In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a push or a pull. A force has both magnitude and direction, making it a vector quantity. It is measured in the SI unit of newton (N). Force is represented by the symbol F (formerly P).
The original form of Newton's second law states that the net force acting upon an object is equal to the rate at which its momentum changes with time. If the mass of the object is constant, this law implies that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object, is in the direction of the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
Concepts related to force include: thrust, which increases the velocity of an object; drag, which decreases the velocity of an object; and torque, which produces changes in rotational speed of an object. In an extended body, each part usually applies forces on the adjacent parts; the distribution of such forces through the body is the internal mechanical stress. Such internal mechanical stresses cause no acceleration of that body as the forces balance one another. Pressure, the distribution of many small forces applied over an area of a body, is a simple type of stress that if unbalanced can cause the body to accelerate. Stress usually causes deformation of solid materials, or flow in fluids.
Development of the concept
Philosophers in antiquity used the concept of force in the study of stationary and moving objects and simple machines, but thinkers such as Aristotle and Archimedes retained fundamental errors in understanding force. In part this was due to an incomplete understanding of the sometimes non-obvious force of friction, and a consequently inadequate view of the nature of natural motion. A fundamental error was the belief that a force is required to maintain motion, even at a constant velocity. Most of the previous misunderstandings about motion and force were eventually corrected by Galileo Galilei and Sir Isaac Newton. With his mathematical insight, Sir Isaac Newton formulated laws of motion that were not improved for nearly three hundred years. By the early 20th century, Einstein developed a theory of relativity that correctly predicted the action of forces on objects with increasing momenta near the speed of light, and also provided insight into the forces produced by gravitation and inertia.
With modern insights into quantum mechanics and technology that can accelerate particles close to the speed of light, particle physics has devised a Standard Model to describe forces between particles smaller than atoms. The Standard Model predicts that exchanged particles called gauge bosons are the fundamental means by which forces are emitted and absorbed. Only four main interactions are known: in order of decreasing strength, they are: strong, electromagnetic, weak, and gravitational. High-energy particle physics observations made during the 1970s and 1980s confirmed that the weak and electromagnetic forces are expressions of a more fundamental electroweak interaction.
Pre-Newtonian concepts
Since antiquity the concept of force has been recognized as integral to the functioning of each of the simple machines. The mechanical advantage given by a simple machine allowed for less force to be used in exchange for that force acting over a greater distance for the same amount of work. Analysis of the characteristics of forces ultimately culminated in the work of Archimedes who was especially famous for formulating a treatment of buoyant forces inherent in fluids.
Aristotle provided a philosophical discussion of the concept of a force as an integral part of Aristotelian cosmology. In Aristotle's view, the terrestrial sphere contained four elements that come to rest at different "natural places" therein. Aristotle believed that motionless objects on Earth, those composed mostly of the elements earth and water, to be in their natural place on the ground and that they will stay that way if left alone. He distinguished between the innate tendency of objects to find their "natural place" (e.g., for heavy bodies to fall), which led to "natural motion", and unnatural or forced motion, which required continued application of a force. This theory, based on the everyday experience of how objects move, such as the constant application of a force needed to keep a cart moving, had conceptual trouble accounting for the behavior of projectiles, such as the flight of arrows. The place where the archer moves the projectile was at the start of the flight, and while the projectile sailed through the air, no discernible efficient cause acts on it. Aristotle was aware of this problem and proposed that the air displaced through the projectile's path carries the projectile to its target. This explanation demands a continuum like air for change of place in general.
Aristotelian physics began facing criticism in medieval science, first by John Philoponus in the 6th century.
The shortcomings of Aristotelian physics would not be fully corrected until the 17th century work of Galileo Galilei, who was influenced by the late medieval idea that objects in forced motion carried an innate force of impetus. Galileo constructed an experiment in which stones and cannonballs were both rolled down an incline to disprove the Aristotelian theory of motion. He showed that the bodies were accelerated by gravity to an extent that was independent of their mass and argued that objects retain their velocity unless acted on by a force, for example friction.
In the early 17th century, before Newton's Principia, the term "force" (Latin: vis) was applied to many physical and non-physical phenomena, e.g., for an acceleration of a point. The product of a point mass and the square of its velocity was named vis viva (live force) by Leibniz. The modern concept of force corresponds to Newton's vis motrix (accelerating force).
Newtonian mechanics
Sir Isaac Newton described the motion of all objects using the concepts of inertia and force, and in doing so he found they obey certain conservation laws. In 1687, Newton published his thesis Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica. In this work Newton set out three laws of motion that to this day are the way forces are described in physics.
First law
Newton's first law of motion states that objects continue to move in a state of constant velocity unless acted upon by an external net force (resultant force). This law is an extension of Galileo's insight that constant velocity was associated with a lack of net force (see a more detailed description of this below). Newton proposed that every object with mass has an innate inertia that functions as the fundamental equilibrium "natural state" in place of the Aristotelian idea of the "natural state of rest". That is, Newton's empirical first law contradicts the intuitive Aristotelian belief that a net force is required to keep an object moving with constant velocity. By making rest physically indistinguishable from non-zero constant velocity, Newton's first law directly connects inertia with the concept of relative velocities. Specifically, in systems where objects are moving with different velocities, it is impossible to determine which object is "in motion" and which object is "at rest". The laws of physics are the same in every inertial frame of reference, that is, in all frames related by a Galilean transformation.
For instance, while traveling in a moving vehicle at a constant velocity, the laws of physics do not change as a result of its motion. If a person riding within the vehicle throws a ball straight up, that person will observe it rise vertically and fall vertically and not have to apply a force in the direction the vehicle is moving. Another person, observing the moving vehicle pass by, would observe the ball follow a curving parabolic path in the same direction as the motion of the vehicle. It is the inertia of the ball associated with its constant velocity in the direction of the vehicle's motion that ensures the ball continues to move forward even as it is thrown up and falls back down. From the perspective of the person in the car, the vehicle and everything inside of it is at rest: It is the outside world that is moving with a constant speed in the opposite direction of the vehicle. Since there is no experiment that can distinguish whether it is the vehicle that is at rest or the outside world that is at rest, the two situations are considered to be physically indistinguishable. Inertia therefore applies equally well to constant velocity motion as it does to rest.
Second law
A modern statement of Newton's second law is a vector equation:
where is the momentum of the system, and is the net (vector sum) force. If a body is in equilibrium, there is zero net force by definition (balanced forces may be present nevertheless). In contrast, the second law states that if there is an unbalanced force acting on an object it will result in the object's momentum changing over time.By the definition of momentum,
If Newton's second law is applied to a system of constant mass, m may be moved outside the derivative operator. The equation then becomes
Newton's second law asserts the direct proportionality of acceleration to force and the inverse proportionality of acceleration to mass. Accelerations can be defined through kinematic measurements. However, while kinematics are well-described through reference frame analysis in advanced physics, there are still deep questions that remain as to what is the proper definition of mass. General relativity offers an equivalence between space-time and mass, but lacking a coherent theory of quantum gravity, it is unclear as to how or whether this connection is relevant on microscales. With some justification, Newton's second law can be taken as a quantitative definition of mass by writing the law as an equality; the relative units of force and mass then are fixed.
Some textbooks use Newton's second law as a definition of force, but this has been disparaged in other textbooks. Notable physicists, philosophers and mathematicians who have sought a more explicit definition of the concept of force include Ernst Mach and Walter Noll.
Newton's second law can be used to measure the strength of forces. For instance, knowledge of the masses of planets along with the accelerations of their orbits allows scientists to calculate the gravitational forces on planets.
Third law
Whenever one body exerts a force on another, the latter simultaneously exerts an equal and opposite force on the first. In vector form, if is the force of body 1 on body 2 and that of body 2 on body 1, then
Newton's Third Law is a result of applying symmetry to situations where forces can be attributed to the presence of different objects. The third law means that all forces are interactions between different bodies, and thus that there is no such thing as a unidirectional force or a force that acts on only one body.
In a system composed of object 1 and object 2, the net force on the system due to their mutual interactions is zero:
Combining Newton's Second and Third Laws, it is possible to show that the linear momentum of a system is conserved. In a system of two particles, if is the momentum of object 1 and the momentum of object 2, then
Special theory of relativity
In the special theory of relativity, mass and energy are equivalent (as can be seen by calculating the work required to accelerate an object). When an object's velocity increases, so does its energy and hence its mass equivalent (inertia). It thus requires more force to accelerate it the same amount than it did at a lower velocity. Newton's Second Law
The relativistic expression relating force and acceleration for a particle with constant non-zero rest mass moving in the direction is:
In the early history of relativity, the expressions and were called longitudinal and transverse mass. Relativistic force does not produce a constant acceleration, but an ever-decreasing acceleration as the object approaches the speed of light. Note that approaches asymptotically an infinite value and is undefined for an object with a non-zero rest mass as it approaches the speed of light, and the theory yields no prediction at that speed.
If is very small compared to , then is very close to 1 and
Descriptions
Since forces are perceived as pushes or pulls, this can provide an intuitive understanding for describing forces. As with other physical concepts (e.g. temperature), the intuitive understanding of forces is quantified using precise operational definitions that are consistent with direct observations and compared to a standard measurement scale. Through experimentation, it is determined that laboratory measurements of forces are fully consistent with the conceptual definition of force offered by Newtonian mechanics.
Forces act in a particular direction and have sizes dependent upon how strong the push or pull is. Because of these characteristics, forces are classified as "vector quantities". This means that forces follow a different set of mathematical rules than physical quantities that do not have direction (denoted scalar quantities). For example, when determining what happens when two forces act on the same object, it is necessary to know both the magnitude and the direction of both forces to calculate the result. If both of these pieces of information are not known for each force, the situation is ambiguous. For example, if you know that two people are pulling on the same rope with known magnitudes of force but you do not know which direction either person is pulling, it is impossible to determine what the acceleration of the rope will be. The two people could be pulling against each other as in tug of war or the two people could be pulling in the same direction. In this simple one-dimensional example, without knowing the direction of the forces it is impossible to decide whether the net force is the result of adding the two force magnitudes or subtracting one from the other. Associating forces with vectors avoids such problems.
Historically, forces were first quantitatively investigated in conditions of static equilibrium where several forces canceled each other out. Such experiments demonstrate the crucial properties that forces are additive vector quantities: they have magnitude and direction. When two forces act on a point particle, the resulting force, the resultant (also called the net force), can be determined by following the parallelogram rule of vector addition: the addition of two vectors represented by sides of a parallelogram, gives an equivalent resultant vector that is equal in magnitude and direction to the transversal of the parallelogram. The magnitude of the resultant varies from the difference of the magnitudes of the two forces to their sum, depending on the angle between their lines of action. However, if the forces are acting on an extended body, their respective lines of application must also be specified in order to account for their effects on the motion of the body.
Free-body diagrams can be used as a convenient way to keep track of forces acting on a system. Ideally, these diagrams are drawn with the angles and relative magnitudes of the force vectors preserved so that graphical vector addition can be done to determine the net force.
As well as being added, forces can also be resolved into independent components at right angles to each other. A horizontal force pointing northeast can therefore be split into two forces, one pointing north, and one pointing east. Summing these component forces using vector addition yields the original force. Resolving force vectors into components of a set of basis vectors is often a more mathematically clean way to describe forces than using magnitudes and directions. This is because, for orthogonal components, the components of the vector sum are uniquely determined by the scalar addition of the components of the individual vectors. Orthogonal components are independent of each other because forces acting at ninety degrees to each other have no effect on the magnitude or direction of the other. Choosing a set of orthogonal basis vectors is often done by considering what set of basis vectors will make the mathematics most convenient. Choosing a basis vector that is in the same direction as one of the forces is desirable, since that force would then have only one non-zero component. Orthogonal force vectors can be three-dimensional with the third component being at right-angles to the other two.
Equilibrium
When all the forces that act upon an object are balanced, then the object is said to be in a state of equilibrium. Hence, equilibrium occurs when the resultant force acting on a point particle is zero (that is, the vector sum of all forces is zero). When dealing with an extended body, it is also necessary that the net torque be zero.
There are two kinds of equilibrium: static equilibrium and dynamic equilibrium.
Static
Static equilibrium was understood well before the invention of classical mechanics. Objects that are at rest have zero net force acting on them.
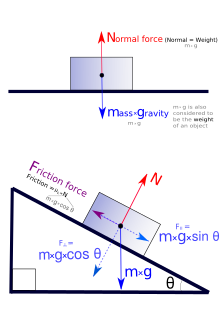
The simplest case of static equilibrium occurs when two forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. For example, an object on a level surface is pulled (attracted) downward toward the center of the Earth by the force of gravity. At the same time, a force is applied by the surface that resists the downward force with equal upward force (called a normal force). The situation produces zero net force and hence no acceleration.
Pushing against an object that rests on a frictional surface can result in a situation where the object does not move because the applied force is opposed by static friction, generated between the object and the table surface. For a situation with no movement, the static friction force exactly balances the applied force resulting in no acceleration. The static friction increases or decreases in response to the applied force up to an upper limit determined by the characteristics of the contact between the surface and the object.
A static equilibrium between two forces is the most usual way of measuring forces, using simple devices such as weighing scales and spring balances. For example, an object suspended on a vertical spring scale experiences the force of gravity acting on the object balanced by a force applied by the "spring reaction force", which equals the object's weight. Using such tools, some quantitative force laws were discovered: that the force of gravity is proportional to volume for objects of constant density (widely exploited for millennia to define standard weights); Archimedes' principle for buoyancy; Archimedes' analysis of the lever; Boyle's law for gas pressure; and Hooke's law for springs. These were all formulated and experimentally verified before Isaac Newton expounded his Three Laws of Motion.
Dynamic
Dynamic equilibrium was first described by Galileo who noticed that certain assumptions of Aristotelian physics were contradicted by observations and logic. Galileo realized that simple velocity addition demands that the concept of an "absolute rest frame" did not exist. Galileo concluded that motion in a constant velocity was completely equivalent to rest. This was contrary to Aristotle's notion of a "natural state" of rest that objects with mass naturally approached. Simple experiments showed that Galileo's understanding of the equivalence of constant velocity and rest were correct. For example, if a mariner dropped a cannonball from the crow's nest of a ship moving at a constant velocity, Aristotelian physics would have the cannonball fall straight down while the ship moved beneath it. Thus, in an Aristotelian universe, the falling cannonball would land behind the foot of the mast of a moving ship. However, when this experiment is actually conducted, the cannonball always falls at the foot of the mast, as if the cannonball knows to travel with the ship despite being separated from it. Since there is no forward horizontal force being applied on the cannonball as it falls, the only conclusion left is that the cannonball continues to move with the same velocity as the boat as it falls. Thus, no force is required to keep the cannonball moving at the constant forward velocity.
Moreover, any object traveling at a constant velocity must be subject to zero net force (resultant force). This is the definition of dynamic equilibrium: when all the forces on an object balance but it still moves at a constant velocity.
A simple case of dynamic equilibrium occurs in constant velocity motion across a surface with kinetic friction. In such a situation, a force is applied in the direction of motion while the kinetic friction force exactly opposes the applied force. This results in zero net force, but since the object started with a non-zero velocity, it continues to move with a non-zero velocity. Aristotle misinterpreted this motion as being caused by the applied force. However, when kinetic friction is taken into consideration it is clear that there is no net force causing constant velocity motion.
Forces in quantum mechanics
The notion "force" keeps its meaning in quantum mechanics, though one is now dealing with operators instead of classical variables and though the physics is now described by the Schrödinger equation instead of Newtonian equations. This has the consequence that the results of a measurement are now sometimes "quantized", i.e. they appear in discrete portions. This is, of course, difficult to imagine in the context of "forces". However, the potentials V(x, y, z) or fields, from which the forces generally can be derived, are treated similarly to classical position variables, i.e., .
This becomes different only in the framework of quantum field theory, where these fields are also quantized.
However, already in quantum mechanics there is one "caveat", namely the particles acting onto each other do not only possess the spatial variable, but also a discrete intrinsic angular momentum-like variable called the "spin", and there is the Pauli exclusion principle relating the space and the spin variables. Depending on the value of the spin, identical particles split into two different classes, fermions and bosons. If two identical fermions (e.g. electrons) have a symmetric spin function (e.g. parallel spins) the spatial variables must be antisymmetric (i.e. they exclude each other from their places much as if there was a repulsive force), and vice versa, i.e. for antiparallel spins the position variables must be symmetric (i.e. the apparent force must be attractive). Thus in the case of two fermions there is a strictly negative correlation between spatial and spin variables, whereas for two bosons (e.g. quanta of electromagnetic waves, photons) the correlation is strictly positive.
Thus the notion "force" loses already part of its meaning.
Feynman diagrams
In modern particle physics, forces and the acceleration of particles are explained as a mathematical by-product of exchange of momentum-carrying gauge bosons. With the development of quantum field theory and general relativity, it was realized that force is a redundant concept arising from conservation of momentum (4-momentum in relativity and momentum of virtual particles in quantum electrodynamics). The conservation of momentum can be directly derived from the homogeneity or symmetry of space and so is usually considered more fundamental than the concept of a force. Thus the currently known fundamental forces are considered more accurately to be "fundamental interactions". When particle A emits (creates) or absorbs (annihilates) virtual particle B, a momentum conservation results in recoil of particle A making impression of repulsion or attraction between particles A A' exchanging by B. This description applies to all forces arising from fundamental interactions. While sophisticated mathematical descriptions are needed to predict, in full detail, the accurate result of such interactions, there is a conceptually simple way to describe such interactions through the use of Feynman diagrams. In a Feynman diagram, each matter particle is represented as a straight line (see world line) traveling through time, which normally increases up or to the right in the diagram. Matter and anti-matter particles are identical except for their direction of propagation through the Feynman diagram. World lines of particles intersect at interaction vertices, and the Feynman diagram represents any force arising from an interaction as occurring at the vertex with an associated instantaneous change in the direction of the particle world lines. Gauge bosons are emitted away from the vertex as wavy lines and, in the case of virtual particle exchange, are absorbed at an adjacent vertex.
The utility of Feynman diagrams is that other types of physical phenomena that are part of the general picture of fundamental interactions but are conceptually separate from forces can also be described using the same rules. For example, a Feynman diagram can describe in succinct detail how a neutron decays into an electron, proton, and neutrino, an interaction mediated by the same gauge boson that is responsible for the weak nuclear force.
Fundamental forces
All of the known forces of the universe are classified into four fundamental interactions. The strong and the weak forces act only at very short distances, and are responsible for the interactions between subatomic particles, including nucleons and compound nuclei. The electromagnetic force acts between electric charges, and the gravitational force acts between masses. All other forces in nature derive from these four fundamental interactions. For example, friction is a manifestation of the electromagnetic force acting between atoms of two surfaces, and the Pauli exclusion principle, which does not permit atoms to pass through each other. Similarly, the forces in springs, modeled by Hooke's law, are the result of electromagnetic forces and the Pauli exclusion principle acting together to return an object to its equilibrium position. Centrifugal forces are acceleration forces that arise simply from the acceleration of rotating frames of reference.
The fundamental theories for forces developed from the unification of different ideas. For example, Sir Isaac Newton unified, with his universal theory of gravitation, the force responsible for objects falling near the surface of the Earth with the force responsible for the falling of celestial bodies about the Earth (the Moon) and around the Sun (the planets). Michael Faraday and James Clerk Maxwell demonstrated that electric and magnetic forces were unified through a theory of electromagnetism. In the 20th century, the development of quantum mechanics led to a modern understanding that the first three fundamental forces (all except gravity) are manifestations of matter (fermions) interacting by exchanging virtual particles called gauge bosons. This Standard Model of particle physics assumes a similarity between the forces and led scientists to predict the unification of the weak and electromagnetic forces in electroweak theory, which was subsequently confirmed by observation. The complete formulation of the Standard Model predicts an as yet unobserved Higgs mechanism, but observations such as neutrino oscillations suggest that the Standard Model is incomplete. A Grand Unified Theory that allows for the combination of the electroweak interaction with the strong force is held out as a possibility with candidate theories such as supersymmetry proposed to accommodate some of the outstanding unsolved problems in physics. Physicists are still attempting to develop self-consistent unification models that would combine all four fundamental interactions into a theory of everything. Einstein tried and failed at this endeavor, but currently the most popular approach to answering this question is string theory.
| Property/Interaction | Gravitation | Weak | Electromagnetic | Strong | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Electroweak) | Fundamental | Residual | |||
| Acts on: | Mass - Energy | Flavor | Electric charge | Color charge | Atomic nuclei |
| Particles experiencing: | All | Quarks, leptons | Electrically charged | Quarks, Gluons | Hadrons |
| Particles mediating: | Graviton (not yet observed) |
W+ W− Z0 | γ | Gluons | Mesons |
| Strength in the scale of quarks: | 10−41 | 10−4 | 1 | 60 | Not applicable to quarks |
| Strength in the scale of protons/neutrons: |
10−36 | 10−7 | 1 | Not applicable to hadrons |
20 |
Gravitational
What we now call gravity was not identified as a universal force until the work of Isaac Newton. Before Newton, the tendency for objects to fall towards the Earth was not understood to be related to the motions of celestial objects. Galileo was instrumental in describing the characteristics of falling objects by determining that the acceleration of every object in free-fall was constant and independent of the mass of the object. Today, this acceleration due to gravity towards the surface of the Earth is usually designated as and has a magnitude of about 9.81 meters per second squared (this measurement is taken from sea level and may vary depending on location), and points toward the center of the Earth. This observation means that the force of gravity on an object at the Earth's surface is directly proportional to the object's mass. Thus an object that has a mass of will experience a force:
For an object in free-fall, this force is unopposed and the net force on the object is its weight. For objects not in free-fall, the force of gravity is opposed by the reaction forces applied by their supports. For example, a person standing on the ground experiences zero net force, since a normal force (a reaction force) is exerted by the ground upward on the person that counterbalances his weight that is directed downward.
Newton's contribution to gravitational theory was to unify the motions of heavenly bodies, which Aristotle had assumed were in a natural state of constant motion, with falling motion observed on the Earth. He proposed a law of gravity that could account for the celestial motions that had been described earlier using Kepler's laws of planetary motion.
Newton came to realize that the effects of gravity might be observed in different ways at larger distances. In particular, Newton determined that the acceleration of the Moon around the Earth could be ascribed to the same force of gravity if the acceleration due to gravity decreased as an inverse square law. Further, Newton realized that the acceleration of a body due to gravity is proportional to the mass of the other attracting body. Combining these ideas gives a formula that relates the mass () and the radius () of the Earth to the gravitational acceleration:
where the vector direction is given by , is the unit vector directed outward from the center of the Earth.
In this equation, a dimensional constant is used to describe the relative strength of gravity. This constant has come to be known as Newton's Universal Gravitation Constant, though its value was unknown in Newton's lifetime. Not until 1798 was Henry Cavendish able to make the first measurement of using a torsion balance; this was widely reported in the press as a measurement of the mass of the Earth since knowing could allow one to solve for the Earth's mass given the above equation. Newton, however, realized that since all celestial bodies followed the same laws of motion, his law of gravity had to be universal. Succinctly stated, Newton's Law of Gravitation states that the force on a spherical object of mass due to the gravitational pull of mass is
where is the distance between the two objects' centers of mass and is the unit vector pointed in the direction away from the center of the first object toward the center of the second object.This formula was powerful enough to stand as the basis for all subsequent descriptions of motion within the solar system until the 20th century. During that time, sophisticated methods of perturbation analysis were invented to calculate the deviations of orbits due to the influence of multiple bodies on a planet, moon, comet, or asteroid. The formalism was exact enough to allow mathematicians to predict the existence of the planet Neptune before it was observed.
Mercury's orbit, however, did not match that predicted by Newton's Law of Gravitation. Some astrophysicists predicted the existence of another planet (Vulcan) that would explain the discrepancies; however no such planet could be found. When Albert Einstein formulated his theory of general relativity (GR) he turned his attention to the problem of Mercury's orbit and found that his theory added a correction, which could account for the discrepancy. This was the first time that Newton's Theory of Gravity had been shown to be inexact.
Since then, general relativity has been acknowledged as the theory that best explains gravity. In GR, gravitation is not viewed as a force, but rather, objects moving freely in gravitational fields travel under their own inertia in straight lines through curved space-time – defined as the shortest space-time path between two space-time events. From the perspective of the object, all motion occurs as if there were no gravitation whatsoever. It is only when observing the motion in a global sense that the curvature of space-time can be observed and the force is inferred from the object's curved path. Thus, the straight line path in space-time is seen as a curved line in space, and it is called the ballistic trajectory of the object. For example, a basketball thrown from the ground moves in a parabola, as it is in a uniform gravitational field. Its space-time trajectory is almost a straight line, slightly curved (with the radius of curvature of the order of few light-years). The time derivative of the changing momentum of the object is what we label as "gravitational force".
Electromagnetic
The electrostatic force was first described in 1784 by Coulomb as a force that existed intrinsically between two charges. The properties of the electrostatic force were that it varied as an inverse square law directed in the radial direction, was both attractive and repulsive (there was intrinsic polarity), was independent of the mass of the charged objects, and followed the superposition principle. Coulomb's law unifies all these observations into one succinct statement.
Subsequent mathematicians and physicists found the construct of the electric field to be useful for determining the electrostatic force on an electric charge at any point in space. The electric field was based on using a hypothetical "test charge" anywhere in space and then using Coulomb's Law to determine the electrostatic force. Thus the electric field anywhere in space is defined as
Meanwhile, the Lorentz force of magnetism was discovered to exist between two electric currents. It has the same mathematical character as Coulomb's Law with the proviso that like currents attract and unlike currents repel. Similar to the electric field, the magnetic field can be used to determine the magnetic force on an electric current at any point in space. In this case, the magnitude of the magnetic field was determined to be
where is the magnitude of the hypothetical test current and is the length of hypothetical wire through which the test current flows. The magnetic field exerts a force on all magnets including, for example, those used in compasses. The fact that the Earth's magnetic field is aligned closely with the orientation of the Earth's axis causes compass magnets to become oriented because of the magnetic force pulling on the needle.Through combining the definition of electric current as the time rate of change of electric charge, a rule of vector multiplication called Lorentz's Law describes the force on a charge moving in a magnetic field. The connection between electricity and magnetism allows for the description of a unified electromagnetic force that acts on a charge. This force can be written as a sum of the electrostatic force (due to the electric field) and the magnetic force (due to the magnetic field). Fully stated, this is the law:
where is the electromagnetic force, is the magnitude of the charge of the particle, is the electric field, is the velocity of the particle that is crossed with the magnetic field ().The origin of electric and magnetic fields would not be fully explained until 1864 when James Clerk Maxwell unified a number of earlier theories into a set of 20 scalar equations, which were later reformulated into 4 vector equations by Oliver Heaviside and Josiah Willard Gibbs. These "Maxwell Equations" fully described the sources of the fields as being stationary and moving charges, and the interactions of the fields themselves. This led Maxwell to discover that electric and magnetic fields could be "self-generating" through a wave that traveled at a speed that he calculated to be the speed of light. This insight united the nascent fields of electromagnetic theory with optics and led directly to a complete description of the electromagnetic spectrum.
However, attempting to reconcile electromagnetic theory with two observations, the photoelectric effect, and the nonexistence of the ultraviolet catastrophe, proved troublesome. Through the work of leading theoretical physicists, a new theory of electromagnetism was developed using quantum mechanics. This final modification to electromagnetic theory ultimately led to quantum electrodynamics (or QED), which fully describes all electromagnetic phenomena as being mediated by wave–particles known as photons. In QED, photons are the fundamental exchange particle, which described all interactions relating to electromagnetism including the electromagnetic force.
Strong nuclear
There are two "nuclear forces", which today are usually described as interactions that take place in quantum theories of particle physics. The strong nuclear force is the force responsible for the structural integrity of atomic nuclei while the weak nuclear force is responsible for the decay of certain nucleons into leptons and other types of hadrons.
The strong force is today understood to represent the interactions between quarks and gluons as detailed by the theory of quantum chromodynamics (QCD). The strong force is the fundamental force mediated by gluons, acting upon quarks, antiquarks, and the gluons themselves. The (aptly named) strong interaction is the "strongest" of the four fundamental forces.
The strong force only acts directly upon elementary particles. However, a residual of the force is observed between hadrons (the best known example being the force that acts between nucleons in atomic nuclei) as the nuclear force. Here the strong force acts indirectly, transmitted as gluons, which form part of the virtual pi and rho mesons, which classically transmit the nuclear force (see this topic for more). The failure of many searches for free quarks has shown that the elementary particles affected are not directly observable. This phenomenon is called color confinement.
Weak nuclear
The weak force is due to the exchange of the heavy W and Z bosons. Since the weak force is mediated by two types of bosons, it can be divided into two types of interaction or "vertices" — charged current, involving the electrically charged W+ and W− bosons, and neutral current, involving electrically neutral Z0 bosons. The most familiar effect of weak interaction is beta decay (of neutrons in atomic nuclei) and the associated radioactivity. This is a type of charged-current interaction. The word "weak" derives from the fact that the field strength is some 1013 times less than that of the strong force. Still, it is stronger than gravity over short distances. A consistent electroweak theory has also been developed, which shows that electromagnetic forces and the weak force are indistinguishable at a temperatures in excess of approximately 1015 kelvins. Such temperatures have been probed in modern particle accelerators and show the conditions of the universe in the early moments of the Big Bang.
Non-fundamental forces
Some forces are consequences of the fundamental ones. In such situations, idealized models can be utilized to gain physical insight.
Normal force
The normal force is due to repulsive forces of interaction between atoms at close contact. When their electron clouds overlap, Pauli repulsion (due to fermionic nature of electrons) follows resulting in the force that acts in a direction normal to the surface interface between two objects. The normal force, for example, is responsible for the structural integrity of tables and floors as well as being the force that responds whenever an external force pushes on a solid object. An example of the normal force in action is the impact force on an object crashing into an immobile surface.
Friction
Friction is a surface force that opposes relative motion. The frictional force is directly related to the normal force that acts to keep two solid objects separated at the point of contact. There are two broad classifications of frictional forces: static friction and kinetic friction.
The static friction force () will exactly oppose forces applied to an object parallel to a surface contact up to the limit specified by the coefficient of static friction () multiplied by the normal force (). In other words, the magnitude of the static friction force satisfies the inequality:
The kinetic friction force () is independent of both the forces applied and the movement of the object. Thus, the magnitude of the force equals:
where is the coefficient of kinetic friction. For most surface interfaces, the coefficient of kinetic friction is less than the coefficient of static friction.
Tension
Tension forces can be modeled using ideal strings that are massless, frictionless, unbreakable, and unstretchable. They can be combined with ideal pulleys, which allow ideal strings to switch physical direction. Ideal strings transmit tension forces instantaneously in action-reaction pairs so that if two objects are connected by an ideal string, any force directed along the string by the first object is accompanied by a force directed along the string in the opposite direction by the second object. By connecting the same string multiple times to the same object through the use of a set-up that uses movable pulleys, the tension force on a load can be multiplied. For every string that acts on a load, another factor of the tension force in the string acts on the load. However, even though such machines allow for an increase in force, there is a corresponding increase in the length of string that must be displaced in order to move the load. These tandem effects result ultimately in the conservation of mechanical energy since the work done on the load is the same no matter how complicated the machine.
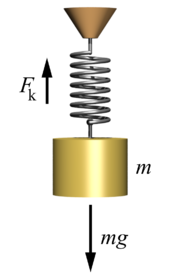
Elastic force
An elastic force acts to return a spring to its natural length. An ideal spring is taken to be massless, frictionless, unbreakable, and infinitely stretchable. Such springs exert forces that push when contracted, or pull when extended, in proportion to the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position. This linear relationship was described by Robert Hooke in 1676, for whom Hooke's law is named. If is the displacement, the force exerted by an ideal spring equals:
where is the spring constant (or force constant), which is particular to the spring. The minus sign accounts for the tendency of the force to act in opposition to the applied load.Continuum mechanics
Newton's laws and Newtonian mechanics in general were first developed to describe how forces affect idealized point particles rather than three-dimensional objects. However, in real life, matter has extended structure and forces that act on one part of an object might affect other parts of an object. For situations where lattice holding together the atoms in an object is able to flow, contract, expand, or otherwise change shape, the theories of continuum mechanics describe the way forces affect the material. For example, in extended fluids, differences in pressure result in forces being directed along the pressure gradients as follows:
where is the volume of the object in the fluid and is the scalar function that describes the pressure at all locations in space. Pressure gradients and differentials result in the buoyant force for fluids suspended in gravitational fields, winds in atmospheric science, and the lift associated with aerodynamics and flight.
A specific instance of such a force that is associated with dynamic pressure is fluid resistance: a body force that resists the motion of an object through a fluid due to viscosity. For so-called "Stokes' drag" the force is approximately proportional to the velocity, but opposite in direction:
where:- is a constant that depends on the properties of the fluid and the dimensions of the object (usually the cross-sectional area), and
- is the velocity of the object.
More formally, forces in continuum mechanics are fully described by a stress–tensor with terms that are roughly defined as
where is the relevant cross-sectional area for the volume for which the stress-tensor is being calculated. This formalism includes pressure terms associated with forces that act normal to the cross-sectional area (the matrix diagonals of the tensor) as well as shear terms associated with forces that act parallel to the cross-sectional area (the off-diagonal elements). The stress tensor accounts for forces that cause all strains (deformations) including also tensile stresses and compressions.
Fictitious forces
There are forces that are frame dependent, meaning that they appear due to the adoption of non-Newtonian (that is, non-inertial) reference frames. Such forces include the centrifugal force and the Coriolis force. These forces are considered fictitious because they do not exist in frames of reference that are not accelerating. Because these forces are not genuine they are also referred to as "pseudo forces".
In general relativity, gravity becomes a fictitious force that arises in situations where spacetime deviates from a flat geometry. As an extension, Kaluza–Klein theory and string theory ascribe electromagnetism and the other fundamental forces respectively to the curvature of differently scaled dimensions, which would ultimately imply that all forces are fictitious.
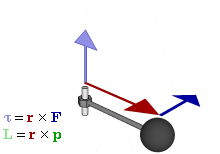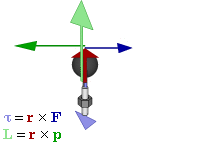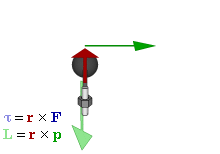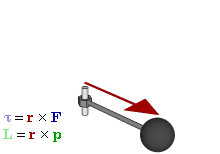
Rotations and torque
Forces that cause extended objects to rotate are associated with torques. Mathematically, the torque of a force is defined relative to an arbitrary reference point as the cross-product:
where is the position vector of the force application point relative to the reference point.Torque is the rotation equivalent of force in the same way that angle is the rotational equivalent for position, angular velocity for velocity, and angular momentum for momentum. As a consequence of Newton's First Law of Motion, there exists rotational inertia that ensures that all bodies maintain their angular momentum unless acted upon by an unbalanced torque. Likewise, Newton's Second Law of Motion can be used to derive an analogous equation for the instantaneous angular acceleration of the rigid body:
where
- is the moment of inertia of the body
- is the angular acceleration of the body.
This provides a definition for the moment of inertia, which is the rotational equivalent for mass. In more advanced treatments of mechanics, where the rotation over a time interval is described, the moment of inertia must be substituted by the tensor that, when properly analyzed, fully determines the characteristics of rotations including precession and nutation.
Equivalently, the differential form of Newton's Second Law provides an alternative definition of torque:
Newton's Third Law of Motion requires that all objects exerting torques themselves experience equal and opposite torques, and therefore also directly implies the conservation of angular momentum for closed systems that experience rotations and revolutions through the action of internal torques.
Centripetal force
For an object accelerating in circular motion, the unbalanced force acting on the object equals:
where is the mass of the object, is the velocity of the object and is the distance to the center of the circular path and is the unit vector pointing in the radial direction outwards from the center. This means that the unbalanced centripetal force felt by any object is always directed toward the center of the curving path. Such forces act perpendicular to the velocity vector associated with the motion of an object, and therefore do not change the speed of the object (magnitude of the velocity), but only the direction of the velocity vector. The unbalanced force that accelerates an object can be resolved into a component that is perpendicular to the path, and one that is tangential to the path. This yields both the tangential force, which accelerates the object by either slowing it down or speeding it up, and the radial (centripetal) force, which changes its direction.
Kinematic integrals
Forces can be used to define a number of physical concepts by integrating with respect to kinematic variables. For example, integrating with respect to time gives the definition of impulse:
Similarly, integrating with respect to position gives a definition for the work done by a force:
which is equivalent to changes in kinetic energy (yielding the work energy theorem).
Power P is the rate of change dW/dt of the work W, as the trajectory is extended by a position change in a time interval dt:
Potential energy
Instead of a force, often the mathematically related concept of a potential energy field can be used for convenience. For instance, the gravitational force acting upon an object can be seen as the action of the gravitational field that is present at the object's location. Restating mathematically the definition of energy (via the definition of work), a potential scalar field is defined as that field whose gradient is equal and opposite to the force produced at every point:
Forces can be classified as conservative or nonconservative. Conservative forces are equivalent to the gradient of a potential while nonconservative forces are not.
Conservative forces
A conservative force that acts on a closed system has an associated mechanical work that allows energy to convert only between kinetic or potential forms. This means that for a closed system, the net mechanical energy is conserved whenever a conservative force acts on the system. The force, therefore, is related directly to the difference in potential energy between two different locations in space, and can be considered to be an artifact of the potential field in the same way that the direction and amount of a flow of water can be considered to be an artifact of the contour map of the elevation of an area.
Conservative forces include gravity, the electromagnetic force, and the spring force. Each of these forces has models that are dependent on a position often given as a radial vector emanating from spherically symmetric potentials. Examples of this follow:
For gravity:
For electrostatic forces:
where is electric permittivity of free space, and is the electric charge of object n.For spring forces:
Nonconservative forces
For certain physical scenarios, it is impossible to model forces as being due to gradient of potentials. This is often due to macrophysical considerations that yield forces as arising from a macroscopic statistical average of microstates. For example, friction is caused by the gradients of numerous electrostatic potentials between the atoms, but manifests as a force model that is independent of any macroscale position vector. Nonconservative forces other than friction include other contact forces, tension, compression, and drag. However, for any sufficiently detailed description, all these forces are the results of conservative ones since each of these macroscopic forces are the net results of the gradients of microscopic potentials.
The connection between macroscopic nonconservative forces and microscopic conservative forces is described by detailed treatment with statistical mechanics. In macroscopic closed systems, nonconservative forces act to change the internal energies of the system, and are often associated with the transfer of heat. According to the Second law of thermodynamics, nonconservative forces necessarily result in energy transformations within closed systems from ordered to more random conditions as entropy increases.
Units of measurement
The SI unit of force is the newton (symbol N), which is the force required to accelerate a one kilogram mass at a rate of one meter per second squared, or kg·m·s−2. The corresponding CGS unit is the dyne, the force required to accelerate a one gram mass by one centimeter per second squared, or g·cm·s−2. A newton is thus equal to 100,000 dynes.
The gravitational foot-pound-second English unit of force is the pound-force (lbf), defined as the force exerted by gravity on a pound-mass in the standard gravitational field of 9.80665 m·s−2. The pound-force provides an alternative unit of mass: one slug is the mass that will accelerate by one foot per second squared when acted on by one pound-force.
An alternative unit of force in a different foot-pound-second system, the absolute fps system, is the poundal, defined as the force required to accelerate a one-pound mass at a rate of one foot per second squared. The units of slug and poundal are designed to avoid a constant of proportionality in Newton's Second Law.
The pound-force has a metric counterpart, less commonly used than the newton: the kilogram-force (kgf) (sometimes kilopond), is the force exerted by standard gravity on one kilogram of mass. The kilogram-force leads to an alternate, but rarely used unit of mass: the metric slug (sometimes mug or hyl) is that mass that accelerates at 1 m·s−2 when subjected to a force of 1 kgf. The kilogram-force is not a part of the modern SI system, and is generally deprecated; however it still sees use for some purposes as expressing aircraft weight, jet thrust, bicycle spoke tension, torque wrench settings and engine output torque. Other arcane units of force include the sthène, which is equivalent to 1000 N, and the kip, which is equivalent to 1000 lbf.
| newton (SI unit) |
dyne | kilogram-force, kilopond |
pound-force | poundal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 N | ≡ 1 kg⋅m/s2 | = 105 dyn | ≈ 0.10197 kp | ≈ 0.22481 lbf | ≈ 7.2330 pdl |
| 1 dyn | = 10–5 N | ≡ 1 g⋅cm/s2 | ≈ 1.0197×10−6 kp | ≈ 2.2481×10−6 lbf | ≈ 7.2330×10−5 pdl |
| 1 kp | = 9.80665 N | = 980665 dyn | ≡ gn × 1 kg | ≈ 2.2046 lbf | ≈ 70.932 pdl |
| 1 lbf | ≈ 4.448222 N | ≈ 444822 dyn | ≈ 0.45359 kp | ≡ gn × 1 lb | ≈ 32.174 pdl |
| 1 pdl | ≈ 0.138255 N | ≈ 13825 dyn | ≈ 0.014098 kp | ≈ 0.031081 lbf | ≡ 1 lb⋅ft/s2 |
| The value of gn as used in the official definition of the kilogram-force is used here for all gravitational units. | |||||
See also Ton-force.
Force measurement
See force gauge, spring scale, load cell