| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Cetus |
| Pronunciation | /ˌtaʊ |
| Right ascension | 01h 44m 04.08338s |
| Declination | −15° 56′ 14.9262″ |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.50 ± 0.01 |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | G8 V |
| U−B color index | +0.21 |
| B−V color index | +0.72 |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −16.68±0.05 km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −1721.05 mas/yr Dec.: +854.16 mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 273.96 ± 0.17 mas |
| Distance | 11.905 ± 0.007 ly (3.650 ± 0.002 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 5.69±0.01 |
| Details | |
| Mass | 0.783±0.012 M☉ |
| Radius | 0.793±0.004 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.52±0.03 L☉ |
| Luminosity (visual, LV) | 0.45 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.4 cgs |
| Temperature | 5,344±50 K |
| Metallicity | 28±3% Sun |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.55±0.05 dex |
| Rotation | 34 days |
| Age | 5.8 Gyr |
| Other designations | |
Tau Ceti, Latinized from τ Ceti, is a single star in the constellation Cetus that is spectrally similar to the Sun, although it has only about 78% of the Sun's mass. At a distance of just under 12 light-years (3.7 parsecs) from the Solar System, it is a relatively nearby star and the closest solitary G-class star. The star appears stable, with little stellar variation, and is metal-deficient.
Observations have detected more than ten times as much dust surrounding Tau Ceti as is present in the Solar System. Since December 2012, there has been evidence of possibly five planets orbiting Tau Ceti, with two of these being potentially in the habitable zone. Because of its debris disk, any planet orbiting Tau Ceti would face far more impact events than Earth. Despite this hurdle to habitability, its solar analog (Sun-like) characteristics have led to widespread interest in the star. Given its stability, similarity and relative proximity to the Sun, Tau Ceti is consistently listed as a target for the Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence (SETI) and appears in some science fiction literature.
It can be seen with the unaided eye as a third-magnitude star. As seen from Tau Ceti, the Sun would be a third-magnitude star in the northern hemisphere constellation Boötes.
Name
The name "Tau Ceti" is the Bayer designation for this star, established in 1603 as part of German celestial cartographer Johann Bayer's Uranometria star catalogue: it is "number T" in Bayer's sequence of constellation Cetus. In the catalogue of stars in the Calendarium of Al Achsasi al Mouakket, written at Cairo about 1650, this star was designated Thālith al Naʽāmāt (ثالث النعامات - thālith al-naʽāmāt), which was translated into Latin as Tertia Struthionum, meaning the third of the ostriches. This star, along with η Cet (Deneb Algenubi), θ Cet (Thanih Al Naamat), ζ Cet (Baten Kaitos), and υ Cet, were Al Naʽāmāt (النعامات), the Hen Ostriches.
In Chinese, the "Square Celestial Granary" (Chinese: 天倉; pinyin: Tiān Cāng) refers to an asterism consisting of τ Ceti, ι Ceti, η Ceti, ζ Ceti, θ Ceti and 57 Ceti. Consequently, τ Ceti itself is known as the "Fifth Star of Square Celestial Granary" (Chinese: 天倉五; pinyin: Tiān Cāng wǔ).
Motion
The proper motion of a star is its rate of movement across the celestial sphere,
determined by comparing its position relative to more distant
background objects. Tau Ceti is considered to be a high-proper-motion
star, although it only has an annual traverse of just under 2 arc seconds.
Thus it will require about 2000 years before the location of this star
shifts by more than a degree. A high proper motion is an indicator of
closeness to the Sun.
Nearby stars can traverse an angle of arc across the sky more rapidly
than the distant background stars and are good candidates for parallax studies. In the case of Tau Ceti, the parallax measurements indicate a distance of 11.9 ly. This makes it one of the closest star systems to the Sun and the next-closest spectral class-G star after Alpha Centauri A.
The radial velocity
of a star is the component of its motion that is toward or away from
the Sun. Unlike proper motion, a star's radial velocity cannot be
directly observed, but can be determined by measuring its spectrum. Due to the Doppler shift, the absorption lines
in the spectrum of a star will be shifted slightly toward the red (or
longer wavelengths) if the star is moving away from the observer, or
toward blue (or shorter wavelengths) when it moves toward the observer.
In the case of Tau Ceti, the radial velocity is about −17 km/s, with the
negative value indicating that it is moving toward the Sun. The star will make its closest approach to the Sun in about 43,000 years, when it comes to within 10.6 ly (3.25 pc).
The distance to Tau Ceti, along with its proper motion and radial
velocity, together give the motion of the star through space. The space velocity relative to the Sun is 37.2 km/s. This result can then be used to compute an orbital path of Tau Ceti through the Milky Way. It has a mean galacto-centric distance of 9.7 kiloparsec (32000 ly) and an orbital eccentricity of 0.22.
Physical properties
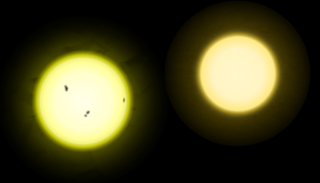
The Sun (left) is both larger and somewhat hotter than the less active Tau Ceti (right).
The Tau Ceti system is believed to have only one stellar component. A
dim optical companion has also been observed with magnitude 13.1. As
of 2000, it was 137 arcseconds distant from the primary. It may be gravitationally bound, but it is considered more likely to be a line-of-sight coincidence.
Most of what is known about the physical properties of Tau Ceti and its system has been determined through spectroscopic measurements. By comparing the spectrum to computed models of stellar evolution, the age, mass, radius and luminosity of Tau Ceti can be estimated. However, using an astronomical interferometer, measurements of the radius of the star can be made directly to an accuracy of 0.5%. Through such means, the radius of Tau Ceti has been measured to be 79.3%±0.4% of the solar radius. This is about the size that is expected for a star with somewhat lower mass than the Sun.
Rotation
The rotation period for Tau Ceti was measured by periodic variations in the classic H and K absorption lines of singly ionized calcium (Ca II). These lines are closely associated with surface magnetic activity,
so the period of variation measures the time required for the activity
sites to complete a full rotation about the star. By this means the
rotation period for Tau Ceti is estimated to be 34 d. Due to the Doppler effect, the rotation rate of a star
affects the width of the absorption lines in the spectrum (light from
the side of the star moving away from the observer will be shifted to a
longer wavelength; light from the side moving towards the observer will
be shifted toward a shorter wavelength). By analyzing the width of these
lines, the rotational velocity of a star can be estimated. The
projected rotation velocity for Tau Ceti is
- veq · sin i ≈ 1 km/s,
where veq is the velocity at the equator, and i is the inclination angle of the rotation axis to the line of sight. For a typical G8 star, the rotation velocity is about 2.5 km/s.
The relatively low rotational velocity measurements may indicate that
Tau Ceti is being viewed from nearly the direction of its pole.
Metallicity
The
chemical composition of a star provides important clues to its
evolutionary history, including the age at which it formed. The interstellar medium of dust and gas from which stars form is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium
with trace amounts of heavier elements. As nearby stars continually
evolve and die, they seed the interstellar medium with an increasing
portion of heavier elements. Thus younger stars tend to have a higher
portion of heavy elements in their atmospheres than do the older stars.
These heavy elements are termed "metals" by astronomers, and the portion
of heavy elements is the metallicity. The amount of metallicity in a star is given in terms of the ratio of iron (Fe), an easily observed heavy element, to hydrogen. A logarithm of the relative iron abundance is compared to the Sun. In the case of Tau Ceti, the atmospheric metallicity is
- dex,
equivalent to about a third the solar abundance. Past measurements have varied from −0.13 to −0.60.
This lower abundance of iron indicates that Tau Ceti is almost
certainly older than the Sun. Its age had previously been estimated to
be about 10 Gyr, but is now thought to be around half that, at 5.8 Gyr. This compares with 4.57 Gyr for the Sun. However, computed age estimates for Tau Ceti can range from 4.4 to 12 Gyr, depending on the model adopted.
Besides rotation, another factor that can widen the absorption features in the spectrum of a star is pressure broadening.
The presence of nearby particles affects the radiation emitted by an
individual particle. So the line width is dependent on the surface
pressure of the star, which in turn is determined by the temperature and
surface gravity. This technique was used to determine the surface
gravity of Tau Ceti. The log g, or logarithm of the star's surface gravity, is about 4.4, very close to the log g = 4.44 for the Sun.
Luminosity and variability
The luminosity of Tau Ceti is equal to only 55% of the Sun's luminosity. A terrestrial planet would need to orbit this star at a distance of about 0.7 AU in order to match the solar insolation level of Earth. This is approximately the same as the average distance between Venus and the Sun.
The chromosphere of Tau Ceti—the portion of a star's atmosphere just above the light-emitting photosphere—currently displays little or no magnetic activity, indicating a stable star. One 9-year study of temperature, granulation, and the chromosphere showed no systematic variations; Ca II emissions around the H and K infrared bands show a possible 11-year cycle, but this is weak relative to the Sun. Alternatively it has been suggested that the star could be in a low-activity state analogous to a Maunder minimum—a historical period, associated with the Little Ice Age in Europe, when sunspots became exceedingly rare on the Sun's surface. Spectral line profiles of Tau Ceti are extremely narrow, indicating low turbulence and observed rotation. The star's oscillations have an amplitude about half that of the Sun and a lower mode lifetime.
Life and planet searches
Principal
factors driving research interest in Tau Ceti are its proximity, its
Sun-like characteristics and their implications for possible planets and
life. For categorization purposes, Hall and Lockwood report that "the
terms 'solarlike star', 'solar analog', and 'solar twin' [are] progressively restrictive descriptions".
Tau Ceti fits the second category, given its similar mass and low
variability, but relative lack of metals. The similarities have inspired
popular culture references for decades, as well as scientific examination.
Tau Ceti has been a target of radial-velocity planetary searches.
As of 1988, observations ruled out any periodical variations
attributable to massive planets around Tau Ceti inside of Jupiter-like
distances. Ever more precise measurements continue to rule out such planets, at least until December 2012. The velocity precision reached is about 11 m/s measured over a 5-year time span. This result excludes the presence of hot Jupiters
and probably excludes any planets with minimal mass greater than or
equal to Jupiter's mass and with orbital periods less than 15 years. In addition, a survey of nearby stars by the Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera
was completed in 1999, including a search for faint companions to Tau
Ceti; none were discovered to limits of the telescope's resolving power.
These searches only excluded larger brown dwarf bodies and giant planets, so smaller, Earth-like planets in orbit around the star were not precluded. If "hot Jupiters" did exist in close orbit, they would likely disrupt the star's habitable zone; their exclusion was thus considered positive for the possibility of Earth-like planets.
General research has shown a positive correlation between the presence
of planets and a relatively high-metallicity parent star, suggesting
that stars with lower metallicity such as Tau Ceti have a lower chance
of having planets.
Primitive life on Tau Ceti's planets might reveal itself through an
atmospheric composition unlikely to be abiotic, just as oxygen on Earth
is indicative of life.
SETI and HabCat
Tau Ceti could have been a search target for the canceled Terrestrial Planet Finder
The most optimistic search project to date was Project Ozma, which was intended to "search for extraterrestrial intelligence" (SETI) by examining selected stars for indications of artificial radio signals. It was run by the astronomer Frank Drake, who selected Tau Ceti and Epsilon Eridani
as the initial targets. Both are located near the Solar System and are
physically similar to the Sun. No artificial signals were found despite
200 hours of observations. Subsequent radio searches of this star system have also turned up negative.
This lack of results has not dampened interest in observing the Tau Ceti system for biosignatures. In 2002, astronomers Margaret Turnbull and Jill Tarter developed the Catalog of Nearby Habitable Systems (HabCat) under the auspices of Project Phoenix, another SETI endeavour. The list contained more than 17000 theoretically habitable systems, approximately 10% of the original sample. The next year, Turnbull would further refine the list to the 30 most promising systems out of 5000 within 100 light-years from the Sun, including Tau Ceti; this will form part of the basis of radio searches with the Allen Telescope Array. She also chose Tau Ceti for a final shortlist of just five stars suitable for searches by the (indefinitely postponed) Terrestrial Planet Finder telescope system, commenting that "these are places I'd want to live if God were to put our planet around another star".
Planetary system
On December 19, 2012, evidence was presented that suggest a system of five planets orbiting Tau Ceti. The planets' estimated minimal masses are between 2 and 6 Earth masses,
and their orbital periods range from 14 to 640 days. One of them,
tentatively named Tau Ceti e, appears to orbit about half as far from
Tau Ceti as Earth does from the Sun. With Tau Ceti's luminosity of 52%
that of the Sun and a distance from the star of 0.552 AU, the planet
would receive 1.71 times as much stellar radiation as Earth does,
slightly less than Venus with 1.91 times Earth's. Nevertheless, some
research places it within the star's habitable zone.
The Planetary Habitability Laboratory has estimated that Tau Ceti f,
which would receive 28.5% as much starlight as Earth, would be narrowly
within the habitable zone of the star as well.
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | ≥2.00 ± 0.80 M⊕ | 0.105 ± 0.006 | 13.965 ± 0.024 | 0.16 ± 0.22 | — | — |
| c | ≥3.1 ± 1.40 M⊕ | 0.195 ± 0.011 | 35.362 ± 0.106 | 0.03 ± 0.28 | — | — |
| d | ≥3.60 ± 1.7 M⊕ | 0.374 ± 0.02 | 94.11 ± 0.7 | 0.08 ± 0.26 | — | — |
| e | ≥4.30 ± 2.1 M⊕ | 0.552 ± 0.03 | 168.12 ± 2.32 | 0.05 ± 0.22 | — | — |
| f | ≥6.6 ± 3.5 M⊕ | 1.35 ± 0.09 AU | 642 ± 37 | 0.03 ± 0.26 | — | — |
| Debris disk | 35–50 (or 2+8 −1–55+5 −5) AU |
35±10° | — | |||
The team that made the discovery in 2013 went on to refine and
improve their methodology, and with updated radial-velocity
measurements, published new results in August 2017. They confirmed Tau
Ceti e and f as candidates, but failed to detect Tau Ceti b and c (which
had appeared to orbit the star at a suspicious 0.4 and 1 times the
star's rotation period, which would have suggested that their apparent
signal is related to stellar rotation rather than an orbiting planet,
although this can be false negative).
Instead they found two new planetary candidates, Tau Ceti g and h, with
orbits of 20 and 49 days. They did find some evidence for the existence
of Tau Ceti d, but, because it did not show up in all data sets, they
were unable to confirm it as a candidate planet.
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g | ≥1.75+0.25 −0.40 M⊕ |
0.133+0.001 −0.002 |
20.00+0.02 −0.01 |
0.06+0.13 −0.06 |
— | — |
| h | ≥1.83+0.68 −0.26 M⊕ |
0.243 ± 0.003 | 49.41+0.08 −0.10 |
0.23+0.16 −0.15 |
— | — |
| e | ≥3.93+0.83 −0.64 M⊕ |
0.538 ± 0.006 | 162.87+1.08 −0.46 |
0.18+0.18 −0.14 |
— | — |
| f | ≥3.93+1.05 −1.37 M⊕ |
1.334+0.017 −0.044 |
636.13+11.70 −47.69 |
0.16+0.07 −0.16 |
— | — |
| Debris disk | 6.2+9.8 −4.6 – 52+3 −8 AU |
35±10° | — | |||
The updated 4-planet model is dynamically packed and potentially
stable for billions of years, but with further refinements more planet
candidates could still be detected (including b and c). The signals
detected from the candidate planets have radial velocities as low as
30 cm/s, and the experimental method used in their detection, as it was
applied to HARPS, could in theory have detected down to around 20 cm/s.
In order to detect an Earth-sized planet candidate between Tau Ceti e
and f, in the system's habitable zone, a radial velocity precision of
approximately 10 cm/s would need to be achieved.
The habitable zone
for this star, defined as the locations where liquid water could be
present on an Earth-sized planet, is at a radius of 0.55–1.16 AU, where 1 AU is the average distance from the Earth to the Sun.
If Tau Ceti is aligned in such a way that it is nearly pole-on to
Earth (as its rotation could indicate), that would mean that the
planets would be, rather than slightly larger to a few times Earth's
mass, they would be on the leagues of tens of Earth masses to even
hundreds. For example, if Tau Ceti f's orbit was inclined 70 degrees
from being head-on to Earth, its mass would be 11.49+3.07
−4 Earth masses, making it a mini-Neptune or mega-Earth on the middle-to-high end, and a larger super-Earth on the lower end. However, this scenario isn't necessarily true; since Tau Ceti's debris disk has an inclination of 35±10, though, this could mean that the planets' orbits are similarly inclined. This would put f from 5.56+1.48
−1.94 to 9.29+2.49
−3.23 Earth masses, which means it's less likely to be a mini-Neptune even at the higher threshold, if it is assumed that the debris disk ad f's orbits are equal.
−4 Earth masses, making it a mini-Neptune or mega-Earth on the middle-to-high end, and a larger super-Earth on the lower end. However, this scenario isn't necessarily true; since Tau Ceti's debris disk has an inclination of 35±10, though, this could mean that the planets' orbits are similarly inclined. This would put f from 5.56+1.48
−1.94 to 9.29+2.49
−3.23 Earth masses, which means it's less likely to be a mini-Neptune even at the higher threshold, if it is assumed that the debris disk ad f's orbits are equal.
Tau Ceti e
Tau Ceti e is a candidate planet orbiting Tau Ceti that was detected by statistical analyses of the data of the star's variations in radial velocity that were obtained using HIRES, AAPS, and HARPS. Its possible properties were refined in 2017: it orbits at a distance of 0.552 AU (between the orbits of Venus and Mercury in the Solar System) with an orbital period of 168 days and has a minimum mass of 3.29 Earth masses. Because the minimum mass of a super-Earth is 5 Earth masses,
Tau Ceti e may be Earth-sized. If it possesses an Earth-like
atmosphere, the surface temperature would be around 68 °C (154 °F).
Tau Ceti f
Tau Ceti f is a candidate super-Earth orbiting Tau Ceti that was discovered in 2012 by statistical analyses of the star's variations in radial velocity, based on data obtained using HIRES, AAPS, and HARPS. It is of interest because its orbit places it in Tau Ceti's extended habitable zone.
However, a 2015 study implies that it has been in the temperate zone
for less than one billion years, so there may not be a detectable biosignature.
Few properties of the planet are known other than its orbit and mass. It orbits Tau Ceti at a distance of 1.35 AU (near Mars's orbit in the Solar System) with an orbital period of 642 days and has a minimum mass of 2.66 Earth masses, which means it may be either a super-Earth or terrestrial planet.
Debris disk
In 2004, a team of UK astronomers led by Jane Greaves discovered that Tau Ceti has more than ten times the amount of cometary and asteroidal
material orbiting it than does the Sun. This was determined by
measuring the disk of cold dust orbiting the star produced by collisions
between such small bodies. This result puts a damper on the possibility of complex life in the system, because any planets would suffer from large impact events
roughly ten times more frequently than Earth. Greaves noted at the time
of her research that "it is likely that [any planets] will experience
constant bombardment from asteroids of the kind believed to have wiped
out the dinosaurs". Such bombardments would inhibit the development of biodiversity between impacts. However, it is possible that a large Jupiter-sized gas giant could deflect comets and asteroids.
The debris disk was discovered by measuring the amount of radiation emitted by the system in the far infrared portion of the spectrum. The disk forms a symmetric feature that is centered on the star, and its outer radius averages 55 AU. The lack of infrared radiation from the warmer parts of the disk near Tau Ceti imply an inner cut-off at a radius of 10 AU. By comparison, the Solar System's Kuiper belt extends from 30 to 50 AU.
To be maintained over a long period of time, this ring of dust must be
constantly replenished through collisions by larger bodies. The bulk of the disk appears to be orbiting Tau Ceti at a distance of 35–50 AU, well outside the orbit of the habitable zone. At this distance, the dust belt may be analogous to the Kuiper belt that lies outside the orbit of Neptune in the Solar System.
Tau Ceti shows that stars need not lose large disks as they age, and such a thick belt may not be uncommon among Sun-like stars. Tau Ceti's belt is only 1/20 as dense as the belt around its young neighbor, Epsilon Eridani.
The relative lack of debris around the Sun may be the unusual case: one
research-team member suggests the Sun may have passed close to another
star early in its history and had most of its comets and asteroids
stripped away.
Stars with large debris disks have changed the way astronomers think
about planet formation because debris disk stars, where dust is
continually generated by collisions, appear to form planets readily.
![{\displaystyle \left[{\frac {\text{Fe}}{\text{H}}}\right]\approx -0.50}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6d77094dd32b1176a3b7a9bd8a651c119f542966)

