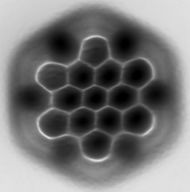
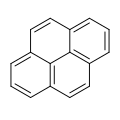
Three representations of hexabenzocoronene,
a polycylic aromatic hydrocarbon. Top: standard line-angle schematic,
where carbon atoms are represented by the vertices of the hexagons and
hydrogen atoms are inferred. Middle: ball-and-stick model showing all carbon and hydrogen atoms. Bottom: atomic force microscopy image.
PAHs are uncharged, non-polar molecules found in coal and in tar deposits. They are also produced by the thermal decomposition of organic matter (for example, in engines and incinerators or when biomass burns in forest fires).
PAHs are abundant in the universe, and have recently been found to have formed possibly as early as the first couple of billion years after the Big Bang, in association with formation of new stars and exoplanets. Some studies suggest that PAHs account for a significant percentage of all carbon in the universe.
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are discussed as possible starting materials for abiotic syntheses of materials required by the earliest forms of life.
Nomenclature, structure, properties
Nomenclature and structure
By definition, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons have multiple cycles, precluding benzene from being considered a PAH. Naphthalene is considered the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon by the US EPA and US CDC for policy contexts. Other authors consider PAHs to start with the tricyclic species phenanthrene and anthracene.
PAHs are not generally considered to contain heteroatoms or carry substituents.
PAHs with five or six-membered rings are most common. Those composed only of six-membered rings are called alternant PAHs, which include benzenoid PAHs. The following are examples of PAHs that vary in the number and arrangement of their rings:
Principal PAH Compounds
Physicochemical properties and bonding
PAHs are nonpolar and lipophilic. Larger PAHs are generally insoluble in water, although some smaller PAHs are soluble and known contaminants in drinking water. The larger members are also poorly soluble in organic solvents and in lipids. They are usually colorless.
The aromaticity varies for PAHs. According to Clar's rule, the resonance structure of a PAH that has the largest number of disjoint aromatic pi sextets—i.e. benzene-like moieties—is the most important for the characterization of the properties of that PAH.
Benzene-substructure resonance analysis for Clar's rule
For example, in phenanthrene
one Clar structure has two sextets—the first and third rings—while the
other resonance structure has just one central sextet; therefore in this
molecule the outer rings have greater aromatic character whereas the
central ring is less aromatic and therefore more reactive. In contrast, in anthracene
the resonance structures have one sextet each, which can be at any of
the three rings, and the aromaticity spreads out more evenly across the
whole molecule. This difference in number of sextets is reflected in the differing ultraviolet–visible spectra of these two isomers, as higher Clar pi-sextets are associated with larger HOMO-LUMO gaps; the highest-wavelength absorbance of phenanthrene is at 293 nm, while anthracene is at 374 nm. Three Clar structures with two sextets each are present in the four-ring chrysene
structure: one having sextets in the first and third rings, one in the
second and fourth rings, and one in the first and fourth rings.[citation needed]
Superposition of these structures reveals that the aromaticity in the
outer rings is greater (each has a sextet in two of the three Clar
structures) compared to the inner rings (each has a sextet in only one
of the three).
Polycyclic aromatic compounds characteristically reduce to the radical anions. The redox potential correlates with the size of the PAH.
-
Half-cell potential of aromatic compounds against the SCE Compound Potential (V) benzene −3.42 biphenyl[15] −2.60 naphthalene −2.51 anthracene −1.96 phenanthrene −1.96 perylene −1.67 pentacene −1.35
Sources and distribution
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are primarily found in natural sources such as creosote. They can result from the incomplete combustion of organic matter. PAHs can also be produced geologically when organic sediments are chemically transformed into fossil fuels such as oil and coal. PAHs are considered ubiquitous in the environment and can be formed from either natural or manmade combustion sources. The dominant sources of PAHs in the environment are thus from human activity: wood-burning and combustion of other biofuels
such as dung or crop residues contribute more than half of annual
global PAH emissions, particularly due to biofuel use in India and
China.
As of 2004, industrial processes and the extraction and use of fossil
fuels made up slightly more than one quarter of global PAH emissions,
dominating outputs in industrial countries such as the United States. Wildfires are another notable source.
Substantially higher outdoor air, soil, and water concentrations of
PAHs have been measured in Asia, Africa, and Latin America than in
Europe, Australia, the U.S., and Canada.
PAHs are typically found as complex mixtures. Lower-temperature combustion, such as tobacco smoking or wood-burning,
tends to generate low molecular weight PAHs, whereas high-temperature
industrial processes typically generate PAHs with higher molecular
weights.
In the aqueous environment
Most PAHs are insoluble in water, which limits their mobility in the environment, although PAHs sorb to fine-grained organic-rich sediments. Aqueous solubility of PAHs decreases approximately logarithmically as molecular mass increases.
Two-ringed PAHs, and to a lesser extent three-ringed PAHs, dissolve in
water, making them more available for biological uptake and degradation. Further, two- to four-ringed PAHs volatilize
sufficiently to appear in the atmosphere predominantly in gaseous form,
although the physical state of four-ring PAHs can depend on
temperature.
In contrast, compounds with five or more rings have low solubility in
water and low volatility; they are therefore predominantly in solid state, bound to particulate air pollution, soils, or sediments.
In solid state, these compounds are less accessible for biological
uptake or degradation, increasing their persistence in the environment.
In galaxies
Spiral galaxy NGC 5529 has been found to have amounts of PAHs.
Human exposure
Human
exposure varies across the globe and depends on factors such as smoking
rates, fuel types in cooking, and pollution controls on power plants,
industrial processes, and vehicles.
Developed countries with stricter air and water pollution controls,
cleaner sources of cooking (i.e., gas and electricity vs. coal or
biofuels), and prohibitions of public smoking tend to have lower levels
of PAH exposure, while developing and undeveloped countries tend to have
higher levels.
Surgical smoke plume have been proven to contain PAHs in several
independent research studies. ref. Int J Occup Med Environ Health. 2014
Apr;27(2):314-25. doi: 10.2478/s13382-014-0250-3. Epub 2014 Apr 9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24715421
For indoor contaminants, surgical plume needs to be noticed as a
serious potential health risk for the 59 million health care workers
around the world.
Burning solid fuels such as coal and biofuels
in the home for cooking and heating is a dominant global source of PAH
emissions that in developing countries leads to high levels of exposure
to indoor particulate air pollution containing PAHs, particularly for women and children who spend more time in the home or cooking.
In industrial countries, people who smoke tobacco products, or who are exposed to second-hand smoke, are among the most highly exposed groups; tobacco smoke contributes to 90% of indoor PAH levels in the homes of smokers.
For the general population in developed countries, the diet is
otherwise the dominant source of PAH exposure, particularly from smoking
or grilling meat or consuming PAHs deposited on plant foods, especially
broad-leafed vegetables, during growth. PAHs are typically at low concentrations in drinking water.
Emissions from vehicles such as cars and trucks can be a substantial outdoor source of PAHs in particulate air pollution. Geographically, major roadways are thus sources of PAHs, which may distribute in the atmosphere or deposit nearby. Catalytic converters are estimated to reduce PAH emissions from gasoline-fired vehicles by 25-fold.
People can also be occupationally exposed during work that involves fossil fuels or their derivatives, wood-burning, carbon electrodes, or exposure to diesel exhaust. Industrial activity that can produce and distribute PAHs includes aluminum, iron, and steel manufacturing; coal gasification, tar distillation, shale oil extraction; production of coke, creosote, carbon black, and calcium carbide; road paving and asphalt manufacturing; rubber tire production; manufacturing or use of metal working fluids; and activity of coal or natural gas power stations.
Environmental distribution and degradation
PAHs typically disperse from urban and suburban non-point sources through road run-off, sewage, and atmospheric circulation and subsequent deposition of particulate air pollution. Soil and river sediment near industrial sites such as creosote manufacturing facilities can be highly contaminated with PAHs. Oil spills, creosote, coal mining dust, and other fossil fuel sources can also distribute PAHs in the environment.
Two- and three-ringed PAHs can disperse widely while dissolved in
water or as gases in the atmosphere, while PAHs with higher molecular
weights can disperse locally or regionally adhered to particulate matter
that is suspended in air or water until the particles land or settle
out of the water column. PAHs have a strong affinity for organic carbon, and thus highly organic sediments in rivers, lakes, and the ocean can be a substantial sink for PAHs.
Algae and some invertebrates such as protozoans, mollusks, and many polychaetes have limited ability to metabolize PAHs and bioaccumulate
disproportionate concentrations of PAHs in their tissues; however, PAH
metabolism can vary substantially across invertebrate species. Most vertebrates metabolize and excrete PAHs relatively rapidly. Tissue concentrations of PAHs do not increase (biomagnify) from the lowest to highest levels of food chains.
PAHs transform slowly to a wide range of degradation products. Biological degradation by microbes is a dominant form of PAH transformation in the environment. Soil-consuming invertebrates such as earthworms speed PAH degradation, either through direct metabolism or by improving the conditions for microbial transformations.
Abiotic degradation in the atmosphere and the top layers of surface
waters can produce nitrogenated, halogenated, hydroxylated, and
oxygenated PAHs; some of these compounds can be more toxic,
water-soluble, and mobile than their parent PAHs.
PAHs in urban soils
The British Geological Survey reported the amount and distribution of PAH compounds including parent and alkylated forms in urban soils at 76 locations in Greater London.
The study showed that parent (16 PAH) content ranged from 4 to 67 mg/kg
(dry soil weight) and an average PAH concentration of 18 mg/kg (dry
soil weight) whereas the total PAH content (33 PAH) ranged from 6 to
88 mg/kg and fluoranthene and pyrene were generally the most abundant PAHs. Benzo[a]pyrene (BaP), the most toxic of the parent PAHs, is widely considered a key marker PAH for environmental assessments; the normal background concentration of BaP in the London urban sites was 6.9 mg/kg (dry soil weight). London
soils contained more stable four- to six-ringed PAHs which were
indicative of combustion and pyrolytic sources, such as coal and oil
burning and traffic-sourced particulates. However, the overall
distribution also suggested that the PAHs in London soils had undergone
weathering and been modified by a variety of pre-and post-depositional
processes such as volatilization and microbial biodegradation.
PAHs in peatlands
Managed burning of moorland vegetation in the UK has been shown to generate PAHs which become incorporated into the peat surface. Burning of moorland vegetation such as heather
initially generates high amounts of two- and three-ringed PAHs relative
to four- to six-ringed PAHs in surface sediments, however, this pattern
is reversed as the lower molecular weight PAHs are attenuated by biotic decay and photodegradation.
Evaluation of the PAH distributions using statistical methods such as
principal component analyses (PCA) enabled the study to link the source
(burnt moorland) to pathway (suspended stream sediment) to the
depositional sink (reservoir bed).
PAHs in rivers, estuarine and coastal sediments
Concentrations of PAHs in river and estuarine sediments
vary according to a variety of factors including proximity to municipal
and industrial discharge points, wind direction and distance from major
urban roadways, as well as tidal regime which controls the diluting
effect of generally cleaner marine sediments relative to freshwater
discharge. Consequently, the concentrations of pollutants in estuaries tends to decrease at the river mouth. Understanding of sediment hosted PAHs in estuaries is important for the protection of commercial fisheries (such as mussels) and general environmental habitat conservation because PAHs can impact the health of suspension and sediment feeding organism.
River-estuary surface sediments in the UK tend to have a lower PAH
content than sediments buried 10–60 cm from the surface reflecting lower
present day industrial activity combined with improvement in
environmental legislation of PAH. Typical PAH concentrations in UK estuaries range from about 19 to 16,163 µg/kg (dry sediment weight) in the River Clyde and 626 to 3,766 µg/kg in the River Mersey. In general estuarine sediments with a higher natural total organic carbon content (TOC) tend to accumulate PAHs due to high sorption capacity of organic matter. A similar correspondence between PAHs and TOC has also been observed in the sediments of tropical mangroves located on the coast of southern China.
Minor sources
Volcanic eruptions may emit PAHs. Certain PAHs such as perylene can also be generated in anaerobic
sediments from existing organic material, although it remains
undetermined whether abiotic or microbial processes drive their
production.
Human health
Cancer is a primary human health risk of exposure to PAHs. Exposure to PAHs has also been linked with cardiovascular disease and poor fetal development.
Cancer
PAHs have been linked to skin, lung, bladder, liver, and stomach cancers in well-established animal model studies. Specific compounds classified by various agencies as possible or probable human carcinogens are identified in the section "Regulation and Oversight" below.
Historical significance
An 18th-century drawing of chimney sweeps.
Historically, PAHs contributed substantially to our understanding of adverse health effects from exposures to environmental contaminants, including chemical carcinogenesis. In 1775, Percivall Pott, a surgeon at St. Bartholomew's Hospital in London, observed that scrotal cancer was unusually common in chimney sweepers and proposed the cause as occupational exposure to soot. A century later, Richard von Volkmann reported increased skin cancers in workers of the coal tar
industry of Germany, and by the early 1900s increased rates of cancer
from exposure to soot and coal tar was widely accepted. In 1915,
Yamigawa and Ichicawa were the first to experimentally produce cancers,
specifically of the skin, by topically applying coal tar to rabbit ears.
In 1922, Ernest Kennaway
determined that the carcinogenic component of coal tar mixtures was an
organic compound consisting of only carbon and hydrogen. This component
was later linked to a characteristic fluorescent pattern that was similar but not identical to benz[a]anthracene, a PAH that was subsequently demonstrated to cause tumors. Cook, Hewett and Hieger then linked the specific spectroscopic fluorescent profile of benzo[a]pyrene to that of the carcinogenic component of coal tar, the first time that a specific compound from an environmental mixture (coal tar) was demonstrated to be carcinogenic.
In the 1930s and later, epidemiologists from Japan, the UK, and the US, including Richard Doll and various others, reported greater rates of death from lung cancer following occupational exposure to PAH-rich environments among workers in coke ovens and coal carbonization and gasification processes.
Mechanisms of carcinogenesis
An adduct formed between a DNA strand and an epoxide derived from a benzo[a]pyrene molecule (center); such adducts may interfere with normal DNA replication.
The structure of a PAH influences whether and how the individual compound is carcinogenic. Some carcinogenic PAHs are genotoxic and induce mutations that initiate cancer; others are not genotoxic and instead affect cancer promotion or progression.
PAHs that affect cancer initiation are typically first chemically modified by enzymes into metabolites that react with DNA, leading to mutations. When the DNA sequence is altered in genes that regulate cell replication, cancer can result. Mutagenic PAHs, such as benzo[a]pyrene,
usually have four or more aromatic rings as well as a "bay region", a
structural pocket that increases reactivity of the molecule to the
metabolizing enzymes. Mutagenic metabolites of PAHs include diol epoxides, quinones, and radical PAH cations. These metabolites can bind to DNA at specific sites, forming bulky complexes called DNA adducts that can be stable or unstable. Stable adducts may lead to DNA replication errors, while unstable adducts react with the DNA strand, removing a purine base (either adenine or guanine). Such mutations, if they are not repaired, can transform genes encoding for normal cell signaling proteins into cancer-causing oncogenes. Quinones can also repeatedly generate reactive oxygen species that may independently damage DNA.
Enzymes in the cytochrome family (CYP1A1, CYP1A2, CYP1B1) metabolize PAHs to diol epoxides.
PAH exposure can increase production of the cytochrome enzymes,
allowing the enzymes to convert PAHs into mutagenic diol epoxides at
greater rates. In this pathway, PAH molecules bind to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and activate it as a transcription factor
that increases production of the cytochrome enzymes. The activity of
these enzymes may at times conversely protect against PAH toxicity,
which is not yet well understood.
Low molecular weight PAHs, with two to four aromatic hydrocarbon rings, are more potent as co-carcinogens
during the promotional stage of cancer. In this stage, an initiated
cell (a cell that has retained a carcinogenic mutation in a key gene
related to cell replication) is removed from growth-suppressing signals
from its neighboring cells and begins to clonally replicate. Low-molecular-weight PAHs that have bay or bay-like regions can dysregulate gap junction channels, interfering with intercellular communication, and also affect mitogen-activated protein kinases that activate transcription factors involved in cell proliferation.
Closure of gap junction protein channels is a normal precursor to cell
division. Excessive closure of these channels after exposure to PAHs
results in removing a cell from the normal growth-regulating signals
imposed by its local community of cells, thus allowing initiated
cancerous cells to replicate. These PAHs do not need to be enzymatically
metabolized first. Low molecular weight PAHs are prevalent in the
environment, thus posing a significant risk to human health at the
promotional phases of cancer.
Cardiovascular disease
Adult exposure to PAHs has been linked to cardiovascular disease. PAHs are among the complex suite of contaminants in tobacco smoke and particulate air pollution and may contribute to cardiovascular disease resulting from such exposures.
In laboratory experiments, animals exposed to certain PAHs have shown increased development of plaques (atherogenesis) within arteries. Potential mechanisms for the pathogenesis
and development of atherosclerotic plaques may be similar to the
mechanisms involved in the carcinogenic and mutagenic properties of
PAHs. A leading hypothesis is that PAHs may activate the cytochrome enzyme CYP1B1 in vascular smooth muscle
cells. This enzyme then metabolically processes the PAHs to quinone
metabolites that bind to DNA in reactive adducts that remove purine
bases. The resulting mutations may contribute to unregulated growth of
vascular smooth muscle cells or to their migration to the inside of the
artery, which are steps in plaque formation. These quinone metabolites also generate reactive oxygen species that may alter the activity of genes that affect plaque formation.
Oxidative stress following PAH exposure could also result in cardiovascular disease by causing inflammation, which has been recognized as an important factor in the development of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Biomarkers
of exposure to PAHs in humans have been associated with inflammatory
biomarkers that are recognized as important predictors of cardiovascular
disease, suggesting that oxidative stress resulting from exposure to
PAHs may be a mechanism of cardiovascular disease in humans.
Developmental impacts
Multiple epidemiological studies of people living in Europe, the United States, and China have linked in utero
exposure to PAHs, through air pollution or parental occupational
exposure, with poor fetal growth, reduced immune function, and poorer neurological development, including lower IQ.
Regulation and oversight
Some governmental bodies, including the European Union as well as NIOSH and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the US, regulate concentrations of PAHs in air, water, and soil. The European Commission has restricted concentrations of 8 carcinogenic PAHs in consumer products that contact the skin or mouth.
Priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons identified by the US EPA, the US Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR), and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) due to their carcinogenicity or genotoxicity and/or ability to be monitored are the following:
|
|
Detection and optical properties
A spectral database exists for tracking polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the universe. Detection of PAHs in materials is often done using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry or liquid chromatography with ultraviolet-visible or fluorescence spectroscopic methods or by using rapid test PAH indicator strips.
PAHs possess very characteristic UV absorbance spectra. These often possess many absorbance bands and are unique for each ring structure. Thus, for a set of isomers,
each isomer has a different UV absorbance spectrum than the others.
This is particularly useful in the identification of PAHs. Most PAHs are
also fluorescent,
emitting characteristic wavelengths of light when they are excited
(when the molecules absorb light). The extended pi-electron electronic
structures of PAHs lead to these spectra, as well as to certain large
PAHs also exhibiting semi-conducting and other behaviors.
Origins of life
The Cat's Paw Nebula lies inside the Milky Way Galaxy and is located in the constellation Scorpius. Green
areas show regions where radiation from hot stars collided with large
molecules and small dust grains called "polycyclic aromatic
hydrocarbons" (PAHs), causing them to fluoresce. (Spitzer space telescope, 2018)
PAHs may be abundant in the universe. They seem to have been formed as early as a couple of billion years after the Big Bang, and are associated with new stars and exoplanets. More than 20% of the carbon in the universe may be associated with PAHs. PAHs are considered possible starting material for the earliest forms of life.
Light emitted by the Red Rectangle nebula and found spectral signatures that suggest the presence of anthracene and pyrene.
This report was considered a controversial hypothesis that as nebulae
of the same type as the Red Rectangle approach the ends of their lives,
convection currents cause carbon and hydrogen in the nebulae's cores to
get caught in stellar winds, and radiate outward. As they cool, the
atoms supposedly bond to each other in various ways and eventually form
particles of a million or more atoms. Adolf Witt and his team inferred that PAHs—which may have been vital in the formation of early life on Earth—can only originate in nebulae.
Two extremely bright stars illuminate a mist of PAHs in this Spitzer image.
More recently, fullerenes (or "buckyballs"), have been detected in other nebulae. Fullerenes are also implicated in the origin of life;
according to astronomer Letizia Stanghellini, "It's possible that
buckyballs from outer space provided seeds for life on Earth." In September 2012, NASA scientists reported results of analog studies in vitro that PAHs, subjected to interstellar medium (ISM) conditions, are transformed, through hydrogenation, oxygenation, and hydroxylation, to more complex organics—"a step along the path toward amino acids and nucleotides, the raw materials of proteins and DNA, respectively". Further, as a result of these transformations, the PAHs lose their spectroscopic signature which could be one of the reasons "for the lack of PAH detection in interstellar ice grains, particularly the outer regions of cold, dense clouds or the upper molecular layers of protoplanetary disks."
NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope includes instruments for obtaining both images and spectra of light emitted by PAHs associated with star formation. These images can trace the surface of star-forming clouds in our own galaxy or identify star forming galaxies in the distant universe.
In June 2013, PAHs were detected in the upper atmosphere of Titan, the largest moon of the planet Saturn.
In October 2018, researchers reported low-temperature chemical pathways from simple organic compounds to complex PAHs. Such chemical pathways may help explain the presence of PAHs in the low-temperature atmosphere of Saturn's moon Titan, and may be significant pathways, in terms of the PAH world hypothesis, in producing precursors to biochemicals related to life as we know it.