Estimates of the number of deaths attributable to the Soviet dictator Joseph Stalin vary widely. The scholarly consensus affirms that archival materials declassified in 1991 contain irrefutable data far superior to sources used prior to 1991 such as statements from emigres and other informants, whereas a minority of authors and journalists maintain that "statistics can never fully describe what happened".
Prior to the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the archival revelations, some historians estimated that the numbers killed by Stalin's regime were 20 million or higher. After the Soviet Union dissolved, evidence from the Soviet archives was declassified and researchers were allowed to study it. This contained official records of 799,455 executions (1921–1953), around 1.7 million deaths in the Gulag, some 390,000 deaths during the dekulakization forced resettlement, and up to 400,000 deaths of persons deported during the 1940s, with a total of about 3.3 million officially recorded victims in these categories. According to historian Stephen Wheatcroft, approximately 1 million of these deaths were "purposive" while the rest happened through neglect and irresponsibility. The deaths of at least 5.5 to 6.5 million persons in the Soviet famine of 1932–1933 are sometimes, though not always, included with the victims of the Stalin era.
Events
Gulag
According to official Soviet estimates, more than 14 million people passed through the Gulag from 1929 to 1953, with a further 7 to 8 million being deported and exiled to remote areas of the Soviet Union, including entire nationalities in several cases.
According to a 1993 study of recently declassified archival Soviet data, a total of 1,053,829 people died in the Gulag (not including labor colonies) from 1934 to 1953 (there was no archival data for the period 1919–1934). More recent archival figures for the deaths in the Gulag, labor colonies and prisons combined for 1931–1953 were 1.713 million. According to historian Michael Ellman, non-state estimates of the actual Gulag death toll are usually higher because historians such as Robert Conquest took into account the likelihood of unreliable record keeping. According to author Anne Applebaum, it was common practice to release prisoners who were either suffering from incurable diseases or near death.
Golfo Alexopoulos, history professor at the University of South Florida, believes that at least 6 million people died as a result of their detention in the gulags. This estimate is disputed by other scholars, with critics such as J. Hardy stating that the evidence Alexopoulos used is indirect and misinterpreted. Historian Dan Healey argues that the estimate has obvious methodological difficulties.
Citing materials pre-1991, author John G. Heidenrich estimates the number of deaths at 12 million. His book is not primarily about estimating deaths from repressive policies in the Soviet Union, and he appears to have relied on Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn's political and literary work The Gulag Archipelago, which historian Stephen G. Wheatcroft explains was not intended as a historical fact but as a challenge to Soviet authorities after their years of secrecy.
According to estimates based on data from Soviet archives post-1991, there were around 1.6 million deaths during the whole period from 1929 to 1953. The tentative historical consensus is that of the 18 million people who passed through the gulag system from 1930 to 1953, between 1.5 and 1.7 million died as a result of their incarceration.
Soviet famine of 1932–1933
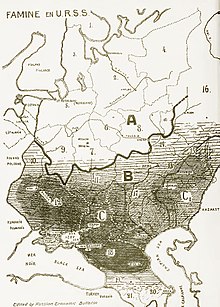
The deaths of 5.7 to perhaps 7.0 million people in the Soviet famine of 1932–1933 and Soviet collectivization of agriculture are included among the victims of repression during the period of Stalin by some historians. This categorization is controversial, as historians differ as to whether the famine in Ukraine was created as a deliberate part of the campaign of repression against kulaks and others was an unintended consequence of the struggle over forced collectivization, or was primarily a result of natural factors.
Judicial executions
According to official figures there were 777,975 judicial executions for political charges from 1929–53, including 681,692 in 1937–1938, the years of the Great Purge. Unofficial estimates estimate a total number of Stalinism repression deaths in 1937–38 at 950,000–1,200,000.
Soviet famine of 1946–1947
The last major famine to hit the Soviet Union began in July 1946, reached its peak in February–August 1947 and then quickly diminished in intensity, although there were still some famine deaths in 1948. Economist Michael Ellman states that the hands of the state could have fed all those who died of starvation. He argues that had the policies of the Soviet regime been different, there might have been no famine at all or a much smaller one. Ellman claims that the famine resulted in an estimated 1 to 1.5 million lives lost in addition to secondary population losses due to reduced fertility.
Population transfer by the Soviet Union
Deportation of kulaks
Large numbers of kulaks regardless of their nationality were resettled to Siberia and Central Asia. According to data from Soviet archives, which were published in 1990, 1,803,392 people were sent to labor colonies and camps in 1930 and 1931, and 1,317,022 reached the destination. Deportations on a smaller scale continued after 1931. Data from the Soviet archives indicates 2.4 million kulaks were deported from 1930–1934. The reported number of kulaks and their relatives who had died in labour colonies from 1932 to 1940 was 389,521. Popular history author Simon Sebag Montefiore estimated that 15 million kulaks and their families were deported by 1937; during the deportation, many people died, but the full number is not known.
Forced settlements in the Soviet Union of 1939–1953
According to Russian historian Pavel Polian, 5.870 million persons were deported to forced settlements from 1920–1952, including 3.125 million from 1939–1952. Those ethnic minorities considered a threat to Soviet security in 1939–52 were forcibly deported to Special Settlements run by the NKVD. Poles, Ukrainians from western regions, Soviet Germans, Balts, and Estonians peoples from the Caucasus and Crimea were the primary victims of this policy. Data from the Soviet archives list 309,521 deaths in the Special Settlements from 1941–48 and 73,454 in 1949–50. According to Polian these people were not allowed to return to their home regions until after the death of Stalin, the exception being Soviet Germans who were not allowed to return to the Volga region of the Soviet Union. According to Soviet archives, the heaviest mortality rate was documented in people from the Northern Caucasus (the Chechens, Ingush) with 144,704 deaths, or 24.7% of the entire deported population, as well as 44,125 deaths from Crimea, or a 19.3% mortality rate.
Katyn massacre
The massacre was prompted by NKVD chief Lavrentiy Beria's proposal to execute all captive members of the Polish officer corps, dated 5 March 1940, approved by the Politburo of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, including its leader Joseph Stalin. The number of victims is estimated at about 22,000.
Total number of victims
Writing in Slavic Review, demographers Barbara Anderson and Brian Silver maintained that limited census data make a precise death count impossible. Instead, they offer a probable range of 3.2 to 5.5 million excess deaths for the entire Soviet Union from 1926 to 1939, a period that covers collectivization, the civil war in the countryside, the purges of the late 1930s and major epidemics of typhus and malaria.
Some historians claim that the death toll was around 20 million, a figure based on Conquest's book The Great Terror (1968), with some estimates relying in part on demographic losses such as Conquest's. In 2001, American historian Richard Pipes argued that the population had decreased by 9 to 10 million people from the 1932 to 1939 censuses. In 2003, British historian Simon Sebag Montefiore suggested that Stalin was ultimately responsible for the deaths of at least 20 million people. In 2006, political scientist Rudolph Rummel wrote that the earlier higher victim total estimates are correct, although he included those killed by the government of the Soviet Union in other Eastern European countries as well. In his most recent edition of The Great Terror (2007), Conquest stated that while exact numbers may never be known with complete certainty, at least 15 million people were killed "by the whole range of Soviet regime's terrors." According to Barbara Anderson and Brian Silver, historians such as Robert Conquest made the most primitive of errors. They asserted that these Cold Warriors overestimated fertility rates and underrated the impact of assimilation, through which many Ukrainians were redesignated as Russians in the 1939 census, confusing population deficits, which included unborn children, with excess deaths.
Historians such as J. Arch Getty, Stephen G. Wheatcroft, and others, insist that the opening of the Soviet archives has vindicated the lower estimates put forth by the revisionist school. In 2011, after assessing twenty years of historical research in Eastern European archives, American historian Timothy D. Snyder stated that Stalin deliberately killed about 6 million, which rise to 9 million if foreseeable deaths arising from policies are taken into account.
Some historians believe that the official archival figures of the categories that were recorded by Soviet authorities are unreliable and incomplete. In addition to failures regarding comprehensive recordings, as one additional example, Canadian historian Robert Gellately and Montefiore argue that the many suspects beaten and tortured to death while in "investigative custody" were likely not to have been counted amongst the executed. Conversely, Wheatcroft states that prior to the opening of the archives for historical research, "our understanding of the scale and the nature of Soviet repression has been extremely poor" and that some specialists who wish to maintain earlier high estimates of the Stalinist death toll are "finding it difficult to adapt to the new circumstances when the archives are open and when there are plenty of irrefutable data" and instead "hang on to their old Sovietological methods with round-about calculations based on odd statements from emigres and other informants who are supposed to have superior knowledge." British historian Michael Ellman argues that mass deaths from famines should be placed in a different category than the repression victims, mentioning that throughout Russian history famines and droughts have been a common occurrence, including the Russian famine of 1921–22, which occurred before Stalin came to power. He also states that famines were widespread throughout the world in the 19th and 20th centuries in countries such as China, India, Ireland, and Russia. Ellman compared the behaviour of the Stalinist regime vis-à-vis the Holodomor to that of the British government (towards Ireland and India) and the G8 in contemporary times. According to Ellman, the G8 "are guilty of mass manslaughter or mass deaths from criminal negligence because of their not taking obvious measures to reduce mass deaths" and Stalin's "behaviour was no worse than that of many rulers in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries." Ben Kiernan, an American academic and historian, described Stalin's era as "by far the bloodiest of Soviet or even Russian history".
| Event | Est. number of deaths |
|---|---|
| Dekulakization | 530,000–600,000 |
| Great Purge | 779,000–1,200,000 |
| Gulag | 1,500,000–1,713,000 |
| Soviet deportations | 450,000–566,000 |
| Katyn massacre | 22,000 |
| Holodomor | 2,500,000–4,000,000 |
| Kazakh famine of 1932–33 | 1,450,000 |
| Total | ~7,231,000–9,551,000 |