The word 'Wikipedia' represented in ASCII binary code, made up of 9 bytes (72 bits).
A binary code represents text, computer processor instructions, or any other data using a two-symbol system. The two-symbol system used is often "0" and "1" from the binary number system. The binary code assigns a pattern of binary digits, also known as bits, to each character, instruction, etc. For example, a binary string of eight bits can represent any of 256 possible values and can, therefore, represent a wide variety of different items.
In computing and telecommunications, binary codes are used for various methods of encoding data, such as character strings, into bit strings. Those methods may use fixed-width or variable-width
strings. In a fixed-width binary code, each letter, digit, or other
character is represented by a bit string of the same length; that bit
string, interpreted as a binary number, is usually displayed in code tables in octal, decimal or hexadecimal notation. There are many character sets and many character encodings for them.
A bit string, interpreted as a binary number, can be translated into a decimal number. For example, the lower case a, if represented by the bit string
01100001 (as it is in the standard ASCII code), can also be represented as the decimal number "97".History of binary code
The modern binary number system, the basis for binary code, was invented by Gottfried Leibniz in 1689 and appears in his article Explication de l'Arithmétique Binaire.
The full title is translated into English as the "Explanation of the
binary arithmetic", which uses only the characters 1 and 0, with some
remarks on its usefulness, and on the light it throws on the ancient
Chinese figures of Fu Xi." (1703). Leibniz's system uses 0 and 1, like the modern binary numeral system. Leibniz encountered the I Ching through French Jesuit Joachim Bouvet and noted with fascination how its hexagrams
correspond to the binary numbers from 0 to 111111, and concluded that
this mapping was evidence of major Chinese accomplishments in the sort
of philosophical visual binary mathematics he admired. Leibniz saw the hexagrams as an affirmation of the universality of his own religious belief.
Binary numerals were central to Leibniz's theology. He believed that binary numbers were symbolic of the Christian idea of creatio ex nihilo or creation out of nothing.
Leibniz was trying to find a system that converts logic’s verbal
statements into a pure mathematical one. After his ideas were ignored,
he came across a classic Chinese text called I Ching or ‘Book of
Changes’, which used 64 hexagrams of six-bit visual binary code. The
book had confirmed his theory that life could be simplified or reduced
down to a series of straightforward propositions. He created a system
consisting of rows of zeros and ones. During this time period, Leibniz
had not yet found a use for this system.
Binary systems predating Leibniz also existed in the ancient world. The aforementioned I Ching that Leibniz encountered dates from the 9th century BC in China. The binary system of the I Ching, a text for divination, is based on the duality of yin and yang. Slit drums with binary tones are used to encode messages across Africa and Asia. The Indian scholar Pingala (around 5th–2nd centuries BC) developed a binary system for describing prosody in his Chandashutram.
The residents of the island of Mangareva in French Polynesia were using a hybrid binary-decimal system before 1450. In the 11th century, scholar and philosopher Shao Yong
developed a method for arranging the hexagrams which corresponds,
albeit unintentionally, to the sequence 0 to 63, as represented in
binary, with yin as 0, yang as 1 and the least significant bit on top. The ordering is also the lexicographical order on sextuples of elements chosen from a two-element set.
In 1605 Francis Bacon
discussed a system whereby letters of the alphabet could be reduced to
sequences of binary digits, which could then be encoded as scarcely
visible variations in the font in any random text.
Importantly for the general theory of binary encoding, he added that
this method could be used with any objects at all: "provided those
objects be capable of a twofold difference only; as by Bells, by
Trumpets, by Lights and Torches, by the report of Muskets, and any
instruments of like nature".
George Boole
published a paper in 1847 called 'The Mathematical Analysis of Logic'
that describes an algebraic system of logic, now known as Boolean algebra.
Boole's system was based on binary, a yes-no, on-off approach that
consisted of the three most basic operations: AND, OR, and NOT. This system was not put into use until a graduate student from Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Claude Shannon,
noticed that the Boolean algebra he learned was similar to an electric
circuit. Shannon wrote his thesis in 1937, which implemented his
findings. Shannon's thesis
became a starting point for the use of the binary code in practical
applications such as computers, electric circuits, and more.
Other forms of binary code
Daoist Bagua
The bit string is not the only type of binary code: in fact, a binary
system in general, is any system that allows only two choices such as a
switch in an electronic system or a simple true or false test.
Braille
Braille
is a type of binary code that is widely used by the blind to read and
write by touch, named for its creator, Louis Braille. This system
consists of grids of six dots each, three per column, in which each dot
has two states: raised or not raised. The different combinations of
raised and flattened dots are capable of representing all letters,
numbers, and punctuation signs.
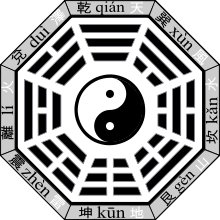
Bagua
The bagua are diagrams used in feng shui, Taoist cosmology and I Ching studies. The ba gua consists of 8 trigrams; bā meaning 8 and guà meaning divination figure. The same word is used for the 64 guà (hexagrams). Each figure combines three lines (yáo) that are either broken (yin) or unbroken (yang). The relationships between the trigrams are represented in two arrangements, the primordial, "Earlier Heaven" or "Fuxi" bagua, and the manifested, "Later Heaven,"or "King Wen" bagua.
Coding systems
ASCII code
The American Standard Code for Information Interchange
(ASCII), uses a 7-bit binary code to represent text and other
characters within computers, communications equipment, and other
devices. Each letter or symbol is assigned a number from 0 to 127. For
example, lowercase "a" is represented by
1100001 as a bit string (which is "97" in decimal). Binary-coded decimal
Binary-coded decimal (BCD) is a binary encoded representation of integer values that uses a 4-bit nibble
to encode decimal digits. Four binary bits can encode up to 16 distinct
values; but, in BCD-encoded numbers, only the first ten values in each
nibble are legal, and encode the decimal digits zero, through nine. The
remaining six values are illegal and may cause either a machine
exception or unspecified behavior, depending on the computer
implementation of BCD arithmetic.
BCD arithmetic is sometimes preferred to floating-point numeric
formats in commercial and financial applications where the complex
rounding behaviors of floating-point numbers is inappropriate.
Early uses of binary codes
- 1875: Émile Baudot "Addition of binary strings in his ciphering system," which, eventually, lead to the ASCII of today.
- 1884: The Linotype machine where the matrices are sorted to their corresponding channels after use by a binary-coded slide rail.
- 1932: C. E. Wynn-Williams "Scale of Two" counter
- 1937: Alan Turing electro-mechanical binary multiplier
- 1937: George Stibitz "excess three" code in the Complex Computer
- 1937: Atanasoff–Berry Computer
- 1938: Konrad Zuse Z1
Current uses of binary
Most modern computers use binary encoding for instructions and data. CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray Discs
represent sound and video digitally in binary form. Telephone calls are
carried digitally on long-distance and mobile phone networks using pulse-code modulation, and on voice over IP networks.
Weight of binary codes
The weight of a binary code, as defined in the table of constant-weight codes, is the Hamming weight of the binary words coding for the represented words or sequences.