The "Pillars of Creation" from the Eagle Nebula. Evidence from the Spitzer Telescope
suggests that the pillars may already have been destroyed by a
supernova explosion, but the light showing us the destruction will not
reach the Earth for another millennium.
A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen, helium and other ionized gases. Originally, the term was used to describe any diffuse astronomical object, including galaxies beyond the Milky Way. The Andromeda Galaxy, for instance, was once referred to as the Andromeda Nebula (and spiral galaxies in general as "spiral nebulae") before the true nature of galaxies was confirmed in the early 20th century by Vesto Slipher, Edwin Hubble and others.
Most nebulae are of vast size; some are hundreds of light years in diameter. A nebula that is barely visible to the human eye from Earth would appear larger, but no brighter, from close by. The Orion Nebula,
the brightest nebula in the sky and occupying an area twice the
diameter of the full Moon, can be viewed with the naked eye but was
missed by early astronomers. Although denser than the space surrounding them, most nebulae are far less dense than any vacuum created on Earth – a nebular cloud the size of the Earth would have a total mass of only a few kilograms.
Many nebulae are visible due to fluorescence caused by embedded hot
stars, while others are so diffuse they can only be detected with long
exposures and special filters. Some nebulae are variably illuminated by T Tauri variable stars.
Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the "Pillars of Creation" in the Eagle Nebula.
In these regions the formations of gas, dust, and other materials
"clump" together to form denser regions, which attract further matter,
and eventually will become dense enough to form stars. The remaining material is then believed to form planets and other planetary system objects.
Observational history
Portion of the Carina Nebula
Around 150 AD, Claudius Ptolemaeus (Ptolemy) recorded, in books VII–VIII of his Almagest, five stars that appeared nebulous. He also noted a region of nebulosity between the constellations Ursa Major and Leo that was not associated with any star. The first true nebula, as distinct from a star cluster, was mentioned by the Persian astronomer Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi, in his Book of Fixed Stars (964). He noted "a little cloud" where the Andromeda Galaxy is located. He also cataloged the Omicron Velorum star cluster as a "nebulous star" and other nebulous objects, such as Brocchi's Cluster. The supernova that created the Crab Nebula, the SN 1054, was observed by Arabic and Chinese astronomers in 1054.
In 1610, Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc discovered the Orion Nebula using a telescope. This nebula was also observed by Johann Baptist Cysat in 1618. However, the first detailed study of the Orion Nebula was not performed until 1659, by Christiaan Huygens, who also believed he was the first person to discover this nebulosity.
In 1715, Edmund Halley published a list of six nebulae. This number steadily increased during the century, with Jean-Philippe de Cheseaux compiling a list of 20 (including eight not previously known) in 1746. From 1751 to 1753, Nicolas Louis de Lacaille cataloged 42 nebulae from the Cape of Good Hope, most of which were previously unknown. Charles Messier then compiled a catalog of 103 "nebulae" (now called Messier objects, which included what are now known to be galaxies) by 1781; his interest was detecting comets, and these were objects that might be mistaken for them.
The number of nebulae was then greatly increased by the efforts of William Herschel and his sister Caroline Herschel. Their Catalogue of One Thousand New Nebulae and Clusters of Stars
was published in 1786. A second catalog of a thousand was published in
1789 and the third and final catalog of 510 appeared in 1802. During
much of their work, William Herschel believed that these nebulae were
merely unresolved clusters of stars. In 1790, however, he discovered a
star surrounded by nebulosity and concluded that this was a true
nebulosity, rather than a more distant cluster.
Beginning in 1864, William Huggins examined the spectra of about 70 nebulae. He found that roughly a third of them had the emission spectrum of a gas. The rest showed a continuous spectrum and thus were thought to consist of a mass of stars. A third category was added in 1912 when Vesto Slipher showed that the spectrum of the nebula that surrounded the star Merope matched the spectra of the Pleiades open cluster. Thus the nebula radiates by reflected star light.
About 1923, following the Great Debate, it had become clear that many "nebulae" were in fact galaxies far from our own.
Slipher and Edwin Hubble
continued to collect the spectra from many different nebulae, finding
29 that showed emission spectra and 33 that had the continuous spectra
of star light.
In 1932, Hubble announced that nearly all nebula are associated with
stars, and their illumination comes from star light. He also discovered
that the emission spectrum nebulae are nearly always associated with
stars having spectral classifications of B or hotter (including all O-type main sequence stars), while nebulae with continuous spectra appear with cooler stars. Both Hubble and Henry Norris Russell concluded that the nebulae surrounding the hotter stars are transfomed in some manner.
Formation
The Triangulum Emission Garren Nebula NGC 604
There are a variety of formation mechanisms for the different types
of nebulae. Some nebulae form from gas that is already in the interstellar medium while others are produced by stars. Examples of the former case are giant molecular clouds,
the coldest, densest phase of interstellar gas, which can form by the
cooling and condensation of more diffuse gas. Examples of the latter
case are planetary nebulae formed from material shed by a star in late
stages of its stellar evolution.
Star-forming regions
are a class of emission nebula associated with giant molecular clouds.
These form as a molecular cloud collapses under its own weight,
proceeding stars. Massive stars may form in the center, and their ultraviolet radiation ionizes the surrounding gas, making it visible at optical wavelengths. The region of ionized hydrogen surrounding the massive stars is known as an H II region while the shells of neutral hydrogen surrounding the H II region are known as photodissociation region. Examples of star-forming regions are the Orion Nebula, the Rosette Nebula and the Omega Nebula.
Feedback from star-formation, in the form of supernova explosions of
massive stars, stellar winds or ultraviolet radiation from massive
stars, or outflows from low-mass stars may disrupt the cloud, destroying
the nebula after several million years.
Other nebulae form as the result of supernova explosions; the death throes of massive, short-lived stars. The materials thrown off from the supernova
explosion are then ionized by the energy and the compact object that
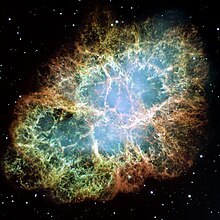
its core produces. One of the best examples of this is the Crab Nebula, in Taurus. The supernova event was recorded in the year 1054 and is labeled SN 1054. The compact object that was created after the explosion lies in the center of the Crab Nebula and its core is now a neutron star.
Still other nebulae form as planetary nebulae. This is the final stage of a low-mass star's life, like Earth's Sun. Stars with a mass up to 8–10 solar masses evolve into red giants
and slowly lose their outer layers during pulsations in their
atmospheres. When a star has lost enough material, its temperature
increases and the ultraviolet radiation it emits can ionize
the surrounding nebula that it has thrown off. Our Sun will produce a
planetary nebula and its core will remain behind in the form of white dwarf.
Types of nebulae
Classical types
Objects named nebulae belong to 4 major groups. Before their nature was understood, galaxies ("spiral nebulae") and star clusters too distant to be resolved as stars were also classified as nebulae, but no longer are.
- H II regions, large diffuse nebulae containing ionized hydrogen
- Planetary nebulae
- Supernova remnant (e.g., Crab Nebula)
- Dark nebula
Not all cloud-like structures are named nebulae; Herbig–Haro objects are an example.
Diffuse nebulae
The Carina Nebula is a diffuse nebula
Most nebulae can be described as diffuse nebulae, which means that they are extended and contain no well-defined boundaries. Diffuse nebulae can be divided into emission nebula, reflection nebulae and "dark nebulae." Visible light nebulae may be divided into emission nebulae that emit spectral line radiation from excited or ionized gas (mostly ionized hydrogen); they are often called HII regions (the term "HII" refers to ionized hydrogen). Reflection nebulae
are visible primarily due to the light they reflect. Reflection nebulae
themselves do not emit significant amounts of visible light, but are
near stars and reflect light from them.
Similar nebulae not illuminated by stars do not exhibit visible
radiation, but may be detected as opaque clouds blocking light from
luminous objects behind them; they are called "dark nebulae".
Although these nebulae have different visibility at optical wavelengths, they are all bright sources of infrared emission, chiefly from dust within the nebulae.
Planetary nebulae
The Oyster Nebula is a planetary nebula located in the constellation of Camelopardalis
Planetary nebulae are the remnants of the final stages of stellar evolution for lower-mass stars. Evolved asymptotic giant branch
stars expel their outer layers outwards due to strong stellar winds,
thus forming gaseous shells, while leaving behind the star's core in the
form of a white dwarf.
The hot white dwarf illuminates the expelled gases producing emission
nebulae with spectra similar to those of emission nebulae found in star formation regions. Technically they are HII regions, because most hydrogen are ionized, but are denser and more compact than nebulae found in star formation regions. Planetary nebulae were given their name by the first astronomical observers who were initially unable to distinguish them from planets, and who tended to confuse them with planets,
which were of more interest to them. Our Sun is expected to spawn a
planetary nebula about 12 billion years after its formation.
Protoplanetary nebula
The Red Rectangle Nebula is an example of a protoplanetary nebula located in the constellation of Monoceros
A protoplanetary nebula (PPN) is an astronomical object at the short-lived episode during a star's rapid stellar evolution between the late asymptotic giant branch (LAGB) phase and the following planetary nebula (PN) phase.
During the AGB phase, the star undergoes mass loss, emitting a
circumstellar shell of hydrogen gas. When this phase comes to an end,
the star enters the PPN phase.
The PPN is energized by the central star, causing it to emit
strong infrared radiation and become a reflection nebula. Collimated
stellar winds from the central star shape and shock the shell into an
axially symmetric form, while producing a fast moving molecular wind.
The exact point when a PPN becomes a planetary nebula (PN) is defined
by the temperature of the central star. The PPN phase continues until
the central star reaches a temperature of 30,000 K, after which it is
hot enough to ionize the surrounding gas.
Supernova remnants
The Crab Nebula, an example of a supernova remnant
A supernova occurs when a high-mass star reaches the end of its life. When nuclear fusion
in the core of the star stops, the star collapses. The gas falling
inward either rebounds or gets so strongly heated that it expands
outwards from the core, thus causing the star to explode. The expanding shell of gas forms a supernova remnant, a special diffuse nebula. Although much of the optical and X-ray emission from supernova remnants originates from ionized gas, a great amount of the radio emission is a form of non-thermal emission called synchrotron emission. This emission originates from high-velocity electrons oscillating within magnetic fields.