| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Added PV capacity by country in 2019 (by percent of world total, clustered by region)
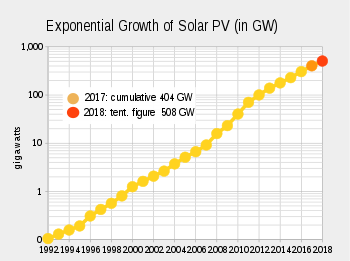
Worldwide growth of photovoltaics has been close to exponential between 1992 and 2018. During this period of time, photovoltaics (PV), also known as solar PV, evolved from a niche market of small-scale applications to a mainstream electricity source.
When solar PV systems were first recognized as a promising renewable energy technology, subsidy programs, such as feed-in tariffs, were implemented by a number of governments in order to provide economic incentives for investments. For several years, growth was mainly driven by Japan and pioneering European countries. As a consequence, cost of solar declined significantly due to experience curve effects like improvements in technology and economies of scale. Several national programs were instrumental in increasing PV deployment, such as the Energiewende in Germany, the Million Solar Roofs project in the United States, and China's 2011 five-year-plan for energy production. Since then, deployment of photovoltaics has gained momentum on a worldwide scale, increasingly competing with conventional energy sources. In the early 21st century a market for utility-scale plants emerged to complement rooftop and other distributed applications. By 2015, some 30 countries had reached grid parity.
Since the 1950s, when the first solar cells were commercially manufactured, there has been a succession of countries leading the world as the largest producer of electricity from solar photovoltaics. First it was the United States, then Japan, followed by Germany, and currently China.
By the end of 2018, global cumulative installed PV capacity reached about 512 gigawatts (GW), of which about 180 GW (35%) were utility-scale plants. Solar power supplied about 3% of global electricity demand in 2019. In 2018, solar PV contributed between 7% and 8% to the annual domestic consumption in Italy, Greece, Germany, and Chile. The largest penetration of solar power in electricity production is found in Honduras (14%). Solar PV contribution to electricity in Australia is edging towards 11%, while in the United Kingdom and Spain it is close to 4%. China and India moved above the world average of 2.55%, while, in descending order, the United States, South Korea, France and South Africa are below the world's average.
Projections for photovoltaic growth are difficult and burdened with many uncertainties. Official agencies, such as the International Energy Agency (IEA) have consistently increased their estimates for decades, while still falling far short of projecting actual deployment in every forecast. Bloomberg NEF projects global solar installations to grow in 2019, adding another 125–141 GW resulting in a total capacity of 637–653 GW by the end of the year. By 2050, the IEA foresees solar PV to reach 4.7 terawatts (4,674 GW) in its high-renewable scenario, of which more than half will be deployed in China and India, making solar power the world's largest source of electricity.
Solar PV nameplate capacity
Nameplate capacity denotes the peak power output of power stations in unit watt prefixed as convenient, to e.g. kilowatt (kW), megawatt (MW) and gigawatt (GW). Because power output for variable renewable sources is unpredictable, a source's average generation is generally significantly lower than the nameplate capacity. In order to have an estimate of the average power output, the capacity can be multiplied by a suitable capacity factor, which takes into account varying conditions - weather, nighttime, latitude, maintenance. Worldwide, the average solar PV capacity factor is 11%. In addition, depending on context, the stated peak power may be prior to a subsequent conversion to alternating current, e.g. for a single photovoltaic panel, or include this conversion and its loss for a grid connected photovoltaic power station.
Wind power has different characteristics, e.g. a higher capacity factor and about four times the 2015 electricity production of solar power. Compared with wind power, photovoltaic power production correlates well with power consumption for air-conditioning in warm countries. As of 2017 a handful of utilities have started combining PV installations with battery banks, thus obtaining several hours of dispatchable generation to help mitigate problems associated with the duck curve after sunset.
Current status
Worldwide
In 2017, photovoltaic capacity increased by 95 GW, with a 29% growth year-on-year of new installations. Cumulative installed capacity exceeded 401 GW by the end of the year, sufficient to supply 2.1 percent of the world's total electricity consumption.
Regions
As of 2018, Asia was the fastest growing region, with almost 75% of global installations. China alone accounted for more than half of worldwide deployment in 2017. In terms of cumulative capacity, Asia was the most developed region with more than half of the global total of 401 GW in 2017. Europe continued to decline as a percentage of the global PV market. In 2017, Europe represented 28% of global capacity, the Americas 19% and Middle East 2%. However with respect to per capita installation the European Union has more than twice the capacity compared to China and 25% more than the US.
Solar PV covered 3.5% and 7% of European electricity demand and peak electricity demand, respectively in 2014.
Countries and territories
Worldwide growth of photovoltaics is extremely dynamic and varies strongly by country. The top installers of 2019 were China, the United States, and India. There are 37 countries around the world with a cumulative PV capacity of more than one gigawatt. The available solar PV capacity in Honduras is sufficient to supply 14.8% of the nation's electrical power while 8 countries can produce between 7% and 9% of their respective domestic electricity consumption.
History of leading countries
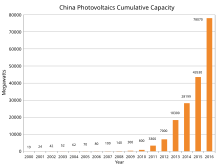
The United States was the leader of installed photovoltaics for many years, and its total capacity was 77 megawatts in 1996, more than any other country in the world at the time. From the late 1990s, Japan was the world's leader of solar electricity production until 2005, when Germany took the lead and by 2016 had a capacity of over 40 gigawatts. In 2015, China surpassed Germany to become the world's largest producer of photovoltaic power, and in 2017 became the first country to surpass 100 GW of installed capacity.
United States (1954–1996)
The United States, where modern solar PV was invented, led installed capacity for many years. Based on preceding work by Swedish and German engineers, the American engineer Russell Ohl at Bell Labs patented the first modern solar cell in 1946. It was also there at Bell Labs where the first practical c-silicon cell was developed in 1954. Hoffman Electronics, the leading manufacturer of silicon solar cells in the 1950s and 1960s, improved on the cell's efficiency, produced solar radios, and equipped Vanguard I, the first solar powered satellite launched into orbit in 1958.
In 1977 US-President Jimmy Carter installed solar hot water panels on the White House (later removed by President Reagan) promoting solar energy and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, originally named Solar Energy Research Institute was established at Golden, Colorado. In the 1980s and early 1990s, most photovoltaic modules were used in stand-alone power systems or powered consumer products such as watches, calculators and toys, but from around 1995, industry efforts have focused increasingly on developing grid-connected rooftop PV systems and power stations. By 1996, solar PV capacity in the US amounted to 77 megawatts–more than any other country in the world at the time. Then, Japan moved ahead.
Japan (1997–2004)
Japan took the lead as the world's largest producer of PV electricity, after the city of Kobe was hit by the Great Hanshin earthquake in 1995. Kobe experienced severe power outages in the aftermath of the earthquake, and PV systems were then considered as a temporary supplier of power during such events, as the disruption of the electric grid paralyzed the entire infrastructure, including gas stations that depended on electricity to pump gasoline. Moreover, in December of that same year, an accident occurred at the multibillion-dollar experimental Monju Nuclear Power Plant. A sodium leak caused a major fire and forced a shutdown (classified as INES 1). There was massive public outrage when it was revealed that the semigovernmental agency in charge of Monju had tried to cover up the extent of the accident and resulting damage. Japan remained world leader in photovoltaics until 2004, when its capacity amounted to 1,132 megawatts. Then, focus on PV deployment shifted to Europe.
Germany (2005–2014)
In 2005, Germany took the lead from Japan. With the introduction of the Renewable Energy Act in 2000, feed-in tariffs were adopted as a policy mechanism. This policy established that renewables have priority on the grid, and that a fixed price must be paid for the produced electricity over a 20-year period, providing a guaranteed return on investment irrespective of actual market prices. As a consequence, a high level of investment security lead to a soaring number of new photovoltaic installations that peaked in 2011, while investment costs in renewable technologies were brought down considerably. In 2016 Germany's installed PV capacity was over the 40 GW mark.
China (2015–present)
China surpassed Germany's capacity by the end of 2015, becoming the world's largest producer of photovoltaic power. China's rapid PV growth continued in 2016 – with 34.2 GW of solar photovoltaics installed. The quickly lowering feed in tariff rates at the end of 2015 motivated many developers to secure tariff rates before mid-year 2016 – as they were anticipating further cuts (correctly so). During the course of the year, China announced its goal of installing 100 GW during the next Chinese Five Year Economic Plan (2016–2020). China expected to spend ¥1 trillion ($145B) on solar construction during that period. Much of China's PV capacity was built in the relatively less populated west of the country whereas the main centres of power consumption were in the east (such as Shanghai and Beijing). Due to lack of adequate power transmission lines to carry the power from the solar power plants, China had to curtail its PV generated power.
History of market development
Prices and costs (1977–present)
| Type of cell or module | Price per Watt |
|---|---|
| Multi-Si Cell (≥18.6%) | $0.071 |
| Mono-Si Cell (≥20.0%) | $0.090 |
| G1 Mono-Si Cell (>21.7%) | $0.099 |
| M6 Mono-Si Cell (>21.7%) | $0.100 |
| 275W - 280W (60P) Module | $0.176 |
| 325W - 330W (72P) Module | $0.188 |
| 305W - 310W Module | $0.240 |
| 315W - 320W Module | $0.190 |
| >325W - >385W Module | $0.200 |
| Source: EnergyTrend, price quotes, average prices, 13 July 2020 | |
The average price per watt dropped drastically for solar cells in the decades leading up to 2017. While in 1977 prices for crystalline silicon cells were about $77 per watt, average spot prices in August 2018 were as low as $0.13 per watt or nearly 600 times less than forty years ago. Prices for thin-film solar cells and for c-Si solar panels were around $.60 per watt. Module and cell prices declined even further after 2014 (see price quotes in table).
This price trend was seen as evidence supporting Swanson's law (an observation similar to the famous Moore's Law) that states that the per-watt cost of solar cells and panels fall by 20 percent for every doubling of cumulative photovoltaic production. A 2015 study showed price/kWh dropping by 10% per year since 1980, and predicted that solar could contribute 20% of total electricity consumption by 2030.
In its 2014 edition of the Technology Roadmap: Solar Photovoltaic Energy report, the International Energy Agency (IEA) published prices for residential, commercial and utility-scale PV systems for eight major markets as of 2013 (see table below). However, DOE's SunShot Initiative report states lower prices than the IEA report, although both reports were published at the same time and referred to the same period. After 2014 prices fell further. For 2014, the SunShot Initiative modeled U.S. system prices to be in the range of $1.80 to $3.29 per watt. Other sources identified similar price ranges of $1.70 to $3.50 for the different market segments in the U.S. In the highly penetrated German market, prices for residential and small commercial rooftop systems of up to 100 kW declined to $1.36 per watt (€1.24/W) by the end of 2014. In 2015, Deutsche Bank estimated costs for small residential rooftop systems in the U.S. around $2.90 per watt. Costs for utility-scale systems in China and India were estimated as low as $1.00 per watt.
| USD/W | Australia | China | France | Germany | Italy | Japan | United Kingdom | United States |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residential | 1.8 | 1.5 | 4.1 | 2.4 | 2.8 | 4.2 | 2.8 | 4.91 |
| Commercial | 1.7 | 1.4 | 2.7 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 3.6 | 2.4 | 4.51 |
| Utility-scale | 2.0 | 1.4 | 2.2 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 2.9 | 1.9 | 3.31 |
| Source: IEA – Technology Roadmap: Solar Photovoltaic Energy report, September 2014' 1U.S figures are lower in DOE's Photovoltaic System Pricing Trends | ||||||||
According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, a "sustained, dramatic decline" in utility-scale solar PV electricity cost driven by lower solar PV module and system costs continued in 2018, with global weighted average levelized cost of energy of solar PV falling to US$0.085 per kilowatt-hour, or 13% lower than projects commissioned the previous year, resulting in a decline from 2010 to 2018 of 77%.
Technologies (1990–present)
There were significant advances in conventional crystalline silicon (c-Si) technology in the years leading up to 2017. The falling cost of the polysilicon since 2009, that followed after a period of severe shortage (see below) of silicon feedstock, pressure increased on manufacturers of commercial thin-film PV technologies, including amorphous thin-film silicon (a-Si), cadmium telluride (CdTe), and copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS), led to the bankruptcy of several thin-film companies that had once been highly touted. The sector faced price competition from Chinese crystalline silicon cell and module manufacturers, and some companies together with their patents were sold below cost.
In 2013 thin-film technologies accounted for about 9 percent of worldwide deployment, while 91 percent was held by crystalline silicon (mono-Si and multi-Si). With 5 percent of the overall market, CdTe held more than half of the thin-film market, leaving 2 percent to each CIGS and amorphous silicon.
- Copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) is the name of the semiconductor material on which the technology is based. One of the largest producers of CIGS photovoltaics in 2015 was the Japanese company Solar Frontier with a manufacturing capacity in the gigawatt-scale. Their CIS line technology included modules with conversion efficiencies of over 15%. The company profited from the booming Japanese market and attempted to expand its international business. However, several prominent manufacturers could not keep up with the advances in conventional crystalline silicon technology. The company Solyndra ceased all business activity and filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in 2011, and Nanosolar, also a CIGS manufacturer, closed its doors in 2013. Although both companies produced CIGS solar cells, it has been pointed out, that the failure was not due to the technology but rather because of the companies themselves, using a flawed architecture, such as, for example, Solyndra's cylindrical substrates.
- The U.S.-company First Solar, a leading manufacturer of CdTe, built several of the world's largest solar power stations, such as the Desert Sunlight Solar Farm and Topaz Solar Farm, both in the Californian desert with 550 MW capacity each, as well as the 102 MWAC Nyngan Solar Plant in Australia (the largest PV power station in the Southern Hemisphere at the time) commissioned in mid-2015. The company was reported in 2013 to be successfully producing CdTe-panels with a steadily increasing efficiency and declining cost per watt. CdTe was the lowest energy payback time of all mass-produced PV technologies, and could be as short as eight months in favorable locations. The company Abound Solar, also a manufacturer of cadmium telluride modules, went bankrupt in 2012.
- In 2012, ECD solar, once one of the world's leading manufacturer of amorphous silicon (a-Si) technology, filed for bankruptcy in Michigan, United States. Swiss OC Oerlikon divested its solar division that produced a-Si/μc-Si tandem cells to Tokyo Electron Limited. Other companies that left the amorphous silicon thin-film market include DuPont, BP, Flexcell, Inventux, Pramac, Schuco, Sencera, EPV Solar, NovaSolar (formerly OptiSolar) and Suntech Power that stopped manufacturing a-Si modules in 2010 to focus on crystalline silicon solar panels. In 2013, Suntech filed for bankruptcy in China.
Silicon shortage (2005–2008)
In the early 2000s, prices for polysilicon, the raw material for conventional solar cells, were as low as $30 per kilogram and silicon manufacturers had no incentive to expand production.
However, there was a severe silicon shortage in 2005, when governmental programmes caused a 75% increase in the deployment of solar PV in Europe. In addition, the demand for silicon from semiconductor manufacturers was growing. Since the amount of silicon needed for semiconductors makes up a much smaller portion of production costs, semiconductor manufacturers were able to outbid solar companies for the available silicon in the market.
Initially, the incumbent polysilicon producers were slow to respond to rising demand for solar applications, because of their painful experience with over-investment in the past. Silicon prices sharply rose to about $80 per kilogram, and reached as much as $400/kg for long-term contracts and spot prices. In 2007, the constraints on silicon became so severe that the solar industry was forced to idle about a quarter of its cell and module manufacturing capacity—an estimated 777 MW of the then available production capacity. The shortage also provided silicon specialists with both the cash and an incentive to develop new technologies and several new producers entered the market. Early responses from the solar industry focused on improvements in the recycling of silicon. When this potential was exhausted, companies have been taking a harder look at alternatives to the conventional Siemens process.
As it takes about three years to build a new polysilicon plant, the shortage continued until 2008. Prices for conventional solar cells remained constant or even rose slightly during the period of silicon shortage from 2005 to 2008. This is notably seen as a "shoulder" that sticks out in the Swanson's PV-learning curve and it was feared that a prolonged shortage could delay solar power becoming competitive with conventional energy prices without subsidies.
In the meantime the solar industry lowered the number of grams-per-watt by reducing wafer thickness and kerf loss, increasing yields in each manufacturing step, reducing module loss, and raising panel efficiency. Finally, the ramp up of polysilicon production alleviated worldwide markets from the scarcity of silicon in 2009 and subsequently lead to an overcapacity with sharply declining prices in the photovoltaic industry for the following years.
Solar overcapacity (2009–2013)
As the polysilicon industry had started to build additional large production capacities during the shortage period, prices dropped as low as $15 per kilogram forcing some producers to suspend production or exit the sector. Prices for silicon stabilized around $20 per kilogram and the booming solar PV market helped to reduce the enormous global overcapacity from 2009 onwards. However, overcapacity in the PV industry continued to persist. In 2013, global record deployment of 38 GW (updated EPIA figure) was still much lower than China's annual production capacity of approximately 60 GW. Continued overcapacity was further reduced by significantly lowering solar module prices and, as a consequence, many manufacturers could no longer cover costs or remain competitive. As worldwide growth of PV deployment continued, the gap between overcapacity and global demand was expected in 2014 to close in the next few years.
IEA-PVPS published in 2014 historical data for the worldwide utilization of solar PV module production capacity that showed a slow return to normalization in manufacture in the years leading up to 2014. The utilization rate is the ratio of production capacities versus actual production output for a given year. A low of 49% was reached in 2007 and reflected the peak of the silicon shortage that idled a significant share of the module production capacity. As of 2013, the utilization rate had recovered somewhat and increased to 63%.
Anti-dumping duties (2012–present)
After anti-dumping petition were filed and investigations carried out, the United States imposed tariffs of 31 percent to 250 percent on solar products imported from China in 2012. A year later, the EU also imposed definitive anti-dumping and anti-subsidy measures on imports of solar panels from China at an average of 47.7 percent for a two-year time span.
Shortly thereafter, China, in turn, levied duties on U.S. polysilicon imports, the feedstock for the production of solar cells. In January 2014, the Chinese Ministry of Commerce set its anti-dumping tariff on U.S. polysilicon producers, such as Hemlock Semiconductor Corporation to 57%, while other major polysilicon producing companies, such as German Wacker Chemie and Korean OCI were much less affected. All this has caused much controversy between proponents and opponents and was subject of debate.
History of deployment
Deployment figures on a global, regional and nationwide scale are well documented since the early 1990s. While worldwide photovoltaic capacity grew continuously, deployment figures by country were much more dynamic, as they depended strongly on national policies. A number of organizations release comprehensive reports on PV deployment on a yearly basis. They include annual and cumulative deployed PV capacity, typically given in watt-peak, a break-down by markets, as well as in-depth analysis and forecasts about future trends.
| Year(a) | Name of PV power station | Country | Capacity MW |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1982 | Lugo | United States | 1 |
| 1985 | Carrisa Plain | United States | 5.6 |
| 2005 | Bavaria Solarpark (Mühlhausen) | Germany | 6.3 |
| 2006 | Erlasee Solar Park | Germany | 11.4 |
| 2008 | Olmedilla Photovoltaic Park | Spain | 60 |
| 2010 | Sarnia Photovoltaic Power Plant | Canada | 97 |
| 2011 | Huanghe Hydropower Golmud Solar Park | China | 200 |
| 2012 | Agua Caliente Solar Project | United States | 290 |
| 2014 | Topaz Solar Farm(b) | United States | 550 |
| 2015 | Longyangxia Dam Solar Park | China | 850 |
| 2016 | Tengger Desert Solar Park | China | 1547 |
| 2019 | Pavagada Solar Park | India | 2050 |
| 2020 | Bhadla Solar Park | India | 2245 |
| Also see list of photovoltaic power stations and list of noteworthy solar parks (a) year of final commissioning (b) capacity given in MWAC otherwise in MWDC | |||
Worldwide annual deployment
Due to the exponential nature of PV deployment, most of the overall capacity has been installed in the years leading up to 2017 (see pie-chart). Since the 1990s, each year has been a record-breaking year in terms of newly installed PV capacity, except for 2012. Contrary to some earlier predictions, early 2017 forecasts were that 85 gigawatts would be installed in 2017. Near end-of-year figures however raised estimates to 95 GW for 2017-installations.
Worldwide cumulative
Worldwide growth of solar PV capacity was an exponential curve between 1992 and 2017. Tables below show global cumulative nominal capacity by the end of each year in megawatts, and the year-to-year increase in percent. In 2014, global capacity was expected to grow by 33 percent from 139 to 185 GW. This corresponded to an exponential growth rate of 29 percent or about 2.4 years for current worldwide PV capacity to double. Exponential growth rate: P(t) = P0ert, where P0 is 139 GW, growth-rate r 0.29 (results in doubling time t of 2.4 years).
Deployment by country
- See section Forecast for projected photovoltaic deployment in 2017
Reached grid-parity before 2014
Reached grid-parity after 2014
Reached grid-parity only for peak prices
U.S. states poised to reach grid-parity
Source: Deutsche Bank, as of February 2015