From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
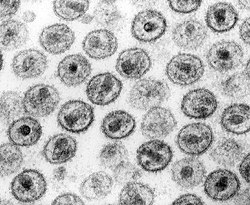
Electron micrograph of the human immunodeficiency virus. HIV/AIDS denialists dispute the existence of HIV or its role in causing AIDS.
HIV/AIDS denialism is the refusal to acknowledge that human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) causes acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS), despite the conclusive evidence. Some of its proponents reject the existence of HIV, while others accept that HIV exists but argue that it is a harmless passenger virus and not the cause of AIDS. Insofar as they acknowledge AIDS as a real disease, they attribute it to some combination of sexual behavior, recreational drugs, malnutrition, poor sanitation, haemophilia, or the effects of the medications used to treat HIV infection (antiretrovirals).
The scientific consensus is that the evidence showing HIV to be the cause of AIDS is conclusive and that HIV/AIDS denialist claims are pseudoscience based on conspiracy theories, faulty reasoning, cherry picking, and misrepresentation of mainly outdated scientific data.
With the rejection of these arguments by the scientific community,
HIV/AIDS denialist material is now targeted at less scientifically
sophisticated audiences and spread mainly through the Internet.
Despite its lack of scientific acceptance, HIV/AIDS denialism has had a significant political impact, especially in South Africa under the presidency of Thabo Mbeki.
Scientists and physicians have raised alarm at the human cost of
HIV/AIDS denialism, which discourages HIV-positive people from using
proven treatments.
Public health researchers have attributed 330,000 to 340,000
AIDS-related deaths, along with 171,000 other HIV infections and 35,000
infant HIV infections, to the South African government's former embrace
of HIV/AIDS denialism.
The interrupted use of antiretroviral treatments is also a major global
concern as it potentially increases the likelihood of the emergence of
antiretroviral-resistant strains of the virus.
History
A constellation of symptoms named "Gay-related immune deficiency" was noted in 1982. In 1983, a group of scientists and doctors at the Pasteur Institute in France, led by Luc Montagnier, discovered a new virus in a patient with signs and symptoms that often preceded AIDS. They named the virus lymphadenopathy-associated virus, or LAV, and sent samples to Robert Gallo's team in the United States. Their findings were peer reviewed and slated for publication in Science.
At a 23 April 1984 press conference in Washington, D.C., Margaret Heckler, Secretary of Health and Human Services,
announced that Gallo and his co-workers had discovered a virus that was
the "probable" cause of AIDS. This virus was initially named HTLV-III. In the same year, Casper Schmidt responded to Gallo's papers with "The Group-Fantasy Origins of AIDS", published in the Journal of Psychohistory. Schmidt posited that AIDS was not an actual disease, but rather an example of "epidemic hysteria",
in which groups of people subconsciously act out social conflicts.
Schmidt compared AIDS to documented cases of epidemic hysteria in the
past which were mistakenly thought to be infectious. (Schmidt himself
would later die of AIDS in 1994.)
In 1986, the viruses discovered by Montagnier and Gallo, found to be genetically indistinguishable, were renamed HIV.
In 1987, molecular biologist Peter Duesberg questioned the link between HIV and AIDS in the journal Cancer Research. Duesberg's publication coincided with the start of major public health campaigns and the development of zidovudine (AZT) as a treatment for HIV/AIDS.
In 1988, a panel of the Institute of Medicine of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences found that "the evidence that HIV causes AIDS is scientifically conclusive." That same year, Science published Blattner, Gallo, and Temin's "HIV causes AIDS", and Duesberg's "HIV is not the cause of AIDS". Also that same year, the Perth Group, a group of denialists based in Perth, Western Australia led by Eleni Papadopulos-Eleopulos, published in the non-peer-reviewed journal Medical Hypotheses their first article questioning aspects of HIV/AIDS research,
arguing that there was "no compelling reason for preferring the viral
hypothesis of AIDS to one based on the activity of oxidising agents."
In 1989, Duesberg exercised his right as a member of the National
Academy of Sciences to bypass the peer review process and published his
arguments in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) unreviewed. The editor of PNAS
initially resisted, but ultimately allowed Duesberg to publish, saying,
"If you wish to make these unsupported, vague, and prejudicial
statements in print, so be it. But I cannot see how this would be
convincing to any scientifically trained reader."
In 1990, the physiologist Robert Root-Bernstein published his first peer-reviewed article detailing his objections to the mainstream view of AIDS and HIV. In it, he questioned both the mainstream view and the "dissident" view as potentially inaccurate.
In 1991, The Group for the Scientific Reappraisal of the HIV-AIDS
Hypothesis, comprising twelve scientists, doctors, and activists,
submitted a short letter to various journals, but the letter was
rejected.
In 1993, Nature published an editorial arguing that Duesberg had forfeited his right of reply by engaging in disingenuous rhetorical techniques and ignoring any evidence that conflicted with his claims. That same year, Papadopulos-Eleopulos and coauthors from the Perth Group alleged in the journal Nature Biotechnology (then edited by fellow denialist Harvey Bialy) that the Western blot test for HIV was not standardized, non-reproducible, and of unknown specificity due to a claimed lack of a "gold standard".
On 28 October 1994, Robert Willner, a physician whose medical license had been revoked for, among other things, treating an AIDS patient with ozone therapy, publicly jabbed his finger with blood he said was from an HIV-infected patient. Willner died in 1995 of a heart attack.
In 1995, The Group for the Scientific Reappraisal of the HIV-AIDS Hypothesis in 1991 published a letter in Science similar to the one they had attempted to publish in 1991. That same year, Continuum, a denialist group, placed an advertisement in the British gay and lesbian magazine The Pink Paper
offering a £1,000 reward to "the first person finding one scientific
paper establishing actual isolation of HIV", according to a set of seven
steps they claimed to have been drawn up by the Pasteur Institute in
1973. The challenge was later dismissed by various scientists, including Duesberg, asserting that HIV undoubtedly exists. Stefan Lanka argued in the same year that HIV does not exist. Also that year, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
released a report concluding that "abundant epidemiologic, virologic
and immunologic data support the conclusion that infection with the
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the underlying cause of AIDS."
In 1996, the British Medical Journal published "Response: arguments contradict the "foreign protein-zidovudine" hypothesis"
as a response to a petition by Duesberg: "In 1991 Duesberg challenged
researchers… We and Darby et al. have provided that evidence". The paper
argued that Duesberg was wrong regarding the cause of AIDS in
haemophiliacs.
In 1997, The Perth Group questioned the existence of HIV, and speculated
that the production of antibodies recognizing HIV proteins can be
caused by allogenic stimuli and autoimmune disorders. They continued to repeat this speculation through at least 2006.
In 1998, Joan Shenton published the book Positively False – Exposing the Myths Around HIV and AIDS,
which promotes AIDS denialism. In the book, Shenton claims that AIDS is
a conspiracy created by pharmaceutical companies to make money from
selling antiretroviral drugs.
In 2006, Celia Farber, a journalist and prominent HIV/AIDS denialist, published an essay in the March issue of Harper's Magazine
entitled "Out of Control: AIDS and the Corruption of Medical Science",
in which she summarized a number of arguments for HIV/AIDS denialism and
alleged incompetence, conspiracy, and fraud on the part of the medical community. Scientists and AIDS activists extensively criticized the article as inaccurate, misleading, and poorly fact-checked.
In 2007, members of the Perth Group testified at an appeals hearing for Andre Chad Parenzee,
asserting that HIV could not be transmitted by heterosexual sex. The
judge concluded, "I reject the evidence of Ms Papadopulos-Eleopulos and
Dr Turner. I conclude… that they are not qualified to give expert
opinions."
In 2009, a paper was published in the then non-peer-reviewed journal Medical Hypotheses by Duesberg and four other researchers which criticized a 2008 study by Chigwedere et al.,
which found that HIV/AIDS denialism in South Africa resulted in
hundreds of thousands of preventable deaths from HIV/AIDS, because the
government delayed the provision of antiretroviral drugs. The paper
concluded that "the claims that HIV has caused huge losses of African
lives are unconfirmed and that HIV is not sufficient or even necessary
to cause the previously known diseases, now called AIDS in the presence
of antibody against HIV."
Later that year, the paper was withdrawn from the journal on the
grounds of it having methodological flaws, and that it contained
assertions "that could potentially be damaging to global public health".
A revised version was later published in Italian Journal of Anatomy and Embryology.
US courts
In 1998, HIV/AIDS denialism and parental rights clashed with the
medical establishment in court when Maine resident Valerie Emerson
fought for the right to refuse to give AZT to her four-year-old son,
Nikolas Emerson, after she witnessed the death of her daughter Tia, who
died at the age of three in 1996. Her right to stop treatment was
upheld by the court in light of "her unique experience." Nikolas Emerson died eight years later. The family refused to reveal whether the death was AIDS related.
South Africa
In 2000, South Africa's President Thabo Mbeki invited several HIV/AIDS denialists to join his Presidential AIDS Advisory Panel. A response named the Durban Declaration was issued affirming the scientific consensus that HIV causes AIDS:
- "The declaration has been signed by over 5,000 people, including
Nobel Prize winners, directors of leading research institutions,
scientific academies and medical societies, notably the US National
Academy of Sciences, the US Institute of Medicine, Max Planck
institutes, the European Molecular Biology Organization, the Pasteur
Institute in Paris, the Royal Society of London, the AIDS Society of
India and the National Institute of Virology in South Africa. In
addition, thousands of individual scientists and doctors have signed,
including many from the countries bearing the greatest burden of the
epidemic. Signatories are of MD, PhD level or equivalent, although
scientists working for commercial companies were asked not to sign."
In 2008, University of Cape Town researcher Nicoli Nattrass, and later that year a group of Harvard scientists led by Zimbabwean physician Pride Chigwedere each independently estimated that Thabo Mbeki's denialist policies led to the early deaths of more than 330,000 South Africans. Barbara Hogan,
the health minister appointed by Mbeki's successor, voiced shame over
the studies' findings and stated: "The era of denialism is over
completely in South Africa."
In 2009, Fraser McNeill wrote an article arguing that South
Africa's reluctance to openly address HIV/AIDS resulted from social
conventions that prevent people from talking about causes of death in
certain situations, rather than from Mbeki's denialist views.
Similarly, political scientist Anthony Butler has argued that "South
African HIV/AIDS policy can be explained without appeals to leadership
irrationality or wider cultural denialism."
In July 2016 Aaron Motsoaledi,
the Health Minister of South Africa, wrote an article for the Centre
for Health Journalism in which he criticised past South African leaders
for their denialism, describing it as an "unlucky moment" in a country
which has since become a leader in treatment and prevention.
Denialists' claims and scientific evidence
The term "HIV/AIDS denialism" denotes the rejection of the mainstream
scientific view that AIDS is a medical condition that is brought about
by HIV infection. The use of the term encompasses the denial of the
existence of the virus (HIV denialism), the denial of the causation of
AIDS by HIV (that is, the proposed link between the virus and the
syndrome), and the denial of the effects on the human body that are
ascribed to HIV (that is, the description and characterization of the
virus). In a framework incorporating the second denial and/or the third,
criticism of the current scientific view has variously been rested on
the claim that HIV has not been adequately isolated, that HIV does not fulfill Koch's postulates, HIV testing is inaccurate, and/or that antibodies to HIV neutralize the virus and render it harmless. Suggested alternative causes of AIDS variously include recreational drugs, malnutrition, and the very antiretroviral drugs used to treat the syndrome.
Such claims have been examined extensively in the peer-reviewed medical and scientific literature; a scientific consensus has arisen that denialist claims have been convincingly disproved, and that HIV does indeed cause AIDS. In the cases cited by Duesberg where HIV "cannot be isolated", PCR or other techniques demonstrate the presence of the virus,
and denialist claims of HIV test inaccuracy result from an incorrect or
outdated understanding of how HIV antibody testing is performed and
interpreted. Regarding Koch's postulates, New Scientist
reported: "It is debatable how appropriate it is to focus on a set of
principles devised for bacterial infections in a century when viruses
had not yet been discovered. HIV does, however, meet Koch's postulates
as long as they are not applied in a ridiculously stringent way". The
author then demonstrated how each postulate has been met – the
suspected cause is strongly associated with the disease, the suspected
pathogen can be both isolated and spread outside the host, and when the
suspected pathogen is transmitted to a new and uninfected host, that
host develops the disease.
The latter was proven in a number of tragic accidents, including an
instance when multiple scientific technicians with no other known risk
factors were exposed to concentrated HIV in a laboratory accident, and
transmission by a dentist to patients, the majority of whom had no other
known risk factor or source of exposure except the same dentist in
common. In 2010, Chigwedere and Max Essex demonstrated in the medical journal AIDS and Behavior that HIV as the cause of AIDS fulfills both Koch's postulates and the Bradford Hill criteria for causality.
Early denialist arguments held that the HIV/AIDS paradigm was
flawed because it had not led to effective treatments. However, the
introduction of highly active antiretroviral therapy
in the mid-1990s and dramatic improvements in survival of HIV/AIDS
patients reversed this argument, as these treatments were based directly
on anti-viral activity and the HIV/AIDS paradigm.
The development of effective anti-AIDS therapies based on targeting of
HIV has been a major factor in convincing some denialist scientists to
accept the causative role of HIV in AIDS.
In a 2010 article on conspiracy theories in science, Ted Goertzel
lists HIV/AIDS denialism as an example where scientific findings are
being disputed on irrational grounds. He describes proponents as relying
on rhetoric, appeal to fairness, and the right to a dissenting opinion rather than on evidence. They frequently invoke the meme of a "courageous independent scientist resisting orthodoxy", invoking the name of persecuted physicist and astronomer Galileo Galilei. Regarding this comparison, Goertzel states:
...being a dissenter from orthodoxy
is not difficult; the hard part is actually having a better theory.
Publishing dissenting theories is important when they are backed by
plausible evidence, but this does not mean giving critics 'equal time'
to dissent from every finding by a mainstream scientist.
— Goertzel, 2010
Denialists often use their critique of the link between HIV and AIDS to promote alternative medicine as a cure, and attempt to convince HIV-positive individuals to avoid ARV therapy in favour of vitamins, massage, yoga and other unproven treatments.
Despite this promotion, denialists will often downplay any association
with alternative therapies, and attempt to portray themselves as
"dissidents". An article in the Skeptical Inquirer stated:
AIDS denialists [prefer] to
characterize themselves as brave "dissidents" attempting to engage a
hostile medical/industrial establishment in genuine scientific "debate."
They complain that their attempts to raise questions and pose
alternative hypotheses have been unjustly rejected or ignored at the
cost of scientific progress itself...Given their resistance to all
evidence to the contrary, today's AIDS dissidents are more aptly
referred to as AIDS denialists.
Several scientists have been associated with HIV/AIDS denialism, although they have not themselves studied AIDS or HIV. One of the most famous and influential is Duesberg, professor of molecular and cell biology at the University of California, Berkeley, who since 1987 has disputed that the scientific evidence shows that HIV causes AIDS. Other scientists associated with HIV/AIDS denialism include biochemists David Rasnick and Harvey Bialy. Kary Mullis, who was awarded a Nobel Prize for his role in the development of the polymerase chain reaction, has expressed sympathy for denialist theories. Biologist Lynn Margulis argued that "there's no evidence that HIV is an infectious virus" and that AIDS symptoms "overlap...completely" with those of syphilis. Pathologist Étienne de Harven also expressed sympathy for HIV/AIDS denial.
Additional notable HIV/AIDS denialists include Australian academic ethicist Hiram Caton, the late mathematician Serge Lang, former college administrator Henry Bauer, journalist Celia Farber, American talk radio host and author on alternative and complementary medicine and nutrition Gary Null, and the late activist Christine Maggiore,
who encouraged HIV-positive mothers to forgo anti-HIV treatment and
whose 3-year-old daughter died of complications of untreated AIDS. Nate Mendel, bassist with the rock band Foo Fighters, expressed support for HIV/AIDS denialist ideas and organized a benefit concert in January 2000 for Maggiore's organization Alive & Well AIDS Alternatives. Organizations of HIV/AIDS denialists include the Perth Group, composed of several Australian hospital workers, and the Immunity Resource Foundation.
HIV/AIDS denialism has received some support from political conservatives in the United States. Duesberg's work has been published in Policy Review, a journal once published by The Heritage Foundation but later acquired by the Hoover Institution, and by Regnery Publishing. Regnery published Duesberg's Inventing the AIDS Virus in 1996, and journalist Tom Bethell's The Politically Incorrect Guide to Science, in which he endorses HIV/AIDS denialism, in 2005. Law professor Phillip E. Johnson has accused the Centers for Disease Control of "fraud" in relation to HIV/AIDS. Describing the political aspects of the HIV/AIDS denialism movement, Sociology professor Steven Epstein wrote in Impure Science
that "... the appeal of Duesberg's views to conservatives—certainly
including those with little sympathy for the gay movement—cannot be
denied." The blog LewRockwell.com has also published articles supportive of HIV/AIDS denialism.
In a follow-up article in Skeptical Inquirer,
Nattrass overviewed the prominent members of the HIV/AIDS denialist
community and discussed the reasons of the intractable staying power of
HIV/AIDS denialism in spite of scientific and medical consensus
supported by over two decades of evidence. She observed that despite
being a disparate group of people with very different background and
professions, the HIV/AIDS denialists self-organize to fill four
important roles:
- "Hero scientists" to provide scientific legitimacy: Most notably
Duesberg who plays the central role of HIV/AIDS denialism from the
beginning. Others include David Rasnick, Étienne de Harven, and Kary Mullis whose Nobel Prize makes him symbolically important.
- "Cultropreneurs" to offer fake cures in place of antiretroviral therapy: Matthias Rath, Gary Null, Michael Ellner, and Roberto Giraldo all promote alternative medicine and remedies with a dose of conspiracy theories in the form of books, healing products, radio shows and counseling services.
- HIV-positive "living icons" to provide proof of concept by appearing to live healthily without antiretroviral therapy: Christine Maggiore
was and still is the most important icon in the HIV/AIDS denialist
movement despite the fact that she died of AIDS related complications in
2008.
- "Praise singers": sympathetic journalists and filmmakers who
publicize the movement with uncritical and favorable opinion. They
include journalists Celia Farber, Liam Scheff and Neville Hodgkinson; filmmakers Brent Leung and Robert Leppo.
Some of them had overlapping roles as board members of Rethinking AIDS and Alive and Well AIDS Alternatives, were involved in the film House of Numbers, The Other Side of AIDS or on Thabo Mbeki's
AIDS Advisory Panel.
Nattrass argued that HIV/AIDS denialism gains social traction through
powerful community-building effects where these four organized
characters form "a symbiotic connection between AIDS denialism and
alternative healing modalities" and they are "facilitated by a shared
conspiratorial stance toward HIV science".
Former denialists
Several of the few prominent scientists who once voiced doubts about
HIV/AIDS have since changed their views and accepted the fact that HIV
plays a role in causing AIDS, in response to an accumulation of newer
studies and data. Root-Bernstein, author of Rethinking AIDS: The Tragic Cost of Premature Consensus
and formerly a critic of the causative role of HIV in AIDS, has since
distanced himself from the HIV/AIDS denialist movement, saying, "Both
the camp that says HIV is a pussycat and the people who claim AIDS is
all HIV are wrong...The denialists make claims that are clearly
inconsistent with existing studies."
Joseph Sonnabend,
who until the late 1990s regarded the issue of AIDS causation as
unresolved, has reconsidered in light of the success of newer
antiretroviral drugs, stating, "The evidence now strongly supports a
role for HIV… Drugs that can save your life can also under different
circumstances kill you. This is a distinction that denialists do not
seem to understand." Sonnabend has also criticized HIV/AIDS denialists for falsely implying that he supports their position, saying:
Some individuals who believe that
HIV plays no role at all in AIDS have implied that I support their
misguided views on AIDS causation by including inappropriate references
to me in their literature and on their web sites. Before HIV was
discovered and its association with AIDS established, I held the
entirely appropriate view that the cause of AIDS was then unknown. I
have successfully treated hundreds of AIDS patients with antiretroviral
medications, and have no doubt that HIV plays a necessary role in this
disease.
A former denialist wrote in the Journal of Medical Ethics in 2004:
The group [of denialists] regularly
points to a substantial number of scientists supportive of its agenda
to re-evaluate the HIV/AIDS hypothesis. Some of those members still
listed are people who have been dead for a number of years. While it is
correct that these people supported the objective of a scientific
re-evaluation of the HIV/AIDS link when they were alive, it is clearly
difficult to ascertain what these people would have made of the
scientific developments and the accumulation of evidence for HIV as the
crucial causative agent in AIDS, which has occurred in the years after
their deaths.
Death of HIV-positive denialists
In 2007, aidstruth.org, a website run by HIV researchers to counter denialist claims, published a partial list of HIV/AIDS denialists who had died of AIDS-related causes. For example, the editors of the magazine Continuum consistently denied the existence of HIV/AIDS. The magazine shut down after both editors died of AIDS-related causes.
In each case, the HIV/AIDS denialist community attributed the deaths to
unknown causes, secret drug use, or stress rather than HIV/AIDS.
Similarly, several HIV-positive former dissidents have reported being
ostracized by the AIDS-denialist community after they developed AIDS and
decided to pursue effective antiretroviral treatment.
In 2008, activist Christine Maggiore died at the age of 52 while under a doctor's care for pneumonia. Maggiore, mother of two children, had founded an organisation
to help other HIV-positive mothers avoid taking antiretroviral drugs
that reduce the risk of HIV transmission from mother to child. After her three-year-old daughter died of AIDS-related pneumonia in 2005, Maggiore continued to believe that HIV is not the cause of AIDS, and she and her husband Robin Scovill sued Los Angeles County and others on behalf of their daughter's estate, for allegedly violating Eliza Scovill's civil rights by releasing an autopsy report that listed her cause of death as AIDS-related pneumonia.
The litigants settled out of court, with the county paying Scovill
$15,000 in March 2009, with no admission of wrongdoing. The Los Angeles
coroner's ruling that Eliza Scovill died of AIDS remains the official
verdict.
Australia: In 2009 representing the then Australian Vaccination-Skeptics Network, President Meryl Dorey
signed a petition claiming that "the AIDS industry and the media" had
tricked the public and the media into believing that HIV causes AIDS.
Canada: The Alberta Reappraising AIDS Society created the
petition in March 2000 and has reportedly since attracted "2,951
doubters" representing groups and individuals. Signatories reportedly
deny "that Aids is heterosexually transmitted".
AIDS-denialist claims have failed to attract support in the
scientific community, where the evidence for the causative role of HIV
in AIDS is considered conclusive. However, the movement has had a
significant impact in the political sphere, culminating with former
South African President Thabo Mbeki's embrace of AIDS-denialist claims.
The resulting governmental refusal to provide effective anti-HIV
treatment in South Africa has been blamed for hundreds of thousands of
premature AIDS-related deaths in South Africa.
North America and Europe
Skepticism about HIV being the cause of AIDS began almost immediately
after the discovery of HIV was announced. One of the earliest prominent
skeptics was the journalist John Lauritsen, who argued in his writings
for the New York Native that amyl nitrite poppers
played a role in AIDS, and that the Centers for Disease Control and
Prevention had used statistical methods that concealed this. Lauritsen's The AIDS War was published in 1993.
Scientific literature
The publication of Duesberg's first AIDS paper in 1987 provided
visibility for denialist claims. Shortly afterwards, the journal Science
reported that Duesberg's remarks had won him "a large amount of media
attention, particularly in the gay press where he is something of a
hero." However, Duesberg's support in the gay community diminished as he made a series of statements perceived as homophobic; in an interview with The Village Voice in 1988, Duesberg stated his belief that the AIDS epidemic was "caused by a lifestyle that was criminal twenty years ago."
In the following few years, others became skeptical of the HIV
theory as researchers initially failed to produce an effective treatment
or vaccine for AIDS. Journalists such as Neville Hodgkinson and Celia Farber
regularly promoted denialist ideas in the American and British media;
several television documentaries were also produced to increase
awareness of the alternative viewpoint. In 1992–1993, The Sunday Times,
where Hodgkinson served as scientific editor, ran a series of articles
arguing that the AIDS epidemic in Africa was a myth. These articles
stressed Duesberg's claims and argued that antiviral therapy was
ineffective, HIV testing unreliable, and that AIDS was not a threat to
heterosexuals. The Sunday Times coverage was heavily criticized as slanted, misleading, and potentially dangerous; the scientific journal Nature
took the unusual step of printing a 1993 editorial calling the paper's
coverage of HIV/AIDS "seriously mistaken, and probably disastrous."
Finding difficulty in publishing his arguments in the scientific literature, Duesberg exercised his right as a member of the National Academy of Sciences to publish in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) without going through the peer review
process. However, Duesberg's paper raised a "red flag" at the journal
and was submitted by the editor for non-binding review. All of the
reviewers found major flaws in Duesberg's paper; the reviewer
specifically chosen by Duesberg noted the presence of "misleading
arguments", "nonlogical statements", "misrepresentations", and political
overtones. Ultimately, the editor of PNAS acquiesced to publication,
writing to Duesberg: "If you wish to make these unsupported, vague, and
prejudicial statements in print, so be it. But I cannot see how this
would be convincing to any scientifically trained reader."
HIV/AIDS denialists often resort to special pleading
to support their assertion, arguing for different causes of AIDS in
different locations and subpopulations. In North America, AIDS is blamed
on the health effects of unprotected anal sex and poppers on homosexual
men, an argument which does not account for AIDS in drug-free
heterosexual women who deny participating in anal sex. In this case,
HIV/AIDS denialists claim the women are having anal sex but refuse to
disclose it. In haemophiliac
North American children who contracted HIV from blood transfusions, the
haemophilia itself or its treatment is claimed to cause AIDS. In
Africa, AIDS is blamed on poor nutrition and sanitation due to poverty.
For wealthy populations in South Africa with adequate nutrition and
sanitation, it is claimed that the antiretroviral drugs used to treat
AIDS cause the condition. In each case, the most parsimonious explanation
and uniting factor – HIV positive status – is ignored, as are the
thousands of studies that converge on the common conclusion that AIDS is
caused by HIV infection.
Haemophilia is considered the best test of the HIV-AIDS
hypothesis by both denialists and AIDS researchers. While Duesberg
claims AIDS in haemophiliacs is caused by contaminated clotting factors
and HIV is a harmless passenger virus,
this result is contradicted by large studies on haemophiliac patients
who received contaminated blood. A comparison of groups receiving high,
medium and low levels of contaminated clotting factors found the death
rates differed significantly depending on HIV status. Of 396 HIV
positive haemophiliacs followed between 1985 and 1993, 153 died. The
comparative figure for the HIV negative group was one out of 66, despite
comparable doses of contaminated clotting factors. A comparison of
individuals receiving blood donations also supports the results; in 1994
there were 6888 individuals with AIDS who had their HIV infection
traced to blood transfusions. Since the introduction of HIV testing,
the number of individuals whose AIDS status can be traced to blood
transfusions was only 29 (as of 1994).
Lay press and on the Internet
With the introduction of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) in 1996–1997, the survival and general health of people with HIV improved significantly. The positive response to treatment with anti-HIV medication cemented
the scientific acceptance of the HIV/AIDS paradigm, and led several
prominent HIV/AIDS denialists to accept the causative role of HIV.
Finding their arguments increasingly discredited by the scientific
community, denialists took their message to the popular press. A former
denialist wrote:
Scientists
among the HIV dissidents used their academic credentials and academic
affiliations to generate interest, sympathy, and allegiances in lay
audiences. They were not professionally troubled about recruiting lay
people—who were clearly unable to evaluate the scientific validity or
otherwise of their views—to their cause.
In addition to elements of the popular and alternative press, AIDS denialist ideas are propagated largely via the Internet.
A 2007 article in PLoS Medicine noted:
Because these denialist assertions
are made in books and on the Internet rather than in the scientific
literature, many scientists are either unaware of the existence of
organized denial groups, or believe they can safely ignore them as the
discredited fringe. And indeed, most of the HIV deniers' arguments were
answered long ago by scientists. However, many members of the general
public do not have the scientific background to critique the assertions
put forth by these groups, and not only accept them but continue to
propagate them.
Lay opinion and AIDS-related behaviors
AIDS activists have expressed concern that denialist arguments about
HIV's harmlessness may be responsible for an upsurge in HIV infections.
Denialist claims continue to exert a significant influence in some
communities; a survey conducted at minority gay pride events in four
American cities in 2005 found that 33% of attendees doubted that HIV
caused AIDS.
Similarly, a 2010 survey of 343 people living with HIV/AIDS found that
one in five of them thought that there was no proof that HIV caused
AIDS, and that HIV treatments did more harm than good. According to Stephen Thomas, director of the University of Pittsburgh Center for Minority Health,
"people are focusing on the wrong thing. They're focusing on
conspiracies rather than protecting themselves, rather than getting
tested and seeking out appropriate care and treatment."
African Americans are exceptionally likely to believe that HIV does not
cause AIDS, partly because they sometimes perceive the role of HIV in
the disease as part of a racist agenda. A 2012 survey of young adults in Cape Town, South Africa found that belief in AIDS denialism was strongly related to an increased probability of engaging in unsafe sex.
South Africa
HIV/AIDS denialist claims have had a major political, social, and
public health impact in South Africa. The government of then President Thabo Mbeki
was sympathetic to the views of HIV/AIDS denialists, with critics
charging that denialist influence was responsible for the slow and
ineffective governmental response to the country's massive AIDS epidemic.
Independent studies have arrived at almost identical estimates of
the human costs of HIV/AIDS denialism in South Africa. According to a
paper written by researchers from the Harvard School of Public Health,
between 2000 and 2005, more than 330,000 deaths and an estimated 35,000
infant HIV infections occurred "because of a failure to accept the use
of available [antiretroviral drugs] to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS in a
timely manner." Nicoli Nattrass of the University of Cape Town
estimates that 343,000 excess AIDS-related deaths and 171,000
infections resulted from the Mbeki administration's policies, an outcome
she refers to in the words of Peter Mandelson as "genocide by sloth".
Durban Declaration
In 2000, when the International AIDS Conference was held in Durban, Mbeki convened a Presidential Advisory Panel containing a number of HIV/AIDS denialists, including Duesberg and David Rasnick. The Advisory Panel meetings were closed to the general press; an invited reporter from the Village Voice
wrote that Rasnick advocated that HIV testing be legally banned and
denied that he had seen "any evidence" of an AIDS catastrophe in South
Africa, while Duesberg "gave a presentation so removed from African
medical reality that it left several local doctors shaking their heads."
In his address to the International AIDS Conference, Mbeki
reiterated his view that HIV was not wholly responsible for AIDS,
leading hundreds of delegates to walk out on his speech. Mbeki also sent a letter to a number of world leaders likening the mainstream AIDS research community to supporters of the apartheid regime. The tone and content of Mbeki's letter led diplomats in the U.S. to initially question whether it was a hoax.
AIDS scientists and activists were dismayed at the president's behavior and responded with the Durban Declaration, a document affirming that HIV causes AIDS, signed by over 5,000 scientists and physicians.
Criticism of governmental response
The former South African health minister Manto Tshabalala-Msimang also attracted heavy criticism, as she often promoted nutritional remedies such as garlic, lemons, beetroot and olive oil, to people suffering from AIDS, while emphasizing possible toxicities of antiretroviral drugs, which she has referred to as "poison". The South African Medical Association has accused Tshabalala-Msimang of "confusing a vulnerable public".
In September 2006, a group of over 80 scientists and academics called
for "the immediate removal of Dr. Tshabalala-Msimang as minister of
health and for an end to the disastrous, pseudoscientific policies that
have characterized the South African government's response to HIV/AIDS." In December 2006, deputy health minister Nozizwe Madlala-Routledge described "denial at the very highest levels" over AIDS.
Former South African president Thabo Mbeki's
government was widely criticized for delaying the rollout of programs
to provide antiretroviral drugs to people with advanced HIV disease and
to HIV-positive pregnant women. The national treatment program began
only after the Treatment Action Campaign
(TAC) brought a legal case against Government ministers, claiming they
were responsible for the deaths of 600 HIV-positive people a day who
could not access medication.
South Africa was one of the last countries in the region to begin such a
treatment program, and roll-out has been much slower than planned.
At the XVI International AIDS Conference, Stephen Lewis,
UN special envoy for AIDS in Africa, attacked Mbeki's government for
its slow response to the AIDS epidemic and reliance on denialist claims:
It [South Africa] is the only
country in Africa … whose government is still obtuse, dilatory and
negligent about rolling out treatment… It is the only country in Africa
whose government continues to promote theories more worthy of a lunatic
fringe than of a concerned and compassionate state.
In 2002, Mbeki requested that HIV/AIDS denialists no longer use his
name in their literature and stop signing documents with "Member of
President Mbeki's AIDS Advisory Panel".
This coincided with the South African government's statement
accompanying its 2002 AIDS campaign, that "...in conducting this
campaign, government's starting point is based on the premise that HIV
causes AIDS". Nonetheless, Mbeki himself continued to promote and defend AIDS-denialist claims. His loyalists attacked former President Nelson Mandela in 2002 when Mandela questioned the government's AIDS policy, and Mbeki attacked Malegapuru William Makgoba, one of South Africa's leading scientists, as a racist defender of "Western science" for opposing HIV/AIDS denialism.
In early 2005, former South African President Nelson Mandela
announced that his son had died of complications of AIDS. Mandela's
public announcement was seen as both an effort to combat the stigma
associated with AIDS, and as a "political statement designed to… force
the President [Mbeki] out of his denial."
Post-Mbeki government in South Africa
In 2008, Mbeki was ousted from power and replaced as President of South Africa by Kgalema Motlanthe. On Motlanthe's first day in office, he removed Manto Tshabalala-Msimang,
the controversial health minister who had promoted AIDS-denialist
claims and recommended garlic, beetroot, and lemon juice as treatments
for AIDS. Barbara Hogan,
newly appointed as health minister, voiced shame at the Mbeki
government's embrace of HIV/AIDS denialism and vowed a new course,
stating: "The era of denialism is over completely in South Africa."