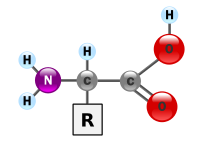
The generic structure of an alpha amino acid in its un-ionized form
Amino acids (
//,
//, or
//) are
biologically important
organic compounds composed of
amine (-NH
2) and
carboxylic acid (-COOH)
functional groups, along with a
side-chain specific to each amino
acid. The key elements of an amino acid are
carbon,
hydrogen,
oxygen, and
nitrogen, though other elements are found in the side-chains of certain amino acids. About 500 amino acids are known
[1] and can be classified in many ways. They can be classified according to the core structural functional groups' locations as
alpha- (α-), beta- (β-), gamma- (γ-) or delta- (δ-) amino acids; other categories relate to
polarity,
pH level, and side-chain group type (
aliphatic,
acyclic,
aromatic, containing hydroxyl or
sulfur, etc.). In the form of
proteins, amino acids comprise the second-largest component (water is the largest) of human
muscles,
cells and other
tissues.
[2] Outside proteins, amino acids perform critical roles in processes such as
neurotransmitter transport and
biosynthesis.
In
biochemistry, amino acids having both the amine and the carboxylic acid groups attached to the
first (alpha-) carbon atom have particular importance. They are known as
2-, alpha-, or
α-amino acids (generic
formula H
2NCHRCOOH in most cases
[3] where R is an
organic substituent known as a "
side-chain");
[4] often the term "amino acid" is used to refer specifically to these. They include the 23
proteinogenic ("protein-building") amino acids,
[5][6][7] which combine into
peptide chains ("polypeptides") to form the building-blocks of a vast array of
proteins.
[8] These are all
L-
stereoisomers ("
left-handed"
isomers), although a few
D-amino acids ("right-handed") occur in
bacterial envelopes and some
antibiotics.
[9] Twenty of the proteinogenic amino acids are encoded directly by triplet
codons in the
genetic code and are known as "standard" amino acids. The other three ("non-standard" or "non-canonical") are
selenocysteine (present in many noneukaryotes as well as most eukaryotes, but not coded directly by DNA),
pyrrolysine (found only in some
archea and one
bacterium) and
N-formylmethionine (which is often the initial amino acid of proteins in bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts). Pyrrolysine and selenocysteine are encoded via variant codons; for example, selenocysteine is encoded by
stop codon and
SECIS element.
[10][11][12] Codon–
tRNA combinations not found in nature can also be used to
"expand" the genetic code and create novel proteins known as
alloproteins incorporating non-proteinogenic amino acids.
[13][14][15]
Many important proteinogenic and non-proteinogenic amino acids also play critical non-protein roles within the body. For example, in the
human brain, glutamate (standard
glutamic acid) and
gamma-amino-butyric acid ("GABA", non-standard gamma-amino acid) are, respectively, the main
excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters;
[16] hydroxyproline (a major component of the
connective tissue collagen) is synthesised from
proline; the standard amino acid
glycine is used to synthesise porphyrins used in
red blood cells; and the non-standard
carnitine is used in
lipid transport.
Nine proteinogenic amino acids are called
"essential" for humans because they cannot be created from other
compounds by the human body and, so, must be taken in as food. Others may be
conditionally essential for certain ages or medical conditions. Essential amino acids may also differ between
species.
[17]
Because of their biological significance, amino acids are important in nutrition and are commonly used in
nutritional supplements,
fertilizers, and
food technology. Industrial uses include the production of
drugs,
biodegradable plastics, and
chiral catalysts.
§History
The first few amino acids were discovered in the early 19th century. In 1806, French chemists
Louis-Nicolas Vauquelin and
Pierre Jean Robiquet isolated a compound in
asparagus that was subsequently named
asparagine, the first amino acid to be discovered.
[18][19] Cystine was discovered in 1810,
[20] although its monomer,
cysteine, remained undiscovered until 1884.
[19][21] Glycine and
leucine were discovered in 1820.
[22] Usage of the term
amino acid in the English language is from 1898.
[23] Proteins were found to yield amino acids after enzymatic digestion or acid
hydrolysis. In 1902,
Emil Fischer and
Franz Hofmeister proposed that proteins are the result of the formation of bonds between the amino group of one amino acid with the carboxyl group of another, in a linear structure that Fischer termed "
peptide".
[24]
§General structure
In the structure shown at the top of the page,
R represents a
side-chain specific to each amino acid. The
carbon atom next to the
carboxyl group (which is therefore numbered 2 in the
carbon chain starting from that functional group) is called the
α–carbon. Amino acids containing an
amino group bonded directly to the alpha carbon are referred to as
alpha amino acids.
[25] These includes amino acids such as
proline which contain
secondary amines, which formerly were often referred to as "imino acids".
[26][27][28]
§Isomerism

The two enantiomers of alanine, D-alanine and L-alanine
The alpha amino acids are the most common form found in nature, but only when occurring in the L-isomer. The alpha carbon is a
chiral carbon atom, with the exception of
glycine which has two indistinguishable hydrogen atoms on the alpha carbon.
[29] Therefore, all alpha amino acids but
glycine can exist in either of two
enantiomers, called
L or
D amino acids, which are mirror images of each other (
see also Chirality). While
L-amino acids represent all of the amino acids found in
proteins during translation in the ribosome,
D-amino acids are found in some proteins produced by enzyme
posttranslational modifications after translation and translocation to the endoplasmic reticulum, as in exotic sea-dwelling organisms such as
cone snails.
[30] They are also abundant components of the
peptidoglycan cell walls of bacteria,
[31] and
D-serine may act as a
neurotransmitter in the brain.
[32] D-amino acids are used in
racemic crystallography to create centrosymmetric crystals, which (depending on the protein) may allow for easier and more robust protein structure determination.
[33] The
L and
D convention for amino acid configuration refers not to the optical activity of the amino acid itself but rather to the optical activity of the isomer of
glyceraldehyde from which that amino acid can, in theory, be synthesized (
D-glyceraldehyde is dextrorotatory;
L-glyceraldehyde is levorotatory). In alternative fashion, the
(S) and (R) designators are used to indicate the absolute
stereochemistry. Almost all of the amino acids in proteins are
(S) at the α carbon, with cysteine being
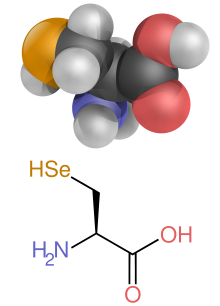
(R) and glycine non-chiral.
[34] Cysteine is unusual since it has a
sulfur atom at the second position in its side-chain, which has a larger
atomic mass than the groups attached to the first carbon, which is attached to the α-carbon in the other standard amino acids, thus the
(R) instead of
(S).
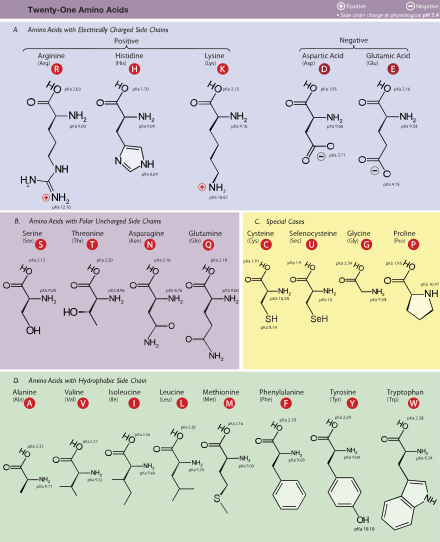
§Side chains

Lysine with the carbon atoms in the side-chain labeled
In amino acids that have a carbon chain attached to the α–carbon (such as
lysine, shown to the right) the carbons are labeled in order as α, β, γ, δ, and so on.
[35] In some amino acids, the amine group is attached to the β or γ-carbon, and these are therefore referred to as
beta or
gamma amino acids.
Amino acids are usually classified by the
properties of their side-chain into four groups. The side-chain can make an amino acid a
weak acid or a
weak base, and a
hydrophile if the side-chain is
polar or a
hydrophobe if it is
nonpolar.
[29] The
chemical structures of the 22 standard amino acids, along with their chemical properties, are described more fully in the article on these
proteinogenic amino acids.
The phrase "
branched-chain amino acids" or BCAA refers to the amino acids having
aliphatic side-chains that are non-linear; these are
leucine,
isoleucine, and
valine.
Proline is the only
proteinogenic amino acid whose side-group links to the α-amino group and, thus, is also the only proteinogenic amino acid containing a secondary amine at this position.
[29] In chemical terms, proline is, therefore, an
imino acid, since it lacks a
primary amino group,
[36] although it is still classed as an amino acid in the current biochemical nomenclature,
[37] and may also be called an "N-alkylated alpha-amino acid".
[38]
§Zwitterions

An amino acid in its (1) un-ionized and (2) zwitterionic forms
The α-
carboxylic acid group of amino acids is a
weak acid, meaning that it releases a
hydron (such as a
proton) at moderate pH values. In other words, carboxylic acid groups (−CO
2H) can be
deprotonated to become negative
carboxylates (−CO
2− ). The negatively charged carboxylate ion predominates at pH values greater than the
pKa of the carboxylic acid group (mean for the 20 common amino acids is about 2.2, see the table of amino acid structures above). In a complementary fashion, the α-
amine of amino acids is a
weak base, meaning that it accepts a hydron at moderate pH values. In other words, α-amino groups (NH
2−) can be
protonated to become positive α-ammonium groups (
+NH
3−). The positively charged α-ammonium group predominates at pH values less than the pKa of the α-ammonium group (mean for the 20 common α-amino acids is about 9.4).
Because all amino acids contain amine and carboxylic acid functional groups, they share
amphiprotic properties.
[29] Below pH 2.2, the predominant form will have a neutral carboxylic acid group and a positive α-ammonium ion (net charge +1), and above pH 9.4, a negative carboxylate and neutral α-amino group (net charge −1). But at pH between 2.2 and 9.4, an amino acid usually contains both a negative carboxylate and a positive α-ammonium group, as shown in structure (2) on the right, so has net zero charge. This molecular state is known as a
zwitterion, from the German
Zwitter meaning
hermaphrodite or
hybrid.
[39] The fully neutral form (structure (1) on the right) is a very minor species in aqueous solution throughout the pH range (less than 1 part in 10
7). Amino acids exist as zwitterions also in the solid phase, and crystallize with salt-like properties unlike typical organic acids or amines.
§Isoelectric point
The variation in titration curves when the amino acids are grouped by category can be seen here. With the exception of tyrosine, using titration to differentiate between hydrophobic amino acids is problematic.
At pH values between the two pKa values, the zwitterion predominates, but coexists in
dynamic equilibrium with small amounts of net negative and net positive ions. At the exact midpoint between the two pKa values, the trace amount of net negative and trace of net positive ions exactly balance, so that average net charge of all forms present is zero.
[40] This pH is known as the
isoelectric point pI, so pI = ½(pKa
1 + pKa
2). The individual amino acids all have slightly different pKa values, so have different isoelectric points. For amino acids with charged side-chains, the pKa of the side-chain is involved. Thus for Asp, Glu with negative side-chains, pI = ½(pKa
1 + pKa
R), where pKa
R is the side-chain pKa. Cysteine also has potentially negative side-chain with pKa
R = 8.14, so pI should be calculated as for Asp and Glu, even though the side-chain is not significantly charged at neutral pH. For His, Lys, and Arg with positive side-chains, pI = ½(pKa
R + pKa
2). Amino acids have zero mobility in electrophoresis at their isoelectric point, although this behaviour is more usually exploited for peptides and proteins than single amino acids. Zwitterions have minimum solubility at their isoelectric point and some amino acids (in particular, with non-polar side-chains) can be isolated by precipitation from water by adjusting the pH to the required isoelectric point.
§Occurrence and functions in biochemistry
§Proteinogenic amino acids
Amino acids are the structural units (monomers) that make up proteins. They join together to form short
polymer chains called
peptides or longer chains called either
polypeptides or
proteins. These polymers are linear and unbranched, with each amino acid within the chain attached to two neighboring amino acids. The process of making proteins is called
translation and involves the step-by-step addition of amino acids to a growing protein chain by a
ribozyme that is called a
ribosome.
[41] The order in which the amino acids are added is read through the
genetic code from an
mRNA template, which is a
RNA copy of one of the organism's
genes.
Twenty-three amino acids are naturally incorporated into polypeptides and are called
proteinogenic or natural amino acids.
[29] Of these, 21 are encoded by the universal
genetic code. The remaining 2,
selenocysteine and
pyrrolysine, are incorporated into proteins by unique synthetic mechanisms.
Selenocysteine is incorporated when the mRNA being translated includes a
SECIS element, which causes the UGA codon to encode selenocysteine instead of a
stop codon.
[42] Pyrrolysine is used by some
methanogenic archaea in enzymes that they use to produce
methane. It is coded for with the codon UAG, which is normally a stop codon in other organisms.
[43] This UAG codon is followed by a
PYLIS downstream sequence.
[44]
§Non-proteinogenic amino acids
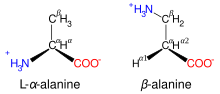
β-alanine and its α-alanine isomer
Aside from the 23
proteinogenic amino acids, there are many other amino acids that are called
non-proteinogenic. Those either are not found in proteins (for example
carnitine,
GABA) or are not produced directly and in isolation by standard cellular machinery (for example,
hydroxyproline and
selenomethionine).
Non-proteinogenic amino acids that are found in proteins are formed by
post-translational modification, which is modification after translation during protein synthesis. These modifications are often essential for the function or regulation of a protein; for example, the
carboxylation of
glutamate allows for better binding of
calcium cations,
[45] and the
hydroxylation of
proline is critical for maintaining
connective tissues.
[46] Another example is the formation of
hypusine in the
translation initiation factor EIF5A, through modification of a lysine residue.
[47] Such modifications can also determine the localization of the protein, e.g., the addition of long hydrophobic groups can cause a protein to bind to a
phospholipid membrane.
[48]
Some non-proteinogenic amino acids are not found in proteins. Examples include
lanthionine,
2-aminoisobutyric acid,
dehydroalanine, and the neurotransmitter
gamma-aminobutyric acid. Non-proteinogenic amino acids often occur as intermediates in the
metabolic pathways for standard amino acids – for example,
ornithine and
citrulline occur in the
urea cycle, part of amino acid
catabolism (see below).
[49] A rare exception to the dominance of α-amino acids in biology is the β-amino acid
beta alanine (3-aminopropanoic acid), which is used in plants and microorganisms in the synthesis of
pantothenic acid (vitamin B
5), a component of
coenzyme A.
[50]
§Non-standard amino acids
The 20 amino acids that are encoded directly by the codons of the universal
genetic code are called
standard or
canonical amino acids. The others are called
non-standard or
non-canonical. Most of the non-standard amino acids are also non-proteinogenic (i.e. they cannot be used to build proteins), but three of them are proteinogenic, as they can be used to build proteins by exploiting information not encoded in the universal genetic code.
The three non-standard proteinogenic amino acids are
selenocysteine (present in many noneukaryotes as well as most eukaryotes, but not coded directly by DNA),
pyrrolysine (found only in some
archea and one
bacterium), and
N-formylmethionine (which is often the initial amino acid of proteins in bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts). For example, 25 human proteins include selenocysteine (Sec) in their primary structure,
[51] and the structurally characterized enzymes (selenoenzymes) employ Sec as the catalytic
moiety in their active sites.
[52] Pyrrolysine and selenocysteine are encoded via variant codons. For example, selenocysteine is encoded by
stop codon and
SECIS element.
[10][11][12]
§In human nutrition
When taken up into the human body from the diet, the 22 standard amino acids either are used to synthesize proteins and other biomolecules or are oxidized to
urea and
carbon dioxide as a source of energy.
[53] The oxidation pathway starts with the removal of the amino group by a
transaminase; the amino group is then fed into the
urea cycle. The other product of transamidation is a
keto acid that enters the
citric acid cycle.
[54] Glucogenic amino acids can also be converted into glucose, through
gluconeogenesis.
[55]
Pyrrolysine trait is restricted to several microbes, and only one organism has both Pyl and Sec. Of the 22 standard amino acids, 9 are called
essential amino acids because the
human body cannot
synthesize them from other
compounds at the level needed for normal growth, so they must be obtained from food.
[56] In addition,
cysteine,
taurine,
tyrosine, and
arginine are considered semiessential amino-acids in children (though taurine is not technically an amino acid), because the metabolic pathways that synthesize these amino acids are not fully developed.
[57][58] The amounts required also depend on the age and health of the individual, so it is hard to make general statements about the dietary requirement for some amino acids.
(*) Essential only in certain cases.
[59][60]
§Classification
Although there are many ways to classify amino acids, these molecules can be assorted into six main groups, on the basis of their structure and the general chemical characteristics of their R groups.
| Class |
Name of the amino acids |
| Aliphatic |
Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine |
| Hydroxyl or Sulfur/Selenium-containing |
Serine, Cysteine, Selenocysteine, Threonine, Methionine |
| Cyclic |
Proline |
| Aromatic |
Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Tryptophan |
| Basic |
Histidine, Lysine, Arginine |
| Acidic and their Amide |
Aspartate, Glutamate, Asparagine, Glutamine |
§Non-protein functions
In humans, non-protein amino acids also have important roles as
metabolic intermediates, such as in the biosynthesis of the
neurotransmitter gamma-amino-butyric acid (GABA). Many amino acids are used to synthesize other molecules, for example:
However, not all of the functions of other abundant non-standard amino acids are known.
Some non-standard amino acids are used as
defenses against herbivores in plants.
[66] For example,
canavanine is an analogue of
arginine that is found in many
legumes,
[67] and in particularly large amounts in
Canavalia gladiata (sword bean).
[68] This amino acid protects the plants from predators such as insects and can cause illness in people if some types of legumes are eaten without processing.
[69] The non-protein amino acid
mimosine is found in other species of legume, in particular
Leucaena leucocephala.
[70] This compound is an analogue of
tyrosine and can poison animals that graze on these plants.
§Uses in industry
Amino acids are used for a variety of applications in industry, but their main use is as additives to
animal feed. This is necessary, since many of the bulk components of these feeds, such as
soybeans, either have low levels or lack some of the
essential amino acids: Lysine, methionine, threonine, and tryptophan are most important in the production of these feeds.
[71] In this industry, amino acids are also used to chelate metal cations in order to improve the absorption of minerals from supplements, which may be required to improve the health or production of these animals.
[72]
The
food industry is also a major consumer of amino acids, in particular,
glutamic acid, which is used as a
flavor enhancer,
[73] and
Aspartame (aspartyl-phenylalanine-1-methyl ester) as a low-calorie
artificial sweetener.
[74] Similar technology to that used for animal nutrition is employed in the human nutrition industry to alleviate symptoms of mineral deficiencies, such as anemia, by improving mineral absorption and reducing negative side effects from inorganic mineral supplementation.
[75]
The chelating ability of amino acids has been used in fertilizers for agriculture to facilitate the delivery of minerals to plants in order to correct mineral deficiencies, such as iron chlorosis. These fertilizers are also used to prevent deficiencies from occurring and improving the overall health of the plants.
[76] The remaining production of amino acids is used in the synthesis of
drugs and
cosmetics.
[71]
§Expanded genetic code
Since 2001, 40 non-natural amino acids have been added into protein by creating a unique codon (recoding) and a corresponding transfer-RNA:aminoacyl – tRNA-synthetase pair to encode it with diverse physicochemical and biological properties in order to be used as a tool to exploring
protein structure and function or to create novel or enhanced proteins.
[13][14]
§Nullomers
Nullomers are codons that in theory code for an amino acid, however in nature there is a selective bias against using this codon in favor of another, for example bacteria prefer to use CGA instead of AGA to code for arginine.
[80] This creates some sequences that do not appear in the genome. This characteristic can be taken advantage of and used to create new selective cancer-fighting drugs
[81] and to prevent cross-contamination of DNA samples from crime-scene investigations.
[82]
§Chemical building blocks
Amino acids are important as low-cost
feedstocks. These compounds are used in
chiral pool synthesis as
enantiomerically pure building-blocks.
[83]
Amino acids have been investigated as precursors
chiral catalysts, e.g., for asymmetric
hydrogenation reactions, although no commercial applications exist.
[84]
§Biodegradable plastics
Amino acids are under development as components of a range of biodegradable polymers. These materials have applications as
environmentally friendly packaging and in medicine in
drug delivery and the construction of
prosthetic implants. These polymers include polypeptides,
polyamides, polyesters, polysulfides, and polyurethanes with amino acids either forming part of their main chains or bonded as side-chains. These modifications alter the physical properties and reactivities of the polymers.
[85] An interesting example of such materials is
polyaspartate, a water-soluble biodegradable polymer that may have applications in disposable
diapers and agriculture.
[86] Due to its solubility and ability to
chelate metal ions, polyaspartate is also being used as a biodegradeable anti-
scaling agent and a
corrosion inhibitor.
[87][88] In addition, the aromatic amino acid
tyrosine is being developed as a possible replacement for toxic
phenols such as
bisphenol A in the manufacture of
polycarbonates.
[89]
§Reactions
As amino acids have both a primary
amine group and a primary
carboxyl group, these chemicals can undergo most of the reactions associated with these functional groups. These include
nucleophilic addition,
amide bond formation, and
imine formation for the amine group, and
esterification,
amide bond formation, and
decarboxylation for the carboxylic acid group.
[90] The combination of these functional groups allow amino acids to be effective polydentate ligands for metal-amino acid chelates.
[91] The multiple side-chains of amino acids can also undergo chemical reactions.
[92] The types of these reactions are determined by the groups on these side-chains and are, therefore, different between the various types of amino acid.

The Strecker amino acid synthesis
§Chemical synthesis
Several methods exist to synthesize amino acids. One of the oldest methods begins with the
bromination at the α-carbon of a carboxylic acid. Nucleophilic substitution with
ammonia then converts the alkyl bromide to the amino acid.
[93] In alternative fashion, the
Strecker amino acid synthesis involves the treatment of an aldehyde with
potassium cyanide and ammonia, this produces an α-amino nitrile as an intermediate. Hydrolysis of the nitrile in acid then yields a α-amino acid.
[94] Using ammonia or ammonium salts in this reaction gives unsubstituted amino acids, whereas substituting primary and secondary amines will yield substituted amino acids.
[95] Likewise, using
ketones, instead of aldehydes, gives α,α-disubstituted amino acids.
[96] The classical synthesis gives
racemic mixtures of α-amino acids as products, but several alternative procedures using asymmetric auxiliaries
[97] or asymmetric catalysts
[98][99] have been developed.
[100]
At the current time, the most-adopted method is an
automated synthesis on a solid support (e.g.,
polystyrene beads), using
protecting groups (e.g.,
Fmoc and
t-Boc) and activating groups (e.g.,
DCC and
DIC).
§Peptide bond formation
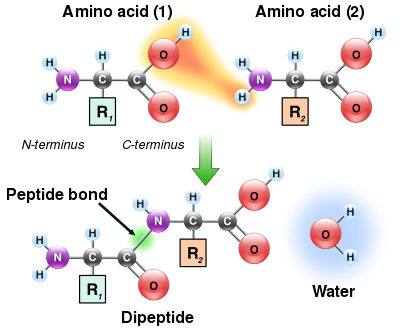
As both the amine and carboxylic acid groups of amino acids can react to form amide bonds, one amino acid molecule can react with another and become joined through an amide linkage. This
polymerization of amino acids is what creates proteins. This
condensation reaction yields the newly formed
peptide bond and a molecule of water. In cells, this reaction does not occur directly; instead, the amino acid is first activated by attachment to a
transfer RNA molecule through an
ester bond. This aminoacyl-tRNA is produced in an
ATP-dependent reaction carried out by an
aminoacyl tRNA synthetase.
[101] This aminoacyl-tRNA is then a substrate for the
ribosome, which catalyzes the attack of the amino group of the elongating protein chain on the ester bond.
[102] As a result of this mechanism, all proteins made by ribosomes are synthesized starting at their N-terminus and moving toward their C-terminus.
However, not all peptide bonds are formed in this way. In a few cases, peptides are synthesized by specific enzymes. For example, the tripeptide
glutathione is an essential part of the defenses of cells against oxidative stress. This peptide is synthesized in two steps from free amino acids.
[103] In the first step,
gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase condenses
cysteine and
glutamic acid through a peptide bond formed between the side-chain carboxyl of the glutamate (the gamma carbon of this side-chain) and the amino group of the cysteine. This dipeptide is then condensed with
glycine by
glutathione synthetase to form glutathione.
[104]
In chemistry, peptides are synthesized by a variety of reactions. One of the most-used in
solid-phase peptide synthesis uses the aromatic oxime derivatives of amino acids as activated units. These are added in sequence onto the growing peptide chain, which is attached to a solid resin support.
[105] The ability to easily synthesize vast numbers of different peptides by varying the types and order of amino acids (using
combinatorial chemistry) has made peptide synthesis particularly important in creating libraries of peptides for use in drug discovery through
high-throughput screening.
[106]
§Biosynthesis
In plants, nitrogen is first assimilated into organic compounds in the form of
glutamate, formed from alpha-ketoglutarate and ammonia in the mitochondrion. In order to form other amino acids, the plant uses
transaminases to move the amino group to another alpha-keto carboxylic acid. For example, aspartate aminotransferase converts glutamate and oxaloacetate to alpha-ketoglutarate and aspartate.
[107] Other organisms use transaminases for amino acid synthesis, too.
Nonstandard amino acids are usually formed through modifications to standard amino acids. For example,
homocysteine is formed through the
transsulfuration pathway or by the demethylation of methionine via the intermediate metabolite
S-adenosyl methionine,
[108] while
hydroxyproline is made by a
posttranslational modification of
proline.
[109]
Microorganisms and plants can synthesize many uncommon amino acids. For example, some microbes make
2-aminoisobutyric acid and
lanthionine, which is a sulfide-bridged derivative of alanine. Both of these amino acids are found in peptidic
lantibiotics such as
alamethicin.
[110] However, in plants,
1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid is a small disubstituted cyclic amino acid that is a key intermediate in the production of the plant hormone
ethylene.
[111]
§Catabolism
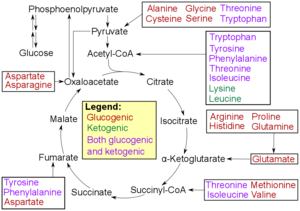
Catabolism of proteinogenic amino acids. Amino acids can be classified according to the properties of their main products as either of the following:
[112]
*
Glucogenic, with the products having the ability to form
glucose by
gluconeogenesis
*
Ketogenic, with the products not having the ability to form glucose. These products may still be used for
ketogenesis or
lipid synthesis.
* Amino acids catabolized into both glucogenic and ketogenic products.
Amino acids must first pass out of organelles and cells into blood circulation via
amino acid transporters, since the amine and carboxylic acid groups are typically ionized. Degradation of an amino acid, occurring in the liver and kidneys, often involves
deamination by moving its amino group to alpha-ketoglutarate, forming glutamate. This process involves transaminases, often the same as those used in amination during synthesis. In many vertebrates, the amino group is then removed through the
urea cycle and is excreted in the form of
urea. However, amino acid degradation can produce
uric acid or ammonia instead. For example,
serine dehydratase converts serine to pyruvate and ammonia.
[113] After removal of one or more amino groups, the remainder of the molecule can sometimes be used to synthesize new amino acids, or it can be used for energy by entering
glycolysis or the
citric acid cycle, as detailed in image at right.
§Physicochemical properties of amino acids
The 20 amino acids encoded directly by the genetic code can be divided into several groups based on their properties. Important factors are charge,
hydrophilicity or
hydrophobicity, size, and functional groups.
[29] These properties are important for
protein structure and
protein–protein interactions. The water-soluble proteins tend to have their hydrophobic residues (Leu, Ile, Val, Phe, and Trp) buried in the middle of the protein, whereas hydrophilic side-chains are exposed to the aqueous solvent. (Note that in
biochemistry, a residue refers to a specific
monomer within the
polymeric chain of a
polysaccharide,
protein or
nucleic acid.) The
integral membrane proteins tend to have outer rings of exposed
hydrophobic amino acids that anchor them into the
lipid bilayer. In the case part-way between these two extremes, some
peripheral membrane proteins have a patch of hydrophobic amino acids on their surface that locks onto the membrane. In similar fashion, proteins that have to bind to positively charged molecules have surfaces rich with negatively charged amino acids like
glutamate and
aspartate, while proteins binding to negatively charged molecules have surfaces rich with positively charged chains like
lysine and
arginine. There are different
hydrophobicity scales of amino acid residues.
[114]
Some amino acids have special properties such as
cysteine, that can form covalent
disulfide bonds to other cysteine residues,
proline that forms
a cycle to the polypeptide backbone, and
glycine that is more flexible than other amino acids.
Many proteins undergo a range of
posttranslational modifications, when additional chemical groups are attached to the amino acids in proteins. Some modifications can produce hydrophobic
lipoproteins,
[115] or hydrophilic
glycoproteins.
[116] These type of modification allow the reversible targeting of a protein to a membrane. For example, the addition and removal of the fatty acid
palmitic acid to cysteine residues in some signaling proteins causes the proteins to attach and then detach from cell membranes.
[117]
§Table of standard amino acid abbreviations and properties
| Alanine |
Ala |
A |
nonpolar |
neutral |
1.8 |
|
|
89 |
| Arginine |
Arg |
R |
Basic polar |
positive |
−4.5 |
|
|
174 |
| Asparagine |
Asn |
N |
polar |
neutral |
−3.5 |
|
|
132 |
| Aspartic acid |
Asp |
D |
acidic polar |
negative |
−3.5 |
|
|
133 |
| Cysteine |
Cys |
C |
nonpolar |
neutral |
2.5 |
250 |
0.3 |
121 |
| Glutamic acid |
Glu |
E |
acidic polar |
negative |
−3.5 |
|
|
147 |
| Glutamine |
Gln |
Q |
polar |
neutral |
−3.5 |
|
|
146 |
| Glycine |
Gly |
G |
nonpolar |
neutral |
−0.4 |
|
|
75 |
| Histidine |
His |
H |
Basic polar |
positive(10%)
neutral(90%) |
−3.2 |
211 |
5.9 |
155 |
| Isoleucine |
Ile |
I |
nonpolar |
neutral |
4.5 |
|
|
131 |
| Leucine |
Leu |
L |
nonpolar |
neutral |
3.8 |
|
|
131 |
| Lysine |
Lys |
K |
Basic polar |
positive |
−3.9 |
|
|
146 |
| Methionine |
Met |
M |
nonpolar |
neutral |
1.9 |
|
|
149 |
| Phenylalanine |
Phe |
F |
nonpolar |
neutral |
2.8 |
257, 206, 188 |
0.2, 9.3, 60.0 |
165 |
| Proline |
Pro |
P |
nonpolar |
neutral |
−1.6 |
|
|
115 |
| Serine |
Ser |
S |
polar |
neutral |
−0.8 |
|
|
105 |
| Threonine |
Thr |
T |
polar |
neutral |
−0.7 |
|
|
119 |
| Tryptophan |
Trp |
W |
nonpolar |
neutral |
−0.9 |
280, 219 |
5.6, 47.0 |
204 |
| Tyrosine |
Tyr |
Y |
polar |
neutral |
−1.3 |
274, 222, 193 |
1.4, 8.0, 48.0 |
181 |
| Valine |
Val |
V |
nonpolar |
neutral |
4.2 |
|
|
117 |
Two additional amino acids are in some species coded for by
codons that are usually interpreted as
stop codons:
In addition to the specific amino acid codes, placeholders are used in cases where
chemical or
crystallographic analysis of a peptide or protein cannot conclusively determine the identity of a residue.
| Ambiguous Amino Acids |
3-Letter |
1-Letter |
| Asparagine or aspartic acid |
Asx |
B |
| Glutamine or glutamic acid |
Glx |
Z |
| Leucine or Isoleucine |
Xle |
J |
| Unspecified or unknown amino acid |
Xaa |
X |
Unk is sometimes used instead of
Xaa, but is less standard.
In addition, many
non-standard amino acids have a specific code. For example, several peptide drugs, such as
Bortezomib and
MG132, are
artificially synthesized and retain their
protecting groups, which have specific codes. Bortezomib is
Pyz-Phe-boroLeu, and MG132 is
Z-Leu-Leu-Leu-al. To aid in the analysis of protein structure,
photo-reactive amino acid analogs are available. These include
photoleucine (
pLeu) and
photomethionine (
pMet).
[122]