-century plague was begun by teams of scientists who visited Hong Kong in 1894, among whom was the French-Swiss bacteriologist Alexandre Yersin, for whom the pathogen was named.
Twelve plague outbreaks in Australia between 1900 and 1925 resulted in over 1,000 deaths, chiefly in Sydney. This led to the establishment of a Public Health Department there which undertook some leading-edge research on plague transmission from rat fleas to humans via the bacillus Yersinia pestis.
The first North American plague epidemic was the San Francisco plague of 1900–1904, followed by another outbreak in 1907–1908.
Modern-day
Modern treatment methods include insecticides, the use of antibiotics, and a plague vaccine. It is feared that the plague bacterium could develop drug resistance and again become a major health threat. One case of a drug-resistant form of the bacterium was found in Madagascar in 1995. Another outbreak in Madagascar was reported in November 2014. In October 2017, the deadliest outbreak of the plague in modern times hit Madagascar, killing 170 people and infecting thousands.
An estimate of the case fatality rate for the modern plague, after the introduction of antibiotics, is 11%, although it may be higher in underdeveloped regions.