Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during reactions with other substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds.
In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both basic and applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the properties of the soil on the Moon (cosmochemistry), how medications work (pharmacology), and how to collect DNA evidence at a crime scene (forensics).
Chemistry has existed under various names since ancient times. It has evolved, and now chemistry encompasses various areas of specialisation, or subdisciplines, that continue to increase in number and interrelate to create further interdisciplinary fields of study. The applications of various fields of chemistry are used frequently for economic purposes in the chemical industry.
Etymology
The word chemistry comes from a modification during the Renaissance of the word alchemy, which referred to an earlier set of practices that encompassed elements of chemistry, metallurgy, philosophy, astrology, astronomy, mysticism, and medicine. Alchemy is often associated with the quest to turn lead or other base metals into gold, though alchemists were also interested in many of the questions of modern chemistry.
The modern word alchemy in turn is derived from the Arabic word al-kīmīā (الكیمیاء). This may have Egyptian origins since al-kīmīā is derived from the Ancient Greek χημία, which is in turn derived from the word Kemet, which is the ancient name of Egypt in the Egyptian language. Alternately, al-kīmīā may derive from χημεία 'cast together'.
Modern principles

The current model of atomic structure is the quantum mechanical model. Traditional chemistry starts with the study of elementary particles, atoms, molecules, substances, metals, crystals and other aggregates of matter. Matter can be studied in solid, liquid, gas and plasma states, in isolation or in combination. The interactions, reactions and transformations that are studied in chemistry are usually the result of interactions between atoms, leading to rearrangements of the chemical bonds which hold atoms together. Such behaviors are studied in a chemistry laboratory.
The chemistry laboratory stereotypically uses various forms of laboratory glassware. However glassware is not central to chemistry, and a great deal of experimental (as well as applied/industrial) chemistry is done without it.

A chemical reaction is a transformation of some substances into one or more different substances. The basis of such a chemical transformation is the rearrangement of electrons in the chemical bonds between atoms. It can be symbolically depicted through a chemical equation, which usually involves atoms as subjects. The number of atoms on the left and the right in the equation for a chemical transformation is equal. (When the number of atoms on either side is unequal, the transformation is referred to as a nuclear reaction or radioactive decay.) The type of chemical reactions a substance may undergo and the energy changes that may accompany it are constrained by certain basic rules, known as chemical laws.
Energy and entropy considerations are invariably important in almost all chemical studies. Chemical substances are classified in terms of their structure, phase, as well as their chemical compositions. They can be analyzed using the tools of chemical analysis, e.g. spectroscopy and chromatography. Scientists engaged in chemical research are known as chemists. Most chemists specialize in one or more sub-disciplines. Several concepts are essential for the study of chemistry; some of them are:
Matter
In chemistry, matter is defined as anything that has rest mass and volume (it takes up space) and is made up of particles. The particles that make up matter have rest mass as well – not all particles have rest mass, such as the photon. Matter can be a pure chemical substance or a mixture of substances.
Atom

The atom is the basic unit of chemistry. It consists of a dense core called the atomic nucleus surrounded by a space occupied by an electron cloud. The nucleus is made up of positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons (together called nucleons), while the electron cloud consists of negatively charged electrons which orbit the nucleus. In a neutral atom, the negatively charged electrons balance out the positive charge of the protons. The nucleus is dense; the mass of a nucleon is approximately 1,836 times that of an electron, yet the radius of an atom is about 10,000 times that of its nucleus.
The atom is also the smallest entity that can be envisaged to retain the chemical properties of the element, such as electronegativity, ionization potential, preferred oxidation state(s), coordination number, and preferred types of bonds to form (e.g., metallic, ionic, covalent).
Element

A chemical element is a pure substance which is composed of a single type of atom, characterized by its particular number of protons in the nuclei of its atoms, known as the atomic number and represented by the symbol Z. The mass number is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in a nucleus. Although all the nuclei of all atoms belonging to one element will have the same atomic number, they may not necessarily have the same mass number; atoms of an element which have different mass numbers are known as isotopes. For example, all atoms with 6 protons in their nuclei are atoms of the chemical element carbon, but atoms of carbon may have mass numbers of 12 or 13.
The standard presentation of the chemical elements is in the periodic table, which orders elements by atomic number. The periodic table is arranged in groups, or columns, and periods, or rows. The periodic table is useful in identifying periodic trends.
Compound

A compound is a pure chemical substance composed of more than one element. The properties of a compound bear little similarity to those of its elements. The standard nomenclature of compounds is set by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). Organic compounds are named according to the organic nomenclature system. The names for inorganic compounds are created according to the inorganic nomenclature system. When a compound has more than one component, then they are divided into two classes, the electropositive and the electronegative components. In addition the Chemical Abstracts Service has devised a method to index chemical substances. In this scheme each chemical substance is identifiable by a number known as its CAS registry number.
Molecule

A molecule is the smallest indivisible portion of a pure chemical substance that has its unique set of chemical properties, that is, its potential to undergo a certain set of chemical reactions with other substances. However, this definition only works well for substances that are composed of molecules, which is not true of many substances (see below). Molecules are typically a set of atoms bound together by covalent bonds, such that the structure is electrically neutral and all valence electrons are paired with other electrons either in bonds or in lone pairs.
Thus, molecules exist as electrically neutral units, unlike ions. When this rule is broken, giving the "molecule" a charge, the result is sometimes named a molecular ion or a polyatomic ion. However, the discrete and separate nature of the molecular concept usually requires that molecular ions be present only in well-separated form, such as a directed beam in a vacuum in a mass spectrometer. Charged polyatomic collections residing in solids (for example, common sulfate or nitrate ions) are generally not considered "molecules" in chemistry. Some molecules contain one or more unpaired electrons, creating radicals. Most radicals are comparatively reactive, but some, such as nitric oxide (NO) can be stable.
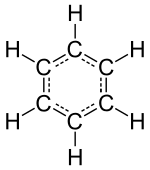
The "inert" or noble gas elements (helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon and radon) are composed of lone atoms as their smallest discrete unit, but the other isolated chemical elements consist of either molecules or networks of atoms bonded to each other in some way. Identifiable molecules compose familiar substances such as water, air, and many organic compounds like alcohol, sugar, gasoline, and the various pharmaceuticals.
However, not all substances or chemical compounds consist of discrete molecules, and indeed most of the solid substances that make up the solid crust, mantle, and core of the Earth are chemical compounds without molecules. These other types of substances, such as ionic compounds and network solids, are organized in such a way as to lack the existence of identifiable molecules per se. Instead, these substances are discussed in terms of formula units or unit cells as the smallest repeating structure within the substance. Examples of such substances are mineral salts (such as table salt), solids like carbon and diamond, metals, and familiar silica and silicate minerals such as quartz and granite.
One of the main characteristics of a molecule is its geometry often called its structure. While the structure of diatomic, triatomic or tetra-atomic molecules may be trivial, (linear, angular pyramidal etc.) the structure of polyatomic molecules, that are constituted of more than six atoms (of several elements) can be crucial for its chemical nature.
Substance and mixture
  | |
  | |
  | |
| Examples of pure chemical substances. From left to right: the elements tin (Sn) and sulfur (S), diamond (an allotrope of carbon), sucrose (pure sugar), and sodium chloride (salt) and sodium bicarbonate (baking soda), which are both ionic compounds. |
A chemical substance is a kind of matter with a definite composition and set of properties. A collection of substances is called a mixture. Examples of mixtures are air and alloys.
Mole and amount of substance
The mole is a unit of measurement that denotes an amount of substance (also called chemical amount). One mole is defined to contain exactly 6.02214076×1023 particles (atoms, molecules, ions, or electrons), where the number of particles per mole is known as the Avogadro constant. Molar concentration is the amount of a particular substance per volume of solution, and is commonly reported in mol/dm3.
Phase

In addition to the specific chemical properties that distinguish different chemical classifications, chemicals can exist in several phases. For the most part, the chemical classifications are independent of these bulk phase classifications; however, some more exotic phases are incompatible with certain chemical properties. A phase is a set of states of a chemical system that have similar bulk structural properties, over a range of conditions, such as pressure or temperature.
Physical properties, such as density and refractive index tend to fall within values characteristic of the phase. The phase of matter is defined by the phase transition, which is when energy put into or taken out of the system goes into rearranging the structure of the system, instead of changing the bulk conditions.
Sometimes the distinction between phases can be continuous instead of having a discrete boundary; in this case the matter is considered to be in a supercritical state. When three states meet based on the conditions, it is known as a triple point and since this is invariant, it is a convenient way to define a set of conditions.
The most familiar examples of phases are solids, liquids, and gases. Many substances exhibit multiple solid phases. For example, there are three phases of solid iron (alpha, gamma, and delta) that vary based on temperature and pressure. A principal difference between solid phases is the crystal structure, or arrangement, of the atoms. Another phase commonly encountered in the study of chemistry is the aqueous phase, which is the state of substances dissolved in aqueous solution (that is, in water).
Less familiar phases include plasmas, Bose–Einstein condensates and fermionic condensates and the paramagnetic and ferromagnetic phases of magnetic materials. While most familiar phases deal with three-dimensional systems, it is also possible to define analogs in two-dimensional systems, which has received attention for its relevance to systems in biology.
Bonding

Atoms sticking together in molecules or crystals are said to be bonded with one another. A chemical bond may be visualized as the multipole balance between the positive charges in the nuclei and the negative charges oscillating about them. More than simple attraction and repulsion, the energies and distributions characterize the availability of an electron to bond to another atom.
The chemical bond can be a covalent bond, an ionic bond, a hydrogen bond or just because of Van der Waals force. Each of these kinds of bonds is ascribed to some potential. These potentials create the interactions which hold atoms together in molecules or crystals. In many simple compounds, valence bond theory, the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion model (VSEPR), and the concept of oxidation number can be used to explain molecular structure and composition.
An ionic bond is formed when a metal loses one or more of its electrons, becoming a positively charged cation, and the electrons are then gained by the non-metal atom, becoming a negatively charged anion. The two oppositely charged ions attract one another, and the ionic bond is the electrostatic force of attraction between them. For example, sodium (Na), a metal, loses one electron to become an Na+ cation while chlorine (Cl), a non-metal, gains this electron to become Cl−. The ions are held together due to electrostatic attraction, and that compound sodium chloride (NaCl), or common table salt, is formed.

In a covalent bond, one or more pairs of valence electrons are shared by two atoms: the resulting electrically neutral group of bonded atoms is termed a molecule. Atoms will share valence electrons in such a way as to create a noble gas electron configuration (eight electrons in their outermost shell) for each atom. Atoms that tend to combine in such a way that they each have eight electrons in their valence shell are said to follow the octet rule. However, some elements like hydrogen and lithium need only two electrons in their outermost shell to attain this stable configuration; these atoms are said to follow the duet rule, and in this way they are reaching the electron configuration of the noble gas helium, which has two electrons in its outer shell.
Similarly, theories from classical physics can be used to predict many ionic structures. With more complicated compounds, such as metal complexes, valence bond theory is less applicable and alternative approaches, such as the molecular orbital theory, are generally used.
Energy
In the context of chemistry, energy is an attribute of a substance as a consequence of its atomic, molecular or aggregate structure. Since a chemical transformation is accompanied by a change in one or more of these kinds of structures, it is invariably accompanied by an increase or decrease of energy of the substances involved. Some energy is transferred between the surroundings and the reactants of the reaction in the form of heat or light; thus the products of a reaction may have more or less energy than the reactants.
A reaction is said to be exergonic if the final state is lower on the energy scale than the initial state; in the case of endergonic reactions the situation is the reverse. A reaction is said to be exothermic if the reaction releases heat to the surroundings; in the case of endothermic reactions, the reaction absorbs heat from the surroundings.
Chemical reactions are invariably not possible unless the reactants surmount an energy barrier known as the activation energy. The speed of a chemical reaction (at given temperature T) is related to the activation energy E, by the Boltzmann's population factor – that is the probability of a molecule to have energy greater than or equal to E at the given temperature T. This exponential dependence of a reaction rate on temperature is known as the Arrhenius equation. The activation energy necessary for a chemical reaction to occur can be in the form of heat, light, electricity or mechanical force in the form of ultrasound.
A related concept free energy, which also incorporates entropy considerations, is a very useful means for predicting the feasibility of a reaction and determining the state of equilibrium of a chemical reaction, in chemical thermodynamics. A reaction is feasible only if the total change in the Gibbs free energy is negative, ; if it is equal to zero the chemical reaction is said to be at equilibrium.
There exist only limited possible states of energy for electrons, atoms and molecules. These are determined by the rules of quantum mechanics, which require quantization of energy of a bound system. The atoms/molecules in a higher energy state are said to be excited. The molecules/atoms of substance in an excited energy state are often much more reactive; that is, more amenable to chemical reactions.
The phase of a substance is invariably determined by its energy and the energy of its surroundings. When the intermolecular forces of a substance are such that the energy of the surroundings is not sufficient to overcome them, it occurs in a more ordered phase like liquid or solid as is the case with water (H2O); a liquid at room temperature because its molecules are bound by hydrogen bonds. Whereas hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a gas at room temperature and standard pressure, as its molecules are bound by weaker dipole–dipole interactions.
The transfer of energy from one chemical substance to another depends on the size of energy quanta emitted from one substance. However, heat energy is often transferred more easily from almost any substance to another because the phonons responsible for vibrational and rotational energy levels in a substance have much less energy than photons invoked for the electronic energy transfer. Thus, because vibrational and rotational energy levels are more closely spaced than electronic energy levels, heat is more easily transferred between substances relative to light or other forms of electronic energy. For example, ultraviolet electromagnetic radiation is not transferred with as much efficacy from one substance to another as thermal or electrical energy.
The existence of characteristic energy levels for different chemical substances is useful for their identification by the analysis of spectral lines. Different kinds of spectra are often used in chemical spectroscopy, e.g. IR, microwave, NMR, ESR, etc. Spectroscopy is also used to identify the composition of remote objects – like stars and distant galaxies – by analyzing their radiation spectra.

The term chemical energy is often used to indicate the potential of a chemical substance to undergo a transformation through a chemical reaction or to transform other chemical substances.
Reaction

When a chemical substance is transformed as a result of its interaction with another substance or with energy, a chemical reaction is said to have occurred. A chemical reaction is therefore a concept related to the "reaction" of a substance when it comes in close contact with another, whether as a mixture or a solution; exposure to some form of energy, or both. It results in some energy exchange between the constituents of the reaction as well as with the system environment, which may be designed vessels—often laboratory glassware.
Chemical reactions can result in the formation or dissociation of molecules, that is, molecules breaking apart to form two or more molecules or rearrangement of atoms within or across molecules. Chemical reactions usually involve the making or breaking of chemical bonds. Oxidation, reduction, dissociation, acid–base neutralization and molecular rearrangement are some examples of common chemical reactions.
A chemical reaction can be symbolically depicted through a chemical equation. While in a non-nuclear chemical reaction the number and kind of atoms on both sides of the equation are equal, for a nuclear reaction this holds true only for the nuclear particles viz. protons and neutrons.
The sequence of steps in which the reorganization of chemical bonds may be taking place in the course of a chemical reaction is called its mechanism. A chemical reaction can be envisioned to take place in a number of steps, each of which may have a different speed. Many reaction intermediates with variable stability can thus be envisaged during the course of a reaction. Reaction mechanisms are proposed to explain the kinetics and the relative product mix of a reaction. Many physical chemists specialize in exploring and proposing the mechanisms of various chemical reactions. Several empirical rules, like the Woodward–Hoffmann rules often come in handy while proposing a mechanism for a chemical reaction.
According to the IUPAC gold book, a chemical reaction is "a process that results in the interconversion of chemical species." Accordingly, a chemical reaction may be an elementary reaction or a stepwise reaction. An additional caveat is made, in that this definition includes cases where the interconversion of conformers is experimentally observable. Such detectable chemical reactions normally involve sets of molecular entities as indicated by this definition, but it is often conceptually convenient to use the term also for changes involving single molecular entities (i.e. 'microscopic chemical events').
Ions and salts

An ion is a charged species, an atom or a molecule, that has lost or gained one or more electrons. When an atom loses an electron and thus has more protons than electrons, the atom is a positively charged ion or cation. When an atom gains an electron and thus has more electrons than protons, the atom is a negatively charged ion or anion. Cations and anions can form a crystalline lattice of neutral salts, such as the Na+ and Cl− ions forming sodium chloride, or NaCl. Examples of polyatomic ions that do not split up during acid–base reactions are hydroxide (OH−) and phosphate (PO43−).
Plasma is composed of gaseous matter that has been completely ionized, usually through high temperature.
Acidity and basicity

A substance can often be classified as an acid or a base. There are several different theories which explain acid–base behavior. The simplest is Arrhenius theory, which states that an acid is a substance that produces hydronium ions when it is dissolved in water, and a base is one that produces hydroxide ions when dissolved in water. According to Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, acids are substances that donate a positive hydrogen ion to another substance in a chemical reaction; by extension, a base is the substance which receives that hydrogen ion.
A third common theory is Lewis acid–base theory, which is based on the formation of new chemical bonds. Lewis theory explains that an acid is a substance which is capable of accepting a pair of electrons from another substance during the process of bond formation, while a base is a substance which can provide a pair of electrons to form a new bond. There are several other ways in which a substance may be classified as an acid or a base, as is evident in the history of this concept.
Acid strength is commonly measured by two methods. One measurement, based on the Arrhenius definition of acidity, is pH, which is a measurement of the hydronium ion concentration in a solution, as expressed on a negative logarithmic scale. Thus, solutions that have a low pH have a high hydronium ion concentration and can be said to be more acidic. The other measurement, based on the Brønsted–Lowry definition, is the acid dissociation constant (Ka), which measures the relative ability of a substance to act as an acid under the Brønsted–Lowry definition of an acid. That is, substances with a higher Ka are more likely to donate hydrogen ions in chemical reactions than those with lower Ka values.
Redox
Redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed by either gaining electrons (reduction) or losing electrons (oxidation). Substances that have the ability to oxidize other substances are said to be oxidative and are known as oxidizing agents, oxidants or oxidizers. An oxidant removes electrons from another substance. Similarly, substances that have the ability to reduce other substances are said to be reductive and are known as reducing agents, reductants, or reducers.
A reductant transfers electrons to another substance and is thus oxidized itself. And because it "donates" electrons it is also called an electron donor. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation number—the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation number, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation number.
Equilibrium
Although the concept of equilibrium is widely used across sciences, in the context of chemistry, it arises whenever a number of different states of the chemical composition are possible, as for example, in a mixture of several chemical compounds that can react with one another, or when a substance can be present in more than one kind of phase.
A system of chemical substances at equilibrium, even though having an unchanging composition, is most often not static; molecules of the substances continue to react with one another thus giving rise to a dynamic equilibrium. Thus the concept describes the state in which the parameters such as chemical composition remain unchanged over time.
Chemical laws
Chemical reactions are governed by certain laws, which have become fundamental concepts in chemistry. Some of them are:
- Avogadro's law
- Beer–Lambert law
- Boyle's law (1662, relating pressure and volume)
- Charles's law (1787, relating volume and temperature)
- Fick's laws of diffusion
- Gay-Lussac's law (1809, relating pressure and temperature)
- Le Chatelier's principle
- Henry's law
- Hess's law
- Law of conservation of energy leads to the important concepts of equilibrium, thermodynamics, and kinetics.
- Law of conservation of mass continues to be conserved in isolated systems, even in modern physics. However, special relativity shows that due to mass–energy equivalence, whenever non-material "energy" (heat, light, kinetic energy) is removed from a non-isolated system, some mass will be lost with it. High energy losses result in loss of weighable amounts of mass, an important topic in nuclear chemistry.
- Law of definite composition, although in many systems (notably biomacromolecules and minerals) the ratios tend to require large numbers, and are frequently represented as a fraction.
- Law of multiple proportions
- Raoult's law
History
The history of chemistry spans a period from the ancient past to the present. Since several millennia BC, civilizations were using technologies that would eventually form the basis of the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.
Chemistry was preceded by its protoscience, alchemy, which operated a non-scientific approach to understanding the constituents of matter and their interactions. Despite being unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry by performing experiments and recording the results. Robert Boyle, although skeptical of elements and convinced of alchemy, played a key part in elevating the "sacred art" as an independent, fundamental and philosophical discipline in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661).
While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, the crucial difference was given by the scientific method that chemists employed in their work. Chemistry, as a body of knowledge distinct from alchemy, became an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry afterwards is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.
Definition
The definition of chemistry has changed over time, as new discoveries and theories add to the functionality of the science. The term "chymistry", in the view of noted scientist Robert Boyle in 1661, meant the subject of the material principles of mixed bodies. In 1663, the chemist Christopher Glaser described "chymistry" as a scientific art, by which one learns to dissolve bodies, and draw from them the different substances on their composition, and how to unite them again, and exalt them to a higher perfection.
The 1730 definition of the word "chemistry", as used by Georg Ernst Stahl, meant the art of resolving mixed, compound, or aggregate bodies into their principles; and of composing such bodies from those principles. In 1837, Jean-Baptiste Dumas considered the word "chemistry" to refer to the science concerned with the laws and effects of molecular forces. This definition further evolved until, in 1947, it came to mean the science of substances: their structure, their properties, and the reactions that change them into other substances—a characterization accepted by Linus Pauling. More recently, in 1998, Professor Raymond Chang broadened the definition of "chemistry" to mean the study of matter and the changes it undergoes.
Background

Early civilizations, such as the Egyptians, Babylonians, and Indians, amassed practical knowledge concerning the arts of metallurgy, pottery and dyes, but did not develop a systematic theory.
A basic chemical hypothesis first emerged in Classical Greece with the theory of four elements as propounded definitively by Aristotle stating that fire, air, earth and water were the fundamental elements from which everything is formed as a combination. Greek atomism dates back to 440 BC, arising in works by philosophers such as Democritus and Epicurus. In 50 BCE, the Roman philosopher Lucretius expanded upon the theory in his poem De rerum natura (On The Nature of Things). Unlike modern concepts of science, Greek atomism was purely philosophical in nature, with little concern for empirical observations and no concern for chemical experiments.
An early form of the idea of conservation of mass is the notion that "Nothing comes from nothing" in Ancient Greek philosophy, which can be found in Empedocles (approx. 4th century BC): "For it is impossible for anything to come to be from what is not, and it cannot be brought about or heard of that what is should be utterly destroyed." and Epicurus (3rd century BC), who, describing the nature of the Universe, wrote that "the totality of things was always such as it is now, and always will be".

In the Hellenistic world the art of alchemy first proliferated, mingling magic and occultism into the study of natural substances with the ultimate goal of transmuting elements into gold and discovering the elixir of eternal life. Work, particularly the development of distillation, continued in the early Byzantine period with the most famous practitioner being the 4th century Greek-Egyptian Zosimos of Panopolis. Alchemy continued to be developed and practised throughout the Arab world after the Muslim conquests, and from there, and from the Byzantine remnants, diffused into medieval and Renaissance Europe through Latin translations.
The Arabic works attributed to Jabir ibn Hayyan introduced a systematic classification of chemical substances, and provided instructions for deriving an inorganic compound (sal ammoniac or ammonium chloride) from organic substances (such as plants, blood, and hair) by chemical means. Some Arabic Jabirian works (e.g., the "Book of Mercy", and the "Book of Seventy") were later translated into Latin under the Latinized name "Geber", and in 13th-century Europe an anonymous writer, usually referred to as pseudo-Geber, started to produce alchemical and metallurgical writings under this name. Later influential Muslim philosophers, such as Abū al-Rayhān al-Bīrūnī and Avicenna disputed the theories of alchemy, particularly the theory of the transmutation of metals.

Improvements of the refining of ores and their extractions to smelt metals was widely used source of information for early chemists in the 16th century, among them Georg Agricola (1494–1555), who published his major work De re metallica in 1556. His work, describing highly developed and complex processes of mining metal ores and metal extraction, were the pinnacle of metallurgy during that time. His approach removed all mysticism associated with the subject, creating the practical base upon which others could and would build. The work describes the many kinds of furnace used to smelt ore, and stimulated interest in minerals and their composition. Agricola has been described as the "father of metallurgy" and the founder of geology as a scientific discipline.
Under the influence of the new empirical methods propounded by Sir Francis Bacon and others, a group of chemists at Oxford, Robert Boyle, Robert Hooke and John Mayow began to reshape the old alchemical traditions into a scientific discipline. Boyle in particular questioned some commonly held chemical theories and argued for chemical practitioners to be more "philosophical" and less commercially focused in The Sceptical Chemyst. He formulated Boyle's law, rejected the classical "four elements" and proposed a mechanistic alternative of atoms and chemical reactions that could be subject to rigorous experiment.

In the following decades, many important discoveries were made, such as the nature of 'air' which was discovered to be composed of many different gases. The Scottish chemist Joseph Black and the Flemish Jan Baptist van Helmont discovered carbon dioxide, or what Black called 'fixed air' in 1754; Henry Cavendish discovered hydrogen and elucidated its properties and Joseph Priestley and, independently, Carl Wilhelm Scheele isolated pure oxygen. The theory of phlogiston (a substance at the root of all combustion) was propounded by the German Georg Ernst Stahl in the early 18th century and was only overturned by the end of the century by the French chemist Antoine Lavoisier, the chemical analogue of Newton in physics. Lavoisier did more than any other to establish the new science on proper theoretical footing, by elucidating the principle of conservation of mass and developing a new system of chemical nomenclature used to this day.
English scientist John Dalton proposed the modern theory of atoms; that all substances are composed of indivisible 'atoms' of matter and that different atoms have varying atomic weights.
The development of the electrochemical theory of chemical combinations occurred in the early 19th century as the result of the work of two scientists in particular, Jöns Jacob Berzelius and Humphry Davy, made possible by the prior invention of the voltaic pile by Alessandro Volta. Davy discovered nine new elements including the alkali metals by extracting them from their oxides with electric current.

British William Prout first proposed ordering all the elements by their atomic weight as all atoms had a weight that was an exact multiple of the atomic weight of hydrogen. J.A.R. Newlands devised an early table of elements, which was then developed into the modern periodic table of elements in the 1860s by Dmitri Mendeleev and independently by several other scientists including Julius Lothar Meyer. The inert gases, later called the noble gases were discovered by William Ramsay in collaboration with Lord Rayleigh at the end of the century, thereby filling in the basic structure of the table.
Organic chemistry was developed by Justus von Liebig and others, following Friedrich Wöhler's synthesis of urea. Other crucial 19th century advances were; an understanding of valence bonding (Edward Frankland in 1852) and the application of thermodynamics to chemistry (J. W. Gibbs and Svante Arrhenius in the 1870s).

Bottom: Observed results: a small portion of the particles were deflected, indicating a small, concentrated charge.
At the turn of the twentieth century the theoretical underpinnings of chemistry were finally understood due to a series of remarkable discoveries that succeeded in probing and discovering the very nature of the internal structure of atoms. In 1897, J.J. Thomson of the University of Cambridge discovered the electron and soon after the French scientist Becquerel as well as the couple Pierre and Marie Curie investigated the phenomenon of radioactivity. In a series of pioneering scattering experiments Ernest Rutherford at the University of Manchester discovered the internal structure of the atom and the existence of the proton, classified and explained the different types of radioactivity and successfully transmuted the first element by bombarding nitrogen with alpha particles.
His work on atomic structure was improved on by his students, the Danish physicist Niels Bohr, the Englishman Henry Moseley and the German Otto Hahn, who went on to father the emerging nuclear chemistry and discovered nuclear fission. The electronic theory of chemical bonds and molecular orbitals was developed by the American scientists Linus Pauling and Gilbert N. Lewis.
The year 2011 was declared by the United Nations as the International Year of Chemistry. It was an initiative of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, and of the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization and involves chemical societies, academics, and institutions worldwide and relied on individual initiatives to organize local and regional activities.
Practice
In the practice of chemistry, pure chemistry is the study of the fundamental principles of chemistry, while applied chemistry applies that knowledge to develop technology and solve real-world problems.
Subdisciplines
Chemistry is typically divided into several major sub-disciplines. There are also several main cross-disciplinary and more specialized fields of chemistry.
- Analytical chemistry is the analysis of material samples to gain an understanding of their chemical composition and structure. Analytical chemistry incorporates standardized experimental methods in chemistry. These methods may be used in all subdisciplines of chemistry, excluding purely theoretical chemistry.

- Biochemistry is the study of the chemicals, chemical reactions and interactions that take place at a molecular level in living organisms. Biochemistry is highly interdisciplinary, covering medicinal chemistry, neurochemistry, molecular biology, forensics, plant science and genetics.
- Inorganic chemistry is the study of the properties and reactions of inorganic compounds, such as metals and minerals. The distinction between organic and inorganic disciplines is not absolute and there is much overlap, most importantly in the sub-discipline of organometallic chemistry.

- Materials chemistry is the preparation, characterization, and understanding of solid state components or devices with a useful current or future function. The field is a new breadth of study in graduate programs, and it integrates elements from all classical areas of chemistry like organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, and crystallography with a focus on fundamental issues that are unique to materials. Primary systems of study include the chemistry of condensed phases (solids, liquids, polymers) and interfaces between different phases.
- Neurochemistry is the study of neurochemicals; including transmitters, peptides, proteins, lipids, sugars, and nucleic acids; their interactions, and the roles they play in forming, maintaining, and modifying the nervous system.
- Nuclear chemistry is the study of how subatomic particles come together and make nuclei. Modern transmutation is a large component of nuclear chemistry, and the table of nuclides is an important result and tool for this field. In addition to medical applications, nuclear chemistry encompasses nuclear engineering which explores the topic of using nuclear power sources for generating energy.

- Organic chemistry is the study of the structure, properties, composition, mechanisms, and reactions of organic compounds. An organic compound is defined as any compound based on a carbon skeleton. Organic compounds can be classified, organized and understood in reactions by their functional groups, unit atoms or molecules that show characteristic chemical properties in a compound.

- Physical chemistry is the study of the physical and fundamental basis of chemical systems and processes. In particular, the energetics and dynamics of such systems and processes are of interest to physical chemists. Important areas of study include chemical thermodynamics, chemical kinetics, electrochemistry, statistical mechanics, spectroscopy, and more recently, astrochemistry. Physical chemistry has large overlap with molecular physics. Physical chemistry involves the use of infinitesimal calculus in deriving equations. It is usually associated with quantum chemistry and theoretical chemistry. Physical chemistry is a distinct discipline from chemical physics, but again, there is very strong overlap.
- Theoretical chemistry is the study of chemistry via fundamental theoretical reasoning (usually within mathematics or physics). In particular the application of quantum mechanics to chemistry is called quantum chemistry. Since the end of the Second World War, the development of computers has allowed a systematic development of computational chemistry, which is the art of developing and applying computer programs for solving chemical problems. Theoretical chemistry has large overlap with (theoretical and experimental) condensed matter physics and molecular physics.

Other subdivisions include electrochemistry, femtochemistry, flavor chemistry, flow chemistry, immunohistochemistry, hydrogenation chemistry, mathematical chemistry, molecular mechanics, natural product chemistry, organometallic chemistry, petrochemistry, photochemistry, physical organic chemistry, polymer chemistry, radiochemistry, sonochemistry, supramolecular chemistry, synthetic chemistry, and many others.
Interdisciplinary
Interdisciplinary fields include agrochemistry, astrochemistry (and cosmochemistry), atmospheric chemistry, chemical engineering, chemical biology, chemo-informatics, environmental chemistry, geochemistry, green chemistry, immunochemistry, marine chemistry, materials science, mechanochemistry, medicinal chemistry, molecular biology, nanotechnology, oenology, pharmacology, phytochemistry, solid-state chemistry, surface science, thermochemistry, and many others.
Industry
The chemical industry represents an important economic activity worldwide. The global top 50 chemical producers in 2013 had sales of US$980.5 billion with a profit margin of 10.3%.
Professional societies
- American Chemical Society
- American Society for Neurochemistry
- Chemical Institute of Canada
- Chemical Society of Peru
- International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
- Royal Australian Chemical Institute
- Royal Netherlands Chemical Society
- Royal Society of Chemistry
- Society of Chemical Industry
- World Association of Theoretical and Computational Chemists





![{\displaystyle r_{p}=\left|\left[e_{p}-\sum _{j=1,j\neq p}^{n}k_{pj}\left|r_{j}-r_{pj}^{o}\right|\right]\right|}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0d90ffed5e4a6921f3feeb1ff1ff58ca526526b5)













