Electric field of a positive point electric charge suspended over an infinite sheet of conducting material. The field is depicted by electric field lines, lines which follow the direction of the electric field in space.
An electric field surrounds an electric charge, and exerts force on other charges in the field, attracting or repelling them. Electric field is sometimes abbreviated as E-field. The electric field is defined mathematically as a vector field that associates to each point in space the (electrostatic or Coulomb) force per unit of charge exerted on an infinitesimal positive test charge at rest at that point. The SI unit for electric field strength is volt per meter (V/m). Newtons per coulomb (N/C) is also used as a unit of electric field strength. Electric fields are created by electric charges, or by time-varying magnetic fields. Electric fields are important in many areas of physics,
and are exploited practically in electrical technology. On an atomic
scale, the electric field is responsible for the attractive force
between the atomic nucleus and electrons that holds atoms together, and the forces between atoms that cause chemical bonding. Electric fields and magnetic fields are both manifestations of the electromagnetic force, one of the four fundamental forces (or interactions) of nature.
Definition
From Coulomb's law a particle with electric charge at position exerts a force on a particle with charge at position of
- where is the unit vector in the direction from point to point , and ε0 is the electric constant (also known as "the absolute permittivity of free space") in C2 m−2 N−1
When the charges and
have the same sign this force is positive, directed away from the other
charge, indicating the particles repel each other. When the charges
have unlike signs the force is negative, indicating the particles
attract.
To make it easy to calculate the Coulomb force on any charge at position this expression can be divided by , leaving an expression that only depends on the other charge (the source charge)
This is the electric field at point due to the point charge ; it is a vector equal to the Coulomb force per unit charge that a positive point charge would experience at the position .
Since this formula gives the electric field magnitude and direction at any point in space (except at the location of the charge itself, , where it becomes infinite) it defines a vector field.
From the above formula it can be seen that the electric field due to a
point charge is everywhere directed away from the charge if it is
positive, and toward the charge if it is negative, and its magnitude
decreases with the inverse square of the distance from the charge.
If there are multiple charges, the resultant Coulomb force on a
charge can be found by summing the vectors of the forces due to each
charge. This shows the electric field obeys the superposition principle:
the total electric field at a point due to a collection of charges is
just equal to the vector sum of the electric fields at that point due to
the individual charges.
- where is the unit vector in the direction from point to point .
This is the definition of the electric field due to the point source charges .
It diverges and becomes infinite at the locations of the charges themselves, and so is not defined there.
Evidence of an electric field: styrofoam peanuts clinging to a cat's fur due to static electricity. The triboelectric effect causes an electrostatic charge
to build up on the fur due to the cat's motions. The electric field of
the charge causes polarization of the molecules of the styrofoam due to electrostatic induction, resulting in a slight attraction of the light plastic pieces to the charged fur. This effect is also the cause of static cling in clothes.
The Coulomb force on a charge of magnitude at any point in space is equal to the product of the charge and the electric field at that point
The units of the electric field in the SI system are newtons per coulomb (N/C), or volts per meter (V/m); in terms of the SI base units they are kg⋅m⋅s−3⋅A−1
The electric field due to a continuous distribution of charge in space (where is the charge density in coulombs per cubic meter) can be calculated by considering the charge in each small volume of space at point as a point charge, and calculating its electric field at point
where is the unit vector pointing from to , then adding up the contributions from all the increments of volume by integrating over the volume of the charge distribution
Sources
Causes and description
Electric fields are caused by electric charges, described by Gauss's law, or varying magnetic fields, described by Faraday's law of induction. Together, these laws are enough to define the behavior of the electric field as a function of charge repartition
and magnetic field. However, since the magnetic field is described as a
function of electric field, the equations of both fields are coupled
and together form Maxwell's equations that describe both fields as a function of charges and currents.
In the special case of a steady state (stationary charges and currents), the Maxwell-Faraday inductive effect disappears. The resulting two equations (Gauss's law and Faraday's law with no induction term ), taken together, are equivalent to Coulomb's law, written as for a charge density
( is position in space). Notice that , the vacuum electric permittivity, must be substituted with , permittivity, when charges are in non-empty media.
Continuous vs. discrete charge representation
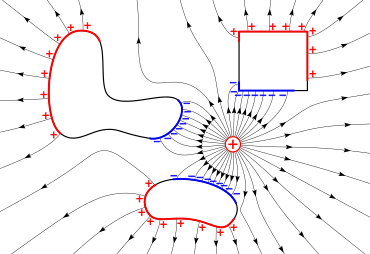
The electric field (lines with arrows) of a charge (+) induces surface charges (red and blue areas) on metal objects due to electrostatic induction.
The equations of electromagnetism are best described in a continuous
description. However, charges are sometimes best described as discrete
points; for example, some models may describe electrons as point sources where charge density is infinite on an infinitesimal section of space.
A charge located at can be described mathematically as a charge density , where the Dirac delta function (in three dimensions) is used. Conversely, a charge distribution can be approximated by many small point charges.
Superposition principle
Electric fields satisfy the superposition principle, because Maxwell's equations are linear. As a result, if and are the electric fields resulting from distribution of charges and , a distribution of charges will create an electric field ; for instance, Coulomb's law is linear in charge density as well.
This principle is useful to calculate the field created by multiple point charges. If charges are stationary in space at ,
in the absence of currents, the superposition principle proves that the
resulting field is the sum of fields generated by each particle as
described by Coulomb's law:
Electrostatic fields
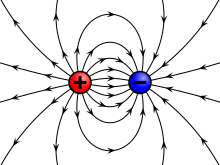
Illustration of the electric field surrounding a positive (red) and a negative (blue) charge
Electrostatic fields are electric fields which do not change with
time, which happens when charges and currents are stationary. In that
case, Coulomb's law fully describes the field.
Electric potential
If a system is static, such that magnetic fields are not
time-varying, then by Faraday's law, the electric field is curl-free. In
this case, one can define an electric potential, that is, a function such that .
This is analogous to the gravitational potential.
Parallels between electrostatic and gravitational fields
Coulomb's law, which describes the interaction of electric charges:
is similar to Newton's law of universal gravitation:
(where ).
This suggests similarities between the electric field E and the gravitational field g, or their associated potentials. Mass is sometimes called "gravitational charge".
Electrostatic and gravitational forces both are central, conservative and obey an inverse-square law.
Uniform fields
A uniform field is one in which the electric field is constant at every point. It can be approximated by placing two conducting plates parallel to each other and maintaining a voltage
(potential difference) between them; it is only an approximation
because of boundary effects (near the edge of the planes, electric field
is distorted because the plane does not continue). Assuming infinite
planes, the magnitude of the electric field E is:
where ΔV is the potential difference between the plates and d
is the distance separating the plates. The negative sign arises as
positive charges repel, so a positive charge will experience a force
away from the positively charged plate, in the opposite direction to
that in which the voltage increases. In micro- and nano-applications,
for instance in relation to semiconductors, a typical magnitude of an
electric field is in the order of 106 V⋅m−1, achieved by applying a voltage of the order of 1 volt between conductors spaced 1 µm apart.
Electrodynamic fields
Electrodynamic fields are electric fields which do change with time, for instance when charges are in motion.
The electric field cannot be described independently of the magnetic field in that case. If A is the magnetic vector potential, defined so that , one can still define an electric potential such that:
One can recover Faraday's law of induction by taking the curl of that equation
which justifies, a posteriori, the previous form for E.
Energy in the electric field
The total energy per unit volume stored by the electromagnetic field is
where ε is the permittivity of the medium in which the field exists, its magnetic permeability, and E and B are the electric and magnetic field vectors.
As E and B fields are coupled, it would be
misleading to split this expression into "electric" and "magnetic"
contributions. However, in the steady-state case, the fields are no
longer coupled. It makes sense in that case to compute the electrostatic energy per unit volume:
The total energy U stored in the electric field in a given volume V is therefore
Further extensions
Definitive equation of vector fields
In the presence of matter, it is helpful to extend the notion of the electric field into three vector fields:
where P is the electric polarization – the volume density of electric dipole moments, and D is the electric displacement field. Since E and P are defined separately, this equation can be used to define D. The physical interpretation of D is not as clear as E (effectively the field applied to the material) or P
(induced field due to the dipoles in the material), but still serves as
a convenient mathematical simplification, since Maxwell's equations can
be simplified in terms of free charges and currents.
Constitutive relation
The E and D fields are related by the permittivity of the material, ε.
For linear, homogeneous, isotropic materials E and D
are proportional and constant throughout the region, there is no
position dependence: For inhomogeneous materials, there is a position
dependence throughout the material:
For anisotropic materials the E and D fields are not parallel, and so E and D are related by the permittivity tensor (a 2nd order tensor field), in component form:
For non-linear media, E and D are not proportional. Materials can have varying extents of linearity, homogeneity and isotropy.