Sustainable energy is a principle in which human use of energy "meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs."
Another definition of sustainable energy is that it is consumed at
insignificant rates compared to its supply and with manageable
collateral effects, especially environmental effects. Sustainable energy strategies generally have two pillars: cleaner methods of producing energy, and the promotion of efficient energy use.
Sustainable energy technologies are deployed to generate electricity, to heat and cool buildings, and to power vehicles. When referring to methods of producing energy, the term "sustainable energy" is often used interchangeably with the term "renewable energy". In general, renewable energy sources such as solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, and tidal energy, are widely considered to be sustainable energy sources. However, implementation of particular renewable energy projects, such as the damming of rivers to generate hydroelectricity or the clearing of forests for production of biofuels , sometimes raises significant sustainability concerns. There is considerable controversy over whether nuclear energy can be considered sustainable.
Costs of sustainable energy sources have decreased immensely throughout the years, and continue to fall. Increasingly, effective government policies support investor confidence and these markets are expanding. Considerable progress is being made in the energy transition from fossil fuels to ecologically sustainable systems, to the point where many studies support 100% renewable energy.
The organizing principle for sustainability is sustainable development, which includes the four interconnected domains: ecology, economics, politics and culture. Sustainability science is the study of sustainable development and environmental science.
Sustainable energy technologies are deployed to generate electricity, to heat and cool buildings, and to power vehicles. When referring to methods of producing energy, the term "sustainable energy" is often used interchangeably with the term "renewable energy". In general, renewable energy sources such as solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, and tidal energy, are widely considered to be sustainable energy sources. However, implementation of particular renewable energy projects, such as the damming of rivers to generate hydroelectricity or the clearing of forests for production of biofuels , sometimes raises significant sustainability concerns. There is considerable controversy over whether nuclear energy can be considered sustainable.
Costs of sustainable energy sources have decreased immensely throughout the years, and continue to fall. Increasingly, effective government policies support investor confidence and these markets are expanding. Considerable progress is being made in the energy transition from fossil fuels to ecologically sustainable systems, to the point where many studies support 100% renewable energy.
The organizing principle for sustainability is sustainable development, which includes the four interconnected domains: ecology, economics, politics and culture. Sustainability science is the study of sustainable development and environmental science.
History
Definitions
The concept of "sustainable development" was described by the World Commission on Environment and Development in its 1987 book Our Common Future. Its definition of "sustainability", now used widely, was:
Sustainable development should meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
In this book, the Commission described four "key elements" of
sustainability with respect to energy: the ability to increase the
supply of energy to meet growing human needs, energy efficiency and
conservation, public health and safety, and "protection of the biosphere
and prevention of more localized forms of pollution."
Energy efficiency and renewable energy are said to be the twin pillars of sustainable energy. In the broader context of sustainable development, there are three pillars, ecology, economy and society. Some ways in which sustainable energy has been defined are:
- "Effectively, the provision of energy such that it meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. ...Sustainable Energy has two key components: renewable energy and energy efficiency." – Renewable Energy and Efficiency Partnership (British)
- "Dynamic harmony between equitable availability of energy-intensive goods and services to all people and the preservation of the earth for future generations." And, "The solution will lie in finding sustainable energy sources and more efficient means of converting and utilizing energy." – Sustainable Energy by J. W. Tester, et al., from MIT Press.
This sets sustainable energy apart from other renewable energy terminology such as alternative energy
by focusing on the ability of an energy source to continue providing
energy. Sustainable energy can produce some pollution of the
environment, as long as it is not sufficient to prohibit heavy use of
the source for an indefinite amount of time. Sustainable energy is also
distinct from low-carbon energy, which is sustainable only in the sense that it does not add to the CO2 in the atmosphere.
Green Energy is energy that can be extracted, generated, and/or
consumed without any significant negative impact to the environment. The
planet has a natural capability to recover which means pollution that
does not go beyond that capability can still be termed green.
Green power is a subset of renewable energy and represents those
renewable energy resources and technologies that provide the highest
environmental benefit. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency defines green power as electricity produced from solar, wind, geothermal, biogas, biomass and low-impact small hydroelectric sources. Customers often buy green power for avoided environmental impacts and its greenhouse gas reduction benefits.
Renewable energy technologies
Renewable energy technologies are essential contributors to sustainable energy as they generally contribute to world energy security, reducing dependence on fossil fuel resources, and providing opportunities for mitigating greenhouse gases. The International Energy Agency states that:
Conceptually, one can define three generations of renewables technologies, reaching back more than 100 years.
First-generation technologies emerged from the industrial revolution at the end of the 19th century and include hydropower, biomass combustion and geothermal power and heat. Some of these technologies are still in widespread use.
Second-generation technologies include solar heating and cooling, wind power, modern forms of bioenergy and solar photovoltaics. These are now entering markets as a result of research, development and demonstration (RD&D) investments since the 1980s. The initial investment was prompted by energy security concerns linked to the oil crises (1973 and 1979) of the 1970s but the continuing appeal of these renewables is due, at least in part, to environmental benefits. Many of the technologies reflect significant advancements in materials.
Third-generation technologies are still under development and include advanced biomass gasification, biorefinery technologies, concentrating solar thermal power, hot dry rock geothermal energy and ocean energy. Advances in nanotechnology may also play a major role.
— International Energy Agency, RENEWABLES IN GLOBAL ENERGY SUPPLY, An IEA Fact Sheet
First- and second-generation technologies have entered the markets,
and third-generation technologies heavily depend on long term research
and development commitments, where the public sector has a role to play.
Various Cost–benefit analysis
work by a disparate array of specialists and agencies have been
conducted to determine the cheapest and quickest paths to decarbonizing
the energy supply of the world. With the topic being one of considerable controversy, particularly on the role of nuclear energy.
First-generation technologies
One of many power plants at The Geysers, a geothermal power field in northern California, with a total output of over 750 MW.
First-generation technologies are most competitive in locations with abundant resources. Their future use depends on the exploration of the available resource potential, particularly in developing countries, and on overcoming challenges related to the environment and social acceptance.
— International Energy Agency, RENEWABLES IN GLOBAL ENERGY SUPPLY, An IEA Fact Sheet
Among sources of renewable energy, hydroelectric plants
have the advantages of being long-lived—many existing plants have
operated for more than 100 years. Also, hydroelectric plants are clean
and have few emissions. Criticisms directed at large-scale hydroelectric
plants include: dislocation of people living where the reservoirs are
planned, and release of significant amounts of carbon dioxide during construction and flooding of the reservoir.
Hydroelectric dams are one of the most widely deployed sources of sustainable energy.
However, it has been found that high emissions are associated only
with shallow reservoirs in warm (tropical) locales, and recent
innovations in hydropower turbine technology are enabling efficient
development of low-impact run-of-the-river hydroelectricity projects.
Generally speaking, hydroelectric plants produce much lower life-cycle
emissions than other types of generation. Hydroelectric power, which
underwent extensive development during growth of electrification in the
19th and 20th centuries, is experiencing resurgence of development in
the 21st century. The areas of greatest hydroelectric growth are the
booming economies of Asia. China is the development leader; however,
other Asian nations are installing hydropower at a rapid pace. This
growth is driven by much increased energy costs—especially for imported
energy—and widespread desires for more domestically produced, clean,
renewable, and economical generation.
Hydroelectric dam in cross section
Geothermal power
plants can operate 24 hours per day, providing base-load capacity, and
the world potential capacity for geothermal power generation is
estimated at 85 GW over the next 30 years. However, geothermal power is
accessible only in limited areas of the world, including the United States, Central America, East Africa, Iceland, Indonesia, and the Philippines. The costs of geothermal energy have dropped substantially from the systems built in the 1970s. Geothermal heat
generation can be competitive in many countries producing geothermal
power, or in other regions where the resource is of a lower temperature.
Enhanced geothermal system
(EGS) technology does not require natural convective hydrothermal
resources, so it can be used in areas that were previously unsuitable
for geothermal power, if the resource is very large. EGS is currently
under research at the U.S. Department of Energy.
Biomass briquettes
are increasingly being used in the developing world as an alternative
to charcoal. The technique involves the conversion of almost any plant
matter into compressed briquettes that typically have about 70% the
calorific value of charcoal. There are relatively few examples of
large-scale briquette production. One exception is in North Kivu, in eastern Democratic Republic of Congo,
where forest clearance for charcoal production is considered to be the
biggest threat to mountain gorilla habitat. The staff of Virunga National Park
have successfully trained and equipped over 3500 people to produce
biomass briquettes, thereby replacing charcoal produced illegally inside
the national park, and creating significant employment for people
living in extreme poverty in conflict-affected areas.
In Europe in the 19th century, there were about 200,000
windmills, slightly more than the modern wind turbines of the 21st
century.
They were mainly used to grind grain and to pump water. The age of coal
powered steam engines replaced this early use of wind power.
Second-generation technologies
Wind power: worldwide installed capacity
Markets for second-generation technologies are strong and growing, but only in a few countries. The challenge is to broaden the market base for continued growth worldwide. Strategic deployment in one country not only reduces technology costs for users there, but also for those in other countries, contributing to overall cost reductions and performance improvement.
— International Energy Agency, RENEWABLES IN GLOBAL ENERGY SUPPLY, An IEA Fact Sheet
Solar heating
systems are a well known second-generation technology and generally
consist of solar thermal collectors, a fluid system to move the heat
from the collector to its point of usage, and a reservoir or tank for
heat storage and subsequent use. The systems may be used to heat
domestic hot water, swimming pool water, or for space heating. The heat can also be used for industrial applications or as an energy input for other uses such as cooling equipment.
In many climates, a solar heating system can provide a very high
percentage (20 to 80%) of domestic hot water energy.
Energy received from the sun by the earth is that of electromagnetic
radiation. Light ranges of visible, infrared, ultraviolet, x-rays, and
radio waves received by the earth through solar energy. The highest
power of radiation comes from visible light. Solar power is complicated
due to changes in seasons and from day to night. Cloud cover can also
add to complications of solar energy, and not all radiation from the sun
reaches earth because it is absorbed and dispersed due to clouds and
gases within the earth's atmospheres.
In the 1980s and early 1990s, most photovoltaic modules provided remote-area power supply, but from around 1995, industry efforts have focused increasingly on developing building integrated photovoltaics and power plants for grid connected applications. Currently the largest photovoltaic power plant in North America is the Nellis Solar Power Plant (15 MW). There is a proposal to build a Solar power station in Victoria, Australia, which would be the world's largest PV power station, at 154 MW. Other large photovoltaic power stations include the Girassol solar power plant (62 MW), and the Waldpolenz Solar Park (40 MW).
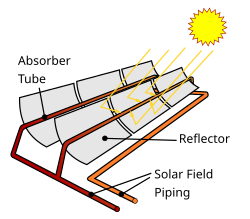
Sketch of a Parabolic Trough Collector
Some of the second-generation renewables, such as wind power, have
high potential and have already realised relatively low production
costs. At the end of 2008, worldwide wind farm capacity was 20,791 megawatts (MW), representing an increase of 28.8 percent during the year, and wind power produced some 1.3% of global electricity consumption. Wind power accounts for approximately 20% of electricity use in Denmark, 9% in Spain, and 7% in Germany.
However, it may be difficult to site wind turbines in some areas for
aesthetic or environmental reasons, and it may be difficult to integrate
wind power into electricity grids in some cases.
Solar thermal power stations have been successfully operating in California commercially since the late 1980s, including the largest solar power plant of any kind, the 350 MW Solar Energy Generating Systems. Nevada Solar One is another 64MW plant which has recently opened. Other parabolic trough power plants being proposed are two 50MW plants in Spain, and a 100MW plant in Israel.
Solar and wind are Intermittent energy sources
that supply electricity 10-40% of the time. To compensate for this
characteristic, it is common to pair their production with already
existing hydroelectricity or natural gas generation. In regions where this isn't available, wind and solar can be paired with significantly more expensive pumped-storage hydroelectricity.
Information on pump, California
Brazil has one of the largest renewable energy programs in the world, involving production of ethanol fuel from sugar cane, and ethanol
now provides 18 percent of the country's automotive fuel. As a result
of this, together with the exploitation of domestic deep water oil
sources, Brazil, which years ago had to import a large share of the
petroleum needed for domestic consumption, recently reached complete
self-sufficiency in oil.
Most cars on the road today in the U.S. can run on blends of up
to 10% ethanol, and motor vehicle manufacturers already produce vehicles
designed to run on much higher ethanol blends. Ford, DaimlerChrysler, and GM
are among the automobile companies that sell "flexible-fuel" cars,
trucks, and minivans that can use gasoline and ethanol blends ranging
from pure gasoline up to 85% ethanol (E85). By mid-2006, there were
approximately six million E85-compatible vehicles on U.S. roads.
Third-generation technologies
MIT's Solar House#1 built in 1939 used seasonal thermal energy storage (STES) for year-round heating.
Third-generation technologies are not yet widely demonstrated or commercialized. They are on the horizon and may have potential comparable to other renewable energy technologies, but still depend on attracting sufficient attention and RD&D funding. These newest technologies include advanced biomass gasification, biorefinery technologies, solar thermal power stations, hot dry rock geothermal energy and ocean energy.
— International Energy Agency, RENEWABLES IN GLOBAL ENERGY SUPPLY, An IEA Fact Sheet
Bio-fuels may be defined as "renewable," yet may not be "sustainable," due to soil degradation.
As of 2012, 40% of American corn production goes toward ethanol.
Ethanol takes up a large percentage of "Clean Energy Use" when in fact,
it is still debatable whether ethanol should be considered as a "Clean
Energy."
According to the International Energy Agency, new bioenergy
(biofuel) technologies being developed today, notably cellulosic ethanol
biorefineries, could allow biofuels to play a much bigger role in the
future than previously thought.
Cellulosic ethanol can be made from plant matter composed primarily of
inedible cellulose fibers that form the stems and branches of most
plants. Crop residues (such as corn stalks, wheat straw and rice straw),
wood waste and municipal solid waste are potential sources of cellulosic biomass. Dedicated energy crops, such as switchgrass, are also promising cellulose sources that can be sustainably produced in many regions of the United States.
The world's first commercial tidal stream generator – SeaGen – in Strangford Lough. The strong wake shows the power in the tidal current.
In terms of ocean energy, another third-generation technology, Portugal has the world's first commercial wave farm, the Aguçadora Wave Park, under construction in 2007. The farm will initially use three Pelamis P-750 machines generating 2.25 MW. and costs are put at 8.5 million euro.
Subject to successful operation, a further 70 million euro is likely to
be invested before 2009 on a further 28 machines to generate 525 MW. Funding for a wave farm in Scotland was announced in February, 2007 by the Scottish Executive, at a cost of over 4 million pounds, as part of a £13 million funding packages for ocean power in Scotland. The farm will be the world's largest with a capacity of 3 MW generated by four Pelamis machines.
In 2007, the world's first turbine to create commercial amounts of energy using tidal power was installed in the narrows of Strangford Lough
in Ireland. The 1.2 MW underwater tidal electricity generator takes
advantage of the fast tidal flow in the lough which can be up to 4m/s. Although the generator is powerful enough to power up to a thousand homes, the turbine has a minimal environmental impact, as it is almost entirely submerged, and the rotors turn slowly enough that they pose no danger to wildlife.
Solar power panels that use nanotechnology,
which can create circuits out of individual silicon molecules, may cost
half as much as traditional photovoltaic cells, according to executives
and investors involved in developing the products. Nanosolar
has secured more than $100 million from investors to build a factory
for nanotechnology thin-film solar panels. The company's plant has a
planned production capacity of 430 megawatts peak power of solar cells
per year. Commercial production started and first panels have been
shipped to customers in late 2007.
Large national and regional research projects on artificial photosynthesis are designing nanotechnology-based systems that use solar energy to split water into hydrogen fuel. and a proposal has been made for a Global Artificial Photosynthesis project In 2011, researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) developed what they are calling an "Artificial Leaf", which is capable of splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen
directly from solar power when dropped into a glass of water. One side
of the "Artificial Leaf" produces bubbles of hydrogen, while the other
side produces bubbles of oxygen.
Most current solar power plants are made from an array of similar
units where each unit is continuously adjusted, e.g., with some step
motors, so that the light converter stays in focus of the sun light. The
cost of focusing light on converters such as high-power solar panels, Stirling engine, etc. can be dramatically decreased with a simple and efficient rope mechanics.
In this technique many units are connected with a network of ropes so
that pulling two or three ropes is sufficient to keep all light
converters simultaneously in focus as the direction of the sun changes.
Japan and China have national programs aimed at commercial scale Space-Based Solar Power (SBSP). The China Academy of Space Technology (CAST) won the 2015 International SunSat Design Competition with this video of their Multi-Rotary Joint design. Proponents of SBSP claim that Space-Based Solar Power would be clean, constant, and global, and could scale to meet all planetary energy demand. A recent multi-agency industry proposal
(echoing the 2008 Pentagon recommendation) won the
SECDEF/SECSTATE/USAID Director D3 (Diplomacy, Development, Defense)
Innovation Challenge.
Enabling technologies for renewable energy
Heat pumps and Thermal energy storage
are classes of technologies that can enable the utilization of
renewable energy sources that would otherwise be inaccessible due to a
temperature that is too low for utilization or a time lag between when
the energy is available and when it is needed. While enhancing the
temperature of available renewable thermal energy, heat pumps have the
additional property of leveraging electrical power (or in some cases
mechanical or thermal power) by using it to extract additional energy
from a low quality source (such as seawater, lake water, the ground, the
air, or waste heat from a process).
Thermal storage technologies allow heat or cold to be stored for periods of time ranging from hours or overnight to interseasonal, and can involve storage of sensible energy (i.e. by changing the temperature of a medium) or latent energy
(i.e. through phase changes of a medium, such between water and slush
or ice). Short-term thermal storage can be used for peak-shaving in
district heating or electrical distribution systems. Kinds of renewable
or alternative energy sources that can be enabled include natural energy
(e.g. collected via solar-thermal collectors, or dry cooling towers
used to collect winter's cold), waste energy (e.g. from HVAC equipment,
industrial processes or power plants), or surplus energy (e.g. as
seasonally from hydropower projects or intermittently from wind farms).
The Drake Landing Solar Community (Alberta, Canada) is illustrative. borehole thermal energy storage
allows the community to get 97% of its year-round heat from solar
collectors on the garage roofs, which most of the heat collected in
summer.
Types of storages for sensible energy include insulated tanks, borehole
clusters in substrates ranging from gravel to bedrock, deep aquifers,
or shallow lined pits that are insulated on top. Some types of storage
are capable of storing heat or cold between opposing seasons
(particularly if very large), and some storage applications require
inclusion of a heat pump. Latent heat is typically stored in ice tanks or what are called phase-change materials (PCMs).
Energy efficiency
Moving
towards energy sustainability will require changes not only in the way
energy is supplied, but in the way it is used, and reducing the amount
of energy required to deliver various goods or services is essential.
Opportunities for improvement on the demand side of the energy equation
are as rich and diverse as those on the supply side, and often offer
significant economic benefits.
Renewable energy and energy efficiency
are sometimes said to be the "twin pillars" of sustainable energy
policy. Both resources must be developed in order to stabilize and
reduce carbon dioxide emissions. Efficiency slows down energy demand
growth so that rising clean energy supplies can make deep cuts in fossil
fuel use. If energy use grows too fast, renewable energy development
will chase a receding target. A recent historical analysis has
demonstrated that the rate of energy efficiency improvements has generally been outpaced by the rate of growth in energy demand, which is due to continuing economic and population growth.
As a result, despite energy efficiency gains, total energy use and
related carbon emissions have continued to increase. Thus, given the
thermodynamic and practical limits of energy efficiency improvements,
slowing the growth in energy demand is essential.
However, unless clean energy supplies come online rapidly, slowing
demand growth will only begin to reduce total emissions; reducing the
carbon content of energy sources is also needed. Any serious vision of a
sustainable energy economy thus requires commitments to both renewables
and efficiency.
Renewable energy (and energy efficiency) are no longer niche
sectors that are promoted only by governments and environmentalists. The
increased levels of investment and the fact that much of the capital is
coming from more conventional financial actors suggest that sustainable
energy options are now becoming mainstream. An example of this would be The Alliance to Save Energy's
Project with Stahl Consolidated Manufacturing, (Huntsville, Alabama,
USA) (StahlCon 7), a patented generator shaft designed to reduce
emissions within existing power generating systems, granted publishing
rights to the Alliance in 2007.
Climate change concerns coupled with high oil prices
and increasing government support are driving increasing rates of
investment in the sustainable energy industries, according to a trend
analysis from the United Nations Environment Programme. According to UNEP,
global investment in sustainable energy in 2007 was higher than
previous levels, with $148 billion of new money raised in 2007, an
increase of 60% over 2006. Total financial transactions in sustainable
energy, including acquisition activity, was $204 billion.
Investment flows in 2007 broadened and diversified, making the
overall picture one of greater breadth and depth of sustainable energy
use. The mainstream capital markets are "now fully receptive to
sustainable energy companies, supported by a surge in funds destined for
clean energy investment".
Smart-grid technology
Smart grid refers to a class of technology people are using to bring
utility electricity delivery systems into the 21st century, using
computer-based remote control and automation.
These systems are made possible by two-way communication technology and
computer processing that has been used for decades in other industries.
They are beginning to be used on electricity networks, from the power
plants and wind farms all the way to the consumers of electricity in
homes and businesses. They offer many benefits to utilities and
consumers—mostly seen in big improvements in energy efficiency on the
electricity grid and in the energy users’ homes and offices.
Green energy and green power
A solar trough array is an example of green energy.
Public seat with integrated solar panel in Singapore-anyone can sit and plug in their mobile phone for free charging
Green energy includes natural energetic processes that can be
harnessed with little pollution. Green power is electricity generated
from renewable energy sources.
Anaerobic digestion, geothermal power, wind power, small-scale hydropower, solar energy, biomass power, tidal power, wave power, and some forms of nuclear power (ones which are able to "burn" nuclear waste through a process known as nuclear transmutation, such as an Integral Fast Reactor, and therefore belong in the "Green Energy" category). Some definitions may also include power derived from the incineration of waste.
Some people, including Greenpeace founder and first member Patrick Moore, George Monbiot, Bill Gates and James Lovelock have specifically classified nuclear power as green energy. Others, including Greenpeace's Phil Radford disagree, claiming that the problems associated with radioactive waste and the risk of nuclear accidents (such as the Chernobyl disaster)
pose an unacceptable risk to the environment and to humanity. However,
newer nuclear reactor designs are capable of utilizing what is now
deemed "nuclear waste" until it is no longer (or dramatically less)
dangerous, and have design features that greatly minimize the
possibility of a nuclear accident. These designs have yet to be
commercialized.
Some have argued that although green energy is a commendable
effort in solving the world's increasing energy consumption, it must be
accompanied by a cultural change that encourages the decrease of the
world's appetite for energy.
In several countries with common carrier arrangements, electricity retailing arrangements make it possible for consumers to purchase green electricity (renewable electricity) from either their utility or a green power provider.
When energy is purchased from the electricity network, the power
reaching the consumer will not necessarily be generated from green
energy sources. The local utility company, electric company, or state power pool buys their electricity from electricity producers who may be generating from fossil fuel, nuclear
or renewable energy sources. In many countries green energy currently
provides a very small amount of electricity, generally contributing less
than 2 to 5% to the overall pool. In some U.S. states, local
governments have formed regional power purchasing pools using Community Choice Aggregation and Solar Bonds to achieve a 51% renewable mix or higher, such as in the City of San Francisco.
By participating in a green energy program a consumer may be
having an effect on the energy sources used and ultimately might be
helping to promote and expand the use of green energy. They are also
making a statement to policy makers that they are willing to pay a price
premium to support renewable energy. Green energy consumers either
obligate the utility companies to increase the amount of green energy
that they purchase from the pool (so decreasing the amount of non-green
energy they purchase), or directly fund the green energy through a green
power provider. If insufficient green energy sources are available, the
utility must develop new ones or contract
with a third party energy supplier to provide green energy, causing
more to be built. However, there is no way the consumer can check
whether or not the electricity bought is "green" or otherwise.
In some countries such as the Netherlands, electricity companies
guarantee to buy an equal amount of 'green power' as is being used by
their green power customers. The Dutch government exempts green power from pollution taxes, which means green power is hardly any more expensive than other power.
A more recent concept for improving our electrical grid is to
beam microwaves from Earth-orbiting satellites or the moon to directly
when and where there is demand. The power would be generated from solar
energy captured on the lunar surface In this system, the receivers would
be "broad, translucent tent-like structures that would receive
microwaves and convert them to electricity". NASA said in 2000 that the
technology was worth pursuing but it is still too soon to say if the
technology will be cost-effective.
The World Wide Fund for Nature and several green electricity labeling organizations created the (now defunct) Eugene Green Energy Standard
under which the national green electricity certification schemes could
be accredited to ensure that the purchase of green energy leads to the
provision of additional new green energy resources.
Innovative green energy trends and solutions were at the center of discussion at EXPO 2017
in Astana, Kazakhstan. Specialized Expo 2017 was themed "Future Energy"
and brought together representatives of 115 countries and 22
international organizations.
Local green energy systems
A small Quietrevolution QR5 Gorlov type
vertical axis wind turbine in Bristol, England. Measuring 3 m in
diameter and 5 m high, it has a nameplate rating of 6.5 kW to the grid.
Those not satisfied with the third-party grid approach to green
energy via the power grid can install their own locally based renewable
energy system. Renewable energy electrical systems from solar to wind to
even local hydro-power in some cases, are some of the many types of
renewable energy systems available locally. Additionally, for those
interested in heating and cooling their dwelling via renewable energy, geothermal heat pump systems that tap the constant temperature of the earth, which is around 7 to 15 degrees Celsius a few feet underground and increases dramatically at greater depths, are an option over conventional natural gas and petroleum-fueled heat approaches. Also, in geographic locations where the Earth's Crust is especially thin, or near volcanoes (as is the case in Iceland)
there exists the potential to generate even more electricity than would
be possible at other sites, thanks to a more significant temperature gradient at these locales.
The advantage of this approach in the United States is that many
states offer incentives to offset the cost of installation of a
renewable energy system. In California, Massachusetts and several other
U.S. states, a new approach to community energy supply called Community Choice Aggregation
has provided communities with the means to solicit a competitive
electricity supplier and use municipal revenue bonds to finance
development of local green energy resources. Individuals are usually
assured that the electricity they are using is actually produced from a
green energy source that they control. Once the system is paid for, the
owner of a renewable energy system will be producing their own renewable
electricity for essentially no cost and can sell the excess to the
local utility at a profit.
Using green energy
A 01 KiloWatt Micro Windmill for Domestic Usage
Renewable energy, after its generation, needs to be stored in a
medium for use with autonomous devices as well as vehicles. Also, to
provide household electricity in remote areas (that is areas which are
not connected to the mains electricity grid),
energy storage is required for use with renewable energy. Energy
generation and consumption systems used in the latter case are usually stand-alone power systems.
Examples are:
- energy carriers as hydrogen, liquid nitrogen, compressed air, oxyhydrogen, batteries, to power vehicles.
- flywheel energy storage, pumped-storage hydroelectricity is more usable in stationary applications (e.g. to power homes and offices). In household power systems, conversion of energy can also be done to reduce smell. For example, organic matter such as cow dung and spoilable organic matter can be converted to biochar. To eliminate emissions, carbon capture and storage is then used.
Usually however, renewable energy is derived from the mains
electricity grid. This means that energy storage is mostly not used, as
the mains electricity grid is organized to produce the exact amount of
energy being consumed at that particular moment. Energy production on
the mains electricity grid is always set up as a combination of
(large-scale) renewable energy plants, as well as other power plants as fossil-fuel power plants and nuclear power.
This combination however, which is essential for this type of energy
supply (as e.g. wind turbines, solar power plants etc.) can only produce
when the wind blows and the sun shines. This is also one of the main
drawbacks of the system as fossil fuel power plants are polluting and are
a main cause of global warming
(nuclear power being an exception). Although fossil fuel power plants
too can be made emissionless (through carbon capture and storage), as
well as renewable (if the plants are converted to e.g. biomass) the best
solution is still to phase out the latter power plants over time.
Nuclear power plants too can be more or less eliminated from their
problem of nuclear waste through the use of nuclear reprocessing and newer plants as fast breeder and nuclear fusion plants.
Renewable energy power plants do provide a steady flow of energy.
For example, hydropower plants, ocean thermal plants, osmotic power
plants all provide power at a regulated pace, and are thus available
power sources at any given moment (even at night, windstill moments
etc.). At present however, the number of steady-flow renewable energy
plants alone is still too small to meet energy demands at the times of
the day when the irregular producing renewable energy plants cannot
produce power.
Besides the greening of fossil fuel and nuclear power plants,
another option is the distribution and immediate use of power from
solely renewable sources. In this set-up energy storage is again not
necessary. For example, TREC
has proposed to distribute solar power from the Sahara to Europe.
Europe can distribute wind and ocean power to the Sahara and other
countries. In this way, power is produced at any given time as at any
point of the planet as the sun or the wind is up or ocean waves and
currents are stirring. This option however is probably not possible in
the short-term, as fossil fuel and nuclear power are still the main
sources of energy on the mains electricity net and replacing them will
not be possible overnight.
Several large-scale energy storage suggestions for the grid have been done. Worldwide there is over 100 GW of Pumped-storage hydroelectricity.
This improves efficiency and decreases energy losses but a conversion
to an energy storing mains electricity grid is a very costly solution.
Some costs could potentially be reduced by making use of energy storage
equipment the consumer buys and not the state. An example is batteries
in electric cars that would double as an energy buffer for the
electricity grid. However besides the cost, setting-up such a system
would still be a very complicated and difficult procedure. Also, energy
storage apparatus' as car batteries are also built with materials that
pose a threat to the environment (e.g. Lithium). The combined production
of batteries for such a large part of the population would still have
environmental concerns. Besides car batteries however, other Grid energy storage projects make use of less polluting energy carriers (e.g. compressed air tanks and flywheel energy storage).
Green energy and labeling by region
European Union
Directive 2004/8/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 February 2004 on the promotion of cogeneration based on a useful heat demand in the internal energy market includes the article 5 (Guarantee of origin of electricity from high-efficiency cogeneration).
European environmental NGOs have launched an ecolabel for green power. The ecolabel is called EKOenergy.
It sets criteria for sustainability, additionality, consumer
information and tracking. Only part of electricity produced by
renewables fulfills the EKOenergy criteria.
A Green Energy Supply Certification Scheme was launched in the United Kingdom in February 2010. This implements guidelines from the Energy Regulator, Ofgem, and sets requirements on transparency, the matching of sales by renewable energy supplies, and additionality.
United States
The United States Department of Energy (DOE), the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and the Center for Resource Solutions (CRS)
recognizes the voluntary purchase of electricity from renewable energy
sources (also called renewable electricity or green electricity) as
green power.
The most popular way to purchase renewable energy as revealed by NREL data is through purchasing Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs). According to a Natural Marketing Institute (NMI) survey 55 percent of American consumers want companies to increase their use of renewable energy.
DOE selected six companies for its 2007 Green Power Supplier Awards, including Constellation NewEnergy; 3Degrees; Sterling Planet; SunEdison; Pacific Power and Rocky Mountain Power; and Silicon Valley Power. The combined green power provided by those six winners equals more than 5 billion kilowatt-hours
per year, which is enough to power nearly 465,000 average U.S.
households. In 2014, Arcadia Power made RECS available to homes and
businesses in all 50 states, allowing consumers to use "100% green
power" as defined by the EPA's Green Power Partnership.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) Green Power Partnership is a voluntary program that supports the organizational procurement of renewable electricity
by offering expert advice, technical support, tools and resources. This
can help organizations lower the transaction costs of buying renewable
power, reduce carbon footprint, and communicate its leadership to key stakeholders.
Throughout the country, more than half of all U.S. electricity
customers now have an option to purchase some type of green power
product from a retail electricity provider.
Roughly one-quarter of the nation's utilities offer green power
programs to customers, and voluntary retail sales of renewable energy in
the United States totaled more than 12 billion kilowatt-hours in 2006, a
40% increase over the previous year.
In the United States, one of the main problems with purchasing
green energy through the electrical grid is the current centralized
infrastructure that supplies the consumer’s electricity. This
infrastructure has led to increasingly frequent brown outs and black
outs, high CO2 emissions, higher energy costs, and power quality issues. An additional $450 billion will be invested to expand this fledgling system over the next 20 years to meet increasing demand.
In addition, this centralized system is now being further overtaxed
with the incorporation of renewable energies such as wind, solar, and
geothermal energies. Renewable resources, due to the amount of space
they require, are often located in remote areas where there is a lower
energy demand. The current infrastructure would make transporting this
energy to high demand areas, such as urban centers, highly inefficient
and in some cases impossible. In addition, despite the amount of
renewable energy produced or the economic viability of such technologies
only about 20 percent will be able to be incorporated into the grid. To
have a more sustainable energy profile, the United States must move
towards implementing changes to the electrical grid that will
accommodate a mixed-fuel economy.
Several initiatives are being proposed to mitigate distribution
problems. First and foremost, the most effective way to reduce USA’s CO2
emissions and slow global warming is through conservation efforts.
Opponents of the current US electrical grid have also advocated for
decentralizing the grid. This system would increase efficiency by
reducing the amount of energy lost in transmission. It would also be
economically viable as it would reduce the amount of power lines that
will need to be constructed in the future to keep up with demand.
Merging heat and power in this system would create added benefits and
help to increase its efficiency by up to 80-90%. This is a significant
increase from the current fossil fuel plants which only have an
efficiency of 34%.
Sustainable energy research
There are numerous organizations within the academic, federal, and
commercial sectors conducting large scale advanced research in the field
of sustainable energy. This research spans several areas of focus
across the sustainable energy spectrum. Most of the research is targeted
at improving efficiency and increasing overall energy yields.
Multiple federally supported research organizations have focused on
sustainable energy in recent years. Two of the most prominent of these
labs are Sandia National Laboratories and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), both of which are funded by the United States Department of Energy and supported by various corporate partners. Sandia has a total budget of $2.4 billion while NREL has a budget of $375 million.
Scientific production towards sustainable energy systems is
rising exponentially, growing from about 500 English journal papers only
about renewable energy in 1992 to almost 9,000 papers in 2011.
Biomass
Biomass is biological material
derived from living, or recently living organisms. It most often refers
to plants or plant-derived materials which are specifically called lignocellulosic biomass.
As an energy source, biomass can either be used directly via combustion
to produce heat, or indirectly after converting it to various forms of biofuel. Conversion of biomass to biofuel can be achieved by different methods which are broadly classified into: thermal, chemical, and biochemical methods. Wood remains the largest biomass energy source today; examples include forest residues – such as dead trees, branches and tree stumps –, yard clippings, wood chips and even municipal solid waste. In the second sense, biomass includes plant or animal matter that can be converted into fibers or other industrial chemicals, including biofuels. Industrial biomass can be grown from numerous types of plants, including miscanthus, switchgrass, hemp, corn, poplar, willow, sorghum, sugarcane, bamboo, and a variety of tree species, ranging from eucalyptus to oil palm (palm oil).
Biomass, biogas and biofuels are burned to produce heat/power and
in doing so harm the environment. Pollutants such as sulphurous oxides
(SOx), nitrous oxides (NOx), and particulate
matter (PM) are produced from this combustion; the World Health
Organisation estimates that 7 million premature deaths are caused each
year by air pollution. Biomass combustion is a major contributor.
Ethanol biofuels
As the primary source of biofuel in North America, many organizations are conducting research in the area of ethanol production. On the Federal level, the USDA
conducts a large amount of research regarding ethanol production in the
United States. Much of this research is targeted towards the effect of
ethanol production on domestic food markets.
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory has conducted various ethanol research projects, mainly in the area of cellulosic ethanol. Cellulosic ethanol
has many benefits over traditional corn based-ethanol. It does not take
away or directly conflict with the food supply because it is produced
from wood, grasses, or non-edible parts of plants.
Moreover, some studies have shown cellulosic ethanol to be more cost
effective and economically sustainable than corn-based ethanol.
Even if we used all the corn crop that we have in the United States and
converted it into ethanol it would only produce enough fuel to serve 13
percent of the United States total gasoline consumption. Sandia National Laboratories conducts in-house cellulosic ethanol research and is also a member of the Joint BioEnergy Institute (JBEI), a research institute founded by the United States Department of Energy with the goal of developing cellulosic biofuels.
Other Biofuels
From 1978 to 1996, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory experimented with producing algae fuel in the "Aquatic Species Program." A self-published article by Michael Briggs, at the University of New Hampshire
Biofuels Group, offers estimates for the realistic replacement of all
motor vehicle fuel with biofuels by utilizing algae that have a natural
oil content greater than 50%, which Briggs suggests can be grown on
algae ponds at wastewater treatment plants.
This oil-rich algae can then be extracted from the system and processed
into biofuels, with the dried remainder further reprocessed to create
ethanol.
The production of algae to harvest oil for biofuels has not yet been
undertaken on a commercial scale, but feasibility studies have been
conducted to arrive at the above yield estimate. During the biofuel
production process algae actually consumes the carbon dioxide in the air
and turns it into oxygen through photosynthesis.
In addition to its projected high yield, algaculture— unlike food
crop-based biofuels — does not entail a decrease in food production,
since it requires neither farmland nor fresh water. Many companies are
pursuing algae bio-reactors for various purposes, including scaling up
biofuels production to commercial levels.
Several groups in various sectors are conducting research on Jatropha curcas, a poisonous shrub-like tree that produces seeds considered by many to be a viable source of biofuels feedstock oil.
Much of this research focuses on improving the overall per acre oil
yield of Jatropha through advancements in genetics, soil science, and
horticultural practices. SG Biofuels,
a San Diego-based Jatropha developer, has used molecular breeding and
biotechnology to produce elite hybrid seeds of Jatropha that show
significant yield improvements over first generation varieties. The Center for Sustainable Energy Farming
(CfSEF) is a Los Angeles-based non-profit research organization
dedicated to Jatropha research in the areas of plant science, agronomy,
and horticulture. Successful exploration of these disciplines is
projected to increase Jatropha farm production yields by 200-300% in the
next ten years.
Thorium
There are potentially two sources of nuclear power. Fission is used in all current nuclear power plants. Fusion
is the reaction that exists in stars, including the sun, and remains
impractical for use on Earth, as fusion reactors are not yet available.
However nuclear power is controversial politically and scientifically
due to concerns about radioactive waste disposal, safety, the risks of a severe accident, and technical and economical problems in dismantling of old power plants.
Thorium is a fissionable material used in thorium-based nuclear power. The thorium fuel cycle claims several potential advantages over a uranium fuel cycle, including greater abundance, superior physical and nuclear properties, better resistance to nuclear weapons proliferation and reduced plutonium and actinide production. Therefore, it is sometimes referred as sustainable.
Solar
The primary obstacle that is preventing the large scale
implementation of solar powered energy generation is the inefficiency of
current solar technology. Currently, photovoltaic (PV) panels only have
the ability to convert around 24% of the sunlight that hits them into
electricity.
At this rate, solar energy still holds many challenges for widespread
implementation, but steady progress has been made in reducing
manufacturing cost and increasing photovoltaic efficiency.
Both Sandia National Laboratories and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), have heavily funded solar research programs. The NREL solar program has a budget of around $75 million and develops research projects in the areas of photovoltaic (PV) technology, solar thermal energy, and solar radiation.
The budget for Sandia’s solar division is unknown, however it accounts
for a significant percentage of the laboratory’s $2.4 billion budget.
Several academic programs have focused on solar research in recent years. The Solar Energy Research Center (SERC) at University of North Carolina (UNC) has the sole purpose of developing cost effective solar technology. In 2008, researchers at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) developed a method to store solar energy by using it to produce hydrogen fuel from water.
Such research is targeted at addressing the obstacle that solar
development faces of storing energy for use during nighttime hours when
the sun is not shining.
In February 2012, North Carolina-based Semprius Inc., a solar
development company backed by German corporation Siemens,
announced that they had developed the world’s most efficient solar
panel. The company claims that the prototype converts 33.9% of the
sunlight that hits it to electricity, more than double the previous
high-end conversion rate. Major projects on artificial photosynthesis or solar fuels are also under way in many developed nations.
Space-Based Solar Power Satellites seek to overcome the problems of storage and provide civilization-scale power that is clean, constant, and global. Japan and China have active national programs aimed at commercial scale Space-Based Solar Power (SBSP), and both nation's hope to orbit demonstrations in the 2030s.
Wind
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory projects that the levelized cost of wind power in the U.S. will decline about 25% from 2012 to 2030.
Bangui Wind Farm in the Philippines.
Wind energy research dates back several decades to the 1970s when NASA developed an analytical model to predict wind turbine power generation during high winds. Today, both Sandia National Laboratories and National Renewable Energy Laboratory
have programs dedicated to wind research. Sandia’s laboratory focuses
on the advancement of materials, aerodynamics, and sensors.
The NREL wind projects are centered on improving wind plant power
production, reducing their capital costs, and making wind energy more
cost effective overall.
The Field Laboratory for Optimized Wind Energy (FLOWE) at Caltech
was established to research renewable approaches to wind energy farming
technology practices that have the potential to reduce the cost, size,
and environmental impact of wind energy production.
The president of Sky WindPower Corporation thinks that wind turbines
will be able to produce electricity at a cent/kWh at an average which in
comparison to coal-generated electricity is a fractional of the cost.
A wind farm is a group of wind turbines
in the same location used to produce electric power. A large wind farm
may consist of several hundred individual wind turbines, and cover an
extended area of hundreds of square miles, but the land between the
turbines may be used for agricultural or other purposes. A wind farm may
also be located offshore.
Many of the largest operational onshore wind farms are located in the USA and China. The Gansu Wind Farm
in China has over 5,000 MW installed with a goal of 20,000 MW by 2020.
China has several other "wind power bases" of similar size. The Alta Wind Energy Center in California is the largest onshore wind farm outside of China, with a capacity of 1020 MW of power.
Europe leads in the use of wind power with almost 66 GW, about 66
percent of the total globally, with Denmark in the lead according to the
countries installed per-capita capacity. As of February 2012, the Walney Wind Farm in United Kingdom is the largest offshore wind farm in the world at 367 MW, followed by Thanet Wind Farm (300 MW), also in the UK.
There are many large wind farms under construction and these include BARD Offshore 1 (400 MW), Clyde Wind Farm (350 MW), Greater Gabbard wind farm (500 MW), Lincs Wind Farm (270 MW), London Array (1000 MW), Lower Snake River Wind Project (343 MW), Macarthur Wind Farm (420 MW), Shepherds Flat Wind Farm (845 MW), and Sheringham Shoal (317 MW).
Wind power has expanded quickly, its share of worldwide electricity usage at the end of 2014 was 3.1%.
Geothermal
Geothermal energy
is produced by tapping into the thermal energy created and stored
within the earth. It arises from the radioactive decay of an isotope of
potassium and other elements found in the Earth's crust.
Geothermal energy can be obtained by drilling into the ground, very
similar to oil exploration, and then it is carried by a heat-transfer
fluid (e.g. water, brine or steam).
Geothermal systems that are mainly dominated by water have the
potential to provide greater benefits to the system and will generate
more power.
Within these liquid-dominated systems, there are possible concerns of
subsidence and contamination of ground-water resources. Therefore,
protection of ground-water resources is necessary in these systems. This
means that careful reservoir production and engineering is necessary in
liquid-dominated geothermal reservoir systems. Geothermal energy is considered sustainable because that thermal energy is constantly replenished.
However, the science of geothermal energy generation is still young and
developing economic viability. Several entities, such as the National Renewable Energy Laboratory and Sandia National Laboratories
are conducting research toward the goal of establishing a proven
science around geothermal energy. The International Centre for
Geothermal Research (IGC), a German geosciences research organization,
is largely focused on geothermal energy development research.
Hydrogen
Over $1 billion of federal money has been spent on the research and
development of hydrogen and a medium for energy storage in the United
States. Both the National Renewable Energy Laboratory and Sandia National Laboratories
have departments dedicated to hydrogen research. Hydrogen is useful for
energy storage, and for use in airplanes and ships, but is not
practical for automobile use, as it is not very efficient, compared to
using a battery — for the same cost a person can travel three times as
far using a battery electric vehicle.
Clean energy investments
Comparing trends in worldwide energy use, the growth of clean energy to 2015 is shown by the green line
Around the world many sub-national governments - regions, states and
provinces - have aggressively pursued sustainable energy investments. In
the United States, California's leadership in renewable energy was
recognized by The Climate Group when it awarded former Governor Arnold
Schwarzenegger its inaugural award for international climate leadership
in Copenhagen in 2009.
In Australia, the state of South Australia - under the leadership of
former Premier Mike Rann - has led the way with wind power comprising
26% of its electricity generation by the end of 2011, edging out coal
fired generation for the first time. South Australia also has had the highest take-up per capita of household solar panels
in Australia following the Rann Government's introduction of solar
feed-in laws and educative campaign involving the installation of solar
photovoltaic installations on the roofs of prominent public buildings,
including the parliament, museum, airport and Adelaide Showgrounds
pavilion and schools.
Rann, Australia's first climate change minister, passed legislation in
2006 setting targets for renewable energy and emissions cuts, the first
legislation in Australia to do so.
Also, in the European Union there is a clear trend of promoting
policies encouraging investments and financing for sustainable energy in
terms of energy efficiency, innovation in energy exploitation and
development of renewable resources, with increased consideration of
environmental aspects and sustainability.
In October 2018, the American Council for an Energy-Efficient
Economy (ACEEE) released its annual "State Energy Efficiency Scorecard."
The scorecard concluded that states and electric utility companies are
continuing to expand energy efficiency measures in order to meet clean
energy goals. In 2017, the U.S. spent $6.6 billion in electricity
efficiency programs. $1.3 billion was spent on natural gas efficiency.
These programs resulted in 27.3 million megawatt hours (MWh) of
electricity saved.
Related journals
Among scientific journals related to the interdisciplinary study of sustainable energy are: