Although environmental pollution can be caused by natural events, the word pollution generally implies that the contaminants have an anthropogenic source – that is, a source created by human activities, such as manufacturing, extractive industries, poor waste management, transportation or agriculture. Pollution is often classed as point source (coming from a highly concentrated specific site, such as a factory, mine, construction site), or nonpoint source pollution (coming from a widespread distributed sources, such as microplastics or agricultural runoff).
Many sources of pollution were unregulated parts of industrialization during the 19th and 20th centuries until the emergence of environmental regulation and pollution policy in the later half of the 20th century. Sites where historically polluting industries released persistent pollutants may have legacy pollution long after the source of the pollution is stopped. Major forms of pollution include air pollution, water pollution, litter, noise pollution, plastic pollution, soil contamination, radioactive contamination, thermal pollution, light pollution, and visual pollution.
Pollution has widespread consequences on human and environmental health, having systematic impact on social and economic systems. In 2019, pollution killed approximately nine million people worldwide (about one in six deaths that year); about three-quarters of these deaths were caused by air pollution. A 2022 literature review found that levels of anthropogenic chemical pollution have exceeded planetary boundaries and now threaten entire ecosystems around the world. Pollutants frequently have outsized impacts on vulnerable populations, such as children and the elderly, and marginalized communities, because polluting industries and toxic waste sites tend to be collocated with populations with less economic and political power. This outsized impact is a core reason for the formation of the environmental justice movement, and continues to be a core element of environmental conflicts, particularly in the Global South.
Because of the impacts of these chemicals, local and international countries' policy have increasingly sought to regulate pollutants, resulting in increasing air and water quality standards, alongside regulation of specific waste streams. Regional and national policy is typically supervised by environmental agencies or ministries, while international efforts are coordinated by the UN Environmental Program and other treaty bodies. Pollution mitigation is an important part of all of the Sustainable Development Goals.
Definitions and types
Various definitions of pollution exist, which may or may not recognize certain types, such as noise pollution or greenhouse gases. The United States Environmental Protection Administration defines pollution as "Any substances in water, soil, or air that degrade the natural quality of the environment, offend the senses of sight, taste, or smell, or cause a health hazard. The usefulness of the natural resource is usually impaired by the presence of pollutants and contaminants." In contrast, the United Nations considers pollution to be the "presence of substances and heat in environmental media (air, water, land) whose nature, location, or quantity produces undesirable environmental effects."

The major forms of pollution are listed below along with the particular contaminants relevant to each of them:
- Air pollution: the release of chemicals and particulates into the atmosphere. Common gaseous pollutants include carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and nitrogen oxides produced by industry and motor vehicles. Photochemical ozone and smog are created as nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons react to sunlight. Particulate matter, or fine dust is characterized by their micrometre size PM10 to PM2.5.
- Electromagnetic pollution: the overabundance of electromagnetic radiation in their non-ionizing form, such as radio and television transmissions, Wi-fi etc. Although there is no demonstrable effect on humans there can be interference with radio-astronomy and effects on safety systems of aircraft and cars.
- Light pollution: includes light trespass, over-illumination and astronomical interference.
- Littering: the criminal throwing of inappropriate man-made objects, unremoved, onto public and private properties.
- Noise pollution: which encompasses roadway noise, aircraft noise, industrial noise as well as high-intensity sonar.
- Plastic pollution: involves the accumulation of plastic products and microplastics in the environment that adversely affects wildlife, wildlife habitat, or humans.
- Soil contamination occurs when chemicals are released by spill or underground leakage. Among the most significant soil contaminants are hydrocarbons, heavy metals, MTBE, herbicides, pesticides and chlorinated hydrocarbons.
- Radioactive contamination, resulting from 20th century activities in atomic physics, such as nuclear power generation and nuclear weapons research, manufacture and deployment. (See alpha emitters and actinides in the environment.)
- Thermal pollution, is a temperature change in natural water bodies caused by human influence, such as use of water as coolant in a power plant.
- Visual pollution, which can refer to the presence of overhead power lines, motorway billboards, scarred landforms (as from strip mining), open storage of trash, municipal solid waste or space debris.
- Water pollution, caused by the discharge of industrial wastewater from commercial and industrial waste (intentionally or through spills) into surface waters; discharges of untreated sewage and chemical contaminants, such as chlorine, from treated sewage; and releases of waste and contaminants into surface runoff flowing to surface waters (including urban runoff and agricultural runoff, which may contain chemical fertilizers and pesticides, as well as human feces from open defecation).
Natural causes
One of the most significant natural sources of pollution are volcanoes, which during eruptions release large quantities of harmful gases into the atmosphere. Volcanic gases include carbon dioxide, which can be fatal in large concentrations and contributes to climate change, hydrogen halides which can cause acid rain, sulfur dioxides, which are harmful to animals and damage the ozone layer, and hydrogen sulfides, which are capable of killing humans at concentrations of less than 1 part per thousand. Volcanic emissions also include fine and ultrafine particles which may contain toxic chemicals and substances such as arsenic, lead, and mercury.
Wildfires, which can be caused naturally by lightning strikes, are also a significant source of air pollution. Wildfire smoke contains significant quantities of both carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide, which can cause suffocation. Large quantities of fine particulates are found within wildfire smoke as well, which pose a health risk to animals.
Human generation
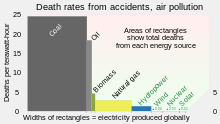
Motor vehicle emissions are one of the leading causes of air pollution. China, United States, Russia, India Mexico, and Japan are the world leaders in air pollution emissions. Principal stationary pollution sources include chemical plants, coal-fired power plants, oil refineries, petrochemical plants, nuclear waste disposal activity, incinerators, large livestock farms (dairy cows, pigs, poultry, etc.), PVC factories, metals production factories, plastics factories, and other heavy industry. Agricultural air pollution comes from contemporary practices which include clear felling and burning of natural vegetation as well as spraying of pesticides and herbicides.
About 400 million metric tons of hazardous wastes are generated each year. The United States alone produces about 250 million metric tons. Americans constitute less than 5% of the world's population, but produce roughly 25% of the world's CO2, and generate approximately 30% of world's waste. In 2007, China overtook the United States as the world's biggest producer of CO2, while still far behind based on per capita pollution (ranked 78th among the world's nations).

Chlorinated hydrocarbons (CFH), heavy metals (such as chromium, cadmium – found in rechargeable batteries, and lead – found in lead paint, aviation fuel, and even in certain countries, gasoline), MTBE, zinc, arsenic, and benzene are some of the most frequent soil contaminants. A series of press reports published in 2001, culminating in the publication of the book Fateful Harvest, revealed a widespread practise of recycling industrial leftovers into fertilizer, resulting in metal poisoning of the soil. Ordinary municipal landfills are the source of many chemical substances entering the soil environment (and often groundwater), emanating from the wide variety of refuse accepted, especially substances illegally discarded there, or from pre-1970 landfills that may have been subject to little control in the U.S. or EU. There have also been some unusual releases of polychlorinated dibenzodioxins, commonly called dioxins for simplicity, such as TCDD.
Pollution can also occur as a result of natural disasters. Hurricanes, for example, frequently result in sewage contamination and petrochemical spills from burst boats or automobiles. When coastal oil rigs or refineries are involved, larger-scale and environmental damage is not unusual. When accidents occur, some pollution sources, such as nuclear power stations or oil ships, can create extensive and potentially catastrophic emissions.
Plastic pollution is choking our oceans by making plastic gyres, entangling marine animals, poisoning our food and water supply, and ultimately inflicting havoc on the health and well-being of humans and wildlife globally. With the exception of a small amount that has been incinerating, virtually every piece of plastic that was ever made in the past still exists in one form or another. And since most of the plastics do not biodegrade in any meaningful sense, all that plastic waste could exist for hundreds or even thousands of years. If plastic production is not circumscribed, plastic pollution will be disastrous and will eventually outweigh fish in oceans.
Greenhouse gas emissions
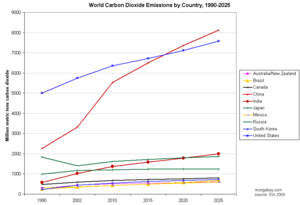
Source: Energy Information Administration.
Carbon dioxide, while vital for photosynthesis, is sometimes referred to as pollution, because raised levels of the gas in the atmosphere are affecting the Earth's climate. Disruption of the environment can also highlight the connection between areas of pollution that would normally be classified separately, such as those of water and air. Recent studies have investigated the potential for long-term rising levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide to cause slight but critical increases in the acidity of ocean waters, and the possible effects of this on marine ecosystems.
In February 2007, a report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), representing the work of 2,500 scientists, economists, and policymakers from more than 120 countries, confirmed that humans have been the primary cause of global warming since 1950. Humans have ways to cut greenhouse gas emissions and avoid the consequences of global warming, a major climate report concluded. But to change the climate, the transition from fossil fuels like coal and oil needs to occur within decades, according to the final report this year from the UN's Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
Effects
Human health
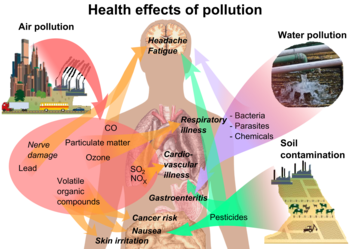
Pollution affects humans in every part of the world. An October 2017 study by the Lancet Commission on Pollution and Health found that global pollution, specifically toxic air, water, soil and workplaces, kills nine million people annually, which is triple the number of deaths caused by AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria combined, and 15 times higher than deaths caused by wars and other forms of human violence. The study concluded that "pollution is one of the great existential challenges of the Anthropocene era. Pollution endangers the stability of the Earth's support systems and threatens the continuing survival of human societies."
Adverse air quality can kill many organisms, including humans. Ozone pollution can cause respiratory disease, cardiovascular disease, throat inflammation, chest pain, and congestion. A 2010 analysis estimated that 1.2 million people died prematurely each year in China alone because of air pollution. China's high smog levels can damage the human body and cause various diseases. In 2019, air pollution caused 1.67 million deaths in India (17.8% of total deaths nationally). Studies have estimated that the number of people killed annually in the United States could be over 50,000. A study published in 2022 in GeoHealth concluded that energy-related fossil fuel emissions in the United States cause 46,900–59,400 premature deaths each year and PM2.5-related illness and death costs the nation $537–$678 billion annually. In the US, deaths caused by coal pollution were highest in 1999, but decreased sharply after 2007. The number dropped by about 95% by 2020, as coal plants have been closed or have scrubbers installed.
In 2019, water pollution caused 1.4 million premature deaths. Contamination of drinking water by untreated sewage in developing countries is an issue, for example, over 732 million Indians (56% of the population) and over 92 million Ethiopians (92.9% of the population) do not have access to basic sanitation. In 2013 over 10 million people in India fell ill with waterborne illnesses in 2013, and 1,535 people died, most of them children. As of 2007, nearly 500 million Chinese lack access to safe drinking water.
Acute exposure to certain pollutants can have short and long term effects. Oil spills can cause skin irritations and rashes. Noise pollution induces hearing loss, high blood pressure, stress, and sleep disturbance. Mercury has been linked to developmental deficits in children and neurologic symptoms. Older people are significantly exposed to diseases induced by air pollution. Those with heart or lung disorders are at additional risk. Children and infants are also at serious risk. Lead and other heavy metals have been shown to cause neurological problems, intellectual disabilities and behavioural problems. Chemical and radioactive substances can cause cancer and birth defects.
Socio economic impacts
The health impacts of pollution have both direct and lasting social consequences. A 2021 study found that exposure to pollution causes an increase in violent crime. A 2019 paper linked pollution to adverse school outcomes for children. A number of studies show that pollution has an adverse effect on the productivity of both indoor and outdoor workers.
Environment
Pollution has been found to be present widely in the natural environment. A 2022 study published in Environmental Science & Technology found that levels of anthropogenic chemical pollution have exceeded planetary boundaries and now threaten entire ecosystems around the world.
There are a number of effects of this:
- Biomagnification describes situations where toxins (such as heavy metals) may pass through trophic levels, becoming exponentially more concentrated in the process.

Global carbon dioxide emissions by jurisdiction (as of 2015) - Carbon dioxide emissions cause ocean acidification, the ongoing decrease in the pH of the Earth's oceans as CO2 becomes dissolved.
- The emission of greenhouse gases leads to global warming which affects ecosystems in many ways.
- Invasive species can outcompete native species and reduce biodiversity. Invasive plants can contribute debris and biomolecules (allelopathy) that can alter soil and chemical compositions of an environment, often reducing native species competitiveness.
- Nitrogen oxides are removed from the air by rain and fertilise land which can change the species composition of ecosystems.
- Smog and haze can reduce the amount of sunlight received by plants to carry out photosynthesis and leads to the production of tropospheric ozone which damages plants.
- Soil can become infertile and unsuitable for plants. This will affect other organisms in the food web.
- Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides can cause acid rain which lowers the pH value of soil.
- Organic pollution of watercourses can deplete oxygen levels and reduce species diversity.
Regulation and monitoring
To protect the environment from the adverse effects of pollution, many nations worldwide have enacted legislation to regulate various types of pollution as well as to mitigate the adverse effects of pollution. At the local level, regulation usually is supervised by environmental agencies or the broader public health system. Different jurisdictions often have different levels regulation and policy choices about pollution. Historically, polluters will lobby governments in less economically developed areas or countries to maintain lax regulation in order to protect industrialisation at the cost of human and environmental health.
The modern environmental regulatory environment has its origins in the United States with the beginning of industrial regulations around Air and Water pollution connected to industry and mining during the 1960s and 1970s.
Because many of pollutants have trans-boundary impacts, the UN and other treaty bodies have been used to regulate pollutants that circulate as air pollution, water pollution or trade in wastes. Early international agreements were successful at addressing Global Environmental issues, such as Montreal Protocol, which banned Ozone depleting chemicals in 1987, with more recent agreements focusing on broader, more widely dispersed chemicals such as persistent organic pollutants in the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants created in 2001, such as PCBs, and the Kyoto Protocol in 1997 which initiated collaboration on addressing greenhouse gases to mitigate climate change. Governments, NPOs, research groups, and citizen scientists monitor pollution with an expanding list of low-cost pollution monitoring tools.Control



Pollution control is a term used in environmental management. It refers to the control of emissions and effluents into air, water or soil. Without pollution control, the waste products from overconsumption, heating, agriculture, mining, manufacturing, transportation and other human activities, whether they accumulate or disperse, will degrade the environment. In the hierarchy of controls, pollution prevention and waste minimization are more desirable than pollution control. In the field of land development, low impact development is a similar technique for the prevention of urban runoff.
Policy, law and monitoring/transparency/life-cycle assessment-attached economics could be developed and enforced to control pollution. A review concluded that there is a lack of attention and action such as work on a globally supported "formal science–policy interface", e.g. to "inform intervention, influence research, and guide funding".
In September 2023 a Global Framework on Chemicals aiming to reduce pollution was agreed during an international conference in Bonn, Germany. The framework includes 28 targets, for example, to "end the use of hazardous pesticides in agriculture where the risks have not been managed" by 2035.
Practices
- Recycling
- Reusing
- Waste minimisation
- Mitigating
- Pollution prevention
- Compost
Devices
- Air pollution control
- Bioremediation
- Dust collection systems
- Scrubbers
- Sewage treatment
- Sedimentation (Primary treatment)
- Activated sludge biotreaters (Secondary treatment; also used for industrial wastewater)
- Aerated lagoons
- Constructed wetlands (also used for urban runoff)
- Industrial wastewater treatment
- Vapor recovery systems
- Phytoremediation
Cost
Pollution has a cost. Manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole of society. A manufacturing activity that causes air pollution is an example of a negative externality in production. A negative externality in production occurs "when a firm's production reduces the well-being of others who are not compensated by the firm." For example, if a laundry firm exists near a polluting steel manufacturing firm, there will be increased costs for the laundry firm because of the dirt and smoke produced by the steel manufacturing firm. If external costs exist, such as those created by pollution, the manufacturer will choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the manufacturer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. Goods and services that involve negative externalities in production, such as those that produce pollution, tend to be overproduced and underpriced since the externality is not being priced into the market.
Pollution can also create costs for the firms producing the pollution. Sometimes firms choose, or are forced by regulation, to reduce the amount of pollution that they are producing. The associated costs of doing this are called abatement costs, or marginal abatement costs if measured by each additional unit. In 2005 pollution abatement capital expenditures and operating costs in the US amounted to nearly $27 billion.
Dirtiest industries
The Pure Earth, an international non-for-profit organization dedicated to eliminating life-threatening pollution in the developing world, issues an annual list of some of the world's most polluting industries. Below is the list for 2016:
- Lead–acid battery recycling
- Mining and extractive metallurgy
- Lead smelting
- Tanning
- Artisanal mining
- Landfills
- Industrial parks
- Chemical industry
- Manufacturing
- Dyeing
A 2018 report by the Institute for Agriculture and Trade Policy and GRAIN says that the meat and dairy industries are poised to surpass the oil industry as the world's worst polluters.
Textile industry

The textile industry is one of the largest polluters in the globalized world of mostly free market dominated socioeconomic systems. Chemically polluted textile wastewater degrades the quality of the soil and water. The pollution comes from the type of conduct of chemical treatments used e.g., in pretreatment, dyeing, printing, and finishing operations that many or most market-driven companies use despite "eco-friendly alternatives". Textile industry wastewater is considered to be one the largest polluters of water and soil ecosystems, causing "carcinogenic, mutagenic, genotoxic, cytotoxic and allergenic threats to living organisms". The textile industry uses over 8000 chemicals in its supply chain, also polluting the environment with large amounts of microplastics and has been identified in one review as the industry sector producing the largest amount of pollution.
A campaign of big clothing brands like Nike, Adidas and Puma to voluntarily reform their manufacturing supply chains to commit to achieving zero discharges of hazardous chemicals by 2020 (global goal) appears to have failed.
The textile industry also creates a lot of pollution that leads to externalities which can cause large economic problems. The problem usually occurs when there is no division of ownership rights. This means that the problem of pollution is largely caused because of incomplete information about which company pollutes and at what scale the damage was caused by the pollution.Fossil fuel related industries
Outdoor air pollution attributable to fossil fuel use alone causes ~3.61 million deaths annually, making it one of the top contributors to human death, beyond being a major driver of climate change whereby greenhouse gases are considered per se as a form of pollution .
Socially optimal level
Society derives some indirect utility from pollution; otherwise, there would be no incentive to pollute. This utility may come from the consumption of goods and services that inherently create pollution (albeit the level can vary) or lower prices or lower required efforts (or inconvenience) to abandon or substitute these goods and services. Therefore, it is important that policymakers attempt to balance these indirect benefits with the costs of pollution in order to achieve an efficient outcome.
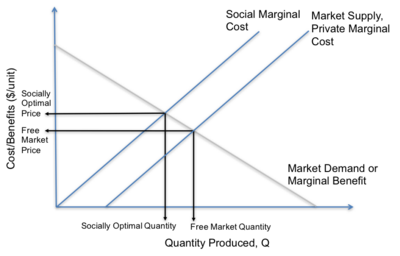
It is possible to use environmental economics to determine which level of pollution is deemed the social optimum. For economists, pollution is an "external cost and occurs only when one or more individuals suffer a loss of welfare". There is a socially optimal level of pollution at which welfare is maximized. This is because consumers derive utility from the good or service manufactured, which will outweigh the social cost of pollution until a certain point. At this point the damage of one extra unit of pollution to society, the marginal cost of pollution, is exactly equal to the marginal benefit of consuming one more unit of the good or service.
Moreover, the feasibility of pollution reduction rates could also be a factor of calculating optimal levels. While a study puts the global mean loss of life expectancy (LLE; similar to YPLL) from air pollution in 2015 at 2.9 years (substantially more than, for example, 0.3 years from all forms of direct violence), it also indicated that a significant fraction of the LLE is unavoidable in terms of current economical-technological feasibility such as aeolian dust and wildfire emission control.
In markets with pollution, or other negative externalities in production, the free market equilibrium will not account for the costs of pollution on society. If the social costs of pollution are higher than the private costs incurred by the firm, then the true supply curve will be higher. The point at which the social marginal cost and market demand intersect gives the socially optimal level of pollution. At this point, the quantity will be lower and the price will be higher in comparison to the free market equilibrium. Therefore, the free market outcome could be considered a market failure because it "does not maximize efficiency".
This model can be used as a basis to evaluate different methods of internalizing the externality, such as tariffs, a Pigouvian tax (such as a carbon tax) and cap and trade systems.
History
Prior to 19th century
Air pollution has always accompanied civilizations. Pollution started from prehistoric times, when man created the first fires. According to a 1983 article in the journal Science, "soot" found on ceilings of prehistoric caves provides ample evidence of the high levels of pollution that was associated with inadequate ventilation of open fires."
Metal forging appears to be a key turning point in the creation of significant air pollution levels outside the home. Core samples of glaciers in Greenland indicate increases in pollution associated with Greek, Roman, and Chinese metal production.

The burning of coal and wood, and the presence of many horses in concentrated areas made the cities the primary sources of pollution. King Edward I of England banned the burning of sea-coal by proclamation in London in 1272, after its smoke became a problem; the fuel was so common in England that this earliest of names for it was acquired because it could be carted away from some shores by the wheelbarrow.
19th century
The Industrial Revolution gave birth to environmental pollution as we know it today. London also recorded one of the earlier extreme cases of water quality problems with the Great Stink on the Thames of 1858, which led to the construction of the London sewerage system soon afterward. Pollution issues escalated as population growth far exceeded the viability of neighborhoods to handle their waste problem. Reformers began to demand sewer systems and clean water.
In 1870, the sanitary conditions in Berlin were among the worst in Europe. August Bebel recalled conditions before a modern sewer system was built in the late 1870s:
Waste-water from the houses collected in the gutters running alongside the curbs and emitted a truly fearsome smell. There were no public toilets in the streets or squares. Visitors, especially women, often became desperate when nature called. In the public buildings the sanitary facilities were unbelievably primitive....As a metropolis, Berlin did not emerge from a state of barbarism into civilization until after 1870.
20th and 21st century
The primitive conditions were intolerable for a world national capital, and the Imperial German government brought in its scientists, engineers, and urban planners to solve the deficiencies and forge Berlin as the world's model city. A British expert in 1906 concluded that Berlin represented "the most complete application of science, order and method of public life," adding "it is a marvel of civic administration, the most modern and most perfectly organized city that there is."
The emergence of great factories and consumption of immense quantities of coal gave rise to unprecedented air pollution, and the large volume of industrial chemical discharges added to the growing load of untreated human waste. Chicago and Cincinnati were the first two American cities to enact laws ensuring cleaner air in 1881. Pollution became a significant issue in the United States in the early twentieth century, as progressive reformers took issue with air pollution caused by coal burning, water pollution caused by bad sanitation, and street pollution caused by the three million horses who worked in American cities in 1900, generating large quantities of urine and manure. As historian Martin Melosi notes, the generation that first saw automobiles replacing horses saw cars as "miracles of cleanliness". By the 1940s, automobile-caused smog was a significant issue in Los Angeles.
Other cities followed around the country until early in the 20th century when the short-lived Office of Air Pollution was created under the Department of the Interior. The cities of Los Angeles experienced extreme smog events and Donora, Pennsylvania, in the late 1940s, serving as another public reminder.
Air pollution would continue to be a problem in England, especially later during the Industrial Revolution, and extending into the recent past with the Great Smog of 1952. Awareness of atmospheric pollution spread widely after World War II, with fears triggered by reports of radioactive fallout from atomic warfare and testing. Then a non-nuclear event – the Great Smog of 1952 in London – killed at least 4000 people. This prompted some of the first major modern environmental legislation: the Clean Air Act of 1956.
Pollution began to draw significant public attention in the United States between the mid-1950s and early 1970s, when Congress passed the Noise Control Act, the Clean Air Act, the Clean Water Act, and the National Environmental Policy Act.

Severe incidents of pollution helped increase consciousness. PCB dumping in the Hudson River resulted in a ban by the EPA on consumption of its fish in 1974. National news stories in the late 1970s – especially the long-term dioxin contamination at Love Canal starting in 1947 and uncontrolled dumping in Valley of the Drums – led to the Superfund legislation of 1980. The pollution of industrial land gave rise to the name brownfield, a term now common in city planning.
The development of nuclear science introduced radioactive contamination, which can remain lethally radioactive for hundreds of thousands of years. Lake Karachay – named by the Worldwatch Institute as the "most polluted spot" on earth – served as a disposal site for the Soviet Union throughout the 1950s and 1960s. Chelyabinsk, Russia, is considered the "Most polluted place on the planet".
Nuclear weapons continued to be tested in the Cold War, especially in the earlier stages of their development. The toll on the worst-affected populations and the growth since then in understanding the critical threat to human health posed by radioactivity has also been a prohibitive complication associated with nuclear power. Though extreme care is practiced in that industry, the potential for disaster suggested by incidents such as those at Three Mile Island, Chernobyl, and Fukushima pose a lingering specter of public mistrust. Worldwide publicity has been intense on those disasters. Widespread support for test ban treaties has ended almost all nuclear testing in the atmosphere.
International catastrophes such as the wreck of the Amoco Cadiz oil tanker off the coast of Brittany in 1978 and the Bhopal disaster in 1984 have demonstrated the universality of such events and the scale on which efforts to address them needed to engage. The borderless nature of the atmosphere and oceans inevitably resulted in the implication of pollution on a planetary level with the issue of global warming. Most recently, the term persistent organic pollutant (POP) has come to describe a group of chemicals such as PBDEs and PFCs, among others. Though their effects remain poorly understood owing to a lack of experimental data, they have been detected in various ecological habitats far removed from industrial activity, such as the Arctic, demonstrating diffusion and bioaccumulation after only a relatively brief period of widespread use.

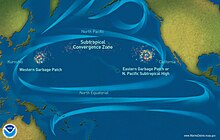
The Great Pacific Garbage Patch is a concentration of plastics in the North Pacific Gyre. It and other garbage patches contain debris that can transport invasive species and that can entangle and be ingested by wildlife. Organizations such as 5 Gyres and the Algalita Marine Research Foundation have researched the Great Pacific Garbage Patch and found microplastics in the water.
Pollution introduced by light at night is becoming a global problem, more severe in urban centres, but contaminating also large territories, far away from towns.
Growing evidence of local and global pollution and an increasingly informed public over time have given rise to environmentalism and the environmental movement, which generally seek to limit human impact on the environment.











