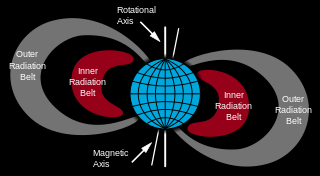
A cross section of Van Allen radiation belts
A Van Allen radiation belt is a zone of energetic charged particles, most of which originate from the solar wind, that are captured by and held around a planet by that planet's magnetic field. Earth has two such belts and sometimes others may be temporarily created. The discovery of the belts is credited to James Van Allen, and as a result, Earth's belts are known as the Van Allen belts. Earth's two main belts extend from an altitude of about 640 to 58,000 km (400 to 36,040 mi) above the surface in which region radiation levels vary. Most of the particles that form the belts are thought to come from solar wind and other particles by cosmic rays. By trapping the solar wind, the magnetic field deflects those energetic particles and protects the atmosphere from destruction.
The belts are located in the inner region of Earth's magnetosphere. The belts trap energetic electrons and protons. Other nuclei, such as alpha particles, are less prevalent. The belts endanger satellites,
which must have their sensitive components protected with adequate
shielding if they spend significant time near that zone. In 2013, NASA reported that the Van Allen Probes
had discovered a transient, third radiation belt, which was observed
for four weeks until it was destroyed by a powerful, interplanetary shock wave from the Sun.
Discovery
Kristian Birkeland, Carl Størmer, and Nicholas Christofilos had investigated the possibility of trapped charged particles before the Space Age. Explorer 1 and Explorer 3 confirmed the existence of the belt in early 1958 under James Van Allen at the University of Iowa. The trapped radiation was first mapped by Explorer 4, Pioneer 3 and Luna 1.
The term Van Allen belts refers specifically to the
radiation belts surrounding Earth; however, similar radiation belts have
been discovered around other planets.
The Sun does not support long-term radiation belts, as it lacks a
stable, global, dipole field. The Earth's atmosphere limits the belts'
particles to regions above 200–1,000 km, (124–620 miles) while the belts do not extend past 8 Earth radii RE. The belts are confined to a volume which extends about 65° on either side of the celestial equator.
Research
Jupiter's variable radiation belts
The NASA Van Allen Probes mission aims at understanding (to the point of predictability) how populations of relativistic electrons and ions in space form or change in response to changes in solar activity and the solar wind.
NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts–funded studies have proposed magnetic scoops to collect antimatter that naturally occurs in the Van Allen belts of Earth, although only about 10 micrograms of antiprotons are estimated to exist in the entire belt.
The Van Allen Probes mission successfully launched on August 30, 2012. The primary mission is scheduled to last two years with expendables expected to last four. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the Living With a Star program of which the Van Allen Probes is a project, along with Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). The Applied Physics Laboratory is responsible for the implementation and instrument management for the Van Allen Probes.
Radiation belts exist around other planets and moons in the solar
system that have magnetic fields powerful enough to sustain them. To
date, most of these radiation belts have been poorly mapped. The Voyager
Program (namely Voyager 2) only nominally confirmed the existence of similar belts around Uranus and Neptune.
Inner belt
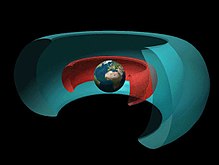
Cutaway drawing
of two radiation belts around Earth: the inner belt (red) dominated by
protons and the outer one (blue) by electrons. Image Credit: NASA
The inner Van Allen Belt extends typically from an altitude of 0.2 to
2 Earth radii (L values of 1 to 3) or 1,000 km (620 mi) to 6,000 km
(3,700 mi) above the Earth. In certain cases when solar activity is stronger or in geographical areas such as the South Atlantic Anomaly, the inner boundary may decline to roughly 200 kilometers above the Earth's surface. The inner belt contains high concentrations of electrons in the range of hundreds of keV
and energetic protons with energies exceeding 100 MeV, trapped by the
strong (relative to the outer belts) magnetic fields in the region.
It is believed that proton energies exceeding 50 MeV in the lower belts at lower altitudes are the result of the beta decay of neutrons
created by cosmic ray collisions with nuclei of the upper atmosphere.
The source of lower energy protons is believed to be proton diffusion
due to changes in the magnetic field during geomagnetic storms.
Due to the slight offset of the belts from Earth's geometric
center, the inner Van Allen belt makes its closest approach to the
surface at the South Atlantic Anomaly.
On March 2014, a pattern resembling 'zebra stripes' was observed
in the radiation belts by the Radiation Belt Storm Probes Ion
Composition Experiment (RBSPICE) onboard Van Allen Probes.
The reason reported was that due to the tilt in Earth's magnetic field
axis, the planet's rotation generated an oscillating, weak electric
field that permeates through the entire inner radiation belt. It was later demonstrated that the zebra stripes were in fact an imprint of ionospheric winds on radiation belts.
Outer belt
Laboratory simulation of the Van Allen belt's influence on the Solar Wind; these aurora-like Birkeland currents were created by the scientist Kristian Birkeland in his terrella, a magnetized anode globe in an evacuated chamber
The outer belt consists mainly of high energy (0.1–10 MeV)
electrons trapped by the Earth's magnetosphere. It is more variable
than the inner belt as it is more easily influenced by solar activity.
It is almost toroidal in shape, beginning at an altitude of three and extending to ten Earth radii (RE) 13,000 to 60,000 kilometres (8,100 to 37,300 mi) above the Earth's surface. Its greatest intensity is usually around 4–5 RE. The outer electron radiation belt is mostly produced by the inward radial diffusion and local acceleration due to transfer of energy from whistler-mode plasma waves to radiation belt electrons. Radiation belt electrons are also constantly removed by collisions with Earth's atmosphere, losses to the magnetopause, and their outward radial diffusion. The gyroradii
of energetic protons would be large enough to bring them into contact
with the Earth's atmosphere. Within this belt, the electrons have a high
flux and at the outer edge (close to the magnetopause), where geomagnetic field lines open into the geomagnetic "tail",
the flux of energetic electrons can drop to the low interplanetary
levels within about 100 km (62 mi), a decrease by a factor of 1,000.
In 2014 it was discovered that the inner edge of the outer belt
is characterized by a very sharp transition, below which highly
relativistic electrons (> 5MeV) cannot penetrate. The reason for this shield-like behavior is not well understood.
The trapped particle population of the outer belt is varied,
containing electrons and various ions. Most of the ions are in the form
of energetic protons, but a certain percentage are alpha particles and O+ oxygen ions, similar to those in the ionosphere but are much more energetic. This mixture of ions suggests that ring current particles probably come from more than one source.
The outer belt is larger than the inner belt and its particle
population fluctuates widely. Energetic (radiation) particle fluxes can
increase and decrease dramatically in response to geomagnetic storms,
which are themselves triggered by magnetic field and plasma
disturbances produced by the Sun. The increases are due to storm-related
injections and acceleration of particles from the tail of the
magnetosphere.
On February 28, 2013, a third radiation belt, consisting of high-energy ultrarelativistic
charged particles, was reported to be discovered. In a news conference
by NASA's Van Allen Probe team, it was stated that this third belt is a
product of coronal mass ejection
from the Sun. It has been represented as a separate creation which
splits the Outer Belt, like a knife, on its outer side, and exists
separately as a storage container of particles for a month's time,
before merging once again with the Outer Belt.
The unusual stability of this third, transient belt has been
explained as due to a 'trapping' by the Earth's magnetic field of
ultrarelativistic particles as they are lost from the second,
traditional outer belt. While the outer zone, which forms and disappears
over a day, is highly variable due to interactions with the atmosphere,
the ultrarelativistic particles of the third belt are thought to not
scatter into the atmosphere, as they are too energetic to interact with
atmospheric waves at low latitudes.
This absence of scattering and the trapping allows them to persist for a
long time, finally only being destroyed by an unusual event, such as
the shock wave from the Sun.
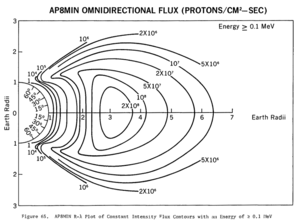
Flux values
In the belts, at a given point, the flux of particles of a given energy decreases sharply with energy.
At the magnetic equator, electrons of energies exceeding 500 keV (resp. 5 MeV) have omnidirectional fluxes ranging from 1.2×106 (resp. 3.7×104) up to 9.4×109 (resp. 2×107) particles per square centimeter per second.
The proton belts contain protons with kinetic energies ranging from about 100 keV (which can penetrate 0.6 µm of lead) to over 400 MeV (which can penetrate 143 mm of lead).
Most published flux values for the inner and outer belts may not
show the maximum probable flux densities that are possible in the belts.
There is a reason for this discrepancy: the flux density and the
location of the peak flux is variable (depending primarily on solar
activity), and the number of spacecraft with instruments observing the
belt in real time has been limited. The Earth has not experienced a
solar storm of Carrington event intensity and duration while spacecraft with the proper instruments have been available to observe the event.
Regardless of the differences of the flux levels in the Inner and
Outer Van Allen belts, the beta radiation levels would be dangerous to
humans if they were exposed for an extended period of time. The Apollo
missions minimised hazards for astronauts by sending spacecraft at high
speeds through the thinner areas of the upper belts, bypassing inner
belts completely.
- Flux values, normal solar conditions
Antimatter confinement
In 2011, a study confirmed earlier speculation that the Van Allen belt could confine antiparticles. The PAMELA experiment detected levels of antiprotons orders of magnitude higher than are expected from normal particle decays while passing through the South Atlantic Anomaly.
This suggests the Van Allen belts confine a significant flux of
antiprotons produced by the interaction of the Earth's upper atmosphere
with cosmic rays. The energy of the antiprotons has been measured in the range from 60–750 MeV.
Research funded by the NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts
concluded that harnessing these antiprotons for spacecraft propulsion
would be feasible. Researchers believed that this approach would have
advantages over antiproton generation at CERN because collecting the
particles in situ eliminates transportation losses and costs. Jupiter
and Saturn are also possible sources but the Earth belt is the most
productive. Jupiter is less productive than might be expected due to
magnetic shielding from cosmic rays of much of its atmosphere. In 2019
CMS announced, that the construction of such device, which would be
capable of collecting these particles has already begun. NASA will use
this device to collect these particles and transport them to institutes
all around the world for further examination. These so-called
„Antimatter- Containers“ could be used for industrial purpose as well in
the future.
Implications for space travel
Comparison of geostationary, GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, Compass (MEO), International Space Station, Hubble Space Telescope, Iridium constellation and graveyard orbits, with the Van Allen radiation belts and the Earth to scale. The Moon's orbit is around 9 times larger than geostationary orbit.
Spacecraft travelling beyond low Earth orbit enter the zone of radiation of the Van Allen belts. Beyond the belts, they face additional hazards from cosmic rays and solar particle events.
A region between the inner and outer Van Allen belts lies at two to
four Earth radii and is sometimes referred to as the "safe zone".
Solar cells, integrated circuits, and sensors can be damaged by radiation. Geomagnetic storms occasionally damage electronic components on spacecraft. Miniaturization and digitization of electronics and logic circuits have made satellites more vulnerable to radiation, as the total electric charge
in these circuits is now small enough so as to be comparable with the
charge of incoming ions. Electronics on satellites must be hardened against radiation to operate reliably. The Hubble Space Telescope, among other satellites, often has its sensors turned off when passing through regions of intense radiation. A satellite shielded by 3 mm of aluminium in an elliptic orbit (200 by 20,000 miles (320 by 32,190 km)) passing the radiation belts will receive about 2,500 rem (25 Sv)
per year (for comparison, a full-body dose of 5 Sv is deadly). Almost
all radiation will be received while passing the inner belt.
The Apollo missions
marked the first event where humans traveled through the Van Allen
belts, which was one of several radiation hazards known by mission
planners.
The astronauts had low exposure in the Van Allen belts due to the short
period of time spent flying through them. Apollo flight trajectories
bypassed the inner belts completely, passing through the thinner areas
of the outer belts.
Astronauts' overall exposure was actually dominated by solar
particles once outside Earth's magnetic field. The total radiation
received by the astronauts varied from mission to mission but was
measured to be between 0.16 and 1.14 rads (1.6 and 11.4 mGy), much less than the standard of 5 rem (50 mSv) per year set by the United States Atomic Energy Commission for people who work with radioactivity.
Causes
It is
generally understood that the inner and outer Van Allen belts result
from different processes. The inner belt, consisting mainly of energetic
protons, is the product of the decay of so-called "albedo"
neutrons which are themselves the result of cosmic ray collisions in
the upper atmosphere. The outer belt consists mainly of electrons. They
are injected from the geomagnetic tail following geomagnetic storms, and
are subsequently energized through wave-particle interactions.
In the inner belt, particles that originate from the Sun are
trapped in the Earth's magnetic field. Particles spiral along the
magnetic lines of flux as they move "longitudinally" along those lines.
As particles move toward the poles, the magnetic field line density
increases and their "longitudinal" velocity is slowed and can be
reversed, reflecting the particle and causing them to bounce back and
forth between the Earth's poles.
In addition to the spiral about and motion along the flux lines, the
electrons move slowly in an eastward direction, while the ions move
westward.
A gap between the inner and outer Van Allen belts, sometimes called safe zone or safe slot, is caused by the Very Low Frequency (VLF) waves which scatter particles in pitch angle
which results in the gain of particles to the atmosphere. Solar
outbursts can pump particles into the gap but they drain again in a
matter of days. The radio waves were originally thought to be generated
by turbulence in the radiation belts, but recent work by James L. Green of the Goddard Space Flight Center comparing maps of lightning activity collected by the Microlab 1 spacecraft with data on radio waves in the radiation-belt gap from the IMAGE
spacecraft suggests that they are actually generated by lightning
within Earth's atmosphere. The radio waves that generate strike the
ionosphere at the correct angle to pass through only at high latitudes,
where the lower ends of the gap approach the upper atmosphere. These
results are still under scientific debate.
Proposed removal
High Voltage Orbiting Long Tether, or HiVOLT, is a concept proposed by Russian physicist V. V. Danilov and further refined by Robert P. Hoyt and Robert L. Forward for draining and removing the radiation fields of the Van Allen radiation belts that surround the Earth. A proposed configuration consists of a system of five 100 km long conducting tethers
deployed from satellites, and charged to a large voltage. This would
cause charged particles that encounter the tethers to have their pitch
angle changed; thus, over time, dissolving the inner belts. Hoyt and
Forward's company, Tethers Unlimited, performed a preliminary analysis
simulation in 2011, and produced a chart depicting a theoretical
radiation flux reduction, to less than 1% of current levels within two months for the inner belts that threaten LEO objects.