In artificial intelligence, an evolutionary algorithm (EA) is a subset of evolutionary computation, a generic population-based metaheuristic optimization algorithm. An EA uses mechanisms inspired by biological evolution, such as reproduction, mutation, recombination, and selection. Candidate solutions to the optimization problem play the role of individuals in a population, and the fitness function determines the quality of the solutions (see also loss function). Evolution of the population then takes place after the repeated application of the above operators.
Evolutionary algorithms often perform well approximating solutions to all types of problems because they ideally do not make any assumption about the underlying fitness landscape. Techniques from evolutionary algorithms applied to the modeling of biological evolution are generally limited to explorations of microevolutionary processes and planning models based upon cellular processes. In most real applications of EAs, computational complexity is a prohibiting factor. In fact, this computational complexity is due to fitness function evaluation. Fitness approximation is one of the solutions to overcome this difficulty. However, seemingly simple EA can solve often complex problems; therefore, there may be no direct link between algorithm complexity and problem complexity.
Evolutionary algorithms often perform well approximating solutions to all types of problems because they ideally do not make any assumption about the underlying fitness landscape. Techniques from evolutionary algorithms applied to the modeling of biological evolution are generally limited to explorations of microevolutionary processes and planning models based upon cellular processes. In most real applications of EAs, computational complexity is a prohibiting factor. In fact, this computational complexity is due to fitness function evaluation. Fitness approximation is one of the solutions to overcome this difficulty. However, seemingly simple EA can solve often complex problems; therefore, there may be no direct link between algorithm complexity and problem complexity.
Implementation
Step Two: Evaluate the fitness of each individual in that population (time limit, sufficient fitness achieved, etc.)
Step Three: Repeat the following regenerational steps until termination:
- Select the best-fit individuals for reproduction. (Parents)
- Breed new individuals through crossover and mutation operations to give birth to offspring.
- Evaluate the individual fitness of new individuals.
- Replace least-fit population with new individuals.
Types
Similar techniques differ in genetic representation and other implementation details, and the nature of the particular applied problem.- Genetic algorithm – This is the most popular type of EA. One seeks the solution of a problem in the form of strings of numbers (traditionally binary, although the best representations are usually those that reflect something about the problem being solved), by applying operators such as recombination and mutation (sometimes one, sometimes both). This type of EA is often used in optimization problems. Another name for it is fetura, from the Latin for breeding.
- Genetic programming – Here the solutions are in the form of computer programs, and their fitness is determined by their ability to solve a computational problem.
- Evolutionary programming – Similar to genetic programming, but the structure of the program is fixed and its numerical parameters are allowed to evolve.
- Gene expression programming – Like genetic programming, GEP also evolves computer programs but it explores a genotype-phenotype system, where computer programs of different sizes are encoded in linear chromosomes of fixed length.
- Evolution strategy – Works with vectors of real numbers as representations of solutions, and typically uses self-adaptive mutation rates.
- Differential evolution – Based on vector differences and is therefore primarily suited for numerical optimization problems.
- Neuroevolution – Similar to genetic programming but the genomes represent artificial neural networks by describing structure and connection weights. The genome encoding can be direct or indirect.
- Learning classifier system – Here the solution is a set of classifiers (rules or conditions). A Michigan-LCS evolves at the level of individual classifiers whereas a Pittsburgh-LCS uses populations of classifier-sets. Initially, classifiers were only binary, but now include real, neural net, or S-expression types. Fitness is typically determined with either a strength or accuracy based reinforcement learning or supervised learning approach.
Comparison to biological processes
A possible limitation of many evolutionary algorithms is their lack of a clear genotype-phenotype distinction. In nature, the fertilized egg cell undergoes a complex process known as embryogenesis to become a mature phenotype. This indirect encoding is believed to make the genetic search more robust (i.e. reduce the probability of fatal mutations), and also may improve the evolvability of the organism. Such indirect (a.k.a. generative or developmental) encodings also enable evolution to exploit the regularity in the environment. Recent work in the field of artificial embryogeny, or artificial developmental systems, seeks to address these concerns. And gene expression programming successfully explores a genotype-phenotype system, where the genotype consists of linear multigenic chromosomes of fixed length and the phenotype consists of multiple expression trees or computer programs of different sizes and shapes.Related techniques
Swarm algorithms include- Ant colony optimization – Based on the ideas of ant foraging by pheromone communication to form paths. Primarily suited for combinatorial optimization and graph problems.
- The runner-root algorithm (RRA) is inspired by the function of runners and roots of plants in nature
- Artificial bee colony algorithm – Based on the honey bee foraging behaviour. Primarily proposed for numerical optimization and extended to solve combinatorial, constrained and multi-objective optimization problems.
- Bees algorithm is based on the foraging behaviour of honey bees. It has been applied in many applications such as routing and scheduling.
- Cuckoo search is inspired by the brooding parasitism of the cuckoo species. It also uses Lévy flights, and thus it suits for global optimization problems.
- Particle swarm optimization – Based on the ideas of animal flocking behaviour. Also primarily suited for numerical optimization problems.
Other population-based metaheuristic methods
- Hunting Search - A method inspired by the group hunting of some animals such as wolves that organize their position to surround the prey, each of them relative to the position of the others and especially that of their leader. It is a continuous optimization method adapted as a combinatorial optimization method.
- Adaptive dimensional search – Unlike nature-inspired metaheuristic techniques, an adaptive dimensional search algorithm does not implement any metaphor as an underlying principle. Rather it uses a simple performance-oriented method, based on the update of the search dimensionality ratio (SDR) parameter at each iteration.
- Firefly algorithm is inspired by the behavior of fireflies, attracting each other by flashing light. This is especially useful for multimodal optimization.
- Harmony search – Based on the ideas of musicians' behavior in searching for better harmonies. This algorithm is suitable for combinatorial optimization as well as parameter optimization.
- Gaussian adaptation – Based on information theory. Used for maximization of manufacturing yield, mean fitness or average information. See for instance Entropy in thermodynamics and information theory.
- Memetic algorithm – A hybrid method, inspired by Richard Dawkins' notion of a meme, it commonly takes the form of a population-based algorithm coupled with individual learning procedures capable of performing local refinements. Emphasizes the exploitation of problem-specific knowledge, and tries to orchestrate local and global search in a synergistic way.
Examples
The computer simulations Tierra and Avida attempt to model macroevolutionary dynamics.Gallery
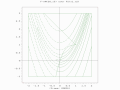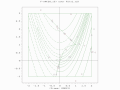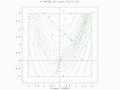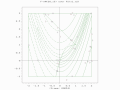
- A two-population EA search over a constrained Rosenbrock function with bounded global optimum.
- A two-population EA search over a constrained Rosenbrock function. Global optimum is not bounded.
- A two-population EA search of a bounded optima of Simionescu's function.