Among other reasons for independence, campaigners assert that Tibet
has been historically independent. However, some dispute this claim by
using different definitions of "Tibet", "historical" and "independence".
The campaigners also argue that Tibetans are currently mistreated and
denied certain human rights,
although the Chinese government disputes this and claims progress in
human rights. Various organizations with overlapping campaigns for
independence and human rights have sought to pressure various
governments to support Tibetan independence or to take punitive action
against China for opposing it.
Historical background
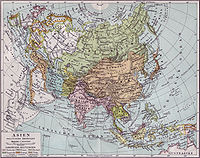
Map of Asia in 1890, showing Tibet within Qing China. The map was published in the Meyers Konversations-Lexikon in Leipzig in 1892.
Map of Asia from the 1925 Finnish encyclopedia Pieni Tietosanakirja, depicting Tibet within Republican China.
After the Mongol Prince Köden took control of the Kokonor region
in 1239, he sent his general Doorda Darqan on a reconnaissance mission
into Tibet in 1240. During this expedition the Kadampa monasteries of
Rwa-sgreng and Rgyal-lha-khang were burned, and 500 people killed. The
death of the Mongol qaghan Ögödei in 1241 brought Mongol military
activity around the world temporarily to a halt. Mongol interests in
Tibet resumed in 1244, when Prince Köden sent an invitation to the
leader of the Sakya sect, to come to his capital and formally surrender
Tibet to the Mongols. The Sakya leader arrived in Kokonor with his two
nephews Drogön Chögyal Phagpa ('Phags-pa; 1235–80) and Chana Dorje
(Phyag-na Rdo-rje; 1239–67) in 1246. This event marked the incorporation
of Tibet into the Mongol Empire. Tibet was under administrative rule of the Yuan dynasty until the 1350s. At that point, Tibet regained its independence.
In 1720, the Qing dynasty army entered Tibet in aid of the locals and defeated the invading forces of the Dzungar Khanate; thus began the period of Qing rule of Tibet. Later, the Chinese emperor assigned the Dalai Lama and Panchen Lama
to be in charge of religious and political matters in Tibet. The Dalai
Lama was leader of the area around Lhasa; the Panchen Lama was leader of
the area of Shigatse Prefecture.
By the early 18th century, the Qing dynasty had started to send resident commissioners (Ambans) to Lhasa. Tibetan factions rebelled in 1750
and killed the resident commissioners after the central government
decided to reduce the number of soldiers to about 100. The Qing army
entered and defeated the rebels and reinstalled the resident
commissioner. The number of soldiers in Tibet was kept at about 2,000.
The defensive duties were assisted by a local force which was
reorganized by the resident commissioner, and the Tibetan government
continued to manage day-to-day affairs as before.
At multiple places such as Lhasa, Batang, Dartsendo, Lhari, Chamdo, and Litang, Green Standard Army troops were garrisoned throughout the Dzungar war. Green Standard Army troops and Manchu Bannermen were both part of the Qing force which fought in Tibet in the war against the Dzungars. It was said that the Sichuan commander Yue Zhongqi (a descendant of Yue Fei) entered Lhasa first when the 2,000 Green Standard soldiers and 1,000 Manchu soldiers of the "Sichuan route" seized Lhasa. According to Mark C. Elliott, after 1728 the Qing used Green Standard Army troops to man the garrison in Lhasa rather than Bannermen. According to Evelyn S. Rawski, both Green Standard Army and Bannermen made up the Qing garrison in Tibet.
According to Sabine Dabringhaus, Green Standard Chinese soldiers
numbering more than 1,300 were stationed by the Qing in Tibet to support
the 3,000-strong Tibetan army.
In the mid 19th century, arriving with an Amban, a community of
Chinese troops from Sichuan who married Tibetan women settled down in
the Lubu neighborhood of Lhasa, where their descendants established a
community and assimilated into Tibetan culture.
Hebalin was the location of where Chinese Muslim troops and their
offspring lived, while Lubu was the place where Han Chinese troops and
their offspring lived.
In 1904, a British mission, accompanied by a large military
escort, invaded Tibet, forcing its way through to Lhasa. The 13th Dalai
Lama escaped. Britain forced The Great Three Tibetan Temple signing of
the Treaty of Lhasa. The head of the mission was Colonel Francis Younghusband.
The principal motivation for the British mission was a fear, which
proved to be unfounded, that Russia was extending its footprint into
Tibet and possibly even giving military aid to the Tibetan government.
But on his way to Lhasa, Younghusband killed 1,300 Tibetans in Gyangzê
(as written in The Great Game
by Peter Hopkirk) because the natives were in fear of what kind of
unequal treaty the British would offer the Tibetans. Some documents
claim that 5,000 Tibetans were killed by the British army.
The Anglo-Chinese Convention of 1906 recognized Chinese suzerainty over the region and the Anglo-Russian Convention of 1907, without Lhasa's or Beijing's acknowledgement, recognized the suzerainty of China over Tibet. The Qing central government claimed for sovereignty and direct rule over Tibet in 1910. The 13th Dalai Lama fled to British India
in February 1910. In the same month, the Chinese government issued a
proclamation 'deposing' the Dalai Lama and instigating the search for a
new incarnation. When he returned from exile, the Dalai Lama declared Tibetan independence (1912).
The subsequent outbreak of World War I and civil war in China meant that the Chinese factions only controlled part of Tibet. The government of the 13th Dalai Lama controlled Ü-Tsang (Dbus-gtsang) and western Kham, roughly coincident with the borders of the Tibet Autonomous Region today. Eastern Kham, separated from it by the Yangtze River, was under the control of Chinese warlord Liu Wenhui. The situation in Amdo (Qinghai) was more complicated, with the Xining area controlled by warlord Ma Bufang (of Hui ethnicity), who constantly strove to exert control over the rest of Amdo (Qinghai).
General Ma Fuxiang, the chairman of the Mongolian and Tibetan Affairs Commission (and also of Hui ethnicity), stated that Tibet was an integral part of the Republic of China.
"Our Party [the Kuomintang] takes the development of the weak and small and resistance to the strong and violent as our sole and most urgent task. This is even more true for those groups which are not of our kind [Ch. fei wo zulei zhe]. Now the peoples [minzu] of Mongolia and Tibet are closely related to us, and we have great affection for one another: our common existence and common honor already have a history of over a thousand years... Mongolia and Tibet's life and death are China's life and death. China absolutely cannot cause Mongolia and Tibet to break away from China's territory, and Mongolia and Tibet cannot reject China to become independent. At this time, there is not a single nation on earth except China that will sincerely develop Mongolia and Tibet."
In 1950, the People's Liberation Army
of the People's Republic of China invaded Tibet, after taking over the
rest of China from the Republic of China during the five years of civil
war. In 1951, the Seventeen Point Agreement for the Peaceful Liberation of Tibet, a treaty signed by representatives of the Dalai Lama and the Panchen Lama, provided for rule by a joint administration under representatives of the central government and the Tibetan government.
The Chinese have claimed that most of the population of Tibet at that time were serfs, bound to land owned by lamas. This claim has been challenged by other researchers. Any attempt at land reform
or the redistribution of wealth would have proved unpopular with the
established landowners. The Seventeen Point Agreement was put into
effect only in Tibet proper; ergo, eastern Kham and Amdo, being outside
the administration of the government of Tibet, were treated like
territory belonging to any other Chinese province,
with land reform implemented in full. As a result, a rebellion broke
out in these regions in June 1956. The rebellion eventually spread to
Lhasa, but was crushed by 1959. The 14th Dalai Lama and other government
principals fled to exile in India.
Beginning in the 1950s the Central Intelligence Agency trained Tibetans as paramilitaries.
CIA and MI6 activities in Tibet (1950-1970)
According to the 14th Dalai Lama, the CIA supported the Tibetan independence movement "not because they (the CIA) cared about Tibetan independence, but as part of their worldwide efforts to destabilize all communist governments".
Agents of Western governments had infiltrated Tibet by the mid-1950s, a few years after Tibet was annexed by the People's Republic of China. British MI6 agent Sydney Wignall, in his autobiography,
reveals that he and John Harrop travelled to Tibet together in 1955
posing as mountaineers. Captured by the Chinese authority, Wignell
recalled that he was surprised to find two CIA agents were already under
Chinese detention.
Clandestine military involvement by the U.S. began following the series of uprisings in the eastern Tibetan region of Kham
in 1956. Several small groups of Khampa fighters were trained by the
CIA camp and then airdropped back into Tibet with supplies. In 1958,
with the rebellion in Kham ongoing, two of these fighters, Athar and Lhotse, attempted to meet with the Dalai Lama
to determine whether he would cooperate with their activities. However,
their request for an audience was refused by the Lord Chamberlain, Phala Thubten Wonden, who believed such a meeting would be impolitic. According to Tsering Shakya, "Phala never told the Dalai Lama or the Kashag of the arrival of Athar and Lhotse. Nor did he inform the Dalai Lama of American willingness to provide aid."
Following a mass uprising in Lhasa in 1959 during the celebration of the Tibetan New Year
and the ensuing Chinese military response, the Dalai Lama went into
exile in India. Some sources state that the Dalai Lama's escape was
assisted by the CIA. After 1959, the CIA trained Tibetan guerrillas and
provided funds and weapons for the fight against China. However,
assistance was reduced during the course of the 1960s and finally ended
when Richard Nixon decided to seek rapprochement with China in the early 1970s. Kenneth Conboy and James Morrison, in The CIA's Secret War in Tibet, reveal how the CIA encouraged Tibetan revolt against China — and eventually came to control its fledgling resistance movement. The New York Times
reported on October 2, 1998 that the Tibetan exile movement received
$1.7 million a year in the 1960s from the CIA. The Dalai Lama said in
his autobiography that his brothers were responsible and that they
didn't tell him about it, knowing what his reaction would be. Lodi
Gyari, the Dalai Lama's personal representative in Washington, said he
had no knowledge of the annual subsidy of $180,000 marked as for the
Dalai Lama or how it was spent. The government in exile say they knew
that the CIA trained and equipped Tibetan guerrillas who raided Tibet
from a base camp in Nepal, and that the effect of those operations "only
resulted in more suffering for the people of Tibet. Worse, these
activities gave the Chinese government the opportunity to blame the
efforts of those seeking to regain Tibetan independence on the
activities of foreign powers--whereas, of course, it was an entirely
Tibetan initiative." The budget figures for the CIA's Tibetan program were as follows:
- Subsidy to the Dalai Lama: US$180,000
- Support of 2,100 Tibetan guerrillas based in Nepal: US$500,000
- Other costs: US$1.06m
- Total: US$1.73m
Positions on the status of Tibet
The status of Tibet before 1950, especially in the period between
1912 and 1950, is largely in dispute between supporters and opponents of
Tibetan independence.
According to supporters of Tibetan independence, Tibet was a distinct nation and state independent between the fall of the Mongol Empire in 1368 and subjugation by the Qing Dynasty
in 1720; and again between the fall of the Qing Dynasty in 1912 and its
incorporation into the PRC in 1951. Moreover, even during the periods
of nominal subjugation to the Yuan and Qing, Tibet was largely self-governing. As such, the Central Tibetan Administration
(CTA) views current PRC rule in Tibet as illegitimate, motivated solely
by the natural resources and strategic value of Tibet, and in violation
of both Tibet's historical status as an independent country and the
right of the Tibetan people to self-determination. It also points to PRC's autocratic and divide-and-rule policies, and assimilationist policies, regarding those as an example of imperialism bent on destroying Tibet's distinct ethnic makeup, culture, and identity, thereby cementing it as an indivisible part of China. After the fall of the Qing Dynasty, both Mongolia and Tibet declared independence and recognized each other as such.
On the other hand, opponents assert that the PRC rules Tibet
legitimately, by saying that Tibet has been part of Chinese history
since the 7th century as the Tibetan Empire had close interactions with the Chinese dynasties through royal marriage. In addition to the de facto power that the Chinese has since then, Yuan Dynasty conquest in the 13th century and that all subsequent Chinese governments (Ming Dynasty, Qing Dynasty, Republic of China, and People's Republic of China) have been exercising de jure sovereignty power over Tibet.
In addition, as this position argues that no country gave Tibet diplomatic recognition
between 1912 and 1950, they say that China, under the Republic of China
government, continued to maintain sovereignty over the region, and the
leaders of Tibet themselves acknowledged Chinese sovereignty by sending
delegates to the following: the Drafting Committee for a new
constitution of the Republic of China in 1925, the National Assembly of the Republic of China in 1931, the fourth National Congress of the Kuomintang
in 1931, a National Assembly for drafting a new Chinese constitution in
1946, and finally to another National Assembly for drafting a new
Chinese constitution in 1948.
Finally, some within the PRC considers all movements aimed at ending
Chinese sovereignty in Tibet, starting with British attempts in the late
19th and early 20th centuries, to the CTA today, as one long campaign
abetted by malicious Western imperialism
aimed at destroying Chinese integrity and sovereignty, thereby
weakening China's position in the world. The PRC also points to what it
calls the autocratic and theocratic policies of the government of Tibet before 1959, as well as its renunciation of South Tibet, claimed by China as a part of historical Tibet occupied by India, as well as the Dalai Lama's association with India, and as such claims the CTA has no moral legitimacy to govern Tibet.
Positions on Tibet after 1950
Tibetan exiles generally say that the number that have died in the Great Leap Forward, violence, or other unnatural causes since 1950 is approximately 1.2 million. However, this number is controversial. According to Patrick French,
a supporter of the Tibetan cause who was able to view the data and
calculations, the estimate is not reliable because the Tibetans were not
able to process the data well enough to produce a credible total, with
many persons double or triple counted. There were, however, many
casualties, perhaps as many as 400,000.
This figure is extrapolated from a calculation Warren W. Smith made
from census reports of Tibet which show 200,000 "missing" from Tibet. Even anti-Communist resources such as the Black Book of Communism
expresses doubt at the 1.2 million figure, but does note that according
to the Chinese census, the total population of ethnic Tibetans in the
PRC was 2.8 million in 1953, but only 2.5 million in 1964. It puts
forward a figure of 800,000 deaths and alleges that as many as 10% of
Tibetans were interned, with few survivors. Chinese demographers have estimated that 90,000 of the 300,000 "missing" Tibetans fled the region.
The Central Tibetan Administration also says that millions of
Chinese immigrants to the TAR are diluting the Tibetans both culturally
and through intermarriage. Exile groups say that despite recent attempts
to restore the appearance of original Tibetan culture to attract
tourism, the traditional Tibetan way of life is now irrevocably changed.
It is also reported that when Hu Yaobang, the general secretary of the Communist Party of China
visited Lhasa in 1980, he was unhappy when he found out the region was
behind neighbouring provinces. Reforms were instituted, and since then
the central government's policy in Tibet has granted most religious
freedoms. But monks and nuns are still sometimes imprisoned,
and many Tibetans (mostly monks and nuns) continue to flee Tibet
yearly. At the same time, many Tibetans believe projects that the PRC
implement to benefit Tibet, such as the China Western Development economic plan or the Qinghai-Tibet Railway, are politically motivated actions to consolidate central control over Tibet by facilitating militarization and Han Chinese
migration while benefiting few Tibetans; they also believe the money
funneled into cultural restoration projects as being aimed at attracting
foreign tourists. They also say that there is still preferential
treatment awarded to Han Chinese in the labor market as opposed to
Tibetans.
The government of the PRC claims that the population of Tibet in
1737 was about 8 million. It claims that due to the 'backward' rule of
the local theocracy, there was rapid decrease in the next two hundred
years and the population in 1959 was only about one million. Today, the population of Greater Tibet
is 7.3 million, of which 5 million is ethnic Tibetan, according to the
2000 census. According to the PRC the increase is viewed as the result
of the abolishment of the theocracy and introduction of a modern, higher
standard of living. Based on the census numbers, the PRC also rejects
claims that the Tibetans are being swamped by Han Chinese; instead the
PRC says that the border for Greater Tibet drawn by the government of
Tibet in Exile is so large that it incorporates regions such as Xining that are not traditionally Tibetan in the first place, hence exaggerating the number of non-Tibetans.
The government of the PRC also rejects claims that the lives of Tibetans have deteriorated, pointing to rights enjoyed by the Tibetan language in education
and in courts and says that the lives of Tibetans have been improved
immensely compared to the Dalai Lama's rule before 1950. Benefits that
are commonly quoted include: the GDP
of Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR) today is 30 times that before 1950; it
has 22,500 km of highways, all built since 1950; all secular education
in the region was created after integration into the PRC; there are 25
scientific research institutes, all built by the PRC; infant mortality has dropped from 43% in 1950 to 0.661% in 2000; life expectancy has risen from 35.5 years in 1950 to 67 in 2000; the collection and publishing of the traditional Epic of King Gesar, which is the longest epic poem in the world and had only been handed down orally before; allocation of 300 million Renminbi since the 1980s to the maintenance and protection of Tibetan monasteries. The Cultural Revolution
and the cultural damage it wrought upon the entire PRC is generally
condemned as a nationwide catastrophe, whose main instigators (in the
PRC's view, the Gang of Four)
have been brought to justice and whose recurrence is unthinkable in an
increasingly modernized China. The China Western Development plan is
viewed by the PRC as a massive, benevolent, and patriotic undertaking by
the eastern coast to help the western parts of China, including Tibet,
catch up in prosperity and living standards.
Supporting organisations
"Free Tibet" LED Banner at Bird's Nest, Beijing, August 19, 2008.
Pro-Tibetan protesters come into contact with pro-Chinese protesters in San Francisco
Organisations which support the Tibetan independence movement include:
- Tibetan Youth Congress - Located at Dharamsala, the seat of the Government of Tibet in Exile in India, claims 30,000 members.
- International Tibet Independence Movement - Located in Indiana, United States. It was formed in March 1995 and is now a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization for informing about Tibetan independence.
- International Tibetan Aid Organization - Located in Amsterdam, Netherlands, this organization was formed in 2004.
However, Tenzin Gyatso, the current Dalai Lama, the spiritual leader of Tibetan Buddhists, is no longer calling for independence. He has spoken in many international venues, including the United States Congress, and the European Parliament.
In 1987, he has also started campaigning for a peaceful resolution to
the issue of the status of Tibet, and has since then advocated that
Tibet should not become independent, but that it should be given
meaningful autonomy within the People's Republic of China. This approach is known as the "Middle Way".
Some organisations either support the "Middle Way" or do not
adopt a definitive stance on whether they support independence or
greater autonomy. Such organisations include:
- Free Tibet Campaign - Located in London, United Kingdom, formed in 1987, stands for the right of Tibetans to determine their own future and for the future of their own country.
- International Tibet Support Network - Located in London, United Kingdom, established in 2000, umbrella organization for Tibet related organization worldwide.
- Shiv Ganga Vidya Mandir, Phaphamau, Allahabad organized a Tibet Freedom Solidarity Rally in Allahabad on 9 April 2016, drawing more than 3000 participants.
Celebrity support and Freedom Concerts
The official flag of Tibet since its introduction in the early 20th century by the 13th Dalai Lama and is now used by the Tibetan Government in Exile in India
The Tibetan independence movement receives considerable publicity from celebrities in the United States and Europe,
although much of their support comes under a non-specific banner of
"Free Tibet", without specifying whether they support independence for
Tibet, or the kind of greater autonomy within China advocated by the
Dalai Lama.
The "Free Tibet" movement is supported by some celebrities, such as Richard Gere and Paris Hilton.
British comedian Russell Brand also occasionally mentions his support for the movement on his BBC Radio 2 show. Richard Gere is one of the most outspoken supporters of the movement and is chairman of the Board of Directors for the International Campaign for Tibet. Actress Sharon Stone caused significant controversy when she suggested that the 2008 Sichuan earthquake may have been the result of "bad karma," because the Chinese "are not being nice to the Dalai Lama, who is a good friend of mine." The Dalai Lama confirmed that he did not share Stone's views, although he confirmed that he had "met the lady".
U.S. actor and martial artist Steven Seagal
has been an active supporter of Tibetan independence for several
decades and makes regular donations to various Tibetan charities around
the world. He has been recognized by Tibetan Lama Penor Rinpoche as the reincarnation of tulku Chungdrag Dorje, the treasure revealer of Palyul Monastery. He also claims to have the special ability of clairvoyance; in a November 2006 interview, he stated: "I was born very different, clairvoyant and a healer".
The Milarepa Fund is an organisation which organises concerts to give publicity to the Tibetan independence movement. The fund was named after Milarepa,
the revered 11th-century Tibetan yogi, who used music to enlighten
people. It was originally established to disburse royalties from the Beastie Boys album Ill Communication
in 1994, to benefit Tibetan monks who were sampled on two songs. The
Milarepa Fund organizers also jointed the Beastie Boys as they headlined
the 1994 Lollapalooza Tour. Inspired by this tour, they began to organise a concert to promote Tibetan independence, in the style of Live Aid.
Organized in June 1996, the first concert (in San Francisco) opened with Icelandic singer Björk and featured acts such as Radiohead, The Smashing Pumpkins, Cibo Matto, Rage Against the Machine, Red Hot Chili Peppers, and De La Soul.
The concerts continued for three more years, which helped to generate
publicity for the Tibetan independence movement. It also reportedly led
to the growth of Tibetan independence organisations such as Students for a Free Tibet and Free Tibet Campaign worldwide.
Gorillaz, the virtual band
have shown support through a TV spot showing animated frontman, 2D,
meditating with fellow supporters outside of the Chinese embassy,
followed by a brief message encouraging people to join the Free Tibet Campaign. In addition, during the holographic performances of "Clint Eastwood", 2D is wearing a shirt saying "FREE TIBET."
During the 2008 Liège–Bastogne–Liège cycling race Australian rider Cadel Evans wore an undershirt with 'Free Tibet' printed on it, bringing attention to the movement months before the 2008 Summer Olympics, held in Beijing.