| Thirty Years' War | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the European wars of religion | |||||||||
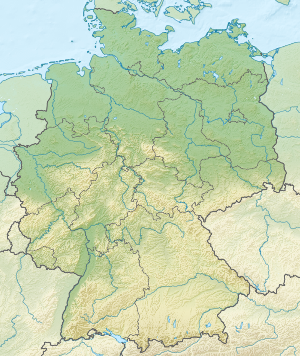
 The Holy Roman Empire in 1600, against modern borders | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
| Anti-Imperial alliance: prior to 1635 | Imperial alliance prior to 1635 | ||||||||
| Post-1635 Peace of Prague | Post-1635 Peace of Prague | ||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
| ||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
|
Maximum Actual
|
Maximum Actual
| ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
|
Combat deaths: 110,000 in Swedish service 80,000 in French service 30,000 in Danish service 50,000 other |
Combat deaths 120,000 in Imperial service 30,000 in Bavarian service 30,000 other | ||||||||
|
Military deaths from disease: 700,000–1,350,000 Total civilian dead: 3,500,000–6,500,000 Total dead: 4,500,000–8,000,000 | |||||||||
The Thirty Years' War was a conflict fought largely within the Holy Roman Empire from 1618 to 1648. Considered one of the most destructive wars in European history, estimates of total deaths caused by the conflict range from 4.5 to 8 million, while some areas of Germany experienced population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War, and the Portuguese Restoration War
Until the 20th century, historians considered it a continuation of the German religious struggle initiated by the Reformation and ended by the 1555 Peace of Augsburg. This divided the Empire into Lutheran and Catholic states, but over the next 50 years the expansion of Protestantism beyond these boundaries gradually destabilised Imperial authority. While religion was a significant factor in starting the war that followed, it is generally agreed that its scope and extent was driven by the contest for European dominance between Habsburgs in Austria and Spain, and the French House of Bourbon.
The war began in 1618 when Ferdinand II was deposed as King of Bohemia and replaced by Frederick V of the Palatinate. Although the Bohemian Revolt was quickly suppressed, fighting expanded into the Palatinate, whose strategic importance drew in the Dutch Republic and Spain, then engaged in the Eighty Years War. Since ambitious external rulers like Christian IV of Denmark and Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden also held territories within the Empire, what began as an internal dynastic dispute was transformed into a far more destructive European conflict.
The first phase from 1618 until 1635 was primarily a civil war between German members of the Holy Roman Empire, with external powers playing supportive roles. After 1635, the Empire became one theatre in a wider struggle between France, supported by Sweden, and Spain in alliance with Emperor Ferdinand III. This concluded with the 1648 Peace of Westphalia, whose provisions included greater autonomy within the Empire for states like Bavaria and Saxony, as well as acceptance of Dutch independence by Spain. By weakening the Habsburgs relative to France, the conflict altered the European balance of power and set the stage for the wars of Louis XIV.
Structural origins
The 1552 Peace of Passau ended the Schmalkaldic War between Protestants and Catholics in the Holy Roman Empire, while the 1555 Peace of Augsburg tried to prevent future conflict by fixing existing boundaries. Under the principle of cuius regio, eius religio, states were either Lutheran, then the most usual form of Protestantism, or Catholic, based on the religion of their ruler. Other provisions protected substantial religious minorities in cities like Donauwörth and confirmed Lutheran ownership of property taken from the Catholic Church since Passau.
The agreement was undermined by the expansion of Protestantism beyond its 1555 boundaries, into areas previously dominated by Catholicism. An additional source of conflict was the growth of Reformed faiths not recognised by Augsburg, especially Calvinism, a theology viewed with hostility by both Lutherans and Catholics. Finally, religion was increasingly superseded by economic and political objectives; Lutheran Saxony, Denmark-Norway and Sweden competed with each other and Calvinist Brandenburg over the Baltic trade.
Managing these issues was complicated by the fragmented nature of the Empire, which had nearly 1,800 separate entities distributed across Germany, the Low Countries, Northern Italy, as well as Alsace and Franche-Comté in modern France. They ranged in size and importance from the seven Prince-electors who voted for the Holy Roman Emperor, down to Prince-bishoprics and Imperial cities like Hamburg. Each member belonged to a regional assembly or Circle, which focused on defence and taxes and often operated as autonomous bodies. Above these structures was the Imperial Diet, which prior to 1663 assembled on an irregular basis, and served primarily as a forum for discussion, rather than legislation.
Although Emperors were elected, since 1440 the position had been held by a member of the Habsburg family. The largest single landowner within the Empire, they controlled territories containing over eight million subjects, including the Archduchy of Austria, Bohemia and Hungary. The Habsburg emperors also ruled Spain until 1556, when it became a separate entity; Spain retained Imperial interests, including the Duchy of Milan, and while the two branches of the family often co-operated, their objectives did not always align. The Spanish Empire was a global maritime superpower whose possessions included the Spanish Netherlands, Milan, the Kingdom of Naples, the Philippines, and most of the Americas. Austria was a land-based power, whose strategic focus was securing a pre-eminent position in Germany and their eastern border against the Ottoman Empire.
Before Augsburg, unity of religion compensated for lack of strong central authority; once removed, it presented opportunities for those who sought to further weaken it. These included ambitious Imperial states like Lutheran Saxony and Catholic Bavaria, as well as France, confronted by Habsburg lands on its borders to the North, South, and along the Pyrenees. A further complication was that many foreign rulers were also Imperial princes, involving them in its internal disputes; Christian IV of Denmark joined the war in 1625 as Duke of Holstein.
Background: 1556 to 1618
Disputes occasionally resulted in full-scale conflict like the 1583 to 1588 Cologne War, caused when its ruler converted to Calvinism. More common were events such as the 1606 'Battle of the Flags' in Donauwörth, when riots broke out after the Lutheran majority blocked a Catholic religious procession. Emperor Rudolf approved intervention by the Catholic Maximilian of Bavaria. In return, he was allowed to annex the town and as agreed at Augsburg, the official religion changed from Lutheran to Catholic.
When the Imperial Diet opened in February 1608, both Lutherans and Calvinists united to demand formal re-confirmation of the Augsburg settlement. However, in return the Habsburg heir Archduke Ferdinand required the immediate restoration of all property taken from the Catholic church since 1555, rather than the previous practice whereby court ruling case by case. This threatened all Protestants, paralysed the Diet, and removed the perception of Imperial neutrality.
Loss of faith in central authority meant towns and rulers began strengthening their fortifications and armies; outside travellers often commented on the growing militarisation of Germany in this period. This was taken a stage further in 1608 when Frederick IV, Elector Palatine formed the Protestant Union and Maximilian responded by setting up the Catholic League in July 1609. Both Leagues were primarily designed to support the dynastic ambitions of their leaders, but their creation combined with the 1609 to 1614 War of the Jülich Succession to increase tensions throughout the Empire. Some historians who see the war as primarily a European conflict argue Jülich marks its beginning, with Spain and Austria backing the Catholic candidate, France and the Dutch Republic the Protestant.
External powers became involved in what was an internal German dispute due to the imminent expiry of the 1609 Twelve Years' Truce, which suspended the Eighty Years War between Spain and the Dutch Republic. Before restarting hostilities, Ambrosio Spinola, commander in the Spanish Netherlands, needed to secure the Spanish Road, an overland route connecting Habsburg possessions in Italy to Flanders. This allowed him to move troops and supplies by road, rather than sea where the Dutch navy was dominant; by 1618, the only part not controlled by Spain ran through the Electoral Palatinate.
Since Emperor Matthias had no surviving children, in July 1617 Philip III of Spain agreed to support Ferdinand's election as king of Bohemia and Hungary. In return, Ferdinand made concessions to Spain in Northern Italy and Alsace, and agreed to support their offensive against the Dutch. Delivering these commitments required his election as Emperor, which was not guaranteed; one alternative was Maximilian of Bavaria, who opposed the increase of Spanish influence in an area he considered his own, and tried to create a coalition with Saxony and the Palatinate to support his candidacy.
A third candidate was the Calvinist Frederick V, Elector Palatine, who succeeded his father in 1610, then in 1613 married Elizabeth Stuart, daughter of James I of England. Four of the electors were Catholic, three Protestant; if this could be changed, it might result in a Protestant Emperor. When Ferdinand was elected king of Bohemia in 1617, he gained control of its electoral vote; however, his conservative Catholicism made him unpopular with the largely Protestant nobility, who were also concerned at the erosion of their rights. In May 1618, these factors combined to bring about the Bohemian Revolt.
Phase I: 1618 to 1635
The Bohemian Revolt
The Jesuit educated Ferdinand once claimed he would rather see his lands destroyed than tolerate heresy for a single day. Appointed to rule the Duchy of Styria in 1595, within eighteen months he eliminated Protestantism in what was previously a stronghold of the Reformation. Focused on retaking the Netherlands, the Spanish Habsburgs preferred to avoid antagonising Protestants elsewhere, and recognised the dangers associated with Ferdinand's fervent Catholicism, but accepted the lack of alternatives.
Ferdinand reconfirmed Protestant religious freedoms when elected king of Bohemia in May 1617, but his record in Styria led to the suspicion he was only awaiting a chance to overturn them. These concerns were exacerbated when a series of legal disputes over property were all decided in favour of the Catholic Church. In May 1618, Protestant nobles led by Count Thurn met in Prague Castle with Ferdinand's two Catholic representatives, Vilem Slavata and Jaroslav Borzita. In what became known as the Third Defenestration of Prague, the two men and their secretary Philip Fabricius were thrown out of the castle windows, although all three survived.
Thurn established a Protestant-dominated government in Bohemia, while unrest expanded into Silesia and the Habsburg heartlands of Lower and Upper Austria, where much of the nobility was also Protestant. Losing control of these threatened the entire Habsburg state, while Bohemia was one of the most prosperous areas of the Empire and its electoral vote crucial to ensuring Ferdinand succeeded Matthias as Emperor. The combination meant their recapture was vital for the Austrian Habsburgs but chronic financial weakness left them dependent on Maximilian and Spain for the resources needed to achieve this.
Spanish involvement inevitably drew in the Dutch, and potentially France, although the strongly Catholic Louis XIII faced his own Protestant rebels at home and refused to support them elsewhere. The revolt also provided opportunities for external opponents of the Habsburgs, including the Ottoman Empire and Savoy. Funded by Frederick and the Duke of Savoy, a mercenary army under Ernst von Mansfeld was sent to support the Bohemian rebels. Attempts by Maximilian and John George of Saxony to broker a negotiated solution ended when Matthias died in March 1619, since many believed the loss of his authority and influence had fatally damaged the Habsburgs.
By mid-June 1619, the Bohemian army under Thurn was outside Vienna and although Mansfeld's defeat by Imperial forces at Sablat forced him to return to Prague, Ferdinand's position continued to worsen. Gabriel Bethlen, Calvinist Prince of Transylvania, invaded Hungary with Ottoman support, although the Habsburgs persuaded them to avoid direct involvement; this was helped when the Ottomans became involved in the 1620 Polish war, followed by the 1623 to 1639 conflict with Persia.
On 19 August, the Bohemian Estates rescinded Ferdinand's 1617 election as king, and formally offered the crown to Frederick on 26th; two days later, Ferdinand was elected Emperor, making war inevitable if Frederick accepted. With the exception of Christian of Anhalt, his advisors urged him to reject it, as did the Dutch, the Duke of Savoy, and his father-in-law James. 17th century Europe was a highly structured and socially conservative society, and their lack of enthusiasm was due to the implications of removing a legally elected ruler, regardless of religion.
As a result, although Frederick accepted the crown and entered Prague in October 1619, his support gradually eroded over the next few months. In July 1620, the Protestant Union proclaimed its neutrality, while John George of Saxony agreed to back Ferdinand in return for Lusatia, and a promise to safeguard the rights of Lutherans in Bohemia. A combined Imperial-Catholic League army funded by Maximilian and led by Count Tilly pacified Upper and Lower Austria before invading Bohemia, where they defeated Christian of Anhalt at the White Mountain in November 1620. Although the battle was far from decisive, the rebels were demoralised by lack of pay, shortages of supplies, and disease, while the countryside had been devastated by Imperial troops. Frederick fled Bohemia and the revolt collapsed.
The Palatinate Campaign
By abandoning Frederick, the German princes hoped to restrict the dispute to Bohemia, but Maximilian's dynastic ambitions made this impossible. In the October 1619 Treaty of Munich, Ferdinand agreed to transfer the Palatinate's electoral vote to Bavaria and allow him to annex the Upper Palatinate. Many Protestants supported Ferdinand because they objected to deposing the legally elected king of Bohemia, and now opposed Frederick's removal on the same grounds. Doing so turned the conflict into a contest between Imperial authority and "German liberties", while Catholics saw an opportunity to regain lands lost since 1555. The combination destabilised large parts of the Empire.
The strategic importance of the Palatinate and its proximity to the Spanish Road drew in external powers; in August 1620, the Spanish under Spinola and Córdoba occupied the Lower Palatinate. James I of England responded to this attack on his son-in-law by sending naval forces to threaten Spanish possessions in the Americas and the Mediterranean, and announced he would declare war if Spinola had not withdrawn his troops by spring 1621. These actions were primarily designed to placate his opponents in Parliament, who considered his pro-Spanish policy a betrayal of the Protestant cause. However, Spanish chief minister Olivares correctly interpreted them as an invitation to open negotiations, and in return for an Anglo-Spanish alliance offered to restore Frederick to his Rhineland possessions.
Since Frederick demanded full restitution of his lands and titles, which was incompatible with the Treaty of Munich, hopes of reaching a negotiated peace quickly evaporated. When the Eighty Years War restarted in April 1621, the Dutch provided Frederick military support to regain his lands, along with a mercenary army under Mansfeld paid for with English subsidies. Over the next eighteen months, Spanish and Catholic League forces won a series of victories; by November 1622, they controlled most of the Palatinate, apart from Frankenthal, held by a small English garrison under Sir Horace Vere. The remnants of Mansfeld's army took refuge in the Dutch Republic, as did Frederick; he spent most of his time in The Hague, until his death in November 1632.
At a meeting of the Imperial Diet in February 1623, Ferdinand forced through provisions transferring Frederick's titles, lands, and electoral vote to Maximilian. He did so with support from the Catholic League, despite strong opposition from Protestant members, as well as the Spanish. The Palatinate was clearly lost; in March, James instructed Vere to surrender Frankenthal, while Tilly's victory over Christian of Brunswick at Stadtlohn in August completed military operations. However, Spanish and Dutch involvement in the campaign was a significant step in internationalising the war, while Frederick's removal meant other Protestant princes began discussing armed resistance to preserve their own rights and territories.
Danish intervention (1625–1629)
With Saxony dominating the Upper Saxon Circle and Brandenburg the Lower, both kreis had remained neutral during the campaigns in Bohemia and the Palatinate. However, Frederick's deposition in 1623 meant John George of Saxony and the Calvinist George William, Elector of Brandenburg became concerned Ferdinand intended to reclaim formerly Catholic bishoprics currently held by Protestants. These fears seemed confirmed when Tilly restored the Roman Catholic Diocese of Halberstadt in early 1625.
As Duke of Holstein, Christian IV was also a member of the Lower Saxon circle, while Denmark's economy relied on the Baltic trade and tolls from traffic through the Øresund. In 1621, Hamburg accepted Danish 'supervision', while his son Frederick became joint-administrator of Lübeck, Bremen, and Verden; possession ensured Danish control of the Elbe and Weser rivers.
Ferdinand had paid Wallenstein for his support against Frederick with estates confiscated from the Bohemian rebels, and now contracted with him to conquer the north on a similar basis. In May 1625, the Lower Saxony kreis elected Christian their military commander, although not without resistance; Saxony and Brandenburg viewed Denmark and Sweden as competitors, and wanted to avoid either becoming involved in the Empire. Attempts to negotiate a peaceful solution failed as the conflict in Germany became part of the wider struggle between France and their Habsburg rivals in Spain and Austria.
In the June 1624 Treaty of Compiègne, France had agreed to subsidise the Dutch war against Spain for a minimum of three years, while in the December 1625 Treaty of The Hague, the Dutch and English agreed to finance Danish intervention in the Empire. Hoping to create a wider coalition against Ferdinand, the Dutch invited France, Sweden, Savoy, and the Republic of Venice to join, but it was overtaken by events. In early 1626, Cardinal Richelieu, main architect of the alliance, faced a new Huguenot rebellion at home and in the March Treaty of Monzón, France withdrew from Northern Italy, re-opening the Spanish Road.
However, the Dutch and English subsidies enabled Christian to devise an ambitious three part campaign plan; while he led the main force down the Weser, Mansfeld would attack Wallenstein in Magdeburg, supported by forces led by Christian of Brunswick and Maurice of Hesse-Kassel. The advance quickly fell apart; Mansfeld was defeated at Dessau Bridge in April, and when Maurice refused to support him, Christian of Brunswick fell back on Wolfenbüttel, where he died of disease shortly after. The Danes were comprehensively beaten at Lutter in August, and Mansfeld's army dissolved following his death in November.
Many of Christian's German allies, such as Hesse-Kassel and Saxony, had little interest in replacing Imperial domination for Danish, while few of the subsidies agreed in the Treaty of the Hague were ever paid. Charles I of England allowed Christian to recruit up to 9,000 Scottish mercenaries, but they took time to arrive, and while able to slow Wallenstein's advance, were insufficient to stop him. By the end of 1627, Wallenstein occupied Mecklenburg, Pomerania, and Jutland, and began making plans to construct a fleet capable of challenging Danish control of the Baltic. He was supported by Spain, for whom it provided an opportunity to open another front against the Dutch.
In May 1628, his deputy von Arnim besieged Stralsund, the only port with large enough shipbuilding facilities, but this brought Sweden into the war. Gustavus Adolphus despatched several thousand Scots and Swedish troops under Alexander Leslie to Stralsund, who was appointed governor. Von Arnim was forced to lift the siege on 4 August, but three weeks later, Christian suffered another defeat at Wolgast. He began negotiations with Wallenstein, who despite his recent victories was concerned by the prospect of Swedish intervention, and thus anxious to make peace.
With Austrian resources stretched by the outbreak of the War of the Mantuan Succession, Wallenstein persuaded Ferdinand to agree to relatively lenient terms in the June 1629 Treaty of Lübeck. Christian retained his German possessions of Schleswig and Holstein, in return for relinquishing Bremen and Verden, and abandoning support for the German Protestants. While Denmark kept Schleswig and Holstein until 1864, this effectively ended its reign as the predominant Nordic state.
Once again, the methods used to obtain victory explain why the war failed to end. Ferdinand paid Wallenstein by letting him confiscate estates, extort ransoms from towns, and allowing his men to plunder the lands they passed through, regardless of whether they belonged to allies or opponents. Anger at such tactics and his growing power came to a head in early 1628 when Ferdinand deposed the hereditary Duke of Mecklenburg, and appointed Wallenstein in his place. Although opposition to this act united all German princes regardless of religion, Maximilian of Bavaria was compromised by his acquisition of the Palatinate; while Protestants wanted Frederick restored and the position returned to that of 1618, the Catholic League argued only for pre-1627.
Made overconfident by success, in March 1629 Ferdinand passed an Edict of Restitution, which required all lands taken from the Catholic church after 1555 to be returned. While technically legal, politically it was extremely unwise, since doing so would alter nearly every single state boundary in North and Central Germany, deny the existence of Calvinism and restore Catholicism in areas where it had not been a significant presence for nearly a century. Well aware none of the princes involved would agree, Ferdinand used the device of an Imperial edict, once again asserting his right to alter laws without consultation. This new assault on 'German liberties' ensured continuing opposition and undermined his previous success.
Swedish intervention; 1630 to 1634
Richelieu stated his policy was to "arrest the course of Spanish progress", and "protect her neighbours from Spanish oppression". With French resources tied up in Italy, he helped negotiate the September 1629 Truce of Altmark between Sweden and Poland, freeing Gustavus Adolphus to enter the war. Partly a genuine desire to support his Protestant co-religionists, like Christian he also wanted to maximise his share of the Baltic trade that provided much of Sweden's income. Using Stralsund as a bridgehead, in June 1630 nearly 18,000 Swedish troops landed in the Duchy of Pomerania. At the same time, Gustavus signed an alliance with Bogislaw XIV, Duke of Pomerania, securing his interests in Pomerania against the Catholic Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, another Baltic competitor linked to Ferdinand by family and religion. As a result, the Poles turned their attention to Russia and into the 1632 to 1634 Smolensk War.
Swedish expectations of widespread German support proved unrealistic and by the end of 1630, their only new ally was the city of Magdeburg, which was besieged by Tilly. Despite the devastation inflicted on their territories by Imperial soldiers, both Saxony and Brandenburg had their own ambitions in Pomerania, which clashed with those of Gustavus; previous experience also showed inviting external powers into the Empire was easier than getting them to leave.
Once again Richelieu used French financial power to reconcile these differences; the 1631 Treaty of Bärwalde provided funds for the Swedes and their Protestant allies, including Saxony and Brandenburg. These payments amounted to 400,000 Reichstaler, or one million livres, per year, plus an additional 120,000 Reichstalers for 1630. Though less than 2% of the total French state budget, it constituted over 25% of the Swedish budget and allowed Gustavus to support an army of 36,000. He won major victories at Breitenfeld in September 1631, then Rain in April 1632, where Tilly was killed.
After Tilly's death, Ferdinand turned once again to Wallenstein; knowing Gustavus was overextended, he marched into Franconia and established himself at Fürth, threatening Swedish supply lines. The largest battle of the war took place in late August, when an assault on the Imperial camp outside the town was bloodily repulsed, arguably the greatest blunder committed by Gustavus during his German campaign. Two months later, the Swedes and Imperialists met at Lützen, both sides suffering heavy casualties; some Swedish units incurred losses of over 60%, while Wallenstein's deputy Pappenheim and Gustavus himself were killed. Fighting continued until dusk when Wallenstein retreated, abandoning his artillery and wounded. Despite their losses, this allowed the Swedes to claim victory, although the result continues to be disputed.
Following the death of Gustavus, Swedish policy was directed by his extremely capable Chancellor Axel Oxenstierna; in April 1633, the Swedes and their German allies formed the Heilbronn League with funding provided by the French and in July their combined forces defeated an Imperial army led by the Bavarian general Bronckhorst-Gronsfeld at Oldendorf. Lützen had severely impacted Wallenstein's prestige, while his domestic opponents claimed he failed to support Bronckhorst-Gronsfeld. Combined with rumours he was preparing to switch sides, Emperor Ferdinand ordered his arrest in February 1634; on 25th, he was assassinated by his own officers in Cheb.
The loss of Wallenstein and his organisation left Emperor Ferdinand reliant on Spain for military support; since their main concern was to re-open the Spanish Road for their campaign against the Dutch, the focus now shifted to the Rhineland and Bavaria. Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand of Austria, newly appointed Governor of the Spanish Netherlands, raised an army of 18,000 in Italy, which met up with an Imperial force of 15,000 at Donauwörth on 2 September 1634. Three days later, they won a decisive victory at Nördlingen which destroyed Swedish power in Southern Germany and led to the defection of their German allies, who now sought to make peace with the Emperor.
Phase II; France joins the war 1635 to 1648
However, Nördlingen triggered direct French intervention and the war continued. As well as agreeing new Swedish subsidies, Richelieu hired mercenaries led by Bernhard of Saxe-Weimar for an offensive in the Rhineland and in May 1635 declared war on Spain, beginning the Franco-Spanish War. A few days later, Ferdinand agreed to the Peace of Prague with the German states; he withdrew the Edict while the Heilbronn and Catholic Leagues were replaced by a single Imperial army, although Saxony and Bavaria retained control of their own forces. This is generally seen as the point when the conflict ceased to be primarily a German civil war.
In March 1635, a French force entered the Valtellina, once again cutting the link between Milan and the Empire. In May, their main army of 35,000 invaded the Spanish Netherlands but was forced to retreat in July after suffering 17,000 casualties from disease and desertion. A Spanish offensive in 1636 reached Corbie in Northern France; although it caused panic in Paris, lack of supplies forced them to retreat, and it was not repeated. In the March 1636 Treaty of Wismar, France formally joined the Thirty Years War in alliance with Sweden; a Swedish army under Johan Banér entered Brandenburg and re-established their position in North-East Germany following the Battle of Wittstock on 4 October 1636.
Ferdinand II died in February 1637 and was succeeded by his son Ferdinand III, who faced a deteriorating military position. In March 1638, Bernhard destroyed an Imperial army at Rheinfelden, while his capture of Breisach in December secured French control of Alsace and severed the Spanish Road. In October, von Hatzfeldt defeated a Swedish-English-Palatine force at Vlotho but the main Imperial army under Matthias Gallas abandoned North-East Germany to the Swedes, unable to sustain itself in the devastated area. Banér defeated the Saxons at Chemnitz in April 1639, then entered Bohemia in May. Ferdinand was forced to divert Piccolomini's army from Thionville, effectively ending direct military cooperation with Spain.
Pressure grew on Spanish minister Olivares to make peace, especially after attempts to hire Polish auxiliaries proved unsuccessful. Cutting the Spanish Road had forced Madrid to resupply their armies in Flanders by sea and in October 1639 a large Spanish convoy was destroyed at the Battle of the Downs. Dutch attacks on their possessions in Africa and the Americas caused unrest in Portugal, then part of the Spanish Empire and combined with heavy taxes caused revolts in both Portugal and Catalonia. After the French captured Arras in August 1640 and overran Artois, Olivares argued it was time to accept Dutch independence and prevent further losses in Flanders. The Empire remained a formidable power but could no longer subsidise Ferdinand, impacting his ability to continue the war.
Despite the death of Bernhard, over the next two years the Franco-Swedish alliance won a series of battles in Germany, including Wolfenbüttel in June 1641 and Kempen in January 1642. At Second Breitenfeld in October 1642, Torstenson inflicted almost 10,000 casualties on an Imperial army led by Archduke Leopold Wilhelm of Austria. The Swedes captured Leipzig in December, giving them a significant new base in Germany, and although they failed to take Freiberg in February 1643, the Saxon army was reduced to a few garrisons.
While he accepted military victory was no longer possible, Ferdinand hoped to restrict peace negotiations to members of the Empire, excluding France and Sweden. Richelieu died in December 1642, followed by Louis XIII on 14 May 1643, leaving the five-year-old Louis XIV as king. His successor Cardinal Mazarin continued the same general policy, while French gains in Alsace allowed him to re-focus on the war against Spain in the Netherlands. On 19 May, Condé won a famous victory over the Spanish at Rocroi, although it was less decisive than often assumed.
By now, the devastation inflicted by 25 years of warfare meant all armies spent more time foraging than fighting. This forced them to become smaller and more mobile, with a greater emphasis on cavalry, shortened the campaigning seasons and restricted them to main supply lines. The French also had to rebuild their army in Germany after it was shattered by an Imperial-Bavarian force led by Franz von Mercy at Tuttlingen in November.
Three weeks after Rocroi, Ferdinand invited Sweden and France to attend peace negotiations in the Westphalian towns of Münster and Osnabrück, but talks were delayed when Christian of Denmark blockaded Hamburg and increased toll payments in the Baltic. This severely impacted the Dutch and Swedish economies and in December 1643 the Swedes began the Torstenson War by invading Jutland, with the Dutch providing naval support. Ferdinand pulled together an Imperial army under Gallas to attack the Swedes from the rear, which proved a disastrous decision. Leaving Wrangel to finish the war in Denmark, in May 1644 Torstenson marched into the Empire; Gallas was unable to stop him, while the Danes sued for peace after their defeat at Fehmarn in October 1644.
Ferdinand restarted peace talks in November, but his position worsened when Gallas' army disintegrated; the remnants retreated into Bohemia, where they were scattered by Torstenson at Jankau in March 1645. In May, a Bavarian force under von Mercy destroyed a French detachment at Herbsthausen, before he was defeated and killed at Second Nördlingen in August. With Ferdinand unable to help, John George of Saxony signed a six-month truce with Sweden in September, followed by the March 1646 Treaty of Eulenberg in which he agreed to remain neutral until the end of the war.
This allowed the Swedes, now led by Wrangel, to put pressure on the peace talks by devastating first Westphalia, then Bavaria; by the autumn of 1646, Maximilian was desperate to end the war he was largely responsible for starting. At this point, Olivares publicised secret discussions initiated by Mazarin in early 1646, in which he offered to exchange Catalonia for the Spanish Netherlands; angered by what they viewed as betrayal and concerned by French ambitions in Flanders, the Dutch agreed a truce with Spain in January 1647. Seeking to release French troops and prevent further Swedish gains by neutralising Bavaria, Mazarin negotiated the Truce of Ulm, signed on 14 March 1647 by Bavaria, Cologne, France, and Sweden.
Turenne, French commander in the Rhineland, was ordered to attack the Spanish Netherlands but the plan fell apart when his mostly German troops mutinied. Bavarian general Johann von Werth declared his loyalty to the Emperor and refused to comply with the truce, forcing Maximilian to do the same. In September, he ordered his army under Bronckhorst-Gronsfeld to link up with the Imperial commander von Holzappel. Outnumbered by a Franco-Swedish army under Wrangel and Turenne, they were defeated at Zusmarshausen in May 1648, while von Holzappel was killed. A rearguard action led by Raimondo Montecuccoli allowed most of the Imperial troops to escape but their retreat allowed Wrangel and Turenne to devastate Bavaria again.
The Swedes sent a second force under von Königsmarck to attack Prague, seizing the castle and Malá Strana district in July. The main objective was to gain as much loot as possible before the war ended; they failed to take the Old Town but captured the Imperial library, along with treasures including the Codex Gigas, now in Stockholm. On 5 November, news arrived that Ferdinand had signed peace treaties with France and Sweden on 24 October, ending the war.
The conflict outside Germany
Northern Italy
Northern Italy had been contested by France and the Habsburgs for centuries, since it was vital for control of South-West France, an area with a long history of opposition to the central authorities. While Spain remained the dominant power in Italy, its reliance on long exterior lines of communication was a potential weakness, especially the Spanish Road; this overland route allowed them to move recruits and supplies from the Kingdom of Naples through Lombardy to their army in Flanders. The French sought to disrupt the Road by attacking the Spanish-held Duchy of Milan or blocking the Alpine passes through alliances with the Grisons.
A subsidiary territory of the Duchy of Mantua was Montferrat and its fortress of Casale Monferrato, whose possession allowed the holder to threaten Milan. Its importance meant when the last duke in the direct line died in December 1627, France and Spain backed rival claimants, resulting in the 1628 to 1631 War of the Mantuan Succession. The French-born Duke of Nevers was backed by France and the Republic of Venice, his rival the Duke of Guastalla by Spain, Ferdinand II, Savoy and Tuscany. This minor conflict had a disproportionate impact on the Thirty Years War, since Pope Urban VIII viewed Habsburg expansion in Italy as a threat to the Papal States. The result was to divide the Catholic church, alienate the Pope from Ferdinand II and make it acceptable for France to employ Protestant allies against him.
In March 1629, the French stormed Savoyard positions in the Pas de Suse, lifted the Spanish siege of Casale and captured Pinerolo. The Treaty of Suza then ceded the two fortresses to France and allowed their troops unrestricted passage through Savoyard territory, giving them control over Piedmont and the Alpine passes into Southern France. However, as soon as the main French army withdrew in late 1629, the Spanish and Savoyards besieged Casale once again, while Ferdinand II provided German mercenaries to support a Spanish offensive which routed the main Venetian field army and forced Nevers to abandon Mantua. By October 1630, the French position seemed so precarious their representatives agreed the Treaty of Ratisbon but since the terms effectively destroyed Richelieu's policy of opposing Habsburg expansion, it was never ratified.
Several factors restored the French position in Northern Italy, notably a devastating outbreak of plague; between 1629 and 1631, over 60,000 died in Milan and 46,000 in Venice, with proportionate losses elsewhere. Richelieu took advantage of the diversion of Imperial resources from Germany to fund a Swedish invasion, whose success forced the Spanish-Savoyard alliance to withdraw from Casale and sign the Treaty of Cherasco in April 1631. Nevers was confirmed as Duke of Mantua and although Richelieu's representative, Cardinal Mazarin, agreed to evacuate Pinerolo, it was later secretly returned under an agreement with Victor Amadeus I, Duke of Savoy. With the exception of the 1639 to 1642 Piedmontese Civil War, this secured the French position in Northern Italy for the next twenty years.
After the outbreak of the Franco-Spanish War in 1635, Richelieu supported a renewed offensive by Victor Amadeus against Milan to tie down Spanish resources. These included an unsuccessful attack on Valenza in 1635, plus minor victories at Tornavento and Mombaldone. However, the anti-Habsburg alliance in Northern Italy fell apart when first Charles of Mantua died in September 1637, then Victor Amadeus in October, whose death led to a struggle for control of the Savoyard state between his widow Christine of France and brothers, Thomas and Maurice.
In 1639, their quarrel erupted into open warfare, with France backing Christine and Spain the two brothers, and resulted in the Siege of Turin. One of the most famous military events of the 17th century, at one stage it featured no less than three different armies besieging each other. However, the revolts in Portugal and Catalonia forced the Spanish to cease operations in Italy and the war was settled on terms favourable to Christine and France.
In 1647, a French-backed rebellion succeeded in temporarily overthrowing Spanish rule in Naples. The Spanish quickly crushed the insurrection and restored their rule over all of southern Italy, defeating multiple French expeditionary forces sent to back the rebels. However, it exposed the weakness of Spanish rule in Italy and the alienation of the local elites from Madrid; in 1650, the governor of Milan wrote that as well as widespread dissatisfaction in the south, the only one of the Italian states that could be relied on was the Duchy of Parma.
Catalonia; Reapers' War
Throughout the 1630s, attempts to increase taxes to pay for the costs of the war in the Netherlands led to protests throughout Spanish territories; in 1640, these erupted into open revolts in Portugal and Catalonia, supported by Richelieu as part of his 'war by diversion'. Prompted by France, the rebels proclaimed the Catalan Republic in January 1641. The Madrid government quickly assembled an army of 26,000 men to crush the revolt, and on 23 January, they defeated the Catalans at Martorell. The French now persuaded the Catalan Courts to recognise Louis XIII as Count of Barcelona, and ruler of the Principality of Catalonia.
Three days later, a combined French-Catalan force defeated the Spanish at Montjuïc, a victory which secured Barcelona. However, the rebels soon found the new French administration differed little from the old, turning the war into a three-sided contest between the Franco-Catalan elite, the rural peasantry, and the Spanish. There was little serious fighting after France took control of Perpignan and Roussillon, establishing the modern Franco-Spanish border in the Pyrenees. In 1651, Spain recaptured Barcelona, ending the revolt.
Outside Europe
In 1580, Philip II of Spain also became ruler of the Portuguese Empire, creating the Iberian Union; long-standing commercial rivals, the 1602 to 1663 Dutch–Portuguese War was an offshoot of the Dutch fight for independence from Spain. The Portuguese dominated the trans-Atlantic economy known as the Triangular trade, in which slaves were transported from West Africa and Portuguese Angola to work on plantations in Portuguese Brazil, which exported sugar and tobacco to Europe. Known by Dutch historians as the 'Great Design", control of this trade would not only be extremely profitable but also deprive the Spanish of funds needed to finance their war in the Netherlands.
The Dutch West India Company was formed in 1621 to achieve this purpose and a Dutch fleet captured the Brazilian port of Salvador, Bahia in 1624. After it was retaken by the Portuguese in 1625, a second fleet established Dutch Brazil in 1630, which was not returned until 1654. The second part was seizing slave trading hubs in Africa, chiefly Angola and São Tomé; supported by the Kingdom of Kongo, whose position was threatened by Portuguese expansion, the Dutch successfully occupied both in 1641.
Spain's inability or unwillingness to provide protection against these attacks increased Portuguese resentment and were major factors in the outbreak of the Portuguese Restoration War in 1640. Although ultimately expelled from Brazil, Angola and São Tomé, the Dutch retained the Cape of Good Hope, as well as Portuguese trading posts in Malacca, the Malabar Coast, the Moluccas and Ceylon.
Peace of Westphalia (1648)
What became known as the Peace of Westphalia consisted of three separate agreements; the Peace of Münster between Spain and the Dutch Republic, the Treaty of Osnabrück between the Empire and Sweden, plus the Treaty of Münster between the Empire and France. Preliminary discussions began in 1642 but only became serious in 1646; a total of 109 delegations attended at one time or other, with talks split between Münster and Osnabrück. The Swedes rejected a proposal that Christian of Denmark act as mediator, and the parties finally agreed on Papal Legate Fabio Chigi and the Venetian envoy Alvise Contarini.
The Peace of Münster was the first to be signed on 30 January 1648; it was part of the Westphalia settlement because the Dutch Republic was still technically part of the Spanish Netherlands and thus Imperial territory. The treaty confirmed Dutch independence, although the Imperial Diet did not formally accept that it was no longer part of the Empire until 1728. The Dutch were also given a monopoly over trade conducted through the Scheldt estuary, ensuring the commercial ascendancy of Amsterdam; Antwerp, capital of the Spanish Netherlands and previously the most important port in Northern Europe, would not recover until the late 19th century.
Negotiations with France and Sweden were conducted in conjunction with the Imperial Diet, and were multi-sided discussions involving many of the German states. This resulted in the treaties of Münster and Osnabrück, making peace with France and Sweden respectively. Ferdinand resisted signing until the last possible moment, doing so on 24 October only after a crushing French victory over Spain at Lens, and with Swedish troops on the verge of taking Prague. It has been argued they were a "major turning point in German and European...legal history", because they went beyond normal peace settlements and effected major constitutional and religious changes to the Empire itself.
Key elements of the Peace were provisions confirming the autonomy of states within the Empire, including Ferdinand's acceptance of the supremacy of the Imperial Diet, and those seeking to prevent future religious conflict. Article 5 reconfirmed the Augsburg settlement, established 1624 as the basis, or "Normaljahr", for determining the dominant religion of a state and guaranteed freedom of worship for religious minorities. Article 7 recognised Calvinism as a Reformed faith and removed the ius reformandi, the requirement that if a ruler changed his religion, his subjects had to follow suit. These terms did not apply to the hereditary lands of the Habsburg monarchy, such as Lower and Upper Austria.
In terms of territorial concessions, Brandenburg-Prussia received Farther Pomerania, and the bishoprics of Magdeburg, Halberstadt, Kammin, and Minden. Frederick's son Charles Louis regained the Lower Palatinate and became the eighth Imperial elector, although Bavaria kept the Upper Palatinate and its electoral vote. Externally, the treaties formally acknowledged the independence of the Dutch Republic and the Swiss Confederacy, effectively autonomous since 1499. In Lorraine, the Three Bishoprics of Metz, Toul and Verdun, occupied by France since 1552, were formally ceded, as were the cities of the Décapole in Alsace, with the exception of Strasbourg and Mulhouse. Sweden received an indemnity of five million thalers, the Imperial territories of Swedish Pomerania, and the Prince-bishoprics of Bremen and Verden, which also gave them a seat in the Imperial Diet.
The Peace was later denounced by Pope Innocent X, who regarded the bishoprics ceded to France and Brandenburg as property of the Catholic church, and thus his to assign. It also disappointed many exiles by accepting Catholicism as the dominant religion in Bohemia, Upper and Lower Austria, all of which were Protestant strongholds prior to 1618. Fighting did not end immediately, since demobilising over 200,000 soldiers was a complex business, and the last Swedish garrison did not leave Germany until 1654. In addition, Mazarin insisted on excluding the Burgundian Circle from the treaty of Münster, allowing France to continue its campaign against Spain in the Low Countries, a war that continued until the 1659 Treaty of the Pyrenees. The political disintegration of the Polish commonwealth led to the 1655 to 1660 Second Northern War with Sweden, which also involved Denmark, Russia and Brandenburg, while two Swedish attempts to impose its control on the port of Bremen failed in 1654 and 1666.
It has been argued the Peace established the principle known as Westphalian sovereignty, the idea of non-interference in domestic affairs by outside powers, although this has since been challenged. The process, or 'Congress' model, was adopted for negotiations at Aix-la-Chapelle in 1668, Nijmegen in 1678, and Ryswick in 1697; unlike the 19th century 'Congress' system, these were to end wars, rather than prevent them, so references to the 'balance of power' can be misleading.
Human and financial cost of the war
Historians often refer to the 'General Crisis' of the mid-17th century, a period of sustained conflict in states such as China, the British Isles, Tsarist Russia and the Holy Roman Empire. In all these areas, war, famine and disease inflicted severe losses on local populations. While the Thirty Years War certainly ranks as one of the worst of these events, 19th century nationalists often increased or exaggerated its impact to illustrate the dangers of a divided Germany. Suggestions of up to 12 million deaths from a population of 18 million are no longer accepted, while claims of material losses are either not supported by contemporary evidence or in some cases exceed prewar tax records.
Note; Decline includes factors such as emigration from rural to more secure urban areas and does not equate to Deaths
By modern standards, the number of soldiers involved was relatively low but the conflict has been described as one of the greatest medical catastrophes in history. Battles generally featured armies of around 13,000 to 20,000 each, the largest being Alte Veste in 1632 with a combined 70,000 to 85,000. Estimates of the total deployed by both sides within Germany range from an average of 80,000 to 100,000 from 1618 to 1626, peaking at 250,000 in 1632 and falling to under 160,000 by 1648.
Until the mid-19th century, most soldiers died of disease; historian Peter Wilson, aggregating figures from known battles and sieges, gives a figure for those either killed or wounded in combat as around 450,000. Since experience shows two to three times that number either died or were incapacitated by disease, that would suggest total military casualties ranged from 1.3 to 1.8 million dead or otherwise rendered unfit for service. One estimate by Pitirim Sorokin calculates an upper limit of 2,071,000 military casualties, although his methodology has been widely disputed by others. In general, historians agree the war was an unprecedented mortality disaster and the vast majority of casualties, whether civilian or military, took place after Swedish intervention in 1630.
Based on local records, military action accounted for less than 3% of civilian deaths; the major causes were starvation (12%), bubonic plague (64%), typhus (4%), and dysentery (5%). Although regular outbreaks of disease were common for decades prior to 1618, the conflict greatly accelerated their spread. This was due to the influx of soldiers from foreign countries, the shifting locations of battle fronts, as well as the displacement of rural populations into already crowded cities. This was not restricted to Germany; disease carried by French and Imperial soldiers allegedly sparked the 1629–1631 Italian plague, leading to an estimated 280,000 deaths, the "worst mortality crisis to affect Italy during the Early modern period". Poor harvests throughout the 1630s and repeated plundering of the same areas led to widespread famine; contemporaries record people eating grass, or too weak to accept alms, while instances of cannibalism were common.
The modern consensus is the population of the Holy Roman Empire declined from 18 to 20 million in 1600 to 11–13 million in 1650, and did not regain pre-war levels until 1750. Nearly 50% of these losses appear to have been incurred during the first period of Swedish intervention from 1630 to 1635. The high mortality rate compared to the Wars of the Three Kingdoms in Britain may partly be due to the reliance of all sides on foreign mercenaries, often unpaid and required to live off the land. Lack of a sense of 'shared community' resulted in atrocities such as the destruction of Magdeburg, in turn creating large numbers of refugees who were extremely susceptible to sickness and hunger. While flight saved lives in the short-term, in the long run it often proved catastrophic.
In 1940, agrarian historian Günther Franz published a detailed analysis of regional data from across Germany covering the period from 1618 to 1648. Broadly confirmed by more recent work, he concluded "about 40% of the rural population fell victim to the war and epidemics; in the cities,...33%". These figures can be misleading, since Franz calculated the absolute decline in pre and post-war populations, or 'total demographic loss'. They therefore include factors unrelated to death or disease, such as permanent migration to areas outside the Empire or lower birthrates, a common but less obvious impact of extended warfare. There were also wide regional variations; some areas in Northwest Germany were relatively peaceful after 1630 and experienced almost no population loss, while those of Mecklenburg, Pomerania and Württemberg fell by nearly 50%.
Although some towns may have overstated their losses to avoid taxes, individual records confirm serious declines; from 1620 to 1650, the population of Munich fell from 22,000 to 17,000, that of Augsburg from 48,000 to 21,000. The financial impact is less clear; while the war caused short-term economic dislocation, especially in the period 1618 to 1623, overall it accelerated existing changes in trading patterns. It does not appear to have reversed ongoing macro-economic trends, such as the reduction of price differentials between regional markets, and a greater degree of market integration across Europe. The death toll may have improved living standards for the survivors; one study shows wages in Germany increased by 40% in real terms between 1603 and 1652.
Social and cultural impact
It has been suggested the breakdown of social order caused by the war was often more significant and longer lasting than the immediate damage. The collapse of local government created landless peasants, who banded together to protect themselves from the soldiers of both sides, and led to widespread rebellions in Upper Austria, Bavaria and Brandenburg. Soldiers devastated one area before moving on, leaving large tracts of land empty of people and changing the eco-system. Food shortages were worsened by an explosion in the rodent population; Bavaria was overrun by wolves in the winter of 1638, its crops destroyed by packs of wild pigs the following spring.
Contemporaries spoke of a 'frenzy of despair' as people sought to make sense of the relentless and often random bloodshed unleashed by the war. Attributed by religious authorities to divine retribution for sin, other attempts to identify a supernatural cause led to a series of Witch-hunts, beginning in Franconia in 1626 and quickly spreading to other parts of Germany. They began in the Bishopric of Würzburg, an area with a history of such events going back to 1616 and now re-ignited by Bishop von Ehrenberg, a devout Catholic eager to assert the church's authority in his territories. By the time he died in 1631, over 900 people from all levels of society had been executed.
The Bamberg witch trials, held in the nearby Bishopric of Bamberg from 1626 to 1631, claimed over one thousand lives; in 1629, 274 died in the Eichstätt witch trials, plus another 50 in the adjacent Duchy of Palatinate-Neuburg. Elsewhere, persecution followed Imperial military success, expanding into Baden and the Palatinate following their reconquest by Tilly, then into the Rhineland. However, the extent to which they were symptomatic of the impact of the conflict on society is debatable, since many took place in areas relatively untouched by the war. Concerned their brutality would discredit the Counter-Reformation, Ferdinand ensured active persecution largely ended by 1630.
Although the war caused immense destruction, it has also been credited with sparking a revival in German literature, including the creation of societies dedicated to "purging of foreign elements" from the German language. One example is Simplicius Simplicissimus, often suggested as one of the earliest examples of the Picaresque novel; written by Hans Jakob Christoffel von Grimmelshausen in 1668, it includes a realistic portrayal of a soldier's life based on his own experiences, many of which are verified by other sources. Other less famous examples include the diaries of Peter Hagendorf, a participant in the Sack of Magdeburg whose description of the everyday brutalities of the war remain compelling.
For German, and to a lesser extent Czech writers, the war continued to be remembered as a defining moment of national trauma, the 18th century poet and playwright Friedrich Schiller being one of many to use it in their work. Variously known as the 'Great German War,' 'Great War' or 'Great Schism', for 19th and early 20th century German nationalists it showed the dangers of a divided Germany and was used to justify the creation of the German Empire in 1871, as well as the Greater Germanic Reich envisaged by the Nazis. Bertolt Brecht used it as the backdrop for his 1939 anti-war play Mother Courage and Her Children, while its enduring cultural resonance is illustrated by the novel Tyll; written by Austro-German author Daniel Kehlmann and also set during the war, it was nominated for the 2020 Booker Prize.
Political consequences
The Peace reconfirmed "German liberties", ending Habsburg attempts to convert the Holy Roman Empire into a more centralised state similar to Spain. Over the next 50 years, Bavaria, Brandenburg-Prussia, Saxony and others increasingly pursued their own policies, while Sweden gained a permanent foothold in the Empire. Despite these setbacks, the Habsburg lands suffered less from the war than many others and became a far more coherent bloc with the absorption of Bohemia, and restoration of Catholicism throughout their territories.
By laying the foundations of the modern nation state, Westphalia changed the relationship between subjects and their rulers. Previously, many had overlapping, sometimes conflicting, political and religious allegiances; they were now understood to be subject first and foremost to the laws and edicts of their respective state authority, not the claims of any other entity, religious or secular. This made it easier to levy national forces of significant size, loyal to their state and its leader; one lesson learned from Wallenstein and the Swedish invasion was the need for their own permanent armies, and Germany as a whole became a far more militarised society.
The benefits of Westphalia for the Swedes proved short-lived. Unlike French gains which were incorporated into France, Swedish territories remained part of the Empire, and they became members of the Lower and Upper Saxon kreis. While this gave them seats in the Imperial Diet, it also brought them into direct conflict with both Brandenburg-Prussia and Saxony, their competitors in Pomerania. The income from their imperial possessions remained in Germany and did not benefit the kingdom of Sweden; although they retained parts of Swedish Pomerania until 1815, much of it was ceded to Prussia in 1679 and 1720.
France arguably gained more from the Thirty Years' War than any other power; by 1648, most of Richelieu's objectives had been achieved. These included separation of the Spanish and Austrian Habsburgs, expansion of the French frontier into the Empire, and an end to Spanish military supremacy in Northern Europe. Although the Franco-Spanish conflict continued until 1659, Westphalia allowed Louis XIV of France to begin replacing Spain as the predominant European power.
While differences over religion remained an issue throughout the 17th century, it was the last major war in Continental Europe in which it can be said to be a primary driver; later conflicts were either internal, such as the Camisards revolt in South-Western France, or relatively minor like the 1712 Toggenburg War. It created the outlines of a Europe that persisted until 1815 and beyond; the nation-state of France, the beginnings of a unified Germany and separate Austro-Hungarian bloc, a diminished but still significant Spain, independent smaller states like Denmark, Sweden and Switzerland, along with a Low Countries split between the Dutch Republic and what became Belgium in 1830.
Involvement

|
|
Directly against Emperor |
|
|
Indirectly against Emperor |
|
|
Directly for Emperor |
|
|
Indirectly for Emperor |