The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast territory was divided into several successor polities. The Roman Empire lost the strengths that had allowed it to exercise effective control over its Western provinces; modern historians posit factors including the effectiveness and numbers of the army, the health and numbers of the Roman population, the strength of the economy, the competence of the emperors, the internal struggles for power, the religious changes of the period, and the efficiency of the civil administration. Increasing pressure from invading barbarians outside Roman culture also contributed greatly to the collapse. Climatic changes and both endemic and epidemic disease drove many of these immediate factors. The reasons for the collapse are major subjects of the historiography of the ancient world and they inform much modern discourse on state failure.
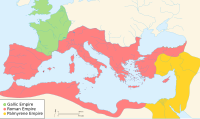
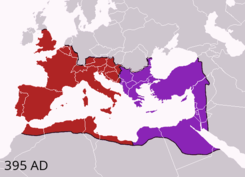
In 376, unmanageable numbers of Goths and other non-Roman people, fleeing from the Huns, entered the Empire. In 395, after winning two destructive civil wars, Theodosius I died, leaving a collapsing field army, and the Empire, still plagued by Goths, divided between the warring ministers of his two incapable sons. Further barbarian groups crossed the Rhine and other frontiers and, like the Goths, were not exterminated, expelled or subjugated. The armed forces of the Western Empire became few and ineffective, and despite brief recoveries under able leaders, central rule was never effectively consolidated.
By 476, the position of Western Roman Emperor wielded negligible military, political, or financial power, and had no effective control over the scattered Western domains that could still be described as Roman. Barbarian kingdoms had established their own power in much of the area of the Western Empire. In 476, the Germanic barbarian king Odoacer deposed the last emperor of the Western Roman Empire in Italy, Romulus Augustulus, and the Senate sent the imperial insignia to the Eastern Roman Emperor Zeno.
While its legitimacy lasted for centuries longer and its cultural influence remains today, the Western Empire never had the strength to rise again. The Eastern Roman, or Byzantine Empire, survived and, although lessened in strength, remained for centuries an effective power of the Eastern Mediterranean.
While the loss of political unity and military control is universally acknowledged, the Fall is not the only unifying concept for these events; the period described as late antiquity emphasizes the cultural continuities throughout and beyond the political collapse.
Historical approaches and modern syntheses
Since 1776, when Edward Gibbon published the first volume of his The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, Decline and Fall has been the theme around which much of the history of the Roman Empire has been structured. "From the eighteenth century onward," historian Glen Bowersock wrote, "we have been obsessed with the fall: it has been valued as an archetype for every perceived decline, and, hence, as a symbol for our own fears."
The Fall is not the only unifying concept for events of this time period; the period described as Late Antiquity emphasizes the cultural continuities throughout and beyond the political collapse.
Another paradigm of the period
From at least the time of Henri Pirenne (1862-1935), scholars have described a continuity of Roman culture and political legitimacy long after 476. Pirenne postponed the demise of classical civilization to the 8th century. He challenged the notion that Germanic barbarians had caused the Western Roman Empire to end, and he refused to equate the end of the Western Roman Empire with the end of the office of emperor in Italy. He pointed out the essential continuity of the economy of the Roman Mediterranean even after the barbarian invasions, and suggested that only the Muslim conquests represented a decisive break with antiquity.
The more recent formulation of a historical period characterized as "Late Antiquity" emphasizes the transformations of ancient to medieval worlds within a cultural continuity. In recent decades archaeologically based argument even extends the continuity in material culture and in patterns of settlement as late as the eleventh century. Observing the political reality of lost control (and the attendant fragmentation of commerce, culture, and language), but also the cultural and archaeological continuities, the process has been described as a complex cultural transformation, rather than a fall. As a result, for many contemporary scholars, "the perception of Late Antiquity has significantly changed: the period is no longer seen as an era of decline and crisis but as an epoch of metamorphosis in the Mediterranean region".
Timespan
A recent synthesis gives four decisive turns of events in the transformation from the height of the empire to the early Middle Ages:
- The Antonine Plague that ended a long period of demographic and economic expansion, weakening but not toppling the empire.
- The Crisis of the Third Century, in which climatic change, renewed pandemic disease, and internal and external political instability led to the near-collapse of the imperial system. Its reconstitution included a new basis for the currency, an expanded professional government apparatus, emperors further distanced from their people, and, shortly, the rise of Christianity, a proselytizing, exclusive religion that anticipated the imminent end of the world.
- The military and political failure of the West, in which mass migration from the Eurasian steppe overcame and dismembered the western part of an internally-weakened empire. The eastern empire rebuilt itself again and began the reconquest of the West.
- In the lands around the Mediterranean the Late Antique Little Ice Age and the Plague of Justinian created one of the worst environmental cataclysms in recorded history. The imperial system crumbled in the next couple of generations and then lost vast territories to the armies of Islam, a new proselytizing, exclusive religion that also looked forward to an imminent end time. The diminished and impoverished Byzantine rump state survived amid perpetual strife between and among the followers of Christianity and Islam.
The loss of centralized political control over the West, and the lessened power of the East, are universally agreed, but the theme of decline has been taken to cover a much wider time span than the hundred years from 376. For Cassius Dio, the accession of the emperor Commodus in 180 CE marked the descent "from a kingdom of gold to one of rust and iron". Since the age of humanism, the process of the Fall has been thought to have begun with Constantine the Great, or with the soldier emperors who seized power through command of the army from 235 through 284, or with Commodus, or even with Augustus.
Gibbon was uncertain about when decline began. "In the first paragraph of his text, Gibbon wrote that he intended to trace the decline from the golden age of the Antonines"; later text has it beginning about A.D. 180 with the death of Marcus Aurelius; while in chapter 7, he pushes the start of the decline to about 52 B.C., the time of Julius Caesar and Pompey and Cicero. Gibbon placed the western empire's end with the removal of the man Gibbon referred to as "the helpless Augustulus" in 476.
Arnold J. Toynbee and James Burke argue that the entire Imperial era was one of steady decay of institutions founded in republican times. Theodor Mommsen excluded the imperial period from his Nobel Prize-winning History of Rome (1854–1856). As one convenient marker for the end, 476 has been used since Gibbon, but other key dates for the fall of the Roman Empire in the West include the Crisis of the Third Century, the Crossing of the Rhine in 406 (or 405), the sack of Rome in 410, and the death of Julius Nepos in 480.
Underlying causes
When Gibbon published his landmark work, it quickly became the standard, and remained so for over 200 years. Peter Brown has written that "Gibbon's work formed the peak of a century of scholarship which had been conducted in the belief that the study of the declining Roman Empire was also the study of the origins of modern Europe". Gibbon was the first to attempt an explanation of causes of a Fall of empire. Historian Gerald J. Gruman explains Gibbon's views as built around two important concepts: "balance" and "excess". Gibbon's interpretation of the causes of the decline and fall of the Roman empire are primarily political and can be grouped under four political headings: universal domination, democracy, militarism and religion.
Universal domination
Gibbon assumes the best course for all nations is to preserve a balance of power between them. Without balance, humans produce domination, or its opposite excess, submergence. Rome's pursuit of empire led to its own demise, because such domination is "artificial and abnormal". Gibbon thought that, in its quest for world dominion, Rome had created a situation that intensified the evils of despotism, lost public freedom, and allowed the universal dominion of their Pax Romana to cause the deterioration of the political virtues. The Roman Empire included many different nations and cultures, and Rome pushed assimilation by offering citizenship in what Gibbon saw as a profligate manner. The citizens of the Roman world-empire "received the name without adopting the spirit of Romans". This led to what Gibbon saw as an obliteration of what it meant to be Roman.
Democracy
Gibbon admired the Roman aristocracy, and believed democracy led to anarchy and instability. He condemned Roman imperialism because it reduced nations to a mediocre uniformity, levelling all classes and individuals to a servile equality. What followed democracy's inevitable collapse was despotism. Gibbon accused despotism of weakening the military virtues (I, 194 and II, 522), of causing excessive taxation (II, 190), of fettering the mind (I, 58), and of producing other consequences fatal to the health of the empire.
Militarism
Like democracy and universal domination, militarism was considered by Gibbon to be one of the major causes of the decline and fall. To Gibbon, a standing army was a threatening element. So were individual soldiers. Gibbon explains, with irony, that the enrollment of barbarian troops accelerated the trend toward the "perversion" of pacifism in the broader society. The hiring of mercenary troops imposed a ruinous financial burden (I, 136), and the quality of those troops deteriorated. Successive generations of the governing class "experienced a failure of nerve, a loss of virtue, and so abdicated to successive groups of non-Romans the role of defending Rome". For Gibbon, that meant "the last sparks of the military flame were finally extinguished" (III, 130).
Religion
Gibbon's treatment of Christianity retains its place in political categorization as Gibbon characterized the Christian community of Antiquity as a polity even during its period of persecution. According to Clifford Ando, "Gibbon identifies three causes of the empire's decline and excuses two more. The two factors absolved are the barbarians and Christianity". This is because Gibbon saw empire as already advanced in decline before either of these became a factor. Christianity typified superstition in Gibbon's view, and its spirituality was subversive of the traditional Roman virtues (IV, 162), but monks and eunuchs were not agents of social change so much as they were symptoms of a decline already taking place.
Contemporary views
Modern historiography diverges from Gibbon. While most of his ideas are no longer accepted in totality, they have been foundational to later discourse and the modern synthesis with archaeology, epidemiology, climatic history, genetic science, and many more new sources of history beyond the documentary sources that were all that was available to Gibbon.
While it is true that Alexander Demandt enumerated 210 different theories on why Rome fell, twenty-first century scholarship sees the primary possibilities among these eight:
Climactic crisis
Scholars have long considered the possibility of worldwide drought. Allegedly, there was a steady decrease in rainfall from 200 CE to 400 CE, leading to fewer crops, famine, and the pressure of barbarians who were themselves pressed by others. The classicist Kyle Harper has summed up new evidence to interpret disease and climate change as important drivers of the political collapse of the empire. He describes a Roman climatic optimum from about 200 BCE to 150 CE, when lands around the Mediterranean were generally warm and well-watered. This made agriculture prosperous, army recruitment easy, and the collection of taxes straightforward. From about 150, the climate became on average somewhat worse for most of the inhabited lands around the Mediterranean. After about 450, the climate worsened further in the Late Antique Little Ice Age that may have directly contributed to the variety of factors that brought Rome down.
The Roman Empire was built on the fringes of the tropics. Its roads and its pirate-free seas, which produced an abundance of trade, also unknowingly created an interconnected disease ecology that unleashed the evolution and spread of pathogens. Pandemics contributed to massive demographic changes, economic crises, and food shortages in the crisis of the third century. Heavy mortality in 165–180 from the Antonine Plague seriously impaired attempts to repel Germanic invaders, but the legions generally held or at least speedily re-instated the borders of the Empire.
Demographic crisis
Population increases that outstrip resources end in depopulation from famine and migration. From 376, massive populations moved into the Empire, driven by the Huns who themselves may have been driven by climate change in the Eurasian steppe, These barbarian invasions led ultimately to barbarian kingdoms over much of the former territory of the Western Empire. But the final blow came only with the Late Antique Little Ice Age and its aftermath, when Rome was already politically fragmented and materially depleted.
Political crisis
Aurelian reunited the empire in 274, and from 284 Diocletian and his successors reorganized it with more emphasis on the military. John the Lydian, writing over two centuries later, reported that Diocletian's army at one point totaled 389,704 men, plus 45,562 in the fleets, and numbers may have increased later. With the limited communications of the time, both the European and the Eastern frontiers needed the attention of their own supreme commanders. Diocletian tried to solve this problem by re-establishing an adoptive succession with a senior (Augustus) and junior (Caesar) emperor in each half of the Empire, but this system of tetrarchy broke down within one generation and the hereditary principle re-established itself with generally unfortunate results. Thereafter civil war became again the main method of establishing new imperial regimes. Although Constantine the Great (in office 306 to 337) again re-united the Empire, towards the end of the fourth century the need for division was generally accepted. From then on, the Empire existed in constant tension between the need for two emperors and their mutual mistrust.
Until late in the fourth century, the united Empire retained sufficient power to launch powerful attacks against its enemies in Germania and in the Sasanian Empire. Receptio of barbarians became widely practised: imperial authorities admitted potentially hostile groups into the Empire, split them up, and allotted to them lands, status, and duties within the imperial system. In this way many groups provided unfree workers (coloni) for Roman landowners, and recruits (laeti) for the Roman army. Sometimes their leaders became officers. Normally the Romans managed the process carefully, with sufficient military force on hand to ensure compliance. Cultural assimilation followed over the next generation or two.
C. Ferraro sees political crisis as a crisis of authority. "The third century revolution, the victory of the masses, the physical destruction of the cultivated class had as its consequence a "bolshevization" fatal to civilization". However, there are no studies demonstrating that leaders of Late Antiquity cannot be favorably compared to those of earlier periods. In empire, Ferraro says the masses lost the kind of liberty that had been available in the Republic, they no longer had a share in determining policy, and as imperial power grew "even the municipal aristocracy was put in custody under the empire". There was a centralization of power in empire, however, the pioneering studies of Sabine MacCormack have shown the court culture that developed with Diocletian was still subject to pressure from below. Imperial proclamations were used to stress the traditional limitations of the imperial office while imperial ceremonies "left room for consensus and popular participation".
Financial crisis
The Empire suffered multiple serious crises during the third century. The rising Sassanid Empire inflicted three crushing defeats on Roman field armies and remained a potent threat for centuries. Other disasters included repeated civil wars, barbarian invasions, and more mass-mortality in the Plague of Cyprian (from 250 onwards). For a short period, the Empire split into a Gallic Empire in the West (260–274), a Palmyrene Empire in the East (260–273), and a central Roman rump state; in 271, Rome abandoned the province of Dacia on the north of the Danube. The Rhine/Danube frontier also came under more effective threats from larger barbarian groupings, which had developed improved agriculture and increased their populations. The average stature of the population in the West suffered a serious decline in the late second century; the population of Northwestern Europe did not recover, though the Mediterranean regions did.
The Empire survived the "Crisis of the Third Century", directing its economy successfully towards defense, but survival came at the price of a more centralized and bureaucratic state. Under Gallienus (Emperor from 253 to 268) the senatorial aristocracy ceased joining the ranks of the senior military commanders. Its typical members lacked interest in military service, and showed incompetence at command.
There was a decline of slavery, but it is unknown whether that was a cause or an effect of economic change, or both, or neither. There was a decline of the cities as many Roman aristocrats moved out and built their own large, self-sufficient manors in the countryside. They became the state's tax collectors largely because of the needs of the army. Monetary instability and an insecure fiscal policy were both exacerbated by war.
Under Constantine, the cities lost their revenue from local taxes, and under Constantius II (r. 337–361) their endowments of property. This worsened the existing difficulty in keeping the city councils up to strength, and the services provided by the cities were scamped or abandoned. Public building projects had declined since the second century. There is no evidence of state participation in, or support for, restoration and maintenance of temples and shrines. Restorations were funded and accomplished privately, which limited what was done. A further financial abuse was Constantius's habit of granting to his immediate entourage the estates of persons condemned for treason and other capital crimes. This practice reduced future though not immediate income, and those close to the emperor gained a strong incentive to encourage his suspicion of conspiracies.
Social crisis
The new supreme rulers disposed of the legal fiction of the early Empire (seeing the emperor as but the first among equals); emperors from Aurelian (r. 270–275) onwards openly styled themselves as dominus et deus, "lord and god", titles appropriate for a master-slave relationship. An elaborate court ceremonial developed, and obsequious flattery became the order of the day. Under Diocletian, the flow of direct requests to the emperor rapidly reduced, and soon ceased altogether. No other form of direct access replaced them, and the emperor received only information filtered through his courtiers.
Official cruelty, supporting extortion and corruption, may also have become more commonplace. While the scale, complexity, and violence of government were unmatched, the emperors lost control over their whole realm insofar as that control came increasingly to be wielded by anyone who paid for it. Meanwhile, the richest senatorial families, immune from most taxation, engrossed more and more of the available wealth and income while also becoming divorced from any tradition of military excellence. One scholar identifies a great increase in the purchasing power of gold, two and a half fold from 274 to the later fourth century. This may be an index of growing economic inequality between a gold-rich elite and a cash-poor peasantry.
Within the late Roman military, many recruits and even officers had barbarian origins. Soldiers are recorded as using possibly-barbarian rituals, such as elevating a claimant on shields. Some scholars have seen this as an indication of weakness. Others disagree, seeing neither barbarian recruits nor new rituals as causing any problem with the effectiveness or loyalty of the army, at least while that army was led by officers who identified as Roman and was effectively disciplined, trained, paid, and supplied.
Moral crisis
"Formerly, says Ammianus, Rome was saved by her austerity, by solidarity between rich and poor, by contempt for death; now she is undone by her luxury and greed (6 Amm. xxxi. 5. 14 and). Innumerable are the statements of Church Fathers that stigmatize the immorality of both the nobles and the poor. Salvianus backs up Ammianus by affirming that greed (avaritia) is a vice common to nearly all Romans".
Intellectual crisis
This is based in the belief that education declined as democracy and the masses rose. However, the educational program designed by Augustine came from Hellenist traditions, and Christianity traditionally spread through education.
Geography
A. H. M. Jones has pointed out that the earlier scholarly views are Western. Most of the weaknesses discussed by scholars were "common to both halves of the empire", with Christianity even more prevalent in the East than the West. Religious disputes were bitter, bureaucracy corrupt and extortionate, it had a caste system, and land fell out of use in the East just as it had in the West. Yet the East stood its ground in the fifth century, fought back in the sixth, and even recovered some territory in the seventh. The East had only one apparent advantage: geography. It was less vulnerable, strategically, than the West. The narrowest sea crossing to its core territories was protected from the northern barbarians by the fortifications and the sea and land forces of Constantinople, while the European frontier from the mouth of the Rhine to that of the Danube is some 2000 kilometres great-circle distance and could be crossed with much less difficulty. "The devastations of the barbarians impoverished and depopulated the [Western] frontier provinces, and their unceasing pressure imposed on the empire a burden of defense which overstrained its administrative machinery and its economic resources. ... [playing] a major part in the fall of the West".
Height of power, systematic weaknesses as direct causes
The Roman Empire reached its greatest geographical extent under Trajan (r. 98–117), who ruled a prosperous state that stretched from Armenia to the Atlantic Ocean. The Empire had large numbers of trained, supplied, and disciplined soldiers, drawn from a growing population. It had a comprehensive civil administration based in thriving cities with effective control over public finances. The literate elite considered theirs to be the only worthwhile form of civilization, giving the Empire ideological legitimacy and a cultural unity based on comprehensive familiarity with Greek and Roman literature and rhetoric. The Empire's power allowed it to maintain extreme differences of wealth and status. André Piganiol writes that in Late Antiquity, "The unheard-of luxury of the wealthy contrasts brutally with the misery of the poor, which reaches utter beggary". Its wide-ranging trade networks permitted even modest households to use goods made by professionals far away.
The empire had both strength and resilience. Its financial system allowed it to raise significant taxes which, despite endemic corruption, supported a large regular army with logistics and training. The cursus honorum, a standardized series of military and civil posts organised for ambitious aristocratic men, ensured that powerful noblemen had the opportunity to become familiar with military and civil command and administration. At a lower level within the army, connecting the aristocrats at the top with the private soldiers, a large number of centurions were well-rewarded, literate, and responsible for training, discipline, administration, and leadership in battle. City governments with their own properties and revenues functioned effectively at a local level; membership of city councils involved lucrative opportunities for independent decision-making, and, despite its obligations, became seen as a privilege. Under a series of emperors who each adopted a mature and capable successor, the Empire did not require civil wars to regulate the imperial succession. Requests could be submitted directly to the better emperors, and the answers had the force of law, putting the imperial power directly in touch with even humble subjects. The cults of polytheist religion were hugely varied, but none claimed that theirs was the only truth. Their followers displayed mutual tolerance, producing a polyphonous religious harmony. Religious strife was rare after the suppression of the Bar Kokhba revolt in 136, after which the devastated Judaea ceased to be a major centre for Jewish unrest.
Nevertheless, it remained a culture based on an early subsistence economy, with only ineffective inklings of a germ theory of disease. Despite its aqueducts, the water supply did not allow good hygiene. Sewage was disposed of on the streets, in open drains, or by scavenging animals. Even in the Roman Climatic Optimum, local harvest failures causing famines were always a possibility. And even in good times, Roman women needed to have, on average, six children each in order to maintain the population. Good nourishment and bodily cleanliness were privileges of the rich, advertised by their firm tread, healthy skin color, and lack of the "dull smell of the underbathed". Infant mortality was very high, and diarrhoeal diseases were a major cause of death. Malaria was endemic in many areas, notably in the city of Rome itself, possibly encouraged by the enthusiasm of rich Romans for water features in their gardens.
Rise of Christianity, possible decline of the armed forces
In 313, Constantine the Great declared official toleration of Christianity. This was followed over the ensuing decades by the search for a definition of Christian orthodoxy all could agree upon. Creeds were developed, but Christianity has never agreed upon an official version of its Bible or its doctrine; instead it has had many different manuscript traditions. Christianity's disputes may have effected decline. Official and private action was taken against heterodox Christians (heretics) from the fourth century up to the modern era. Limited action against pagans, who were mostly ignored, was based on the contempt that accompanied Christianity's sense of triumph after Constantine. Christianity opposed sacrifice and magic, and Christian emperors made laws that favored Christianity. Constantine's successors generally continued this approach, and by the end of the fourth century, Christianity had become the religion of any ambitious civil official.
The wealth of the Christian Church increased dramatically in the fifth century. Immense resources, both public and private, were used for building churches, storage barns for the grain used for charity, new hospitals for the poor, and in support of those in religious life without other income. Bishops in wealthy cities were thus able to offer patronage in the long-established manner of Roman aristocrats. Ammianus described some who "enriched from the offerings of matrons, ride seated in carriages, wearing clothing chosen with care, and serve banquets so lavish that their entertainments outdo the tables of kings".
But the move to Christianity probably had no significant effects on public finances. The large temple complexes, with professional full-time priests, festivals, and large numbers of sacrifices (which became free food for the masses), had also been expensive to maintain. They had already been negatively impacted by the empire's financial struggles in the third century. The numbers of clergy, monks, and nuns increased to perhaps half the size of the actual army, and they have been considered as a drain on limited manpower.
The numbers and effectiveness of the regular soldiers may have declined during the fourth century. Payrolls were inflated, so that pay could be diverted and exemptions from duty sold. The soldiers' opportunities for personal extortion were multiplied by residence in cities, while their effectiveness was reduced by concentration on extortion instead of military exercises. However, extortion, gross corruption, and occasional ineffectiveness were not new to the Roman army. There is no consensus whether its effectiveness significantly declined before 376. Ammianus Marcellinus, himself a professional soldier, repeats longstanding observations about the superiority of contemporary Roman armies being due to training and discipline, not to individual size or strength. Despite a possible decrease in the Empire's ability to assemble and supply large armies, Rome maintained an aggressive and potent stance against perceived threats almost to the end of the fourth century.
313–376: Civil and foreign wars
Constantine settled Franks on the lower left bank of the Rhine. Their communities required a line of fortifications to keep them in check, indicating that Rome had lost almost all local control. Under Constantius, bandits came to dominate areas such as Isauria, which were well within the empire. The tribes of Germania also became more populous and more threatening. In Gaul, which did not really recover from the invasions of the third century, there was widespread insecurity and economic decline in the 300s, perhaps worst in Armorica. By 350, after decades of pirate attacks, virtually all villas in Armorica were deserted. Local use of money ceased about 360. Repeated attempts to economize on military expenditure included billeting troops in cities, where they could less easily be kept under military discipline and could more easily extort from civilians. Except in the rare case of a determined and incorruptible general, these troops proved ineffective in action and dangerous to civilians. Frontier troops were often given land rather than pay. As they farmed for themselves, their direct costs diminished, but so did their effectiveness, and their pay gave much less stimulus to the frontier economy. However, except for the provinces along the lower Rhine, the agricultural economy was generally doing well.
On January 18 350, the imperial magister officiorum gave a banquet in Augustodunum while his master, Western Emperor Constans, was away hunting. During the feast Magnus Magnentius, commander of the imperial household troops, appeared in an imperial purple toga and announced himself to be the new Emperor. Constans was soon murdered and Magnentius took over most of his western domains. He made peace overtures to Constantius in the East, but these failed. In the ensuing bloody civil war Magnentius marched against Constantius with as many troops as he could mobilize, stripping the Rhine frontier of its most effective troops. Magnentius died and so did many of his men. Meanwhile, Constantius sent messages to the German tribes east of the Rhine, inviting them to attack Gaul, which they did. In the next few years a strip some 40 miles wide to the west of the Rhine was occupied by the Germans, and a further 120 miles into Gaul the surviving population and garrisons had fled.
Julian (r. 360–363) won victories against Germans who had invaded Gaul. He launched a drive against official corruption, which allowed the tax demands in Gaul to be reduced to one-third of their previous amount, while all government requirements were still met. In civil legislation, Julian was notable for his pro-pagan policies. Julian lifted the ban on sacrifices, restored and reopened temples, and dismantled the privileged tax status and revenue concessions of the Christians. He gave generous tax remissions to the cities which he favored, and disfavor to those who remained Christian. Julian ordered toleration of varieties of Christianity banned as heretical by Constantius; possibly, he would not have been able to persecute effectively such a large and powerful group as Christians had now become.
Julian prepared for civil war against Constantius, who again encouraged the Germans to attack Gaul. However Julian's campaigns had been effective and only one small Alemannic raid, speedily dealt with by Julian, resulted. Constantius died before any serious fighting and Julian was acknowledged as master of the entire Empire. He launched an expensive campaign against the Sasanian Persians,. He succeeded in marching to the Sassanid capital of Ctesiphon, but, at the suggestion of a Persian agent, burned his boats and supplies to show resolve in continuing operations. The Sassanids then burned crops so the Roman army had no food. Finding himself cut off without supplies in enemy territory, Julian began a land retreat, and during the Battle of Samarra, he was mortally wounded.
Julian's successor Jovian, acclaimed by a demoralized army, began his brief reign (363–364) while trapped in Mesopotamia without supplies. To purchase safe passage home, he had to concede areas of northern Mesopotamia, including the strategically important fortress of Nisibis. This fortress had been Roman since before the Peace of Nisibis in 299.
The brothers Valens (r. 364–378) and Valentinian I (r. 364–375) energetically tackled the threats of barbarian attacks on all the Western frontiers. They also tried to alleviate the burdens of taxation, which had risen continuously over the previous forty years; Valens in the East reduced the tax demand by half in his fourth year. Both of them were Christians, and re-confiscated the temple lands which Julian had restored. But they were generally tolerant of other beliefs. Valentinian in the West refused to intervene in Christian controversy. In the East, Valens had to deal with Christians who did not conform to his ideas of orthodoxy, and persecution formed part of his response. He tolerated paganism, even keeping some of Julian's associates in their trusted positions. He confirmed the rights and privileges of the pagan priests, and confirmed the right of pagans to be the exclusive caretakers of their temples.
Valentinian died of an apoplexy while shouting at envoys of Germanic leaders. His successors in the West were children, his sons Gratian (r. 375–383) and Valentinian II (r. 375–392). Gratian, "alien from the art of government both by temperament and by training", removed the Altar of Victory from the Senate House. He also rejected the pagan title of Pontifex Maximus.
376–395: Invasions, civil wars, and religious discord
Battle of Adrianople
In 376, the East faced an enormous barbarian influx across the Danube, mostly Goths, who were fleeing from the Huns. They were exploited by corrupt officials rather than effectively relieved and resettled, and they took up arms and were joined by more Goths and some Alans and Huns. Valens was in Asia with his main field army preparing for an assault on the Sasanian Empire. Redirection of the army and its logistic support would have required time, and Gratian's armies were distracted by Germanic invasions across the Rhine. In 378, Valens attacked the invaders with the Eastern field army, now perhaps 20,000 men, probably much fewer than the forces that Julian had led into Mesopotamia a little over a decade before, and possibly only 10% of the soldiers nominally available in the Danube provinces. In the Battle of Adrianople (9 August 378), Valens lost much of that army and his own life. All of the Balkan provinces were thus exposed to raiding, without effective response from the remaining garrisons who were "more easily slaughtered than sheep". Cities were able to hold their own defensive walls against barbarians who had no siege equipment, therefore the cities generally remained intact, although the countryside suffered.
Partial recovery in the Balkans, internal corruption and financial desperation
Gratian appointed a new Augustus, a proven general from Hispania called Theodosius. During the next four years, he partially re-established the Roman position in the East. These campaigns depended on effective imperial coordination and mutual trust — between 379 and 380, Theodosius controlled not only the Eastern empire, but also, by agreement, the diocese of Illyricum. Theodosius was unable to recruit enough Roman troops, relying on barbarian warbands without Roman military discipline or loyalty. (In contrast, during the Cimbrian War, the Roman Republic, controlling a smaller area than the western Empire, had been able to reconstitute large regular armies of citizens after greater defeats than Adrianople. That war had ended with the near-extermination of the invading barbarian supergroups, each supposed to have more than 100,000 warriors.)
The final Gothic settlement was acclaimed with relief, even the official panegyrist admitting that these Goths could not be expelled or exterminated, nor reduced to unfree status. Instead they were either recruited into the imperial forces, or settled in the devastated provinces along the south bank of the Danube, where the regular garrisons were never fully re-established. In some later accounts, and widely in recent work, this is regarded as a treaty settlement, the first time that barbarians were given a home within the Empire, in which they retained their political and military cohesion. No formal treaty is recorded, nor details of whatever agreement was actually made. When the Goths are next mentioned in Roman records, they have different leaders and are soldiers of a sort. In 391, Alaric, a Gothic leader, rebelled against Roman control. Goths attacked the emperor himself, but within a year Alaric was accepted as a leader of Theodosius's Gothic troops and this rebellion was over.
Theodosius's financial position must have been difficult, since he had to pay for expensive campaigning from a reduced tax base. The business of subduing barbarian warbands also demanded substantial gifts of precious metal. At least one extra levy provoked desperation and rioting, in which the emperor's statues were destroyed. Nevertheless, he is represented as financially generous as emperor, though frugal in his personal life. By the end of the 380s, Theodosius and the court were in Mediolanum, and northern Italy was experiencing a period of prosperity for the great landowners who took advantage of the court's need for food, "turning agrarian produce into gold", while repressing and misusing the poor who grew it and brought it in. Paulinus the Deacon, notary of Ambrose the bishop of Milan, described these men as creating a court where "everything was up for sale". Ambrose himself preached a series of sermons aimed at his wealthy constituents, asserting that avarice leads to a breakdown in society.
For centuries, Theodosius was regarded as a champion of Christian orthodoxy who decisively stamped out paganism. His predecessors Constantine, Constantius II, and Valens had all been semi-Arians, whereas Theodosius supported Nicene Christianity which eventually became the orthodox version of Christology for most later Christian churches - his Edict of Thessalonica described Arian Christians as "foolish madmen". Therefore, as far as Ambrose and the Christian literary tradition that followed him were concerned, Theodosius deserved most of the credit for the final triumph of Christianity. Modern scholars see this as a Christian interpretation of history rather than as a representation of history. Theodosius did not stamp out paganism, which continued into the seventh century.
Civil wars
Theodosius had to face a powerful usurper in the West; Magnus Maximus declared himself Emperor in 383, stripped troops from the outlying regions of Roman Britain (probably replacing some with federate chieftains and their war-bands) and invaded Gaul. His troops killed Gratian and he was accepted as Augustus in the Gallic provinces, where he was responsible for the first official executions of Christian heretics. To compensate the Western court for the loss of Gaul, Hispania, and Britannia, Theodosius ceded the diocese of Dacia and the diocese of Macedonia to their control. In 387 Maximus invaded Italy, forcing Valentinian II to flee to the East, where he accepted Nicene Christianity. Maximus boasted to Ambrose of the numbers of barbarians in his forces, and hordes of Goths, Huns, and Alans followed Theodosius. Maximus negotiated with Theodosius for acceptance as Augustus of the West, but Theodosius refused, gathered his armies, and counterattacked, winning the civil war in 388. There were heavy troop losses on both sides of the conflict. Later Welsh legend has Maximus's defeated troops resettled in Armorica, instead of returning to Britannia, and by 400, Armorica was controlled by Bagaudae rather than by imperial authority.
Theodosius restored Valentinian II, still a very young man, as Augustus in the West. He also appointed Arbogast, a pagan general of Frankish origin, as Valentinian's commander-in-chief and guardian. Valentinian quarreled in public with Arbogast, failed to assert any authority, and died, either by suicide or by murder, at the age of 21. Arbogast and Theodosius failed to come to terms and Arbogast nominated an imperial official, Eugenius (r. 392–394), as emperor in the West. Eugenius made some modest attempts to win pagan support, and with Arbogast led a large army to fight another destructive civil war. They were defeated and killed at the Battle of the Frigidus, which was attended by further heavy losses; especially among the Gothic federates of Theodosius. The north-eastern approaches to Italy were never effectively garrisoned again.
Theodosius died a few months later in early 395, leaving his young sons Honorius (r. 393–423) and Arcadius (r. 383–408) as emperors. In the immediate aftermath of Theodosius's death, the magister militum Stilicho, married to Theodosius's niece, asserted himself in the West as the guardian of Honorius and commander of the remains of the defeated Western army. He also claimed control over Arcadius in Constantinople, but Rufinus, magister officiorum on the spot, had already established his own power there. Henceforward the Empire was not under the control of one man, until much of the West had been permanently lost. Neither Honorius nor Arcadius ever displayed any ability either as rulers or as generals, and both lived as the puppet rulers of their courts. Stilicho tried to reunite the Eastern and Western courts under his personal control, but in doing so achieved only the continued hostility of all of Arcadius's successive supreme ministers.
Military, financial, and political ineffectiveness: the process of failure
The ineffectiveness of Roman military responses during Stilicho's rule and afterwards has been described as "shocking". There is little evidence of indigenous field forces or of adequate training, discipline, pay, or supply for the barbarians who formed most of the available troops. Local defence was occasionally effective, but was often associated with withdrawal from central control and taxes. In many areas, barbarians under Roman authority attacked culturally-Roman "Bagaudae". The fifth-century Western emperors, with brief exceptions, were individuals incapable of ruling effectively or even of controlling their own courts. Those exceptions were responsible for brief, but remarkable resurgences of Roman power.
Corruption, in this context the diversion of finance from the needs of the army, may have contributed greatly to the Fall. The rich senatorial aristocrats in Rome itself became increasingly influential during the fifth century; they supported armed strength in theory, but did not wish to pay for it or to offer their own workers as army recruits. They did, however, pass large amounts of money to the Christian Church. At a local level, from the early fourth century, the town councils lost their property and their power, which often became concentrated in the hands of a few local despots beyond the reach of the law.
395–406: Stilicho
Without an authoritative ruler, the Balkan provinces fell rapidly into disorder. Alaric was disappointed in his hopes for promotion to magister militum after the battle of the Frigidus. He again led Gothic tribesmen in arms and established himself as an independent power, burning the countryside as far as the walls of Constantinople. Alaric's ambitions for long-term Roman office were never quite acceptable to the Roman imperial courts, and his men could never settle long enough to farm in any one area. They showed no inclination to leave the Empire and face the Huns from whom they had fled in 376. Meanwhile, the Huns were still stirring up further migrations, with migrating tribes often attacking the Roman Empire in turn. Alaric's group was never destroyed nor expelled from the Empire, nor acculturated under effective Roman domination.
Stilicho's attempts to unify the Empire, revolts, and invasions
Alaric took his Gothic army on what Stilicho's propagandist Claudian described as a "pillaging campaign" that began first in the East. Alaric's forces made their way along the coast to Athens, where he sought to force a new peace upon the Romans. His march in 396 passed through Thermopylae. Stilicho sailed from Italy to Roman Greece with his remaining mobile forces, posing a clear threat to Rufinus' control of the Eastern empire. The bulk of Rufinus' forces were occupied with Hunnic incursions in Asia Minor and Syria, leaving Thracia undefended. Stilicho's propagandist Claudian reports that only Stilicho's attack stemmed the plundering, as he pushed Alaric's forces north into Epirus. Burns' interpretation is that Alaric and his men had been recruited by Rufinus's Eastern regime, and sent to Thessaly to stave off Stilicho's threat. No battle took place. Zosimus adds that Stilicho's troops destroyed and pillaged too, and let Alaric's men escape with their plunder.
Many of Stilicho's Eastern forces wanted to go home and he had to let them go (though Claudian claims that he did so willingly). Some went to Constantinople under the command of one Gainas, a Goth with a large Gothic following. On arrival, Gainas murdered Rufinus, and was appointed magister militum for Thrace by Eutropius, the new supreme minister and the only eunuch consul of Rome. Eutropius reportedly controlled Arcadius "as if he were a sheep". Stilicho obtained a few more troops from the German frontier and continued to campaign ineffectively against the Eastern empire; again he was successfully opposed by Alaric and his men. During the next year, 397, Eutropius personally led his troops to victory over some Huns who were marauding in Asia Minor. With his position thus strengthened, he declared Stilicho a public enemy, and he established Alaric as magister militum per Illyricum. A poem by Synesius advises the emperor to display manliness and remove a "skin-clad savage" (probably Alaric) from the councils of power and his barbarians from the Roman army. We do not know if Arcadius ever became aware of the existence of this advice, but it had no recorded effect. Synesius, from a province suffering the widespread ravages of a few poor but greedy barbarians, also complained of "the peacetime war, one almost worse than the barbarian war and arising from military indiscipline and the officer's greed."
The magister militum in the Diocese of Africa declared for the East and stopped the supply of grain to Rome. Italy had not fed itself for centuries and could not do so now. In 398, Stilicho sent his last reserves, a few thousand men, to re-take the Diocese of Africa. He strengthened his position further when he married his daughter Maria to Honorius. Throughout this period Stilicho, and all other generals, were desperately short of recruits and supplies for them. In 400, Stilicho was charged to press into service any "laetus, Alamannus, Sarmatian, vagrant, son of a veteran" or any other person liable to serve. He had reached the bottom of his recruitment pool. Though personally not corrupt, he was very active in confiscating assets; the financial and administrative machine was not producing enough support for the army.
In 399, Tribigild's rebellion in Asia Minor allowed Gainas to accumulate a significant army (mostly Goths), become supreme in the Eastern court, and execute Eutropius. He now felt that he could dispense with Alaric's services and he nominally transferred Alaric's province to the West. This administrative change removed Alaric's Roman rank and his entitlement to legal provisioning for his men, leaving his army—the only significant force in the ravaged Balkans—as a problem for Stilicho. In 400, the citizens of Constantinople revolted against Gainas and massacred as many of his people, soldiers and their families, as they could catch. Some Goths at least built rafts and tried to cross the strip of sea that separates Asia from Europe; the Roman navy slaughtered them. By the beginning of 401, Gainas' head rode a pike through Constantinople while another Gothic general became consul. Meanwhile, groups of Huns started a series of attacks across the Danube, and the Isaurians marauded far and wide in Anatolia.
In 401 Stilicho travelled over the Alps to Raetia, to scrape up further troops. He left the Rhine defended only by the "dread" of Roman retaliation, rather than by adequate forces able to take the field. Early in spring, Alaric, probably desperate, invaded Italy, and he drove Honorius westward from Mediolanum, besieging him in Hasta Pompeia in Liguria. Stilicho returned as soon as the passes had cleared, meeting Alaric in two battles (near Pollentia and Verona) without decisive results. The Goths, weakened, were allowed to retreat back to Illyricum where the Western court again gave Alaric office, though only as comes and only over Dalmatia and Pannonia Secunda rather than the whole of Illyricum. Stilicho probably supposed that this pact would allow him to put Italian government into order and recruit fresh troops. He may also have planned with Alaric's help to relaunch his attempts to gain control over the Eastern court.
However, in 405, Stilicho was distracted by a fresh invasion of Northern Italy. Another group of Goths fleeing the Huns, led by one Radagaisus, devastated the north of Italy for six months before Stilicho could muster enough forces to take the field against them. Stilicho recalled troops from Britannia, and the depth of the crisis was shown when he urged all Roman soldiers to allow their personal slaves to fight beside them. His forces, including Huns and Alans, may in the end have totalled rather less than 15,000 men. Radagaisus was defeated and executed, while 12,000 prisoners from the defeated horde were drafted into Stilicho's service. Stilicho continued negotiations with Alaric; Flavius Aetius, son of one of Stilicho's major supporters, was sent as a hostage to Alaric in 405.
In 406, Stilicho heard of new invaders and rebels who had appeared in the northern provinces. He insisted on making peace with Alaric, probably on the basis that Alaric would prepare to move either against the Eastern court or against the rebels in Gaul. The Senate deeply resented peace with Alaric.
In 407, Alaric marched into Noricum and demanded a large payment for his expensive efforts in Stilicho's interests. The senate, "inspired by the courage, rather than the wisdom, of their predecessors," preferred war. One senator famously declaimed Non est ista pax, sed pactio servitutis ("This is not peace, but a pact of servitude"). Stilicho paid Alaric four thousand pounds of gold nevertheless. Stilicho sent Sarus, a Gothic general, over the Alps to face the usurper Constantine III. Sarus lost this campaign and barely escaped, having to leave his baggage to the bandits who now infested the Alpine passes.
The empress Maria, daughter of Stilicho, died in 407 or early 408 and her sister Aemilia Materna Thermantia married Honorius. In the East, Arcadius died on 1 May 408 and was replaced by his son Theodosius II. Stilicho seems to have planned to march to Constantinople, and to install there a regime loyal to himself. He may also have intended to give Alaric a senior official position, and to send him against the rebels in Gaul. Before he could do so, while he was away at Ticinum at the head of a small detachment, a bloody coup d'état against his supporters took place at Honorius's court. It was led by Stilicho's own creature, one Olympius.
408–410: End of effective regular field armies, starvation in Italy, sack of Rome
Stilicho's fall and Alaric's reaction
Stilicho had news of the coup at Bononia, where he was probably waiting for Alaric. His army of barbarian troops, including a guard of Huns and many Goths under Sarus, discussed attacking the forces of the coup, but Stilicho prevented them when he heard that the Emperor had not been harmed. Sarus's Gothic troops then massacred the Hun contingent in their sleep, and Stilicho withdrew from the quarreling remains of his army to Ravenna. He ordered that his former soldiers should not be admitted into the cities in which their families were billeted. Stilicho was forced to flee to a church for sanctuary, promised his life, and killed.
Alaric was again declared an enemy of the Emperor. The conspiracy then massacred the families of the federate troops (as presumed supporters of Stilicho, although they had probably rebelled against him), and the troops defected en masse to Alaric. The conspirators seem to have let their main army disintegrate, and had no policy except hunting down anyone they regarded as supporters of Stilicho. Italy was left without effective indigenous defence forces thereafter. Heraclianus, a co-conspirator of Olympius, became governor of the Diocese of Africa. He consequently controlled the source of most of Italy's grain, and he supplied food only in the interests of Honorius's regime.
As a declared 'enemy of the Emperor', Alaric was denied the legitimacy that he needed to collect taxes and hold cities without large garrisons, which he could not afford to detach. He again offered to move his men, this time to Pannonia, in exchange for a modest sum of money and the modest title of Comes. He was refused, as Olympius's clique still regarded him as a supporter of Stilicho. He moved into Italy, probably using the route and supplies arranged for him by Stilicho, bypassing the imperial court in Ravenna which was protected by widespread marshland and had a port, and he menaced the city of Rome itself. In 407, there was no equivalent of the determined response to the catastrophic Battle of Cannae in 216 BCE, when the entire Roman population, even slaves, had been mobilized to resist the enemy.
Alaric's military operations centred on the port of Rome, through which Rome's grain supply had to pass. Alaric's first siege of Rome in 408 caused dreadful famine within the walls. It was ended by a payment that, though large, was less than one of the richest senators could have produced. The super-rich aristocrats made little contribution; pagan temples were stripped of ornaments to make up the total. With promises of freedom, Alaric also recruited many of the slaves in Rome.
Alaric withdrew to Tuscany and recruited more slaves. Ataulf, a Goth nominally in Roman service and brother-in-law to Alaric, marched through Italy to join Alaric. He took casualties from a small force of Hunnic mercenaries led by Olympius. Sarus was an enemy of Ataulf, and on Ataulf's arrival went back into imperial service.
Alaric besieges Rome
In 409 Olympius fell to further intrigue, having his ears cut off before he was beaten to death. Alaric tried again to negotiate with Honorius, but his demands (now even more moderate, only frontier land and food) were inflated by the messenger and Honorius responded with insults, which were reported verbatim to Alaric. He broke off negotiations and the standoff continued. Honorius's court made overtures to the usurper Constantine III in Gaul and arranged to bring Hunnic forces into Italy, Alaric ravaged Italy outside the fortified cities (which he could not garrison), and the Romans refused open battle (for which they had inadequate forces). Late in the year, Alaric sent bishops to express his readiness to leave Italy if Honorius would only grant his people a supply of grain. Honorius, sensing weakness, flatly refused.
Alaric moved to Rome and captured Galla Placidia, sister of Honorius. The Senate in Rome, despite its loathing for Alaric, was now desperate enough to give him almost anything he wanted. They had no food to offer, but they tried to give him imperial legitimacy; with the Senate's acquiescence, he elevated Priscus Attalus as his puppet emperor, and he marched on Ravenna. Honorius was planning to flee to Constantinople when a reinforcing army of 4,000 soldiers from the East disembarked in Ravenna. These garrisoned the walls and Honorius held on. He had Constantine's principal court supporter executed and Constantine abandoned plans to march to Honorius's defence. Attalus failed to establish his control over the Diocese of Africa, and no grain arrived in Rome where the famine became even more frightful. Jerome reports cannibalism within the walls. Attalus brought Alaric no real advantage, failing also to come to any useful agreement with Honorius (to whom Attalus offered mutilation, humiliation, and exile). Indeed, Attalus's claim was a marker of threat to Honorius, and Alaric dethroned him after a few months.
In 410 Alaric took Rome by starvation, and sacked it for three days. He invited its remaining barbarian slaves to join him, which many did. There was relatively little destruction. In some Christian holy places, Alaric's men even refrained from wanton violence, and Jerome tells the story of a virgin who was escorted to a church by the invaders, after they had given her mother a beating from which she later died. The city of Rome was the seat of the richest senatorial noble families and the centre of their cultural patronage. To pagans it was the sacred origin of the empire, and to Christians the seat of the heir of Saint Peter. At the time, this position was held by Pope Innocent I, the most authoritative bishop of the West. Rome had not fallen to an enemy since the Battle of the Allia, over eight centuries before. Refugees spread the news and their stories throughout the Empire, and the meaning of the fall was debated with religious fervour. Both Christians and pagans wrote embittered tracts, blaming paganism or Christianity respectively for the loss of Rome's supernatural protection and all attacking Stilicho's earthly failures. Some Christian responses anticipated the imminence of the Last Judgment. Augustine of Hippo in his book "City of God" ultimately rejected the pagan and Christian idea that religion should have worldly benefits. He instead developed the doctrine that the City of God in heaven, undamaged by mundane disasters, was the true objective of Christians. More practically, Honorius was briefly persuaded to set aside the laws forbidding pagans to be military officers, so that one Generidus could re-establish Roman control in Dalmatia. Generidus did this with unusual effectiveness. His techniques were remarkable for this period, in that they included training his troops, disciplining them, and giving them appropriate supplies even if he had to use his own money. The penal laws were reinstated no later than 25 August 410, meaning that the overall trend of repression of paganism continued.
Procopius mentions a story in which Honorius, on hearing the news that Rome had "perished", was shocked. The emperor thought that the news was in reference to his favorite chicken, which he had named "Roma". On hearing that Rome itself had fallen, he breathed a sigh of relief:
At that time they say that the Emperor Honorius in Ravenna received the message from one of the eunuchs, evidently a keeper of the poultry, that Roma had perished. And he cried out and said, "And yet it has just eaten from my hands!" For he had a very large cockerel, Roma by name; and the eunuch comprehending his words said that it was the city of Roma which had perished at the hands of Alaric, and the emperor with a sigh of relief answered quickly: "But I thought that my fowl Roma had perished." So great, they say, was the folly with which this emperor was possessed.
— Procopius, The Vandalic War (De Bellis III.2.25–26)
The Goths move out of Italy
Alaric then moved south, intending to sail to Africa. His ships were wrecked in a storm, and he shortly died of fever. His successor Athaulf, still regarded as an usurper and given only occasional and short-term grants of supplies, moved north into the turmoil of Gaul. In this region, there was some prospect of food. His supergroup of barbarians are called the Visigoths in modern works: they may now have been developing their own sense of identity.
405–418: In the Gallic provinces; barbarians and usurpers, loss of Britannia, partial loss of Hispania and Gaul
The Crossing of the Rhine in 405/6 brought unmanageable numbers of Germanic and Alan barbarians (perhaps some 30,000 warriors, 100,000 people) into Gaul. They may have been trying to get away from the Huns, who about this time advanced to occupy the Great Hungarian Plain. For the next few years these barbarian tribes wandered in search of food and employment, while Roman forces fought each other in the name of Honorius and a number of competing claimants to the imperial throne.
The remaining troops in Britannia elevated a succession of imperial usurpers. The last, Constantine III, raised an army from the remaining troops in Britannia, invaded Gaul and defeated forces loyal to Honorius led by Sarus. Constantine's power reached its peak in 409 when he controlled Gaul and beyond, he was joint consul with Honorius and his magister militum Gerontius defeated the last Roman force to try to hold the borders of Hispania. It was led by relatives of Honorius; Constantine executed them. Gerontius went to Hispania, where he may have settled the Sueves and the Asding Vandals. Gerontius then fell out with his master and elevated one Maximus as his own puppet emperor. He defeated Constantine and was besieging him in Arelate when Honorius's general Constantius arrived from Italy with an army (possibly, composed mainly of Hun mercenaries). Gerontius's troops deserted him, and he committed suicide. Constantius continued the siege, defeating a relieving army. Constantine surrendered in 411 with a promise that his life would be spared, and was then executed.
In 410, the Roman civitates of Britannia rebelled against Constantine and evicted his officials. They asked for help from Honorius, who replied that they should look to their own defence. While the British may have regarded themselves as Roman for several generations, and British armies may at times have fought in Gaul, no central Roman government is known to have appointed officials in Britannia thereafter. The supply of coinage to the Diocese of Britannia ceases with Honorius.
In 411, Jovinus rebelled and took over Constantine's remaining troops on the Rhine. He relied on the support of Burgundians and Alans, to whom he offered supplies and land. In 413, Jovinus also recruited Sarus. Athaulf destroyed their regime in the name of Honorius, afterwards both Jovinus and Sarus were executed. The Burgundians were settled on the left bank of the Rhine. Athaulf then operated in the south of Gaul, sometimes with short-term supplies from the Romans. All usurpers had been defeated, but large barbarian groups remained un-subdued in both Gaul and Hispania. The imperial government was quick to restore the Rhine frontier. The invading tribes of 407 moved into Hispania at the end of 409; the Visigoths left Italy at the beginning of 412 and settled themselves around Narbo.
Heraclianus was still in command in the diocese of Africa. He was the last member of the clique which had overthrown Stilicho to retain power. In 413 he led an invasion of Italy, and lost to a subordinate of Constantius. He then fled back to Africa, where he was murdered by Constantius's agents.
In January 414 Roman naval forces blockaded Athaulf in Narbo, where he married Galla Placidia. The choir at the wedding included Attalus, a puppet emperor without revenues or soldiers. Athaulf famously declared that he had abandoned his intention to set up a Gothic empire, because of the irredeemable barbarity of his followers, and instead he sought to restore the Roman Empire. He handed Attalus over to Honorius's regime for mutilation, humiliation, and exile. He also abandoned Attalus's supporters. One of them, Paulinus Pellaeus, recorded that the Goths considered themselves merciful because they allowed him and his household to leave destitute, but alive, without being raped. Athaulf moved out of Gaul, to Barcelona where his infant son by Galla Placidia was buried, and where he was assassinated by one of his household retainers, possibly a former follower of Sarus. His ultimate successor Wallia had no agreement with the Romans; his people had to plunder in Hispania for food.
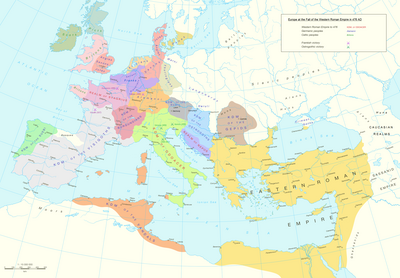
Settlement of 418; barbarians within the empire
In 416 Wallia reached agreement with Constantius; he sent Galla Placidia back to Honorius and received provisions, six hundred thousand modii of wheat. From 416 to 418, Wallia's Goths campaigned in Hispania on Constantius's behalf, exterminating the Siling Vandals in Baetica and reducing the Alans to the point where the survivors sought the protection of the king of the Asding Vandals. (After retrenchment they formed another barbarian supergroup, but for the moment they were reduced in numbers and effectively cowed.) In 418, by agreement with Constantius, Wallia's Goths accepted land to farm in Aquitania. Constantius also reinstituted an annual council of the southern Gallic provinces, to meet at Arelate. Although Constantius rebuilt the western field army to some extent, he did so only by replacing half of its units (vanished in the wars since 395) by re-graded barbarians, and by garrison troops removed from the frontier. The Notitia Dignitatum gives a list of the units of the western field army circa 425. It does not give strengths for these units, but A. H. M. Jones used the Notitia to estimate the total strength of the field armies in the West at 113,000 : Gaul, "about" 35,000; Italy, "nearly" 30,000; Britain 3,000; in Spain, 10–11,000, in the diocese of Illyricum 13–14,000, and in the diocese of Africa 23,000.
Constantius had married the princess Galla Placidia (despite her protests) in 417. The couple soon had two children, Honoria and Valentinian III. Constantius was elevated to the position of Augustus in 420. This earned him the hostility of the Eastern court, which had not agreed to his elevation. Nevertheless, Constantius had achieved an unassailable position at the Western court, in the imperial family, and as the able commander-in-chief of a partially restored army.
This settlement represented a real success for the Empire - a poem by Rutilius Namatianus celebrates his voyage back to Gaul in 417 and his confidence in a restoration of prosperity. But it marked huge losses of territory and of revenue; Rutilius travelled by ship past the ruined bridges and countryside of Tuscany, and in the west the river Loire had become the effective northern boundary of Roman Gaul. In the east of Gaul the Franks controlled large areas; the effective line of Roman control until 455 ran from north of Cologne (lost to the Ripuarian Franks in 459) to Boulogne. The Italian areas which had been compelled to support the Goths had most of their taxes remitted for several years. Even in southern Gaul and Hispania large barbarian groups remained, with thousands of warriors, in their own non-Roman military and social systems. Some occasionally acknowledged a degree of Roman political control, but without the local application of Roman leadership and military power they and their individual subgroups pursued their own interests.
421–433: Renewed dissension after the death of Constantius, partial loss of the Diocese of Africa
Constantius died in 421, after only seven months as Augustus. He had been careful to make sure that there was no successor in waiting, and his own children were far too young to take his place. Honorius was unable to control his own court, and the death of Constantius initiated more than ten years of instability. Initially Galla Placidia sought Honorius's favour in the hope that her son might ultimately inherit. Other court interests managed to defeat her, and she fled with her children to the Eastern court in 422. Honorius himself died, shortly before his thirty-ninth birthday, in 423. After some months of intrigue, the patrician Castinus installed Joannes as Western Emperor, but the Eastern Roman government proclaimed the child Valentinian III instead, his mother Galla Placidia acting as regent during his minority. Joannes had few troops of his own. He sent Aetius to raise help from the Huns. An Eastern army landed in Italy, captured Joannes, cut his hand off, abused him in public, and killed him with most of his senior officials. Aetius returned, three days after Joannes' death, at the head of a substantial Hunnic army which made him the most powerful general in Italy. After some fighting, Placidia and Aetius came to an agreement; the Huns were paid off and sent home, while Aetius received the position of magister militum.
Galla Placidia, as Augusta, mother of the Emperor, and his guardian until 437, could maintain a dominant position in court, but women in Ancient Rome did not exercise military power, and she could not herself become a general. She tried for some years to avoid reliance on a single dominant military figure, maintaining a balance of power between her three senior officers, Aetius (magister militum in Gaul), Count Boniface (governor in the Diocese of Africa), and Flavius Felix (magister militum praesentalis in Italy). Meanwhile, the Empire deteriorated seriously. Apart from the losses in the Diocese of Africa, Hispania was slipping out of central control and into the hands of local rulers and Suevic bandits. In Gaul the Rhine frontier had collapsed, the Visigoths in Aquitaine may have launched further attacks on Narbo and Arelate, and the Franks, increasingly powerful although disunited, were the major power in the north-east. Armorica was controlled by Bagaudae, local leaders not under the authority of the Empire. Aetius at least campaigned vigorously and mostly victoriously, defeating aggressive Visigoths, Franks, fresh Germanic invaders, Bagaudae in Armorica, and a rebellion in Noricum. Not for the first time in Rome's history, a triumvirate of mutually distrustful rulers proved unstable. In 427, Felix tried to recall Boniface from Africa. Boniface refused, and overcame Felix's invading force. Boniface probably recruited some Vandal troops among others.
In 428 the Vandals and Alans were united under the able, ferocious, and long-lived king Genseric; he moved his entire people to Tarifa near Gibraltar, divided them into 80 groups nominally of 1,000 people (perhaps 20,000 warriors in total), and crossed from Hispania to Mauretania without opposition. They spent a year moving slowly to Numidia, defeating Boniface. He returned to Italy where Aetius had recently had Felix executed. Boniface was promoted to magister militum and earned the enmity of Aetius, who may have been absent in Gaul at the time. In 432 the two met at the Battle of Ravenna, which left Aetius's forces defeated and Boniface mortally wounded. Aetius temporarily retired to his estates, but after an attempt to murder him he raised another Hunnic army (probably by conceding parts of Pannonia to them) and in 433 he returned to Italy, overcoming all rivals. He never threatened to become an Augustus himself and thus maintained the support of the Eastern court, where Valentinian's cousin Theodosius II reigned until 450.
433–454: Ascendancy of Aetius, loss of Carthage
Aetius campaigned vigorously, somewhat stabilizing the situation in Gaul and in Hispania. He relied heavily on his forces of Huns. With a ferocity celebrated centuries later in the Nibelungenlied, the Huns slaughtered many Burgundiones on the middle Rhine, re-establishing the survivors as Roman allies, the first Kingdom of the Burgundians. This may have returned some sort of Roman authority to Trier. Eastern troops reinforced Carthage, temporarily halting the Vandals, who in 435 agreed to limit themselves to Numidia and leave the most fertile parts of North Africa in peace. Aetius concentrated his limited military resources to defeat the Visigoths again, and his diplomacy restored a degree of order to Hispania. However, his general Litorius was badly defeated by the Visigoths at Toulouse, and a new Suevic king, Rechiar, began vigorous assaults on what remained of Roman Hispania. At one point Rechiar even allied with Bagaudae. These were Romans not under imperial control; some of their reasons for rebellion may be indicated by the remarks of a Roman captive under Attila who was happy in his lot, giving a lively account of "the vices of a declining empire, of which he had so long been the victim; the cruel absurdity of the Roman princes, unable to protect their subjects against the public enemy, unwilling to trust them with arms for their own defence; the intolerable weight of taxes, rendered still more oppressive by the intricate or arbitrary modes of collection; the obscurity of numerous and contradictory laws; the tedious and expensive forms of judicial proceedings; the partial administration of justice; and the universal corruption, which increased the influence of the rich, and aggravated the misfortunes of the poor."
Vegetius's advice on re-forming an effective army may be dated to the early 430s, (though a date in the 390s has also been suggested). He identified many deficiencies in the military, especially mentioning that the soldiers were no longer properly equipped:
From the foundation of the city till the reign of the Emperor Gratian, the foot wore cuirasses and helmets. But negligence and sloth having by degrees introduced a total relaxation of discipline, the soldiers began to think their armor too heavy, as they seldom put it on. They first requested leave from the Emperor to lay aside the cuirass and afterwards the helmet. In consequence of this, our troops in their engagements with the Goths were often overwhelmed with their showers of arrows. Nor was the necessity of obliging the infantry to resume their cuirasses and helmets discovered, notwithstanding such repeated defeats, which brought on the destruction of so many great cities. Troops, defenseless and exposed to all the weapons of the enemy, are more disposed to fly than fight. What can be expected from a foot-archer without cuirass or helmet, who cannot hold at once his bow and shield; or from the ensigns whose bodies are naked, and who cannot at the same time carry a shield and the colors? The foot soldier finds the weight of a cuirass and even of a helmet intolerable. This is because he is so seldom exercised and rarely puts them on.
A religious polemic of about this time complains bitterly of the oppression and extortion suffered by all but the richest Romans. Many wished to flee to the Bagaudae or even to foul-smelling barbarians. "Although these men differ in customs and language from those with whom they have taken refuge, and are unaccustomed too, if I may say so, to the nauseous odor of the bodies and clothing of the barbarians, yet they prefer the strange life they find there to the injustice rife among the Romans. So you find men passing over everywhere, now to the Goths, now to the Bagaudae, or whatever other barbarians have established their power anywhere ... We call those men rebels and utterly abandoned, whom we ourselves have forced into crime. For by what other causes were they made Bagaudae save by our unjust acts, the wicked decisions of the magistrates, the proscription and extortion of those who have turned the public exactions to the increase of their private fortunes and made the tax indictions their opportunity for plunder?"
Gildas, a 6th-century monk and author of De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae, wrote that "No sooner were the ravages of the enemy checked, than the island [Britain] was deluged with a most extraordinary plenty of all things, greater than was before known, and with it grew up every kind of luxury and licentiousness."
Nevertheless, effective imperial protection from barbarian ravages was eagerly sought. About this time authorities in Britannia asked Aetius for help: "To Aetius, now consul for the third time: the groans of the Britons." And again a little further, thus: "The barbarians drive us to the sea; the sea throws us back on the barbarians: thus two modes of death await us, we are either slain or drowned." The Romans, however, could not assist them..."
The Visigoths passed another waymark on their journey to full independence; they made their own foreign policy, sending princesses to make (rather unsuccessful) marriage alliances with Rechiar of the Sueves and with Huneric, son of the Vandal king Genseric.
In 439, the Vandals moved eastward, temporarily abandoning Numidia. They captured Carthage, where they established the Vandal Kingdom, an independent state with a powerful navy. This brought immediate financial crisis to the Western Empire. The diocese of Africa was prosperous, normally required few troops to keep it secure, contributed large tax revenues, and exported wheat to feed Rome and many other areas. Roman troops assembled in Sicily, but the planned counter-attack never happened. Huns attacked the Eastern empire, and "the troops, which had been sent against Genseric, were hastily recalled from Sicily; the garrisons, on the side of Persia, were exhausted; and a military force was collected in Europe, formidable by their arms and numbers, if the generals had understood the science of command, and the soldiers the duty of obedience. The armies of the Eastern empire were vanquished in three successive engagements ... From the Hellespont to Thermopylae, and the suburbs of Constantinople, [Attila] ravaged, without resistance, and without mercy, the provinces of Thrace and Macedonia" Attila's invasions of the East were stopped by the Theodosian Walls; at this heavily fortified Eastern end of the Mediterranean there were no significant barbarian invasions across the sea into the rich southerly areas of Anatolia, the Levant, and Egypt. Despite internal and external threats, and more religious discord than the West, these provinces remained prosperous contributors to tax revenue; despite the ravages of Attila's armies and the extortions of his peace treaties, tax revenue generally continued to be adequate for the essential state functions of the Eastern empire.
Genseric settled his Vandals as landowners. In 442, he was able to negotiate very favourable peace terms with the Western court. He kept his latest gains and his eldest son Huneric was honoured by betrothal to Valentinian III's daughter Eudocia. She carried the legitimacy of the conjoined Valentinianic and Theodosian dynasties. Huneric's Gothic wife was suspected of trying to poison her father-in-law Genseric; he sent her home without her nose or ears, and his Gothic alliance came to an early end. The Romans regained Numidia, and Rome again received a grain supply from Africa.
The losses of income from the Diocese of Africa were equivalent to the costs of nearly 40,000 infantry or over 20,000 cavalry. The imperial regime had to increase taxes. Despite admitting that the peasantry could pay no more, and that a sufficient army could not be raised, the imperial regime protected the interests of landowners displaced from Africa and allowed wealthy individuals to avoid taxes.
444–453: Attacks by the empire of Attila the Hun
In 444, the Huns were united under Attila. His subjects included Huns, outnumbered several times over by other groups, predominantly Germanic peoples. His power rested partly on his continued ability to reward his favoured followers with precious metals, and he continued to attack the Eastern Empire until 450, by when he had extracted vast sums of money and many other concessions.
Attila may not have needed any excuse to turn West, but he received one in the form of a plea for help from Honoria, the Emperor's sister, who was being forced into a marriage which she resented. Attila claimed Honoria as his wife, and half of the Western Empire's territory as his dowry. Faced with refusal, he invaded Gaul in 451 with a huge army. In the bloody battle of the Catalaunian Plains, the invasion was stopped by the combined forces of the barbarians within the Western empire. They were coordinated by Aetius, and supported by what troops he could muster. The next year, Attila invaded Italy and proceeded to march upon Rome. An outbreak of disease in his army, lack of supplies, reports that Eastern Roman troops were attacking his noncombatant population in Pannonia, and, possibly, Pope Leo I's plea for peace induced him to halt this campaign. Attila unexpectedly died a year later (453) and his empire crumbled as his followers fought for power. The life of Severinus of Noricum gives glimpses of the general insecurity, and ultimate retreat of the Romans on the Upper Danube in the aftermath of Attila's death. The Romans were without adequate forces; the barbarians inflicted haphazard extortion, murder, kidnap, and plunder on the Romans and on each other. "So long as the Roman dominion lasted, soldiers were maintained in many towns at the public expense to guard the boundary wall. When this custom ceased, the squadrons of soldiers and the boundary wall were blotted out together. The troop at Batavis, however, held out. Some soldiers of this troop had gone to Italy to fetch the final pay to their comrades, and no one knew that the barbarians had slain them on the way."
In 454, Aetius was personally stabbed to death by Valentinian. "[Valentinian] thought he had slain his master; he found that he had slain his protector: and he fell a helpless victim to the first conspiracy which was hatched against his throne." Valentinian himself was murdered by the dead general's supporters a year later. A rich senatorial aristocrat, Petronius Maximus, who had encouraged both murders, then seized the throne. He broke the engagement between the princess Eudocia and Huneric, heir to the Vandal throne. This amounted to a declaration of war with the Vandals. Petronius had time to send Avitus to ask for the help of the Visigoths in Gaul before a Vandal fleet arrived in Italy. Petronius was unable to muster any effective defence, tried to flee the city, and was torn to pieces by a mob who paraded the bits around on a pole. The Vandals entered Rome, and plundered it for two weeks. Despite the shortage of money for the defence of the state, considerable private wealth had accumulated since the previous sack in 410. The Vandals sailed away with large amounts of treasure and also with the princess Eudocia. She became the wife of one Vandal king and the mother of another, Hilderic.
The Vandals conquered Sicily. Their fleet became a constant danger to Roman sea trade, and to the coasts and islands of the western Mediterranean.
455–456: Failure of Avitus, further losses in Gaul, rise of Ricimer
Avitus, at the Visigothic court in Burdigala, declared himself Emperor. He moved on Rome with Visigothic support. He gained acceptance by Majorian and Ricimer, commanders of the remaining army of Italy. This was the first time that a barbarian kingdom had played a key role in the imperial succession. Avitus's son-in-law Sidonius Apollinaris wrote propaganda to present the Visigothic king Theoderic II as a reasonable man with whom a Roman regime could do business. Theoderic's payoff included precious metal from stripping the remaining public ornaments of Italy, and an unsupervised campaign in Hispania. There he not only defeated the Sueves, executing his brother-in-law Rechiar, but he also plundered Roman cities. The Burgundians expanded their kingdom in the Rhône valley, while the Vandals took the remains of the Diocese of Africa. In 456, the Visigothic army was too heavily engaged in Hispania to be an effective threat to Italy. Ricimer had just destroyed a pirate fleet of sixty Vandal ships. Majorian and Ricimer marched against Avitus, and defeated him near Placentia. He was forced to become Bishop of Placentia, and died (possibly murdered) a few weeks later.
457–467: Resurgence under Majorian, attempt to recover Africa, control by Ricimer
Majorian and Ricimer were now in control of Italy. Ricimer was the son of a Suevic king, and his mother was the daughter of a Gothic one, so he could not aspire to an imperial throne. After some months, allowing for negotiation with the new emperor of Constantinople and the defeat of 900 Alamannic invaders of Italy by one of his subordinates, Majorian was acclaimed as Augustus.
Majorian is described by Gibbon as "a great and heroic character". He rebuilt the army and navy of Italy with vigour and set about recovering the remaining Gallic provinces, which had not recognized his elevation. He defeated the Visigoths at the Battle of Arelate, reducing them to federate status and obliging them to give up their claims in Hispania; he moved on to subdue the Burgundians, the Gallo-Romans around Lugdunum (who were granted tax concessions and whose senior officials were appointed from their own ranks), and the Suevi and Bagaudae in Hispania. Marcellinus, magister militum in Dalmatia and the pagan general of a well-equipped army, acknowledged him as emperor and recovered Sicily from the Vandals. Aegidius also acknowledged Majorian and took effective charge of northern Gaul. (Aegidius may also have used the title "King of the Franks"). Abuses in tax collection were reformed and the city councils were strengthened. Both were actions necessary to rebuild the strength of the Empire, but disadvantageous to the richest aristocrats. Majorian prepared a fleet at Carthago Nova for the essential reconquest of the Diocese of Africa.
The fleet was burned by traitors, and Majorian made peace with the Vandals and returned to Italy. Here Ricimer met him, arrested him, and executed him five days later. Marcellinus in Dalmatia and Aegidius around Soissons in northern Gaul rejected both Ricimer and his puppets and maintained some version of Roman rule in their areas. Ricimer later ceded Narbo and its hinterland to the Visigoths in exchange for their help against Aegidius; this made it impossible for Roman armies to march from Italy to Hispania. Ricimer was then the effective ruler of Italy (but little else) for several years. From 461 to 465 the pious Italian aristocrat Libius Severus reigned. There is no record of anything significant that he even tried to achieve, he was never acknowledged by the East whose help Ricimer needed, and he died conveniently in 465.
467–472: Anthemius; an Emperor and an army from the East
After two years without a Western Emperor, the Eastern court nominated Anthemius, a successful general who had a strong claim to the Eastern throne. He arrived in Italy with an army, supported by Marcellinus and his fleet. Anthemius married his daughter Alypia to Ricimer, and he was proclaimed Augustus in 467. In 468, at vast expense, the Eastern empire assembled an enormous force to help the West retake the Diocese of Africa. Marcellinus rapidly drove the Vandals from Sardinia and Sicily, and a land invasion evicted them from Tripolitania. The commander in chief with the main force defeated a Vandal fleet near Sicily, and landed at Cape Bon. Here Genseric offered to surrender, if he could have a five-day truce to prepare the process. He used the respite to prepare a full-scale attack preceded by fireships, which destroyed most of the Roman fleet and killed many of its soldiers. The Vandals were confirmed in their possession of the Diocese of Africa. They soon retook Sardinia and Sicily. Marcellinus was murdered, possibly on orders from Ricimer. The Praetorian prefect of Gaul, Arvandus, tried to persuade the new king of the Visigoths to rebel, on the grounds that Roman power in Gaul was finished anyway; the king refused.
Anthemius was still in command of an army in Italy. Additionally, in northern Gaul, a British army led by one Riothamus, operated in imperial interests. Anthemius sent his son Anthemiolus over the Alps, with an army, to request the Visigoths to return southern Gaul to Roman control. This would have allowed the Empire land access to Hispania again. The Visigoths refused, and defeated the forces of both Riothamus and Anthemius; with the Burgundians, they took over almost all of the remaining imperial territory in southern Gaul.
Ricimer then quarreled with Anthemius, and besieged him in Rome, which surrendered in July 472, after more months of starvation. Anthemius was captured and executed (on Ricimer's orders) by the Burgundian prince Gundobad. In August, Ricimer died of a pulmonary haemorrhage. Olybrius, his new emperor, named Gundobad as his patrician, then shortly died himself.
472–476: Final emperors, puppets of the warlords
After the death of Olybrius there was a further interregnum until March 473, when Gundobad proclaimed Glycerius emperor. He may have made some attempt to intervene in Gaul; if so, it was unsuccessful.
In 474 Julius Nepos, nephew and successor of the general Marcellinus, arrived in Rome with soldiers and authority from the eastern emperor Leo I. By that time, Gundobad had left to contest the Burgundian throne in Gaul. Glycerius gave up without a fight, retiring to become bishop of Salona in Dalmatia. Julius Nepos ruled Italy and Dalmatia from Ravenna, and appointed Orestes, a former secretary of Attila, as magister militum.
In 475, Orestes promised land in Italy to various Germanic mercenaries, Heruli, Scirian and Torcilingi, in exchange for their support. He drove Julius Nepos out of Ravenna and proclaimed his own son Flavius Momyllus Romulus Augustus (Romulus Augustulus) as Emperor, on October 31. His surname 'Augustus' was given the diminutive form 'Augustulus' by rivals, because he was still a minor. Romulus was never recognized outside Italy as a legitimate ruler.
In 476, Orestes refused to honour his promises of land to his mercenaries, who revolted under the leadership of Odoacer. Orestes fled to the city of Pavia on August 23, 476, where the city's bishop gave him sanctuary. Orestes was soon forced to flee Pavia, when Odoacer's army broke through the city walls and ravaged the city. Odoacer's army chased Orestes to Piacenza, where they captured and executed him on August 28, 476.
On September 4, 476, Odoacer forced Romulus Augustulus, whom his father Orestes had proclaimed to be Rome's Emperor, to abdicate. The Anonymus Valesianus wrote that Odoacer, "taking pity on his youth" (he was then 16 years old), spared Romulus' life and granted him an annual pension of 6,000 solidi before sending him to live with relatives in Campania. Odoacer installed himself as ruler over Italy, and sent the Imperial insignia to Constantinople.
From 476: Last Emperor, rump states
By convention, the Western Roman Empire is deemed to have ended on 4 September 476, when Odoacer deposed Romulus Augustulus and proclaimed himself ruler of Italy. This convention is subject to many qualifications. In Roman constitutional theory, the Empire was still simply united under one emperor, implying no abandonment of territorial claims. In areas where the convulsions of the dying Empire had made organized self-defence legitimate, rump states continued under some form of Roman rule after 476. Julius Nepos still claimed to be Emperor of the West, and controlled Dalmatia until his murder in 480. Syagrius son of Aegidius ruled the Domain of Soissons until his murder in 486. The indigenous inhabitants of Mauretania developed kingdoms of their own, independent of the Vandals, and with strong Roman traits. They again sought imperial recognition with the reconquests of Justinian I, and they later put up effective resistance to the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb. The civitates of Britannia continued to look to their own defence as Honorius had authorized; they maintained literacy in Latin and other identifiably Roman traits for some time although they sank to a level of material development inferior even to their pre-Roman Iron Age ancestors.
Odoacer began to negotiate with the East Roman (Byzantine) emperor Zeno, who was busy dealing with unrest in the East. Zeno eventually granted Odoacer the status of patrician and accepted him as his own viceroy of Italy. Zeno, however, insisted that Odoacer had to pay homage to Julius Nepos as the Emperor of the Western Empire. Odoacer never returned any territory or real power, but he did issue coins in the name of Julius Nepos throughout Italy. The murder of Julius Nepos in 480 (Glycerius may have been among the conspirators) prompted Odoacer to invade Dalmatia, annexing it to his Kingdom of Italy. In 488 the Eastern emperor authorized a troublesome Goth, Theoderic (later known as "the Great") to take Italy. After several indecisive campaigns, in 493 Theoderic and Odoacer agreed to rule jointly. They celebrated their agreement with a banquet of reconciliation, at which Theoderic's men murdered Odoacer's, and Theoderic personally cut Odoacer in half.
The mostly powerless, but still influential Western Roman Senate continued to exist in the city of Rome under the rule of the Ostrogothic kingdom and, later, the Byzantine Empire for at least another century, before disappearing at an unknown date in the early 7th century.
Legacy
The Roman Empire was not only a political unity enforced by the use of military power; it was also the combined and elaborated civilization of the Mediterranean Basin and beyond. It included manufacture, trade, and architecture, widespread secular literacy, written law, and an international language of science and literature. The Western barbarians lost much of these higher cultural practices, but their redevelopment in the Middle Ages by polities aware of the Roman achievement formed the basis for the later development of Europe.
Observing the cultural and archaeological continuities through and beyond the period of lost political control, the process has been described as a complex cultural transformation, rather than a fall.