| War on drugs | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Map of major drug trade routes | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Allies of the United States | Drug traffickers | ||||||
The war on drugs is a global campaign, led by the U.S. federal government, of drug prohibition, military aid, and military intervention, with the aim of reducing the illegal drug trade in the United States. The initiative includes a set of drug policies that are intended to discourage the production, distribution, and consumption of psychoactive drugs that the participating governments and the UN have made illegal. The term was popularized by the media shortly after a press conference given on June 18, 1971, by President Richard Nixon—the day after publication of a special message from President Nixon to the Congress on Drug Abuse Prevention and Control—during which he declared drug abuse "public enemy number one". That message to the Congress included text about devoting more federal resources to the "prevention of new addicts, and the rehabilitation of those who are addicted" but that part did not receive the same public attention as the term "war on drugs". Two years prior to this, Nixon had formally declared a "war on drugs" that would be directed toward eradication, interdiction, and incarceration. In 2015, the Drug Policy Alliance, which advocates for an end to the War on Drugs, estimated that the United States spends $51 billion annually on these initiatives, and in 2021, after 50 years of the drug war, others have estimated that the US has spent a cumulative $1 trillion on it.
On May 13, 2009, Gil Kerlikowske—the Director of the Office of National Drug Control Policy (ONDCP)—signaled that the Obama administration did not plan to significantly alter drug enforcement policy, but also that the administration would not use the term "War on Drugs", because Kerlikowske considers the term to be "counter-productive". ONDCP's view is that "drug addiction is a disease that can be successfully prevented and treated... making drugs more available will make it harder to keep our communities healthy and safe".
In June 2011, the Global Commission on Drug Policy released a critical report on the War on Drugs, declaring: "The global war on drugs has failed, with devastating consequences for individuals and societies around the world. Fifty years after the initiation of the UN Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, and years after President Nixon launched the US government's war on drugs, fundamental reforms in national and global drug control policies are urgently needed." The report was criticized by organizations that oppose a general legalization of drugs.
History
19th century
Morphine was first isolated from opium between 1803 and 1805, and hypodermic syringes were first constructed in 1851. This was particularly significant during the American Civil War, when wounded soldiers were treated with morphine. This led to widespread morphine addiction among veterans of the war.
Until 1912, products such as heroin were sold over-the-counter in a form of cough syrup. Doctors also prescribed heroin for irritable babies, bronchitis, insomnia, "nervous conditions," hysteria, menstrual cramps, and "vapors", leading to mass addiction. In addition, laudanum, an opioid, was a common part of the home medicine cabinet.
In fiction, Conan Doyle portrayed the hero, Sherlock Holmes, as a cocaine addict.
Citizens did not reach a consensus on dealing with the long-term effects of hard drug usage until towards the end of the 19th century.
20th century
The first U.S. law that restricted the distribution and use of certain drugs was the Harrison Narcotics Tax Act of 1914. The first local laws came as early as 1860. In 1919, the United States passed the 18th Amendment, prohibiting the sale, manufacture, and transportation of alcohol, with exceptions for religious and medical use. In 1920, the United States passed the National Prohibition Act (Volstead Act), enacted to carry out the provisions in the law of the 18th Amendment.
During World War I many soldiers were treated with morphine and became addicts.
The Federal Bureau of Narcotics was established in the United States Department of the Treasury by an act of June 14, 1930 (46 Stat. 585). In 1933, the federal prohibition for alcohol was repealed by passage of the 21st Amendment. In 1935, President Franklin D. Roosevelt publicly supported the adoption of the Uniform State Narcotic Drug Act. The New York Times used the headline "Roosevelt Asks Narcotic War Aid".
In 1937, the Marihuana Tax Act of 1937 was passed. Several scholars have claimed that the goal was to destroy the hemp industry, largely as an effort of businessmen Andrew Mellon, Randolph Hearst, and the Du Pont family. These scholars argue that with the invention of the decorticator, hemp became a very cheap substitute for the paper pulp that was used in the newspaper industry. These scholars believe that Hearst felt that this was a threat to his extensive timber holdings. Mellon, United States Secretary of the Treasury and the wealthiest man in America, had invested heavily in the DuPont's new synthetic fiber, nylon, and considered its success to depend on its replacement of the traditional resource, hemp. However, there were circumstances that contradict these claims. One reason for doubts about those claims is that the new decorticators did not perform fully satisfactorily in commercial production. Production of fiber from hemp, requiring harvest, transport and processing, was a labor-intensive process. Technological developments decreased the labor required but not sufficiently to eliminate this disadvantage.
On October 27, 1970, Congress passed the Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970, which, among other things, categorized controlled substances based on their medicinal use and potential for addiction. In 1971, two congressmen released a report on the growing heroin epidemic among U.S. servicemen in Vietnam; ten to fifteen percent of the servicemen were addicted to heroin, and President Nixon declared drug abuse to be "public enemy number one."
Although Nixon declared "drug abuse" to be public enemy number one in 1971, the policies that his administration implemented as part of the Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970 were a continuation of drug prohibition policies in the U.S., which started in 1914.
The Nixon campaign in 1968, and the Nixon White House after that, had two enemies: the antiwar left and black people. You understand what I'm saying? We knew we couldn't make it illegal to be either against the war or black, but by getting the public to associate the hippies with marijuana and blacks with heroin, and then criminalizing both heavily, we could disrupt those communities. We could arrest their leaders, raid their homes, break up their meetings, and vilify them night after night on the evening news. Did we know we were lying about the drugs? Of course we did.
— John Ehrlichman, to Dan Baum for Harper's Magazine in 1994, about President Richard Nixon's war on drugs, declared in 1971.
In 1973, the Drug Enforcement Administration was created to replace the Bureau of Narcotics and Dangerous Drugs.
The Nixon Administration also repealed the federal 2–10-year mandatory minimum sentences for possession of marijuana and started federal demand reduction programs and drug-treatment programs. Robert DuPont, the "Drug czar" in the Nixon Administration, stated it would be more accurate to say that Nixon ended, rather than launched, the "war on drugs". DuPont also argued that it was the proponents of drug legalization that popularized the term "war on drugs".
The presidency of Ronald Reagan saw an expansion in the federal focus of preventing drug abuse and for prosecuting offenders. In the first term of the presidency Ronald Reagan signed the Comprehensive Crime Control Act of 1984, which expanded penalties towards possession of cannabis, established a federal system of mandatory minimum sentences, and established procedures for civil asset forfeiture. From 1980 to 1984 the federal annual budget of the FBI's drug enforcement units went from 8 million to 95 million. According to historian Elizabeth Hinton, Reagan was a strong proponent of criminalizing drug users during his presidency in the 1980s; she wrote that "[he] led Congress in criminalizing drug users, especially African American drug users, by concentrating and stiffening penalties for the possession of the crystalline rock form of cocaine, known as "crack", rather than the crystallized methamphetamine that White House officials recognized was as much of a problem among low-income white Americans". Though he was a Republican, support for Reagan's crime legislation was bipartisan. According to Hinton, Democrats supported his legislation as they had since the Johnson administration.
In 1982, Vice President George H. W. Bush and his aides began pushing for the involvement of the CIA and U.S. military in drug interdiction efforts.
The Office of National Drug Control Policy (ONDCP) was originally established by the National Narcotics Leadership Act of 1988, which mandated a national anti-drug media campaign for youth, which would later become the National Youth Anti-Drug Media Campaign. The director of ONDCP is commonly known as the Drug czar, and it was first implemented in 1989 under President George H. W. Bush, and raised to cabinet-level status by Bill Clinton in 1993. These activities were subsequently funded by the Treasury and General Government Appropriations Act of 1998. The Drug-Free Media Campaign Act of 1998 codified the campaign at 21 U.S.C. § 1708.
21st century
In the early 21st century, the war on drugs began being referred to as "the new Jim Crow". This mentality was further popularized by lawyer and civil rights advocate Michelle Alexander, who wrote The New Jim Crow: Mass Incarceration in the Age of Colorblindness in 2010.
At the turn of the century, incarceration rates in the United States disproportionately consisted of African-American men, according to an article from the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU). In 2001, "the number of black men in prison (792,000) [had] already equaled the number of men enslaved in 1820. With the current momentum of the drug war fueling an ever expanding prison-industrial complex, if current trends continue, only 15 years remain before the United States incarcerates as many African-American men as were forced into chattel bondage at slavery's peak, in 1860".
During his time in office, Barack Obama implemented a "tough but smart" approach to the war on drugs. While he claimed that his methodology differed from those of previous presidents, in reality, his practices were very similar. He promoted a universal drug issue, but his binary "tough but smart" solution maintained the mentality of criminalizing drug offenders.
An international group called the Global Commission on Drug Policy composed of former heads of state and government released a report on June 2, 2011, stating that "The global war on drugs has failed." The commission was made up of 22 self-appointed members including a number of prominent international politicians and writers. U.S. Surgeon General Regina Benjamin also released the first-ever National Prevention Strategy, a framework towards preventing drug abuse and promoting healthy, active lifestyles.
On May 21, 2012, the U.S. Government published an updated version of its drug policy. The director of ONDCP stated simultaneously that this policy is somewhat different from the "War on Drugs":
- The U.S. Government sees the policy as a "third-way" approach to drug control; an approach that is based on the results of a huge investment in research from some of the world's preeminent scholars on the disease of substance abuse.
- The policy does not see drug legalization as the "silver bullet" solution to drug control.
- It is not a policy where success is measured by the number of arrests made or prisons built.
At the same meeting was a declaration signed by the representatives of Italy, the Russian Federation, Sweden, the United Kingdom and the United States in line with this: "Our approach must be a balanced one, combining effective enforcement to restrict the supply of drugs, with efforts to reduce demand and build recovery; supporting people to live a life free of addiction."
A 2013 ACLU report declared the anti-marijuana crusade a "war on people of color". The report found that "African Americans [were] 3.73 times more likely than whites to be apprehended despite nearly identical usage rates, and marijuana violations accounting for more than half of drug arrests nationwide during the previous decade". In a manner of speaking, Barack Obama's "tough but smart" binary approach to the war on drugs stunted its own progress. On one hand, nonwhite drug offenders received less excessive criminal sanctions, but on the other, by examining criminals as strictly violent or nonviolent, mass incarceration persisted.
In March 2016 the International Narcotics Control Board stated that the International Drug Control treaties do not mandate a "war on drugs".
According to 2020 articles from the ACLU and The New York Times, Republicans and Democrats agreed that the time has come to end the war on drugs. While on the presidential campaign trail, Joe Biden claimed that he would take the necessary steps to alleviate the war on drugs and end the opioid epidemic.
On December 4, 2020, the United States House of Representatives passed a marijuana reform bill, the Marijuana Opportunity Reinvestment and Expungement Act (also known as the MORE Act), which decriminalized marijuana by removing it from the list of scheduled substances. Additionally, according to the ACLU, it "expunges past convictions and arrests, and taxes marijuana to reinvest in communities targeted by the war on drugs". The MORE Act decriminalizes marijuana, and removes it from the list of substances under the Controlled Substances Act. The MORE Act was received in the Senate in December 2020.
Over time, states in the US have approached the matter of drug liberalization at various paces. For example, as of December 2020, Oregon became the first US state to decriminalize all drugs. The state government's response has shifted from a criminal approach to a public health approach.
Based on ideology from modern political scientists and economic theorists, some contend the war on drugs has persisted as a way to facilitate the deregulation of free economic markets through its methods of mass incarceration.
Domestic policy
Arrests and incarceration
According to Human Rights Watch, the War on Drugs caused soaring arrest rates that disproportionately targeted African Americans due to various factors. John Ehrlichman, an aide to Nixon, said that Nixon used the war on drugs to criminalize and disrupt black and hippie communities and their leaders.
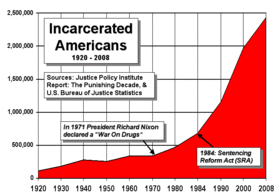
The present state of incarceration in the U.S. as a result of the war on drugs arrived in several stages. By 1971, different steps on drugs had been implemented for more than 50 years (since 1914, 1937, etc.) with only a very small increase of inmates per 100,000 citizens. During the first 9 years after Nixon coined the expression "War on Drugs", statistics showed only a minor increase in the total number of imprisoned.
After 1980, the situation began to change. In the 1980s, while the number of arrests for all crimes had risen by 28%, the number of arrests for drug offenses rose 126%. The result of increased demand was the development of privatization and the for-profit prison industry. The US Department of Justice, reporting on the effects of state initiatives, has stated that, from 1990 through 2000, "the increasing number of drug offenses accounted for 27% of the total growth among black inmates, 7% of the total growth among Hispanic inmates, and 15% of the growth among white inmates." In addition to prison or jail, the United States provides for the deportation of many non-citizens convicted of drug offenses.
In 1994, the New England Journal of Medicine reported that the "War on Drugs" resulted in the incarceration of one million Americans each year. In 2008, the Washington Post reported that of 1.5 million Americans arrested each year for drug offenses, half a million would be incarcerated. In addition, one in five black Americans would spend time behind bars due to drug laws.
Federal and state policies also impose collateral consequences on those convicted of drug offenses, separate from fines and prison time, that are not applicable to other types of crime. For example, a number of states have enacted laws to suspend for six months the driver's license of anyone convicted of a drug offense; these laws were enacted in order to comply with a federal law known as the Solomon–Lautenberg amendment, which threatened to penalize states that did not implement the policy. Other examples of collateral consequences for drug offenses, or for felony offenses in general, include loss of professional license, loss of ability to purchase a firearm, loss of eligibility for food stamps, loss of eligibility for Federal Student Aid, loss of eligibility to live in public housing, loss of ability to vote, and deportation.
Sentencing disparities
In 1986, the U.S. Congress passed laws that created a 100 to 1 sentencing disparity for the trafficking or possession of crack when compared to penalties for trafficking of powder cocaine, which had been widely criticized as discriminatory against minorities, mostly blacks, who were more likely to use crack than powder cocaine. This 100:1 ratio had been required under federal law since 1986. Persons convicted in federal court of possession of 5 grams of crack cocaine received a minimum mandatory sentence of 5 years in federal prison. On the other hand, possession of 500 grams of powder cocaine carries the same sentence. In 2010, the Fair Sentencing Act cut the sentencing disparity to 18:1.
According to Human Rights Watch, crime statistics show that—in the United States in 1999—compared to non-minorities, African Americans were far more likely to be arrested for drug crimes, and received much stiffer penalties and sentences.
Statistics from 1998 show that there were wide racial disparities in arrests, prosecutions, sentencing and deaths. African-American drug users made up for 35% of drug arrests, 55% of convictions, and 74% of people sent to prison for drug possession crimes. Nationwide African-Americans were sent to state prisons for drug offenses 13 times more often than other races, even though they supposedly constituted only 13% of regular drug users.
Anti-drug legislation over time has also displayed an apparent racial bias. University of Minnesota Professor and social justice author Michael Tonry writes, "The War on Drugs foreseeably and unnecessarily blighted the lives of hundreds and thousands of young disadvantaged black Americans and undermined decades of effort to improve the life chances of members of the urban black underclass."
In 1968, President Lyndon B. Johnson decided that the government needed to make an effort to curtail the social unrest that blanketed the country at the time. He decided to focus his efforts on illegal drug use, an approach that was in line with expert opinion on the subject at the time. In the 1960s, it was believed that at least half of the crime in the U.S. was drug-related, and this number grew as high as 90 percent in the next decade. He created the Reorganization Plan of 1968 which merged the Bureau of Narcotics and the Bureau of Drug Abuse to form the Bureau of Narcotics and Dangerous Drugs within the Department of Justice. The belief during this time about drug use was summarized by journalist Max Lerner in his work America as a Civilization (1957):
As a case in point we may take the known fact of the prevalence of reefer and dope addiction in Negro areas. This is essentially explained in terms of poverty, slum living, and broken families, yet it would be easy to show the lack of drug addiction among other ethnic groups where the same conditions apply.
Richard Nixon became president in 1969, and did not back away from the anti-drug precedent set by Johnson. Nixon began orchestrating drug raids nationwide to improve his "watchdog" reputation. Lois B. Defleur, a social historian who studied drug arrests during this period in Chicago, stated that, "police administrators indicated they were making the kind of arrests the public wanted". Additionally, some of Nixon's newly created drug enforcement agencies would resort to illegal practices to make arrests as they tried to meet public demand for arrest numbers. From 1972 to 1973, the Office of Drug Abuse and Law Enforcement performed 6,000 drug arrests in 18 months, the majority of the arrested black.
The next two presidents, Gerald Ford and Jimmy Carter, responded with programs that were essentially a continuation of their predecessors. Shortly after Ronald Reagan became president in 1981, he delivered a speech on the topic. Reagan announced, "We're taking down the surrender flag that has flown over so many drug efforts; we're running up a battle flag."
Then, driven by the 1986 cocaine overdose of black basketball star Len Bias, Reagan was able to pass the Anti-Drug Abuse Act through Congress. This legislation appropriated an additional $1.7 billion to fund the War on Drugs. More importantly, it established 29 new, mandatory minimum sentences for drug offenses. In the entire history of the country up until that point, the legal system had only seen 55 minimum sentences in total. A major stipulation of the new sentencing rules included different mandatory minimums for powder and crack cocaine. At the time of the bill, there was public debate as to the difference in potency and effect of powder cocaine, generally used by whites, and crack cocaine, generally used by blacks, with many believing that "crack" was substantially more powerful and addictive. Crack and powder cocaine are closely related chemicals, crack being a smokeable, freebase form of powdered cocaine hydrochloride which produces a shorter, more intense high while using less of the drug. This method is more cost-effective, and therefore more prevalent on the inner-city streets, while powder cocaine remains more popular in white suburbia. The Reagan administration began shoring public opinion against "crack", encouraging DEA official Robert Putnam to play up the harmful effects of the drug. Stories of "crack whores" and "crack babies" became commonplace; by 1986, Time had declared "crack" the issue of the year. Riding the wave of public fervor, Reagan established much harsher sentencing for crack cocaine, handing down stiffer felony penalties for much smaller amounts of the drug.
Reagan protégé and former Vice-President George H. W. Bush was next to occupy the oval office, and the drug policy under his watch held true to his political background. Bush maintained the hard line drawn by his predecessor and former boss, increasing narcotics regulation when the first National Drug Control Strategy was issued by the Office of National Drug Control in 1989.
The next three presidents – Clinton, Bush and Obama – continued this trend, maintaining the War on Drugs as they inherited it upon taking office. During this time of passivity by the federal government, it was the states that initiated controversial legislation in the War on Drugs. Racial bias manifested itself in the states through such controversial policies as the "stop and frisk" police practices in New York city and the "three strikes" felony laws began in California in 1994.
In August 2010, President Obama signed the Fair Sentencing Act into law that dramatically reduced the 100-to-1 sentencing disparity between powder and crack cocaine, which disproportionately affected minorities.
Commonly used illegal drugs
Commonly used illegal drugs include heroin, cocaine, methamphetamine, and marijuana.
Heroin is an opiate that is highly addictive. If caught selling or possessing heroin, a perpetrator can be charged with a felony and face two–four years in prison and could be fined to a maximum of $20,000.
Crystal meth is composed of methamphetamine hydrochloride. It is marketed as either a white powder or in a solid (rock) form. The possession of crystal meth can result in a punishment varying from a fine to a jail sentence. As with other drug crimes, sentencing length may increase depending on the amount of the drug found in the possession of the defendant.
Cocaine possession is illegal across the U.S. The penalties for possession vary by state, or if charges are federal.
Marijuana is the most popular illegal drug worldwide. The punishment for possession of it is less than for the possession of cocaine or heroin. In some U.S. states, the drug is legal. Approximately half of all adult Americans have tried marijuana.
Foreign interventions
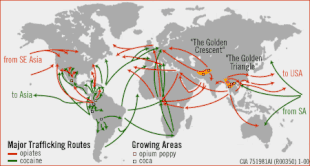
Some scholars have claimed that the phrase "War on Drugs" is propaganda cloaking an extension of earlier military or paramilitary operations. Others have argued that large amounts of "drug war" foreign aid money, training, and equipment actually goes to fighting leftist insurgencies and is often provided to groups who themselves are involved in large-scale narco-trafficking, such as corrupt members of the Colombian military.
War in Vietnam
From 1963 to the end of the Vietnam War in 1975, marijuana usage became common among U.S. soldiers in non-combat situations. Some servicemen also used heroin. Many of the servicemen ended the heroin use after returning to the United States but came home addicted. In 1971, the U.S. military conducted a study of drug use among American servicemen and women. It found that daily usage rates for drugs on a worldwide basis were as low as two percent. However, in the spring of 1971, two congressmen released an alarming report alleging that 15% of the servicemen in Vietnam were addicted to heroin. Marijuana use was also common in Vietnam. Soldiers who used drugs had more disciplinary problems. The frequent drug use had become an issue for the commanders in Vietnam; in 1971 it was estimated that 30,000 servicemen were addicted to drugs, most of them to heroin.
From 1971 on, therefore, returning servicemen were required to take a mandatory heroin test. Servicemen who tested positive upon returning from Vietnam were not allowed to return home until they had passed the test with a negative result. The program also offered a treatment for heroin addicts.
Elliot Borin's article "The U.S. Military Needs its Speed"—published in Wired on February 10, 2003—reports:
But the Defense Department, which distributed millions of amphetamine tablets to troops during World War II, Vietnam and the Gulf War, soldiers on, insisting that they are not only harmless but beneficial.
In a news conference held in connection with Schmidt and Umbach's Article 32 hearing, Dr. Pete Demitry, an Air Force physician and a pilot, claimed that the "Air Force has used (Dexedrine) safely for 60 years" with "no known speed-related mishaps."
The need for speed, Demitry added "is a life-and-death issue for our military."
Operation Intercept
One of the first anti-drug efforts in the realm of foreign policy was President Nixon's Operation Intercept, announced in September 1969, targeted at reducing the amount of cannabis entering the United States from Mexico. The effort began with an intense inspection crackdown that resulted in an almost shutdown of cross-border traffic. Because the burden on border crossings was controversial in border states, the effort only lasted twenty days.
Operation Just Cause
On December 20, 1989, the United States invaded Panama as part of Operation Just Cause, which involved 25,000 American troops. Gen. Manuel Noriega, head of the government of Panama, had been giving military assistance to Contra groups in Nicaragua at the request of the U.S. which, in exchange, tolerated his drug trafficking activities, which they had known about since the 1960s. When the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) tried to indict Noriega in 1971, the CIA prevented them from doing so. The CIA, which was then directed by future president George H. W. Bush, provided Noriega with hundreds of thousands of dollars per year as payment for his work in Latin America. When CIA pilot Eugene Hasenfus was shot down over Nicaragua by the Sandinistas, documents aboard the plane revealed many of the CIA's activities in Latin America, and the CIA's connections with Noriega became a public relations "liability" for the U.S. government, which finally allowed the DEA to indict him for drug trafficking, after decades of tolerating his drug operations. Operation Just Cause, whose purpose was to capture Noriega and overthrow his government; Noriega found temporary asylum in the Papal Nuncio, and surrendered to U.S. soldiers on January 3, 1990. He was sentenced by a court in Miami to 45 years in prison.
Plan Colombia
As part of its Plan Colombia program, the United States government currently provides hundreds of millions of dollars per year of military aid, training, and equipment to Colombia, to fight left-wing guerrillas such as the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC-EP), which has been accused of being involved in drug trafficking.
Private U.S. corporations have signed contracts to carry out anti-drug activities as part of Plan Colombia. DynCorp, the largest private company involved, was among those contracted by the State Department, while others signed contracts with the Defense Department.
Colombian military personnel have received extensive counterinsurgency training from U.S. military and law enforcement agencies, including the School of Americas (SOA). Author Grace Livingstone has stated that more Colombian SOA graduates have been implicated in human rights abuses than currently known SOA graduates from any other country. All of the commanders of the brigades highlighted in a 2001 Human Rights Watch report on Colombia were graduates of the SOA, including the III brigade in Valle del Cauca, where the 2001 Alto Naya Massacre occurred. US-trained officers have been accused of being directly or indirectly involved in many atrocities during the 1990s, including the Massacre of Trujillo and the 1997 Mapiripán Massacre.
In 2000, the Clinton administration initially waived all but one of the human rights conditions attached to Plan Colombia, considering such aid as crucial to national security at the time.
The efforts of U.S. and Colombian governments have been criticized for focusing on fighting leftist guerrillas in southern regions without applying enough pressure on right-wing paramilitaries and continuing drug smuggling operations in the north of the country. Human Rights Watch, congressional committees and other entities have documented the existence of connections between members of the Colombian military and the AUC, which the U.S. government has listed as a terrorist group, and that Colombian military personnel have committed human rights abuses which would make them ineligible for U.S. aid under current laws.
In 2010, the Washington Office on Latin America concluded that both Plan Colombia and the Colombian government's security strategy "came at a high cost in lives and resources, only did part of the job, are yielding diminishing returns and have left important institutions weaker."
A 2014 report by the RAND Corporation, which was issued to analyze viable strategies for the Mexican drug war considering successes experienced in Colombia, noted:
Between 1999 and 2002, the United States gave Colombia $2.04 billion in aid, 81 percent of which was for military purposes, placing Colombia just below Israel and Egypt among the largest recipients of U.S. military assistance. Colombia increased its defense spending from 3.2 percent of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2000 to 4.19 percent in 2005. Overall, the results were extremely positive. Greater spending on infrastructure and social programs helped the Colombian government increase its political legitimacy, while improved security forces were better able to consolidate control over large swaths of the country previously overrun by insurgents and drug cartels.
It also notes that, "Plan Colombia has been widely hailed as a success, and some analysts believe that, by 2010, Colombian security forces had finally gained the upper hand once and for all."
Mérida Initiative
The Mérida Initiative is a security cooperation between the United States and the government of Mexico and the countries of Central America. It was approved on June 30, 2008, and its stated aim is combating the threats of drug trafficking and transnational crime. The Mérida Initiative appropriated $1.4 billion in a three-year commitment (2008–2010) to the Mexican government for military and law enforcement training and equipment, as well as technical advice and training to strengthen the national justice systems. The Mérida Initiative targeted many very important government officials, but it failed to address the thousands of Central Americans who had to flee their countries due to the danger they faced every day because of the war on drugs. There is still not any type of plan that addresses these people. No weapons are included in the plan.
Aerial herbicide application
The United States regularly sponsors the spraying of large amounts of herbicides such as glyphosate over the jungles of Central and South America as part of its drug eradication programs. Environmental consequences resulting from aerial fumigation have been criticized as detrimental to some of the world's most fragile ecosystems; the same aerial fumigation practices are further credited with causing health problems in local populations.
Operations in Honduras
In 2012, the U.S. sent DEA agents to Honduras to assist security forces in counternarcotics operations. Honduras has been a major stop for drug traffickers, who use small planes and landing strips hidden throughout the country to transport drugs. The U.S. government made agreements with several Latin American countries to share intelligence and resources to counter the drug trade. DEA agents, working with other U.S. agencies such as the State Department, the CBP, and Joint Task Force-Bravo, assisted Honduras troops in conducting raids on traffickers' sites of operation.
Public support and opposition
Several critics have compared the wholesale incarceration of the dissenting minority of drug users to the wholesale incarceration of other minorities in history. Psychiatrist Thomas Szasz, for example, wrote in 1997 "Over the past thirty years, we have replaced the medical-political persecution of illegal sex users ('perverts' and 'psychopaths') with the even more ferocious medical-political persecution of illegal drug users."
United States
The War on Drugs has been a highly contentious issue since its inception. A poll on October 2, 2008, found that three in four Americans believed that the War On Drugs was failing.
The social consequences of the drug war have been widely criticized by such organizations as the American Civil Liberties Union as being racially biased against minorities and disproportionately responsible for the exploding United States prison population. According to a report commissioned by the Drug Policy Alliance, and released in March 2006 by the Justice Policy Institute, America's "Drug-Free Zones" are ineffective at keeping youths away from drugs, and instead create strong racial disparities in the judicial system.
In 2014, a Pew Research Center poll found more than six in ten Americans state that state governments moving away from mandatory prison terms for drug law violations is a good thing, while three out of ten Americans say these policy changes are a bad thing. This a substantial shift from the same poll questions since 2001. In 2014 a Pew Research Center poll found that 67 percent of Americans feel that a movement towards treatment for drugs like cocaine and heroin is better versus the 26 percent who feel that prosecution is the better route.
In 2018, a Rasmussen Report poll found that less than 10 percent of Americans think that the War on Drugs is being won and that 75 percent found that Americans believe that America is not winning the War on Drugs.
Mexico
Mexican citizens, unlike American citizens, support the current measures their government is taking against drug cartels in the War on Drugs. A Pew Research Center poll in 2010 found that 80 percent supported the current use of the army in the War on Drugs to combat drug traffickers with about 55 percent saying that they have been making progress in the war. A year later in 2011 a Pew Research Center poll uncovered that 71 percent of Mexicans find that "illegal drugs are a very big problem in their country". 77 percent of Mexicans also found that drug cartels and the violence associated with them are as well a big challenge for Mexico. The poll also found that the percentages believing that illegal drugs and violence related to the cartel were higher in the North, with 87 percent for illegal drug use and 94 percent cartel-related violence being a problem. This compared to the other locations: South, Mexico City and the greater area of Mexico City, and Central Mexico which are all about 18 percent or lower than the North on Illegal drug use being a problem for the country. These respective areas are also lower than the North by 19 percent or more on the issue of drug cartel-related violence being an issue for the country.
In 2013 a Pew Research Center poll found that 74 percent of Mexican citizens would support the training of their police and military, the poll also found that another 55 percent would support the supplying of weapons and financial aid. Though the poll indicates a support of U.S. aid, 59 percent were against troops on the ground by the U.S. military. Also in 2013 Pew Research Center found in a poll that 56 percent of Mexican citizens believe that the United States and Mexico are both to blame for drug violence in Mexico. In that same poll, 20 percent believe that the United States is solely to blame and 17 percent believe that Mexico is solely to blame.
Latin America
At a meeting in Guatemala in 2012, three former presidents from Guatemala, Mexico and Colombia said that the war on drugs had failed and that they would propose a discussion on alternatives, including decriminalization, at the Summit of the Americas in April of that year. Guatemalan President Otto Pérez Molina said that the war on drugs was exacting too high a price on the lives of Central Americans and that it was time to "end the taboo on discussing decriminalization". At the summit, the government of Colombia pushed for the most far-reaching change to drugs policy since the war on narcotics was declared by Nixon four decades prior, citing the catastrophic effects it had had in Colombia.
Canada
In Canada, enforcement is not carried out using the military, even when Canada is a major supplier of recreational drugs including meth, and ecstasy.
Socioeconomic effects
Permanent underclass creation
Penalties for drug crimes among American youth almost always involve permanent or semi-permanent removal from opportunities for education, strip them of voting rights, and later involve creation of criminal records which make employment more difficult. One-fifth of the US prison population are incarcerated for a drug offence. Thus, some authors maintain that the War on Drugs has resulted in the creation of a permanent underclass of people who have few educational or job opportunities, often as a result of being punished for drug offenses which in turn have resulted from attempts to earn a living in spite of having no education or job opportunities.
Costs to taxpayers
According to a 2008 study published by Harvard economist Jeffrey A. Miron, the annual savings on enforcement and incarceration costs from the legalization of drugs would amount to roughly $41.3 billion, with $25.7 billion being saved among the states and over $15.6 billion accrued for the federal government. Miron further estimated at least $46.7 billion in tax revenue based on rates comparable to those on tobacco and alcohol: $8.7 billion from marijuana, $32.6 billion from cocaine and heroin, and $5.4 billion from other drugs.
Low taxation in Central American countries has been credited with weakening the region's response in dealing with drug traffickers. Many cartels, especially Los Zetas have taken advantage of the limited resources of these nations. 2010 tax revenue in El Salvador, Guatemala, and Honduras, composed just 13.53% of GDP. As a comparison, in Chile and the U.S., taxes were 18.6% and 26.9% of GDP respectively. However, direct taxes on income are very hard to enforce and in some cases tax evasion is seen as a national pastime.
Impact on growers
The status of coca and coca growers has become an intense political issue in several countries, including Colombia and particularly Bolivia, where the president, Evo Morales, a former coca growers' union leader, has promised to legalise the traditional cultivation and use of coca. Indeed, legalization efforts have yielded some successes under the Morales administration when combined with aggressive and targeted eradication efforts. The country saw a 12–13% decline in coca cultivation in 2011 under Morales, who has used coca growers' federations to ensure compliance with the law rather than providing a primary role for security forces.
The coca eradication policy has been criticised for its negative impact on the livelihood of coca growers in South America. In many areas of South America the coca leaf has traditionally been chewed and used in tea and for religious, medicinal and nutritional purposes by locals. For this reason many insist that the illegality of traditional coca cultivation is unjust. In many areas the U.S. government and military has forced the eradication of coca without providing for any meaningful alternative crop for farmers, and has additionally destroyed many of their food or market crops, leaving them starving and destitute.
Allegations of official involvement in drug trafficking
The CIA, DEA, State Department, and several other U.S. government agencies have been alleged to have relations with various groups which are involved in drug trafficking.
CIA and Contra cocaine trafficking
Senator John Kerry's 1988 U.S. Senate Committee on Foreign Relations report on Contra drug links concludes that members of the U.S. State Department "who provided support for the Contras are involved in drug trafficking... and elements of the Contras themselves knowingly receive financial and material assistance from drug traffickers." The report further states that "the Contra drug links include... payments to drug traffickers by the U.S. State Department of funds authorized by the Congress for humanitarian assistance to the Contras, in some cases after the traffickers had been indicted by federal law enforcement agencies on drug charges, in others while traffickers were under active investigation by these same agencies."
In 1996, journalist Gary Webb published reports in the San Jose Mercury News, and later in his book Dark Alliance, claiming that: "For the better part of a decade, a San Francisco Bay Area drug ring sold tons of cocaine to the Crips and Bloods street gangs of Los Angeles and funneled millions in drug profits to a Latin American guerrilla army run by the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency." This drug ring "opened the first pipeline between Colombia's cocaine cartels and the black neighborhoods of Los Angeles" and, as a result, "The cocaine that flooded in helped spark a crack explosion in urban America."
Webb's premise regarding the U.S. Government connection was initially attacked at the time by the media. The series remains controversial. The series resulted in three federal investigations (i.e., by the CIA, Department of Justice, and the House Intelligence Committee) into the claims of "Dark Alliance". The reports rejected the series' main claims but were critical of some CIA and law enforcement actions. The CIA report found no evidence that "any past or present employee of CIA, or anyone acting on behalf of CIA, had any direct or indirect dealing" with Ross, Blandón, or Meneses or that any of the other figures mentioned in "Dark Alliance" were ever employed by or associated with or contacted by the agency. The Department of Justice report stated that "We did not find that he [Blandón] had any ties to the CIA, that the CIA intervened in his case in any way, or that any connections to the Contras affected his treatment." The House Committee report examined the support that Meneses and Blandón gave to the local Contra organization in San Francisco and the Contras in general, the report concluded that it was "not sufficient to finance the organization" and did not consist of "millions," contrary to the claims of the "Dark Alliance" series. This support "was not directed by anyone within the Contra movement who had an association with the CIA," and the Committee found "no evidence that the CIA or the Intelligence Community was aware of these individuals’ support."
According to Rodney Campbell, an editorial assistant to Nelson Rockefeller, during World War II, the United States Navy, concerned that strikes and labor disputes in U.S. eastern shipping ports would disrupt wartime logistics, released the mobster Lucky Luciano from prison, and collaborated with him to help the mafia take control of those ports. Labor union members were terrorized and murdered by mafia members as a means of preventing labor unrest and ensuring smooth shipping of supplies to Europe.
According to Alexander Cockburn and Jeffrey St. Clair, in order to prevent Communist party members from being elected in Italy following World War II, the CIA worked closely with the Sicilian Mafia, protecting them and assisting in their worldwide heroin smuggling operations. The mafia was in conflict with leftist groups and was involved in assassinating, torturing, and beating leftist political organizers.
Efficacy
| External video | |
|---|---|
In 1986, the US Defense Department funded a two-year study by the RAND Corporation, which found that the use of the armed forces to interdict drugs coming into the United States would have little or no effect on cocaine traffic and might, in fact, raise the profits of cocaine cartels and manufacturers. The 175-page study, "Sealing the Borders: The Effects of Increased Military Participation in Drug Interdiction", was prepared by seven researchers, mathematicians and economists at the National Defense Research Institute, a branch of the RAND, and was released in 1988. The study noted that seven prior studies in the past nine years, including one by the Center for Naval Research and the Office of Technology Assessment, had come to similar conclusions. Interdiction efforts, using current armed forces resources, would have almost no effect on cocaine importation into the United States, the report concluded.
During the early-to-mid-1990s, the Clinton administration ordered and funded a major cocaine policy study, again by RAND. The Rand Drug Policy Research Center study concluded that $3 billion should be switched from federal and local law enforcement to treatment. The report said that treatment is the cheapest way to cut drug use, stating that drug treatment is twenty-three times more effective than the supply-side "war on drugs".
The National Research Council Committee on Data and Research for Policy on Illegal Drugs published its findings in 2001 on the efficacy of the drug war. The NRC Committee found that existing studies on efforts to address drug usage and smuggling, from U.S. military operations to eradicate coca fields in Colombia, to domestic drug treatment centers, have all been inconclusive, if the programs have been evaluated at all: "The existing drug-use monitoring systems are strikingly inadequate to support the full range of policy decisions that the nation must make.... It is unconscionable for this country to continue to carry out a public policy of this magnitude and cost without any way of knowing whether and to what extent it is having the desired effect." The study, though not ignored by the press, was ignored by top-level policymakers, leading Committee Chair Charles Manski to conclude, as one observer notes, that "the drug war has no interest in its own results".
In mid-1995, the US government tried to reduce the supply of methamphetamine precursors to disrupt the market of this drug. According to a 2009 study, this effort was successful, but its effects were largely temporary.
During alcohol prohibition, the period from 1920 to 1933, alcohol use initially fell but began to increase as early as 1922. It has been extrapolated that even if prohibition had not been repealed in 1933, alcohol consumption would have quickly surpassed pre-prohibition levels. One argument against the War on Drugs is that it uses similar measures as Prohibition and is no more effective.
In the six years from 2000 to 2006, the U.S. spent $4.7 billion on Plan Colombia, an effort to eradicate coca production in Colombia. The main result of this effort was to shift coca production into more remote areas and force other forms of adaptation. The overall acreage cultivated for coca in Colombia at the end of the six years was found to be the same, after the U.S. Drug Czar's office announced a change in measuring methodology in 2005 and included new areas in its surveys. Cultivation in the neighboring countries of Peru and Bolivia increased, some would describe this effect like squeezing a balloon.
Richard Davenport-Hines, in his book The Pursuit of Oblivion, criticized the efficacy of the War on Drugs by pointing out that
10–15% of illicit heroin and 30% of illicit cocaine is intercepted. Drug traffickers have gross profit margins of up to 300%. At least 75% of illicit drug shipments would have to be intercepted before the traffickers' profits were hurt.
Alberto Fujimori, president of Peru from 1990 to 2000, described U.S. foreign drug policy as "failed" on grounds that
for 10 years, there has been a considerable sum invested by the Peruvian government and another sum on the part of the American government, and this has not led to a reduction in the supply of coca leaf offered for sale. Rather, in the 10 years from 1980 to 1990, it grew 10-fold.
At least 500 economists, including Nobel Laureates Milton Friedman, George Akerlof and Vernon L. Smith, have noted that reducing the supply of marijuana without reducing the demand causes the price, and hence the profits of marijuana sellers, to go up, according to the laws of supply and demand. The increased profits encourage the producers to produce more drugs despite the risks, providing a theoretical explanation for why attacks on drug supply have failed to have any lasting effect. The aforementioned economists published an open letter to President George W. Bush stating "We urge...the country to commence an open and honest debate about marijuana prohibition... At a minimum, this debate will force advocates of current policy to show that prohibition has benefits sufficient to justify the cost to taxpayers, foregone tax revenues and numerous ancillary consequences that result from marijuana prohibition."
The declaration from the World Forum Against Drugs, 2008 state that a balanced policy of drug abuse prevention, education, treatment, law enforcement, research, and supply reduction provides the most effective platform to reduce drug abuse and its associated harms and call on governments to consider demand reduction as one of their first priorities in the fight against drug abuse.
Despite over $7 billion spent annually towards arresting and prosecuting nearly 800,000 people across the country for marijuana offenses in 200 (FBI Uniform Crime Reports), the federally funded Monitoring the Future Survey reports about 85% of high school seniors find marijuana "easy to obtain". That figure has remained virtually unchanged since 1975, never dropping below 82.7% in three decades of national surveys. The Drug Enforcement Administration states that the number of users of marijuana in the U.S. declined between 2000 and 2005 even with many states passing new medical marijuana laws making access easier, though usage rates remain higher than they were in the 1990s according to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health.
ONDCP stated in April 2011 that there has been a 46 percent drop in cocaine use among young adults over the past five years, and a 65 percent drop in the rate of people testing positive for cocaine in the workplace since 2006. At the same time, a 2007 study found that up to 35% of college undergraduates used stimulants not prescribed to them.
A 2013 study found that prices of heroin, cocaine and cannabis had decreased from 1990 to 2007, but the purity of these drugs had increased during the same time.
According to data collected by the Federal Bureau of Prisons 45.3% of all criminal charges were drug related and 25.5% of sentences for all charges last 5–10 years. Furthermore, non-whites make up 41.4% of the federal prison system's population and over half are under the age of 40. The Bureau of Justice Statistics contends that over 80% of all drug related charges are for possession rather than the sale or manufacture of drugs. In 2015 The U.S. government spent over to $25 billion on supply reduction, while allocating only $11 billion for demand reduction. Supply reduction includes: interdiction, eradication, and law enforcement; demand reduction includes: education, prevention, and treatment. The War on Drugs is often called a policy failure.
Legality
The legality of the War on Drugs has been challenged on four main grounds in the U.S.
- It is argued that drug prohibition, as presently implemented, violates the substantive due process doctrine in that its benefits do not justify the encroachments on rights that are supposed to be guaranteed by the Fifth and Fourteenth Amendments to the U.S. Constitution. On July 27, 2011, U.S. District Judge Mary S. Scriven ruled that Florida's legislation purporting to eliminate intent as an element of the crime of drug possession was unconstitutional. Commentators explained the ruling in terms of due process.
- Freedom of religious conscience legally allows some (for example, members of the Native American Church) to use peyote with definite spiritual or religious motives. The sacramental use of dimethyltryptamine in the form of ayahuasca is also allowed for members of União do Vegetal. However, the Free Exercise Clause of the First Amendment mentions no requirement for someone to be affiliated with an official church to exercise this freedom.
- It has been argued that the Commerce Clause means that the power to regulate drug use should be state law not federal law. However, Supreme Court rulings go against this argument because production and consumption in one locality will change the price in another locality because it affects the overall supply and demand for the product and interstate price in a globalized, market economy.
- The inequity of prosecuting the war on certain drugs but not alcohol or tobacco has also been called into question.
Alternatives
Several authors believe that the United States' federal and state governments have chosen wrong methods for combatting the distribution of illicit substances. Aggressive, heavy-handed enforcement funnels individuals through courts and prisons; instead of treating the cause of the addiction, the focus of government efforts has been on punishment. By making drugs illegal rather than regulating them, the War on Drugs creates a highly profitable black market. Jefferson Fish has edited scholarly collections of articles offering a wide variety of public health based and rights based alternative drug policies.
In the year 2000, the United States drug-control budget reached 18.4 billion dollars, nearly half of which was spent financing law enforcement while only one sixth was spent on treatment. In the year 2003, 53 percent of the requested drug control budget was for enforcement, 29 percent for treatment, and 18 percent for prevention. The state of New York, in particular, designated 17 percent of its budget towards substance-abuse-related spending. Of that, a mere one percent was put towards prevention, treatment, and research.
In a survey taken by Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), it was found that substance abusers that remain in treatment longer are less likely to resume their former drug habits. Of the people that were studied, 66 percent were cocaine users. After experiencing long-term in-patient treatment, only 22 percent returned to the use of cocaine. Treatment had reduced the number of cocaine abusers by two-thirds. By spending the majority of its money on law enforcement, the federal government had underestimated the true value of drug-treatment facilities and their benefit towards reducing the number of addicts in the U.S.
In 2004 the federal government issued the National Drug Control Strategy. It supported programs designed to expand treatment options, enhance treatment delivery, and improve treatment outcomes. For example, the Strategy provided SAMHSA with a $100.6 million grant to put towards their Access to Recovery (ATR) initiative. ATR is a program that provides vouchers to addicts to provide them with the means to acquire clinical treatment or recovery support. The project's goals are to expand capacity, support client choice, and increase the array of faith-based and community-based providers for clinical treatment and recovery support services. The ATR program will also provide a more flexible array of services based on the individual's treatment needs.
The 2004 Strategy additionally declared a significant 32 million dollar raise in the Drug Courts Program, which provides drug offenders with alternatives to incarceration. As a substitute for imprisonment, drug courts identify substance-abusing offenders and place them under strict court monitoring and community supervision, as well as provide them with long-term treatment services. According to a report issued by the National Drug Court Institute, drug courts have a wide array of benefits, with only 16.4 percent of the nation's drug court graduates rearrested and charged with a felony within one year of completing the program (versus the 44.1% of released prisoners who end up back in prison within 1-year). Additionally, enrolling an addict in a drug court program costs much less than incarcerating one in prison. According to the Bureau of Prisons, the fee to cover the average cost of incarceration for Federal inmates in 2006 was $24,440. The annual cost of receiving treatment in a drug court program ranges from $900 to $3,500. Drug courts in New York State alone saved $2.54 million in incarceration costs.
Describing the failure of the War on Drugs, New York Times columnist Eduardo Porter noted:
Jeffrey Miron, an economist at Harvard who studies drug policy closely, has suggested that legalizing all illicit drugs would produce net benefits to the United States of some $65 billion a year, mostly by cutting public spending on enforcement as well as through reduced crime and corruption. A study by analysts at the RAND Corporation, a California research organization, suggested that if marijuana were legalized in California and the drug spilled from there to other states, Mexican drug cartels would lose about a fifth of their annual income of some $6.5 billion from illegal exports to the United States.
Many believe that the War on Drugs has been costly and ineffective largely because inadequate emphasis is placed on treatment of addiction. The United States leads the world in both recreational drug usage and incarceration rates. 70% of men arrested in metropolitan areas test positive for an illicit substance, and 54% of all men incarcerated will be repeat offenders.