Sir Joseph John Thomson OM PRS (18 December 1856 – 30 August 1940) was an English physicist and Nobel Laureate in Physics, credited with the discovery and identification of the electron, the first subatomic particle to be discovered.
In 1897, Thomson showed that cathode rays were composed of previously unknown negatively charged particles (now called electrons), which he calculated must have bodies much smaller than atoms and a very large charge-to-mass ratio. Thomson is also credited with finding the first evidence for isotopes of a stable (non-radioactive) element in 1913, as part of his exploration into the composition of canal rays (positive ions). His experiments to determine the nature of positively charged particles, with Francis William Aston, were the first use of mass spectrometry and led to the development of the mass spectrograph.
Thomson was awarded the 1906 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the conduction of electricity in gases.
Education and personal life
Joseph John Thomson was born 18 December 1856 in Cheetham Hill, Manchester, Lancashire,
England. His mother, Emma Swindells, came from a local textile family.
His father, Joseph James Thomson, ran an antiquarian bookshop founded by
a great-grandfather. He had a brother, Frederick Vernon Thomson, who
was two years younger than he was. J. J. Thomson was a reserved yet devout Anglican.
His early education was in small private schools where he
demonstrated outstanding talent and interest in science. In 1870, he was
admitted to Owens College in Manchester (now University of Manchester) at the unusually young age of 14. His parents planned to enroll him as an apprentice engineer to Sharp-Stewart & Co, a locomotive manufacturer, but these plans were cut short when his father died in 1873.
He moved on to Trinity College, Cambridge, in 1876. In 1880, he obtained his Bachelor of Arts degree in mathematics (Second Wrangler in the Tripos and 2nd Smith's Prize). He applied for and became a Fellow of Trinity College in 1881. Thomson received his Master of Arts degree (with Adams Prize) in 1883.
Family
In 1890, Thomson married Rose Elisabeth Paget, one of his former students, daughter of Sir George Edward Paget, KCB, a physician and then Regius Professor of Physic at Cambridge at the church of St. Mary the Less. They had one son, George Paget Thomson, and one daughter, Joan Paget Thomson.
Career and research
Overview
On 22 December 1884, Thomson was appointed Cavendish Professor of Physics at the University of Cambridge. The appointment caused considerable surprise, given that candidates such as Osborne Reynolds or Richard Glazebrook
were older and more experienced in laboratory work. Thomson was known
for his work as a mathematician, where he was recognized as an
exceptional talent.
He was awarded a Nobel Prize in 1906, "in recognition of the
great merits of his theoretical and experimental investigations on the
conduction of electricity by gases." He was knighted in 1908 and appointed to the Order of Merit in 1912. In 1914, he gave the Romanes Lecture in Oxford on "The atomic theory". In 1918, he became Master of Trinity College, Cambridge, where he remained until his death. Joseph John Thomson died on 30 August 1940; his ashes rest in Westminster Abbey, near the graves of Sir Isaac Newton and his former student, Ernest Rutherford.
One of Thomson's greatest contributions to modern science was in his role as a highly gifted teacher. One of his students was Ernest Rutherford, who later succeeded him as Cavendish Professor of Physics. In addition to Thomson himself, six of his research assistants (Charles Glover Barkla, Niels Bohr, Max Born, William Henry Bragg, Owen Willans Richardson and Charles Thomson Rees Wilson) won Nobel Prizes in physics, and two (Francis William Aston and Ernest Rutherford) won Nobel prizes in chemistry. In addition, Thomson's son (George Paget Thomson) won the 1937 Nobel Prize in physics for proving the wave-like properties of electrons.
Early work
Thomson's prize-winning master's work, Treatise on the motion of vortex rings, shows his early interest in atomic structure. In it, Thomson mathematically described the motions of William Thomson's vortex theory of atoms.
Thomson published a number of papers addressing both mathematical and experimental issues of electromagnetism. He examined the electromagnetic theory of light of James Clerk Maxwell, introduced the concept of electromagnetic mass of a charged particle, and demonstrated that a moving charged body would apparently increase in mass.
Much of his work in mathematical modelling of chemical processes can be thought of as early computational chemistry. In further work, published in book form as Applications of dynamics to physics and chemistry
(1888), Thomson addressed the transformation of energy in mathematical
and theoretical terms, suggesting that all energy might be kinetic. His next book, Notes on recent researches in electricity and magnetism (1893), built upon Maxwell's Treatise upon electricity and magnetism, and was sometimes referred to as "the third volume of Maxwell".
In it, Thomson emphasized physical methods and experimentation and
included extensive figures and diagrams of apparatus, including a number
for the passage of electricity through gases. His third book, Elements of the mathematical theory of electricity and magnetism (1895) was a readable introduction to a wide variety of subjects, and achieved considerable popularity as a textbook.
A series of four lectures, given by Thomson on a visit to Princeton University in 1896, were subsequently published as Discharge of electricity through gases (1897). Thomson also presented a series of six lectures at Yale University in 1904.
Discovery of the electron
Several scientists, such as William Prout and Norman Lockyer,
had suggested that atoms were built up from a more fundamental unit,
but they envisioned this unit to be the size of the smallest atom,
hydrogen. Thomson in 1897 was the first to suggest that one of the
fundamental units was more than 1,000 times smaller than an atom,
suggesting the subatomic particle now known as the electron. Thomson
discovered this through his explorations on the properties of cathode
rays. Thomson made his suggestion on 30 April 1897 following his
discovery that cathode rays (at the time known as Lenard rays) could travel much further through air than expected for an atom-sized particle.
He estimated the mass of cathode rays by measuring the heat generated
when the rays hit a thermal junction and comparing this with the
magnetic deflection of the rays. His experiments suggested not only that
cathode rays were over 1,000 times lighter than the hydrogen atom, but
also that their mass was the same in whichever type of atom they came
from. He concluded that the rays were composed of very light, negatively
charged particles which were a universal building block of atoms. He
called the particles "corpuscles", but later scientists preferred the
name electron which had been suggested by George Johnstone Stoney in 1891, prior to Thomson's actual discovery.
In April 1897, Thomson had only early indications that the
cathode rays could be deflected electrically (previous investigators
such as Heinrich Hertz
had thought they could not be). A month after Thomson's announcement of
the corpuscle, he found that he could reliably deflect the rays by an
electric field if he evacuated the discharge tube to a very low
pressure. By comparing the deflection of a beam of cathode rays by
electric and magnetic fields he obtained more robust measurements of the
mass-to-charge ratio that confirmed his previous estimates.
This became the classic means of measuring the charge-to-mass ratio of
the electron. (The charge itself was not measured until Robert A. Millikan's oil drop experiment in 1909.)
Thomson believed that the corpuscles emerged from the atoms of the trace gas inside his cathode ray tubes.
He thus concluded that atoms were divisible, and that the corpuscles
were their building blocks. In 1904, Thomson suggested a model of the
atom, hypothesizing that it was a sphere of positive matter within which
electrostatic forces determined the positioning of the corpuscles.[2]
To explain the overall neutral charge of the atom, he proposed that
the corpuscles were distributed in a uniform sea of positive charge. In
this "plum pudding" model, the electrons were seen as embedded in the
positive charge like plums in a plum pudding (although in Thomson's
model they were not stationary, but orbiting rapidly).
Isotopes and mass spectrometry
In the bottom right corner of this photographic plate are markings for the two isotopes of neon: neon-20 and neon-22.
In 1912, as part of his exploration into the composition of the streams of positively charged particles then known as canal rays, Thomson and his research assistant F. W. Aston
channelled a stream of neon ions through a magnetic and an electric
field and measured its deflection by placing a photographic plate in its
path.
They observed two patches of light on the photographic plate (see image
on right), which suggested two different parabolas of deflection, and
concluded that neon is composed of atoms of two different atomic masses
(neon-20 and neon-22), that is to say of two isotopes. This was the first evidence for isotopes of a stable element; Frederick Soddy had previously proposed the existence of isotopes to explain the decay of certain radioactive elements.
J. J. Thomson's separation of neon isotopes by their mass was the first example of mass spectrometry, which was subsequently improved and developed into a general method by F. W. Aston and by A. J. Dempster.
Experiments with cathode rays
Earlier, physicists debated whether cathode rays were immaterial like light ("some process in the aether")
or were "in fact wholly material, and ... mark the paths of particles
of matter charged with negative electricity", quoting Thomson. The aetherial hypothesis was vague, but the particle hypothesis was definite enough for Thomson to test.
Magnetic deflection
Thomson first investigated the magnetic deflection
of cathode rays. Cathode rays were produced in the side tube on the
left of the apparatus and passed through the anode into the main bell jar, where they were deflected by a magnet. Thomson detected their path by the fluorescence
on a squared screen in the jar. He found that whatever the material of
the anode and the gas in the jar, the deflection of the rays was the
same, suggesting that the rays were of the same form whatever their
origin.
Electrical charge
The
cathode ray tube by which J. J. Thomson demonstrated that cathode rays
could be deflected by a magnetic field, and that their negative charge
was not a separate phenomenon.
While supporters of the aetherial theory accepted the possibility that negatively charged particles are produced in Crookes tubes, they believed that they are a mere by-product and that the cathode rays themselves are immaterial. Thomson set out to investigate whether or not he could actually separate the charge from the rays.
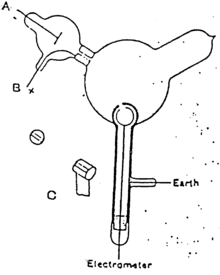
Thomson constructed a Crookes tube with an electrometer
set to one side, out of the direct path of the cathode rays. Thomson
could trace the path of the ray by observing the phosphorescent patch it
created where it hit the surface of the tube. Thomson observed that the
electrometer registered a charge only when he deflected the cathode ray
to it with a magnet. He concluded that the negative charge and the rays
were one and the same.
Electrical deflection
Thomson's
illustration of the Crookes tube by which he observed the deflection of
cathode rays by an electric field (and later measured their
mass-to-charge ratio). Cathode rays were emitted from the cathode C,
passed through slits A (the anode) and B (grounded), then through the electric field generated between plates D and E, finally impacting the surface at the far end.
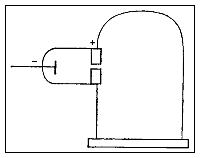
In May–June 1897, Thomson investigated whether or not the rays could be deflected by an electric field. Previous experimenters had failed to observe this, but Thomson believed their experiments were flawed because their tubes contained too much gas.
Thomson constructed a Crookes tube
with a better vacuum. At the start of the tube was the cathode from
which the rays projected. The rays were sharpened to a beam by two metal
slits – the first of these slits doubled as the anode, the second was
connected to the earth. The beam then passed between two parallel
aluminium plates, which produced an electric field between them when
they were connected to a battery. The end of the tube was a large sphere
where the beam would impact on the glass, created a glowing patch.
Thomson pasted a scale to the surface of this sphere to measure the
deflection of the beam. Note that any electron beam would collide with
some residual gas atoms within the Crookes tube, thereby ionizing them
and producing electrons and ions in the tube (space charge);
in previous experiments this space charge electrically screened the
externally applied electric field. However, in Thomson's Crookes tube
the density of residual atoms was so low that the space charge from the
electrons and ions was insufficient to electrically screen the
externally applied electric field, which permitted Thomson to
successfully observe electrical deflection.
When the upper plate was connected to the negative pole of the
battery and the lower plate to the positive pole, the glowing patch
moved downwards, and when the polarity was reversed, the patch moved
upwards.
Measurement of mass-to-charge ratio
In his classic experiment, Thomson measured the mass-to-charge ratio
of the cathode rays by measuring how much they were deflected by a
magnetic field and comparing this with the electric deflection. He used
the same apparatus as in his previous experiment, but placed the
discharge tube between the poles of a large electromagnet. He found that
the mass-to-charge ratio was over a thousand times lower than that of a hydrogen ion (H+), suggesting either that the particles were very light and/or very highly charged. Significantly, the rays from every cathode yielded the same mass-to-charge ratio. This is in contrast to anode rays
(now known to arise from positive ions emitted by the anode), where the
mass-to-charge ratio varies from anode-to-anode. Thomson himself
remained critical of what his work established, in his Nobel Prize
acceptance speech referring to "corpuscles" rather than "electrons".
Thomson's calculations can be summarised as follows (notice that
we reproduce here Thomson's original notations, using F instead of E for
the electric field and H instead of B for the magnetic field):
The electric deflection is given by ,
where Θ is the angular electric deflection, F is applied electric
intensity, e is the charge of the cathode ray particles, l is the length
of the electric plates, m is the mass of the cathode ray particles and v
is the velocity of the cathode ray particles. The magnetic deflection
is given by , where φ is the angular magnetic deflection and H is the applied magnetic field intensity.
The magnetic field was varied until the magnetic and electric deflections were the same, when . This can be simplified to give . The electric deflection was measured separately to give Θ and H, F and l were known, so m/e could be calculated.
Conclusions
As the cathode rays carry a charge of negative electricity, are deflected by an electrostatic force as if they were negatively electrified, and are acted on by a magnetic force in just the way in which this force would act on a negatively electrified body moving along the path of these rays, I can see no escape from the conclusion that they are charges of negative electricity carried by particles of matter.
— J. J. Thomson
As to the source of these particles, Thomson believed they emerged from the molecules of gas in the vicinity of the cathode.
If, in the very intense electric field in the neighbourhood of the cathode, the molecules of the gas are dissociated and are split up, not into the ordinary chemical atoms, but into these primordial atoms, which we shall for brevity call corpuscles; and if these corpuscles are charged with electricity and projected from the cathode by the electric field, they would behave exactly like the cathode rays.
— J. J. Thomson
Thomson imagined the atom as being made up of these corpuscles orbiting in a sea of positive charge; this was his plum pudding model. This model was later proved incorrect when his student Ernest Rutherford showed that the positive charge is concentrated in the nucleus of the atom.
Other work
In 1905, Thomson discovered the natural radioactivity of potassium.
In 1906, Thomson demonstrated that hydrogen had only a single electron per atom. Previous theories allowed various numbers of electrons.
Awards and honours
Plaque commemorating J. J. Thomson's discovery of the electron outside the old Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge
Thomson was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society (FRS) and appointed to the Cavendish Professorship of Experimental Physics at the Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge in 1884. Thomson won numerous awards and honours during his career including:
- Adams Prize (1882)
- Royal Medal (1894)
- Hughes Medal (1902)
- Hodgkins Medal (1902)
- Nobel Prize for Physics (1906)
- Elliott Cresson Medal (1910)
- Copley Medal (1914)
- Franklin Medal (1922)
Thomson was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society on 12 June 1884 and served as President of the Royal Society from 1915 to 1920.
In November 1927, J. J. Thomson opened the Thomson building, named in his honour, in the Leys School, Cambridge.
Posthumous honours
In 1991, the thomson (symbol: Th) was proposed as a unit to measure mass-to-charge ratio in mass spectrometry in his honour.
J J Thomson Avenue, on the University of Cambridge's West Cambridge site, is named after Thomson.