From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The afterlife (also referred to as life after death or the world to come) is a purported existence in which the essential part of an individual's identity or their stream of consciousness continues to live after the death
of their physical body. According to various ideas about the afterlife,
the essential aspect of the individual that lives on after death may be
some partial element, or the entire soul or spirit, of an individual, which carries with it and may confer personal identity or, on the contrary nirvana. Belief in an afterlife is in contrast to the belief in oblivion after death.
In some views, this continued existence takes place in a spiritual realm, and in other popular views, the individual may be reborn into this world
and begin the life cycle over again, likely with no memory of what they
have done in the past. In this latter view, such rebirths and deaths
may take place over and over again continuously until the individual
gains entry to a spiritual realm or otherworld. Major views on the afterlife derive from religion, esotericism and metaphysics.
Some belief systems, such as those in the Abrahamic tradition, hold that the dead go to a specific plane of existence after death, as determined by God, or other divine judgment, based on their actions or beliefs during life. In contrast, in systems of reincarnation, such as those in the Indian religions, the nature of the continued existence is determined directly by the actions of the individual in the ended life.
Different metaphysical models
Theists
generally believe some afterlife awaits people when they die. Members
of some generally non-theistic religions tend to believe in an afterlife
but without reference to a deity. The Sadducees were an ancient Jewish sect that generally believed that there was a God but no existence after death.
Many religions, whether they believe in the soul's existence in another world like Christianity, Islam, and many pagan
belief systems, or reincarnation like many forms of Hinduism and
Buddhism, believe that one's status in the afterlife is a consequence of
one's conduct during life.
Reincarnation
Reincarnation is the philosophical or religious concept that an aspect of a living being starts a new life in a different physical body or form after each death. It is also called rebirth or transmigration and is a part of the Saṃsāra doctrine of cyclic existence. It is a central tenet of all major Indian religions, namely Buddhism, Hinduism, Jainism, and Sikhism. The idea of reincarnation is found in many ancient cultures, and a belief in rebirth/metempsychosis was held by historic Greek figures, such as Pythagoras, Socrates, and Plato. It is also a common belief of various ancient and modern religions such as Spiritism, Theosophy, and Eckankar. It is found as well in many tribal societies around the world, in places such as Australia, East Asia, Siberia, and South America.
Although the majority of denominations within the Abrahamic religions of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam
do not believe that individuals reincarnate, particular groups within
these religions do refer to reincarnation; these groups include the
mainstream historical and contemporary followers of Kabbalah, the Cathars, Alawites, the Druze, and the Rosicrucians. The historical relations between these sects and the beliefs about reincarnation that were characteristic of Neoplatonism, Orphism, Hermeticism, Manicheanism, and Gnosticism of the Roman era as well as the Indian religions have been the subject of recent scholarly research. Unity Church and its founder Charles Fillmore teach reincarnation.
Rosicrucians speak of a life review period occurring immediately after death and before entering the afterlife's planes of existence (before the silver cord is broken), followed by a judgment, more akin to a final review or end report over one's life.
Heaven and Hell
Heaven, the heavens, Seven Heavens, pure lands, Tian, Jannah, Valhalla, or the Summerland, is a common religious, cosmological, or transcendent place where beings such as gods, angels, jinn, saints, or venerated ancestors are said to originate, be enthroned, or live. According to the beliefs of some religions, heavenly beings can descend to earth or incarnate, and earthly beings can ascend to heaven in the afterlife, or in exceptional cases enter heaven alive.
Heaven is often described as a "higher place", the holiest place, a paradise, in contrast to hell or the underworld or the "low places", and universally or conditionally accessible by earthly beings according to various standards of divinity, goodness, piety, faith or other virtues or right beliefs or simply the will of God. Some believe in the possibility of a heaven on Earth in a world to come.
In Hinduism, heaven is considered as Svarga loka. There are seven positive regions the soul can go to after death and seven negative regions. After completing its stay in the respective region, the soul is subjected to rebirth in different living forms according to its karma. This cycle can be broken after a soul achieves Moksha or Nirvana.
Any place of existence, either of humans, souls or deities, outside the
tangible world (heaven, hell, or other) is referred to as otherworld.
Hell, in many religious and folkloric traditions, is a place of torment and punishment in the afterlife. Religions with a linear divine history often depict hell as an eternal destination, while religions with a cyclic history often depict a hell as an intermediary period between incarnations. Typically, these traditions locate hell in another dimension or under the earth's surface and often include entrances to hell from the land of the living. Other afterlife destinations include purgatory and limbo.
Traditions that do not conceive of the afterlife as a place of punishment or reward merely describe hell as an abode of the dead, the grave, a neutral place (for example, Sheol or Hades) located under the surface of earth.
Ancient religions
Ancient Egyptian religion
The afterlife played an important role in Ancient Egyptian religion, and its belief system is one of the earliest known in recorded history. When the body died, parts of its soul known as ka (body double) and the ba (personality) would go to the Kingdom of the Dead. While the soul dwelt in the Fields of Aaru, Osiris
demanded work as restitution for the protection he provided. Statues
were placed in the tombs to serve as substitutes for the deceased.
Arriving at one's reward in afterlife was a demanding ordeal,
requiring a sin-free heart and the ability to recite the spells,
passwords and formulae of the Book of the Dead. In the Hall of Two Truths, the deceased's heart was weighed against the Shu feather of truth and justice taken from the headdress of the goddess Ma'at. If the heart was lighter than the feather, they could pass on, but if it were heavier they would be devoured by the demon Ammit.
Egyptians also believed that being mummified and put in a sarcophagus
(an ancient Egyptian "coffin" carved with complex symbols and designs,
as well as pictures and hieroglyphs) was the only way to have an
afterlife. What are referred to as the Coffin Texts,
are inscribed on a coffin and serve as a guide for the challenges in
the afterlife. The Coffin texts are more or less a duplication of the Pyramid Texts, which would serve as a guide for Egyptian pharaohs or queens in the afterlife. Only if the corpse had been properly embalmed and entombed in a mastaba, could the dead live again
in the Fields of Yalu and accompany the Sun on its daily ride. Due to
the dangers the afterlife posed, the Book of the Dead was placed in the
tomb with the body as well as food, jewelry, and 'curses'. They also
used the "opening of the mouth".
Ancient Egyptian civilization was based on religion; their belief
in the rebirth after death became the driving force behind their
funeral practices. Death was simply a temporary interruption, rather
than complete cessation, of life, and that eternal life could be ensured
by means like piety to the gods, preservation of the physical form
through mummification, and the provision of statuary and other funerary equipment. Each human consisted of the physical body, the ka, the ba, and the akh.
The Name and Shadow were also living entities. To enjoy the afterlife,
all these elements had to be sustained and protected from harm.
On 30 March 2010, a spokesman for the Egyptian Culture Ministry
claimed it had unearthed a large red granite door in Luxor with
inscriptions by User, a powerful adviser to the 18th Dynasty Queen Hatshepsut
who ruled between 1479 BC and 1458 BC, the longest of any woman. It
believes the false door is a 'door to the Afterlife'. According to the
archaeologists, the door was reused in a structure in Roman Egypt.
Ancient Greek and Roman religions
The Greek god Hades is known in Greek mythology as the king of the underworld, a place where souls live after death. The Greek god Hermes,
the messenger of the gods, would take the dead soul of a person to the
underworld (sometimes called Hades or the House of Hades). Hermes would
leave the soul on the banks of the River Styx, the river between life and death.
Charon,
also known as the ferry-man, would take the soul across the river to
Hades, if the soul had gold: Upon burial, the family of the dead soul
would put coins under the deceased's tongue. Once crossed, the soul
would be judged by Aeacus, Rhadamanthus and King Minos. The soul would be sent to Elysium, Tartarus, or Asphodel Fields.
The Elysian Fields were for the ones that lived pure lives. It
consisted of green fields, valleys and mountains, everyone there was
peaceful and contented, and the Sun always shone there. Tartarus was for
the people that blasphemed against the gods, or were simply rebellious
and consciously evil.
The Asphodel Fields were for a varied selection of human souls:
Those whose sins equalled their goodness, were indecisive in their
lives, or were not judged. Those who had sinned went to the deepest pit,
Tartarus. In Tartarus, the soul would be punished by being burned in
lava, or stretched on racks. Some heroes of Greek legend are allowed to
visit the underworld. The Romans had a similar belief system about the
afterlife, with Hades becoming known as Pluto. In the ancient Greek myth about the Labours of Heracles, the hero Heracles had to travel to the underworld to capture Cerberus, the three-headed guard dog, as one of his tasks.
In Dream of Scipio, Cicero describes what seems to be an out of body experience, of the soul traveling high above the Earth, looking down at the small planet, from far away.
In Book VI of Virgil's Aeneid, the hero, Aeneas,
travels to the underworld to see his father. By the River Styx, he sees
the souls of those not given a proper burial, forced to wait by the
river until someone buries them. While down there, along with the dead,
he is shown the place where the wrongly convicted reside, the fields of
sorrow where those who committed suicide and now regret it reside,
including Aeneas' former lover, the warriors and shades, Tartarus (where
the titans and powerful non-mortal enemies of the Olympians reside)
where he can hear the groans of the imprisoned, the palace of Pluto, and the fields of Elysium where the descendants of the divine and bravest heroes reside. He sees the river of forgetfulness, Lethe,
which the dead must drink to forget their life and begin anew. Lastly,
his father shows him all of the future heroes of Rome who will live if
Aeneas fulfills his destiny in founding the city.
Norse religion
The Poetic and Prose Eddas,
the oldest sources for information on the Norse concept of the
afterlife, vary in their description of the several realms that are
described as falling under this topic. The most well-known are:
- Valhalla: (lit. "Hall of the Slain" i.e. "the Chosen Ones") Half the warriors who die in battle join the god Odin who rules over a majestic hall called Valhalla in Asgard.
- Fólkvangr: (lit. "Field of the Host") The other half join the goddess Freyja in a great meadow known as Fólkvangr.
- Hel: (lit. "The Covered Hall")
- Niflhel: (lit. "The Dark" or "Misty Hel")
Abrahamic religions
Baháʼí Faith
The teachings of the Baháʼí Faith
state that the nature of the afterlife is beyond the understanding of
those living, just as an unborn fetus cannot understand the nature of
the world outside of the womb. The Baháʼí writings state that the soul is immortal and after death it will continue to progress until it finally attains God's presence.
In Baháʼí belief, souls in the afterlife will continue to retain their
individuality and consciousness and will be able to recognize and
communicate spiritually with other souls whom they have made deep
profound friendships with, such as their spouses.
The Baháʼí scriptures also state there are distinctions between
souls in the afterlife, and that souls will recognize the worth of their
own deeds and understand the consequences of their actions. It is
explained that those souls that have turned toward God will experience
gladness, while those who have lived in error will become aware of the
opportunities they have lost. Also, in the Baháʼí view, souls will be
able to recognize the accomplishments of the souls that have reached the
same level as themselves, but not those that have achieved a rank
higher than them.
Christianity
Mainstream Christianity professes belief in the Nicene Creed, and English versions of the Nicene Creed in current use include the phrase: "We look for the resurrection of the dead, and the life of the world to come."
When questioned by the Sadducees about the resurrection of the dead (in a context relating to who one's spouse would be if one had been married several times in life), Jesus said that marriage will be irrelevant after the resurrection as the resurrected will be like the angels in heaven.
Jesus also maintained that the time would come when the dead would hear the voice of the Son of God,
and all who were in the tombs would come out; those who have heard His
"[commandments] and believes in the one who sent [Him]" to the
resurrection of life, but those who do not to the resurrection of
condemnation.
The Book of Enoch describes Sheol as divided into four compartments for four types of the dead: the faithful saints who await resurrection in Paradise,
the merely virtuous who await their reward, the wicked who await
punishment, and the wicked who have already been punished and will not
be resurrected on Judgment Day. The Book of Enoch is considered apocryphal by most denominations of Christianity and all denominations of Judaism.
The book of 2 Maccabees
gives a clear account of the dead awaiting a future resurrection and
judgment, plus prayers and offerings for the dead to remove the burden
of sin.
The author of Luke recounts the story of Lazarus and the rich man, which shows people in Hades awaiting the resurrection either in comfort or torment. The author of the Book of Revelation writes about God and the angels versus Satan and demons in an epic battle at the end of times when all souls are judged. There is mention of ghostly bodies of past prophets, and the transfiguration.
The non-canonical Acts of Paul and Thecla speak of the efficacy of prayer for the dead, so that they might be "translated to a state of happiness".
Hippolytus of Rome pictures the underworld (Hades) as a place where the righteous dead, awaiting in the bosom of Abraham their resurrection, rejoice at their future prospect, while the unrighteous are tormented at the sight of the "lake of unquenchable fire" into which they are destined to be cast.
Gregory of Nyssa discusses the long-before believed possibility of purification of souls after death.
Pope Gregory I repeats the concept, articulated over a century earlier by Gregory of Nyssa that the saved suffer purification after death, in connection with which he wrote of "purgatorial flames".
The noun "purgatorium" (Latin: place of cleansing)
is used for the first time to describe a state of painful purification
of the saved after life. The same word in adjectival form (purgatorius -a -um, cleansing), which appears also in non-religious writing, was already used by Christians such as Augustine of Hippo and Pope Gregory I to refer to an after-death cleansing.
During the Age of Enlightenment, theologians and philosophers presented various philosophies and beliefs. A notable example is Emanuel Swedenborg
who wrote some 18 theological works which describe in detail the nature
of the afterlife according to his claimed spiritual experiences, the
most famous of which is Heaven and Hell. His report of life there covers a wide range of topics, such as marriage in heaven (where all angels are married), children in heaven (where they are raised by angel parents), time and space
in heaven (there are none), the after-death awakening process in the
World of Spirits (a place halfway between Heaven and Hell and where
people first wake up after death), the allowance of a free will choice
between Heaven or Hell (as opposed to being sent to either one by God),
the eternity of Hell (one could leave but would never want to), and that all angels or devils were once people on earth.
The Catholic Church
The "Spiritual Combat", a written work by Lorenzo Scupoli, states that four assaults are attempted by the "evil one" at the hour of death. The Catholic conception of the afterlife teaches that after the body dies, the soul is judged, the righteous and free of sin enter Heaven. However, those who die in unrepented mortal sin go to hell. In the 1990s, the Catechism of the Catholic Church
defined hell not as punishment imposed on the sinner but rather as the
sinner's self-exclusion from God. Unlike other Christian groups, the
Catholic Church teaches that those who die in a state of grace, but
still carry venial sin go to a place called Purgatory where they undergo purification to enter Heaven.
Limbo
Despite popular opinion, Limbo, which was elaborated upon by
theologians beginning in the Middle Ages, was never recognized as a dogma of the Catholic Church,
yet, at times, it has been a very popular theological theory within the
Church. Limbo is a theory that unbaptized but innocent souls, such as
those of infants, virtuous individuals who lived before Jesus Christ was born on earth, or those that die before baptism exist in neither Heaven or Hell proper. Therefore, these souls neither merit the beatific vision, nor are subjected to any punishment, because they are not guilty of any personal sin although they have not received baptism, so still bear original sin. So they are generally seen as existing in a state of natural, but not supernatural, happiness, until the end of time.
In other Christian denominations it has been described as an intermediate place or state of confinement in oblivion and neglect.
Purgatory
The notion of purgatory is associated particularly with the Catholic Church.
In the Catholic Church, all those who die in God's grace and
friendship, but still imperfectly purified, are indeed assured of their
eternal salvation; but after death they undergo purification, so as to
achieve the holiness necessary to enter the joy of heaven or the final
purification of the elect, which is entirely different from the
punishment of the damned. The tradition of the church, by reference to
certain texts of scripture, speaks of a "cleansing fire" although it is
not always called purgatory.
Anglicans of the Anglo-Catholic tradition generally also hold to the belief. John Wesley, the founder of Methodism, believed in an intermediate state between death and the resurrection of the dead
and in the possibility of "continuing to grow in holiness there", but
Methodism does not officially affirm this belief and denies the
possibility of helping by prayer any who may be in that state.
Orthodox Christianity
The
Orthodox Church is intentionally reticent on the afterlife, as it
acknowledges the mystery especially of things that have not yet
occurred. Beyond the second coming of Jesus, bodily resurrection, and
final judgment, all of which is affirmed in the Nicene Creed
(325 CE), Orthodoxy does not teach much else in any definitive manner.
Unlike Western forms of Christianity, however, Orthodoxy is
traditionally non-dualist and does not teach that there are two separate
literal locations of heaven and hell, but instead acknowledges that
"the 'location' of one's final destiny—heaven or hell—as being
figurative."
Instead, Orthodoxy teaches that the final judgment is simply
one's uniform encounter with divine love and mercy, but this encounter
is experienced multifariously depending on the extent to which one has
been transformed, partaken of divinity, and is therefore compatible or
incompatible with God. "The monadic, immutable, and ceaseless object of
eschatological encounter is therefore the love and mercy of God, his
glory which infuses the heavenly temple, and it is the subjective human
reaction which engenders multiplicity or any division of experience." For instance, St. Isaac the Syrian
observes that "those who are punished in Gehenna, are scourged by the
scourge of love. ... The power of love works in two ways: it torments
sinners ... [as] bitter regret. But love inebriates the souls of the
sons of Heaven by its delectability."
In this sense, the divine action is always, immutably, and uniformly
love and if one experiences this love negatively, the experience is then
one of self-condemnation because of free will rather than condemnation
by God.
Orthodoxy therefore uses the description of Jesus' judgment in
John 3:19–21 as their model: "19 And this is the judgment: the light has
come into the world, and people loved the darkness rather than the
light because their works were evil. 20 For everyone who does wicked
things hates the light and does not come to the light, lest his works
should be exposed. 21 But whoever does what is true comes to the light,
so that it may be clearly seen that his works have been carried out in
God." As a characteristically Orthodox understanding, then, Fr. Thomas Hopko
writes, "[I]t is precisely the presence of God's mercy and love which
cause the torment of the wicked. God does not punish; he forgives... .
In a word, God has mercy on all, whether all like it or not. If we like
it, it is paradise; if we do not, it is hell. Every knee will bend
before the Lord. Everything will be subject to Him. God in Christ will
indeed be "all and in all," with boundless mercy and unconditional
pardon. But not all will rejoice in God's gift of forgiveness, and that
choice will be judgment, the self-inflicted source of their sorrow and
pain."
Moreover, Orthodoxy includes a prevalent tradition of apokatastasis, or the restoration of all things in the end. This has been taught most notably by Origen, but also many other Church fathers and Saints, including Gregory of Nyssa. The Second Council of Constantinople
(553 CE) affirmed the orthodoxy of Gregory of Nyssa while
simultaneously condemning Origen's brand of universalism because it
taught the restoration back to our pre-existent state, which Orthodoxy
doesn't teach. It is also a teaching of such eminent Orthodox
theologians as Olivier Clément, Metropolitan Kallistos Ware, and Bishop Hilarion Alfeyev. Although apokatastasis is not a dogma of the church but instead a theologoumenon,
it is no less a teaching of the Orthodox Church than its rejection. As
Met. Kallistos Ware explains, "It is heretical to say that all must be
saved, for this is to deny free will; but, it is legitimate to hope that
all may be saved," as insisting on torment without end also denies free will.
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
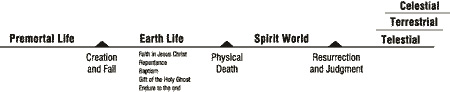
Plan of Salvation in LDS Religion
Joseph F. Smith of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
presents an elaborate vision of the afterlife. It is revealed as the
scene of an extensive missionary effort by righteous spirits in paradise
to redeem those still in darkness—a spirit prison or "hell" where the
spirits of the dead remain until judgment. It is divided into two parts:
Spirit Prison and Paradise. Together these are also known as the Spirit
World (also Abraham's Bosom; see Luke 16:19–25). They believe that
Christ visited spirit prison (1 Peter 3:18–20) and opened the gate for those who repent to cross over to Paradise. This is similar to the Harrowing of Hell doctrine of some mainstream Christian faiths.
Both Spirit Prison and Paradise are temporary according to Latter-day
Saint beliefs. After the resurrection, spirits are assigned
"permanently" to three degrees of heavenly glory, determined by how they
lived – Celestial, Terrestrial, and Telestial. (1 Cor 15:44–42;
Doctrine and Covenants, Section 76) Sons of Perdition, or those who have known and seen God and deny it, will be sent to the realm of Satan, which is called Outer Darkness, where they shall live in misery and agony forever. However, according to Mormon faith, since most persons lack the amount of knowledge to commit the Eternal sin, they are incapable of becoming sons of perdition.
The Celestial Kingdom is believed to be a place where the
righteous can live eternally with their families. Progression does not
end once one has entered the Celestial Kingdom, but it extends
eternally. According to "True to the Faith" (a handbook on doctrines in
the LDS faith), "The celestial kingdom is the place prepared for those
who have "received the testimony of Jesus" and been "made perfect
through Jesus the mediator of the new covenant, who wrought out this
perfect atonement through the shedding of his own blood" (Doctrine and
Covenants, 76:51, 69). To inherit this gift, we must receive the
ordinances of salvation, keep the commandments, and repent of our sins."
Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses occasionally use terms such as "afterlife" to refer to any hope for the dead, but they understand Ecclesiastes 9:5 to preclude belief in an immortal soul. Individuals judged by God to be wicked, such as in the Great Flood or at Armageddon,
are given no hope of an afterlife. However, they believe that after
Armageddon there will be a bodily resurrection of "both righteous and
unrighteous" dead (but not the "wicked"). Survivors of Armageddon and
those who are resurrected are then to gradually restore earth to a
paradise. After Armageddon, unrepentant sinners are punished with eternal death (non-existence).
Seventh-day Adventists
Creation and Death Equation
The Seventh-day Adventist Church's beliefs regarding the afterlife
differ from other Christian churches. Rather than ascend to Heaven or
descend to Hell, Adventists believe the dead "remain unconscious until
the return of Christ in judgement". The concept that the dead remain
dead until resurrection is one of the fundamental beliefs of Seventh-day
Adventist.
Adventists believe that death is an unconscious state (a “sleep”). This
is based on Matt. 9:24; Mark 5:39; John 11:11-14; 1 Cor. 15:51, 52; 1
Thess. 4:13-17; 2 Peter 3:4; Eccl. 9:5, 6, 10. At death, all
consciousness ends. The dead person does not know anything and does not
do anything.
They believe that death is creation, only in reverse. Ecclesiastes
12:7. When a person dies, the body turns to dust again, and the spirit
goes back to God, who gave it. The spirit of every person who
dies—whether saved or unsaved—returns to God at death. The spirit that
returns to God at death is the breath of life.
Islam
The Islamic belief in the afterlife, called al-ākhira (Arabic: الآخرة, lit. 'aftertime, hereafter') and as stated in the Quran, is descriptive. Mankind (as well as the jinn) is destined for either the "garden/gardens" (janna/jannāt) for the righteous, or the "hellfire" (an-nār) for the wicked, respectively also referred to as "Paradise" (al-firdaws) and "Gehenna" or "Gehinnom" (jahannam).
The level of comfort in the immediate afterlife of the al-qabr or "the grave" (compare the Jewish concept of Sheol), according to some commentators, depends wholly on their level of iʾmān or faith in God. In order for one to achieve proper and firm iʾmān one must have a righteous conduct, lest his level of faith dwindles and eventually withers away if one does not practice Islam long enough, and be led on the straight path (aṣ-ṣirāṭ al-mustaqīm) which is walked on by those who have been divinely graced and not have incurred divine wrath. In the Quran, God warns of grievous punishment to those who do not believe in the afterlife, and admonishes mankind that hellfire is prepared for the disbelievers.
Islam teaches that the purpose of Man's creation is entirely to
worship God alone, which includes being kind to other humans as well as
animals and plants, by not oppressing them. The Quran repeatedly reminds
the reader that the worldly life (ḥayāt ad-dunyā) is nothing but
a test and to determine each individual's ultimate abode, which is
eternal and everlasting. Some Quranic verses describing the Islamic paradise refer to perpetually youthful attendants which inhabit it, and they are described as both male and female servants: the females are referred to as ḥūr whereas the males are referred to as ghilmān, wildān, and suqāh. The slave boys are referred to in the Quran as "immortal boys" (56:17, 76:19) or "young men" (52:24) who serve wine and meals to the blessed.
In the 20th century, discussions about the afterlife address the
interconnection between human action and divine judgment, the need for
moral rectitude, and the eternal consequences of human action in this
life and world.
A central doctrine of Islamic faith is the Last Day (al-yawm al-ākhir), on which the world will come to an end and God will raise all mankind (as well as the jinn) from the dead and evaluate their worldly actions. The Last Day is also called the Encompassing Day (al-yawm al-muḥīṭ), more commonly known as the "Day of Resurrection" (yawm al-qiyāma), "Day of Judgment" (yawm ad-dīn), and "Day of Reckoning" (yawm al-ḥisāb), as well as both the "Day of Separation" (yawm al-faṣl) and "Day of Gathering" (yawm al-jamʿ), and is also referred to as as-Sāʿah, meaning "the Hour" signaled by the blowing of the horn/trumpet.
Until the Last Day, deceased souls remain in their graves awaiting the resurrection and judgment.
However, they will begin to feel immediately a taste of their destiny
to come. Those bound for hell will suffer in their graves, while those
bound for heaven will be in peace until that time.
Jannah and Jahannam both have different levels. Jannah has eight gates and eight levels. The higher the level the better it is and the happier you are. Jahannam
possess 7 deep terrible layers. The lower the layer the worse it is.
Individuals will arrive at both everlasting places during Judgment Day,
which commences after the angel Israfil
blows the trumpet the second time. Islam teaches the continued
existence of the soul and a transformed physical existence after death.
The resurrection that will take place on the Last Day is physical, and
is explained by suggesting that God will re-create the decayed body
(17:100: "Could they not see that God who created the heavens and the
earth is able to create the like of them?").
On the Last Day, resurrected humans and jinn will be judged by
God according to their deeds. One's eternal destination depends on
balance of good to bad deeds in life. They are either granted admission
to Paradise, where they will enjoy spiritual and physical pleasures
forever, or condemned to Hell to suffer spiritual and physical torment
for eternity. The day of judgment is described as passing over Hell on a
narrow bridge (as thin as human hair and sharper than a razor) in order
to enter Paradise. Those who fall, weighted by their bad deeds, will go
to Hell.
In Islam, believers are those who believed in oneness of God and
did not associate any partners with him or did not give the attributes
of God to any other entity. It is an established belief that if a
believer goes to hell for his sins being greater than his good deeds, he
will not remain in hell forever. When punishment for his sins will be
over, God will forgive him and grant him heaven.
Ahmadiyya
Ahmadi Muslims believe that the afterlife is not material but of a spiritual nature. According to Mirza Ghulam Ahmad, founder of the Ahmadiyya Muslim Community,
the soul will give birth to another rarer entity and will resemble the
life on this earth in the sense that this entity will bear a similar
relationship to the soul as the soul bears relationship with the human
existence on earth. On earth, if a person leads a righteous life and
submits to the will of God, his or her tastes become attuned to enjoying
spiritual pleasures as opposed to carnal desires. With this, an
"embryonic soul" begins to take shape. Different tastes are said to be
born which a person given to carnal passions finds no enjoyment. For
example, sacrifice of one's own rights over that of others becomes
enjoyable, or that forgiveness becomes second nature. In such a state a
person finds contentment and peace at heart and at this stage, according
to Ahmadiyya beliefs, it can be said that a soul within the soul has
begun to take shape.
Sufism
The Sufi Muslim scholar Ibn 'Arabi defined Barzakh
as the intermediate realm or "isthmus". It is between the world of
corporeal bodies and the world of spirits, and is a means of contact
between the two worlds. Without it, there would be no contact between
the two and both would cease to exist. He described it as simple and
luminous, like the world of spirits, but also able to take on many
different forms just like the world of corporeal bodies can. In broader
terms Barzakh, "is anything that separates two things". It has been
called the dream world in which the dreamer is in both life and death.
Judaism
Sheol
Sheol, in the Hebrew Bible,
is a place of darkness (Job x. 21, 22) to which all the dead go, both
the righteous and the unrighteous, regardless of the moral choices made
in life, (Gen. xxxvii. 36; Ezek. xxxii.; Isa. xiv.; Job xxx. 23), a
place of stillness, (Ps. lxxxviii. 13, xciv. 17; Eccl. ix. 10), at the
longest possible distance from heaven (Job xi. 8; Amos ix. 2; Ps.
cxxxix. 8).
The inhabitants of Sheol are the "shades" (rephaim), entities without personality or strength. Under some circumstances they are thought to be able to be contacted by the living, as the Witch of Endor contacts the shade of Samuel for Saul, but such practices are forbidden (Deuteronomy 18:10).
While the Hebrew Bible appears to describe Sheol as the permanent place of the dead, in the Second Temple period
(roughly 500 BC – 70 AD) a more diverse set of ideas developed. In some
texts, Sheol is considered to be the home of both the righteous and the
wicked, separated into respective compartments; in others, it was
considered a place of punishment, meant for the wicked dead alone. When the Hebrew scriptures were translated into Greek in ancient Alexandria around 200 BC, the word "Hades" (the Greek underworld) was substituted for Sheol. This is reflected in the New Testament where Hades is both the underworld of the dead and the personification of the evil it represents.
World to Come
The Talmud
offers a number of thoughts relating to the afterlife. After death, the
soul is brought for judgment. Those who have led pristine lives enter
immediately into the Olam Haba or world to come.
Most do not enter the world to come immediately, but now experience a
period of review of their earthly actions and they are made aware of
what they have done wrong. Some view this period as being a
"re-schooling", with the soul gaining wisdom as one's errors are
reviewed. Others view this period to include spiritual discomfort for
past wrongs. At the end of this period, not longer than one year, the
soul then takes its place in the world to come. Although discomforts are
made part of certain Jewish conceptions of the afterlife, the concept
of eternal damnation is not a tenet of the Jewish afterlife. According to the Talmud, extinction of the soul
is reserved for a far smaller group of malicious and evil leaders,
either whose very evil deeds go way beyond norms, or who lead large
groups of people to utmost evil. This is also part of Maimonides' 13 principles of faith.
Maimonides describes the Olam Haba
in spiritual terms, relegating the prophesied physical resurrection to
the status of a future miracle, unrelated to the afterlife or the Messianic era.
According to Maimonides, an afterlife continues for the soul of every
human being, a soul now separated from the body in which it was "housed"
during its earthly existence.
The Zohar describes Gehenna not as a place of punishment for the wicked but as a place of spiritual purification for souls.
Reincarnation in Jewish tradition
Although there is no reference to reincarnation in the Talmud or any prior writings,
according to rabbis such as Avraham Arieh Trugman, reincarnation is
recognized as being part and parcel of Jewish tradition. Trugman
explains that it is through oral tradition that the meanings of the
Torah, its commandments and stories, are known and understood. The
classic work of Jewish mysticism,
the Zohar, is quoted liberally in all Jewish learning; in the Zohar the
idea of reincarnation is mentioned repeatedly. Trugman states that in
the last five centuries the concept of reincarnation, which until then
had been a much hidden tradition within Judaism, was given open
exposure.
Shraga Simmons
commented that within the Bible itself, the idea [of reincarnation] is
intimated in Deut. 25:5–10, Deut. 33:6 and Isaiah 22:14, 65:6.
Yirmiyahu Ullman wrote that reincarnation is an "ancient,
mainstream belief in Judaism". The Zohar makes frequent and lengthy
references to reincarnation. Onkelos,
a righteous convert and authoritative commentator of the same period,
explained the verse, "Let Reuben live and not die ..." (Deuteronomy
33:6) to mean that Reuben should merit the World to Come directly, and
not have to die again as a result of being reincarnated. Torah scholar,
commentator and kabbalist, Nachmanides
(Ramban 1195–1270), attributed Job's suffering to reincarnation, as
hinted in Job's saying "God does all these things twice or three times
with a man, to bring back his soul from the pit to... the light of the
living' (Job 33:29, 30)."
Reincarnation, called gilgul, became popular in folk belief, and is found in much Yiddish literature among Ashkenazi Jews.
Among a few kabbalists, it was posited that some human souls could end
up being reincarnated into non-human bodies. These ideas were found in a
number of Kabbalistic works from the 13th century, and also among many
mystics in the late 16th century. Martin Buber's early collection of stories of the Baal Shem Tov's life includes several that refer to people reincarnating in successive lives.
Among well known (generally non-kabbalist or anti-kabbalist) rabbis who rejected the idea of reincarnation are Saadia Gaon, David Kimhi, Hasdai Crescas, Yedayah Bedershi (early 14th century), Joseph Albo, Abraham ibn Daud, the Rosh and Leon de Modena. Saadia Gaon, in Emunoth ve-Deoth (Hebrew: "beliefs and opinions") concludes Section VI with a refutation of the doctrine of metempsychosis
(reincarnation). While rebutting reincarnation, Saadia Gaon further
states that Jews who hold to reincarnation have adopted non-Jewish
beliefs. By no means do all Jews today believe in reincarnation, but
belief in reincarnation is not uncommon among many Jews, including
Orthodox.
Other well-known rabbis who are reincarnationists include Yonassan Gershom, Abraham Isaac Kook, Talmud scholar Adin Steinsaltz, DovBer Pinson, David M. Wexelman, Zalman Schachter,
and many others. Reincarnation is cited by authoritative biblical
commentators, including Ramban (Nachmanides), Menachem Recanti and
Rabbenu Bachya.
Among the many volumes of Yitzchak Luria, most of which come down
from the pen of his primary disciple, Chaim Vital, are insights
explaining issues related to reincarnation. His Shaar HaGilgulim, "The Gates of Reincarnation", is a book devoted exclusively to the subject of reincarnation in Judaism.
Rabbi Naftali Silberberg of The Rohr Jewish Learning Institute
notes that "Many ideas that originate in other religions and belief
systems have been popularized in the media and are taken for granted by
unassuming Jews."
Indian religions
Buddhism
Buddhists maintain that rebirth takes place without an unchanging self or soul passing from one form to another. The type of rebirth will be conditioned by the moral tone of the person's actions (kamma or karma).
For example, if a person has committed harmful actions by body, speech
and mind based on greed, hate and delusion, would have his/her rebirth
in a lower realm, i.e. an animal, a hungry ghost
or a hell realm, is to be expected. On the other hand, where a person
has performed skillful actions based on generosity, loving-kindness (metta), compassion and wisdom, rebirth in a happy realm, i.e. human or one of the many heavenly realms, can be expected.
Yet the mechanism of rebirth with kamma is not deterministic. It
depends on various levels of kamma. The most important moment that
determines where a person is reborn into is the last thought moment. At
that moment, heavy kamma would ripen if there were performed, if not
then near death kamma, if not then habitual kamma, finally if none of
the above happened, then residual kamma from previous actions can ripen. According to Theravada Buddhism, there are 31 realms of existence that one can be reborn into.
Pure Land Buddhism of Mahayana believes in a special place apart from the 31 planes of existence called Pure Land.
It is believed that each Buddha has their own pure land, created out of
their merits for the sake of sentient beings who recall them mindfully
to be able to be reborn in their pure land and train to become a Buddha
there. Thus the main practice of pure land Buddhism is to chant a
Buddha's name.
In Tibetan Buddhism the Tibetan Book of the Dead
explains the intermediate state of humans between death and
reincarnation. The deceased will find the bright light of wisdom, which
shows a straightforward path to move upward and leave the cycle of
reincarnation. There are various reasons why the deceased do not follow
that light. Some had no briefing about the intermediate state in the
former life. Others only used to follow their basic instincts like
animals. And some have fear, which results from foul deeds in the former
life or from insistent haughtiness. In the intermediate state the
awareness is very flexible, so it is important to be virtuous, adopt a
positive attitude, and avoid negative ideas. Ideas which are rising from
subconsciousness can cause extreme tempers and cowing visions. In this
situation they have to understand, that these manifestations are just
reflections of the inner thoughts. No one can really hurt them, because
they have no more material body. The deceased get help from different Buddhas
who show them the path to the bright light. The ones who do not follow
the path after all will get hints for a better reincarnation. They have
to release the things and beings on which or whom they still hang from
the life before. It is recommended to choose a family where the parents
trust in the Dharma and to reincarnate with the will to care for the welfare of all beings.
"Life is cosmic energy of the universe and after death it merges
in universe again and as the time comes to find the suitable place for
the entity died in the life condition it gets born. There are 10 life
states of any life: Hell, hunger, anger, animality, rapture, humanity,
learning, realization, bodhisatva and buddhahood. The life dies in which
life condition it reborn in the same life condition."
Hinduism
There are two major views of afterlife in Hinduism: mythical and
philosophical. The philosophies of Hinduism consider each individual
consists of 3 bodies: physical body compose of water and bio-matter (sthūla śarīra), an energetic/psychic/mental/subtle body (sūkṣma-śarīra) and a causal body (kāraṇa śarīra) comprising subliminal stuff i.e. mental impressions etc.
The individual is a stream of consciousness (Ātman)
which flows through all the physical changes of the body and at the
death of the physical body, flows on into another physical body. The two
components that transmigrate are the subtle body and the causal body.
The thought that occupies the mind at the time of death determines the quality of our rebirth (antim smaraṇa), hence Hinduism advises to be mindful of one's thoughts and cultivate positive wholesome thoughts - Mantra chanting (Japa) is commonly practiced for this.
The mythical includes the philosophical but adds heaven and hell myths.
When one leaves the physical body at death he appears in the court of Lord Yama, the God of Death for an exit interview. The panel consists of Yama and Chitragupta - the cosmic accountant, and Varuna
the cosmic intelligence officer. He is counseled about his life,
achievements and failures and is shown a mirror in which his entire life
is reflected. (Philosophically these three men are projections of one's
mind) Yama the Lord of Justice then sends him to a heavenly realm (svarga)
if he has been exceptionally benevolent and beneficent for a period of
Rest and Recreation. his period is limited in time by the weight of his
good deeds. If he has been exceptionally malevolent and caused immense
suffering to other beings then he is sent to a cosmic gulag (naraka) for his sins. After one has exhausted his karmas, he takes birth again to continue his spiritual evolution.
Rebirth can take place as a god (deva), a human (manuṣya) an
animal (tiryak) — but it is generally taught that the spiritual
evolution takes place from lower to higher species. In certain cases of
traumatic death a person can take the form of a Preta or Hungry Ghost -
and remains in an earth-bound state interminably - until certain
ceremonies are done to liberate them. This mythological part is
extensively elaborated in the Hindu Puranas especially in the Garuda Purana.
The Upanishads are the first scriptures in Hinduism which explicitly mention about Afterlife, The Bhagavad Gita,
a famous Hindu script, says that just as a man discards his old clothes
and wears new ones; similarly the Atman discards the old body and takes
on a new one. In Hinduism, the belief is that the body is nothing but a
shell, the consciousness inside is immutable and indestructible and
takes on different lives in a cycle of birth and death. The end of this
cycle is called mukti (Sanskrit: मुक्ति) and staying finally with the ultimate reality forever; is moksha (Sanskrit: मोक्ष) or liberation
Jainism
Jainism
also believes in the afterlife. They believe that the soul takes on a
body form based on previous karmas or actions performed by that soul
through eternity. Jains believe the soul is eternal and that the freedom
from the cycle of reincarnation is the means to attain eternal bliss.
Sikhism
The essential doctrine of Sikhism
is to experience the divine through simple living, meditation and
contemplation while being alive. Sikhism also has the belief of being in
union with God while living. Accounts of afterlife are considered to be
aimed at the popular prevailing views of the time so as to provide a
referential framework without necessarily establishing a belief in the
afterlife. Thus while it is also acknowledged that living the life of a
householder is above the metaphysical truth, Sikhism can be considered
agnostic to the question of an afterlife. Some scholars also interpret
the mention of reincarnation to be naturalistic akin to the biogeochemical cycles.
But if one analyses the Sikh Scriptures carefully, one may find
that on many occasions the afterlife and the existence of heaven and
hell are mentioned in Guru Granth Sahib and in Dasam Granth,
so from that it can be concluded that Sikhism does believe in the
existence of heaven and hell; however, heaven and hell are created to
temporarily reward and punish, and one will then take birth again until
one merges in God. According to the Sikh scriptures, the human form is
the closet form to God
and the best opportunity for a human being to attain salvation and
merge back with God. Sikh Gurus said that nothing dies, nothing is born,
everything is ever present, and it just changes forms. Like standing in
front of a wardrobe, you pick up a dress and wear it and then you
discard it. You wear another one. Thus, in the view of Sikhism, your
soul is never born and never dies. Your soul is a part of God and hence
lives forever.
Others
Traditional African religions
Traditional African religions are diverse in their beliefs in an afterlife. Hunter-gatherer societies such as the Hadza have no particular belief in an afterlife, and the death of an individual is a straightforward end to their existence. Ancestor cults are found throughout Sub-Saharan Africa, including cultures like the Yombe, Beng, Yoruba and Ewe,
"[T]he belief that the dead come back into life and are reborn into
their families is given concrete expression in the personal names that
are given to children....What is reincarnated are some of the dominant
characteristics of the ancestor and not his soul. For each soul remains
distinct and each birth represents a new soul." The Yoruba, Dogon
and LoDagoa have eschatological ideas similar to Abrahamic religions,
"but in most African societies, there is a marked absence of such
clear-cut notions of heaven and hell, although there are notions of God
judging the soul after death." In some societies like the Mende, multiple beliefs coexist. The Mende believe that people die twice: once during the process of joining the secret society,
and again during biological death after which they become ancestors.
However, some Mende also believe that after people are created by God
they live ten consecutive lives, each in progressively descending
worlds. One cross-cultural theme is that the ancestors are part of the world of the living, interacting with it regularly.
Shinto
It is common for families to participate in ceremonies for children at a shrine, yet have a Buddhist funeral at the time of death. In old Japanese legends, it is often claimed that the dead go to a place called yomi
(黄泉), a gloomy underground realm with a river separating the living
from the dead mentioned in the legend of Izanami and Izanagi. This yomi very closely resembles the Greek Hades; however, later myths include notions of resurrection and even Elysium-like descriptions such as in the legend of Okuninushi and Susanoo. Shinto tends to hold negative views on death and corpses as a source of pollution called kegare. However, death is also viewed as a path towards apotheosis
in Shintoism as can be evidenced by how legendary individuals become
enshrined after death. Perhaps the most famous would be Emperor Ojin who was enshrined as Hachiman the God of War after his death.
Unitarian Universalism
Some Unitarian Universalists believe in universalism: that all souls will ultimately be saved and that there are no torments of hell. Unitarian Universalists differ widely in their theology hence there is no exact same stance on the issue.
Although Unitarians historically believed in a literal hell, and
Universalists historically believed that everyone goes to heaven, modern
Unitarian Universalists can be categorized into those believing in a
heaven, reincarnation and oblivion. Most Unitarian Universalists believe
that heaven and hell are symbolic places of consciousness and the faith
is largely focused on the worldly life rather than any possible
afterlife.
Spiritualism
According to Edgar Cayce,
the afterlife consisted of nine realms equated with the nine planets of
astrology. The first, symbolized by Saturn, was a level for the
purification of the souls. The second, Mercury's realm, gives us the
ability to consider problems as a whole. The third of the nine soul
realms is ruled by Earth and is associated with the Earthly pleasures.
The fourth realm is where we find out about love and is ruled by Venus.
The fifth realm is where we meet our limitations and is ruled by Mars.
The sixth realm is ruled by Neptune, and is where we begin to use our
creative powers and free ourselves from the material world. The seventh
realm is symbolized by Jupiter, which strengthens the soul's ability to
depict situations, to analyze people and places, things, and conditions.
The eighth afterlife realm is ruled by Uranus and develops psychic
ability. The ninth afterlife realm is symbolized by Pluto, the
astrological realm of the unconscious. This afterlife realm is a
transient place where souls can choose to travel to other realms or
other solar systems, it is the souls liberation into eternity, and is
the realm that opens the doorway from our solar system into the cosmos
point of view.
Mainstream Spiritualists
postulate a series of seven realms that are not unlike Edgar Cayce's
nine realms ruled by the planets. As it evolves, the soul moves higher
and higher until it reaches the ultimate realm of spiritual oneness. The
first realm, equated with hell, is the place where troubled souls spend
a long time before they are compelled to move up to the next level. The
second realm, where most souls move directly, is thought of as an
intermediate transition between the lower planes of life and hell and
the higher perfect realms of the universe. The third level is for those
who have worked with their karmic inheritance. The fourth level is that
from which evolved souls teach and direct those on Earth. The fifth
level is where the soul leaves human consciousness behind. At the sixth
plane, the soul is finally aligned with the cosmic consciousness and has
no sense of separateness or individuality. Finally, the seventh level,
the goal of each soul, is where the soul transcends its own sense of
"soulfulness" and reunites with the World Soul and the universe.
Wicca
The Wiccan afterlife is most commonly described as The Summerland.
Here, souls rest, recuperate from life, and reflect on the experiences
they had during their lives. After a period of rest, the souls are
reincarnated, and the memory of their previous lives is erased. Many
Wiccans see The Summerland as a place to reflect on their life actions.
It is not a place of reward, but rather the end of a life journey at an
end point of incarnations.
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism states that the urvan, the disembodied spirit,
lingers on earth for three days before departing downward to the kingdom
of the dead that is ruled by Yima. For the three days that it rests on
Earth, righteous souls sit at the head of their body, chanting the Ustavaiti Gathas with joy, while a wicked person sits at the feet of the corpse, wails and recites the Yasna.
Zoroastrianism states that for the righteous souls, a beautiful maiden,
which is the personification of the soul's good thoughts, words and
deeds, appears. For a wicked person, a very old, ugly, naked hag
appears. After three nights, the soul of the wicked is taken by the
demon Vizaresa (Vīzarəša), to Chinvat bridge, and is made to go to darkness (hell).
Yima is believed to have been the first king
on earth to rule, as well as the first man to die. Inside of Yima's
realm, the spirits live a shadowy existence, and are dependent on their
own descendants which are still living on Earth. Their descendants are
to satisfy their hunger and clothe them, through rituals done on earth.
Rituals which are done on the first three days are vital and
important, as they protect the soul from evil powers and give it
strength to reach the underworld. After three days, the soul crosses Chinvat bridge which is the Final Judgment of the soul. Rashnu and Sraosha are present at the final judgment. The list is expanded sometimes, and include Vahman and Ormazd. Rashnu is the yazata
who holds the scales of justice. If the good deeds of the person
outweigh the bad, the soul is worthy of paradise. If the bad deeds
outweigh the good, the bridge narrows down to the width of a blade-edge,
and a horrid hag pulls the soul in her arms, and takes it down to hell
with her.
Misvan Gatu is the "place of the mixed ones" where the souls lead
a gray existence, lacking both joy and sorrow. A soul goes here if
his/her good deeds and bad deeds are equal, and Rashnu's scale is equal.
Parapsychology
The Society for Psychical Research
was founded in 1882 with the express intention of investigating
phenomena relating to Spiritualism and the afterlife. Its members
continue to conduct scientific research on the paranormal to this day.
Some of the earliest attempts to apply scientific methods
to the study of phenomena relating to an afterlife were conducted by
this organization. Its earliest members included noted scientists like William Crookes, and philosophers such as Henry Sidgwick and William James.
Parapsychological investigation of the afterlife includes the study of haunting, apparitions of the deceased, instrumental trans-communication, electronic voice phenomena, and mediumship.
A study conducted in 1901 by physician Duncan MacDougall sought to measure the weight lost by a human when the soul "departed the body" upon death.
MacDougall weighed dying patients in an attempt to prove that the soul
was material, tangible and thus measurable. Although MacDougall's
results varied considerably from "21 grams", for some people this figure
has become synonymous with the measure of a soul's mass. The title of the 2003 movie 21 Grams
is a reference to MacDougall's findings. His results have never been
reproduced, and are generally regarded either as meaningless or
considered to have had little if any scientific merit.
Frank Tipler has argued that physics can explain immortality, although such arguments are not falsifiable and, in Karl Popper's views, they do not qualify as science.
After 25 years of parapsychological research Susan Blackmore came to the conclusion that, according to her experiences, there is not enough empirical evidence for many of these cases.
Mediumship
Mediums purportedly act as a vessel for communications from spirits in other realms. Mediumship is not specific to one culture or religion; it can be identified in several belief systems, most notably Spiritualism.
While the practice gained popularity in Europe and North America in the
19th century, evidence of mediumship dates back thousands of years in
Asia. Mediums who claim to have contact with deceased people include Tyler Henry and Pascal Voggenhuber.
Near death research
Research also includes the study of the near death experience. Scientists who have worked in this area include Elisabeth Kübler-Ross, Raymond Moody, Sam Parnia, Michael Sabom, Bruce Greyson, Peter Fenwick, Jeffrey Long, Susan Blackmore, Charles Tart, William James, Ian Stevenson, Michael Persinger, Pim van Lommel, Penny Sartori, Walter van Laack among others.
Philosophy
Modern philosophy
There is a view based on the philosophical question of personal identity, termed open individualism by Daniel Kolak.
It concludes that individual conscious experience is illusory, and
because consciousness continues after death in all conscious beings, you do not die. This position has been supported by notable physicists such as Erwin Schrödinger and Freeman Dyson.
Certain problems arise with the idea of a particular person continuing after death. Peter van Inwagen, in his argument regarding resurrection, notes that the materialist must have some sort of physical continuity. John Hick also raises questions regarding personal identity in his book, Death and Eternal Life,
using an example of a person ceasing to exist in one place while an
exact replica appears in another. If the replica had all the same
experiences, traits, and physical appearances of the first person, we
would all attribute the same identity to the second, according to Hick.
Process philosophy
In the panentheistic model of process philosophy and theology the writers Alfred North Whitehead and Charles Hartshorne rejected the idea that the universe was made of substance,
instead saying reality is composed of living experiences (occasions of
experience). According to Hartshorne people do not experience subjective
(or personal) immortality in the afterlife, but they do have objective
immortality because their experiences live on forever in God, who contains all that was. However other process philosophers such as David Ray Griffin have written that people may have subjective experience after death.
Science
Psychological proposals for the origin of a belief in an afterlife
include cognitive disposition, cultural learning, and as an intuitive
religious idea.
In one study, children were able to recognize the ending of physical,
mental, and perceptual activity in death, but were hesitant to conclude
the ending of will, self, or emotion in death.
In 2008, a large-scale study conducted by the University of
Southampton involving 2060 patients from 15 hospitals in the United
Kingdom, United States and Austria was launched. The AWARE (AWAreness
during REsuscitation) study examined the broad range of mental
experiences in relation to death. In a large study, researchers also
tested the validity of conscious experiences for the first time using
objective markers, to determine whether claims of awareness compatible
with out-of-body experiences correspond with real or hallucinatory
events.
The results revealed that 40% of those who survived a cardiac arrest
were aware during the time that they were clinically dead and before
their hearts were restarted. One patient also had a verified out-of-body
experience (over 80% of patients did not survive their cardiac arrest
or were too sick to be interviewed), but his cardiac arrest occurred in a
room without markers. Dr. Parnia in the interview stated, "The evidence
thus far suggests that in the first few minutes after death,
consciousness is not annihilated." The study continues in AWARE II, which is set to be completed in September 2020.
Studies have also been done on the widely reported phenomenon of Near Death Experiences.
Experiencers commonly report being transported to a different “realm”
or “plane of existence” and they have been shown to display a lasting
positive aftereffect on most experiencers.












