| Abortion | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Induced miscarriage, termination of pregnancy |
| Specialty | Obstetrics and gynecology |
| ICD-10-PCS | O04 |
| ICD-9-CM | 779.6 |
| MeSH | D000028 |
| MedlinePlus | 007382 |
Abortion is the ending of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus before it can survive outside the uterus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or spontaneous abortion. When deliberate steps are taken to end a pregnancy, it is called an induced abortion, or less frequently "induced miscarriage". The unmodified word abortion generally refers to an induced abortion. A similar procedure after the fetus has potential to survive outside the womb is known as a "late termination of pregnancy" or less accurately as a "late term abortion".
When properly done, abortion is one of the safest procedures in medicine, but unsafe abortion is a major cause of maternal death, especially in the developing world. Making safe abortion legal and accessible reduces maternal deaths. It is safer than childbirth, which has a 14 times higher risk of death in the United States. Modern methods use medication or surgery for abortions. The drug mifepristone in combination with prostaglandin appears to be as safe and effective as surgery during the first and second trimester of pregnancy. The most common surgical technique involves dilating the cervix and using a suction device. Birth control, such as the pill or intrauterine devices, can be used immediately following abortion. When performed legally and safely on a woman who desires it, induced abortions do not increase the risk of long-term mental or physical problems. In contrast, unsafe abortions (those performed by unskilled individuals, with hazardous equipment, or in unsanitary facilities) cause 47,000 deaths and 5 million hospital admissions each year. The World Health Organization recommends safe and legal abortions be available to all women.
Around 56 million abortions are performed each year in the world, with about 45% done unsafely. Abortion rates changed little between 2003 and 2008, before which they decreased for at least two decades as access to family planning and birth control increased. As of 2018, 37% of the world's women had access to legal abortions without limits as to reason. Countries that permit abortions have different limits on how late in pregnancy abortion is allowed.
Historically, abortions have been attempted using herbal medicines, sharp tools, forceful massage, or through other traditional methods. Abortion laws and cultural or religious views of abortions are different around the world. In some areas abortion is legal only in specific cases such as rape, problems with the fetus, poverty, risk to a woman's health, or incest. There is debate over the moral, ethical, and legal issues of abortion. Those who oppose abortion often argue that an embryo or fetus is a human with a right to life, and they may compare abortion to murder. Those who support the legality of abortion often hold that it is part of a woman's right to make decisions about her own body. Others favor legal and accessible abortion as a public health measure.
Types
Induced
An induced abortion may be classified as therapeutic (done in response to a health condition of the women or fetus) or elective (chosen for other reasons).Approximately 205 million pregnancies occur each year worldwide. Over a third are unintended and about a fifth end in induced abortion. Most abortions result from unintended pregnancies. In the United Kingdom, 1 to 2% of abortions are done due to genetic problems in the fetus. A pregnancy can be intentionally aborted in several ways. The manner selected often depends upon the gestational age of the embryo or fetus, which increases in size as the pregnancy progresses. Specific procedures may also be selected due to legality, regional availability, and doctor or a woman's personal preference.
Reasons for procuring induced abortions are typically characterized as either therapeutic or elective. An abortion is medically referred to as a therapeutic abortion when it is performed to save the life of the pregnant woman; to prevent harm to the woman's physical or mental health; to terminate a pregnancy where indications are that the child will have a significantly increased chance of mortality or morbidity; or to selectively reduce the number of fetuses to lessen health risks associated with multiple pregnancy. An abortion is referred to as an elective or voluntary abortion when it is performed at the request of the woman for non-medical reasons. Confusion sometimes arises over the term "elective" because "elective surgery" generally refers to all scheduled surgery, whether medically necessary or not.
Spontaneous
Miscarriage, also known as spontaneous abortion, is the unintentional expulsion of an embryo or fetus before the 24th week of gestation. A pregnancy that ends before 37 weeks of gestation resulting in a live-born infant is a "premature birth" or a "preterm birth". When a fetus dies in utero after viability, or during delivery, it is usually termed "stillborn". Premature births and stillbirths are generally not considered to be miscarriages although usage of these terms can sometimes overlap.Only 30% to 50% of conceptions progress past the first trimester. The vast majority of those that do not progress are lost before the woman is aware of the conception, and many pregnancies are lost before medical practitioners can detect an embryo. Between 15% and 30% of known pregnancies end in clinically apparent miscarriage, depending upon the age and health of the pregnant woman. 80% of these spontaneous abortions happen in the first trimester.
The most common cause of spontaneous abortion during the first trimester is chromosomal abnormalities of the embryo or fetus, accounting for at least 50% of sampled early pregnancy losses. Other causes include vascular disease (such as lupus), diabetes, other hormonal problems, infection, and abnormalities of the uterus. Advancing maternal age and a woman's history of previous spontaneous abortions are the two leading factors associated with a greater risk of spontaneous abortion. A spontaneous abortion can also be caused by accidental trauma; intentional trauma or stress to cause miscarriage is considered induced abortion or feticide.
Methods
Practice of Induced Abortion Methods
Induced Miscarr.
Gestational age may determine which abortion methods are practiced.
Medical
Medical abortions are those induced by abortifacient pharmaceuticals. Medical abortion became an alternative method of abortion with the availability of prostaglandin analogs in the 1970s and the antiprogestogen mifepristone (also known as RU-486) in the 1980s.The most common early first-trimester medical abortion regimens use mifepristone in combination with misoprostol (or sometimes another prostaglandin analog, gemeprost) up to 10 weeks (70 days) gestational age, methotrexate in combination with a prostaglandin analog up to 7 weeks gestation, or a prostaglandin analog alone. Mifepristone–misoprostol combination regimens work faster and are more effective at later gestational ages than methotrexate–misoprostol combination regimens, and combination regimens are more effective than misoprostol alone. This regimen is effective in the second trimester. Medical abortion regimens involving mifepristone followed by misoprostol in the cheek between 24 and 48 hours later are effective when performed before 70 days' gestation.
In very early abortions, up to 7 weeks gestation, medical abortion using a mifepristone–misoprostol combination regimen is considered to be more effective than surgical abortion (vacuum aspiration), especially when clinical practice does not include detailed inspection of aspirated tissue. Early medical abortion regimens using mifepristone, followed 24–48 hours later by buccal or vaginal misoprostol are 98% effective up to 9 weeks gestational age; from 9 to 10 weeks efficacy decreases modestly to 94%. If medical abortion fails, surgical abortion must be used to complete the procedure.
Early medical abortions account for the majority of abortions before 9 weeks gestation in Britain, France, Switzerland, and the Nordic countries. In the United States, the percentage of early medical abortions performed in non-hospital facilities is 31% as of 2014.
Medical abortion regimens using mifepristone in combination with a prostaglandin analog are the most common methods used for second-trimester abortions in Canada, most of Europe, China and India, in contrast to the United States where 96% of second-trimester abortions are performed surgically by dilation and evacuation.
Surgical
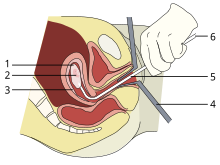
A vacuum aspiration abortion at eight weeks gestational age (six weeks after fertilization).
1: Amniotic sac
2: Embryo
3: Uterine lining
4: Speculum
5: Vacurette
6: Attached to a suction pump
1: Amniotic sac
2: Embryo
3: Uterine lining
4: Speculum
5: Vacurette
6: Attached to a suction pump
Up to 15 weeks' gestation, suction-aspiration or vacuum aspiration are the most common surgical methods of induced abortion. Manual vacuum aspiration (MVA) consists of removing the fetus or embryo, placenta, and membranes by suction using a manual syringe, while electric vacuum aspiration
(EVA) uses an electric pump. These techniques can both be used very
early in pregnancy. MVA can be used up to 14 weeks but is more often
used earlier in the U.S. EVA can be used later.
MVA, also known as "mini-suction" and "menstrual extraction" or EVA can be used in very early pregnancy when cervical dilation may not be required. Dilation and curettage
(D&C) refers to opening the cervix (dilation) and removing tissue
(curettage) via suction or sharp instruments. D&C is a standard
gynecological procedure performed for a variety of reasons, including
examination of the uterine lining for possible malignancy, investigation
of abnormal bleeding, and abortion. The World Health Organization recommends sharp curettage only when suction aspiration is unavailable.
Dilation and evacuation (D&E), used after 12 to 16 weeks, consists of opening the cervix
and emptying the uterus using surgical instruments and suction. D&E
is performed vaginally and does not require an incision. Intact dilation and extraction(D&X)
refers to a variant of D&E sometimes used after 18 to 20 weeks when
removal of an intact fetus improves surgical safety or for other
reasons.
Abortion may also be performed surgically by hysterotomy or gravid hysterectomy. Hysterotomy abortion is a procedure similar to a caesarean section and is performed under general anesthesia.
It requires a smaller incision than a caesarean section and can be used
during later stages of pregnancy. Gravid hysterectomy refers to
removal of the whole uterus while still containing the pregnancy.
Hysterotomy and hysterectomy are associated with much higher rates of
maternal morbidity and mortality than D&E or induction abortion.
First-trimester procedures can generally be performed using local anesthesia, while second-trimester methods may require deep sedation or general anesthesia.
Labor induction abortion
In places lacking the necessary medical skill for dilation and
extraction, or where preferred by practitioners, an abortion can be
induced by first inducing labor and then inducing fetal demise if necessary.
This is sometimes called "induced miscarriage". This procedure may be
performed from 13 weeks gestation to the third trimester. Although it is
very uncommon in the United States, more than 80% of induced abortions
throughout the second trimester are labor-induced abortions in Sweden
and other nearby countries.
Only limited data are available comparing this method with dilation and extraction.
Unlike D&E, labor-induced abortions after 18 weeks may be
complicated by the occurrence of brief fetal survival, which may be
legally characterized as live birth. For this reason, labor-induced
abortion is legally risky in the United States.
Other methods
Historically, a number of herbs reputed to possess abortifacient properties have been used in folk medicine. Among these are: tansy, pennyroyal, black cohosh, and the now-extinct silphium.
In 1978 one woman in Colorado died and another was seriously
injured when they attempted to procure an abortion by taking pennyroyal
oil.
Because the indiscriminant use of herbs as abortifacients can cause serious—even lethal—side effects, such as multiple organ failure, such use is not recommended by physicians.
Abortion is sometimes attempted by causing trauma to the abdomen.
The degree of force, if severe, can cause serious internal injuries
without necessarily succeeding in inducing miscarriage. In Southeast Asia, there is an ancient tradition of attempting abortion through forceful abdominal massage. One of the bas reliefs decorating the temple of Angkor Wat in Cambodia depicts a demon performing such an abortion upon a woman who has been sent to the underworld.
Reported methods of unsafe, self-induced abortion include misuse of misoprostol
and insertion of non-surgical implements such as knitting needles and
clothes hangers into the uterus. These and other methods to terminate
pregnancy may be called "induced miscarriage". Such methods are rarely
used in countries where surgical abortion is legal and available.
Safety
An abortion flyer in South Africa
The health risks of abortion depend principally upon whether the procedure is performed safely or unsafely. The World Health Organization defines unsafe abortions as those performed by unskilled individuals, with hazardous equipment, or in unsanitary facilities. Legal abortions performed in the developed world are among the safest procedures in medicine. In the United States as of 2012, abortion was estimated to be about 14 times safer for women than childbirth. CDC estimated in 2019 that US pregnancy-related mortality was 17.2 maternal deaths per 100,000 live births, while the US abortion mortality rate is 0.7 maternal deaths per 100,000 procedures.
In the UK, guidelines of the Royal College of Obstetricians and
Gynaecologists state that "Women should be advised that abortion is
generally safer than continuing a pregnancy to term."
Worldwide, on average, abortion is safer than carrying a pregnancy to
term. A 2007 study reported that "26% of all pregnancies worldwide are
terminated by induced abortion," whereas "deaths from improperly
performed [abortion] procedures constitute 13% of maternal mortality
globally."
In Indonesia in 2000 it was estimated that 2 million pregnancies ended
in abortion, 4.5 million pregnancies were carried to term, and 14-16
percent of maternal deaths resulted from abortion.
In the US from 2000 to 2009, abortion had a lower mortality rate than plastic surgery, and a similar or lower mortality rate than running a marathon.
Five years after seeking abortion services, women who gave birth after
being denied an abortion reported worse health than women who had either
first or second trimester abortions. The risk of abortion-related mortality increases with gestational age, but remains lower than that of childbirth. Outpatient abortion is as safe from 64 to 70 days' gestation as it before 63 days.
There is little difference in terms of safety and efficacy
between medical abortion using a combined regimen of mifepristone and
misoprostol and surgical abortion (vacuum aspiration) in early first
trimester abortions up to 10 weeks gestation.
Medical abortion using the prostaglandin analog misoprostol alone is
less effective and more painful than medical abortion using a combined
regimen of mifepristone and misoprostol or surgical abortion.
Vacuum aspiration in the first trimester is the safest method of surgical abortion, and can be performed in a primary care office, abortion clinic, or hospital. Complications, which are rare, can include uterine perforation, pelvic infection, and retained products of conception requiring a second procedure to evacuate. Infections account for one-third of abortion-related deaths in the United States.
The rate of complications of vacuum aspiration abortion in the first
trimester is similar regardless of whether the procedure is performed in
a hospital, surgical center, or office. Preventive antibiotics (such as doxycycline or metronidazole) are typically given before abortion procedures, as they are believed to substantially reduce the risk of postoperative uterine infection; however, antibiotics are not routinely given with abortion pills.
The rate of failed procedures does not appear to vary significantly
depending on whether the abortion is performed by a doctor or a mid-level practitioner.
Complications after second-trimester abortion are similar to
those after first-trimester abortion, and depend somewhat on the method
chosen.
The risk of death from abortion approaches roughly half the risk of
death from childbirth the farther along a woman is in pregnancy; from 1
in a million before 9 weeks gestation to nearly 1 in 10 thousand at 21
weeks or more (as measured from the last menstrual period).
Some purported risks of abortion are promoted primarily by anti-abortion groups,
but lack scientific support. For example, the question of a link between induced abortion and breast cancer has been investigated extensively. Major medical and scientific bodies (including the World Health Organization, National Cancer Institute, American Cancer Society, Royal College of OBGYN and American Congress of OBGYN) have concluded that abortion does not cause breast cancer.
In the past even illegality has not automatically meant that the abortions were unsafe. Referring to the U.S., historian Linda Gordon states: "In fact, illegal abortions in this country have an impressive safety record." According to Rickie Solinger,
A related myth, promulgated by a broad spectrum of people concerned about abortion and public policy, is that before legalization abortionists were dirty and dangerous back-alley butchers.... [T]he historical evidence does not support such claims.
Authors Jerome Bates and Edward Zawadzki describe the case of an
illegal abortionist in the eastern U.S. in the early 20th century who
was proud of having successfully completed 13,844 abortions without any
fatality.
In 1870s New York City the famous abortionist/midwife Madame Restell (Anna Trow Lohman) appears to have lost very few women among her more than 100,000 patients—a
lower mortality rate than the childbirth mortality rate at the time. In
1936 the prominent professor of obstetrics and gynecology Frederick J. Taussig wrote that a cause of increasing mortality during the years of illegality in the U.S. was that
With each decade of the past fifty years the actual and proportionate frequency of this accident [perforation of the uterus] has increased, due, first, to the increase in the number of instrumentally induced abortions; second, to the proportionate increase in abortions handled by doctors as against those handled by midwives; and, third, to the prevailing tendency to use instruments instead of the finger in emptying the uterus.
Mental health
Current evidence finds no relationship between most induced abortions and mental-health problems other than those expected for any unwanted pregnancy. A report by the American Psychological Association
concluded that a woman's first abortion is not a threat to mental
health when carried out in the first trimester, with such women no more
likely to have mental-health problems than those carrying an unwanted
pregnancy to term; the mental-health outcome of a woman's second or
greater abortion is less certain. Some older reviews concluded that abortion was associated with an increased risk of psychological problems; however, they did not use an appropriate control group.
Although some studies show negative mental-health outcomes in
women who choose abortions after the first trimester because of fetal
abnormalities, more rigorous research would be needed to show this conclusively.
Some proposed negative psychological effects of abortion have been
referred to by anti-abortion advocates as a separate condition called "post-abortion syndrome", but this is not recognized by medical or psychological professionals in the United States.
A long term-study among US women found that about 99% of women
felt that they made the right decision five years after they had an
abortion. Relief was the primary emotion with few women feeling sadness
or guilt. Social stigma was a main factor predicting negative emotions
and regret years later.
Unsafe abortion
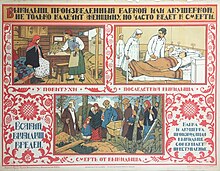
Soviet
poster circa 1925, warning against midwives performing abortions. Title
translation: ""Miscarriages induced by either grandma or self-taught
midwives not only maim the woman, they also often lead to death."
Women seeking an abortion may use unsafe methods, especially when abortion is legally restricted. They may attempt self-induced abortion
or seek the help of a person without proper medical training or
facilities. This can lead to severe complications, such as incomplete
abortion, sepsis, hemorrhage, and damage to internal organs.
Unsafe abortions are a major cause of injury and death among
women worldwide. Although data are imprecise, it is estimated that
approximately 20 million unsafe abortions are performed annually, with
97% taking place in developing countries. Unsafe abortions are believed to result in millions of injuries. Estimates of deaths vary according to methodology, and have ranged from 37,000 to 70,000 in the past decade; deaths from unsafe abortion account for around 13% of all maternal deaths. The World Health Organization believes that mortality has fallen since the 1990s.
To reduce the number of unsafe abortions, public health organizations
have generally advocated emphasizing the legalization of abortion,
training of medical personnel, and ensuring access to
reproductive-health services.
In response, opponents of abortion point out that abortion bans in no
way affect prenatal care for women who choose to carry their fetus to
term. The Dublin Declaration on Maternal Health, signed in 2012, notes,
"the prohibition of abortion does not affect, in any way, the
availability of optimal care to pregnant women."
A major factor in whether abortions are performed safely or not
is the legal standing of abortion. Countries with restrictive abortion
laws have higher rates of unsafe abortion and similar overall abortion
rates compared to those where abortion is legal and available.
For example, the 1996 legalization of abortion in South Africa had an
immediate positive impact on the frequency of abortion-related
complications, with abortion-related deaths dropping by more than 90%.
Similar reductions in maternal mortality have been observed after other
countries have liberalized their abortion laws, such as Romania and Nepal.
A 2011 study concluded that in the United States, some state-level
anti-abortion laws are correlated with lower rates of abortion in that
state. The analysis, however, did not take into account travel to other states without such laws to obtain an abortion.
In addition, a lack of access to effective contraception contributes to
unsafe abortion. It has been estimated that the incidence of unsafe
abortion could be reduced by up to 75% (from 20 million to 5 million
annually) if modern family planning and maternal health services were
readily available globally.
Rates of such abortions may be difficult to measure because they can be
reported variously as miscarriage, "induced miscarriage", "menstrual
regulation", "mini-abortion", and "regulation of a delayed/suspended
menstruation".
Forty percent of the world's women are able to access therapeutic and elective abortions within gestational limits, while an additional 35 percent have access to legal abortion if they meet certain physical, mental, or socioeconomic criteria. While maternal mortality seldom results from safe abortions, unsafe abortions result in 70,000 deaths and 5 million disabilities per year. Complications of unsafe abortion account for approximately an eighth of maternal mortalities worldwide, though this varies by region. Secondary infertility caused by an unsafe abortion affects an estimated 24 million women. The rate of unsafe abortions has increased from 44% to 49% between 1995 and 2008.
Health education, access to family planning, and improvements in health
care during and after abortion have been proposed to address this
phenomenon.
Live birth
In 2019, a US Senate Bill entitled the "Born-Alive Abortion Survivors
Protection Act" raised the issue of live birth after abortion. The bill would mandate that medical providers resuscitate neonates delivered showing signs of life during an abortion process.
During the debate around this issue, US Republicans falsely alleged
that medical providers "execute" live-born babies. Existing US laws
would punish execution as homicide. Furthermore, US abortion experts
refute the claim that a "born-alive" fetus is a common event and reject
laws that would mandate resuscitation against the wishes of the parents.
Only 1.3% of abortions occur after 21 weeks of pregnancy in the
US. Although it is very uncommon, women undergoing surgical abortion
after this gestational age sometimes give birth to a fetus that may
survive briefly. The periviable period is considered to be between 20 and 25 weeks gestation. Long-term survival is possible after 22 weeks.
However, odds of long-term survival between 22 and 23 weeks are 2–3
percent and odds of survival between 23 and 24 weeks are 20 percent.
"Intact survival", which means survival of a neonate without subsequent
damage to organs such as the brain or bowel is 1% at 22 weeks and 13%
at 23 weeks. Survival odds increase with increasing gestational age.
If medical staff observe signs of life, they may be required to
provide care: emergency medical care if the child has a good chance of
survival and palliative care if not. Induced fetal demise
before termination of pregnancy after 20–21 weeks gestation is
recommended by some sources to avoid this and to comply with the US Partial Birth Abortion Ban.
Induced fetal demise does not improve the safety of an abortion
procedure and may incur risks to the health of the woman having the
abortion.
Incidence
There are two commonly used methods of measuring the incidence of abortion:
- Abortion rate – number of abortions per 1000 women between 15 and 44 years of age
- Abortion percentage – number of abortions out of 100 known pregnancies (pregnancies include live births, abortions and miscarriages)
In many places, where abortion is illegal or carries a heavy social stigma, medical reporting of abortion is not reliable. For this reason, estimates of the incidence of abortion must be made without determining certainty related to standard error.
The number of abortions performed worldwide seems to have
remained stable in recent years, with 41.6 million having been performed
in 2003 and 43.8 million having been performed in 2008.
The abortion rate worldwide was 28 per 1000 women, though it was 24 per
1000 women for developed countries and 29 per 1000 women for developing
countries.
The same 2012 study indicated that in 2008, the estimated abortion
percentage of known pregnancies was at 21% worldwide, with 26% in
developed countries and 20% in developing countries.
On average, the incidence of abortion is similar in countries
with restrictive abortion laws and those with more liberal access to
abortion. However, restrictive abortion laws are associated with
increases in the percentage of abortions performed unsafely.
The unsafe abortion rate in developing countries is partly attributable
to lack of access to modern contraceptives; according to the Guttmacher Institute,
providing access to contraceptives would result in about 14.5 million
fewer unsafe abortions and 38,000 fewer deaths from unsafe abortion
annually worldwide.
The rate of legal, induced abortion varies extensively worldwide.
According to the report of employees of Guttmacher Institute it ranged
from 7 per 1000 women (Germany and Switzerland) to 30 per 1000 women
(Estonia) in countries with complete statistics in 2008. The proportion
of pregnancies that ended in induced abortion ranged from about 10%
(Israel, the Netherlands and Switzerland) to 30% (Estonia) in the same
group, though it might be as high as 36% in Hungary and Romania, whose
statistics were deemed incomplete.
An American study in 2002 concluded that about half of women having abortions were using a form of contraception at the time of becoming pregnant. Inconsistent use was reported by half of those using condoms and three-quarters of those using the birth control pill; 42% of those using condoms reported failure through slipping or breakage.
The Guttmacher Institute estimated that "most abortions in the United
States are obtained by minority women" because minority women "have much
higher rates of unintended pregnancy".
The abortion rate may also be expressed as the average number of
abortions a woman has during her reproductive years; this is referred to
as total abortion rate (TAR).
Gestational age and method
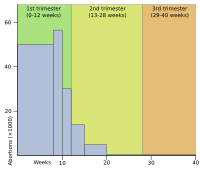
Histogram of abortions by gestational age in England and Wales during 2004. (top) Abortion in the United States by gestational age, 2004. (bottom)
Abortion rates also vary depending on the stage of pregnancy and the method practiced. In 2003, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
(CDC) reported that 26% of reported legal induced abortions in the
United States were known to have been obtained at less than 6 weeks'
gestation, 18% at 7 weeks, 15% at 8 weeks, 18% at 9 through 10 weeks,
10% at 11 through 12 weeks, 6% at 13 through 15 weeks, 4% at 16 through
20 weeks and 1% at more than 21 weeks. 91% of these were classified as
having been done by "curettage" (suction-aspiration, dilation and curettage, dilation and evacuation), 8% by "medical" means (mifepristone), >1% by "intrauterine instillation" (saline or prostaglandin), and 1% by "other" (including hysterotomy and hysterectomy).
According to the CDC, due to data collection difficulties the data must
be viewed as tentative and some fetal deaths reported beyond 20 weeks
may be natural deaths erroneously classified as abortions if the removal
of the dead fetus is accomplished by the same procedure as an induced
abortion.
The Guttmacher Institute estimated there were 2,200 intact dilation and extraction procedures in the US during 2000; this accounts for <0 .2="" abortions="" class="reference" id="cite_ref-169" number="" of="" performed="" sup="" that="" the="" total="" year.="">[168]
Similarly, in England and Wales in 2006, 89% of terminations occurred
at or under 12 weeks, 9% between 13 and 19 weeks, and 2% at or over 20
weeks. 64% of those reported were by vacuum aspiration, 6% by D&E,
and 30% were medical. There are more second trimester abortions in developing countries such as China, India and Vietnam than in developed countries.
Motivation
Personal
A bar chart depicting selected data from a 1998 AGI meta-study on the reasons women stated for having an abortion.
The reasons why women have abortions are diverse and vary across the world. Some of the reasons may include an inability to afford a child, domestic violence, lack of support, feeling they are too young, and the wish to complete education or advance a career. Additional reasons include not being willing to raise a child conceived as a result of rape or incest.
Societal
Some abortions are undergone as the result of societal pressures.
These might include the preference for children of a specific sex or
race, disapproval of single or early motherhood, stigmatization of
people with disabilities, insufficient economic support for families,
lack of access to or rejection of contraceptive methods, or efforts
toward population control (such as China's one-child policy). These factors can sometimes result in compulsory abortion or sex-selective abortion.
Maternal and fetal health
An additional factor is maternal health which was listed as the main
reason by about a third of women in 3 of 27 countries and about 7% of
women in a further 7 of these 27 countries.
In the U.S., the Supreme Court decisions in Roe v. Wade and Doe v. Bolton:
"ruled that the state's interest in the life of the fetus became
compelling only at the point of viability, defined as the point at which
the fetus can survive independently of its mother. Even after the point
of viability, the state cannot favor the life of the fetus over the
life or health of the pregnant woman. Under the right of privacy,
physicians must be free to use their "medical judgment for the
preservation of the life or health of the mother." On the same day that
the Court decided Roe, it also decided Doe v. Bolton, in which the Court
defined health very broadly: "The medical judgment may be exercised in
the light of all factors—physical, emotional, psychological, familial,
and the woman's age—relevant to the well-being of the patient. All these
factors may relate to health. This allows the attending physician the
room he needs to make his best medical judgment."
\
Public opinion shifted in America following television personality Sherri Finkbine's discovery during her fifth month of pregnancy that she had been exposed to thalidomide. Unable to obtain a legal abortion in the United States, she traveled to Sweden. From 1962 to 1965, an outbreak of German measles left 15,000 babies with severe birth defects. In 1967, the American Medical Association
publicly supported liberalization of abortion laws. A National Opinion
Research Center poll in 1965 showed 73% supported abortion when the
mother's life was at risk, 57% when birth defects were present and 59%
for pregnancies resulting from rape or incest.
Cancer
The rate of cancer during pregnancy is 0.02–1%, and in many cases,
cancer of the mother leads to consideration of abortion to protect the
life of the mother, or in response to the potential damage that may
occur to the fetus during treatment. This is particularly true for cervical cancer,
the most common type of which occurs in 1 of every 2,000–13,000
pregnancies, for which initiation of treatment "cannot co-exist with
preservation of fetal life (unless neoadjuvant chemotherapy is chosen)". Very early stage cervical cancers (I and IIa) may be treated by radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection, radiation therapy,
or both, while later stages are treated by radiotherapy. Chemotherapy
may be used simultaneously. Treatment of breast cancer during pregnancy
also involves fetal considerations, because lumpectomy is discouraged in favor of modified radical mastectomy unless late-term pregnancy allows follow-up radiation therapy to be administered after the birth.
Exposure to a single chemotherapy drug is estimated to cause a 7.5–17% risk of teratogenic effects on the fetus, with higher risks for multiple drug treatments. Treatment with more than 40 Gy
of radiation usually causes spontaneous abortion. Exposure to much
lower doses during the first trimester, especially 8 to 15 weeks of
development, can cause intellectual disability or microcephaly,
and exposure at this or subsequent stages can cause reduced
intrauterine growth and birth weight. Exposures above 0.005–0.025 Gy
cause a dose-dependent reduction in IQ.
It is possible to greatly reduce exposure to radiation with abdominal
shielding, depending on how far the area to be irradiated is from the
fetus.
The process of birth itself may also put the mother at risk.
"Vaginal delivery may result in dissemination of neoplastic cells into
lymphovascular channels, haemorrhage, cervical laceration and
implantation of malignant cells in the episiotomy site, while abdominal
delivery may delay the initiation of non-surgical treatment."
History and religion
Bas-relief at Angkor Wat, Cambodia, c. 1150, depicting a demon inducing an abortion by pounding the abdomen of a pregnant woman with a pestle.
"French Periodical Pills". An example of a clandestine advertisement published in a January 1845 edition of the Boston Daily Times.
Since ancient times abortions have been done using a number of methods, including herbal medicines, sharp tools, with force, or through other traditional methods. Induced abortion has long history and can be traced back to civilizations as varied as China under Shennong (c. 2700 BCE), Ancient Egypt with its Ebers Papyrus (c. 1550 BCE), and the Roman Empire in the time of Juvenal (c. 200 CE). One of the earliest known artistic representations of abortion is in a bas relief at Angkor Wat (c. 1150). Found in a series of friezes that represent judgment after death in Hindu and Buddhist culture, it depicts the technique of abdominal abortion.
Some medical scholars and abortion opponents have suggested that the Hippocratic Oath forbade Ancient Greek physicians from performing abortions; other scholars disagree with this interpretation, and state that the medical texts of Hippocratic Corpus contain descriptions of abortive techniques right alongside the Oath. The physician Scribonius Largus wrote in 43 CE that the Hippocratic Oath prohibits abortion, as did Soranus, although apparently not all doctors adhered to it strictly at the time. According to Soranus' 1st or 2nd century CE work Gynaecology,
one party of medical practitioners banished all abortives as required
by the Hippocratic Oath; the other party—to which he belonged—was
willing to prescribe abortions, but only for the sake of the mother's
health. Aristotle, in his treatise on government Politics (350 BCE), condemns infanticide as a means of population control. He preferred abortion in such cases, with the restriction
"[that it] must be practised on it before it has developed sensation
and life; for the line between lawful and unlawful abortion will be
marked by the fact of having sensation and being alive".
In Christianity, Pope Sixtus V (1585–90) was the first Pope before 1869 to declare that abortion is homicide regardless of the stage of pregnancy;
and his pronouncement of 1588 was reversed three years later by his
successor. Through most of its history the Catholic Church was divided
on whether it believed that early abortion was murder, and it did not
begin vigorously opposing abortion until the 19th century.
Several historians have written that prior to the 19th century most
Catholic authors did not regard termination of pregnancy before
"quickening" or "ensoulment" as an abortion. From 1750, excommunication became the punishment for abortions. Statements made in 1992 in the Catechism of the Catholic Church, the codified summary of the Church's teachings, opposed abortion.
A 1995 survey reported that Catholic women are as likely as the general population to terminate a pregnancy, Protestants are less likely to do so, and Evangelical Christians are the least likely to do so. Islamic tradition has traditionally permitted abortion until a point in time when Muslims believe the soul enters the fetus, considered by various theologians to be at conception, 40 days after conception, 120 days after conception, or quickening. However, abortion is largely heavily restricted or forbidden in areas of high Islamic faith such as the Middle East and North Africa.
In Europe and North America, abortion techniques advanced
starting in the 17th century. However, conservatism by most physicians
with regards to sexual matters prevented the wide expansion of safe
abortion techniques.
Other medical practitioners in addition to some physicians advertised
their services, and they were not widely regulated until the 19th
century, when the practice (sometimes called restellism) was banned in both the United States and the United Kingdom. Church groups as well as physicians were highly influential in anti-abortion movements.
In the US, according to some sources, abortion was more dangerous than
childbirth until about 1930 when incremental improvements in abortion
procedures relative to childbirth made abortion safer.
However, other sources maintain that in the 19th century early
abortions under the hygienic conditions in which midwives usually worked
were relatively safe.
In addition, some commentators have written that, despite improved
medical procedures, the period from the 1930s until legalization also
saw more zealous enforcement of anti-abortion laws, and concomitantly an
increasing control of abortion providers by organized crime.
Soviet Russia (1919), Iceland (1935) and Sweden (1938) were among
the first countries to legalize certain or all forms of abortion.
In 1935 Nazi Germany, a law was passed permitting abortions for those
deemed "hereditarily ill", while women considered of German stock were
specifically prohibited from having abortions. Beginning in the second half of the twentieth century, abortion was legalized in a greater number of countries.
Society and culture
Abortion debate
Induced abortion has long been the source of considerable debate. Ethical, moral, philosophical, biological, religious and legal issues surrounding abortion are related to value systems. Opinions of abortion may be about fetal rights, governmental authority, and women's rights.
In both public and private debate, arguments presented in favor
of or against abortion access focus on either the moral permissibility
of an induced abortion, or justification of laws permitting or
restricting abortion. The World Medical Association
Declaration on Therapeutic Abortion notes, "circumstances bringing the
interests of a mother into conflict with the interests of her unborn
child create a dilemma and raise the question as to whether or not the
pregnancy should be deliberately terminated." Abortion debates, especially pertaining to abortion laws,
are often spearheaded by groups advocating one of these two positions.
Anti-abortion groups who favor greater legal restrictions on abortion,
including complete prohibition, most often describe themselves as
"pro-life" while abortion rights groups who are against such legal
restrictions describe themselves as "pro-choice". Generally, the former position argues that a human fetus is a human person with a right to live, making abortion morally the same as murder. The latter position argues that a woman has certain reproductive rights, especially the right to decide whether or not to carry a pregnancy to term.
Modern abortion law
International status of abortion law
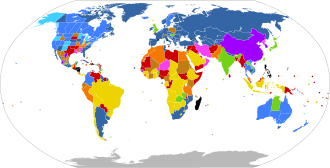
UN 2013 report on abortion law.
UN 2013 report on abortion law.
Legal on request
Legal for maternal life, health, mental health, rape and/or fetal defects, and also for socioeconomic factors
Illegal with exception for maternal life, health, mental health and/or rape, and also for fetal defects
Illegal with exception for maternal life, health and/or mental health, and also for rape
Illegal with exception for maternal life, health, and/or mental health
Illegal with exception for maternal life
Illegal with no exceptions
No information
Current laws pertaining to abortion are diverse. Religious, moral,
and cultural factors continue to influence abortion laws throughout the
world. The right to life, the right to liberty, the right to security of person, and the right to reproductive health are major issues of human rights that sometimes constitute the basis for the existence or absence of abortion laws.
In jurisdictions where abortion is legal, certain requirements
must often be met before a woman may obtain a safe, legal abortion (an
abortion performed without the woman's consent is considered feticide). These requirements usually depend on the age of the fetus, often using a trimester-based system to regulate the window of legality, or as in the U.S., on a doctor's evaluation of the fetus' viability. Some jurisdictions require a waiting period before the procedure, prescribe the distribution of information on fetal development, or require that parents be contacted if their minor daughter requests an abortion. Other jurisdictions may require that a woman obtain the consent of the fetus' father
before aborting the fetus, that abortion providers inform women of
health risks of the procedure—sometimes including "risks" not supported
by the medical literature—and that multiple medical authorities certify
that the abortion is either medically or socially necessary. Many
restrictions are waived in emergency situations. China, which has ended
their one-child policy, and now has a two child policy, has at times incorporated mandatory abortions as part of their population control strategy.
Other jurisdictions ban abortion almost entirely. Many, but not
all, of these allow legal abortions in a variety of circumstances. These
circumstances vary based on jurisdiction, but may include whether the
pregnancy is a result of rape or incest, the fetus' development is
impaired, the woman's physical or mental well-being is endangered, or
socioeconomic considerations make childbirth a hardship. In countries where abortion is banned entirely, such as Nicaragua,
medical authorities have recorded rises in maternal death directly and
indirectly due to pregnancy as well as deaths due to doctors' fears of
prosecution if they treat other gynecological emergencies.
Some countries, such as Bangladesh, that nominally ban abortion, may
also support clinics that perform abortions under the guise of menstrual
hygiene. This is also a terminology in traditional medicine. In places where abortion is illegal or carries heavy social stigma, pregnant women may engage in medical tourism and travel to countries where they can terminate their pregnancies. Women without the means to travel can resort to providers of illegal abortions or attempt to perform an abortion by themselves.
The organization Women on Waves,
has been providing education about medical abortions since 1999. The
NGO created a mobile medical clinic inside a shipping container, which
then travels on rented ships to countries with restrictive abortion
laws. Because the ships are registered in the Netherlands, Dutch law
prevails when the ship is in international waters. While in port, the
organization provides free workshops and education; while in
international waters, medical personnel are legally able to prescribe
medical abortion drugs and counseling.
Sex-selective abortion
Sonography and amniocentesis allow parents to determine sex before childbirth. The development of this technology has led to sex-selective abortion, or the termination of a fetus based on sex. The selective termination of a female fetus is most common.
Sex-selective abortion is partially responsible for the
noticeable disparities between the birth rates of male and female
children in some countries. The preference for male children is reported
in many areas of Asia, and abortion used to limit female births has
been reported in Taiwan, South Korea, India, and China.
This deviation from the standard birth rates of males and females
occurs despite the fact that the country in question may have officially
banned sex-selective abortion or even sex-screening. In China, a historical preference for a male child has been exacerbated by the one-child policy, which was enacted in 1979.
Many countries have taken legislative steps to reduce the incidence of sex-selective abortion. At the International Conference on Population and Development
in 1994 over 180 states agreed to eliminate "all forms of
discrimination against the girl child and the root causes of son
preference", conditions also condemned by a PACE resolution in 2011. The World Health Organization and UNICEF,
along with other United Nations agencies, have found that measures to
reduce access to abortion are much less effective at reducing
sex-selective abortions than measures to reduce gender inequality.
Anti-abortion violence
In a number of cases, abortion providers and these facilities have
been subjected to various forms of violence, including murder, attempted
murder, kidnapping, stalking, assault, arson, and bombing.
Anti-abortion violence is classified by both governmental and scholarly
sources as terrorism.
In the U.S. and Canada, over 8,000 incidents of violence, trespassing,
and death threats have been recorded by providers since 1977, including
over 200 bombings/arsons and hundreds of assaults. The majority of abortion opponents have not been involved in violent acts.
In the United States, four physicians who performed abortions have been murdered: David Gunn (1993), John Britton (1994), Barnett Slepian (1998), and George Tiller
(2009). Also murdered, in the U.S. and Australia, have been other
personnel at abortion clinics, including receptionists and security
guards such as James Barrett, Shannon Lowney, Lee Ann Nichols, and
Robert Sanderson. Woundings (e.g., Garson Romalis)
and attempted murders have also taken place in the United States and
Canada. Hundreds of bombings, arsons, acid attacks, invasions, and
incidents of vandalism against abortion providers have occurred. Notable perpetrators of anti-abortion violence include Eric Robert Rudolph, Scott Roeder, Shelley Shannon, and Paul Jennings Hill, the first person to be executed in the United States for murdering an abortion provider.
Legal protection of access to abortion
has been brought into some countries where abortion is legal. These
laws typically seek to protect abortion clinics from obstruction,
vandalism, picketing, and other actions, or to protect women and
employees of such facilities from threats and harassment.
Far more common than physical violence is psychological pressure.
In 2003, Chris Danze organized anti-abortion organizations throughout
Texas to prevent the construction of a Planned Parenthood facility in Austin. The organizations released the personal information online, of those involved with construction, sending them up to 1200 phone calls a day and contacting their churches. Some protestors record women entering clinics on camera.
Other animals
Spontaneous abortion occurs in various animals. For example, in sheep
it may be caused by stress or physical exertion, such as crowding
through doors or being chased by dogs. In cows, abortion may be caused by contagious disease, such as brucellosis or Campylobacter, but can often be controlled by vaccination. Eating pine needles can also induce abortions in cows.
Several plants, including broomweed, skunk cabbage, poison hemlock, and tree tobacco, are known to cause fetal deformities and abortion in cattle and in sheep and goats. In horses, a fetus may be aborted or resorbed if it has lethal white syndrome (congenital intestinal aganglionosis). Foal embryos that are homozygous for the dominant white gene (WW) are theorized to also be aborted or resorbed before birth. In many species of sharks and rays, stress-induced abortions occur frequently on capture.
Viral infection can cause abortion in dogs.
Cats can experience spontaneous abortion for many reasons, including
hormonal imbalance. A combined abortion and spaying is performed on
pregnant cats, especially in Trap-Neuter-Return programs, to prevent unwanted kittens from being born.
Female rodents may terminate a pregnancy when exposed to the smell of a male not responsible for the pregnancy, known as the Bruce effect.
Abortion may also be induced in animals, in the context of animal husbandry.
For example, abortion may be induced in mares that have been mated
improperly, or that have been purchased by owners who did not realize
the mares were pregnant, or that are pregnant with twin foals. Feticide can occur in horses and zebras due to male harassment of pregnant mares or forced copulation, although the frequency in the wild has been questioned. Male gray langur monkeys may attack females following male takeover, causing miscarriage.