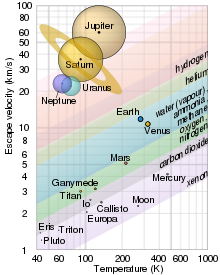
Graphs
of escape velocity against surface temperature of some Solar System
objects showing which gases are retained. The objects are drawn to
scale, and their data points are at the black dots in the middle.
Atmospheric escape is the loss of planetary atmospheric gases to outer space.
A number of different mechanisms can be responsible for atmospheric
escape; these processes can be divided into thermal escape, non-thermal
(or suprathermal) escape, and impact erosion. The relative importance of
each loss process depends on the planet's escape velocity, its atmosphere composition, and its distance from its sun. Escape occurs when molecular kinetic energy overcomes gravitational energy; in other words, a molecule can escape when it is moving faster than the escape velocity of its planet. Categorizing the rate of atmospheric escape in exoplanets is important to determining whether an atmosphere persists, and so the exoplanet's habitability and likelihood of life.
Thermal escape mechanisms
Thermal escape occurs if the molecular velocity due to thermal energy
is sufficiently high. Thermal escape happens at all scales, from the
molecular level (Jeans escape) to bulk atmospheric outflow (hydrodynamic
escape).
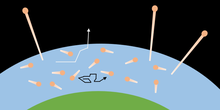
A
visualization of Jeans escape. Temperature defines a range of molecular
energy. Above the exobase, molecules with enough energy escape, while
in the lower atmosphere, molecules are trapped by collisions with other
molecules.
Jeans Escape
One classical thermal escape mechanism is Jeans escape, named after British astronomer Sir James Jeans, who first described this process of atmospheric loss. In a quantity of gas, the average velocity of any one molecule is measured by the gas's temperature,
but the velocities of individual molecules change as they collide with
one another, gaining and losing kinetic energy. The variation in kinetic
energy among the molecules is described by the Maxwell distribution. The kinetic energy (), mass (), and velocity () of a molecule are related by . Individual molecules in the high tail of the distribution (where a few particles have much higher speeds than the average) may reach escape velocity and leave the atmosphere, provided they can escape before undergoing another collision; this happens predominantly in the exosphere, where the mean free path is comparable in length to the pressure scale height. The number of particles able to escape depends on the molecular concentration at the exobase, which is limited by diffusion through the thermosphere.
Three factors strongly contribute to the relative importance of
Jeans escape: mass of the molecule, escape velocity of the planet, and
heating of the upper atmosphere by radiation from the parent star.
Heavier molecules are less likely to escape because they move slower
than lighter molecules at the same temperature. This is why hydrogen escapes from an atmosphere more easily than carbon dioxide.
Second, a planet with a larger mass has more gravity, so the escape
velocity is greater, and fewer particles will gain the energy required
to escape. This is why the gas giant planets still retain significant amounts of hydrogen, which escape more readily from Earth's atmosphere.
Finally, the distance a planet orbits from a star also plays a part; a
close planet has a hotter atmosphere, with higher velocities and hence, a
greater likelihood of escape. A distant body has a cooler atmosphere,
with lower velocities, and less chance of escape.
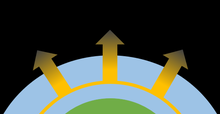
A
visualization of hydrodynamic escape. At some level in the atmosphere,
the bulk gas will be heated and begin to expand. As the gas expands, it
accelerates and escapes the atmosphere. In this process, lighter, faster
molecules drag heavier, slower molecules out of the atmosphere.
Hydrodynamic escape
An
atmosphere with high pressure and temperature can also undergo
hydrodynamic escape. In this case, a large amount of thermal energy,
usually through extreme ultraviolet
radiation, is absorbed by the atmosphere. As molecules are heated, they
expand upwards and are further accelerated until they reach escape
velocity. In this process, lighter molecules can drag heavier molecules
with them through collisions as a larger quantity of gas escapes. Hydrodynamic escape has been observed for exoplanets close to their host star, including the hot Jupiter HD 209458b.
Non-thermal (suprathermal) escape
Escape can also occur due to non-thermal interactions. Most of these processes occur due to photochemistry or charged particle (ion) interactions.
Photochemical escape
In the upper atmosphere, high energy ultraviolet photons can react more readily with molecules. Photodissociation can break a molecule into smaller components and provide enough energy for those components to escape. Photoionization produces ions, which can get trapped in the planet's magnetosphere or undergo dissociative recombination.
In the first case, these ions may undergo escape mechanisms described
below. In the second case, the ion recombines with an electron, releases
energy, and can escape.
Sputtering escape
Excess kinetic energy from the solar wind can impart sufficient energy to eject atmospheric particles, similar to sputtering
from a solid surface. This type of interaction is more pronounced in
the absence of a planetary magnetosphere, as the electrically charged
solar wind is deflected by magnetic fields, which mitigates the loss of atmosphere.
The
fast ion captures an electron from a slow neutral in a charge exchange
collision. The new, fast neutral can escape the atmosphere, and the new,
slow ion is trapped on magnetic field lines.
Charge exchange escape
Ions
in the solar wind or magnetosphere can charge exchange with molecules
in the upper atmosphere. A fast-moving ion can capture the electron from
a slow atmospheric neutral, creating a fast neutral and a slow ion. The
slow ion is trapped on the magnetic field lines, but the fast neutral
can escape.
Polar wind escape
Atmospheric molecules can also escape from the polar regions on a planet with a magnetosphere, due to the polar wind.
Near the poles of a magnetosphere, the magnetic field lines are open,
allowing a pathway for ions in the atmosphere to exhaust into space.
Atmospheric
escape from impact erosion is concentrated in a cone (red dash-dotted
line) centered at the impact site. The angle of this cone increases with
impact energy to eject a maximum of all the atmosphere above a tangent
plane (orange dotted line).
Impact erosion
The impact of a large meteoroid
can lead to the loss of atmosphere. If a collision is sufficiently
energetic, it is possible for ejecta, including atmospheric molecules,
to reach escape velocity.
In order to have a significant effect on atmospheric escape, the radius of the impacting body must be larger than the scale height.
The projectile can impart momentum, and thereby facilitate escape of
the atmosphere, in three main ways: (a) the meteroid heats and
accelerates the gas it encounters as it travels through the atmosphere,
(b) solid ejecta from the impact crater heat atmospheric particles
through drag as they are ejected, and (c) the impact creates vapor which
expands away from the surface. In the first case, the heated gas can
escape in a manner similar to hydrodynamic escape, albeit on a more
localized scale. Most of the escape from impact erosion occurs due to
the third case. The maximum atmosphere that can be ejected is above a plane tangent to the impact site.
Dominant atmospheric escape and loss processes in the Solar System
Earth
Atmospheric
escape of hydrogen on Earth is due to Jeans escape (~10 - 40%), charge
exchange escape (~ 60 - 90%), and polar wind escape (~ 10 - 15%),
currently losing about 3 kg/s of hydrogen.
The Earth additionally loses approximately 50 g/s of helium primarily
through polar wind escape. Escape of other atmospheric constituents is
much smaller. A Japanese research team in 2017 found evidence of a small number of oxygen ions on the moon that came from the Earth.
In 1 billion years, the Sun will be 10% brighter than it is now,
making it hot enough for Earth to lose enough hydrogen to space to cause
it to lose all of its water.
Venus
Recent models indicate that hydrogen escape on Venus
is almost entirely due to suprathermal mechanisms, primarily
photochemical reactions and charge exchange with the solar wind. Oxygen
escape is dominated by charge exchange and sputtering escape. Venus Express measured the effect of coronal mass ejections
on the rate of atmospheric escape of Venus, and researchers found a
factor of 1.9 increase in escape rate during periods of increased
coronal mass ejections compared with calmer space weather.
Mars
Primordial Mars also suffered from the cumulative effects of multiple small impact erosion events, and recent observations with MAVEN suggest that 66% of the 36Ar in the Martian atmosphere has been lost over the last 4 billion years due to suprathermal escape, and the amount of CO2 lost over the same time period is around 0.5 bar or more.
The MAVEN mission has also explored the current rate of
atmospheric escape of Mars. Jeans escape plays an important role in the
continued escape of hydrogen on Mars, contributing to a loss rate that
varies between 160 - 1800 g/s.
Oxygen loss is dominated by suprathermal methods: photochemical (~
1300 g/s), charge exchange (~ 130 g/s), and sputtering (~ 80 g/s) escape
combine for a total loss rate of ~ 1500 g/s. Other heavy atoms, such as
carbon and nitrogen, are primarily lost due to photochemical reactions
and interactions with the solar wind.
Titan and Io
Saturn's moon Titan and Jupiter's moon Io
have atmospheres and are subject to atmospheric loss processes. They
have no magnetic fields of their own, but orbit planets with powerful
magnetic fields, which protects these moons from the solar wind when its
orbit is within the bow shock. However Titan spends roughly half of its transit time outside of the bow-shock, subjected to unimpeded solar winds. The kinetic energy
gained from pick-up and sputtering associated with the solar winds
increases thermal escape throughout the transit of Titan, causing
neutral hydrogen to escape. The escaped hydrogen maintains an orbit following in the wake of Titan, creating a neutral hydrogen torus around Saturn. Io, in its transit around Jupiter, encounters a plasma cloud. Interaction with the plasma cloud induces sputtering, kicking off sodium particles. The interaction produces a stationary banana-shaped charged sodium cloud along a part of the orbit of Io.
Observations of exoplanet atmospheric escape
Studies
of exoplanets have measured atmospheric escape as a means of
determining atmospheric composition and habitability. The most common
method is Lyman-alpha line absorption. Much as exoplanets are discovered using the dimming of a distant star's brightness (transit), looking specifically at wavelengths corresponding to hydrogen absorption describes the amount of hydrogen present in a sphere around the exoplanet. This method indicates that the hot Jupiters HD209458b and HD189733b and Hot Neptune GJ436b are experiencing significant atmospheric escape.
Other atmospheric loss mechanisms
Sequestration
is not a form of escape from the planet, but a loss of molecules from
the atmosphere and into the planet. It occurs on Earth when water vapor condenses to form rain or glacial ice, when carbon dioxide is sequestered in sediments or cycled through the oceans, or when rocks are oxidized (for example, by increasing the oxidation states of ferric rocks from Fe2+ to Fe3+). Gases can also be sequestered by adsorption, where fine particles in the regolith capture gas which adheres to the surface particles.