| Value of G | Unit |
|---|---|
| 6.67430(15)×10−11 | N⋅m2⋅kg−2 |
| 6.67430(15)×10−8 | dyn⋅cm2⋅g−2 |
| 4.3009172706(3)×10−3 | pc⋅M⊙−1⋅(km/s)2 |

The gravitational constant (also known as the universal gravitational constant, the Newtonian constant of gravitation, or the Cavendish gravitational constant), denoted by the capital letter G, is an empirical physical constant involved in the calculation of gravitational effects in Sir Isaac Newton's law of universal gravitation and in Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity.
In Newton's law, it is the proportionality constant connecting the gravitational force between two bodies with the product of their masses and the inverse square of their distance. In the Einstein field equations, it quantifies the relation between the geometry of spacetime and the energy–momentum tensor (also referred to as the stress–energy tensor).
The measured value of the constant is known with some certainty to four significant digits. In SI units, its value is approximately 6.674×10−11 N⋅m2/kg2.
The modern notation of Newton's law involving G was introduced in the 1890s by C. V. Boys. The first implicit measurement with an accuracy within about 1% is attributed to Henry Cavendish in a 1798 experiment.
Definition
According to Newton's law of universal gravitation, the magnitude of the attractive force (F) between two bodies each with a spherically symmetric density distribution is directly proportional to the product of their masses, m1 and m2, and inversely proportional to the square of the distance, r, directed along the line connecting their centres of mass:
The gravitational constant appears in the Einstein field equations of general relativity,
Value and uncertainty
The gravitational constant is a physical constant that is difficult to measure with high accuracy. This is because the gravitational force is an extremely weak force as compared to other fundamental forces at the laboratory scale.
In SI units, the 2018 Committee on Data for Science and Technology (CODATA)-recommended value of the gravitational constant (with standard uncertainty in parentheses) is:
This corresponds to a relative standard uncertainty of 2.2×10−5. (22 ppm)
Natural units
Due to its use as a defining constant in some systems of natural units, particularly geometrized unit systems such as Planck units and Stoney units, the value of the gravitational constant will generally have a numeric value of 1 or a value close to it when expressed in terms of those units. Due to the significant uncertainty in the measured value of G in terms of other known fundamental constants, a similar level of uncertainty will show up in the value of many quantities when expressed in such a unit system.
Orbital mechanics
In astrophysics, it is convenient to measure distances in parsecs (pc), velocities in kilometres per second (km/s) and masses in solar units M⊙. In these units, the gravitational constant is:
This way of expressing G shows the relationship between the average density of a planet and the period of a satellite orbiting just above its surface.
For elliptical orbits, applying Kepler's 3rd law, expressed in units characteristic of Earth's orbit:
where distance is measured in terms of the semi-major axis of Earth's orbit (the astronomical unit, AU), time in years, and mass in the total mass of the orbiting system (M = M☉ + M🜨 + M☾).
The above equation is exact only within the approximation of the Earth's orbit around the Sun as a two-body problem in Newtonian mechanics, the measured quantities contain corrections from the perturbations from other bodies in the solar system and from general relativity.
From 1964 until 2012, however, it was used as the definition of the astronomical unit and thus held by definition:
The quantity GM—the product of the gravitational constant and the mass of a given astronomical body such as the Sun or Earth—is known as the standard gravitational parameter (also denoted μ). The standard gravitational parameter GM appears as above in Newton's law of universal gravitation, as well as in formulas for the deflection of light caused by gravitational lensing, in Kepler's laws of planetary motion, and in the formula for escape velocity.
This quantity gives a convenient simplification of various gravity-related formulas. The product GM is known much more accurately than either factor is.
| Body | μ = GM | Value | Relative uncertainty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sun | GM☉ | 1.32712440018(8)×1020 m3⋅s−2 | 6×10−11 |
| Earth | GM🜨 | 3.986004418(8)×1014 m3⋅s−2 | 2×10−9 |
Calculations in celestial mechanics can also be carried out using the units of solar masses, mean solar days and astronomical units rather than standard SI units. For this purpose, the Gaussian gravitational constant was historically in widespread use, k = 0.01720209895 radians per day, expressing the mean angular velocity of the Sun–Earth system. The use of this constant, and the implied definition of the astronomical unit discussed above, has been deprecated by the IAU since 2012.
History of measurement
Early history
The existence of the constant is implied in Newton's law of universal gravitation as published in the 1680s (although its notation as G dates to the 1890s), but is not calculated in his Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica where it postulates the inverse-square law of gravitation. In the Principia, Newton considered the possibility of measuring gravity's strength by measuring the deflection of a pendulum in the vicinity of a large hill, but thought that the effect would be too small to be measurable. Nevertheless, he had the opportunity to estimate the order of magnitude of the constant when he surmised that "the mean density of the earth might be five or six times as great as the density of water", which is equivalent to a gravitational constant of the order:
- G ≈ (6.7±0.6)×10−11 m3⋅kg−1⋅s−2
A measurement was attempted in 1738 by Pierre Bouguer and Charles Marie de La Condamine in their "Peruvian expedition". Bouguer downplayed the significance of their results in 1740, suggesting that the experiment had at least proved that the Earth could not be a hollow shell, as some thinkers of the day, including Edmond Halley, had suggested.
The Schiehallion experiment, proposed in 1772 and completed in 1776, was the first successful measurement of the mean density of the Earth, and thus indirectly of the gravitational constant. The result reported by Charles Hutton (1778) suggested a density of 4.5 g/cm3 (4+1/2 times the density of water), about 20% below the modern value. This immediately led to estimates on the densities and masses of the Sun, Moon and planets, sent by Hutton to Jérôme Lalande for inclusion in his planetary tables. As discussed above, establishing the average density of Earth is equivalent to measuring the gravitational constant, given Earth's mean radius and the mean gravitational acceleration at Earth's surface, by setting
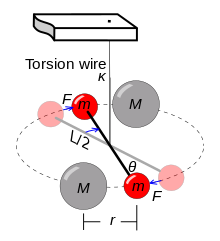
The first direct measurement of gravitational attraction between two bodies in the laboratory was performed in 1798, seventy-one years after Newton's death, by Henry Cavendish. He determined a value for G implicitly, using a torsion balance invented by the geologist Rev. John Michell (1753). He used a horizontal torsion beam with lead balls whose inertia (in relation to the torsion constant) he could tell by timing the beam's oscillation. Their faint attraction to other balls placed alongside the beam was detectable by the deflection it caused. In spite of the experimental design being due to Michell, the experiment is now known as the Cavendish experiment for its first successful execution by Cavendish.
Cavendish's stated aim was the "weighing of Earth", that is, determining the average density of Earth and the Earth's mass. His result, ρ🜨 = 5.448(33) g·cm−3, corresponds to value of G = 6.74(4)×10−11 m3⋅kg−1⋅s−2. It is surprisingly accurate, about 1% above the modern value (comparable to the claimed standard uncertainty of 0.6%).
19th century
The accuracy of the measured value of G has increased only modestly since the original Cavendish experiment. G is quite difficult to measure because gravity is much weaker than other fundamental forces, and an experimental apparatus cannot be separated from the gravitational influence of other bodies.
Measurements with pendulums were made by Francesco Carlini (1821, 4.39 g/cm3), Edward Sabine (1827, 4.77 g/cm3), Carlo Ignazio Giulio (1841, 4.95 g/cm3) and George Biddell Airy (1854, 6.6 g/cm3).
Cavendish's experiment was first repeated by Ferdinand Reich (1838, 1842, 1853), who found a value of 5.5832(149) g·cm−3, which is actually worse than Cavendish's result, differing from the modern value by 1.5%. Cornu and Baille (1873), found 5.56 g·cm−3.
Cavendish's experiment proved to result in more reliable measurements than pendulum experiments of the "Schiehallion" (deflection) type or "Peruvian" (period as a function of altitude) type. Pendulum experiments still continued to be performed, by Robert von Sterneck (1883, results between 5.0 and 6.3 g/cm3) and Thomas Corwin Mendenhall (1880, 5.77 g/cm3).
Cavendish's result was first improved upon by John Henry Poynting (1891), who published a value of 5.49(3) g·cm−3, differing from the modern value by 0.2%, but compatible with the modern value within the cited standard uncertainty of 0.55%. In addition to Poynting, measurements were made by C. V. Boys (1895) and Carl Braun (1897), with compatible results suggesting G = 6.66(1)×10−11 m3⋅kg−1⋅s−2. The modern notation involving the constant G was introduced by Boys in 1894 and becomes standard by the end of the 1890s, with values usually cited in the cgs system. Richarz and Krigar-Menzel (1898) attempted a repetition of the Cavendish experiment using 100,000 kg of lead for the attracting mass. The precision of their result of 6.683(11)×10−11 m3⋅kg−1⋅s−2 was, however, of the same order of magnitude as the other results at the time.
Arthur Stanley Mackenzie in The Laws of Gravitation (1899) reviews the work done in the 19th century. Poynting is the author of the article "Gravitation" in the Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition (1911). Here, he cites a value of G = 6.66×10−11 m3⋅kg−1⋅s−2 with an uncertainty of 0.2%.
Modern value
Paul R. Heyl (1930) published the value of 6.670(5)×10−11 m3⋅kg−1⋅s−2 (relative uncertainty 0.1%), improved to 6.673(3)×10−11 m3⋅kg−1⋅s−2 (relative uncertainty 0.045% = 450 ppm) in 1942.
However, Heyl used the statistical spread as his standard deviation, and he admitted himself that measurements using the same material yielded very similar results while measurements using different materials yielded vastly different results. He spent the next 12 years after his 1930-paper to do more precise measurements, hoping that the composition-dependent effect would go away, but it did not, as he noted in his final paper from the year 1942.
Published values of G derived from high-precision measurements since the 1950s have remained compatible with Heyl (1930), but within the relative uncertainty of about 0.1% (or 1,000 ppm) have varied rather broadly, and it is not entirely clear if the uncertainty has been reduced at all since the 1942 measurement. Some measurements published in the 1980s to 2000s were, in fact, mutually exclusive. Establishing a standard value for G with a standard uncertainty better than 0.1% has therefore remained rather speculative.
By 1969, the value recommended by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) was cited with a standard uncertainty of 0.046% (460 ppm), lowered to 0.012% (120 ppm) by 1986. But the continued publication of conflicting measurements led NIST to considerably increase the standard uncertainty in the 1998 recommended value, by a factor of 12, to a standard uncertainty of 0.15%, larger than the one given by Heyl (1930).
The uncertainty was again lowered in 2002 and 2006, but once again raised, by a more conservative 20%, in 2010, matching the standard uncertainty of 120 ppm published in 1986. For the 2014 update, CODATA reduced the uncertainty to 46 ppm, less than half the 2010 value, and one order of magnitude below the 1969 recommendation.
The following table shows the NIST recommended values published since 1969:

| Year | G (10−11·m3⋅kg−1⋅s−2) |
Standard uncertainty | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1969 | 6.6732(31) | 460 ppm |
|
| 1973 | 6.6720(49) | 730 ppm |
|
| 1986 | 6.67449(81) | 120 ppm |
|
| 1998 | 6.673(10) | 1,500 ppm |
|
| 2002 | 6.6742(10) | 150 ppm |
|
| 2006 | 6.67428(67) | 100 ppm |
|
| 2010 | 6.67384(80) | 120 ppm |
|
| 2014 | 6.67408(31) | 46 ppm |
|
| 2018 | 6.67430(15) | 22 ppm |
|
In the January 2007 issue of Science, Fixler et al. described a measurement of the gravitational constant by a new technique, atom interferometry, reporting a value of G = 6.693(34)×10−11 m3⋅kg−1⋅s−2, 0.28% (2800 ppm) higher than the 2006 CODATA value. An improved cold atom measurement by Rosi et al. was published in 2014 of G = 6.67191(99)×10−11 m3⋅kg−1⋅s−2. Although much closer to the accepted value (suggesting that the Fixler et al. measurement was erroneous), this result was 325 ppm below the recommended 2014 CODATA value, with non-overlapping standard uncertainty intervals.
As of 2018, efforts to re-evaluate the conflicting results of measurements are underway, coordinated by NIST, notably a repetition of the experiments reported by Quinn et al. (2013).
In August 2018, a Chinese research group announced new measurements based on torsion balances, 6.674184(78)×10−11 m3⋅kg−1⋅s−2 and 6.674484(78)×10−11 m3⋅kg−1⋅s−2 based on two different methods. These are claimed as the most accurate measurements ever made, with a standard uncertainties cited as low as 12 ppm. The difference of 2.7σ between the two results suggests there could be sources of error unaccounted for.
Constancy
Analysis of observations of 580 type Ia supernovae shows that the gravitational constant has varied by less than one part in ten billion per year over the last nine billion years.














