The tobacco industry comprises those persons and companies
engaged in the growth, preparation for sale, shipment, advertisement,
and distribution of tobacco
and tobacco-related products. It is a global industry; tobacco can grow
in any warm, moist environment, which means it can be farmed on all
continents except Antarctica.
Tobacco, one of the most widely used addictive substances in the world, is a plant native to the Americas and historically one of the half-dozen most important crops grown by American farmers. More specifically, tobacco refers to any of various plants of the genus Nicotiana (especially N. tabacum) native to tropical America and widely cultivated for their leaves, which are dried and processed chiefly for smoking in pipes, cigarettes, and cigars; it is also cut to form chewing tobacco or ground to make snuff or dipping tobacco, as well as other less common preparations. From 1617 to 1793 tobacco was the most valuable staple export from the English American mainland colonies and the United States. Until the 1960s, the United States not only grew but also manufactured and exported more tobacco than any other country.
Tobacco is an agricultural commodity product, similar in economic terms to agricultural foodstuffs: the price is in part determined by crop yields, which vary depending on local weather conditions. The price also varies by specific species or cultivar grown, the total quantity on the market ready for sale, the area where it is grown, the health of the plants, and other characteristics individual to product quality.
Since 1964 conclusive medical evidence of the deadly effects of tobacco consumption has led to a sharp decline in official support for producers and manufacturers of tobacco, although it contributes to the agricultural, fiscal, manufacturing, and exporting sectors of the economy. Laws around the world now often have some restrictions on smoking, but almost 6 trillion cigarettes are still produced each year, representing over a 12% increase since the year 2000. China accounts for over 40% of current world production. Tobacco is often heavily taxed to gain revenues for governments and as an incentive for people not to smoke.
Tobacco, one of the most widely used addictive substances in the world, is a plant native to the Americas and historically one of the half-dozen most important crops grown by American farmers. More specifically, tobacco refers to any of various plants of the genus Nicotiana (especially N. tabacum) native to tropical America and widely cultivated for their leaves, which are dried and processed chiefly for smoking in pipes, cigarettes, and cigars; it is also cut to form chewing tobacco or ground to make snuff or dipping tobacco, as well as other less common preparations. From 1617 to 1793 tobacco was the most valuable staple export from the English American mainland colonies and the United States. Until the 1960s, the United States not only grew but also manufactured and exported more tobacco than any other country.
Tobacco is an agricultural commodity product, similar in economic terms to agricultural foodstuffs: the price is in part determined by crop yields, which vary depending on local weather conditions. The price also varies by specific species or cultivar grown, the total quantity on the market ready for sale, the area where it is grown, the health of the plants, and other characteristics individual to product quality.
Since 1964 conclusive medical evidence of the deadly effects of tobacco consumption has led to a sharp decline in official support for producers and manufacturers of tobacco, although it contributes to the agricultural, fiscal, manufacturing, and exporting sectors of the economy. Laws around the world now often have some restrictions on smoking, but almost 6 trillion cigarettes are still produced each year, representing over a 12% increase since the year 2000. China accounts for over 40% of current world production. Tobacco is often heavily taxed to gain revenues for governments and as an incentive for people not to smoke.
History
For a history of how tobacco has been grown and marketed, see tobacco, smoking and articles on similar topics.
Position of industry
The phrase "tobacco industry" generally refers to the companies involved in the manufacture of cigarettes, cigars, snuff, chewing tobacco and pipe tobacco. China National Tobacco Co.
has become the largest tobacco company in the world by volume.
Following extensive merger and acquisition activity in the 1990s and
2000s, four firms dominate international markets - in alphabetical
order:
Altria, formerly called the Philip Morris Cos.
(Philip Morris Companies Inc.), still owns the Philip Morris tobacco
business in the United States, but Philip Morris International has been
fully independent since 2008. In most countries these companies either
have long-established dominance, or have purchased the major domestic
producer or producers (often a former state monopoly). Until 2014 the United States had one other substantial independent firm, Lorillard, which Reynolds American, Inc. acquired. India has its own major player, ITC Limited (25.4%-owned by British American Tobacco). A small number of state monopolies survive, as well as some small independent firms.
Tobacco advertising
is becoming increasingly restricted by the governments of countries
around the world citing health issues as a reason to restrict tobaccos
appeal.
Industry outlook in the United States
Anti-smoking ad, 1905
The tobacco industry in the United States has suffered greatly since
the mid-1990s, when it was successfully sued by several U.S. states. The
suits claimed that tobacco causes cancer, that companies in the
industry knew this, and that they deliberately understated the
significance of their findings, contributing to the illness and death of
many citizens in those states.
The industry was found to have decades of internal memos confirming in detail that tobacco (which contains nicotine) is both addictive and carcinogenic (cancer-causing). The industry had long denied that nicotine is addictive.
The suit resulted in a large cash settlement
being paid by a group of tobacco companies to the states that sued.
Further, since the suit was settled, other individuals have come forth,
in class action lawsuits, claiming individual damages. New suits of this nature will probably continue for a long time.
Since the settlement is a heavy tax on the profits of the tobacco
industry in the US, regressive against smokers, and further settlements
being made only add to the financial burden of these companies, it is
debatable if the industry has a money-producing long term outlook.
The tobacco industry has historically been largely successful in
this litigation process, with the majority of cases being won by the
industry. During the first 42 years of tobacco litigation (between 1954
and 1996) the industry maintained a clean record in litigation thanks to tactics described in a R.J. Reynolds Tobacco Company internal memo as "the way we won these cases, to paraphrase Gen. Patton, is not by spending all of Reynolds' money, but by making the other son of a bitch spend all of his." Between 1995 and 2005 only 59% of cases were won by the tobacco industry either outright or on appeal in the US,
but the continued success of the industry's efforts to win these cases
is questionable. In Florida, the industry has lost 77 of the 116 "Engle
progeny" cases that have gone to trial. The U.S. Supreme Court has
also denied the industry's major grounds for appeal of Engle cases.
In June 2009, U.S. President Barack Obama signed into law the Family Smoking Prevention and Tobacco Control Act which has been called a "sweeping anti-smoking" bill.
Among other restrictions, this Act banned the use of any constituent,
additive, herb or spice that adds a "characterizing flavor" to the
tobacco product or smoke (Section 907)(a)(1)(A). The aim of this ban is to prevent children and teenagers from becoming addicted to cigarettes at a young age with the US Department of Health and Human Services citing that "studies have shown that 17 year old
smokers are three times as likely to use flavored cigarettes as are smokers over the age of 25". This ban however does not apply to menthol cigarettes, which are exempt from the bill.
Lawsuits against the tobacco industry are primarily restricted to
the United States due to differences in legal systems in other
countries. Many businesses class ongoing lawsuits as a cost of doing
business in the US and feel their revenue will be only marginally
affected by the activities.
Large tobacco companies have entered the electronic cigarette market by either buying some of the small e-cigarette companies or by starting their own e-cigarette companies. By 2014 all the major multinational tobacco companies had entered the e-cigarette market. They did so either by buying existing e-cigarette companies (including Ruyan, the original Chinese e-cigarette company, which was bought by Imperial Tobacco) or by developing their own products. A 2017 review states, "The tobacco industry dominates the e-cigarette market." All of the large tobacco companies are selling e-cigarettes.
A 2017 review states, "Small companies initially dominated the ENDS
market, and these firms had no links to the tobacco industry. Today,
however, all transnational tobacco companies sell these products.
Increased concentration of the ENDS market in the hands of the
transnational tobacco companies is concerning to the public health
community, given the industry's legacy of obfuscating many fundamental
truths about their products and misleading the public with false claims,
including that low-tar and so-called "light" cigarettes would reduce
the harms associated with smoking. Although industry representatives are
claiming interest in ENDS because of their harm-reduction potential,
many observers believe that profit remains the dominant motivation."
Major tobacco companies are dominating the political and
policy-making environments just as they have in conventional cigarette
policy making.
As they have done to influence tobacco control policies for
conventional cigarettes, the large companies often try to stay out of
sight and work through third parties that can obscure their links to the
tobacco industry.
The one difference from the historical pattern of industry efforts to
shape tobacco policy from behind the scenes is that there are also
genuine independent sellers of e-cigarettes and associated users
(so-called vape shops) who are not necessarily being directed by the
cigarette companies.
These smaller operators are, however, losing market share to the big
tobacco companies, and the real political power is now being exercised
by the cigarette companies.
The cigarette companies try to take advantage of the existence of
independent players while acting through the industry's traditional
allies and front groups.
Tobacco control
On May 11, 2004, the U.S. became the 108th country to sign the World Health Organization's Global Treaty on Tobacco Control.
This treaty places broad restrictions on the sale, advertising,
shipment, and taxation of tobacco products. The U.S. has not yet
ratified this treaty in its senate and does not yet have a schedule for doing so.
Most recently, there has been discussion within the tobacco
control community of transforming the tobacco industry through the
replacement of tobacco corporations
by other types of business organizations that can be established to
provide tobacco to the market while not attempting to increase market
demand.
On February 20, 2007, the US Supreme Court ruled that the Altria Group
(formerly Philip Morris) did not have to pay $79.5 million in punitive
damages awarded to Mayola Williams in a 1999 Oregon court ruling, when
she sued Phillip Morris for responsibility in the cancer death of her
husband, Jesse Williams. The Supreme Court's decision overturns a ruling made by the Oregon Supreme Court that upheld the award.
On April 3, 2008, The U.S. Court of Appeals for the Second
Circuit threw out a $800 billion class-action lawsuit filed on behalf of
a group or class of people who smoked light cigarettes. The plaintiffs'
lawyers were confident that they would be able to win this suit due to
the success of the Schwab case
wherein tobacco companies were found guilty of fraud-like charges
because they were selling the idea that light cigarettes were safer than
regular cigarettes. The ruling by the three-judge panel will not allow
the suit to be pursued as a class, but instead need proof for why
individual smokers chose light cigarettes over regular cigarettes.
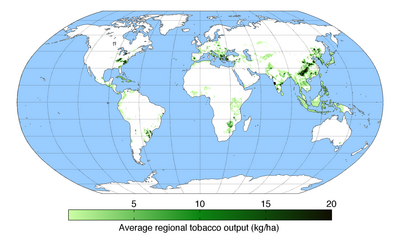
Production by country or region
Map of tobacco production across the world
The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization estimates the following production of unprocessed tobacco by country/region in 2000. (Figures are in thousands of tonnes.)
| Country or region | Production in thousands of tons |
|---|---|
| 2,298.8 | |
| 595.4 | |
| 520.7 | |
| 408.2 | |
| 314.5 | |
| 204.9 | |
| 193.9 | |
| 166.6 | |
| 116.8 | |
| 108.0 |
Cigarette Production by Factory
Much
of global tobacco production is used in the manufacturing of
cigarettes. The following is a chart compiled by Dr. Robert Proctor
detailing the largest cigarette factories, accompanied by their
estimated annual death toll due to the harms of cigarettes to health.
Tobacco industry in popular culture
The
tobacco industry has had a long relationship with the entertainment
industry. In silent era movies, back-lit smoke was often used by
filmmakers to create sense of mystery and sensuality in a scene. Later,
cigarettes were deliberately placed in the hands of Hollywood stars as
an early phase of product placement,
until health regulating bodies tightened rules on tobacco advertisement
and anti-smoking groups pressured actors and studio executives against
such tactics. Big Tobacco has since been the subject focus of films such as the docudrama The Insider (1999) and Thank You For Smoking (2005).
These issues have also constituted a recurring storyline in the AMC series Mad Men, from season 1 beginning with the pilot episode ("Smoke Gets In Your Eyes") through season 7's midseason finale, "Waterloo".