From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In biology, histones are highly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes.[1][2] They are the chief protein components of chromatin, acting as spools around which DNA winds, and play a role in gene regulation. Without histones, the unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long (a length to width ratio of more than 10 million to 1 in human DNA). For example, each human cell has about 1.8 meters of DNA, (~6 ft) but wound on the histones it has about 90 micrometers (0.09 mm) of chromatin, which, when duplicated and condensed during mitosis, result in about 120 micrometers of chromosomes.[3]
| Core histone H2A/H2B/H3/H4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|

PDB rendering of Complex between nucleosome core particle (h3,h4,h2a,h2b) and 146 bp long DNA fragment based on 1aoi.
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
| Symbol | Histone | ||
| Pfam | PF00125 | ||
| Pfam clan | CL0012 | ||
| InterPro | IPR007125 | ||
| SCOP | 1hio | ||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1hio | ||
linker histone H1 and H5 family
| |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | Linker_histone |
| Pfam | PF00538 |
| InterPro | IPR005818 |
| SMART | SM00526 |
| SCOP | 1hst |
| SUPERFAMILY | 1hst |
Classes
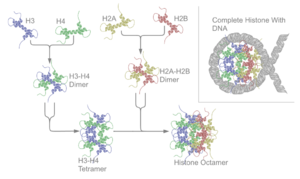
Five major families of histones exist: H1/H5, H2A, H2B, H3 and H4.[2][4][5] Histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 are known as the core histones, while histones H1 and H5 are known as the linker histones.Two of each of the core histones assemble to form one octameric nucleosome core, approximately 63 Angstroms in diameter (a solenoid (DNA)-like particle). 147 base pairs of DNA wrap around this core particle 1.65 times in a left-handed super-helical turn to give a particle of around 100 Angstroms across.[6] The linker histone H1 binds the nucleosome at the entry and exit sites of the DNA, thus locking the DNA into place[7] and allowing the formation of higher order structure. The most basic such formation is the 10 nm fiber or beads on a string conformation. This involves the wrapping of DNA around nucleosomes with approximately 50 base pairs of DNA separating each pair of nucleosomes (also referred to as linker DNA). Higher-order structures include the 30 nm fiber (forming an irregular zigzag) and 100 nm fiber, these being the structures found in normal cells. During mitosis and meiosis, the condensed chromosomes are assembled through interactions between nucleosomes and other regulatory proteins.
The following is a list of human histone proteins:
| Super family | Family | Subfamily | Members |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linker | H1 | H1F | H1F0, H1FNT, H1FOO, H1FX |
| H1H1 | HIST1H1A, HIST1H1B, HIST1H1C, HIST1H1D, HIST1H1E, HIST1H1T | ||
| Core | H2A | H2AF | H2AFB1, H2AFB2, H2AFB3, H2AFJ, H2AFV, H2AFX, H2AFY, H2AFY2, H2AFZ |
| H2A1 | HIST1H2AA, HIST1H2AB, HIST1H2AC, HIST1H2AD, HIST1H2AE, HIST1H2AG, HIST1H2AI, HIST1H2AJ, HIST1H2AK, HIST1H2AL, HIST1H2AM | ||
| H2A2 | HIST2H2AA3, HIST2H2AC | ||
| H2B | H2BF | H2BFM, H2BFS, H2BFWT | |
| H2B1 | HIST1H2BA, HIST1H2BB, HIST1H2BC, HIST1H2BD, HIST1H2BE, HIST1H2BF, HIST1H2BG, HIST1H2BH, HIST1H2BI, HIST1H2BJ, HIST1H2BK, HIST1H2BL, HIST1H2BM, HIST1H2BN, HIST1H2BO | ||
| H2B2 | HIST2H2BE | ||
| H3 | H3A1 | HIST1H3A, HIST1H3B, HIST1H3C, HIST1H3D, HIST1H3E, HIST1H3F, HIST1H3G, HIST1H3H, HIST1H3I, HIST1H3J | |
| H3A2 | HIST2H3C | ||
| H3A3 | HIST3H3 | ||
| H4 | H41 | HIST1H4A, HIST1H4B, HIST1H4C, HIST1H4D, HIST1H4E, HIST1H4F, HIST1H4G, HIST1H4H, HIST1H4I, HIST1H4J, HIST1H4K, HIST1H4L | |
| H44 | HIST4H4 |
Structure
The nucleosome core is formed of two H2A-H2B dimers and a H3-H4 tetramer, forming two nearly symmetrical halves by tertiary structure (C2 symmetry; one macromolecule is the mirror image of the other).[6] The H2A-H2B dimers and H3-H4 tetramer also show pseudodyad symmetry. The 4 'core' histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) are relatively similar in structure and are highly conserved through evolution, all featuring a 'helix turn helix turn helix' motif (which allows the easy dimerisation). They also share the feature of long 'tails' on one end of the amino acid structure - this being the location of post-translational modification (see below).It has been proposed that histone proteins are evolutionarily related to the helical part of the extended AAA+ ATPase domain, the C-domain, and to the N-terminal substrate recognition domain of Clp/Hsp100 proteins. Despite the differences in their topology, these three folds share a homologous helix-strand-helix (HSH) motif.[8]
Using an electron paramagnetic resonance spin-labeling technique, British researchers measured the distances between the spools around which eukaryotic cells wind their DNA. They determined the spacings range from 59 to 70 Å.[9]
In all, histones make five types of interactions with DNA:
- Helix-dipoles form alpha-helixes in H2B, H3, and H4 cause a net positive charge to accumulate at the point of interaction with negatively charged phosphate groups on DNA
- Hydrogen bonds between the DNA backbone and the amide group on the main chain of histone proteins
- Nonpolar interactions between the histone and deoxyribose sugars on DNA
- Salt bridges and hydrogen bonds between side chains of basic amino acids (especially lysine and arginine) and phosphate oxygens on DNA
- Non-specific minor groove insertions of the H3 and H2B N-terminal tails into two minor grooves each on the DNA molecule
Histones are subject to post translational modification by enzymes primarily on their N-terminal tails, but also in their globular domains[citation needed]. Such modifications include methylation, citrullination, acetylation, phosphorylation, SUMOylation, ubiquitination, and ADP-ribosylation. This affects their function of gene regulation (see "Function" section).
In general, genes that are active have less bound histone, while inactive genes are highly associated with histones during interphase[citation needed]. It also appears that the structure of histones has been evolutionarily conserved, as any deleterious mutations would be severely maladaptive. All histones have a highly positively charged N-terminus with many lysine and arginine residues.
History
Histones were discovered in 1884 by Albrecht Kossel. The word "histone" dates from the late 19th century and is from the German word "Histon", a word itself of uncertain origin - perhaps from the Greek histanai or histos.Until the early 1990s, histones were dismissed by most as inert packing material for eukaryotic nuclear DNA, a view based in part on the "ball and stick" models of Mark Ptashne and others, who believed that transcription was activated by protein-DNA and protein-protein interactions on largely naked DNA templates, as is the case in bacteria.
During the 1980s, work by Michael Grunstein[10] demonstrated that eukaryotic histones actually repress gene transcription, and that the function of transcriptional activators is to overcome this repression. It is now known that histones play both positive and negative roles in gene expression, forming the basis of the histone code. The work of Vincent Allfrey on histone modification was pioneering and he is regarded as father of epigenetics.[11]
The discovery of the H5 histone appears to date back to the 1970s,[12][13] and it is now considered an isoform of Histone H1.[2][4][5]
Conservation across species
Histones are found in the nuclei of eukaryotic cells, and in certain Archaea, namely Thermoproteales and Euryarchaea, but not in bacteria. The unicellular algae known as dinoflagellates are the only eukaryotes that are known to completely lack histones.[14]Archaeal histones may well resemble the evolutionary precursors to eukaryotic histones. Histone proteins are among the most highly conserved proteins in eukaryotes, emphasizing their important role in the biology of the nucleus.[2]:939 In contrast mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely because this allows them to achieve an even higher packaging ratio.[15]
Core histones are highly conserved proteins; that is, there are very few differences among the amino acid sequences of the histone proteins of different species. Linker histone usually has more than one form within a species and is also less conserved than the core histones.[citation needed]
There are some variant forms in some of the major classes. They share amino acid sequence homology and core structural similarity to a specific class of major histones but also have their own feature that is distinct from the major histones. These minor histones usually carry out specific functions of the chromatin metabolism. For example, histone H3-like CenpA is associated with only the centromere region of the chromosome. Histone H2A variant H2A.Z is associated with the promoters of actively transcribed genes and also involved in the prevention of the spread of silent heterochromatin.[16] Furthermore, H2A.Z has roles in chromatin for genome stability.[17]
Another H2A variant H2A.X binds to the DNA with double-strand breaks and marks the region undergoing DNA repair.[18] Histone H3.3 is associated with the body of actively transcribed genes.[19]
Function
Compacting DNA strands
Histones act as spools around which DNA winds. This enables the compaction necessary to fit the large genomes of eukaryotes inside cell nuclei: the compacted molecule is 40,000 times shorter than an unpacked molecule.Chromatin regulation
Histones undergo posttranslational modifications that alter their interaction with DNA and nuclear proteins. The H3 and H4 histones have long tails protruding from the nucleosome, which can be covalently modified at several places. Modifications of the tail include methylation, acetylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination, SUMOylation, citrullination, and ADP-ribosylation. The core of the histones H2A, H2B, and H3 can also be modified.Combinations of modifications are thought to constitute a code, the so-called "histone code".[20][21] Histone modifications act in diverse biological processes such as gene regulation, DNA repair, chromosome condensation (mitosis) and spermatogenesis (meiosis).[22]
The common nomenclature of histone modifications is:
- The name of the histone (e.g., H3)
- The single-letter amino acid abbreviation (e.g., K for Lysine) and the amino acid position in the protein
- The type of modification (Me: methyl, P: phosphate, Ac: acetyl, Ub: ubiquitin)
- The number of modifications (only Me is known to occur in more than one copy per residue. 1, 2 or 3 is mono-, di- or tri-methylation)
Examples of histone modifications in transcription regulation include:
| Type of modification |
Histone | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H3K4 | H3K9 | H3K14 | H3K27 | H3K79 | H3K36 | H4K20 | H2BK5 | |
| mono-methylation | activation[23] | activation[24] | activation[24] | activation[24][25] | activation[24] | activation[24] | ||
| di-methylation | repression[26] | repression[26] | activation[25] | |||||
| tri-methylation | activation[27] | repression[24] | repression[24] | activation,[25] repression[24] |
activation | repression[26] | ||
| acetylation | activation[27] | activation[27] | activation[28] | |||||
Functions of histone modifications
A huge catalogue of histone modifications have been described, but a functional understanding of most is still lacking. Collectively, it is thought that histone modifications may underlie a histone code, whereby combinations of histone modifications have specific meanings. However, most functional data concerns individual prominent histone modifications that are biochemically amenable to detailed study.Chemistry of histone modifications
Lysine methylation
The addition of one, two or three methyl groups to lysine has little effect on the chemistry of the histone; methylation leaves the charge of the lysine intact and adds a minimal number of atoms so steric interactions are mostly unaffected. However, proteins containing Tudor, chromo or PHD domains, amongst others, can recognise lysine methylation with exquisite sensitivity and differentiate mono, di and tri-methyl lysine, to the extent that, for some lysines (e.g.: H4K20) mono, di and tri-methylation appear to have different meanings. Because of this, lysine methylation tends to be a very informative mark and dominates the known histone modification functions.
Arginine methylation
What was said above of the chemistry of lysine methylation also applies to arginine methylation, and some protein domains—e.g., Tudor domains—can be specific for methyl arginine instead of methyl lysine. Arginine is known to be mono- or di-methylated, and methylation can be symmetric or asymmetric, potentially with different meanings.
Lysine acetylation
Addition of an acetyl group has a major chemical effect on lysine as it neutralises the positive charge. This reduces electrostatic attraction between the histone and the negatively charged DNA backbone, loosening the chromatin structure; highly acetylated histones form more accessible chromatin and tend to be associated with active transcription. Lysine acetylation appears to be less precise in meaning than methylation, in that histone acetyltransferases tend to act on more than one lysine; presumably this reflects the need to alter multiple lysines to have a significant effect on chromatin structure.
Serine/Threonine/Tyrosine phosphorylation
Addition of a negatively charged phosphate group can lead to major changes in protein structure, leading to the well-characterised role of phosphorylation in controlling protein function. It is not clear what structural implications histone phosphorylation has, but histone phosphorylation has clear functions as a post-translational modification, and binding domains such as BRCT have been characterised.
Functions in transcription
Most well-studied histone modifications are involved in control of transcription.Actively transcribed genes
Two histone modifications are particularly associated with active transcription:H3K4 trimethylation is performed by the COMPASS complex.[32][33][34] Despite the conservation of this complex and histone modification from yeast to mammals, it is not entirely clear what role this modification plays. However, it is an excellent mark of active promoters and the level of this histone modification at a gene’s promoter is broadly correlated with transcriptional activity of the gene. The formation of this mark is tied to transcription in a rather convoluted manner: early in transcription of a gene, RNA polymerase II undergoes a switch from initiating’ to ‘elongating’, marked by a change in the phosphorylation states of the RNA polymerase II C terminal domain (CTD). The same enzyme that phosphorylates the CTD also phosphorylates the Rad6 complex,[35][36] which in turn adds a ubiquitin mark to H2B K123 (K120 in mammals).[37] H2BK123Ub occurs throughout transcribed regions, but this mark is required for COMPASS to trimethylate H3K4 at promoters.[38][39]
- Trimethylation of H3 lysine 36 (H3K36Me3) in the body of active genes
Repressed genes
Three histone modifications are particularly associated with repressed genes:- Trimethylation of H3 lysine 27 (H3K27Me3)
- Di and tri-methylation of H3 lysine 9 (H3K9Me2/3)
- Trimethylation of H4 lysine 20 (H4K20Me3)
Bivalent promoters
Analysis of histone modifications in embryonic stem cells (and other stem cells) revealed many gene promoters carrying both H3K4Me3 and H3K27Me3, in other words these promoters display both activating and repressing marks simultaneously. This peculiar combination of modifications marks genes that are poised for transcription; they are not required in stem cells, but are rapidly required after differentiation into some lineages. Once the cell starts to differentiate, these bivalent promoters are resolved to either active or repressive states depending on the chosen lineage.[57]Other functions
DNA damage
Marking sites of DNA damage is an important function for histone modifications.- Phosphorylation of H2AX at serine 139 (γH2AX)
- Acetylation of H3 lysine 56 (H3K56Ac)
Chromosome condensation
- Phosphorylation of H3 at serine 10 (phospho-H3S10)
Phosphorylation H2B at serine 10 in yeast or serine 14 in mammalian cells (phospho-H2BS10/14)
Phosphorylation of H2B at serine 10 (yeast) or serine 14 (mammals) is also linked to chromatin condensation, but for the very different purpose of mediating chromosome condensation during apoptosis.[75][76] This mark is not simply a late acting bystander in apoptosis as yeast carrying mutations of this residue are resistant to hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptotic cell death.